tow DODGE RAM 2001 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 46 of 2889

down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot bar
inward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 95 of 2889
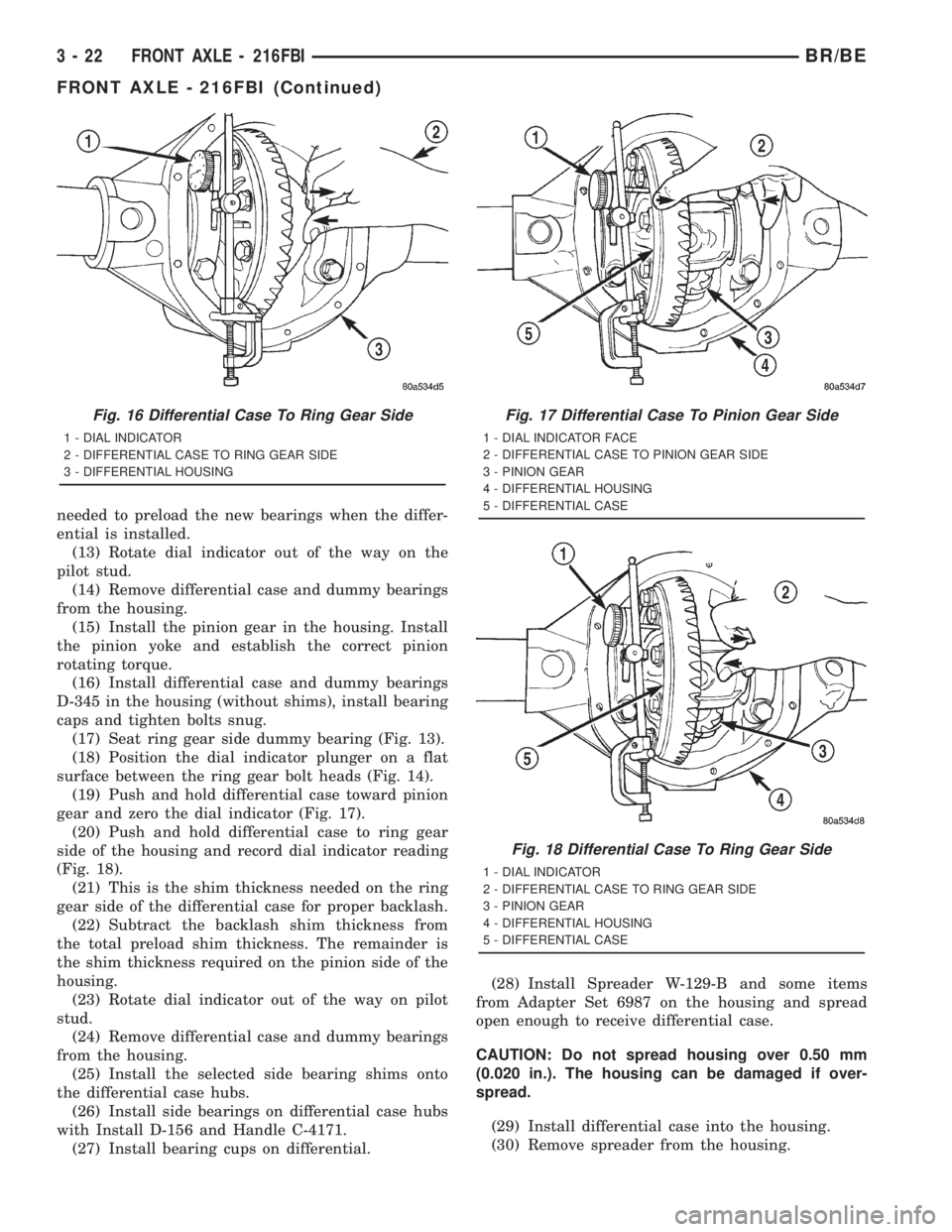
needed to preload the new bearings when the differ-
ential is installed.
(13) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on the
pilot stud.
(14) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(15) Install the pinion gear in the housing. Install
the pinion yoke and establish the correct pinion
rotating torque.
(16) Install differential case and dummy bearings
D-345 in the housing (without shims), install bearing
caps and tighten bolts snug.
(17) Seat ring gear side dummy bearing (Fig. 13).
(18) Position the dial indicator plunger on a flat
surface between the ring gear bolt heads (Fig. 14).
(19) Push and hold differential case toward pinion
gear and zero the dial indicator (Fig. 17).
(20) Push and hold differential case to ring gear
side of the housing and record dial indicator reading
(Fig. 18).
(21) This is the shim thickness needed on the ring
gear side of the differential case for proper backlash.
(22) Subtract the backlash shim thickness from
the total preload shim thickness. The remainder is
the shim thickness required on the pinion side of the
housing.
(23) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on pilot
stud.
(24) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(25) Install the selected side bearing shims onto
the differential case hubs.
(26) Install side bearings on differential case hubs
with Install D-156 and Handle C-4171.
(27) Install bearing cups on differential.(28) Install Spreader W-129-B and some items
from Adapter Set 6987 on the housing and spread
open enough to receive differential case.
CAUTION: Do not spread housing over 0.50 mm
(0.020 in.). The housing can be damaged if over-
spread.
(29) Install differential case into the housing.
(30) Remove spreader from the housing.
Fig. 16 Differential Case To Ring Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 17 Differential Case To Pinion Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 18 Differential Case To Ring Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - 22 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 96 of 2889

(31) Rotate the differential case several times to
seat the side bearings.
(32) Position the indicator plunger against a ring
gear tooth (Fig. 19).
(33) Push and hold ring gear upward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate.
(34) Zero dial indicator face to pointer.
(35) Push and hold ring gear downward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate. Dial indicator
reading should be between 0.12 mm (0.005 in.) and
0.20 mm (0.008 in.). If backlash is not within specifi-
cations transfer the necessary amount of shim thick-
ness from one side of the housing to the other (Fig.
20).
(36) Verify differential case and ring gear runout
by measuring ring to pinion gear backlash at eight
locations around the ring gear. Readings should not
vary more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in.). If readings vary
more than specified, the ring gear or the differential
case is defective.
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform
Gear Contact Pattern Analysis procedure.
GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring and pinion gear contact patterns will
show if the pinion depth is correct. It will also show
if the ring gear backlash has been adjusted correctly.
The backlash can be adjusted within specifications to
achieve desired tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on the ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
21)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
Fig. 19 Ring Gear Backlash Measurement
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 20 Backlash Shim
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 23
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 106 of 2889

REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
(3) Remove shift motor housing cover, gasket and
shield from the housing (Fig. 28).
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove E-clips from the shift motor housing
and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove O-ring seal from the shift motor shaft.
(3) Clean and inspect all components. Replaced
any component that is excessively worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert shift motor shaft through the hole in the
housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset should be
toward the differential.
(3) Install E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shift motor housing gasket and cover.
Ensure shift fork is correctly guided into the shift
collar groove.
(2) Install shift motor housing shield and tighten
the bolts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.).(3) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5
hypoid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(4) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
REMOVAL
Single cardan U-joint components are not service-
able. If defective they must be replaced as a unit.
CAUTION: Clamp only the narrow forged portion of
the yoke in the vise. To avoid distorting the yoke,
do not over tighten the vise jaws.
(1) Remove axle shaft.
(2) Remove the bearing cap retaining snap rings
(Fig. 30).
NOTE: Saturate bearing caps with penetrating oil
prior to removal.
(3) Locate a socket with an inside diameter is
larger than the bearing cap. Place the socket (receiv-
er) against the yoke and around the perimeter of the
bearing cap to be removed.
(4) Locate a socket with an outside diameter is
smaller than the bearing cap. Place the socket (driv-
er) against the opposite bearing cap.
Fig. 28 Shift Motor Housing
1 - INDICATOR LAMP SWITCH
2 - DISCONNECT HOUSING
3 - VACUUM SHIFT MOTOR
4 - AXLE SHAFT
5 - SEAL
6 - SHIFT COLLAR
7 - SHIFT FORK
8 - BEARING
9 - INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFT
Fig. 29 Shift Motor Components
1 - INDICATOR SWITCH
2 - E-CLIP
3 - O-RING
4 - SHIFT MOTOR
5 - SHIFT FORK
6 - VACUUM PORTS
7 - DISCONNECT HOUSING AND GASKET
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 33
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR (Continued)
Page 128 of 2889
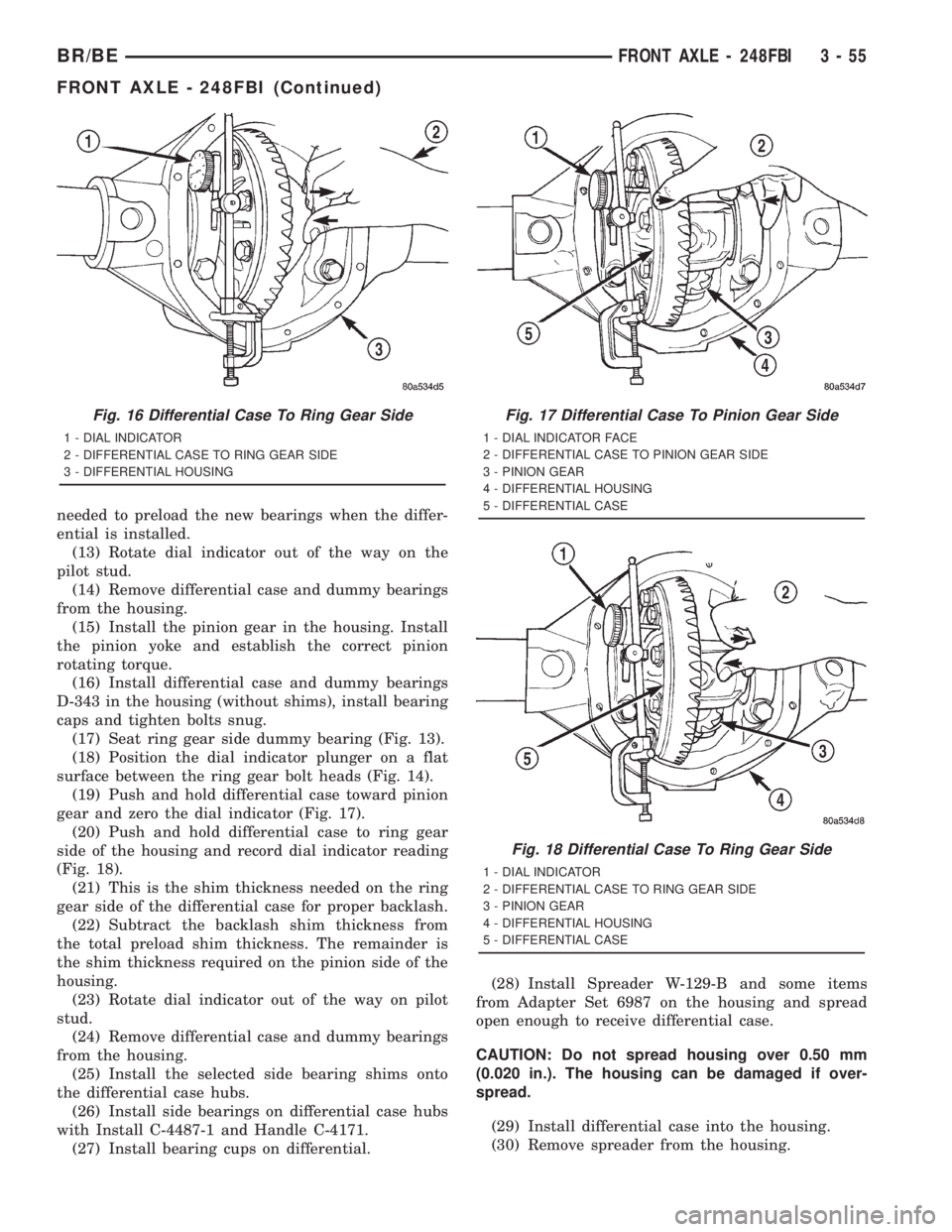
needed to preload the new bearings when the differ-
ential is installed.
(13) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on the
pilot stud.
(14) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(15) Install the pinion gear in the housing. Install
the pinion yoke and establish the correct pinion
rotating torque.
(16) Install differential case and dummy bearings
D-343 in the housing (without shims), install bearing
caps and tighten bolts snug.
(17) Seat ring gear side dummy bearing (Fig. 13).
(18) Position the dial indicator plunger on a flat
surface between the ring gear bolt heads (Fig. 14).
(19) Push and hold differential case toward pinion
gear and zero the dial indicator (Fig. 17).
(20) Push and hold differential case to ring gear
side of the housing and record dial indicator reading
(Fig. 18).
(21) This is the shim thickness needed on the ring
gear side of the differential case for proper backlash.
(22) Subtract the backlash shim thickness from
the total preload shim thickness. The remainder is
the shim thickness required on the pinion side of the
housing.
(23) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on pilot
stud.
(24) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(25) Install the selected side bearing shims onto
the differential case hubs.
(26) Install side bearings on differential case hubs
with Install C-4487-1 and Handle C-4171.
(27) Install bearing cups on differential.(28) Install Spreader W-129-B and some items
from Adapter Set 6987 on the housing and spread
open enough to receive differential case.
CAUTION: Do not spread housing over 0.50 mm
(0.020 in.). The housing can be damaged if over-
spread.
(29) Install differential case into the housing.
(30) Remove spreader from the housing.
Fig. 16 Differential Case To Ring Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 17 Differential Case To Pinion Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 18 Differential Case To Ring Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 55
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 129 of 2889

(31) Rotate the differential case several times to
seat the side bearings.
(32) Position the indicator plunger against a ring
gear tooth (Fig. 19).
(33) Push and hold ring gear upward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate.
(34) Zero dial indicator face to pointer.
(35) Push and hold ring gear downward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate. Dial indicator
reading should be between 0.12 mm (0.005 in.) and
0.20 mm (0.008 in.). If backlash is not within specifi-
cations transfer the necessary amount of shim thick-
ness from one side of the housing to the other (Fig.
20).
(36) Verify differential case and ring gear runout
by measuring ring to pinion gear backlash at eight
locations around the ring gear. Readings should not
vary more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in.). If readings vary
more than specified, the ring gear or the differential
case is defective.
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform
Gear Contact Pattern Analysis procedure.
GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring and pinion gear contact patterns will
show if the pinion depth is correct. It will also show
if the ring gear backlash has been adjusted correctly.
The backlash can be adjusted within specifications to
achieve desired tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on the ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
21)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
Fig. 19 Ring Gear Backlash Measurement
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 20 Backlash Shim
3 - 56 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 138 of 2889

REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
(3) Remove shift motor housing cover, gasket and
shield from the housing (Fig. 28).
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove E-clips from the shift motor housing
and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove O-ring seal from the shift motor shaft.
(3) Clean and inspect all components. Replaced
any component that is excessively worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert shift motor shaft through the hole in the
housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset should be
toward the differential.
(3) Install E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shift motor housing gasket and cover.
Ensure shift fork is correctly guided into the shift
collar groove.
(2) Install shift motor housing shield and tighten
the bolts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.).(3) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5
hypoid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(4) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
REMOVAL
Single cardan U-joint components are not service-
able. If defective they must be replaced as a unit.
CAUTION: Clamp only the narrow forged portion of
the yoke in the vise. To avoid distorting the yoke,
do not over tighten the vise jaws.
(1) Remove axle shaft.
(2) Remove the bearing cap retaining snap rings
(Fig. 30).
NOTE: Saturate the bearing caps with penetrating
oil prior to removal.
(3) Locate a socket with an inside diameter is
larger than the bearing cap. Place the socket (receiv-
er) against the yoke and around the perimeter of the
bearing cap to be removed.
(4) Locate a socket with an outside diameter is
smaller than the bearing cap. Place the socket (driv-
er) against the opposite bearing cap.
Fig. 28 Shift Motor Housing
1 - INDICATOR LAMP SWITCH
2 - DISCONNECT HOUSING
3 - VACUUM SHIFT MOTOR
4 - AXLE SHAFT
5 - SEAL
6 - SHIFT COLLAR
7 - SHIFT FORK
8 - BEARING
9 - INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFT
Fig. 29 Shift Motor Components
1 - INDICATOR SWITCH
2 - E-CLIP
3 - O-RING
4 - SHIFT MOTOR
5 - SHIFT FORK
6 - VACUUM PORTS
7 - DISCONNECT HOUSING AND GASKET
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 65
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR (Continued)
Page 160 of 2889

measurements will be taken with the same gear
teeth meshed.
(4) Loosen the right-side, tighten the left-side
threaded adjuster. Obtain backlash of 0.003 to 0.004
inch (0.076 to 0.102 mm) with each adjuster tight-
ened to 14 N´m (10 ft. lbs.). Seat the bearing cups
with the procedure described above.
(5) Tighten the differential bearing cap bolts 136
N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(6) Tighten the right-side threaded adjuster to 102
N´m (75 ft. lbs.). Seat the bearing cups with the pro-
cedure described above. Continue to tighten theright-side adjuster and seat bearing cups until the
torque remains constant at 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.)
(7) Measure the ring gear backlash. The range of
backlash is 0.13 to 0.203 mm (0.005 to 0.008 inch).
(8) Continue increasing the torque at the right-
side threaded adjuster until the specified backlash is
obtained.
NOTE: The left-side threaded adjuster torque
should have approximately 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.). If
the torque is considerably less, the complete
adjustment procedure must be repeated.
(9) Tighten the left-side threaded adjuster until
102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) torque is indicated. Seat the
bearing rollers with the procedure described above.
Do this until the torque remains constant.
(10) Install the threaded adjuster locks and
tighten the lock screws to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform the
Gear Contact procedure.GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring gear and pinion teeth contact patterns
will show if the pinion depth is correct in the hous-
ing. It will also show if the ring gear backlash has
been adjusted correctly. The backlash can be adjusted
within specifications to achieve desired tooth contact
patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist, and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on a ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
14)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
SIDE GEAR CLEARANCE
When measuring side gear clearance, check each
gear independently. If it necessary to replace a side
gear, replace both gears as a matched set.
(1) Install the axle shafts and C-locks and pinion
shaft.
(2) Measure each side gear clearance. Insert a
matched pair of feeler gauge blades between the gear
Fig. 12 Threaded Adjuster Tool
1 - AXLE TUBE
2 - BACKING PLATE
3 - THREAD ADJUSTER WRENCH
Fig. 13 Ring Gear Backlash
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - RING GEAR
3 - EXCITER RING
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 87
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 191 of 2889

(12) Add 0.38 mm (0.015 in.) to the zero end play
total. This total represents the thickness of shims
needed to preload the new bearings when the differ-
ential is installed.
(13) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on the
pilot stud.(14) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.
(15) Install the pinion gear in the housing. Install
the pinion yoke and establish the correct pinion
rotating torque.
(16) Install differential case and dummy bearings
D-343 in the housing (without shims), install bearing
caps and tighten bolts snug.
(17) Seat ring gear side dummy bearing (Fig. 13).
(18) Position the dial indicator plunger on a flat
surface between the ring gear bolt heads (Fig. 14).
(19) Push and hold differential case toward pinion
gear and zero the dial indicator (Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 Differential Side Play Measurement
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
3 - PILOT STUD
4 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 15 Dial Indicator Location
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
2 - PILOT STUD
3 - DIAL INDICATOR ARM
4 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
Fig. 16 Differential Case To Ring Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 17 Differential Case To Pinion Gear Side
1 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - 118 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 193 of 2889

GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring and pinion gear contact patterns will
show if the pinion depth is correct. It will also show
if the ring gear backlash has been adjusted correctly.
The backlash can be adjusted within specifications to
achieve desired tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on the ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
21)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
Fig. 20 Backlash Shim
3 - 120 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)