sensor DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 860 of 1502
•
FUEL
SYSTEM
14 - 41
THROTTLE
BODY
FUEL
RAIL
CONNECTING
HOSES
THROTTLE
BODY
MOUNTING
BOLTS
J9214-31
Fig.
18
Throttle
Body
MOUNTING
SCREWS
MAP
SENSOR
RUBBER
FITTING
J9314-87
Fig.
19 Air Control
Passage
FUEL
RAIL
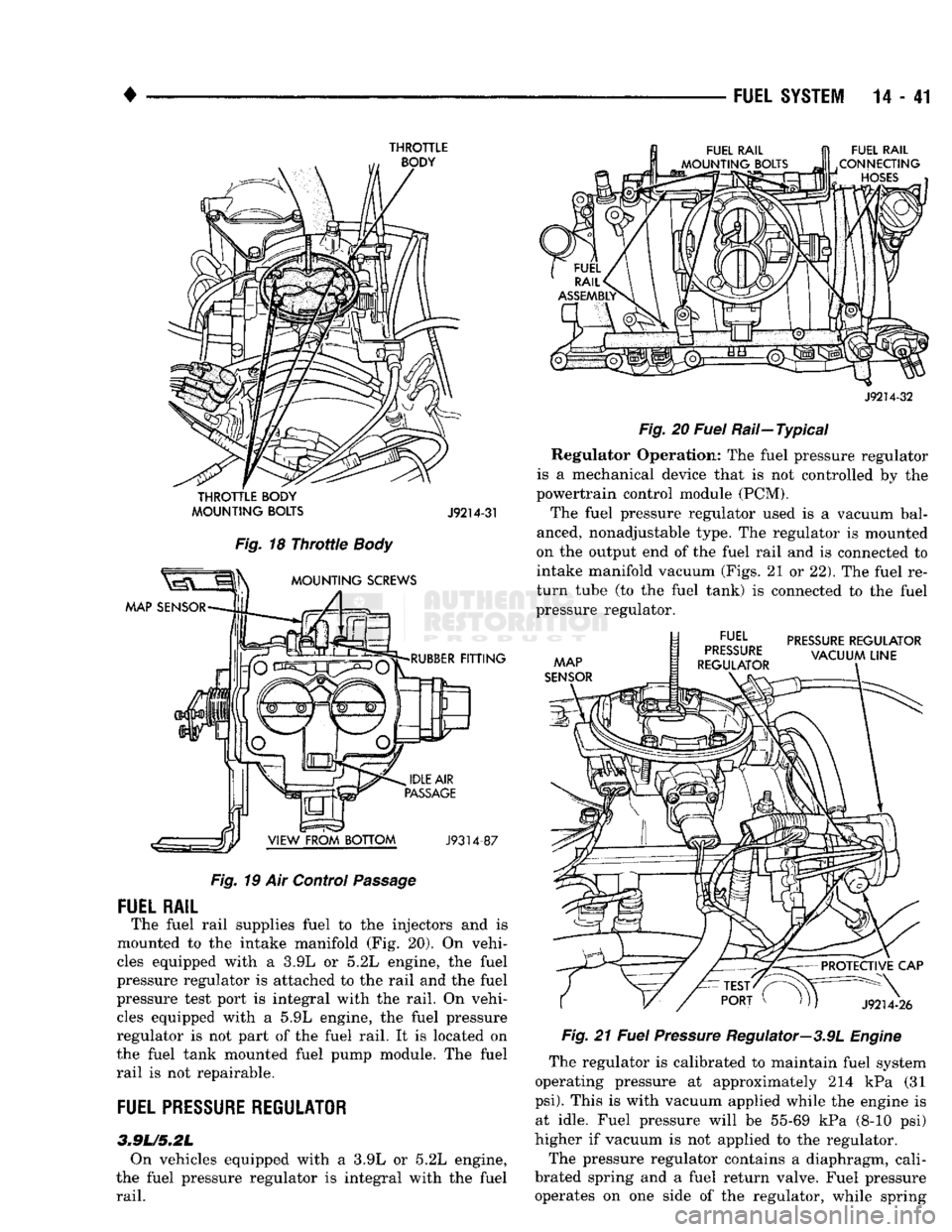
The fuel rail supplies fuel to the injectors and is
mounted to the intake manifold (Fig. 20). On vehi
cles equipped with a 3.9L or 5.2L engine, the fuel
pressure regulator is attached to the rail and the fuel
pressure test port is integral with the rail. On vehi cles equipped with a 5.9L engine, the fuel pressure
regulator is not part of the fuel rail. It is located on
the fuel tank mounted fuel pump module. The fuel
rail is not repairable.
FUEL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
3.9L/5.2L On vehicles equipped with a 3.9L or 5.2L engine,
the fuel pressure regulator is integral with the fuel
rail.
J9214-32
Fig.
20
Fuel
Rail—Typical Regulator Operation: The fuel pressure regulator
is a mechanical device that is not controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM).
The fuel pressure regulator used is a vacuum bal
anced, nonadjustable type. The regulator is mounted
on the output end of the fuel rail and is connected to
intake manifold vacuum (Figs. 21 or 22). The fuel re
turn tube (to the fuel tank) is connected to the fuel
pressure regulator.
MAP
SENSOR
docc EL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
„
VACUUM
LINE
REGULATOR
PROTECTIVE
CAP
J9214-26
Fig.
21
Fuel
Pressure
Regulator—3.9L
Engine
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure at approximately 214 kPa (31
psi).
This is with vacuum applied while the engine is at idle. Fuel pressure will be 55-69 kPa (8-10 psi)
higher if vacuum is not applied to the regulator.
The pressure regulator contains a diaphragm, cali
brated spring and a fuel return valve. Fuel pressure operates on one side of the regulator, while spring
Page 862 of 1502
MULTI-PORT
FUEL
INJECTION
(MPI)—GENERAL DIAGNOSIS—EXCEPT DIESEL
INDEX
page
Camshaft Position Sensor Testing
............
52
Charge
Air
Temperature Sensor Test
52
Coolant Temperature Sensor Test
52
Crankshaft Position Sensor Test
54
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
60
DRB
II
Scan
Tool
........................
60
Fuel
Injector
Test
57
Fuel Pump Pressure Test
57
Idle
Air
Control
(IAC) Motor Test
55
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Test
. 53
page
On-Board
Diagnostics (OBD)
59
Oxygen
(02)
Sensor Heating Element Test
54
Powertrain
Control
Module (PCM) 60-Way Connector
. 47
Relays—Operation/Testing
56
Starter
Motor Relay Test
57
System
Schematics
. 47
Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) Test
54
Visual Inspection
43
VISUAL
INSPECTION
A visual inspection
for
loose, disconnected,
or
incor
rectly routed wires
and
hoses should
be
made. This should
be
done before attempting
to
diagnose
or
ser
vice
the
fuel injection system.
A
visual check will
help spot these faults
and
save unnecessary test
and
diagnostic time.
A
thorough visual inspection will
in
clude
the
following checks: (1) Verify that
the
60-way connector
is
fully
in
serted into
the
connector
of the
powertrain control
module
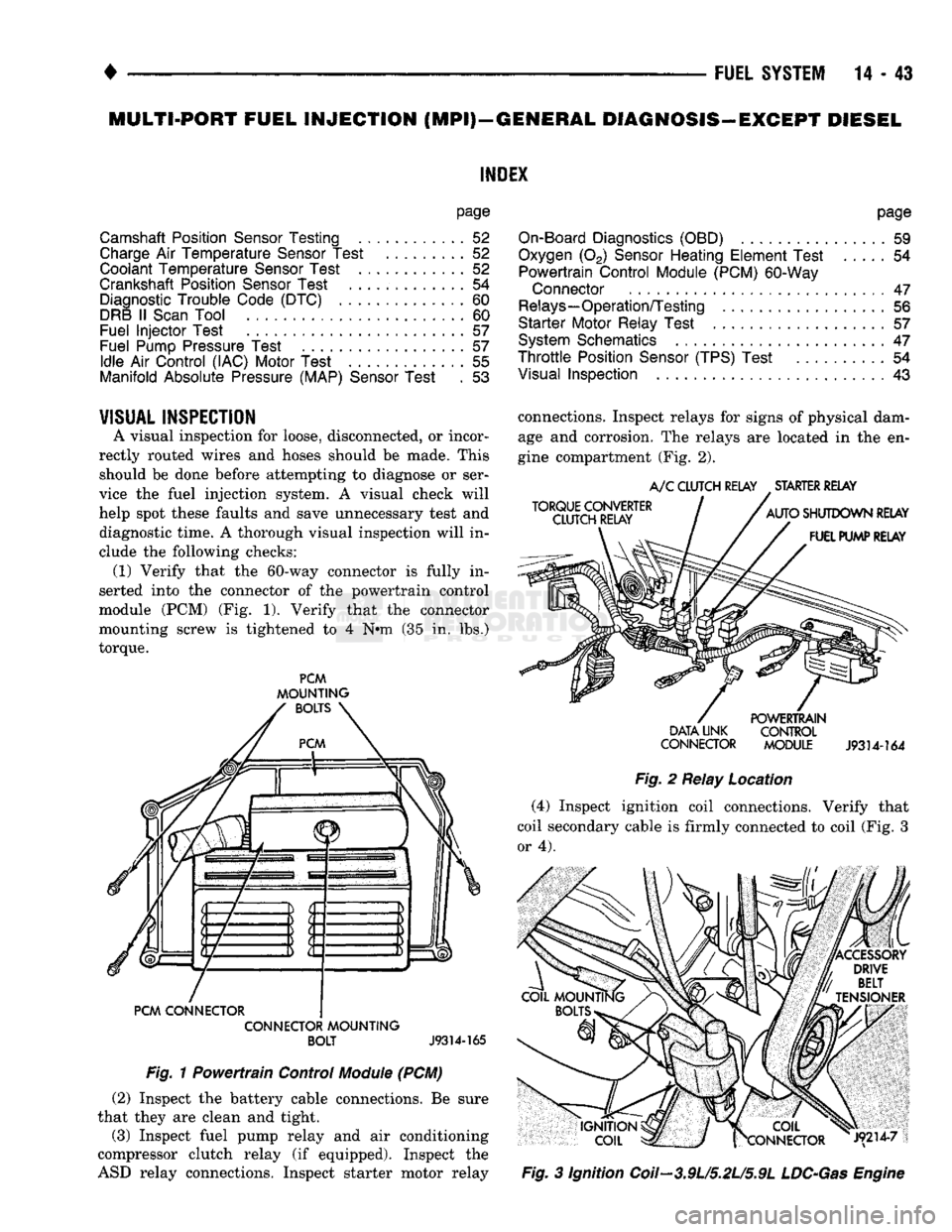
(PCM) (Fig. 1).
Verify that
the
connector
mounting screw
is
tightened
to 4 N#m (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
PCM
MOUNTING
BOLTS
PCM CONNECTOR CONNECTOR MOUNTING BOLT
J9314-165
Fig.
1
Powertrain Control
Module
(PCM) (2) Inspect
the
battery cable connections.
Be
sure
that they
are
clean
and
tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay
and air
conditioning
compressor clutch relay
(if
equipped). Inspect
the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay connections. Inspect relays
for
signs
of
physical dam
age
and
corrosion.
The
relays
are
located
in the en
gine compartment
(Fig. 2).
TORQUE CONVERTER
CLUTCH RELAY
A/C
CLUTCH RELAY STARTER RELAY
AUTO SHUTDOWN RELAY FUEL PUMP RELAY POWERTRAIN
DATA UNK CONTROL
CONNECTOR MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
2
Relay Location (4) Inspect ignition coil connections. Verify that
coil secondary cable
is
firmly connected
to
coil (Fig.
3
or 4).
|X COIL
frCONNECTOR J9214-7
Fig.
3
Ignition Coil—3.9U5.2L/5.9L
LDC-Gas
Engine
Page 863 of 1502
14 - 44
FUEL
SYSTEM
•
Fig.
4 ignition Coil—5.9L
HDC-Gas
Engine
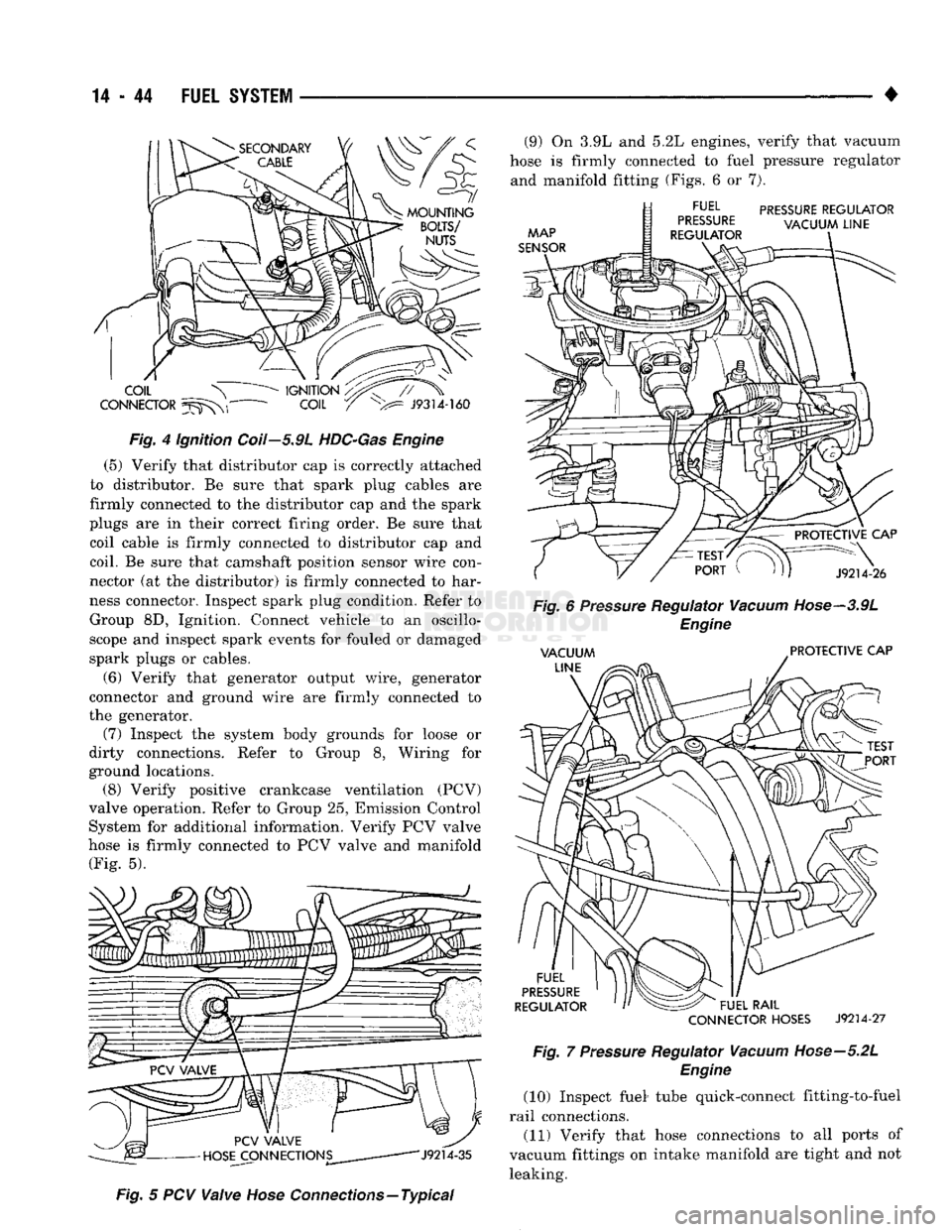
(5) Verify that distributor cap is correctly attached
to distributor. Be sure that spark plug cables are
firmly connected to the distributor cap and the spark
plugs are in their correct firing order. Be sure that coil cable is firmly connected to distributor cap and
coil. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire con
nector (at the distributor) is firmly connected to har
ness connector. Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition. Connect vehicle to an oscillo
scope and inspect spark events for fouled or damaged
spark plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator. (7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for
ground locations. (8) Verify positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
valve operation. Refer to Group 25, Emission Control System for additional information. Verify PCV valve
hose is firmly connected to PCV valve and manifold (Fig. 5).
Fig.
5 PCV
Valve
Hose
Connections—Typical (9) On 3.9L and 5.2L engines, verify that vacuum
hose is firmly connected to fuel pressure regulator and manifold fitting (Figs. 6 or 7).
CONNECTOR
HOSES
J9214-27
Fig.
7
Pressure
Regulator
Vacuum
Hose—5.2L
Engine
(10) Inspect fuel* tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections. (11) Verify that hose connections to all ports of
vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not leaking.
Page 864 of 1502
•
FUEL
SYSTEM
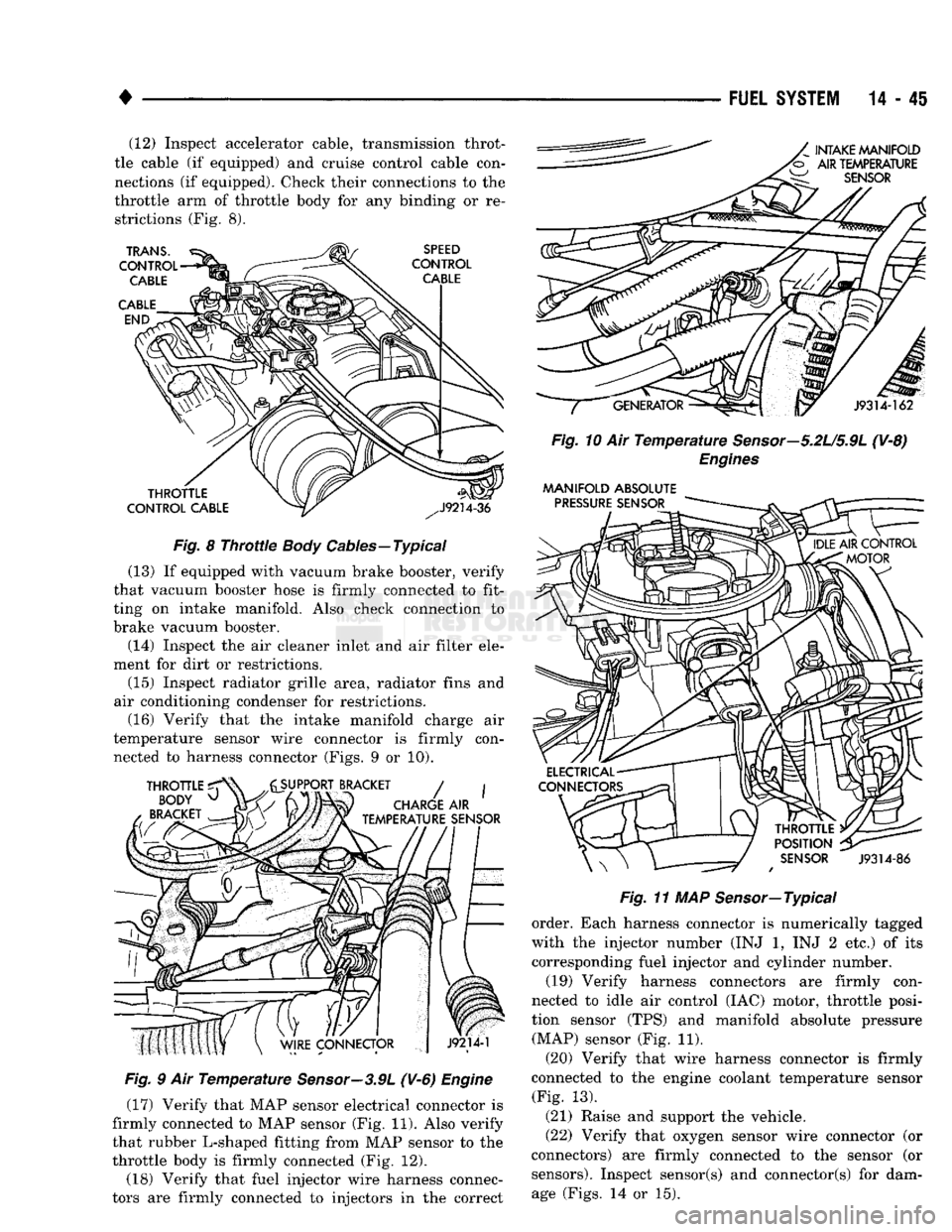
14-45 (12) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt
tle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable con
nections (if equipped). Check their connections to the
throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or re strictions (Fig. 8).
Fig.
8
Throttle
Body
Cables—Typical
(13) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
that vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fit
ting on intake manifold. Also check connection to
brake vacuum booster.
(14) Inspect the air cleaner inlet and air filter ele
ment for dirt or restrictions.
(15) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions. (16) Verify that the intake manifold charge air
temperature sensor wire connector is firmly con nected to harness connector (Figs. 9 or 10).
Fig.
9 Air
Temperature
Sensor—3.9L
(V-6)
Engine
(17) Verify that MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 11). Also verify
that rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sensor to the
throttle body is firmly connected (Fig. 12).
(18) Verify that fuel injector wire harness connec
tors are firmly connected to injectors in the correct
Fig.
10 Air
Temperature
Sensor—5.2U5.9L
(V-8)
Engines
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
Fig.
11 MAP Sensor—Typical
order. Each harness connector is numerically tagged
with the injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its
corresponding fuel injector and cylinder number.
(19) Verify harness connectors are firmly con
nected to idle air control (IAC) motor, throttle posi
tion sensor (TPS) and manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig. 11).
(20) Verify that wire harness connector is firmly
connected to the engine coolant temperature sensor (Fig. 13).
(21) Raise and support the vehicle.
(22) Verify that oxygen sensor wire connector (or
connectors) are firmly connected to the sensor (or sensors). Inspect sensor(s) and connector(s) for damage (Figs. 14 or 15).
Page 865 of 1502
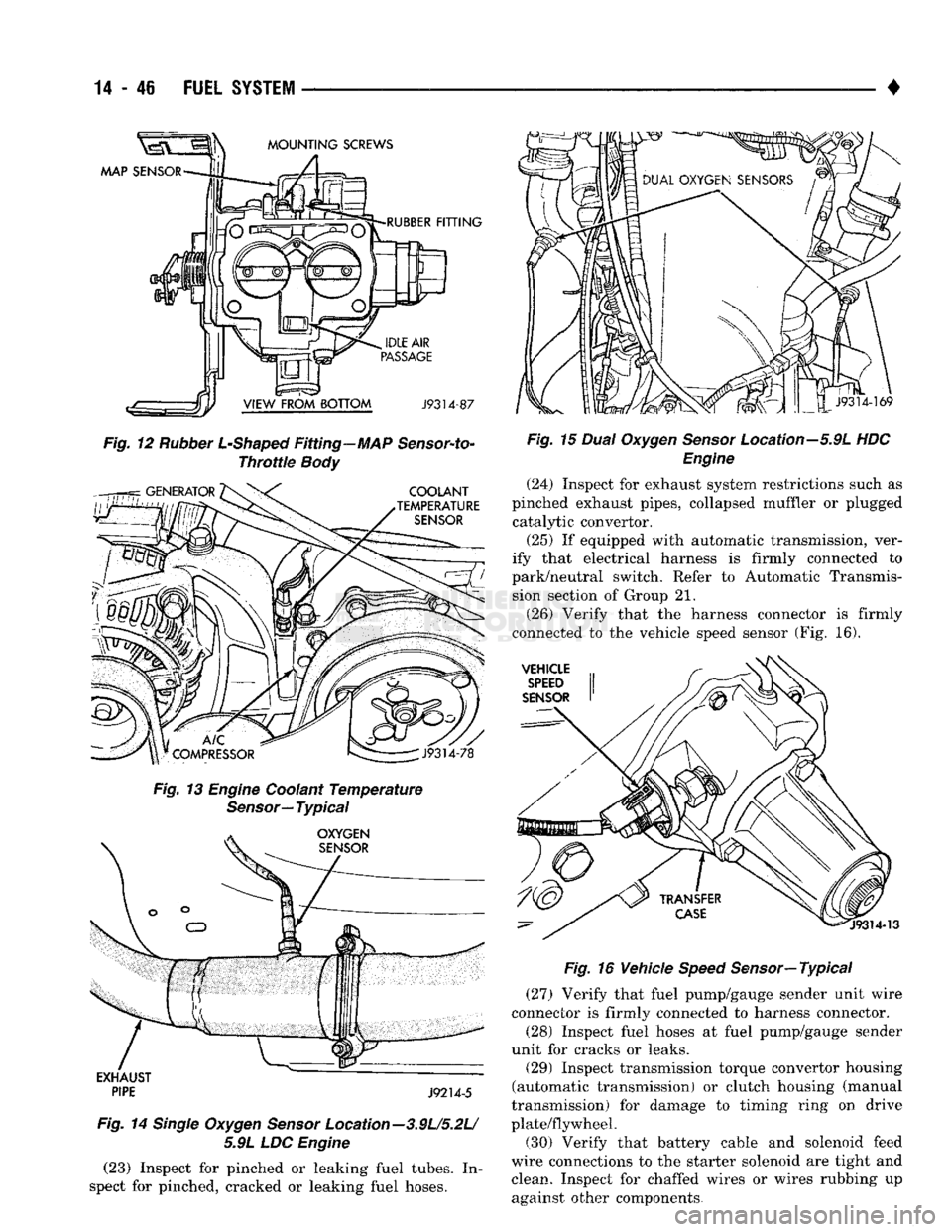
14
- 46
FUEL
SYSTEM
Fig.
12
Rubber
L-Shaped
Fitting—MAP
Sensor-to-
Throttie
Body
Fig.
13
Engine
Coolant
Temperature
Sensor—
Typical
EXHAUST
~~
PIPE
J9214-5
Fig.
14
Single
Oxygen
Sensor
Location-3.9U5.2L/ 5.9L LDC
Engine
(23) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes. In
spect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses. •
Fig.
15
Dual
Oxygen
Sensor
Location—5.9L HDC
Engine
(24) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such as
pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or plugged catalytic convertor.
(25) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver
ify that electrical harness is firmly connected to
park/neutral switch. Refer to Automatic Transmis sion section of Group 21.
(26) Verify that the harness connector is firmly
connected to the vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 16).
Fig.
16 Vehicle
Speed
Sensor—
Typical
(27) Verify that fuel pump/gauge sender unit wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
(28) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump/gauge sender
unit for cracks or leaks.
(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel. (30) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight and clean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up against other components.
Page 867 of 1502
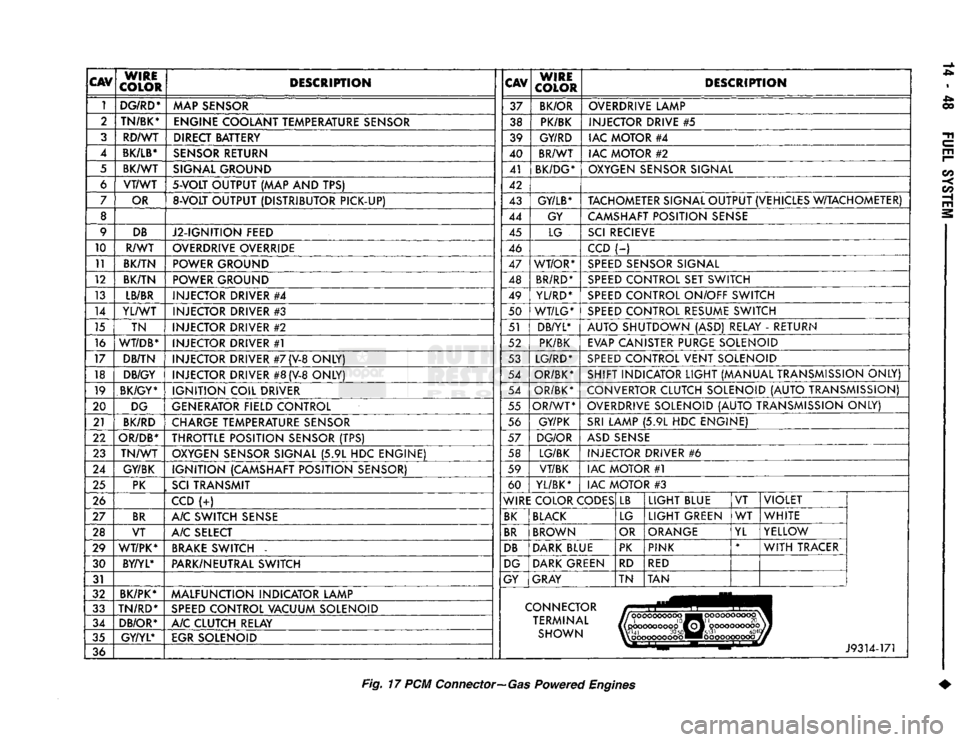
CAV
WIRE
COLOR DESCRIPTION
CAV
WIRE
COLOR DESCRIPTION
1 DG/RD*
MAP SENSOR 37
BK/OR OVERDRIVE LAMP
2 TN/BK*
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR 38 PK/BK INJECTOR DRIVE
#5
3 RD/WT DIRECT BATTERY 39 GY/RD IAC MOTOR
#4
4
BK/LB*
SENSOR RETURN 40 BR/WT
IAC MOTOR
#2
5 BK/WT SIGNAL GROUND 41
BK/DG* OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL
6 VT/WT
5-VOLT
OUTPUT
(MAP AND TPS)
42
7 OR
8-VOLT
OUTPUT (DISTRIBUTOR PICK-UP) 43
GY/LB*
TACHOMETER SIGNAL OUTPUT (VEHICLES W/TACHOMETER)
8 44 GY CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSE
9 DB
J2-IGNITION FEED 45
LG SCI RECIEVE
10 R/WT OVERDRIVE OVERRIDE
46 CCD
(-)
11 BK/TN POWER GROUND 47 WT/OR* SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
12 BK/TN POWER GROUND 48 BR/RD* SPEED CONTROL
SET
SWITCH
13 LB/BR
INJECTOR DRIVER
#4
49
YL/RD* SPEED CONTROL ON/OFF SWITCH
14 YL/WT
INJECTOR DRIVER
#3
50 WT/LG* SPEED CONTROL RESUME SWITCH
15 TN INJECTOR DRIVER
#2
51 DB/YL*
AUTO SHUTDOWN
(ASD)
RELAY
-
RETURN
16
WT/DB*
INJECTOR DRIVER
#1
52 PK/BK
EVAP CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
17 DB/TN INJECTOR DRIVER
#7
(V-8
ONLY) 53 LG/RD* SPEED CONTROL VENT SOLENOID
18 DB/GY
INJECTOR DRIVER
#8
(V-8
ONLY) 54
OR/BK* SHIFT INDICATOR LIGHT (MANUAL TRANSMISSION ONLY)
19 BK/GY*
IGNITION COIL DRIVER 54
OR/BK* CONVERTOR CLUTCH SOLENOID (AUTO TRANSMISSION)
20 DG
GENERATOR FIELD CONTROL 55
OR/WT OVERDRIVE SOLENOID (AUTO TRANSMISSION ONLY)
21 BK/RD
CHARGE TEMPERATURE SENSOR 56
GY/PK SRI LAMP
(5.9L HDC
ENGINE)
22
OR/DB*
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(TPS)
57
DG/OR ASD SENSE
23 TN/WT
OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL
(5.9L HDC
ENGINE) 58 LG/BK
INJECTOR DRIVER
#6
24 GY/BK IGNITION (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR) 59
VT/BK IAC MOTOR
#1
25 PK
,
SCI
TRANSMIT 60
YL/BK* IAC MOTOR
#3
26 CCD
(-:-)
WIRE COLOR CODES LB
LIGHT BLUE
VT VIOLET
27 BR
A/C SWITCH SENSE BK BLACK
LG LIGHT GREEN
WT
WHITE
28 VT A/C SELECT BR BROWN
OR ORANGE
YL YELLOW
29 WT/PK* BRAKE SWITCH
-
DB DARK BLUE PK
PINK *
WITH TRACER
30 BY/YL*
PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCH DG DARK GREEN
RD
RED
31 GY
GRAY TN TAN
32 BK/PK*
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
33 TN/RD*
SPEED CONTROL VACUUM SOLENOID CONNECTOR
34 DB/OR* A/C CLUTCH RELAY TERMINAL
|(pcKX>coooop0ffoj'
oooooooooojj
35 GY/YL*
EGR SOLENOID SHOWN W'41
30
50«M#5l31
604
%\
oooooooooo ••ooooooooooj
36 J9314-171
Fig.
17 PCM
Connector—Gas
Powered
Engines
Page 868 of 1502
•
THROTTLE
POSITION
SENSOR
CO
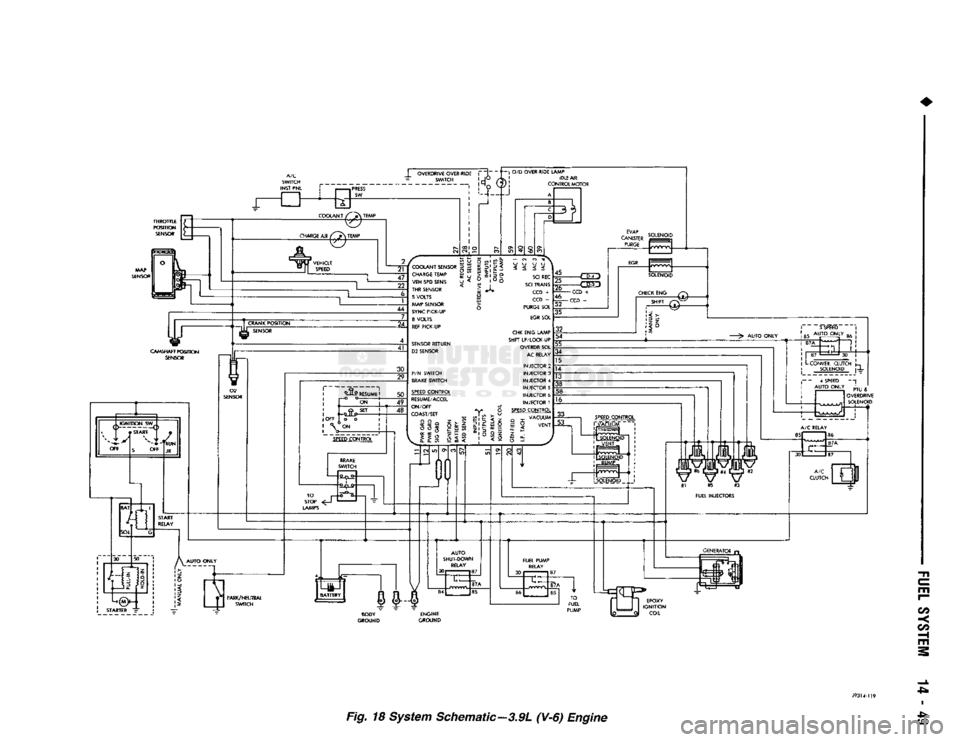
Fig. 18 System Schematic—3.9L (V-6) Engine
CO
Page 871 of 1502

14-52
FUEL
SYSTEM
•
CAMSHAFT
POSITION
SENSOR
TESTING
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition Systems for testing.
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of the engine coolant
temperature sensor and its circuitry, refer to DRB II
tester and appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Proce
dures manual. To test the sensor only, refer to the
following: (1) Disconnect wire harness connector from coolant
temperature sensor (Fig. 21). Engines with air conditioning; When removing
the connector from sensor, do not pull directly on
wiring harness. Fabricate an L-shaped hook tool
from a coat hanger (approximately eight inches
long).
Place the hook part of tool under the connector
for removal. The connector is snapped onto the sen sor. It is not equipped with a lock type tab.
Fig.
21
Engine
Coolant
Temperature
Sensor—
Typical
(2) Test the resistance of the sensor with a high in
put impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. The resis
tance (as measured across the sensor terminals) should be less than 1340 ohms with the engine
warm. Refer to the Coolant Temperature sensor/ Charge Air Temperature sensor resistance chart. Re
place the sensor if it is not within the range of resistance specified in the chart.
(3) Test continuity of the wire harness. Do this be
tween the powertrain control module (PCM) wire
harness connector terminal 2 and the sensor connec
tor terminal. Also test continuity of wire harness ter
minal 4 to the sensor connector terminal. Repair the
wire harness if an open circuit is indicated.
(4) After tests are completed, connect electrical
connector to sensor. The sensor connector is symmet
rical (not indexed). It can be installed to the sensor in either direction. SENSOR RESISTANCE (OHMS)-COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR/CHARGE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
TEMPERATURE
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
C F
MIN MAX
-40 -40 291,490 381,710
-20 -4 85,850 108,390
-10 14 49,250 61,430
0 32 29,330 35,990
10 50 17,990 21,810
20 68 11,370 13,610
25 77 9,120 10,880
30 86 7,370 8,750
40 104 4,900 5,750
50 122 3,330 3,880
60 140 2,310 2,670
70 158 1,630 1,870
80 176 1,170 1,340
90 194 860 970
100 212 640 720
no 230 480 540
120 248 370 410
J928D-4
CHARGE
AIR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of the intake manifold
charge air temperature sensor and its circuitry, refer
to DRB II tester and appropriate Powertrain Diag nostics Procedures manual. To test the sensor only,
refer to the following: (1) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
charge air temperature sensor (Fig. 22).
Fig.
22
Charge
Air
Temperature
Sensor—Typical
(2) Test the resistance of the sensor with an input
impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. The resistance (as measured across the sensor terminals) should be
less than 1340 ohms with the engine warm. Refer to
the Coolant Temperature sensor/Charge Air Temper-
Page 872 of 1502
•
FUEL
SYSTEM
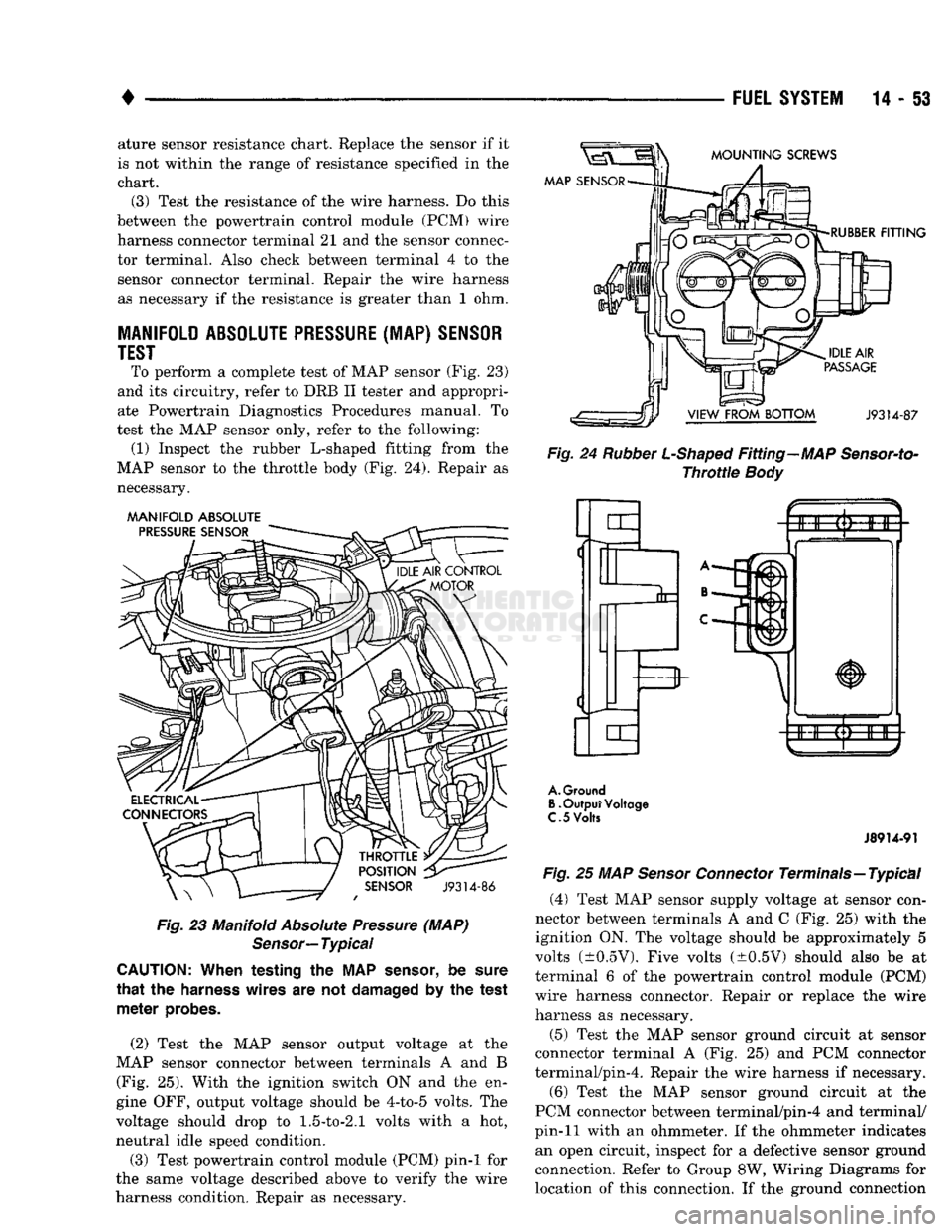
14-53 ature sensor resistance chart. Replace the sensor if it
is not within the range of resistance specified in the chart. (3) Test the resistance of the wire harness. Do this
between the powertrain control module (PCM) wire
harness connector terminal 21 and the sensor connec tor terminal. Also check between terminal 4 to the sensor connector terminal. Repair the wire harness
as necessary if the resistance is greater than 1 ohm.
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE
(MAP)
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of MAP sensor (Fig. 23)
and its circuitry, refer to DRB II tester and appropri
ate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the MAP sensor only, refer to the following: (1) Inspect the rubber L-shaped fitting from the
MAP sensor to the throttle body (Fig. 24). Repair as necessary.
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
Fig.
23 Manifold
Absolute
Pressure
(MAP)
Sensor—
Typical
CAUTION:
When testing the MAP
sensor,
be
sure
that
the
harness
wires are not
damaged
by the test
meter
probes.
(2) Test the MAP sensor output voltage at the
MAP sensor connector between terminals A and B (Fig. 25). With the ignition switch ON and the en
gine OFF, output voltage should be 4-to-5 volts. The
voltage should drop to
1.5-to-2.1
volts with a hot,
neutral idle speed condition.
(3) Test powertrain control module (PCM) pin-1 for
the same voltage described above to verify the wire
harness condition. Repair as necessary.
Fig.
24
Rubber
L-Shaped
Fitting—MAP
Sensor-to-
Throttle
Body
A.
Ground
B.
Output Voltage
C.
5
Volts
J8914-91
Fig.
25 MAP
Sensor
Connector
Terminals—Typical
(4)
Test MAP sensor supply voltage at sensor con
nector between terminals A and C (Fig. 25) with the ignition ON. The voltage should be approximately 5
volts (±0.5V). Five volts (±0.5V) should also be at
terminal 6 of the powertrain control module (PCM)
wire harness connector. Repair or replace the wire
harness as necessary.
(5) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at sensor
connector terminal A (Fig. 25) and PCM connector
terminal/pin-4. Repair the wire harness if necessary.
(6) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at the
PCM connector between terminal/pin-4 and terminal/
pin-11 with an ohmmeter. If the ohmmeter indicates an open circuit, inspect for a defective sensor ground
connection. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for
location of this connection. If the ground connection
Page 873 of 1502
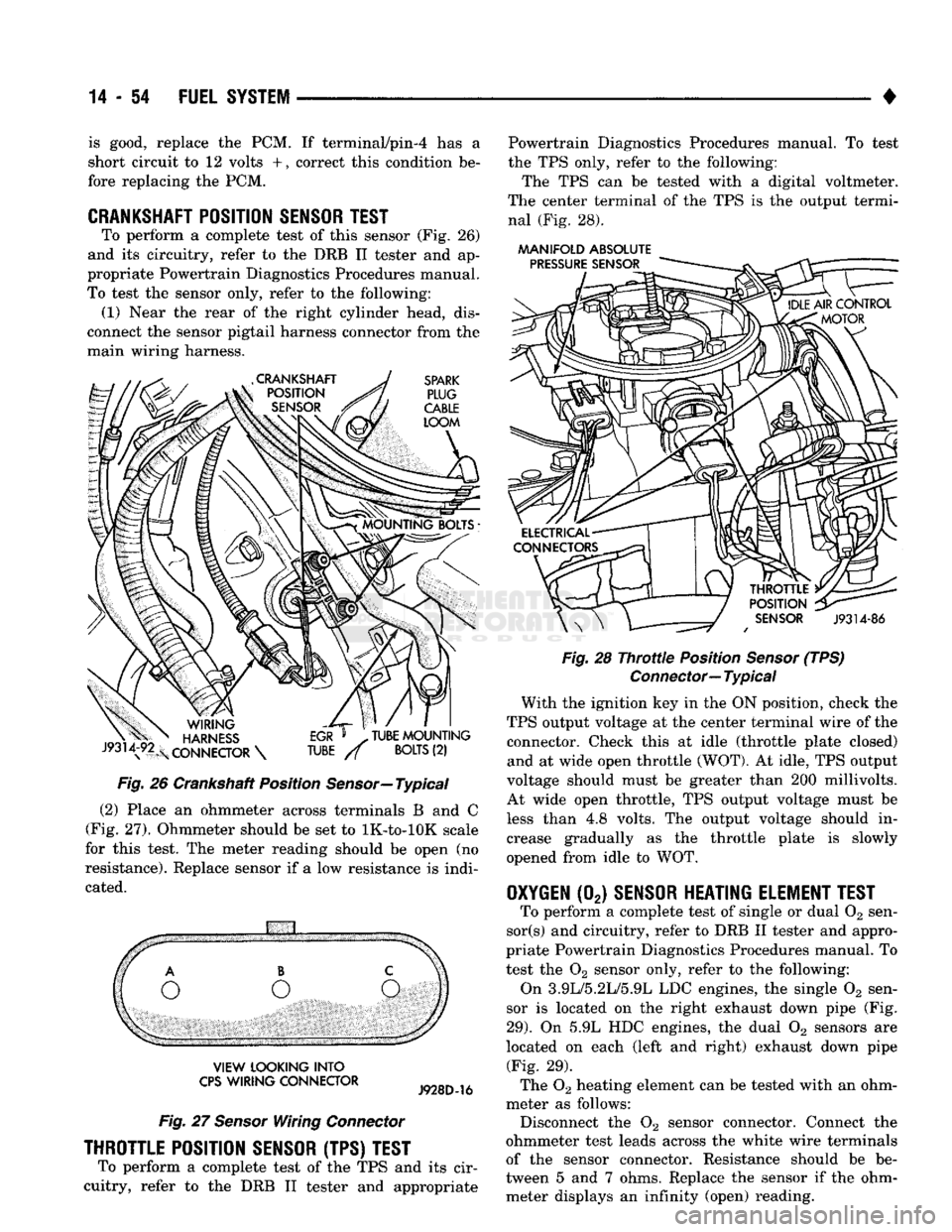
14-54 FUEL SYSTEM
• is good, replace the PCM. If terminal/pin-4 has a
short circuit to 12 volts +, correct this condition be
fore replacing the PCM.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor (Fig. 26)
and its circuitry, refer to the DRB II tester and ap
propriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual.
To test the sensor only, refer to the following: (1) Near the rear of the right cylinder head, dis
connect the sensor pigtail harness connector from the
main wiring harness.
Fig.
26 Crankshaft Position
Sensor—
Typical
(2) Place an ohmmeter across terminals B and C
(Fig. 27). Ohmmeter should be set to lK-to-lOK scale
for this test. The meter reading should be open (no
resistance). Replace sensor if a low resistance is indi
cated.
VIEW
LOOKING
INTO
CPS
WIRING
CONNECTOR
Fig.
27
Sensor
Wiring
Connector
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) TEST
To perform a complete test of the TPS and its cir
cuitry, refer to the DRB II tester and appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To test
the TPS only, refer to the following:
The TPS can be tested with a digital voltmeter.
The center terminal of the TPS is the output termi nal (Fig. 28).
AAANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
Fig.
28
Throttle
Position
Sensor
(TPS)
Connector—
Typical
With the ignition key in the ON position, check the
TPS output voltage at the center terminal wire of the connector. Check this at idle (throttle plate closed) and at wide open throttle (WOT). At idle, TPS output
voltage should must be greater than 200 millivolts.
At wide open throttle, TPS output voltage must be
less than 4.8 volts. The output voltage should in
crease gradually as the throttle plate is slowly
opened from idle to WOT.
OXYGEN
(02)
SENSOR HEATING ELEMENT TEST
To perform a complete test of single or dual 02 sen-
sor(s) and circuitry, refer to DRB II tester and appro
priate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the 02 sensor only, refer to the following:
On 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L LDC engines, the single 02 sen
sor is located on the right exhaust down pipe (Fig.
29).
On 5.9L HDC engines, the dual 02 sensors are
located on each (left and right) exhaust down pipe (Fig. 29).
The 02 heating element can be tested with an ohm
meter as follows: Disconnect the 02 sensor connector. Connect the
ohmmeter test leads across the white wire terminals
of the sensor connector. Resistance should be be
tween 5 and 7 ohms. Replace the sensor if the ohm meter displays an infinity (open) reading.