DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2101 of 2627

SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²Park (P)
²Reverse (R)
²Neutral (N)
²Drive (D)
²Manual second (2)
²Manual low (1)
OPERATION
MANUAL LOW (1) range provides first gear only.
Overrun braking is also provided in this range.
MANUAL SECOND (2) range provides first and sec-
ond gear only.
DRIVE range provides FIRST, SECOND, THIRD,
OVERDRIVE FOURTH, and OVERDRIVE FIFTH (if
applicable) gear ranges. The shift into OVERDRIVE
FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear ranges
occurs only after the transmission has completed the
shift into D THIRD gear range. No further movement
of the shift mechanism is required to complete the
3-4 or 4-5 (if applicable) shifts.
The FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear
upshifts occur automatically when the overdrive
selector switch is in the ON position. No upshift to
FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable) gears will occur if
any of the following are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to THIRD is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 or 4-5 (if
applicable) shifts to occur.
Upshifts into FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable)
will be delayed when the transmission fluid temper-
ature is below 4.5É C (40É F) or above 115.5É C (240É
F).
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th (if
applicable) gears, the solenoid switch valve will be in
the upshifted position and directs the fluid into the
torque converter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
21 - 398 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2102 of 2627

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 117) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, anoverrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump and contains an o-ring seal to better control oil
flow.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid.
Fig. 117 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 399
SOLENOIDS (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2627

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 118) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 118 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 400 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2104 of 2627

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 119) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 119 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
2 - ENGINE ROTATION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 401
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2105 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 120) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 121).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 122) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmis-
sion and buffer the powertrain against torsional
vibrations, the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Sole-
noid to achieve a smooth application of the torque
converter clutch. This function, referred to as Elec-
tronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) can
occur at various times depending on the following
variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle²Engine speed
Fig. 120 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 121 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 122 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 402 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2106 of 2627
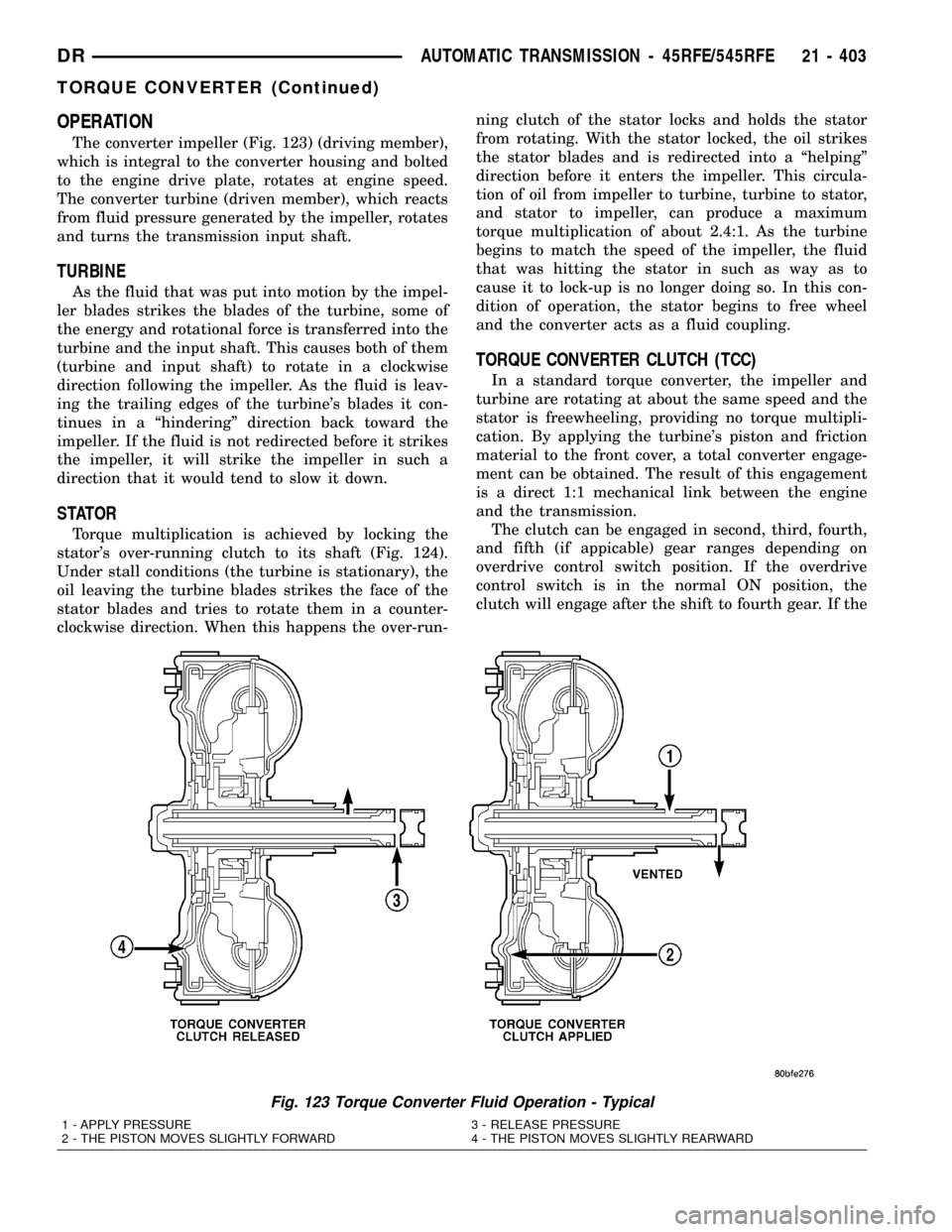
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 123) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 124).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over-run-ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston and friction
material to the front cover, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The clutch can be engaged in second, third, fourth,
and fifth (if appicable) gear ranges depending on
overdrive control switch position. If the overdrive
control switch is in the normal ON position, the
clutch will engage after the shift to fourth gear. If the
Fig. 123 Torque Converter Fluid Operation - Typical
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 403
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2107 of 2627

control switch is in the OFF position, the clutch will
engage after the shift to third gear.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after Partial
EMCC control brings the engine speed within thedesired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 125). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
Fig. 124 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 404 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2108 of 2627

(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode.
OPERATION
When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the
solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset, the TCM energizes the
relay. Prior to this, the TCM verifies that the con-
tacts are open by checking for no voltage at the
switched battery terminals. After this is verified, the
voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the TCM mon-
itors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is part of
the solenoid module, which is mounted to the top of
the valve body inside the transmission.
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has five
switch contact pins that:
²Determine shift lever position
²Supply ground to the Starter Relay in Park and
Neutral only.
²
Supply +12 V to the backup lamps in Reverse only.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transmission
temperature to the TCM and PCM.
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) communi-
cates shift lever position to the TCM as a combina-
tion of open and closed switches. Each shift lever
position has an assigned combination of switch states
(open/closed) that the TCM receives from four sense
circuits. The TCM interprets this information and
determines the appropriate transmission gear posi-
tion and shift schedule.
There are many possible combinations of open and
closed switches (codes). Seven of these possible codes
are related to gear position and five are recognized
as ªbetween gearº codes. This results in many codes
which shouldnever occur. These are called
ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result in a DTC,
and the TCM will then determine the shift lever
position based on pressure switch data. This allows
reasonably normal transmission operation with a
TRS failure.
GEAR C5 C4 C3 C2 C1
ParkCL OP OP CL CL
Temp 1CL OP OP CL OP
ReverseOP OP OP CL OP
Temp 2OP OP CL CL OP
Neutral 1OP OP CL CL CL
Neutral 2OP CL CL CL CL
Temp 3OP CL CL CL OP
DriveOP CL CL OP OP
Temp 4OP CL OP OP OP
Manual 2CL CL OP OP OP
Temp 5CL OP OP OP OP
Manual 1CL OP CL OP OP
Fig. 125 Checking Torque Converter Seating-Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 405
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2109 of 2627

TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/
TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission solenoid/TRS assembly is inter-
nal to the transmission and mounted on the valve
body assembly (Fig. 126). The assembly consists of
six solenoids that control hydraulic pressure to the
six friction elements (transmission clutches), and the
torque converter clutch. The pressure control sole-
noid is located on the side of the solenoid/TRS assem-
bly. The solenoid/TRS assembly also contains five
pressure switches that feed information to the TCM.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
Solenoids are used to control the L/R, 2C, 4C, OD,
and UD friction elements. The reverse clutch is con-
trolled by line pressure and the position of the man-
ual valve in the valve body. All the solenoids are
contained within the Solenoid and Pressure Switch
Assembly. The solenoid and pressure switch assembly
contains one additional solenoid, Multi-Select (MS),
which serves primarily to provide 2nd and 3rd gear
limp-in operation.
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The TCM energizes or operates the solenoids individ-
ually by grounding the return wire of the solenoid as
necessary. When a solenoid is energized, the solenoid
valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or closed
(vented or applied), depending on its default operat-
ing state. The result is an apply or release of a fric-
tional element.
The MS and UD solenoids are normally applied to
allow transmission limp-in in the event of an electri-
cal failure.The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
should be detected by the TCM during this test. If no
spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to verify
the failure. In addition to the periodic testing, the
solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or pres-
sure switch error occurs.
Fig. 126 Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
1 - PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SELECTOR PLATE
3 - 23-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SOLENOID PACK
5 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
6 - VALVE BODY
21 - 406 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2110 of 2627

PRESSURE SWITCHES
The TCM relies on five pressure switches to moni-
tor fluid pressure in the L/R, 2C, 4C, UD, and OD
hydraulic circuits. The primary purpose of these
switches is to help the TCM detect when clutch cir-
cuit hydraulic failures occur. The switches close at 23
psi and open at 11 psi, and simply indicate whether
or not pressure exists. The switches are continuously
monitored by the TCM for the correct states (open or
closed) in each gear as shown in the following charts
45RFE PRESSURE SWITCH STATES and 545RFE
PRESSURE SWITCH STATES :
45RFE PRESSURE SWITCH STATES
GEAR L/R 2C 4C UD OD
ROP OP OP OP OP
P/NCL OP OP OP OP
1STCL* OP OP CL OP
2NDOP CL OP CL OP
2ND
PRIMEOP OP CL CL OP
DOP OP OP CL CL
FOURTHOP OP CL OP CL
*L/R is closed if output speed is below 100 rpm in
Drive and Manual 2. L/R is open in Manual 1.
545RFE PRESSURE SWITCH STATES
GEAR L/R 2C 4C UD OD
ROP OP OP OP OP
P/NCL OP OP OP OP
1STCL* OP OP CL OP
2NDOP CL OP CL OP
2ND
PRIMEOP OP CL CL OP
DOP OP OP CL CL
4THOP OP CL OP CL
5THOP CL OP OP CL
*L/R is closed if output speed is below 100 rpm in
Drive and Manual 2. L/R is open in Manual 1.
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set if the
TCM senses any switch open or closed at the wrong
time in a given gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve body from the transmission
(Fig. 127).
(2) Remove the screws holding the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body (Fig. 128).
(3) Separate the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly from the valve body.
Fig. 127 Valve Body Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
Fig. 128 Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
Screws
1 - SOLENOID PACK BOLTS (15)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 407
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)