DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2061 of 2627

SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Output Shaft End Play 0.22-0.55
mm0.009-0.021
in.
Input Shaft End Play 0.46-0.89
mm0.018-0.035
in.
2C Clutch Pack
Clearance0.455-1.335
mm0.018-0.053
in.
4C Clutch Pack
Clearance0.770-1.390
mm0.030-0.055
in.
L/R Clutch Pack
Clearance1.00-1.74
mm0.039-0.069
in.
OD Clutch Pack
Clearance1.103-1.856
mm0.043-0.073
in.
Component Metric Inch
UD Clutch Pack
Clearance0.84-1.54
mm0.033-0.061
in.
Reverse Clutch Pack
Clearance0.81-1.24
mm0.032-0.049
in.
Recommended fluid MoparTAT F + 4
GEAR RATIOS
1ST 3.00:1
2ND 1.67:1
2ND Prime 1.50:1
3RD 1.0:1
4TH 0.75:1
5TH 0.67:1
REVERSE 3.00:1
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 17.5 - 155
Bolt, torque convertor 31 23 -
Bolt/nut, crossmember 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to crankshaft 75 55 -
Bolt, oil pan 11.8 - 105
Screw, primary fluid filter 4.5 - 40
Bolt, oil pump 28.2 - 250
Bolt, oil pump body to cover 4.5 - 40
Screw, plate to oil pump body 4.5 - 40
Bolt, valve body to case 11.8 - 105
Plug, pressure test port 5.1 - 45
Bolt, reaction shaft support 11.8 - 105
Screw, valve body to transfer plate 5.6 - 50
Screw, solenoid module to transfer plate 5.7 - 50
Screw, accumulator cover 8 - 70
Screw, detent spring 4.5 - 40
Bolt, input speed sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, output speed sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, line pressure sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, extension housing 54 40 -
Valve, cooler return filter bypass 4.5 - 40
Screw, manual valve cam retaining 4.5 - 40
Bolt, manual lever 28.2 - 250
21 - 358 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2062 of 2627
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3293SP
Dial Indicator - C-3339
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
Compressor, Spring - 8249
Compressor, Spring - 8250
Compressor, Spring - 8251
Installer, Piston - 8252
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 359
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2063 of 2627
Installer, Seal - 8253
Installer, Seal - 8254
Installer, Snap-ring - 8255
Stand, Support - 8257
Adapter, Pressure Tap - 8258-A
Adapter, Line Pressure - 8259
Fixture, Input Clutch Pressure - 8260
Plate, Alignment - 8261
21 - 360 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2064 of 2627
End Play Set - 8266
Compressor, Spring - 8285
Installer, Bearing - 8320
Wrench, Filter - 8321
Installer, Piston - 8504
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 361
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2065 of 2627
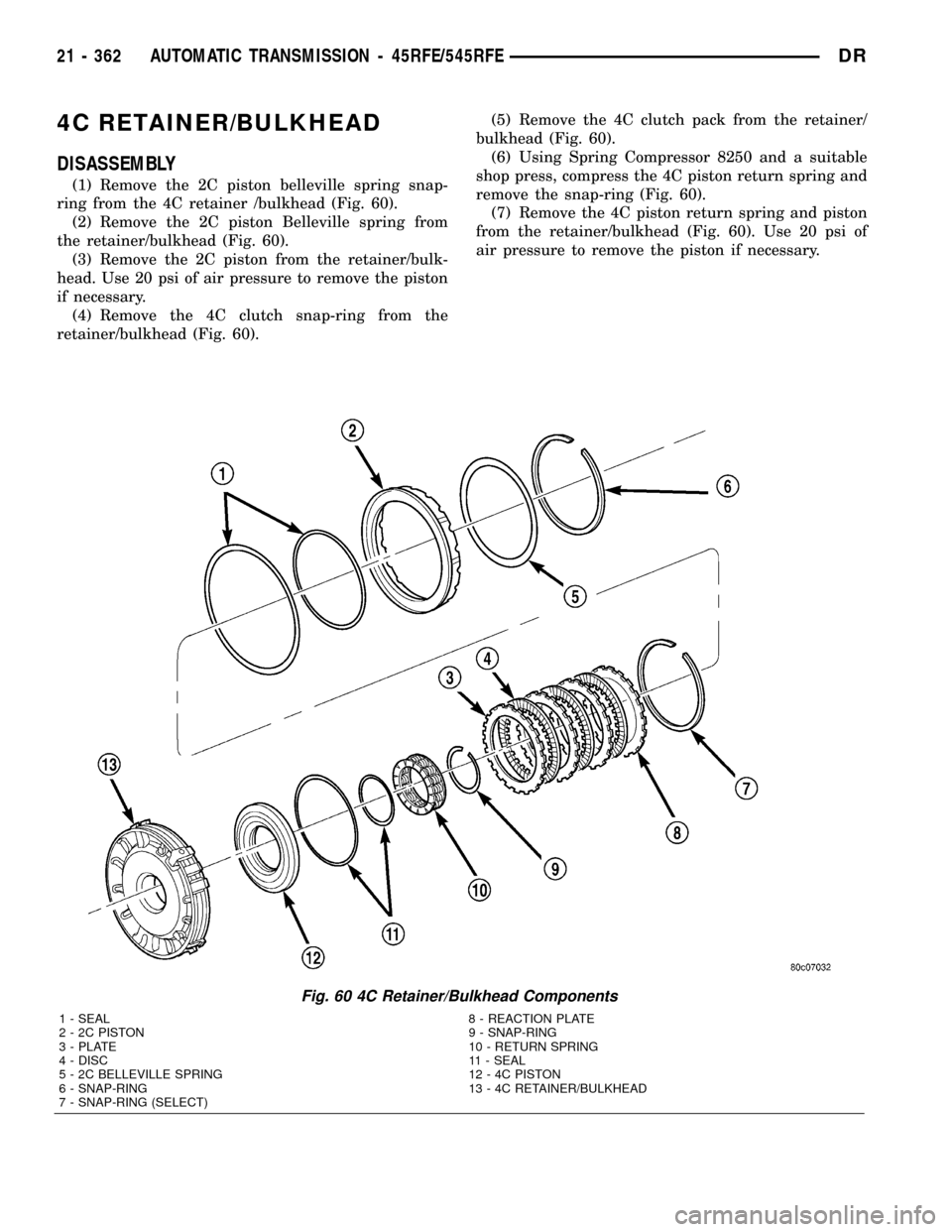
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the 2C piston belleville spring snap-
ring from the 4C retainer /bulkhead (Fig. 60).
(2) Remove the 2C piston Belleville spring from
the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 60).
(3) Remove the 2C piston from the retainer/bulk-
head. Use 20 psi of air pressure to remove the piston
if necessary.
(4) Remove the 4C clutch snap-ring from the
retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 60).(5) Remove the 4C clutch pack from the retainer/
bulkhead (Fig. 60).
(6) Using Spring Compressor 8250 and a suitable
shop press, compress the 4C piston return spring and
remove the snap-ring (Fig. 60).
(7) Remove the 4C piston return spring and piston
from the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 60). Use 20 psi of
air pressure to remove the piston if necessary.
Fig. 60 4C Retainer/Bulkhead Components
1 - SEAL 8 - REACTION PLATE
2 - 2C PISTON 9 - SNAP-RING
3 - PLATE 10 - RETURN SPRING
4 - DISC 11 - SEAL
5 - 2C BELLEVILLE SPRING 12 - 4C PISTON
6 - SNAP-RING 13 - 4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
7 - SNAP-RING (SELECT)
21 - 362 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2066 of 2627

ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install new seals on the 2C and 4C pistons
(Fig. 60).
(3) Lubricate all seals with MopartATF +4 prior
to installation.
(4) Install the 4C piston into the 4C retainer/bulk-
head (Fig. 60).
(5) Position the 4C piston return spring onto the
4C piston.
(6) Using Spring Compressor 8250 and a suitable
shop press, compress the 4C piston return spring and
install the snap-ring (Fig. 61).
(7) Assemble and install the 4C clutch pack into
the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 60) with the steel separa-
tor plate against the piston.(8) Install the 4C reaction plate and snap-ring into
the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 60). The 4C reaction plate
is non-directional.
(9) Measure the 4C clutch clearance. The correct
clutch clearance is 0.77-1.39 mm (0.030-0.055 in.).
The snap-ring is selectable. Install the chosen snap-
ring and re-measure to verify the selection.
(10) Install the 2C piston into the retainer/bulk-
head (Fig. 60).
(11) Position the 2C Belleville spring onto the 2C
piston.
(12) Position the 2C Belleville spring snap-ring
onto the 2C Belleville spring (Fig. 60).
(13) Using Spring Compressor 8249 and a suitable
shop press (Fig. 62), compress the belleville spring
until the snap-ring is engaged with the snap-ring
groove in the retainer/bulkhead.
Fig. 61 Compress 4C Piston Return Spring Using
Tool 8250
1 - PRESS
2 - TOOL 8250Fig. 62 Compress 2C Belleville Spring Using Tool
8249
1 - PRESS
2 - TOOL 8249
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 363
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD (Continued)
Page 2067 of 2627

ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transfer case from the transmis-
sion.
(2) Using a screw mounted on a slide hammer,
remove the adapter housing seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the adapter seal bore in the adapter
housing of any residue or particles remaining from
the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the adapter housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 63). A properly
installed seal is flush to the face of the seal bore.
(3) Install the transfer case onto the transmission.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The Brake Transmission Shifter Interlock (BTSI)
(Fig. 64), is a solenoid operated system. It consists of
a solenoid permanently mounted on the gearshift
cable.
OPERATION
The system locks the shifter into the PARK position.
The interlock system is engaged whenever the ignition
switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY position. An
additional electrically activated feature will prevent
shifting out of the PARK position unless the brake pedalis depressed approximately one-half an inch. A magnetic
holding device in line with the park lock cable is ener-
gized when the ignition is in the RUN position. When
the key is in the RUN position and the brake pedal is
depressed, the shifter is unlocked and will move into
any position. The interlock system also prevents the
ignition switch from being turned to the LOCK or
ACCESSORY position, unless the shifter is fully locked
into the PARK position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
(1) Verify that the key can only be removed in the
PARK position
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK And the shift
handle pushbutton is in the ªOUTº position, the igni-
tion key cylinder should rotate freely from OFF to
LOCK. When the shifter is in any other gear or neu-
tral position, the ignition key cylinder should not
rotate to the LOCK position.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the OFF posi-
tion.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal pushbutton force and ignition
key cylinder is in the RUN or START positions
unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi-
mately 1/2 inch (12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the ACCESSORY
or LOCK positions.
(6)
Shifting between any gears, NEUTRAL or into
PARK may be done without depressing foot brake pedal
with ignition switch in RUN or START positions.
Fig. 63 Adapter Housing Seal Installation
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
Fig. 64 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
21 - 364 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2068 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK
Correct cable adjustment is important to proper
interlock operation. The gearshift cable must be cor-
rectly adjusted in order to shift out of PARK.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Remove the steering column trim as necessary
for access to the brake transmission shift interlock.
(2) Shift the transmission into the PARK position.
(3) Pull upward on both the BTSI lock tab and the
gearshift cable lock tab (Fig. 65).
(4) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(5) Verify positive engagement of the transmission
park lock by attempting to rotate the propeller shaft.
The shaft will not rotate when the park lock is
engaged.
(6) Turn ignition switch to LOCK position.Be
sure ignition key cylinder is in the LOCK posi-
tion. Cable will not adjust correctly in any
other position.
(7) Ensure that the cable is free to self-adjust by
pushing cable rearward and releasing.
(8) Push the gearshift cable lock tab down until it
snaps in place.
(9) Locate the BTSI alignment hole in the bottom
of the BTSI mechanism between the BTSI lock tab
and the BTSI connector.(10) Move the BTSI assembly up or down on the
gearshift cable until an appropriate size drill bit can
be inserted into the alignment hole and through the
assembly.
(11) Push the BTSI lock tab down until it snaps
into place and remove the drill bit.
(12) Install any steering column trim previously
removed.
BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.
²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
Fig. 65 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 365
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2070 of 2627
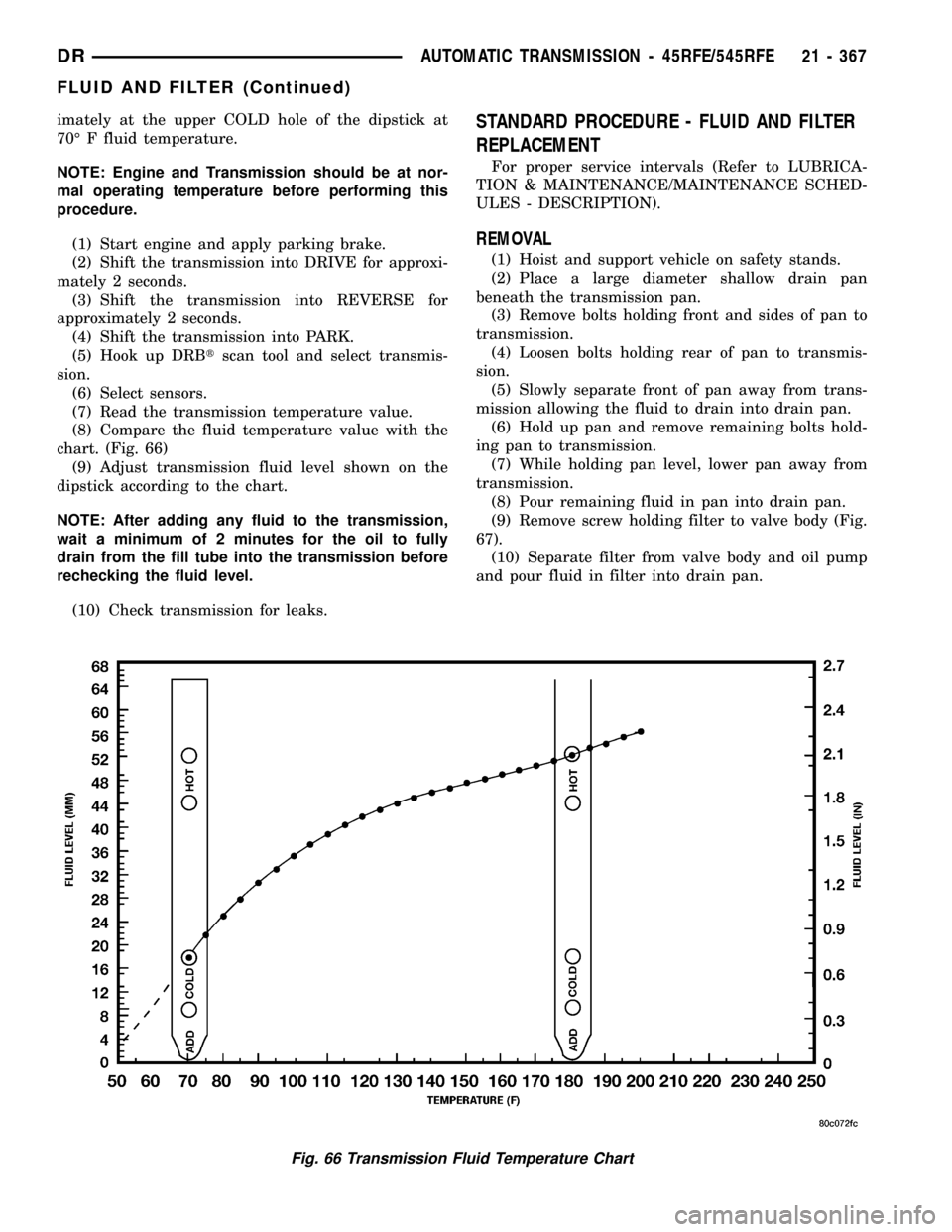
imately at the upper COLD hole of the dipstick at
70É F fluid temperature.
NOTE: Engine and Transmission should be at nor-
mal operating temperature before performing this
procedure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select transmis-
sion.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart. (Fig. 66)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission.
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan away from trans-
mission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan away from
transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screw holding filter to valve body (Fig.
67).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and oil pump
and pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
Fig. 66 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 367
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)