central timer module DODGE RAM 2001 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 655 of 2889

DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH
Switch Position
Resistance
Driver Side Passenger Side
Neutral Neutral 12 Kilohms
Lock (Clockwise)Lock (Counter
Clockwise)644 Ohms
Unlock (Counter
Clockwise)Unlock
(Clockwise)1565 Ohms
(3)
If a door cylinder lock switch fails any of the
resistance tests, replace the faulty switch as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the door outside latch handle mount-
ing hardware and linkage from the inside of the door.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR - FRONT/EXTERIOR
HANDLE - REMOVAL).
(3) From the outside of the door, pull the door out-
side latch handle out from the door far enough to
access the door cylinder lock switch (Fig. 1).
(4) Disengage the door cylinder lock switch from
the back of the lock cylinder.
(5) Disconnect the door cylinder lock switch pigtail
wire connector from the door wire harness connector.(6) Disengage the retainers that secure the door
cylinder lock switch pigtail wire harness to the inner
door panel.
(7) Remove the door cylinder lock switch from the
door.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the door cylinder lock switch into the
door (Fig. 1).
(2) Engage the retainers that secure the door cyl-
inder lock switch pigtail wire harness to the inner
door panel.
(3) Reconnect the door cylinder lock switch pigtail
wire connector to the door wire harness connector.
(4) Reinstall the door cylinder lock switch onto the
back of the lock cylinder.
(5) Reinstall the door outside latch handle mount-
ing hardware and linkage on the inside of the door.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR - FRONT/EXTERIOR
HANDLE - INSTALLATION).
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
POWER LOCK MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
Models equipped with the optional power lock sys-
tem have a power operated door locking mechanism
located within each front door. The lock mechanisms
are actuated by a reversible electric power lock motor
that is integral to the door latch unit within each
front door. A single short pigtail wire with a molded
plastic connector insulator connects the door lock
motor to the vehicle electrical system through a take
out and connector of each front door wire harness.
The power lock motors cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the entire door
latch unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
On models with a base version of the Central
Timer Module (CTM), the power lock motor is con-
trolled by the battery and ground feeds from the
power lock switches. On models with the high-line or
premium versions of the CTM, the power lock motor
is controlled by the battery and ground feeds from
the power lock and unlock relays, which are integral
and internal to the high-line and premium versions
of the CTM. A positive and negative battery connec-
tion to the two motor terminals will cause the power
lock motor plunger to move in one direction. Revers-
ing the current through these same two connections
will cause the power lock motor plunger to move in
the opposite direction.
The power lock motors and circuits can be tested
using conventional diagnostic tools and methods.
Fig. 1 Door Cylinder Lock Switch
1 - DOOR OUTSIDE LATCH HANDLE
2 - DOOR
3 - DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH
4 - CONNECTOR
5 - RETAINERS
8N - 6 POWER LOCKSBR/BE
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH (Continued)
Page 656 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER LOCK
MOTOR
On models with a base version of the Central
Timer Module (CTM), confirm proper power lock
switch operation before you proceed with this diagno-
sis. On models with a high-line or premium version
of the CTM, confirm proper power lock switch, power
lock switch output circuit, and CTM operation before
you proceed with this diagnosis. Remember, the
power lock switch controls the output to the power
lock motors on models with a base CTM, while the
CTM controls the output to the power lock motors on
models with a high-line or premium CTM. Refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Check each power lock motor for correct opera-
tion while moving the power lock switch to both the
Lock and Unlock positions. If both of the power lock
motors are inoperative, go to Step 2. If one power
lock motor is inoperative, go to Step 3.
(2) If both of the power lock motors are inopera-
tive, the problem may be caused by one shorted
motor. Disconnecting a shorted power lock motor
from the power lock circuit will allow the good power
lock motors to operate. Disconnect the wire harness
connector from each power lock motor, one at a time,
and recheck both the lock and unlock functions by
operating the power lock switch. If both power lock
motors are still inoperative after the above test,
check for a short or open circuit between the power
lock motors and either the power lock switch (base
CTM) or the CTM (high-line or premium CTM). If
disconnecting one power lock motor causes the other
motor to become functional, go to Step 3 to test the
disconnected motor.
(3) Once it is determined which power lock motor
is inoperative, that motor can be tested as follows.
Disconnect the door wire harness connector from the
inoperative power lock motor. Apply 12 volts to the
lock and unlock driver circuit cavities of the power
lock motor pigtail wire connector to check its opera-
tion in one direction. Reverse the polarity to check
the motor operation in the opposite direction. If OK,
repair the shorted or open circuits between the power
lock motor and the power lock switch (base CTM) or
the CTM (high-line or premium CTM) as required. If
not OK, replace the faulty power lock motor.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
TRANSMITTER
DESCRIPTION
The Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system Radio
Frequency (RF) transmitter is equipped with three
buttons, labeled Lock, Unlock, and Panic. It is also
equipped with a key ring and is designed to serve as
a key fob. The operating range of the transmitter
radio signal is up to 7 meters (23 feet) from the RKE
receiver. The RKE receiver is integral to the high-
line or premium Central Timer Module (CTM) in this
vehicle.
Each RKE transmitter has a different vehicle
access code, which must be programmed into the
memory of the RKE receiver in the vehicle in order
to operate the RKE system. The RKE receiver can
retain the access codes for up to four transmitters in
its memory. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
LOCKS/REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMIT-
TER - STANDARD PROCEDURE - RKE TRANS-
MITTER PROGRAMMING).
The RKE transmitter operates on two Duracell
DL2016, Panasonic CR2016 (or equivalent) batteries.
Typical battery life is from one to two years. The
RKE transmitter cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitters.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REMOTE KEYLESS
ENTRY TRANSMITTER
(1) Replace the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
transmitter batteries. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
POWER LOCKS/REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
TRANSMITTER - STANDARD PROCEDURE - RKE
TRANSMITTER BATTERIES). Test each of the RKE
transmitter functions. If OK, discard the faulty bat-
teries. If not OK, go to Step 2.
(2) Program the suspect RKE transmitter and
another known good transmitter into the RKE
receiver. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
LOCKS/REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMIT-
TER - STANDARD PROCEDURE - RKE TRANS-
MITTER PROGRAMMING).
(3) Test the RKE system operation with both
transmitters. If both transmitters fail to operate the
power lock system, a DRBIIItscan tool is required
for further diagnosis of the RKE system. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. If the known
good RKE transmitter operates the power locks and
BR/BEPOWER LOCKS 8N - 7
POWER LOCK MOTOR (Continued)
Page 657 of 2889

the suspect transmitter does not, replace the faulty
RKE transmitter.
NOTE: Be certain to perform the RKE Transmitter
Programming procedure again following this test.
This procedure will erase the access code of the
test transmitter from the RKE receiver.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RKE TRANSMITTER
PROGRAMMING
To program the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
transmitter access codes into the RKE receiver in the
high-line or premium Central Timer Module (CTM)
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RKE TRANSMITTER
BATTERIES
The Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter case
snaps open and shut for battery access. To replace
the RKE transmitter batteries:
(1) Using a trim stick or a thin coin, gently pry at
the notch in the center seam of the RKE transmitter
case halves located near the key ring until the two
halves unsnap.
(2) Lift the back half of the transmitter case off of
the RKE transmitter.
(3) Remove the two batteries from the RKE trans-
mitter.
(4) Replace the two batteries with new Duracell
DL2016, or their equivalent. Be certain that the bat-
teries are installed with their polarity correctly ori-
ented.
(5) Align the two RKE transmitter case halves
with each other, and squeeze them firmly and evenly
together using hand pressure until they snap back
into place.
POWER LOCK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The power lock system can be controlled by a two-
way momentary switch integral to the power window
and lock switch and bezel unit on the trim panel of
each front door. Each power lock switch is illumi-
nated by a Light-Emitting Diode (LED) that is inte-
gral to the switch paddle. The LED of each switch is
illuminated whenever the ignition switch is in the
On position.
The power lock switches and their LEDs cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire power window and lock switch and bezel unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
On models with a base version of the Central
Timer Module (CTM), the power lock switches are
hard-wired to the power lock motors. The power lock
switch provides the correct battery and ground feeds
to the power lock motors to lock or unlock the door
latches.
On models with a high-line or premium version of
the CTM, the power lock switch controls battery cur-
rent signals to the lock and unlock sense inputs of
the CTM. The CTM then relays the correct battery
and ground feeds to the power lock motors to lock or
unlock the door latches.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER LOCK
SWITCH
The Light-Emitting Diode (LED) illumination
lamps for all of the power window and lock switch
and bezel unit switch paddles receive battery current
through the power window circuit breaker in the
Junction Block (JB). If all of the LEDs are inopera-
tive in either or both power window and lock switch
and bezel units, be certain to diagnose the power
window system before replacing the switch unit.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If only one LED in a
power window and lock switch and bezel unit is inop-
erative, replace the faulty switch and bezel unit.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse (Fuse 13 - 10
ampere) in the Junction Block (JB). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
(Fuse 13 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit between
the JB and the Power Distribution Center (PDC) as
required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power window and lock switch and
bezel unit from the door trim panel. Disconnect the
door wire harness connector for the power window
and lock switch unit from the switch connector recep-
tacle.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
door wire harness connector for the power window
and lock switch unit. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK,
repair the open fused B(+) circuit between the power
window and lock switch unit and the JB as required.
8N - 8 POWER LOCKSBR/BE
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER (Continued)
Page 658 of 2889
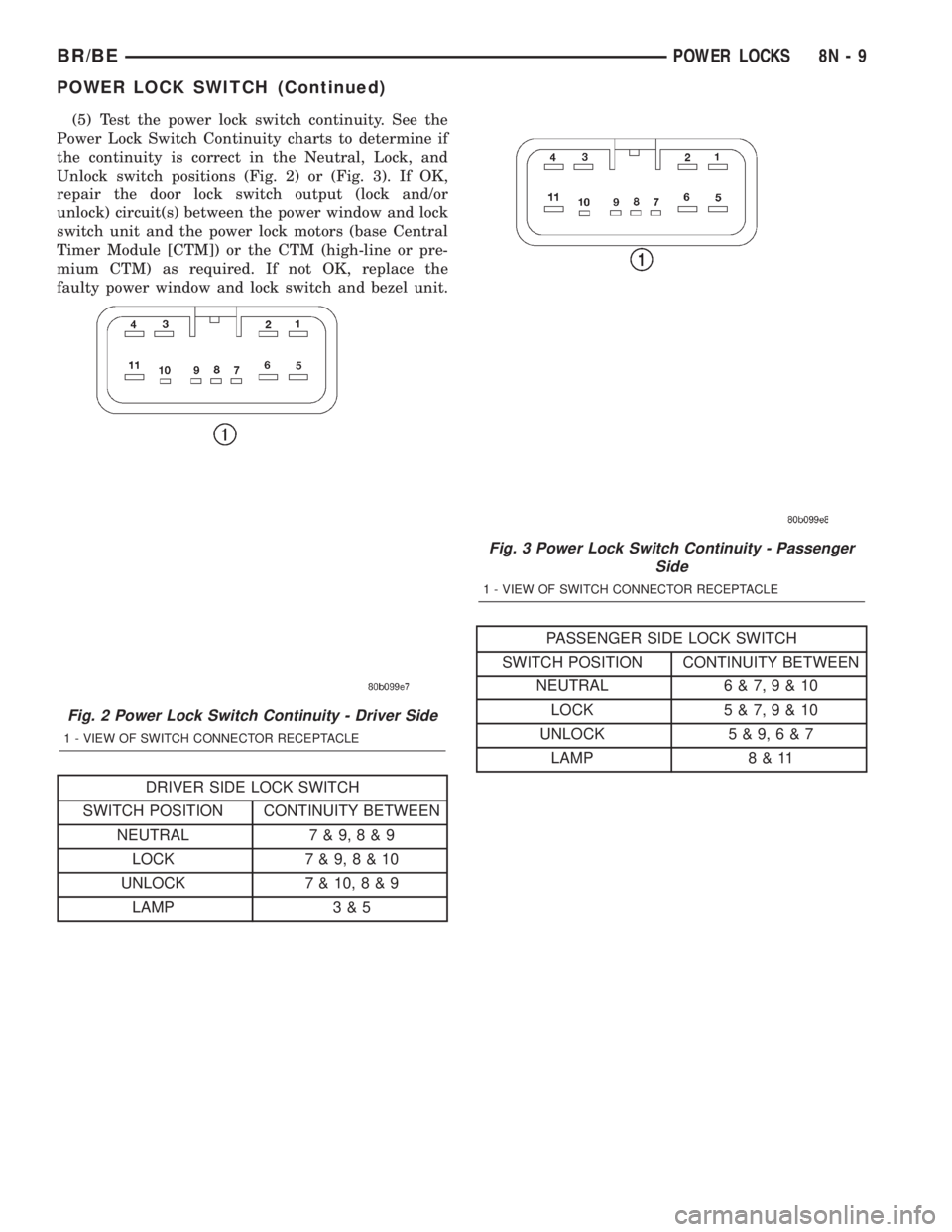
(5) Test the power lock switch continuity. See the
Power Lock Switch Continuity charts to determine if
the continuity is correct in the Neutral, Lock, and
Unlock switch positions (Fig. 2) or (Fig. 3). If OK,
repair the door lock switch output (lock and/or
unlock) circuit(s) between the power window and lock
switch unit and the power lock motors (base Central
Timer Module [CTM]) or the CTM (high-line or pre-
mium CTM) as required. If not OK, replace the
faulty power window and lock switch and bezel unit.
DRIVER SIDE LOCK SWITCH
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
NEUTRAL 7 & 9,8&9
LOCK 7 & 9,8&10
UNLOCK 7 & 10,8&9
LAMP 3 & 5
PASSENGER SIDE LOCK SWITCH
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
NEUTRAL 6 & 7,9&10
LOCK 5 & 7,9&10
UNLOCK 5 & 9,6&7
LAMP 8 & 11
Fig. 2 Power Lock Switch Continuity - Driver Side
1 - VIEW OF SWITCH CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
Fig. 3 Power Lock Switch Continuity - Passenger
Side
1 - VIEW OF SWITCH CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
BR/BEPOWER LOCKS 8N - 9
POWER LOCK SWITCH (Continued)
Page 703 of 2889

(1) Reach through the opening between the rear
seat back and the floor panel to position the rear seat
belt buckle/buckle unit (right side) or lap belt/buckle
unit (left side) onto the stud on the rear floor panel
(Fig. 24).
(2) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
rear seat belt buckle/buckle unit (right side) or lap
belt/buckle unit (left side) anchor plate to the stud on
the rear floor panel. Tighten the nut to 40 N´m (29 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Route the lap belt and buckles between the
rear seat back and rear seat cushion.
(4) Disengage the rear seat from its stowed posi-
tion by pulling the release handle on the underside of
the rear seat cushion.
(5) Fold the rear seat cushion down toward the
rear floor panel until the unit is latched in its open
position.
SEAT BELT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The seat belt switch is a small, normally closed,
single pole, single throw, leaf contact, momentary
switch. Only one seat belt switch is installed in the
vehicle, and it is integral to the buckle of the driver
seat belt buckle-half, located near the inboard side of
the driver side front seating position. The seat belt
switch is connected to the vehicle electrical system
through a two-wire pigtail wire and connector on the
seat belt buckle-half, which is connected to a wire
harness connector and take out of the body wire har-
ness.
The seat belt switch cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, the entire driver seat belt
buckle-half unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The seat belt switch is designed to control a path
to ground for the seat belt switch sense input of the
Electro-Mechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC).
When the driver side seat belt tip-half is inserted in
the seat belt buckle, the switch opens the path to
ground; and, when the driver side seat belt tip-half is
removed from the seat belt buckle, the switch closes
the ground path. The switch is actuated by the latch
mechanism within the seat belt buckle. The EMIC
monitors the driver seat belt switch status, then con-
trols the seatbelt indicator and sends hard wired
chime requests to the Central Timer Module (CTM)
based upon that input.The seat belt switch receives ground through its
pigtail wire connection to the body wire harness from
another take out of the body wire harness. An eyelet
terminal connector on that ground take out is
secured under a nut to a ground stud on the left
lower B-pillar (standard cab models) or the left lower
cowl side inner panel (club cab and quad cab models).
The seat belt switch is connected in series between
ground and the seat belt switch sense input of the
EMIC.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT BELT
SWITCH
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the body wire harness connector for
the seat belt switch from the seat belt switch pigtail
wire connector located near the floor panel under the
driver side front seat cushion. Check for continuity
between the seat belt switch sense circuit and the
ground circuit cavities in the seat belt switch pigtail
wire connector. There should be continuity with the
driver side seat belt tip-half and buckle-half unfas-
tened, and no continuity with tip-half and buckle-half
fastened. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace the
faulty driver side seat belt buckle-half unit.
(2) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity in the body wire harness connector for the
seat belt switch and a good ground. There should be
continuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
open ground circuit to ground (G301 - standard cab,
or G300 - club/quad cab) as required.
8O - 28 RESTRAINTSBR/BE
REAR SEAT BELT BUCKLE (Continued)
Page 720 of 2889

VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM........3VTSS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION............................3
OPERATION.............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
VTSS INDICATOR.......................3
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is an
available factory-installed option on this model when
it is also equipped with the high-line or premium
Central Timer Module (CTM). The VTSS is designed
to provide perimeter protection against unauthorized
use or tampering by monitoring the vehicle doors and
the ignition system. If unauthorized vehicle use or
tampering is detected, the system responds by puls-
ing the horn, flashing the headlamps, and preventing
the engine from operating.
The VTSS includes the following major compo-
nents, which are described in further detail else-
where in this service manual:
²Central Timer Module- The high-line or pre-
mium Central Timer Module (CTM) is located under
the driver side end of the instrument panel, inboard
of the instrument panel steering column opening.
The high-line or premium CTM contains a micropro-
cessor and software that allow it to provide many
electronic functions and features not available with
base version of the CTM, including the VTSS. The
CTM provides all of the proper VTSS features and
outputs based upon the monitored inputs. The CTM
circuitry monitors hard wired switch inputs, as well
as message inputs received from other vehicle elec-
tronic modules over the Chrysler Collision Detection
(CCD) data bus network. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/BODY CON-
TROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION).
²Door Ajar Switch- A door ajar switch is
located on the hinge pillar of each front door in the
vehicle. These switches provide an input to the VTSS
indicating whether the door is opened or closed.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING -
INTERIOR/DOOR AJAR SWITCH - DESCRIPTION).
²Door Cylinder Lock Switch- A door cylinder
lock switch is located on the back of each front door
lock cylinder. This switch provides an input to theVTSS indicating whether the system should remain
armed or be disarmed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
POWER LOCKS/DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH
- DESCRIPTION).
²Horn Relay- The horn relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment near the battery. The horn relay is nor-
mally activated by the horn switch to control the
sounding of the vehicle horn or horns. However, it
can also be activated by an output of the Central
Timer Module (CTM) to provide an audible indication
that unauthorized vehicle use or tampering has been
detected. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HORN/HORN
RELAY - DESCRIPTION).
²Headlamp Relay- The headlamp relay (also
known as the security relay) is located in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine compart-
ment near the battery. The headlamp relay is nor-
mally activated by the Central Timer Module (CTM)
based upon inputs from the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) panic mode feature. However, it can also be
activated by an output of the CTM to flash the head-
lamp low beams to provide a highly visible indication
that unauthorized vehicle use or tampering has been
detected. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/HEADLAMP RELAY - DESCRIP-
TION).
²VTSS Indicator- A red Light Emitting Diode
(LED) located on the lower surface of the overhead
console near the windshield is illuminated by an out-
put of the Central Timer Module (CTM) to indicate
the status of the VTSS. This LED is integral to the
electronic circuit board for the Compass Mini-Trip
Computer (CMTC). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
OVERHEAD CONSOLE/COMPASS/MINI-TRIP
COMPUTER - DESCRIPTION).
The engine no-run feature of the VTSS relies upon
communication between the high-line or premium
CTM and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) over
the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD) data bus net-
work.
Hard wired circuitry connects many of the VTSS
components to each other through the electrical sys-
BR/BEVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 1
Page 721 of 2889

tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
VTSS components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
A Central Timer Module (CTM) is used on this
model to control and integrate many of the electronic
functions and features included in the Vehicle Theft
Security System (VTSS). In the VTSS, the CTM
receives inputs indicating the status of the door ajar
switches, the door cylinder lock switch, and the igni-
tion switch. The programming in the CTM allows it
to process the information from all of these inputs
and send control outputs to energize or de-energize
the horn relay, the headlamp relay, and the VTSS
indicator. The control of these inputs and outputs are
what constitute all of the features of the VTSS. Fol-
lowing is information on the operation of each of the
VTSS features. Refer to the owner's manual in the
vehicle glove box for more information on the fea-
tures, use and operation of the VTSS.
ENABLING
The high-line or premium version of the CTM must
have the VTSS function electronically enabled in
order for the VTSS to perform as designed. The logic
in the CTM keeps its VTSS function dormant until it
is enabled using a DRBIIIž scan tool. The VTSS
function of the high-line or premium CTM is enabled
on vehicles equipped with the VTSS option at the
factory, but a service replacement CTM must be
VTSS-enabled by the dealer using a DRBIIIž scan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
The VTSS engine no-run feature is disabled when
it is shipped from the factory. This is done by pro-
gramming within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The logic in the PCM prevents the VTSS
engine no-run feature from arming until the engine
start counter within the PCM sees twenty engine
starts. The VTSS no-run feature must be enabled by
the dealer when the vehicle is received from the
assembly plant. Once the VTSS engine no-run fea-
ture has been enabled, it cannot be disabled unless
the PCM is replaced with a new unit. The sameVTSS engine no-run feature enable logic will apply
anytime the PCM is replaced with a new unit.
ARMING
Passive arming of the VTSS occurs when the vehi-
cle is exited with the key removed from the ignition
switch, the headlamps are turned off, and the doors
are locked while they are open using the power lock
switch, or locked after they are closed by turning
either front door lock cylinder to the lock position
using the key. The power lock switch will not func-
tion if the key is in the ignition switch or the head-
lamps are turned on with the driver side front door
open. The VTSS will not arm if the doors are locked
using the mechanical lock button. Active arming of
the VTSS occurs when the ªLockº button on the
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter is
depressed to lock the vehicle. For active arming to
occur, the doors must be closed and the ignition
switch must be in the Off position when the RKE
transmitter ªLockº button is depressed. However,
once the VTSS arming process has been completed,
the ignition switch can be turned to the Accessory
position without triggering the alarm.
Once the VTSS begins passive or active arming,
the security indicator lamp in the overhead console
will flash rapidly for about fifteen seconds. This indi-
cates that the VTSS arming is in progress. Turning a
key in the ignition switch, opening a door, or unlock-
ing a door by any means during the fifteen second
arming process will cause the VTSS indicator to stop
flashing and the arming process to abort. Once the
fifteen second arming function is successfully com-
pleted, the indicator will flash at a slower rate, indi-
cating that the VTSS is armed.
DISARMING
Passive disarming of the VTSS occurs when the
vehicle is unlocked using the key to unlock either
front door. Active disarming of the VTSS occurs when
the vehicle is unlocked by depressing the ªUnlockº
button of the RKE transmitter. Once the alarm has
been activated (horn pulsing, headlamps flashing,
and the engine no-run feature), either disarming
method will also deactivate the alarm. Depressing
the ªPanicº button on the RKE transmitter willnot
disarm the VTSS.
POWER-UP MODE
When the armed VTSS senses that the battery has
been disconnected and reconnected, it enters its pow-
er-up mode. In the power-up mode the alarm system
remains armed following a battery failure or discon-
nect. If the VTSS was armed prior to a battery dis-
connect or failure, the technician or vehicle operator
will have to actively or passively disarm the alarm
system after the battery is reconnected. The pow-
8Q - 2 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYBR/BE
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 722 of 2889

er-up mode will also apply if the battery goes dead
while the system is armed, and battery jump-starting
is attempted. The engine no-run feature will prevent
the engine from starting until the alarm system has
been actively or passively disarmed. The VTSS will
be armed until the technician or vehicle operator has
actively or passively disarmed the alarm system. If
the VTSS is in the disarmed mode prior to a battery
disconnect or failure, it will remain disarmed after
the battery is reconnected or replaced, or if jump-
starting is attempted.
TAMPER ALERT
The VTSS tamper alert feature will sound the horn
three times upon disarming, if the alarm was trig-
gered and has since timed-out (about fifteen min-
utes). This feature alerts the vehicle operator that
the VTSS alarm was activated while the vehicle was
unattended.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY SYSTEM
The VTSS-related hard wired inputs to and out-
puts from the high-line or premium Central Timer
Module (CTM) may be diagnosed and tested using
conventional diagnostic tools and procedures. Refer
to the appropriate wiring information. The wiring
information includes wiring diagrams, proper wire
and connector repair procedures, further details on
wire harness routing and retention, as well as pin-
out and location views for the various wire harness
connectors, splices and grounds.
However, conventional diagnostic methods may not
prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the CTM, the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM), or the Chrysler
Collision Detection (CCD) data bus network. In order
to obtain conclusive testing of the VTSS, the CTM,
the PCM, and the CCD data bus network must also
be checked. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the VTSS requires the use of a
DRBIIIž scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. The DRBIIIž scan tool can provide
confirmation that the CCD data bus network is func-
tional, that all of the electronic modules are sending
and receiving the proper messages over the CCD
data bus, and that these modules are receiving the
proper hard wired inputs and responding with the
proper hard wired outputs needed to perform their
functions. See the ªVehicle Theft Security Systemº
menu item on the DRBIIIž scan tool.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
VTSS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) indica-
tor consists of a red Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
located on the electronic circuit board of the Compass
Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC) within the overhead
console. The LED extends through a hole in the
CMTC lens located near the forward end of the over-
head console housing near the windshield.
The VTSS indicator cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, the entire CMTC unit
must be replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVER-
HEAD CONSOLE/COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COM-
PUTER - DESCRIPTION).
OPERATION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) indica-
tor gives a visible indication of the VTSS arming sta-
tus. One side of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) in the
VTSS indicator is connected to battery current
through a fused B(+) circuit and a fuse in the Junc-
tion Block (JB), so the indicator remains functional
regardless of the ignition switch position. The other
side of the LED is hard wired to the Central Timer
Module (CTM), which controls the operation of the
VTSS indicator by pulling this side of the LED cir-
cuit to ground. When the VTSS arming is in
progress, the CTM will flash the LED rapidly on and
off for about fifteen seconds. When the VTSS has
been successfully armed, the CTM will flash the LED
on and off continually at a much slower rate until
the VTSS has been disarmed. The VTSS indicator
can be diagnosed using conventional diagnostic tools
and methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VTSS INDICATOR
The diagnosis found here addresses an inoperative
Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) indicator con-
dition. If the problem being diagnosed is related to
indicator accuracy, be certain to confirm that the
problem is with the indicator and not with an inop-
erative VTSS. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE
THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM- DIAGNOSIS AND
BR/BEVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 3
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 724 of 2889

WIPERS/WASHERS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WIPERS/WASHERS
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
WIPER & WASHER SYSTEM...............3
CLEANING...............................6
INSPECTION.............................6
WASHER FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................8
WASHER HOSES/TUBES
DESCRIPTION............................8
OPERATION.............................8
WASHER NOZZLE
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................9
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................9
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
WASHER RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION...........................10OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................11
WIPER ARM
DESCRIPTION...........................11
OPERATION.............................12
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................12
WIPER BLADE
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................13
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
WIPER MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................14
OPERATION.............................14
REMOVAL..............................14
INSTALLATION...........................15
WIPER RELAY
DESCRIPTION...........................15
OPERATION.............................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................16
WIPER RELAY.........................16
REMOVAL..............................17
INSTALLATION...........................17
WIPERS/WASHERS
DESCRIPTION
An electrically operated intermittent wiper and
washer system is standard factory-installed safety
equipment on this model. The wiper and washer sys-
tem includes the following major components, which
are described in further detail elsewhere in this ser-
vice information:
²Central Timer Module- The Central Timer
Module (CTM) is located under the driver side end of
the instrument panel, inboard of the instrument
panel steering column opening. A base version of the
CTM is used on base models of this vehicle. The base
version of the CTM combines the functions of a
chime module and an intermittent wipe module in a
single unit. The high-line version of the CTM is used
on high-line vehicles. The high-line CTM provides all
of the functions of the base version of the CTM, but
also is used to control and integrate many additionalelectronic functions and features included on high-
line models. The premium version of the CTM is the
same as the high-line version, but is used only on
models equipped with the heated seat option. The
high-line and premium versions of the CTM contain
integrated circuitry, a central processing unit and the
programming to provide all of the proper wiper and
washer system features based upon the monitored
inputs. The high-line and premium CTM circuitry
monitors hard wired switch inputs, as well as mes-
sage inputs received from other vehicle electronic
modules on the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD)
data bus network. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/BODY CONTROL/
CENTRAL TIMER MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Multi-Function Switch- The multi-function
switch is secured to the left side of the steering col-
umn, just below the steering wheel. Only the control
stalk for the multi-function switch is visible, the
remainder of the switch is concealed beneath the
steering column shrouds. The multi-function switch
BR/BEWIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 1
Page 726 of 2889

activates the washer pump/motor, which dispenses
washer fluid onto the windshield glass through the
washer nozzles.
When the ignition switch is in the Accessory or On
positions, battery current from a fuse in the Junction
Block (JB) is provided through a fused ignition
switch output (run-acc) circuit to the wiper motor
park switch, the wiper relay, and the multi-function
switch. The internal circuitry of the multi-function
switch provides a direct hard wired battery current
output to the low speed or high speed brushes of the
wiper motor when the Lo or Hi switch setting is
selected, which causes the wipers to cycle at the
selected speed. The intermittent wipe, and wipe-af-
ter-wash features of the wiper and washer system
are provided by the electronic intermittent wipe logic
circuit within the Central Timer Module (CTM). In
order to provide the intermittent wipe feature, the
CTM monitors the wiper switch state and the wiper
motor park switch state. In order to provide the
wipe-after-wash feature, the CTM monitors both the
washer switch state and the wiper motor park switch
state. When a Delay position is selected with the
multi-function switch control knob, the CTM logic cir-
cuit responds by calculating the correct delay inter-
val. The CTM then energizes the wiper relay by
pulling the relay control coil to ground. The ener-
gized wiper relay directs battery current through the
normally open contact of the relay back through the
internal circuitry of the multi-function switch to the
low speed brush of the wiper motor. The CTM moni-
tors the wiper motor operation through the wiper
park switch sense circuit, which allows the CTM to
determine the proper timing to begin the next wiper
blade sweep. The normal delay intervals are driver
adjustable from about one-half second to about eigh-
teen seconds.
The high-line and premium CTM also provides a
speed sensitive intermittent wipe feature. By moni-
toring vehicle speed messages received from the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) over the Chrysler
Collision Detection (CCD) data bus network, the
high-line or premium CTM is able to adjust the delay
intervals to compensate for vehicle speed. Above
about sixteen kilometers-per-hour (ten miles-per-
hour) the delay is driver adjustable from about one-
half second to about eighteen seconds. Below about
sixteen kilometers-per-hour (ten miles-per-hour) the
delay times are doubled by the CTM, from about one
second to about thirty-six seconds.
When the Off position of the multi-function switch
wiper control knob is selected, one of two events is
possible. The event that will occur depends upon the
position of the wiper blades on the windshield at the
moment that the Off position is selected. If the wiper
blades are in the down position on the windshieldwhen the Off position is selected, the park switch
that is integral to the wiper motor is closed to ground
and the wiper motor ceases to operate. If the wiper
blades are not in the down position on the windshield
at the moment the Off position is selected, the park
switch is closed to battery current through a fused
ignition switch output (run-acc) circuit. The park
switch sense circuit directs this battery current to
the low speed brush of the wiper motor through the
normally closed contact of the wiper relay and the
internal Off position circuitry of the multi-function
switch. This causes the wiper motor to continue run-
ning until the wiper blades are in the down position
on the windshield and the park switch is again
closed to ground.
When the Wash position of the multi-function
switch is selected, the Wash position circuitry within
the switch directs battery current to the washer
pump/motor. The CTM monitors the washer switch
state through a washer switch sense input. When the
washer switch is closed with the wiper system turned
Off, the CTM operates the wiper motor through the
wiper relay in the same manner as it does to provide
the Delay mode operation. After the state of the
washer switch changes to open, the CTM monitors
the wiper motor through the wiper park switch sense
circuit, which allows the CTM to monitor the number
of wiper blade sweeps.
Proper testing of the CTM, the PCM, or the CCD
data bus vehicle speed messages requires a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation. Refer to the owner's manual in the vehicle
glove box for more information on the features and
operation of the wiper and washer system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIPER &
WASHER SYSTEM
WIPER SYSTEM
The diagnosis found here addresses an electrically
inoperative wiper system. If the wiper motor oper-
ates, but the wipers do not move on the windshield,
replace the faulty wiper module. If the wipers oper-
ate, but chatter, lift, or do not clear the glass, clean
and inspect the wiper system components as
required. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/
WASHERS - INSPECTION) and (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS - CLEANING). Refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
The following tests will help to diagnose the hard
wired components and circuits of the wiper system.
BR/BEWIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 3
WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)