DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 1901 of 5267

11. Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
12. Refill engine oil.
13. Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
14. Connect battery negative cable.
15. Start engine and check for oil and coolant leaks.
Page 1902 of 5267

TENSIONER - TIMING CHAIN
DESCRIPTION
The timing chain tensioner is a stamped steel constant tension mechanicaldesign. It is mounted to the front of the
engine, behind the timing chain drive.
OPERATION
The timing chain tension is maintained by routing the timing chain throughthe tensioner assembly. A nylon covered
spring steel arm presses on the timing chain maintaining the correct chaintension.
Page 1903 of 5267

page page
ENGINE - 5.9L DIESEL - SERVICE
INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L DIESEL .............. 2596
DESCRIPTION - CRANKCASE BREATHER . . 2597
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2597
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SMOKE
DIAGNOSIS CHARTS..................... 2599
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION/LEAKAGE TESTS......... 2602
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.......... 2603
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.......... 2604
STANDARD PROCEDURE—HYDROSTATIC
LOCK.................................... 2604
REMOVAL - ENGINE ........................ 2605
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ................... 2610
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 5.9L DIESEL ........... 2615
TORQUE ................................. 2617
SPECIAL TOOLS
5.9L DIESEL ENGINE ..................... 2619
ENGINE DATA PLATE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2621
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL ................................. 2622
INSTALLATION ............................. 2623
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2624
REMOVAL ................................. 2624
CLEANING
CLEANING ............................... 2626
CLEANING—CROSSHEADS ............... 2626
CLEANING—PUSHRODS .................. 2626
INSPECTION
INSPECTION............................. 2627
INSPECTION - CROSSHEADS . . ........... 2627
INSPECTION—PUSHRODS................ 2628
INSTALLATION ............................. 2628
COVER - CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ROCKER HOUSING ........... 2632
REMOVAL - CYL HEAD COVER ............ 2632
REMOVAL - CYL HEAD COVER GASKET . . . 2634
CLEANING
CLEANING CYLINDER HEAD COVER ...... 2634
INSPECTION - CYLINDER HEAD COVER ..... 2634INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - ROCKER HOUSING ....... 2634
INSTALLATION - CYL HEAD COVER ....... 2635
INSTALLATION - CYL HEAD COVER
GASKET................................. 2636
VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2638
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVES,
GUIDES AND SPRINGS................... 2638
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE LASH
ADJUSTMENT AND VERIFICATION......... 2643
REMOVAL ................................. 2644
INSTALLATION ............................. 2646
ROCKER ARM
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2647
REMOVAL ................................. 2647
CLEANING ................................. 2648
INSPECTION............................... 2648
INSTALLATION ............................. 2649
ENGINE BLOCK
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
BLOCK REFACING........................ 2651
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
BORE - DE-GLAZE........................ 2651
STANDARD PROCEDURE—CYLINDER
BORE REPAIR............................ 2652
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAM BORE
REPAIR.................................. 2655
INSPECTION............................... 2655
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK)
REMOVAL
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS................... 2657
CAMSHAFT .............................. 2657
INSPECTION
............................... 2659
INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS................... 2661
CAMSHAFT .............................. 2661
BEARINGS - CONNECTING ROD
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING
ROD BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT
JOURNAL CLEARANCE................... 2663
CRANKSHAFT & GEAR
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2664
REMOVAL - GEAR .......................... 2664
INSTALLATION - GEAR ..................... 2664
BEARINGS - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING
CLEARANCE ............................. 2665
Page 1904 of 5267

SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2667
INSTALLATION ............................. 2668
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - REAR
REMOVAL ................................. 2670
INSTALLATION ............................. 2670
RETAINER - CRANK REAR OIL SEAL
REMOVAL ................................. 2671
INSTALLATION ............................. 2671
TAPPETS - VALVE
REMOVAL ................................. 2673
CLEANING ................................. 2674
INSPECTION ............................... 2674
INSTALLATION ............................. 2674
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2677
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAD GASKET
SELECTION .............................. 2677
REMOVAL ................................. 2678
CLEANING—PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD . 2678
INSPECTION
INSPECTION - PISTONS .................. 2678
INSPECTION - CONNECTING ROD........ 2680
INSTALLATION ............................. 2680
RINGS - PISTON
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING .................................. 2682
DAMPER - CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL ................................. 2684
INSPECTION ............................... 2684
INSTALLATION ............................. 2684
MOUNT - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2685
INSTALLATION ............................. 2686
MOUNT - REAR
REMOVAL ................................. 2687
INSTALLATION ............................. 2687
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2688
OPERATION ............................... 2688
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING—ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE .............................. 2692
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
LEVEL................................... 2693STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE................................. 2693
COOLER - ENGINE OIL & LINES
CLEANING
CLEANING AND INSPECTION............. 2694
FILTER - ENGINE OIL
REMOVAL ................................. 2695
INSTALLATION ............................. 2695
PA N - E N G I N E O I L
REMOVAL ................................. 2696
CLEANING ................................. 2696
INSPECTION............................... 2696
INSTALLATION ............................. 2696
VALVE-OILPRESSURERELIEF
REMOVAL ................................. 2697
CLEANING ................................. 2697
INSPECTION............................... 2697
INSTALLATION ............................. 2697
SWITCH - OIL PRESSURE
REMOVAL ................................. 2698
INSTALLATION ............................. 2698
PUMP - ENGINE OIL
REMOVAL ................................. 2699
CLEANING ................................. 2699
INSPECTION............................... 2699
INSTALLATION ............................. 2700
MANIFOLD - INTAKE
REMOVAL ................................. 2702
CLEANING ................................. 2703
INSPECTION............................... 2703
INSTALLATION ............................. 2703
MANIFOLD - EXHAUST
REMOVAL ................................. 2704
CLEANING ................................. 2704
INSPECTION............................... 2704
INSTALLATION ............................. 2704
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIMING
VERIFICATION ........................... 2706
CASE - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2707
INSTALLATION ............................. 2708
COVER - TIMING
REMOVAL ................................. 2710
INSTALLATION ............................. 2710
Page 1905 of 5267

ENGINE - 5.9L DIESEL - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L DIESEL
The cylinder block is constructed of cast iron. The casting is a skirted design which incorporates longitudal ribs for
superior strength and noise reduction. The block incorporates metric straight thread o-ring fittings at lubrication oil
access points. The engine is manufactured with the cylinders being a non-sleeved type cylinder. However, one
approved service method is to bore out the cylinders and add cylinder sleeves to the cylinder block.
The cylinders are numbered front to rear ; 1 to 6. The
firing order is 1–5–3–6–2–4.
Page 1906 of 5267

DESCRIPTION - CRANKCASE BREATHER
The crankcase breather assembly is integrated into
the cylinder head cover (3) and is not serviced seper-
ately. The external fittings (2) to the breather tube and
breather drain tube are serviceable.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL
PRESSURE LOW1. Low oil level. 1. (a) Check and fill with clean engine oil.
(b) Check for a severe external oil leak that
could reduce the pressure.
2. Oil viscosity thin, diluted or wrong
specification.2. (a) Verify the correct engine oil is being
used. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from fuel
dilution.
3. Improperly operating pressure
switch/gauge.3. Verify the pressure switch is functioning
correctly. If not, replace switch/gauge.
4. Relief valve stuck open. 4. Check/replace valve.
6. If cooler was replaced, shipping
plugs may have been left in cooler6. Check/remove shipping plugs.
7. Worn oil pump. 7. Check and replace oil pump.
8. Suction tube loose or seal leaking. 8. Check and replace seal.
9. Loose main bearing cap. 9. Check and install new bearing. Tighten
cap to proper torque.
10. Worn bearings or wrong bearings
installed.10. Inspect and replace connecting rod or
main bearings. Check and replace directed
piston cooling nozzles.
Page 1907 of 5267
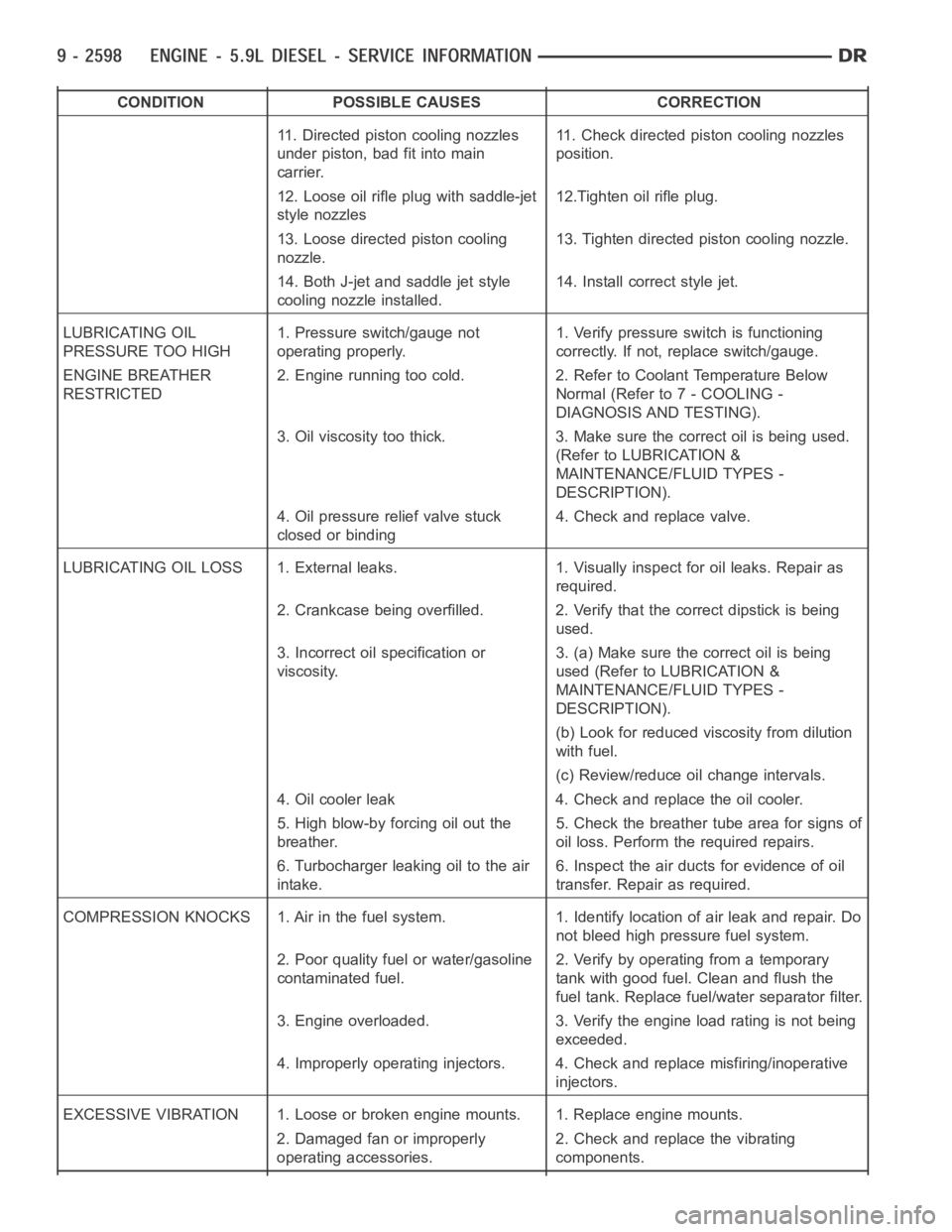
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
11. Directed piston cooling nozzles
under piston, bad fit into main
carrier.11. Check directed piston cooling nozzles
position.
12. Loose oil rifle plug with saddle-jet
style nozzles12.Tighten oil rifle plug.
13. Loose directed piston cooling
nozzle.13. Tighten directed piston cooling nozzle.
14. Both J-jet and saddle jet style
cooling nozzle installed.14. Install correct style jet.
LUBRICATING OIL
PRESSURE TOO HIGH1. Pressure switch/gauge not
operating properly.1. Verify pressure switch is functioning
correctly. If not, replace switch/gauge.
ENGINE BREATHER
RESTRICTED2. Engine running too cold. 2. Refer to Coolant Temperature Below
Normal (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Oil viscosity too thick. 3. Make sure the correct oil is being used.
(Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
4. Oil pressure relief valve stuck
closed or binding4. Check and replace valve.
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks.Repair as
required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3. (a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from dilution
with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce oil change intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for signs of
oil loss. Perform the required repairs.
6. Turbocharger leaking oil to the air
intake.6. Inspect the air ducts for evidence of oil
transfer. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in the fuel system. 1. Identify location of air leak and repair. Do
not bleed high pressure fuel system.
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a temporary
tank with good fuel. Clean and flush the
fuel tank. Replace fuel/water separator filter.
3. Engine overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not being
exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 4. Check and replace misfiring/inoperative
injectors.
EXCESSIVE VIBRATION 1. Loose or broken engine mounts. 1. Replace engine mounts.
2. Damaged fan or improperly
operating accessories.2. Check and replace the vibrating
components.
Page 1908 of 5267
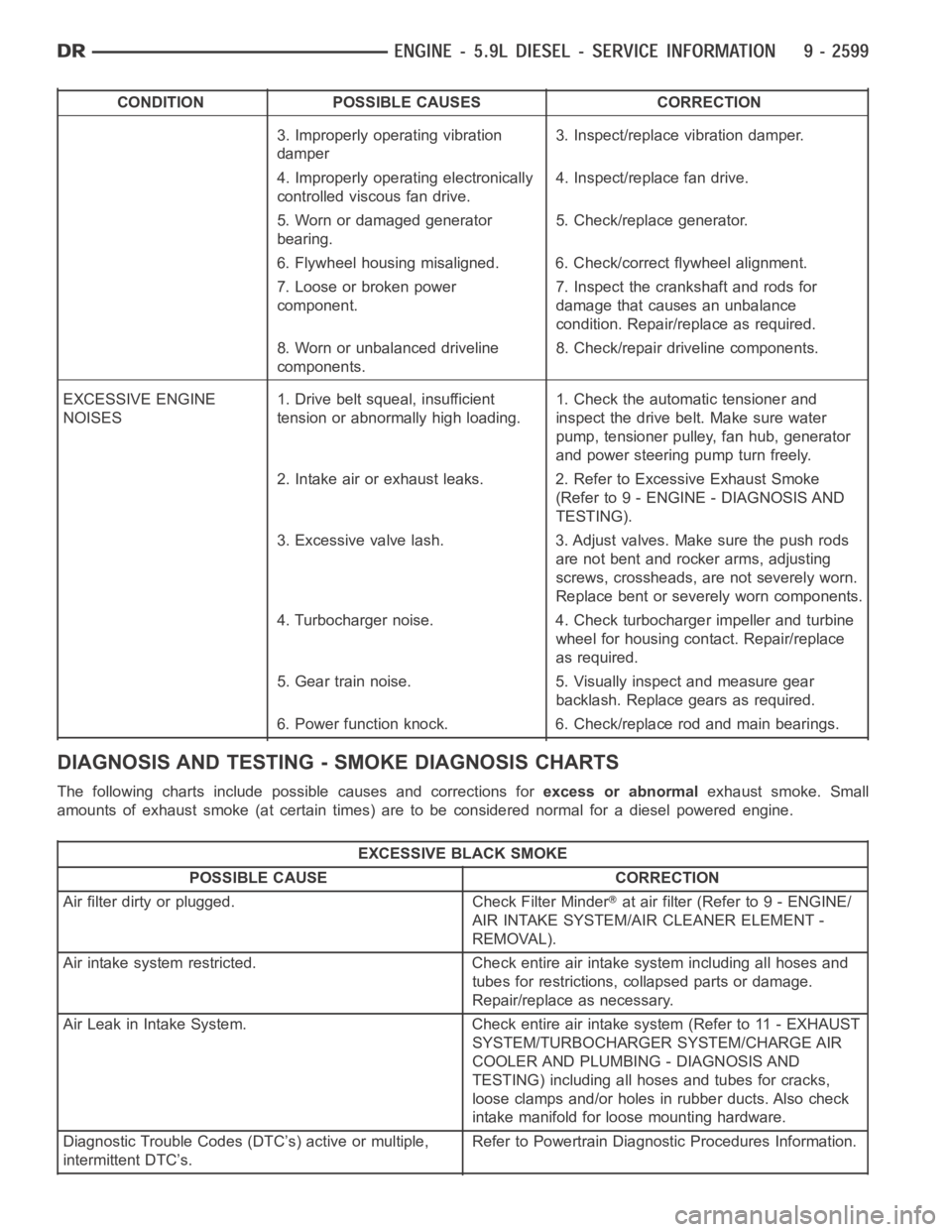
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Improperly operating vibration
damper3. Inspect/replace vibration damper.
4. Improperly operating electronically
controlled viscous fan drive.4. Inspect/replace fan drive.
5. Worn or damaged generator
bearing.5. Check/replace generator.
6. Flywheel housing misaligned. 6. Check/correct flywheel alignment.
7. Loose or broken power
component.7. Inspect the crankshaft and rods for
damage that causes an unbalance
condition. Repair/replace as required.
8. Worn or unbalanced driveline
components.8. Check/repair driveline components.
EXCESSIVE ENGINE
NOISES1. Drive belt squeal, insufficient
tension or abnormally high loading.1. Check the automatic tensioner and
inspect the drive belt. Make sure water
pump, tensioner pulley, fan hub, generator
and power steering pump turn freely.
2. Intake air or exhaust leaks. 2. Refer to Excessive Exhaust Smoke
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Excessive valve lash. 3. Adjust valves. Make sure the push rods
are not bent and rocker arms, adjusting
screws, crossheads, are not severely worn.
Replace bent or severely worn components.
4. Turbocharger noise. 4. Check turbocharger impeller and turbine
wheel for housing contact. Repair/replace
as required.
5. Gear train noise. 5. Visually inspect and measure gear
backlash. Replace gears as required.
6. Power function knock. 6. Check/replace rod and main bearings.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -SMOKE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The following charts include possible causes and corrections forexcess or abnormalexhaust smoke. Small
amounts of exhaust smoke (at certain times) are to be considered normal fora diesel powered engine.
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air filter dirty or plugged. Check Filter Minder
at air filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
REMOVAL).
Air intake system restricted. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for restrictions, collapsed parts or damage.
Repair/replace as necessary.
Air Leak in Intake System. Check entire air intake system (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM/CHARGE AIR
COOLER AND PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) including all hoses and tubes for cracks,
loose clamps and/or holes in rubber ducts. Also check
intake manifold for loose mounting hardware.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC’s) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC’s.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Page 1909 of 5267
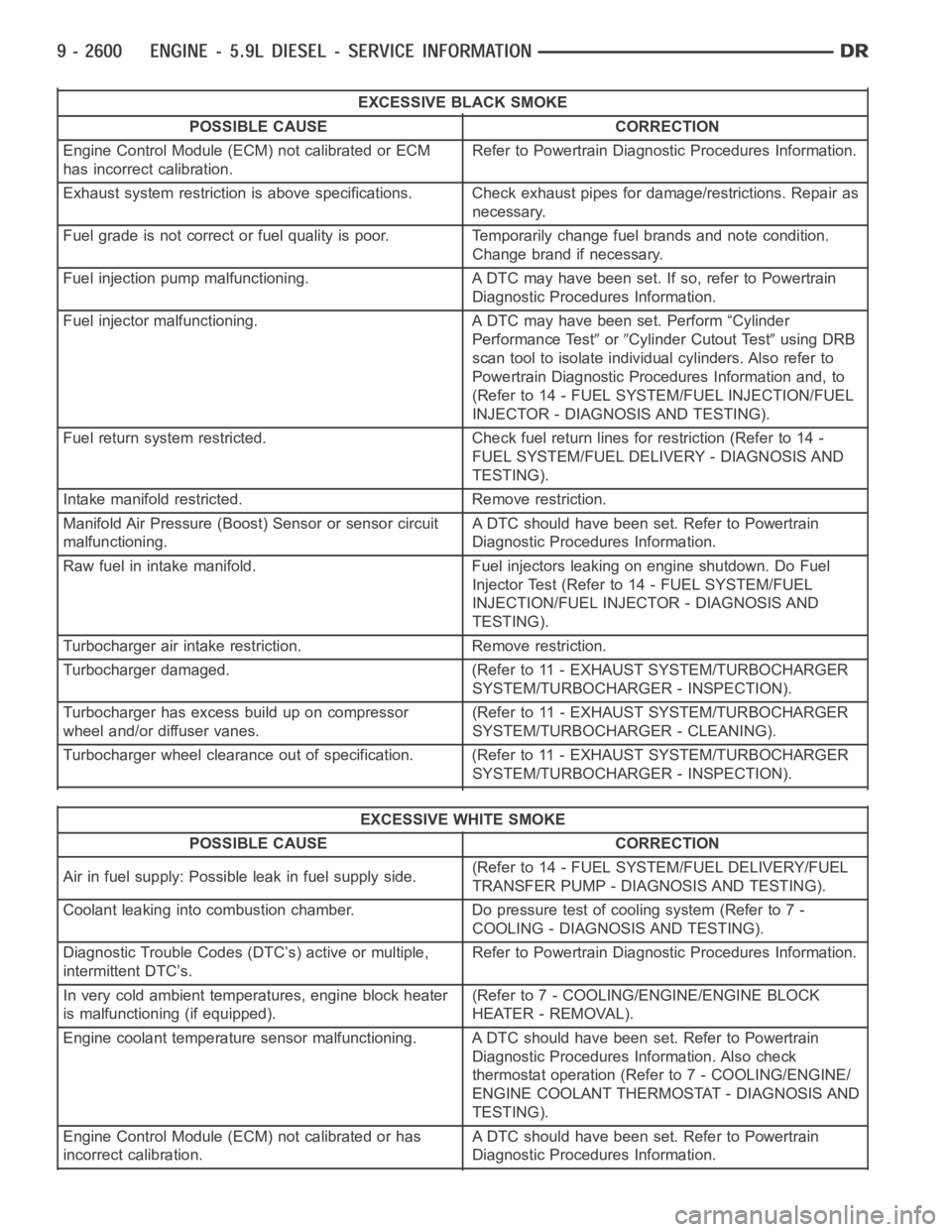
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipesfor damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer toPowertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform “Cylinder
Performance Test
orCylinder Cutout Testusing DRB
scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer to
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and, to
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. DoFuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUSTSYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side.(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC’s) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC’s.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater
is malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK
HEATER - REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have beenset. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information. Also check
thermostat operation (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has
incorrect calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Page 1910 of 5267

EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel
filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform “Cylinder
Performance Test
orCylinder cutout Testusing DRB
scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer to
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and,
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
Fuel injector protrusion not correct. Check washer (shim) at bottom of fuel injector for
correct thickness. (Referto 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION)
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel supply side restriction. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
Fuel transfer (lift) pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Refer toPowertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Intake/Exhaust valve adjustments not correct (too tight). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/
EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Intake manifold air temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should havebeen set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Intake manifold heater circuit not functioning correctly in
cold weather.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information. Also check heater
elements for correct operation.
Intake manifold heater elements not functioning
correctly in cold weather.A DTC should have been set if heater elements are
malfunctioning. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Internal engine damage (scuffed cylinder). Analyze engine oil and inspect oil filter to locate area of
probable damage.
Restriction in fuel supply side of fuel system. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
EXCESSIVE BLUE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Dirty air cleaner or restricted turbocharger intake duct. Check Filter Minder
at air filter housing. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
ELEMENT - REMOVAL).
Air leak in boost system between turbocharger
compressor outlet and intake manifold.Service air charge system..
Obstruction in exhaust manifold. Remove exhaust manifold and inspect forblockage
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).