dimensions DODGE RAM 2002 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1072 of 2255

HEADLAMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The headlamp (or security) relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay. The termi-
nal designations and functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the micro-relay
terminal orientation (or footprint) is different, cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the relay case dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The headlamp relay is a electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the headlamps when
the high-line or premium Central Timer Module
(CTM) grounds the relay coil. See Headlamp Relay in
the Diagnosis and Testing section of this group for
more information.
The headlamp (or security) relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC), in the engine com-
partment. Refer to the PDC label for relay identifica-
tion and location.
The headlamp relay cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 15).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for headlamp (or
security) relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the headlamp relay from the PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the headlamp relay by aligning the
relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
MICRO-RELAY
DESCRIPTION
A micro-relay is a conventional International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO) micro relay (Fig. 16).
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The relay is
Fig. 14 Power Distribution Center
1 - COVER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
Fig. 15 Power Distribution Center
1 - COVER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
Fig. 16 ISO MICRO RELAY
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
BR/BE8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 13
HORN RELAY (Continued)
Page 1073 of 2255

contained within a small, rectangular, molded plastic
housing and is connected to all of the required inputs
and outputs by five integral male spade-type termi-
nals that extend from the bottom of the relay base.
Relays cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty
or damaged, the unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
A micro-relay is an electromechanical switch that
uses a low current input from one source to control a
high current output to another device. The movable
common feed contact point is held against the fixed
normally closed contact point by spring pressure.
When the relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic
field is produced by the coil windings. This electro-
magnetic field draws the movable relay contact point
away from the fixed normally closed contact point,
and holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. A
resistor is connected in parallel with the relay coil in
the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes and
electromagnetic interference that can be generated as
the electromagnetic field of the relay coil collapses.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MICRO-RELAY
(1) Remove the relay from its mounting location.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 67.5 - 82.5 ohms. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, reinstall the relay and use a DRBIIIt
scan tool to perform further testing. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the relay by grasping it firmly and
pulling it straight out from its receptacle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the micro-relay terminals with the termi-
nal cavities in the receptacle.(2) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the relay
until the terminals are fully seated in the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
A relay is an electromechanical device that
switches fused battery current to a electrical compo-
nent when the ignition switch is turned to the Acces-
sory or Run positions, or when controlled by a
electronic module. The relays are located in the junc-
tion block or power distribution center (Fig. 17).
The relay is a International Standards Organiza-
tion (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to the ISO speci-
fications have common physical dimensions, current
capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal functions.
A relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor and three (two fixed and one movable) elec-
trical contacts. The movable (common feed) relay con-
tact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor is connected in
parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the relay,
and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are pro-
duced when the coil is de-energized.
Fig. 17 TYPE 1 RELAY
8W - 97 - 14 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
MICRO-RELAY (Continued)
Page 1223 of 2255
INSTALLATION
(1) If previously removed, install the push rods in
their original location (Fig. 62).Verify that they
are seated in the tappets.
(2) Lubricate the valve tips and install the cross-
heads in their original locations.
(3) Lubricate the crossheads and push rod sockets
and install the rocker arms and pedestals (Fig. 60) in
their original locations. Tighten bolts to 36 N´m (27
ft. lbs.) torque.
(4)Verify valve lash adjustment (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Install cylinder head cover and reusable gasket
(Fig. 59) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Connect battery negative cables.
ENGINE BLOCK
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BLOCK
REFACING
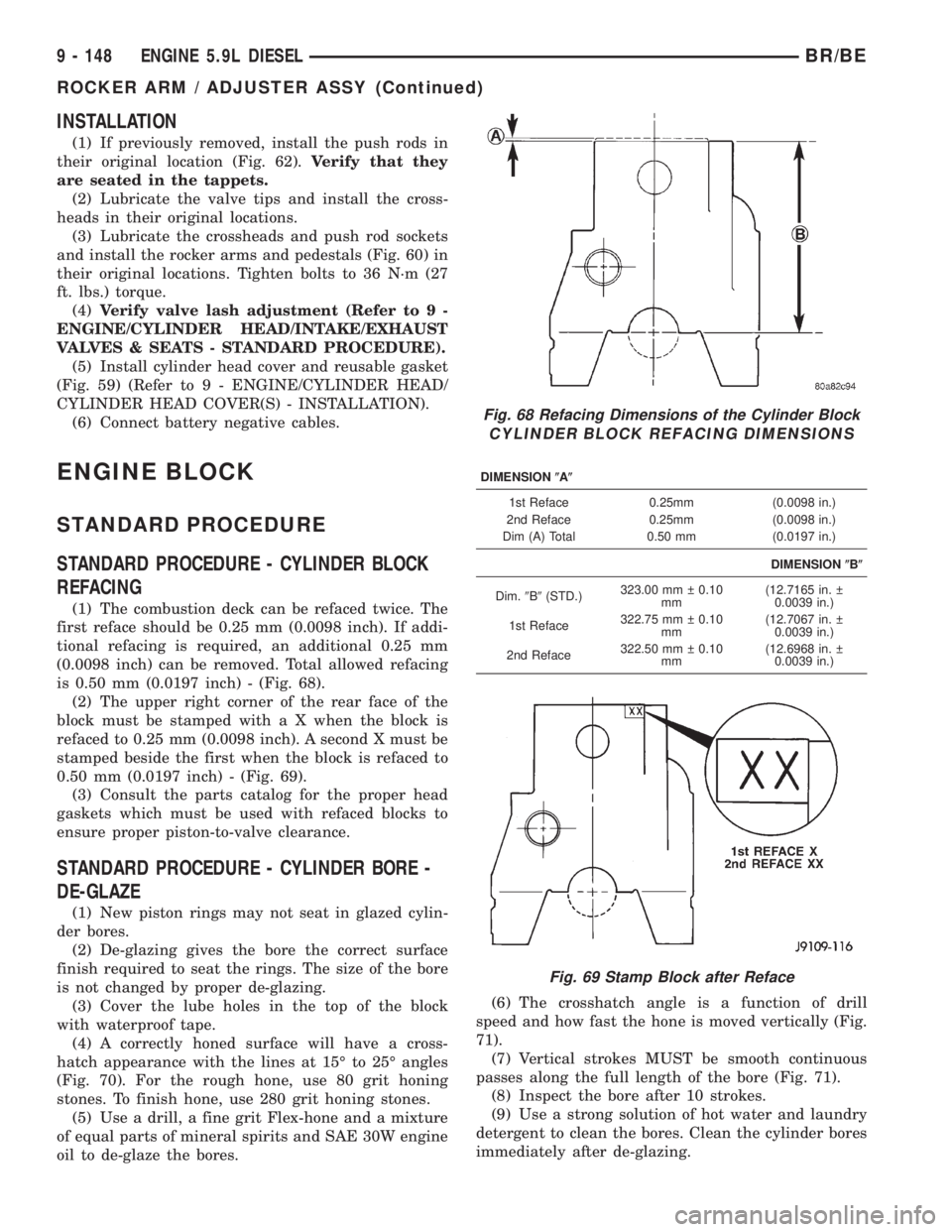
(1) The combustion deck can be refaced twice. The
first reface should be 0.25 mm (0.0098 inch). If addi-
tional refacing is required, an additional 0.25 mm
(0.0098 inch) can be removed. Total allowed refacing
is 0.50 mm (0.0197 inch) - (Fig. 68).
(2) The upper right corner of the rear face of the
block must be stamped with a X when the block is
refaced to 0.25 mm (0.0098 inch). A second X must be
stamped beside the first when the block is refaced to
0.50 mm (0.0197 inch) - (Fig. 69).
(3) Consult the parts catalog for the proper head
gaskets which must be used with refaced blocks to
ensure proper piston-to-valve clearance.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE -
DE-GLAZE
(1) New piston rings may not seat in glazed cylin-
der bores.
(2) De-glazing gives the bore the correct surface
finish required to seat the rings. The size of the bore
is not changed by proper de-glazing.
(3) Cover the lube holes in the top of the block
with waterproof tape.
(4) A correctly honed surface will have a cross-
hatch appearance with the lines at 15É to 25É angles
(Fig. 70). For the rough hone, use 80 grit honing
stones. To finish hone, use 280 grit honing stones.
(5) Use a drill, a fine grit Flex-hone and a mixture
of equal parts of mineral spirits and SAE 30W engine
oil to de-glaze the bores.(6) The crosshatch angle is a function of drill
speed and how fast the hone is moved vertically (Fig.
71).
(7) Vertical strokes MUST be smooth continuous
passes along the full length of the bore (Fig. 71).
(8) Inspect the bore after 10 strokes.
(9) Use a strong solution of hot water and laundry
detergent to clean the bores. Clean the cylinder bores
immediately after de-glazing.
Fig. 68 Refacing Dimensions of the Cylinder Block
CYLINDER BLOCK REFACING DIMENSIONS
DIMENSION(A(
1st Reface 0.25mm (0.0098 in.)
2nd Reface 0.25mm (0.0098 in.)
Dim (A) Total 0.50 mm (0.0197 in.)
DIMENSION(B(
Dim.9B9(STD.)323.00 mm 0.10
mm(12.7165 in.
0.0039 in.)
1st Reface322.75 mm 0.10
mm(12.7067 in.
0.0039 in.)
2nd Reface322.50 mm 0.10
mm(12.6968 in.
0.0039 in.)
Fig. 69 Stamp Block after Reface
9 - 148 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY (Continued)
Page 1224 of 2255

(10) Rinse the bores until the detergent is removed
and blow the block dry with compressed air.
(11) Check the bore cleanliness by wiping with a
white, lint free, lightly oiled cloth. If grit residue is
still present, repeat the cleaning process until all res-
idue is removed. Wash the bores and the complete
block assembly with solvent and dry with compressed
air.
(12) Be sure to remove the tape covering the lube
holes after the cleaning process is complete.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
REPAIR
Cylinder bore(s) can be repaired by one of two
methods:
²Method 1:ÐOver boring and using oversize pis-
tons and rings.
²Method 2:ÐBoring and installing a repair sleeve
to return the bore to standard dimensions.
METHOD 1ÐOVERSIZE BORE
Cylinder bore(s) can be repaired by one of two
methods:
Oversize pistons and rings are available in two
sizes - 0.50 mm (0.0197 inch) and 1.00 mm (0.0393
inch).Any combination of standard, 0.50 mm (0.0197
inch) or 1.00 mm (0.0393 inch) overbore may be used
in the same engine.
If more than 1.00 mm (0.0393 inch) overbore is
needed, a repair sleeve can be installed (refer to
Method 2ÐRepair Sleeve).
Cylinder block bores may be bored twice before use
of a repair sleeve is required (Fig. 72). The first bore
is 0.50 mm (0.0197 inch) oversize. The second bore is
1.00 mm (0.0393 inch) oversize.
After boring to size, use a honing stone to chamfer
the edge of the bore (Fig. 72).
CYLINDER BORE DIMENSION CHART
DESCRIPTION MEASUREMENT
BORING DIAMETER
DIMENSION1st. REBORE - 102.469
mm (4.0342 in.)
2nd. REBORE - 102.969
mm (4.0539 in.)
HONING DIAMETER
DIMENSIONSSTANDARD - 102.020
0.020 mm (4.0165
0.0008 in.)
1st. REBORE - 102.520
0.020 mm (4.0362
0.0008 in.)
2nd. REBORE - 103.020
0.020 mm 4.0559
0.0008 in.)
CHAMFER
DIMENSIONSApprox. 1.25 mm (0.049
in.) by 15É
A correctly honed surface will have a crosshatch
appearance with the lines at 15É to 25É angles with
the top of the cylinder block (Fig. 73). For the rough
hone, use 80 grit honing stones. To finish hone, use
280 grit honing stones.
Fig. 70 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
Fig. 71 De-Glazing Drill Speed and Vertical SpeedFig. 72 Cylinder Bore Dimensions
1 - CHAMFER
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 149
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1225 of 2255
A maximum of 1.2 micrometer (48 microinch) sur-
face finish must be obtained.
After finish honing is complete, immediately clean
the cylinder bores with a strong solution of laundry
detergent and hot water.
After rinsing, blow the block dry.
Check the bore cleanliness by wiping with a white,
lint-free, lightly- oiled cloth. There should be no grit
residue present.
If the block is not to be used right away, coat it
with a rust- preventing compound.
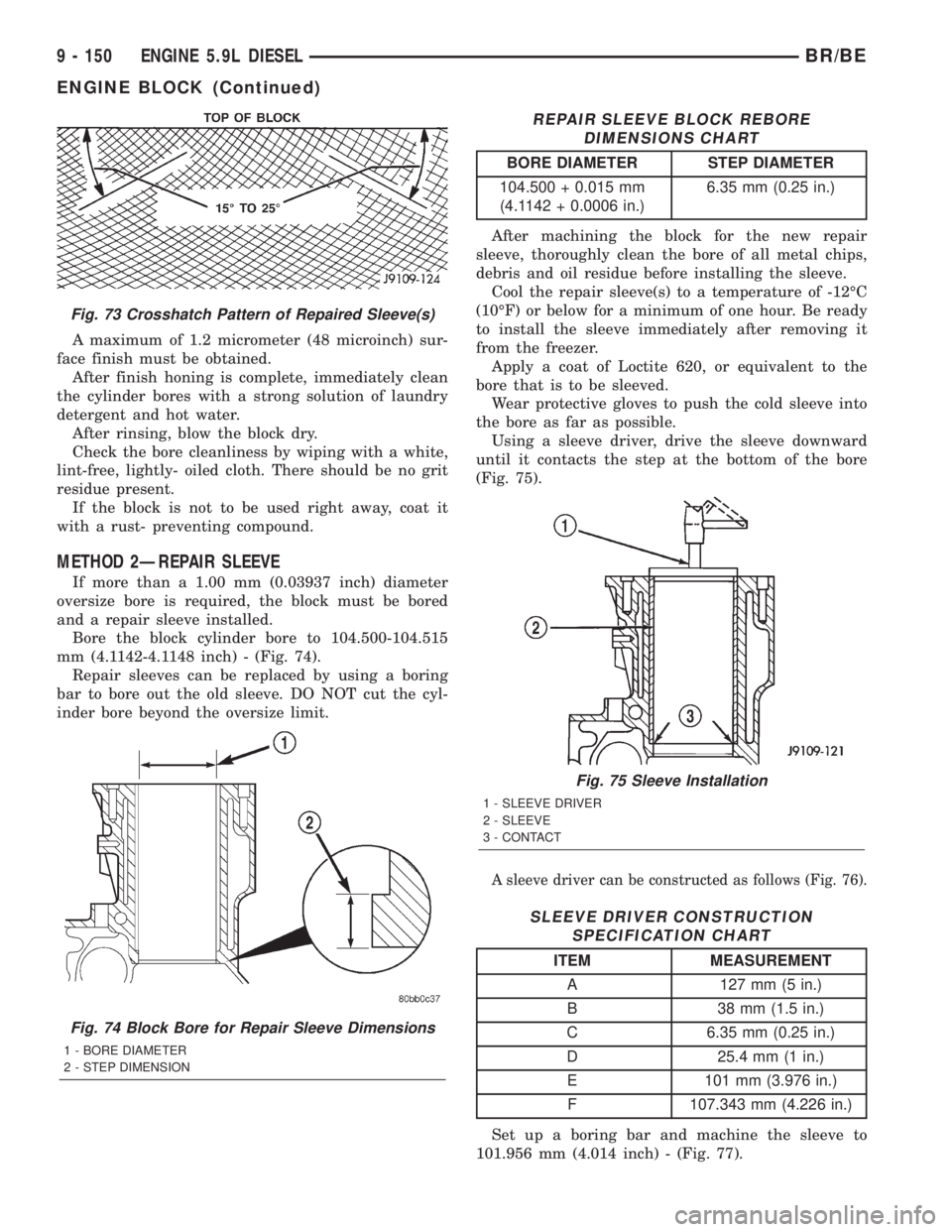
METHOD 2ÐREPAIR SLEEVE
If more than a 1.00 mm (0.03937 inch) diameter
oversize bore is required, the block must be bored
and a repair sleeve installed.
Bore the block cylinder bore to 104.500-104.515
mm (4.1142-4.1148 inch) - (Fig. 74).
Repair sleeves can be replaced by using a boring
bar to bore out the old sleeve. DO NOT cut the cyl-
inder bore beyond the oversize limit.
REPAIR SLEEVE BLOCK REBORE
DIMENSIONS CHART
BORE DIAMETER STEP DIAMETER
104.500 + 0.015 mm
(4.1142 + 0.0006 in.)6.35 mm (0.25 in.)
After machining the block for the new repair
sleeve, thoroughly clean the bore of all metal chips,
debris and oil residue before installing the sleeve.
Cool the repair sleeve(s) to a temperature of -12ÉC
(10ÉF) or below for a minimum of one hour. Be ready
to install the sleeve immediately after removing it
from the freezer.
Apply a coat of Loctite 620, or equivalent to the
bore that is to be sleeved.
Wear protective gloves to push the cold sleeve into
the bore as far as possible.
Using a sleeve driver, drive the sleeve downward
until it contacts the step at the bottom of the bore
(Fig. 75).
A sleeve driver can be constructed as follows (Fig. 76).
SLEEVE DRIVER CONSTRUCTION
SPECIFICATION CHART
ITEM MEASUREMENT
A 127 mm (5 in.)
B 38 mm (1.5 in.)
C 6.35 mm (0.25 in.)
D 25.4 mm (1 in.)
E 101 mm (3.976 in.)
F 107.343 mm (4.226 in.)
Set up a boring bar and machine the sleeve to
101.956 mm (4.014 inch) - (Fig. 77).
Fig. 73 Crosshatch Pattern of Repaired Sleeve(s)
Fig. 74 Block Bore for Repair Sleeve Dimensions
1 - BORE DIAMETER
2 - STEP DIMENSION
Fig. 75 Sleeve Installation
1 - SLEEVE DRIVER
2 - SLEEVE
3 - CONTACT
9 - 150 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1226 of 2255

After removing the boring bar, use a honing stone
to chamfer the corner of the repair sleeve(s) - (Fig.
77).
SLEEVE MACHINING DIMENSIONS CHART
ITEM MEASUREMENT
SLEEVE PROTRUSION MIN. - FLUSH WITH
BLOCK
MAX. - 0.050 mm
(0.0019 in.)
SLEEVE DIAMETER 101.956 mm (4.014 in.)
SLEEVE CHAMFER APPROX. 1.25 mm
(0.049 in.) by 15É
A correctly honed surface will have a crosshatch
appearance with the lines at 15É to 25É angles with
the top of the cylinder block. For the rough hone, use
80 grit honing stones. To finish hone, use 280 grit
honing stones.Finished bore inside dimension is 102.020 0.020
mm (4.0165 0.0008 inch).
A maximum of 1.2 micrometer (48 microinch) sur-
face finish must be obtained.
After finish honing is complete, immediately clean
the cylinder bores with a strong solution of laundry
detergent and hot water.
After rinsing, blow the block dry with compressed
air.
Wipe the bore with a white, lint-free, lightly oiled
cloth. Make sure there is no grit residue present.
Apply a rust-preventing compound if the block will
not be used immediately.
A standard diameter piston and a piston ring set
must be used with a sleeved cylinder bore.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCAM BORE REPAIR
The front cam bushing bore can be bored to 59.235
Mm 0.013 mm (2.332 inch 0.0006 inch) oversize.
DO NOT bore the intermediate or rear cam bore to
the front cam bore oversize dimensions. Intermediate
and rear cam bores may be bored to 57.235 mm
0.013 mm (2.253 inch 0.0006± inch) oversize.
A surface finish of 2.3 micrometers (92 microinch)
must be maintained. Not more than 20% of an area
of any one bore may be 3.2 micrometers (126 micro-
inch).
Camshaft bores can be repaired individually. It is
not necessary to repair undamaged cam bores in
order to repair individually damaged cam bores. The
standard front bushing cannot be used to repair
intermediate or rear bores.
Install all cam bushings flush or below the front
cam bore surface. The oil hole must align to allow a
3.2 mm (0.125 inch) rod to pass through freely (Fig.
78).
INSPECTION
Measure the combustion deck face using a straight
edge and a feeler gauge (Fig. 79). The distortion of
the combustion deck face is not to exceed 0.010 mm
(0.0004 inch) in any 50.00 mm (2.0 inch) diameter.
Fig. 76 Sleeve Driver Construction
1 - DRIVE
2 - HANDLE
Fig. 77 Sleeve Machining Dimensions
1 - DIAMETER
2 - PROTRUSION
3 - CHAMFER
Fig. 78 Oil Hole Alignment
1 - CAMSHAFT BUSHING
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 151
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1295 of 2255
FRAME FASTENERS
Bolts, nuts and rivets can be used to repair frames
or to install a reinforcement section on the frame.
Bolts can be used in place of rivets. When replacing
rivets with bolts, install the next larger size diameter
bolt to assure proper fit. If necessary, ream the hole
out just enough to sufficiently receive the bolt.
Conical-type washers are preferred over the split-
ring type lock washers. Normally, grade-5 bolts are
adequate for frame repair.Grade-3 bolts or softer
should not be used.Tightening bolts/nuts with thecorrect torque, refer to the Introduction Group at the
front of this manual for tightening information.
SPECIFICATIONS
FRAME DIMENSION
Frame dimensions are listed in Millimeters (mm)
scale. All dimensions are from center to center of
Principal Locating Point (PLP), or from center to cen-
ter of PLP and fastener location (Fig. 10) .
DIMENSIONS FOR DIFFERING WHEELBASES*
WHEELBASE LENGTH
ALENGTH
BLENGTH
C
118 2118.0 3663.6 4185.4
134 2118.0 3994.5 4693.4
138 2626.0 4096.1 4693.4
154 2626.0 4502.5 5201.4
162 2118.0 4705.0 5042.5
*Measurements are in Millimeters (mm).
13 - 8 FRAME & BUMPERSBR/BE
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1296 of 2255
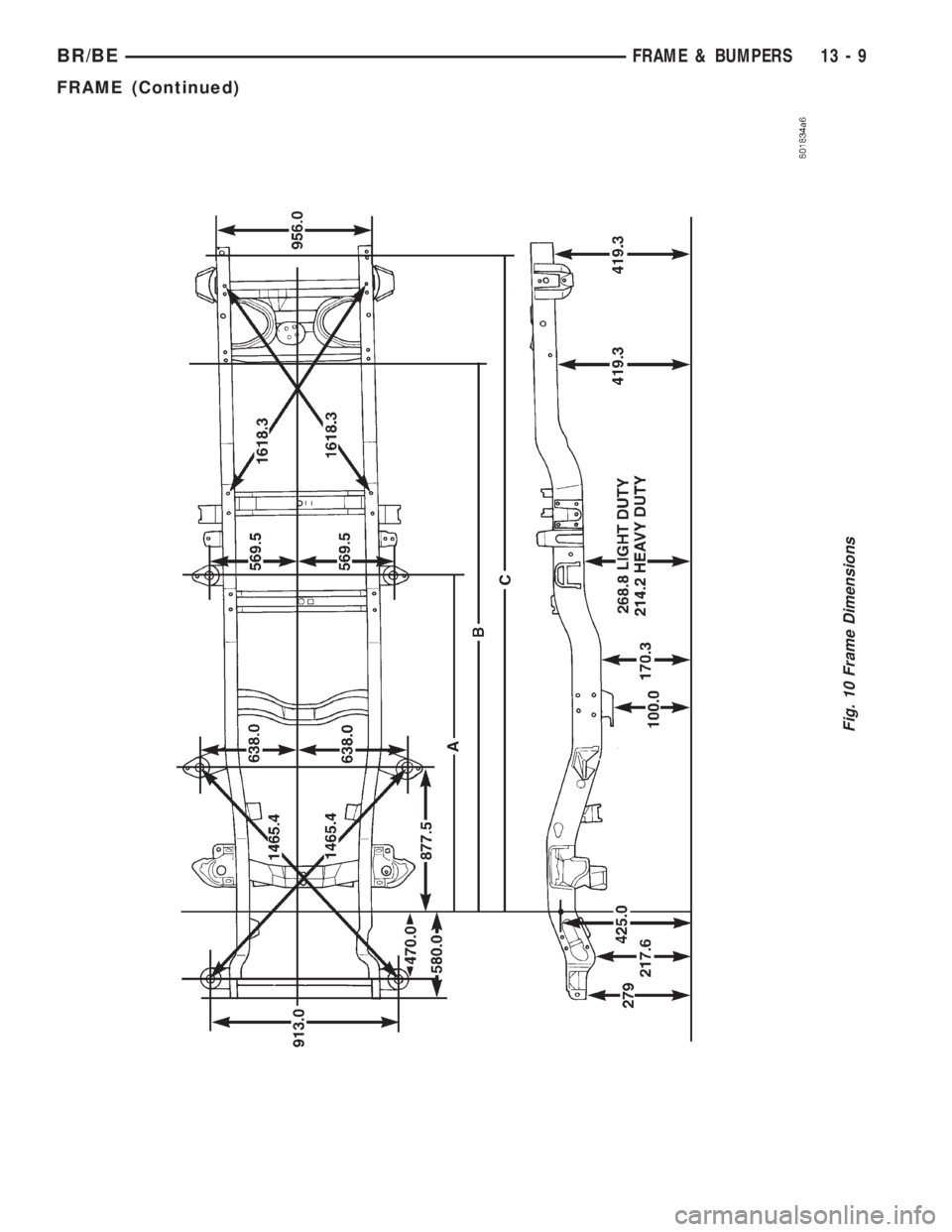
Fig. 10 Frame Dimensions
BR/BEFRAME & BUMPERS 13 - 9
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2255
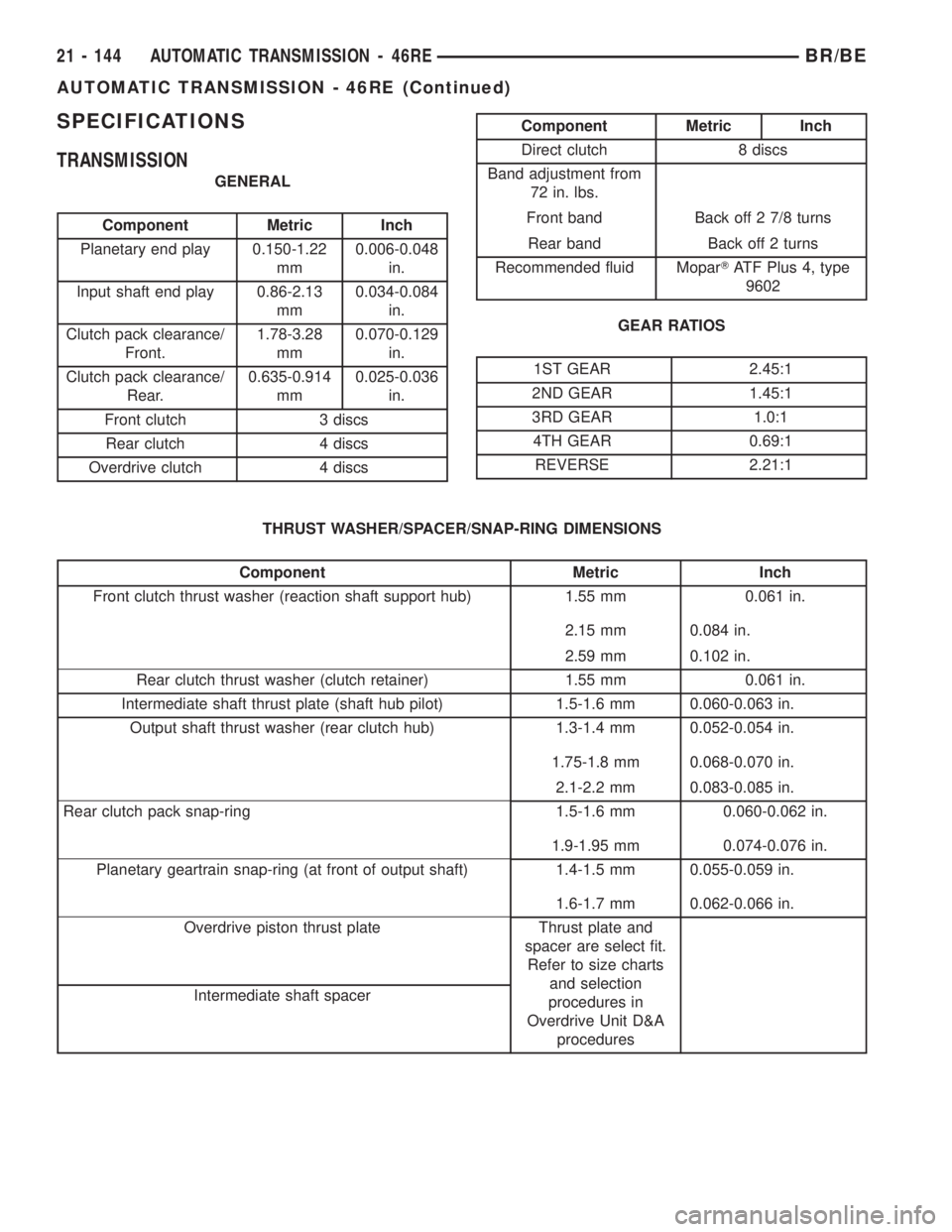
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Planetary end play 0.150-1.22
mm0.006-0.048
in.
Input shaft end play 0.86-2.13
mm0.034-0.084
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Front.1.78-3.28
mm0.070-0.129
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Rear.0.635-0.914
mm0.025-0.036
in.
Front clutch 3 discs
Rear clutch 4 discs
Overdrive clutch 4 discs
Component Metric Inch
Direct clutch 8 discs
Band adjustment from
72 in. lbs.
Front band Back off 2 7/8 turns
Rear band Back off 2 turns
Recommended fluid MoparTATF Plus 4, type
9602
GEAR RATIOS
1ST GEAR 2.45:1
2ND GEAR 1.45:1
3RD GEAR 1.0:1
4TH GEAR 0.69:1
REVERSE 2.21:1
THRUST WASHER/SPACER/SNAP-RING DIMENSIONS
Component Metric Inch
Front clutch thrust washer (reaction shaft support hub) 1.55 mm 0.061 in.
2.15 mm 0.084 in.
2.59 mm 0.102 in.
Rear clutch thrust washer (clutch retainer) 1.55 mm 0.061 in.
Intermediate shaft thrust plate (shaft hub pilot) 1.5-1.6 mm 0.060-0.063 in.
Output shaft thrust washer (rear clutch hub) 1.3-1.4 mm 0.052-0.054 in.
1.75-1.8 mm 0.068-0.070 in.
2.1-2.2 mm 0.083-0.085 in.
Rear clutch pack snap-ring 1.5-1.6 mm 0.060-0.062 in.
1.9-1.95 mm 0.074-0.076 in.
Planetary geartrain snap-ring (at front of output shaft) 1.4-1.5 mm 0.055-0.059 in.
1.6-1.7 mm 0.062-0.066 in.
Overdrive piston thrust plate Thrust plate and
spacer are select fit.
Refer to size charts
and selection
procedures in
Overdrive Unit D&A
procedures Intermediate shaft spacer
21 - 144 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1767 of 2255
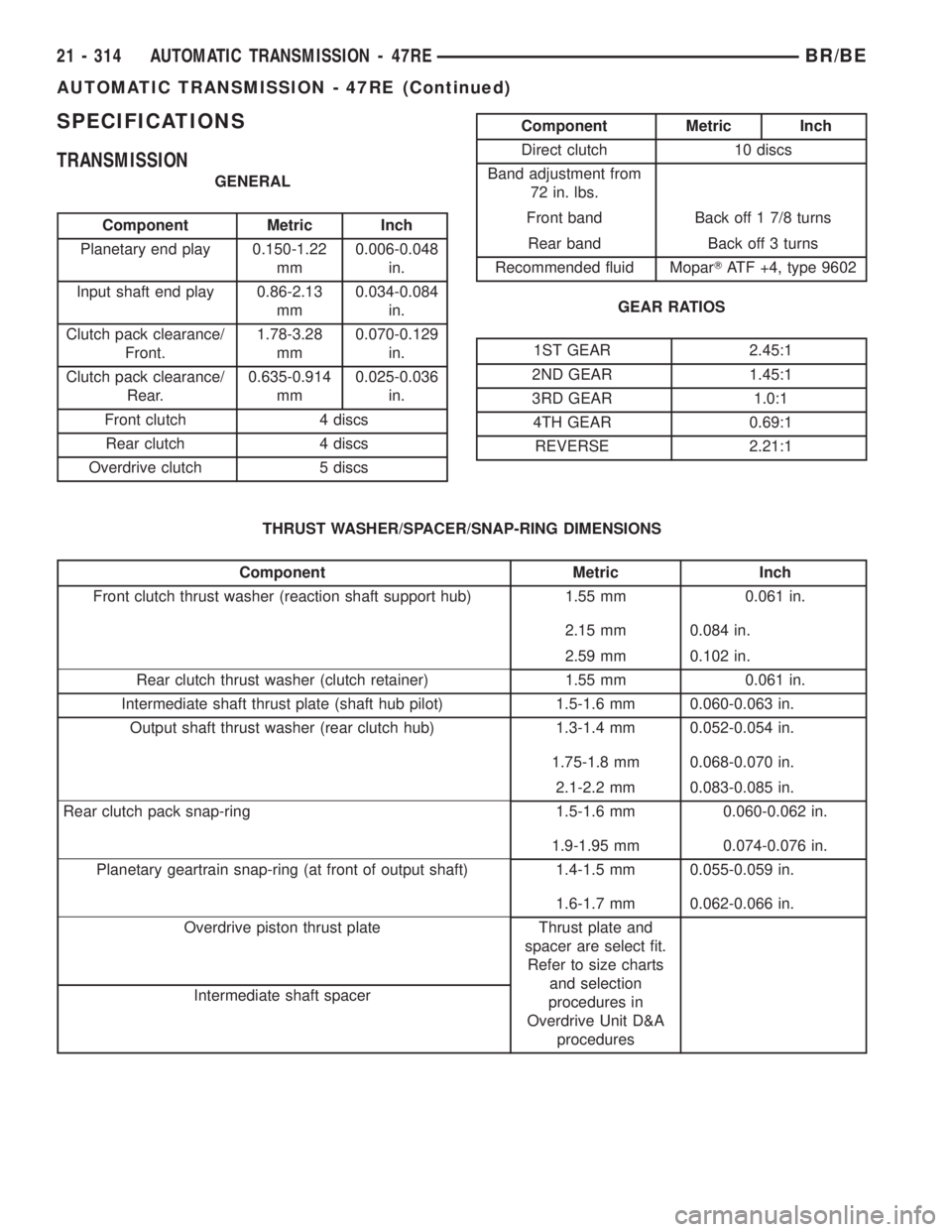
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Planetary end play 0.150-1.22
mm0.006-0.048
in.
Input shaft end play 0.86-2.13
mm0.034-0.084
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Front.1.78-3.28
mm0.070-0.129
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Rear.0.635-0.914
mm0.025-0.036
in.
Front clutch 4 discs
Rear clutch 4 discs
Overdrive clutch 5 discs
Component Metric Inch
Direct clutch 10 discs
Band adjustment from
72 in. lbs.
Front band Back off 1 7/8 turns
Rear band Back off 3 turns
Recommended fluid MoparTATF +4, type 9602
GEAR RATIOS
1ST GEAR 2.45:1
2ND GEAR 1.45:1
3RD GEAR 1.0:1
4TH GEAR 0.69:1
REVERSE 2.21:1
THRUST WASHER/SPACER/SNAP-RING DIMENSIONS
Component Metric Inch
Front clutch thrust washer (reaction shaft support hub) 1.55 mm 0.061 in.
2.15 mm 0.084 in.
2.59 mm 0.102 in.
Rear clutch thrust washer (clutch retainer) 1.55 mm 0.061 in.
Intermediate shaft thrust plate (shaft hub pilot) 1.5-1.6 mm 0.060-0.063 in.
Output shaft thrust washer (rear clutch hub) 1.3-1.4 mm 0.052-0.054 in.
1.75-1.8 mm 0.068-0.070 in.
2.1-2.2 mm 0.083-0.085 in.
Rear clutch pack snap-ring 1.5-1.6 mm 0.060-0.062 in.
1.9-1.95 mm 0.074-0.076 in.
Planetary geartrain snap-ring (at front of output shaft) 1.4-1.5 mm 0.055-0.059 in.
1.6-1.7 mm 0.062-0.066 in.
Overdrive piston thrust plate Thrust plate and
spacer are select fit.
Refer to size charts
and selection
procedures in
Overdrive Unit D&A
procedures Intermediate shaft spacer
21 - 314 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE (Continued)