DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 4341 of 5267

POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
Moldings standing away from body surface can catch wind and whistle.
Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
Misaligned movable components.
Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
Weld burn through holes.
Improperly installed roof rack cross bars.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
BODY LUBRICATION
All mechanisms and linkages should be lubricated when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation and provide
protection against rust and excessive wear. The weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to prolong their life as well
as to improve door sealing.
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operating mechanisms should be inspected and cleaned. Pivot/sliding con-
tact areas on the mechanisms should then be lubricated.
1. When necessary, lubricate the operating mechanisms with the specifiedlubricants.
2. Apply silicone lubricant to a clothand wipe it on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil passenger’s cloth-
ing.
3. Before applying lubricant, the component should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess lubricant should be
removed.
4. The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch striker, and safety latch should be lubricated periodically.
5. The door lock cylinders should be lubricated twice each year (preferably autumn and spring).
Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant directly into the lock cylinder.
Apply a small amount to the key and insert it into the lock cylinder.
Rotate it to the locked position and then back to the unlocked position several times.
Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with a clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
HEAT STAKING
1. Remove trim panel.
2. Bend or move the trim panel components at the heat staked joints. Observethe heat staked locations and/or
component seams for looseness.
3. Heat stake the components.
a. If the heat staked or component seam location is loose, hold the two components tightly together and using
a soldering gun with a flat tip, melt the material securing the components together. Do not over heat the
affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim panel may occur.
b. Iftheheatstakedmaterialisbrokenormissing,useahotglueguntoapplynewmaterialtotheareatobe
repaired. The panels that are being heat staked must be held together whiletheapplyingtheglue.Oncethe
new material is in place, it may be necessary to use a soldering gun to melt the newly applied material. Do
not over heat the affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim panel mayoccur.
4. Allow the repaired area to cool and verify the repair.
5. Install trim panel.
BUZZ, SQUEAK & RATTLE
Buzz, Squeak & Rattles (BSR) may be caused by any one or more of the followingand may be corrected as indi-
cated:
Loose fasteners should be tightened to specifications.
Damaged or missing clips should be replaced.
Damaged trim panels should be replaced.
Incorrectly installed trim panels should be reinstalled properly.
Page 4342 of 5267
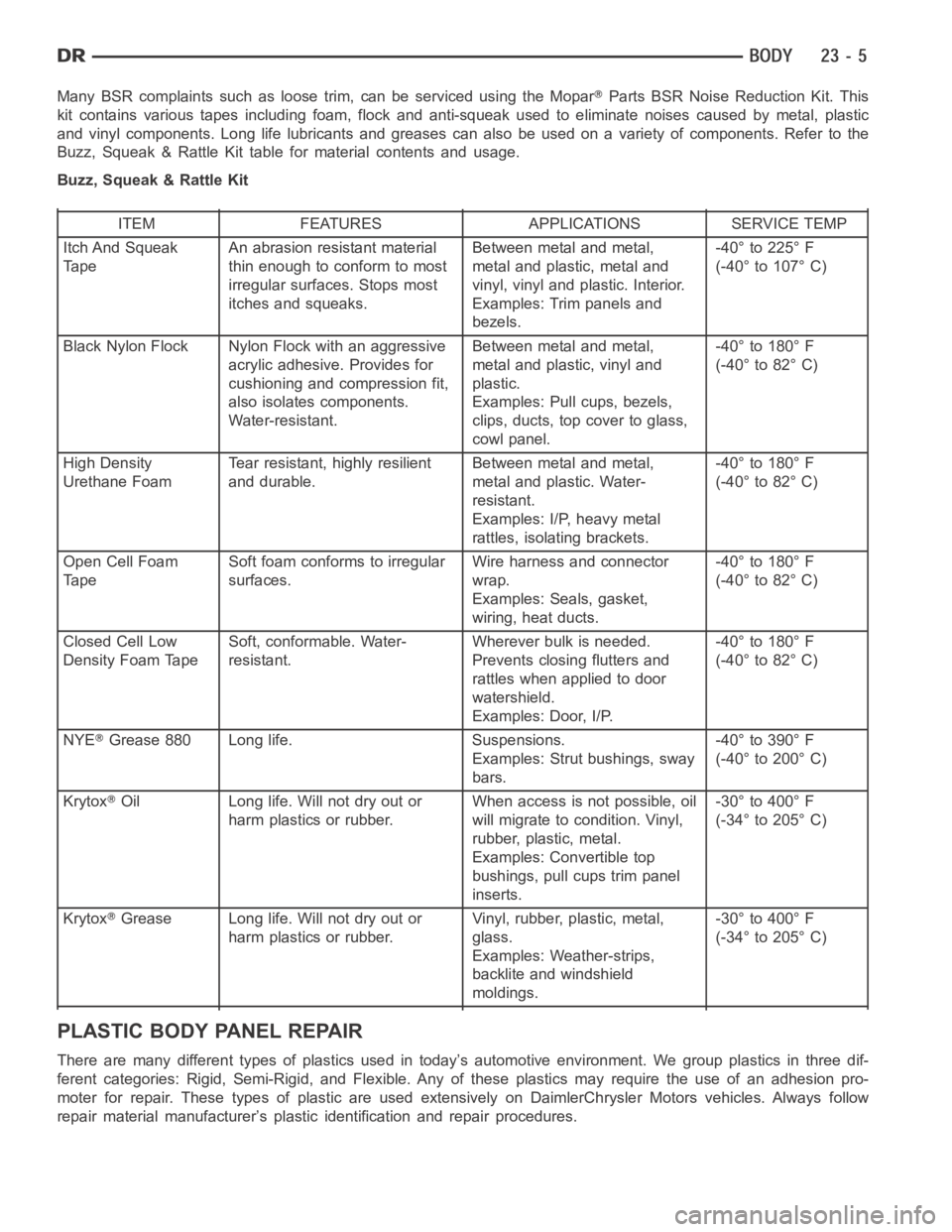
Many BSR complaints such as loose trim, can be serviced using the MoparParts BSR Noise Reduction Kit. This
kit contains various tapes including foam, flock and anti-squeak used to eliminate noises caused by metal, plastic
and vinyl components. Long life lubricants and greases can also be used on avariety of components. Refer to the
Buzz, Squeak & Rattle Kit table for material contents and usage.
Buzz, Squeak & Rattle Kit
ITEM FEATURES APPLICATIONS SERVICE TEMP
Itch And Squeak
TapeAn abrasion resistant material
thin enough to conform to most
irregular surfaces. Stops most
itches and squeaks.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic, metal and
vinyl, vinyl and plastic. Interior.
Examples: Trim panels and
bezels.-40° to 225° F
(-40° to 107° C)
Black Nylon Flock Nylon Flock with an aggressive
acrylic adhesive. Provides for
cushioning and compression fit,
also isolates components.
Water-resistant.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic, vinyl and
plastic.
Examples: Pull cups, bezels,
clips, ducts, top cover to glass,
cowl panel.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
High Density
Urethane FoamTear resistant, highly resilient
and durable.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic. Water-
resistant.
Examples: I/P, heavy metal
rattles, isolating brackets.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
Open Cell Foam
TapeSoft foam conforms to irregular
surfaces.Wire harness and connector
wrap.
Examples: Seals, gasket,
wiring, heat ducts.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
Closed Cell Low
Density Foam TapeSoft, conformable. Water-
resistant.Wherever bulk is needed.
Prevents closing flutters and
rattles when applied to door
watershield.
Examples: Door, I/P.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
NYE
Grease 880 Long life. Suspensions.
Examples: Strut bushings, sway
bars.-40° to 390° F
(-40° to 200° C)
Krytox
Oil Long life. Will not dry out or
harm plastics or rubber.When access is not possible, oil
will migrate to condition. Vinyl,
rubber, plastic, metal.
Examples: Convertible top
bushings, pull cups trim panel
inserts.-30° to 400° F
(-34° to 205° C)
Krytox
Grease Long life. Will not dry out or
harm plastics or rubber.Vinyl, rubber, plastic, metal,
glass.
Examples: Weather-strips,
backlite and windshield
moldings.-30° to 400° F
(-34° to 205° C)
PLASTIC BODY PANEL REPAIR
There are many different types of plastics used in today’s automotive environment. We group plastics in three dif-
ferent categories: Rigid, Semi-Rigid, and Flexible. Any of these plastics may require the use of an adhesion pro-
moter for repair. These types of plastic are used extensively on DaimlerChrysler Motors vehicles. Always follow
repair material manufacturer’s plastic identification and repair procedures.
Page 4343 of 5267

Rigid Plastics:
Examples of rigid plastic use: Fascias, Hoods, Doors, and other Body Panels, which include SMC, ABS, and Poly-
carbonates.
Semi-Rigid Plastics:
Examples of semi-rigid plastic use: Interior Panels, Under Hood Panels, and other Body Trim Panels.
Flexible Plastics:
Examples of flexible plastic use: Fascias, Body Moldings, and upper and lower Fascia Covers.
Repair Procedure:
The repair procedure for all three categories of plastics is basically thesame. The one difference is the material
used for the repair. The materials must be specific for each substrate, rigid repair material for rigid plastic repair,
semi-rigid repair material for semi-rigid plastic repair and flexible repair material for flexible plastic repair.
Adhesion Promoter/Surface Modifier:
Adhesion Promoters/Surface Modifiers are required for certain plastics. All three categories may have plastics that
require the use of adhesion promoter/surface modifiers. Always follow repair material manufacturer’s plastic identi-
fication and repair procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTION AND WARNINGS
WARNING:
Eye protection should be used when servicing components. Personal injurycan result.
Use an OSHA approved breathing mask when mixing epoxy, grinding, and spraying paint or solvents in
a confined area. Personal injury can result.
Avoid prolonged skin contact with resin, petroleum, or alcohol based solvents. Personal injury can
result.
Do not venture under a hoisted vehicle that is not properly supported on safety stands. Personal injury
can result.
NOTE:
When holes must be drilled or cut in bodypanels, verify locations of internal body components and elec-
trical wiring. Damage to vehicle can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on undamaged painted surfaces around repair areas. Dam-
age to finish can result.
RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN
APILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY, BAYBLEND DOORS, INSTRUMENT
PA N E L S
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
Page 4344 of 5267
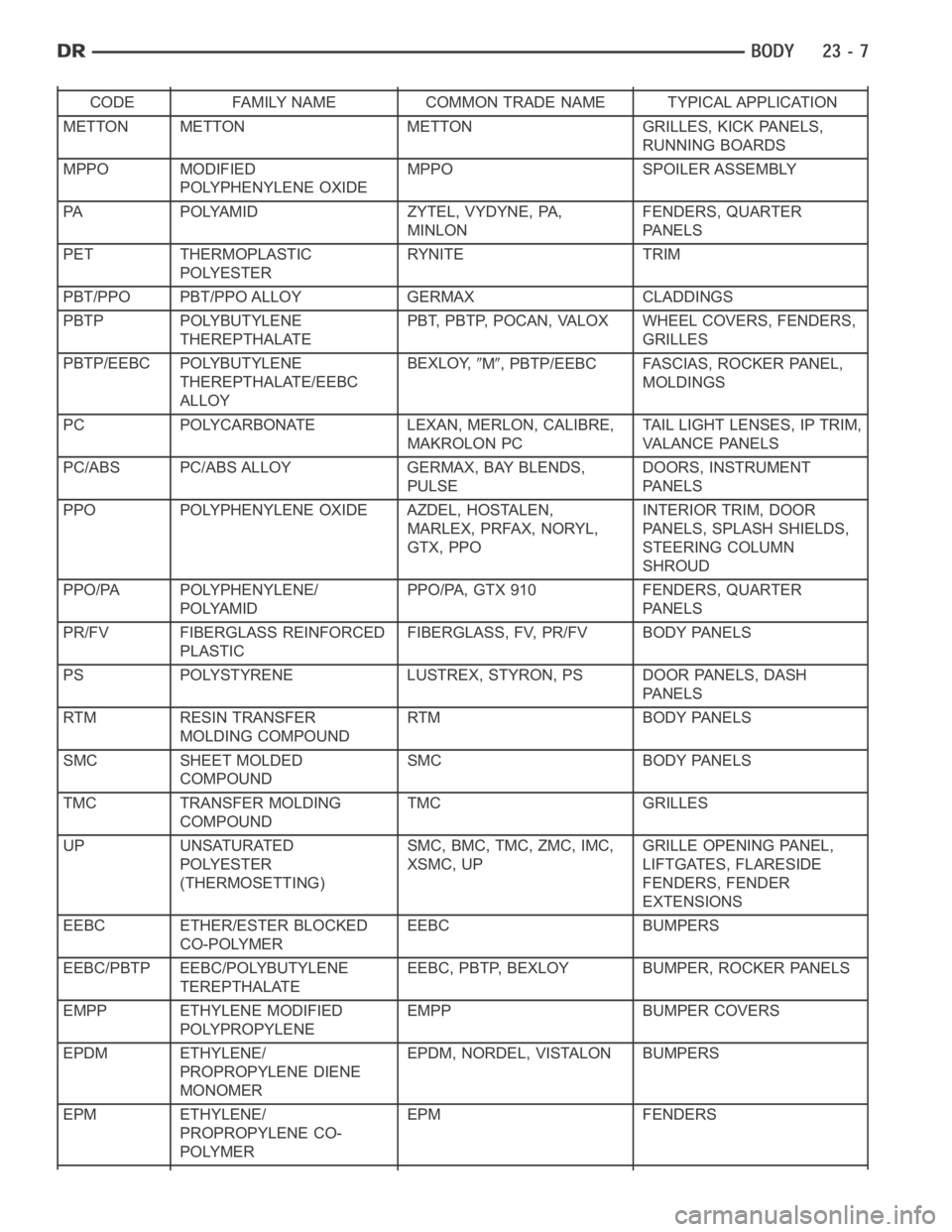
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,
M, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VA L A N C E PA N E L S
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PA N E L S
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PA N E L S
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
Page 4345 of 5267

CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
MPU FOAM POLYURETHANE MPU SPOILERS
PE POLYETHYLENE ALATHON, DYLAN,
LUPOLEN, MARLEX—
PP POLYPROPYLENE
(BLENDS)NORYL, AZDEL, MARLOX,
DYLON, PRAVEXINNER FENDER, SPOILERS,
KICK PANELS
PP/EPDM PP/EPDM ALLOY PP/EPDM SPOILERS, GRILLES
PUR POLYURETHANE COLONELS, PUR, PU FASCIAS, BUMPERS
PUR/PC PUR/PC ALLOY TEXIN BUMPERS
PVC POLYVINYL CHLORIDE APEX, GEON, VINYLITE BODY MOLDINGS, WIRE
INSULATION, STEERING
WHEELS
RIM REACTION INJECTED
MOLDED POLYURETHANERIM, BAYFLEX FRONT FASCIAS, MODULAR
WINDOWS
RRIM REINFORCED REACTION
INJECTED MOLDEDPUR, RRIM FASCIAS, BODY PANELS,
BODY TRIMS
TPE THERMO POLYETHYLENE TPE, HYTREL, BEXLOY-V FASCIAS, BUMPERS,
CLADDINGS
TPO THERMOPOLYOLEFIN POLYTROPE, RENFLEX,
SANTOPRENE, VISAFLEX,
ETA, APEX, TPO, SHIELDS,
CLADDINGSBUMPERS, END CAPS,
TELCAR, RUBBER, STRIPS,
SIGHT, INTERIOR B POST
TPP THERMO-POLYPROPYLENE TPP BUMPERS
TPU THERMOPOLYURETHANE,
POLYESTERTPU, HYTREL, TEXIN,
ESTANEBUMPERS, BODY SIDE,
MOLDINGS, FENDERS,
FASCIAS
PANEL SECTIONING
If it is required to section a large panel for a plastic
repair, it will be necessary to reinforce the panel. To
bond two plastic panels together, a reinforcement
must overlap both panels. The panels must be “V’d” at
a 20 degree angle. The area to be reinforced should
be washed, then sanded. Be sure to wipe off any
excess soap and water when finished. Lightly sand or
abrade the plastic with an abrasive pad or sandpaper.
Blow off any dust with compressed air or wipe with a
clean dry rag.
When bonding plastic panels, follow repair material
manufacturers recommendations. Be sure that enough
adhesive has been applied to allow squeeze out and
to fill the full bond line. Once the pieces have been
brought together, do not move them until the adhesive
is cured. The assembly can be held together with
clamps, rivets, etc. A faster cure can be obtained by heating with a heat lamp or heat gun. After the parts have been
bonded and have had time to cure, rough sand the seam and apply the final adhesive filler to the area being
repaired. Smooth the filler with a spreader, wooden tongue depressor, or squeegee. For fine texturing, a small
amount of water can be applied to the filler surface while smoothing. The cured filler can be sanded as necessary
and, as a final step, cleanup can be done with soapy water. Wipe the surface clean with a dry cloth allowing time
for the panel to dry before moving on with the repair.
Page 4346 of 5267

PANEL REINFORCEMENT
Structural repair procedures for rigid panels with large
cracks and holes will require a reinforcement backing.
Reinforcements can be made with several applications
of glass cloth saturated with structural adhesive. Semi-
rigid or flexible repair materials should be used for
semi-rigid or flexible backing reinforcement and open
meshed fiberglass dry wall tape can be used to form a
reinforcement. The dry wall tape allows the resin to
penetrate through and make a good bond between the
panel and the adhesive. Structurally, the more dry wall
tape used, the stronger the repair.
Another kind of repair that can be done to repair large
cracks and holes is to use a scrap piece of similar
plastic and bond with structural adhesive. The rein-
forcement should cover the entire break and should
have a generous amount of overlap on either side of
thecrackedorbrokenarea.
When repairing plastic, the damaged area is first “V’d”
out, or beveled. Large bonding areas are desirable
when repairing plastic because small repairs are less
likely to hold permanently. Beveling the area around a
crack at a 20 degree angle will increase the bonding
surface for a repair. It is recommended that sharp
edges be avoided because the joint may show
through after the panel is refinished.
Panel repair for both flexible and rigid panels are
basically the same. The primary difference
between flexible panel repair and rigid panel
repair is in the adhesive materials used.
The technician should first decide what needs to
be done when working on any type of body
panel. One should determine if it is possible to
return the damage part to its original strength
and appearance without exceeding the value of
the replacement part.
When plastic repairs are required, it is recom-
mended that the part be left on the vehicle when ever possible. That will save time, and the panel will remain
stationary during the repair. Misalignment can cause stress in the repairareas and can result in future failure.
Page 4347 of 5267

VISUAL INSPECTION
Composite materials can mask the severity of an acci-
dent. Adhesive bond lines, interior structure of the
doors, and steel structures need to be inspected care-
fully to get a true damage assessment. Close inspec-
tion may require partial removal of interior trim or inner
panels.
Identify the type of repair: Puncture or Crack - Dam-
age that has penetrated completely through the panel.
Damage is confined to one general area; a panel sec-
tion is not required. However, a backer panel, open
fiberglass tape, or matted material must be bonded
from behind.
PANEL SURFACE PREPARATION
If a body panel has been punctured, cracked, or crushed, the damaged area must be removed from the panel to
achieve a successful repair. All spider web cracks leading away from a damaged area must be stopped or removed.
To stop a running crack in a panel, drill a 6 mm (0.250 in.) hole at the end of the crack farthest away from the
damage. If spider web cracks can not be stopped, the panel would require replacement. The surfaces around the
damaged area should be stripped of paint and freed from wax and oil. Scuff surfaces around repair area with 360
grit wet/dry sandpaper, or equivalent, to assure adhesion of repair materials.
PATCHING PANELS
A panel that has extensive puncture type damage can
be repaired by cutting out the damaged material. Use
a suitable reciprocating saw or cut off wheel to remove
the section of the panel that is damaged. The piece
cut out can be used as a template to shape the new
patch. It is not necessary to have access to the back
of the panel to install a patch. Bevel edges of cutout
at 20 degrees to expose a larger bonding area on the
outer side. This will allow for an increased reinforce-
ment areas.
Page 4348 of 5267

PANEL PATCH FABRICATIONS
A patch can be fabricated from any rigid fiberglass
panel that has comparable contour with the repair
area. Lift gates and fenders can be used to supply
patch material. If existing material is not available or
compatible, a patch can be constructed with adhesive
and reinforcement mesh (dry wall tape). Perform the
following operation if required:
1. Cover waxed paper or plastic with adhesive backed
nylon mesh (dry wall tape) larger than the patch
required.
2. Tape waxed paper or plastic sheet with mesh to a
surface that has a compatible contour to the repair
area.
3. Apply a liberal coat of adhesive over the reinforce-
ment mesh. If necessary apply a second or third
coat of adhesive and mesh after first coat has cured. The thickness of the patch should be the same as the
repair area.
4. After patch has cured, peel waxed paper or plastic from the back of the patch.
5. If desired, a thin film coat of adhesive can be applied to the back of the patch to cover mesh for added strength.
PANEL PATCH INSTALLATION
1. Make a paper or cardboard pattern the size and
shape of the cutout hole in the panel.
2. Trim 3 mm (0.125 in.) from edges of pattern so
patch will have a gap between connecting sur-
faces.
3. Using the pattern as a guide, cut the patch to size.
4. Cut scrap pieces of patch material into 50 mm (2
in.) squares to use as patch supports to sustain the
patch in the cutout.
5. Drill 4 mm (0.160 in.) holes 13 mm (0.5 in.) in from
edge of cutout hole.
6. Drill 4 mm (0.160 in.) holes 13 mm (0.5 in.) away
from edge of patch across from holes drilled
around cutout.
7. Drill 3 mm (0.125 in.) holes in the support squares
13 mm (0.5 in.) from the edge in the center of one
side.
8. Scuff the backside of the body panel around the cutout hole with a scuff pad or sandpaper.
9. Mix enough adhesive to cover one side of all support squares.
10. Apply adhesive to cover one side of all support squares.
11. Using number 8 sheet metal screws,secure support squares to back side of body panel with adhesive sand-
wiched between the panel and squares.
Page 4349 of 5267

12. Position patch in cutout against support squares
and adjust patch until the gap is equal along all
sides.
13. Drill 3 mm (0.125 in.) holes in the support squares
through the pre-drilled holes in the patch.
14. Apply a coat of adhesive to the exposed ends of
the support squares.
15. Install screws to hold the patch to support
squares. Tighten screws until patch surface is
flush with panel surface.
16. Allow adhesive to cure, and remove all screws.
Page 4350 of 5267

17. Using a 125 mm (5 in.) 24 grit disc grinder, grind
a50mm(2in.)to75mm(3in.)wideand2mm
(0.080 in.) deep path across the gaps around the
patch. With compressed air, blow dust from
around patch.
18. Apply adhesive backed nylon mesh (dry wall tape)
over gaps around patch.
19. Mix enough adhesive to cover the entire patch
area.
20. Apply adhesive over the mesh around patch, and
smooth epoxy with a wide spreader to reduce fin-
ish grinding. Use two to three layers of mesh and
adhesive to create a stronger repair.
PATCHED PANEL SURFACING
After patch panel is installed, the patch area can be finished using the same methods as finishing other types of
body panels. If mesh material is exposed in the patched area, grind surfacedown, and apply a coat of high quality
rigid plastic body filler. Prime, block sand, and paint as required.