AUX FIAT UNO 1983 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 136 of 303

Weber 32 (continued) TLF 4/252 (and 251) TLF 27/251
Exhaust gas CO at idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 2.0% 0.5 to 1.5%
Fast idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.65 to 0.75 mm -
Float level (with gasket) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26.75 to 27.25 mm 26.75 to 27.25 mm
Float travel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33.7 to 34.7 mm 33.7 to 34.7 mm
Full power jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.50 mm 0.55 mm
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.47 mm 0.45 mm
Idle mixture adjustment port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.50 mm 1.50 mm
Idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750 to 800 rpm 800 to 850 rpm
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.05 mm 1.05 mm
Needle valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.50 mm 1.50 mm
Pump jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 mm 0.40 mm
Pump outlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 mm 0.40 mm
Superfeed jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 mm 0.45 mm
Superfeed mixture jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.00 mm 3.00 mm
Venturi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm 22 mm
Weber 30/32 DMTE 30/150
Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1116 cc engine (95 RON unleaded engine)
Exhaust gas CO at idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 2.0%
Float level (with gasket fitted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.5 to 7.5 mm
Idle pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 to 3.5 mm
Idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 to 900 rpm
Needle valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.50 mm
Pull down capsule bush . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.20 mm
Primary Secondary
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.10 1.80
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F30 F30
Idle air jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.15 0.70
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.50 -
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.47 0.40
Full power jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 -
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.90 1.05
Main venturi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 23
Pump discharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 -
Pump jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.45 -
Secondary venturi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 -
Weber 30/32 DMTE 10/150
Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1116 cc
Accelerator pump capacity (ten strokes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.5 to 12.5 cc
Anti-flooding device (automatic - Y) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.75 to 4.25 mm
Anti-flooding device (mechanical - X) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 to 9.5 mm
Excess fuel discharge orifice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40
Exhaust gas CO at idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 to 1.5%
Float setting (fuel level) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.5 to 7.5 mm
Idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 to 900 rpm
Needle valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm
Primary and secondary valve plate openings:
X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.5 to 14.5 mm
Y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.5 to 15.5 mm
Primary valve plate opening (X) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.45 to 6.95 mm
Throttle valve plate opening - fast idle (A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.90 to 0.95 mm
Primary Secondary
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195 195
Accelerator pump jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 40
Auxiliary venturi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.5 5
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F42 F38
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 70
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 95
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19.0 mm 23.0 mm
Solex C 30/32 - CIC8
Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1116 cc
All calibration as for the Weber 30/32 DMTE 10/150 except for the following:
Primary Secondary
Accelerator pump jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 50
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230 190
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47.5 40
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 100
Needle valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.6 1.6
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•11
13
Page 162 of 303

Initial start-up after major
overhaul
28Refer to Chapter 1, Section 45, but note
that an oil pressure gauge is fitted to indicate
oil pressure.
29Check the ignition static timing as
described in Section 10.
30Check the engine idle speed and CO level
as described in Section 9.
7 Engine-
1372 cc ie and 1372 cc
Turbo ie
PART A: GENERAL
Description
1The 1372 cc engine is similar in design to
the OHC engine fitted to the FIAT Tipo
variants. The engine is of four-cylinder, in-line,
overhead camshaft type, mounted
transversely at the front of the vehicle.
2The crankshaft runs in five main bearings.
Thrustwashers are fitted to the rear (flywheel
end) main bearing in order to control
crankshaft endfloat.
3The connecting rods are attached to the
crankshaft by horizontally split shell-type
big-end bearings. The pistons are attached to
the connecting rods by fully-floating gudgeon
pins which are secured by circlips. The
aluminium alloy pistons are fitted with three
piston rings: two compression rings and an oil
control ring.
4The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt
and operates the valves via bucket and shim
type cam followers. The camshaft is located in
a separate housing on top of the cylinder
head.
5The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by double valve springs, and operate
in guides pressed into the cylinder head.
6The auxiliary shaft, which is also driven by
the toothed belt, drives the oil pump.
7Lubrication is by means of a gear type
pump which draws oil through a strainer
located in the sump, and forces it through a
full-flow filter into the engine oil galleries fromwhere it is distributed to the crankshaft,
camshaft and auxiliary shaft. The big-end
bearings are supplied with oil via internal
drillings in the crankshaft. The undersides of
the pistons are cooled by oil spray nozzles
located in each main bearing location in the
crankcase.
8A crankcase ventilation system is
employed, whereby piston blow-by gases are
drawn via an oil separator into the air cleaner,
from where they are drawn into the inlet
manifold and re-burnt with fresh air/fuel
mixture.
9The 1372 cc ie engine is fitted with a Bosch
Mono-Jetronic single point fuel injection (SPi)
system. Whilst the higher performance
1372 cc Turbo ie engine is fitted with a Bosch
L3.1 (L3.2 from 1992) Jetronic multi-point
injection (MPi) system and turbocharger with
intercooler and oil cooling. The L3.2 system
models are fitted with catalytic converters.
Maintenanceª
10At the intervals specified in Section 3 or
“Routine maintenance” at the beginning of
this Manual, carry out the following tasks.
11Check the engine oil level as follows. With
the vehicle parked on level ground, and with
the engine having been stopped for a few
minutes, withdraw the oil level dipstick, wipe it
on a clean rag, and re-insert it fully. Withdraw
the dipstick again and read off the oil level
relative to the MAX and MIN marks. The oil
level should be between the marks. If the level
is at or below the MIN mark, top up through
the filler on the camshaft cover without delay
(photo). The quantity of oil required to raise
the level from MIN to MAX on the dipstick is
approximately 1.0 litre (1.8 pints). Do not
overfill.
12Renew the engine oil and filter as
described in Section 2 of Chapter 1 (photos).
13Check and if necessary adjust the valve
clearances as described in Part B of this
Section.
14Inspect the engine for signs of oil, coolant
or fuel leaks and rectify as necessary.
15Inspect the crankcase ventilation hose for
blockage or damage. Clean or renew as
necessary.
16Check the condition and tension of thetiming belt as described in Part B of this
Section.
17Renew the timing belt as described in
Part B of this Section.
PART B:
OPERATIONS POSSlBLE
WITH ENGINE IN CAR
Valve clearances -
checking and adjustment#
1It is important to ensure that the valve
clearances are set correctly, as incorrect
clearances will result in incorrect valve timing
thus affecting engine performance.
2The clearances must be checked and
adjusted with the engine cold.
3On the ie engine, refer to Section 9 in this
Chapter for details and remove the air cleaner
unit.
4On the ie engine disconnect the crankcase
ventilation hose from the injector unit and
position the hose out of the way.
5On Turbo ie engines, loosen off the clips
and remove the air hose to the inlet manifold
(above the camshaft cover).
6On Turbo ie engines, disconnect the
accelerator cable from the throttle housing
and the support bracket on the camshaft
cover.
7Unscrew the securing nuts and washers
and remove the camshaft cover, noting that
on later models two of the nuts also secure
the hose clip assembly. Recover the gasket.
8Numbering from the front (timing belt) end
of the engine, the exhaust valves are 1, 4, 5
and 8, and the inlet valves are 2, 3, 6 and 7.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•37
7A.12B Engine oil filter removal using a
strap wrench - 1372 cc engine7A.12A Engine sump drain plug - 1372 cc
engine7A.11 Topping up the engine oil level -
1372 cc engine
Fig. 13.15 Engine oil level dipstick location
and level markings on the 1372 cc ie and
Turbo ie engines (Sec 7A)
13
Page 165 of 303
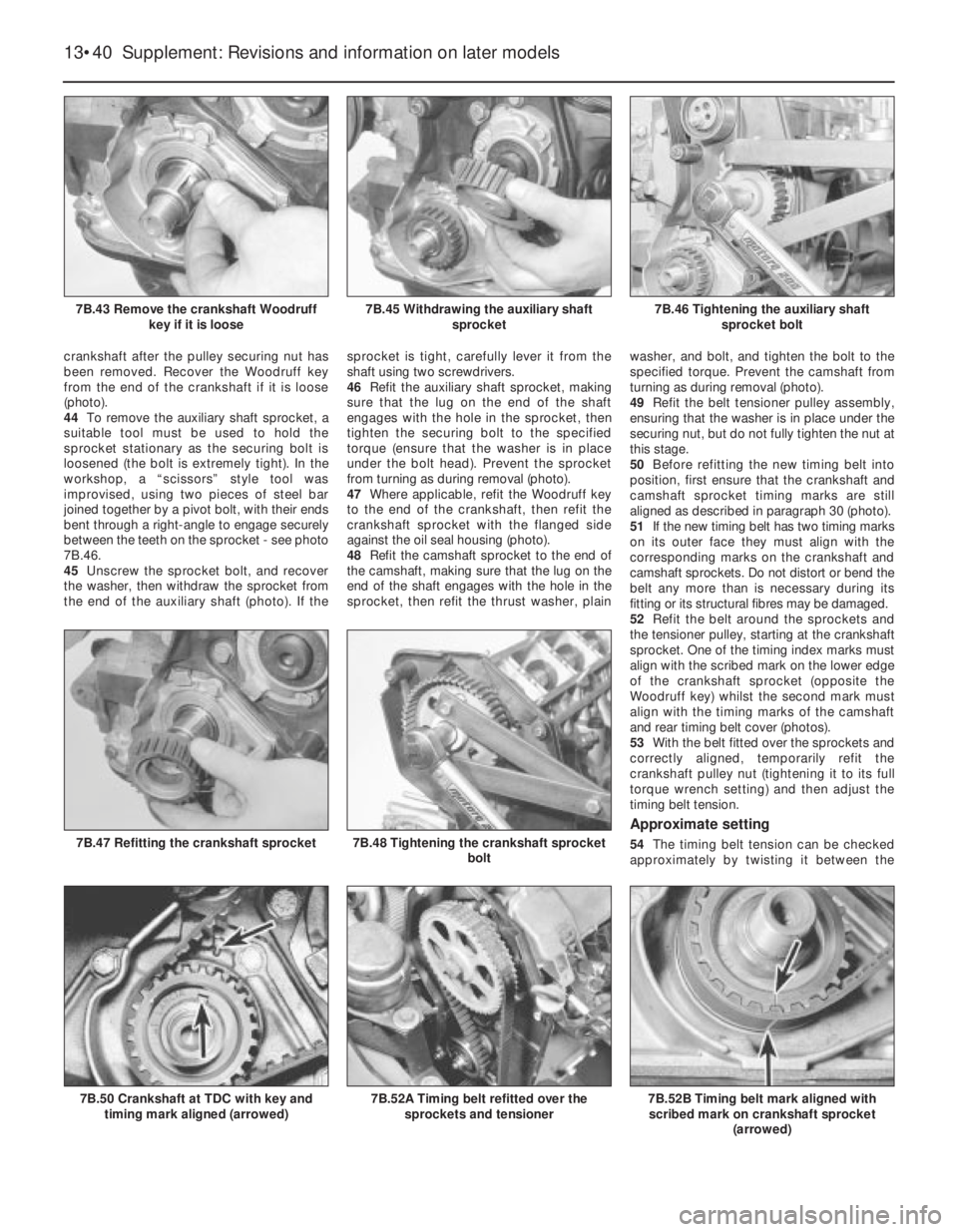
crankshaft after the pulley securing nut has
been removed. Recover the Woodruff key
from the end of the crankshaft if it is loose
(photo).
44To remove the auxiliary shaft sprocket, a
suitable tool must be used to hold the
sprocket stationary as the securing bolt is
loosened (the bolt is extremely tight). In the
workshop, a “scissors” style tool was
improvised, using two pieces of steel bar
joined together by a pivot bolt, with their ends
bent through a right-angle to engage securely
between the teeth on the sprocket - see photo
7B.46.
45Unscrew the sprocket bolt, and recover
the washer, then withdraw the sprocket from
the end of the auxiliary shaft (photo). If thesprocket is tight, carefully lever it from the
shaft using two screwdrivers.
46Refit the auxiliary shaft sprocket, making
sure that the lug on the end of the shaft
engages with the hole in the sprocket, then
tighten the securing bolt to the specified
torque (ensure that the washer is in place
under the bolt head). Prevent the sprocket
from turning as during removal (photo).
47Where applicable, refit the Woodruff key
to the end of the crankshaft, then refit the
crankshaft sprocket with the flanged side
against the oil seal housing (photo).
48Refit the camshaft sprocket to the end of
the camshaft, making sure that the lug on the
end of the shaft engages with the hole in the
sprocket, then refit the thrust washer, plainwasher, and bolt, and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque. Prevent the camshaft from
turning as during removal (photo).
49Refit the belt tensioner pulley assembly,
ensuring that the washer is in place under the
securing nut, but do not fully tighten the nut at
this stage.
50Before refitting the new timing belt into
position, first ensure that the crankshaft and
camshaft sprocket timing marks are still
aligned as described in paragraph 30 (photo).
51If the new timing belt has two timing marks
on its outer face they must align with the
corresponding marks on the crankshaft and
camshaft sprockets. Do not distort or bend the
belt any more than is necessary during its
fitting or its structural fibres may be damaged.
52Refit the belt around the sprockets and
the tensioner pulley, starting at the crankshaft
sprocket. One of the timing index marks must
align with the scribed mark on the lower edge
of the crankshaft sprocket (opposite the
Woodruff key) whilst the second mark must
align with the timing marks of the camshaft
and rear timing belt cover (photos).
53With the belt fitted over the sprockets and
correctly aligned, temporarily refit the
crankshaft pulley nut (tightening it to its full
torque wrench setting) and then adjust the
timing belt tension.
Approximate setting
54The timing belt tension can be checked
approximately by twisting it between the
13•40 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.52B Timing belt mark aligned with
scribed mark on crankshaft sprocket
(arrowed)7B.52A Timing belt refitted over the
sprockets and tensioner7B.50 Crankshaft at TDC with key and
timing mark aligned (arrowed)
7B.48 Tightening the crankshaft sprocket
bolt7B.47 Refitting the crankshaft sprocket
7B.46 Tightening the auxiliary shaft
sprocket bolt7B.45 Withdrawing the auxiliary shaft
sprocket7B.43 Remove the crankshaft Woodruff
key if it is loose
Page 166 of 303

thumb and forefinger at the centre of the run
between the auxiliary shaft sprocket and the
camshaft sprocket. Using this method it
should just be possible to twist the belt
through 90º using moderate pressure.
55To adjust the tension, loosen off the
tensioner pulley nut then insert two rods (or
screwdrivers) into position in the pulley holes
and position a lever between them.
56Gently lever the tensioner pulley in the
required direction to set the tension as
described, then initially tighten the pulley nut
to lock the tensioner in the required position.
57Remove the tools from the tensioner,
recheck the tension and then tighten the
tensioner pulley nut securely.
58Rotate the crankshaft clockwise through
two complete turns using a socket or spanner
on the crankshaft pulley nut, then recheck the
belt tension. To avoid the possibility of
unscrewing the pulley nut, remove the spark
plugs to enable the engine to be turned over
easier.
59If further adjustment is required, repeat
the previously mentioned procedures. If in
doubt, err on the slightly tight side when
adjusting the tension. If the belt is set too
loose, it may jump off the sprockets resulting
in serious damage.
60Remove the crankshaft pulley retaining
nut, fit the timing belt cover, then refit and
tighten the pulley nut to the specified torque
setting.
61Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal. Tighten the retaining
nuts/bolts to the specified torque settings
where given. Adjust the tension of the
alternator drivebelt as described in Section 8.
Adjustment using FIAT special
tools
62Assemble the special tools and fit them to
the belt tensioner pulley as shown in
Fig. 13.16. When fitted, the tool rod must be
as vertical as possible and it is important to
note that no sliding weights must be attached
to tool No. 1860745100.
63Slacken the tensioner pulley nut, if not
already done. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise
through two complete turns using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft pulley nut. The
special tool rod may move from the vertical asthe engine is turned over, in which case the
joint will need to be re-adjusted to return the
rod to the vertical and the operation repeated.
64With the two revolutions of the crankshaft
completed, tighten the belt tensioner pulley
nut securely and remove the special tools.
65Remove the crankshaft pulley retaining
nut, fit the timing belt cover, then refit and
tighten the pulley nut to its specified torque
setting.
66Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal. Tighten the retaining
nuts/bolts to the specified torque settings
where given. Adjust the tension of the
alternator drivebelt as described in Sec-
tion 8.
Camshaft front oil seal -
renewal#
67The camshaft front oil seal may be
renewed with the engine in the vehicle, and
the camshaft in situ, as follows.
68Remove the timing belt and the camshaft
sprocket as described previously in this
Section.
69Punch or drill a small hole in the centre of
the exposed oil seal. Screw in a self-tapping
screw, and pull on the screw with pliers to
extract the seal.
70Clean the oil seal seat with a wooden or
plastic scraper.
71Lubricate the lips of the new seal with
clean engine oil, and drive it into position until
it is flush with the housing, using a suitable
socket or tube. Take care not to damage the
seal lips during fitting. Note that the seal lips
should face inwards.
72Refit the camshaft sprocket and thetiming belt as described previously in this
Section.
Camshaft, housing and
followers -
removal and refitting
#
Note: The engine must be cold when
removing the camshaft housing. Do not
remove the camshaft housing from a hot
engine. New camshaft housing and camshaft
cover gaskets must be used on refitting.
73If the engine is still in the vehicle,
disconnect the battery negative lead.
74Refer to paragraphs 3 to 7 in this part of
this Section for details and remove the
camshaft cover.
75Remove the camshaft sprocket and timing
belt as described previously in this Section.
76Remove the three securing nuts and the
single securing bolt, and withdraw the upper
section of the rear timing belt cover.
77Unscrew the camshaft housing securing
bolts. There are seven bolts which are
accessible from outside the camshaft
housing, and five shorter bolts which are
accessible from inside the housing (these
bolts are normally covered by the camshaft
cover). Note that each bolt is fitted with two
washers (photo).
78Carefully lift the camshaft housing from
the cylinder head. Be prepared for the cam
followers to drop from their bores in the
camshaft housing as the camshaft housing is
lifted, and ensure that the cam followers are
identified for position so that they can be
refitted in their original positions (this can be
achieved by placing each cam follower over
its relevant valve in the cylinder head).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•41
Fig. 13.16 FIAT special tool No. 1860745100 (A) for timing belt adjustment shown fitted to
the tensioner pulley - 1372 cc ie and Turbo ie engines (Sec 7B)
Use with adapter No. 1860745200 on 1372 cc ie engines and No. 1860745300 on 1372 cc
Turbo ie engines
7B.77 Removing one of the camshaft
housing shorter securing bolts
13
Page 173 of 303
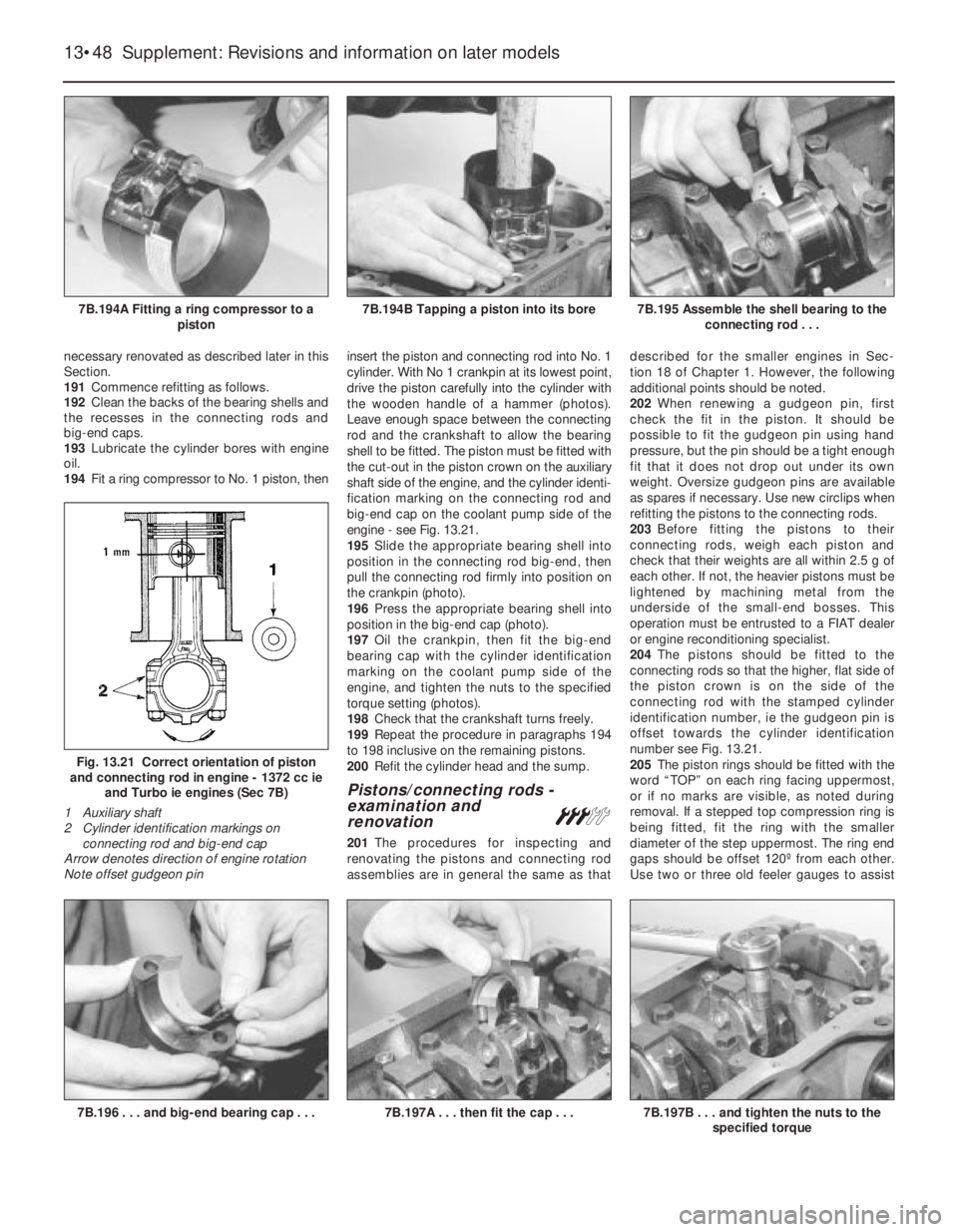
necessary renovated as described later in this
Section.
191Commence refitting as follows.
192Clean the backs of the bearing shells and
the recesses in the connecting rods and
big-end caps.
193Lubricate the cylinder bores with engine
oil.
194Fit a ring compressor to No. 1 piston, theninsert the piston and connecting rod into No. 1
cylinder. With No 1 crankpin at its lowest point,
drive the piston carefully into the cylinder with
the wooden handle of a hammer (photos).
Leave enough space between the connecting
rod and the crankshaft to allow the bearing
shell to be fitted. The piston must be fitted with
the cut-out in the piston crown on the auxiliary
shaft side of the engine, and the cylinder identi-
fication marking on the connecting rod and
big-end cap on the coolant pump side of the
engine - see Fig. 13.21.
195Slide the appropriate bearing shell into
position in the connecting rod big-end, then
pull the connecting rod firmly into position on
the crankpin (photo).
196Press the appropriate bearing shell into
position in the big-end cap (photo).
197Oil the crankpin, then fit the big-end
bearing cap with the cylinder identification
marking on the coolant pump side of the
engine, and tighten the nuts to the specified
torque setting (photos).
198Check that the crankshaft turns freely.
199Repeat the procedure in paragraphs 194
to 198 inclusive on the remaining pistons.
200Refit the cylinder head and the sump.
Pistons/connecting rods -
examination and
renovation
#
201The procedures for inspecting and
renovating the pistons and connecting rod
assemblies are in general the same as thatdescribed for the smaller engines in Sec-
tion 18 of Chapter 1. However, the following
additional points should be noted.
202When renewing a gudgeon pin, first
check the fit in the piston. It should be
possible to fit the gudgeon pin using hand
pressure, but the pin should be a tight enough
fit that it does not drop out under its own
weight. Oversize gudgeon pins are available
as spares if necessary. Use new circlips when
refitting the pistons to the connecting rods.
203Before fitting the pistons to their
connecting rods, weigh each piston and
check that their weights are all within 2.5 g of
each other. If not, the heavier pistons must be
lightened by machining metal from the
underside of the small-end bosses. This
operation must be entrusted to a FIAT dealer
or engine reconditioning specialist.
204The pistons should be fitted to the
connecting rods so that the higher, flat side of
the piston crown is on the side of the
connecting rod with the stamped cylinder
identification number, ie the gudgeon pin is
offset towards the cylinder identification
number see Fig. 13.21.
205The piston rings should be fitted with the
word “TOP” on each ring facing uppermost,
or if no marks are visible, as noted during
removal. If a stepped top compression ring is
being fitted, fit the ring with the smaller
diameter of the step uppermost. The ring end
gaps should be offset 120º from each other.
Use two or three old feeler gauges to assist
13•48 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.197B . . . and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque
Fig. 13.21 Correct orientation of piston
and connecting rod in engine - 1372 cc ie
and Turbo ie engines (Sec 7B)
1 Auxiliary shaft
2 Cylinder identification markings on
connecting rod and big-end cap
Arrow denotes direction of engine rotation
Note offset gudgeon pin
7B.197A . . . then fit the cap . . .7B.196 . . . and big-end bearing cap . . .
7B.195 Assemble the shell bearing to the
connecting rod . . .7B.194B Tapping a piston into its bore7B.194A Fitting a ring compressor to a
piston
Page 176 of 303

fittings are disconnected from the engine and
transmission and positioned out of the way.
Enlist the aid of an assistant to help steady
and guide the power unit down through the
engine compartment as it is removed, If
available, position a suitable engine trolley or
crawler board under the engine/transmission
so that when lowered, the power unit can be
withdrawn from the front end of the vehicle
and moved to the area where it is to be
cleaned and dismantled.
38Carefully lower the engine and
transmission unit, ensuring that no fittings
become snagged. Detach the hoist and
withdraw the power unit from under the
vehicle.
39To separate the engine from the
transmission, unbolt and remove the starter
motor, then unscrew the retaining bolts and
withdraw the transmission from the engine. As
it is withdrawn, do not allow the weight of the
engine or transmission to be taken by the
input shaft.
40To remove the clutch unit, refer to
Chapter 5 for details.
1372 cc Turbo ie
engine/transmission -
removal and separation
#
41The engine and transmission removal and
refitting details for Turbo-engined models are
similar to those described for the non-Turbo
models in the previous sub-Section, but the
following differences should be noted.
42To provide access for the disconnection
of the turbo and related components, first
remove the inlet manifold. Removal of the inlet
manifold and the turbocharger is described in
Section 9 of this Chapter.
43The ignition distributor on the Turbo
engine is driven from the auxiliary shaft and is
mounted at the front of the engine, towards
the timing cover end.
44The right-hand driveshaft has a steady
bearing and this will need to be unbolted and
detached.
Engine dismantling - general
45Refer to Chapter 1, Section 14 for details.
Auxiliary shaft - removal,
inspection and refitting #
46Remove the engine and transmission from
the vehicle as described previously in this
Section part.
47Drain the engine oil and remove the sump
as described in Part B of this Section.
48Remove the oil pump as described in Part
B of this Section.
49Remove the timing belt and the auxiliary
shaft sprocket as described in Part B of this
Section.
50Unscrew the three retaining bolts and
remove the auxiliary shaft cover. Remove the
gasket.
51Withdraw the auxiliary shaft from the
cylinder block.
52Examine the shaft and its bearing bushes
in the cylinder block for signs of excessive
wear and/or damage and renew it if
necessary. Bush renewal is described in
paragraph 79 in this Section.
53The cover gasket and the oil seal should
always be renewed whenever the cover is
removed. To renew the seal, support the
cover on blocks of wood and drive out the old
seal using a suitable drift inserted in the
cut-out in the back of the cover. Clean the
seal location in the housing. Drive the new
seal into place using a suitable metal tube or
socket (photo). The sealing lip must face
towards the cylinder block. Smear the sealing
lips with clean engine oil before installation.
54Commence refitting by lubricating theauxiliary shaft journals with clean engine oil,
then insert the shaft into the cylinder block
(photo).
55Refit the auxiliary shaft cover, using a new
gasket, and tighten the securing bolts
(photos).
56Refit the auxiliary shaft sprocket, timing
belt, cover and crankshaft pulley as described
in Part B of this Section.
57Refit the engine and transmission with
reference to Part D of this Section.
Engine -
complete dismantling#
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
58Detach and remove the following ancillary
items. Where applicable, refer to the
appropriate Chapter or Section within this
Chapter for more detailed removal instructions.
Engine oil dipstick
Ignition distributor and HT leads
Fuel pump
Alternator
Oil filter
Oil vapour recovery unit
Inlet and exhaust manifolds and associated
fuel injection components (as applicable)
Clutch unit
59Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the timing cover and drivebelt.
60Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the cylinder head unit.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•51
7C.54 Inserting the auxiliary shaft into the
cylinder block (rear timing belt cover
removed)7C.53 Driving a new oil seal into the
auxiliary shaft cover7C.36C Transmission front mounting
7C.55B . . . and tighten the securing bolts7C.55A Refit the auxiliary shaft cover with
a new gasket . . .
13
Page 177 of 303

61Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the flywheel.
62Refer to the previous sub-Section for
details and remove the auxiliary shaft.
63Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the sump.
64Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the oil pump unit.
65Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the front and rear crankshaft oil
seals.
66Refer to Part B of this Section and remove
the piston/connecting rod assemblies.
67Refer to Part B of this Section for details
and remove the crankshaft and main bearing
assemblies.
Crankshaft and main
bearings - removal#
68Unscrew the securing bolts and remove
the front and rear crankshaft oil seal housings.
Recover the gaskets.
69Check the main bearing caps for identifi-
cation marks and if necessary use a
centre-punch to identify them. Normally the
caps have identifying notches cut into their
top face nearest the timing belt end of the
engine, with the exception of No 5 cap
(flywheel end) which has no marking (photo).
70Before removing the crankshaft, check
that the endfloat is within the specified limits.
Ideally a dial gauge should be used, but
alternatively feeler gauges can be used as
follows. Push the crankshaft as far as possible
towards the timing end of the engine, and
using a feeler gauge, measure the gap
between the rear face of the flywheel
mounting flange on the crankshaft and the
outer face of the thrust washer (photo). Now
push the crankshaft as far as possible in the
opposite direction and take the same
measurement again. The difference between
the two measurements is the crankshaft
endfloat. If the endfloat is outside the
specified limits, new thrustwashers will be
required.
71Unscrew the bolts and tap off the main
bearing caps complete with bearing shells. If
the bearing shells are to be re-used, tape
them to their respective caps.
72Lift the crankshaft from the crankcase.
73Extract the bearing shells from thecrankcase, keeping them identified for
location if they are to be re-used, and recover
the thrust washers from No. 5 main bearing
location.
Engine components -
examination and
renovation
#
74With the engine completely stripped,
clean all the components and examine them
for wear. Each part should be checked and
where necessary renewed or renovated as
described elsewhere in this Section. Renew
main and big-end bearing shells as a matter of
course, unless it is known that they have had
little wear and are in perfect condition.
75If in doubt as to whether to renew a
component which is still just serviceable,
consider the time and effort which will be
incurred should the component fail at an early
date. Obviously the age and expected life of
the vehicle must influence the standards
applied.
76Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of course. FIAT specify
that the main cylinder head bolts should be
renewed after they have been used (ie
tightened) four times - if in any doubt as to the
number of times the bolts have been used,
renew them in any case as a precaution
against possible failure.
77Take the opportunity to renew the engine
core plugs while they are easily accessible.
Knock out the old plugs with a hammer and
chisel or punch. Clean the plug seats, smearthe new plugs with sealant and tap them
squarely into position.
78Clean and examine the cylinder block as
described in paragraphs 2 to 7 of Section 18,
Chapter 1.
79If the auxiliary shaft bushes are
excessively worn or are oval, they must be
renewed. When the new bushes are installed,
they may need to be reamed to suit. The
renewal of the auxiliary shaft bushes is
therefore best entrusted to an engine
reconditioner or FIAT dealer. When the
bushes are renewed, ensure that the oil hole
in each bush is aligned with the oil channel in
the cylinder block.
PART D: ENGINE
REASSEMBLY
Reassembly - general
1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 19.
Crankshaft and main
bearings - refitting#
2Ensure that the crankcase and crankshaft
are thoroughly clean, and that the oilways are
clear. If possible, blow through the oil drillings
with compressed air, and inject clean engine
oil into them.
3Unless they are virtually new, the old main
bearing shells should be renewed. Failure to
do so is a false economy.
4If new bearing shells are being fitted, wipe
away all traces of protective grease.
5Note that there is a tag on the back of each
bearing shell, which engages with a groove in
the relevant seat in the crankcase or bearing
cap.
6Wipe clean the bearing shell locations in the
crankcase with a non-fluffy rag, then lubricate
them and fit the five upper halves of the
bearing shells to their seats. Note that the
centre (No. 3) bearing shell is plain, whereas
all the other shells have oil grooves (photos).
7Fit the thrustwashers to the No. 5 main
bearing shell location, with the grooved side
of each washer facing away from the face of
the cylinder block - ie towards the thrust face
of the crankshaft (photos).
8Wipe the bearing shell locations in the
13•52 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7D.6B . . . all others have oil groove7D.6A No. 3 main bearing shell is plain . . .
7C.70 Measuring crankshaft endfloat using
feeler gauge method7C.69 Identification notches on No. 3 main
bearing cap
Page 178 of 303
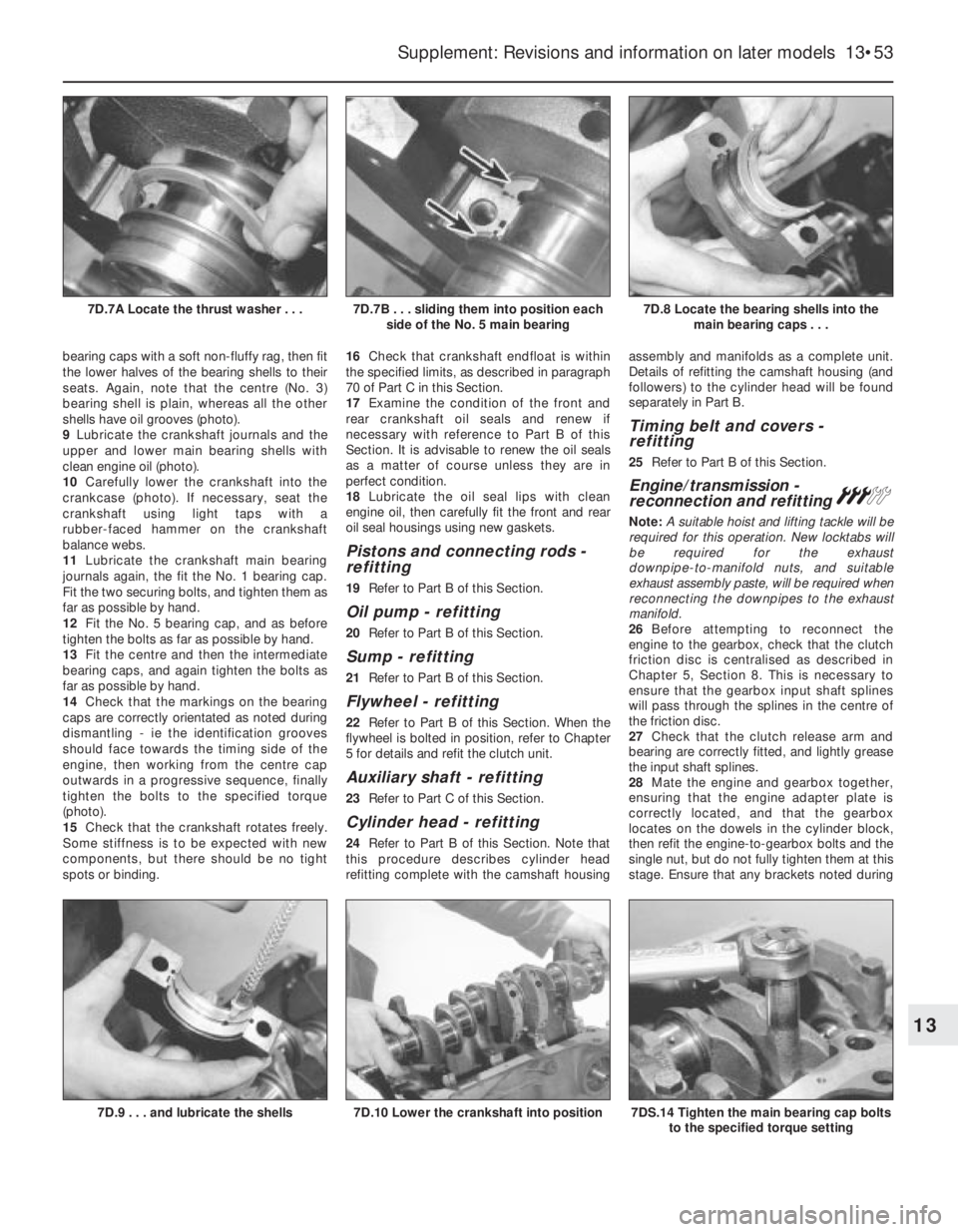
bearing caps with a soft non-fluffy rag, then fit
the lower halves of the bearing shells to their
seats. Again, note that the centre (No. 3)
bearing shell is plain, whereas all the other
shells have oil grooves (photo).
9Lubricate the crankshaft journals and the
upper and lower main bearing shells with
clean engine oil (photo).
10Carefully lower the crankshaft into the
crankcase (photo). If necessary, seat the
crankshaft using light taps with a
rubber-faced hammer on the crankshaft
balance webs.
11Lubricate the crankshaft main bearing
journals again, the fit the No. 1 bearing cap.
Fit the two securing bolts, and tighten them as
far as possible by hand.
12Fit the No. 5 bearing cap, and as before
tighten the bolts as far as possible by hand.
13Fit the centre and then the intermediate
bearing caps, and again tighten the bolts as
far as possible by hand.
14Check that the markings on the bearing
caps are correctly orientated as noted during
dismantling - ie the identification grooves
should face towards the timing side of the
engine, then working from the centre cap
outwards in a progressive sequence, finally
tighten the bolts to the specified torque
(photo).
15Check that the crankshaft rotates freely.
Some stiffness is to be expected with new
components, but there should be no tight
spots or binding.16Check that crankshaft endfloat is within
the specified limits, as described in paragraph
70 of Part C in this Section.
17Examine the condition of the front and
rear crankshaft oil seals and renew if
necessary with reference to Part B of this
Section. It is advisable to renew the oil seals
as a matter of course unless they are in
perfect condition.
18Lubricate the oil seal lips with clean
engine oil, then carefully fit the front and rear
oil seal housings using new gaskets.
Pistons and connecting rods -
refitting
19Refer to Part B of this Section.
Oil pump - refitting
20Refer to Part B of this Section.
Sump - refitting
21Refer to Part B of this Section.
Flywheel - refitting
22Refer to Part B of this Section. When the
flywheel is bolted in position, refer to Chapter
5 for details and refit the clutch unit.
Auxiliary shaft - refitting
23Refer to Part C of this Section.
Cylinder head - refitting
24Refer to Part B of this Section. Note that
this procedure describes cylinder head
refitting complete with the camshaft housingassembly and manifolds as a complete unit.
Details of refitting the camshaft housing (and
followers) to the cylinder head will be found
separately in Part B.
Timing belt and covers -
refitting
25Refer to Part B of this Section.
Engine/transmission -
reconnection and refitting#
Note: A suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be
required for this operation. New locktabs will
be required for the exhaust
downpipe-to-manifold nuts, and suitable
exhaust assembly paste, will be required when
reconnecting the downpipes to the exhaust
manifold.
26Before attempting to reconnect the
engine to the gearbox, check that the clutch
friction disc is centralised as described in
Chapter 5, Section 8. This is necessary to
ensure that the gearbox input shaft splines
will pass through the splines in the centre of
the friction disc.
27Check that the clutch release arm and
bearing are correctly fitted, and lightly grease
the input shaft splines.
28Mate the engine and gearbox together,
ensuring that the engine adapter plate is
correctly located, and that the gearbox
locates on the dowels in the cylinder block,
then refit the engine-to-gearbox bolts and the
single nut, but do not fully tighten them at this
stage. Ensure that any brackets noted during
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•53
7D.8 Locate the bearing shells into the
main bearing caps . . .7D.7B . . . sliding them into position each
side of the No. 5 main bearing
7DS.14 Tighten the main bearing cap bolts
to the specified torque setting7D.10 Lower the crankshaft into position7D.9 . . . and lubricate the shells
13
7D.7A Locate the thrust washer . . .
Page 183 of 303

35Clean the mating faces of the thermostat
cover and cylinder head, and use a new
gasket when refitting the cover.
36Refill the cooling system as described
earlier in this Section.
Coolant pump -
removal and refittingÁ
Note: A new coolant pump gasket must be
used on refitting. If the pump is found to be
worn it must be renewed as a complete unit as
dismantling and repair is not possible.
37Disconnect the battery negative lead.
38Drain the cooling system as described
earlier in this Section.
39Remove the coolant/alternator drivebelt
as described in the next sub-Section.
40Unscrew the four coolant pump securing
bolts, noting that two of the bolts also secure
the alternator adjuster bracket, and withdraw
the pump from the housing (photo). Recover
the gasket.
41Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
42Use a new gasket between the pump and
the housing.
43Refit and tension the coolant
pump/alternator drivebelt as described in the
next sub-Section.
44On completion, refill the cooling system
as described earlier in this Section.
Coolant pump/alternator
drivebelt - checking,
renewal and tensioning
Á
45At the intervals specified in Section 3 or
“Routine maintenance” at the beginning of
this manual (as applicable), the drivebelt
should be checked and if necessary
re-tensioned.
46Access to the drivebelt is made from the
underside of the car on the right-hand side.
Loosen off the front right-hand roadwheel
retaining bolts, then raise and support the car
on axle stands at the front. Remove the front
roadwheel on the right-hand side.
47Remove the underwing shield from the
right-hand wheel arch by drifting the
compression pins out from the retaining
clips. Prise free the clips and remove the
shield.
48Additional, though somewhat restricted,
access can be obtained from above by
removing the air cleaner unit on the non-Turbo
ie-engine (photo).
49Check the full length of the drivebelt for
cracks and deterioration. It will be necessary
to turn the engine in order to check the
portions of the drivebelt in contact with the
pulleys. If a drivebelt is unserviceable, renew it
as follows (photo).
50Loosen the alternator mounting and
adjuster nuts and bolts and pivot the
alternator towards the cylinder block.51Slip the drivebelt from the alternator,
coolant pump and crankshaft pulleys.
52Fit the new drivebelt around the pulleys,
then lever the alternator away from the
cylinder block until the specified belt tension
is achieved. Lever the alternator using a
wooden or plastic lever at the pulley end to
prevent damage. It is helpful to partially
tighten the adjuster nut before tensioning the
drivebelt (photo).
53When the specified tension has been
achieved, tighten the mounting and adjuster
nuts and bolts (photo).
PART D: HEATER UNIT- LATER
MODELS
Heater unit -
removal and refitting
Á
1The heater unit is removed complete with
the facia/control panel. Commence by
draining the cooling system as described
previously in this Section.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Refer to Section 15 of this Chapter for
details and remove the ashtray/cigar lighter
and the auxiliary control panel.
4Undo the upper screw retaining the heater
unit to the facia (see Fig. 13.31).
5Remove the radio from the central facia.
6Undo the retaining screw on each side at
the front of the gear lever console. Prise free
13•58 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.31 Removing the heater unit-to-
facia upper retaining screw (Sec 8D)8C.53 Tightening the alternator adjuster
nut8C.52 Fitting a new coolant
pump/alternator drivebelt around the
pulleys
8C.49 Alternator/water pump drivebelt and
tensioner viewed from the right-hand
wheel arch8C.48 Top side view of water pump,
alternator and drivebelt8C.40 Coolant pump/alternator bracket
bolt removal
Page 211 of 303

6On 999, 1108 and 1372 cc engines, the
distributor is driven from the rear end of the
camshaft.
7On the 1116 and 1299/1301 cc engines, the
distributor is driven from an extension of the
oil pump driveshaft which is geared to the
auxiliary shaft.
8The distributor contains a reluctor mounted
on its shaft, and a magnet and stator fixed to
the baseplate.
9Ignition advance is controlled in the
conventional way mechanically by centrifugal
weights and a diaphragm unit for vacuum
advance.
10Instead of the conventional method of
interrupting the low tension circuit to generate
high tension voltage in the coil by means of a
mechanical contact breaker, when the
electronic ignition is switched on, the
switching of the transistors in the electronic
control unit (ECU) prevents current flow in the
coil primary windings.
11Once the crankshaft rotates, the reluctor
moves through the magnetic field created by
the stator and when the reluctor teeth are in
alignment with the stator projections a small
AC voltage is created. The ECU amplifies this
voltage and applies it to switch the transistors
and so provide an earth path for the primary
circuit.
12As the reluctor teeth move out of
alignment with the stator projections the AC
voltage changes, the transistors in the ECU
are switched again to interrupt the primary
circuit earth path. This causes a high voltage
to be induced in the secondary winding.
Distributor
(breakerless type) -
removal and refitting
#
13Removal of the distributor on the 903,1116, 1299 and 1301 cc engines is as
described in Chapter 4, Section 6.
14On 999, 1108 and 1372 cc engines, mark
the position of the distributor clamp plate in
relation to the cylinder head surface.
15Unclip the distributor cap and move it to
one side with the HT leads attached.
16Disconnect the LT lead plug and, where
applicable, the vacuum hose (photo).
17Unscrew the distributor fixing nuts and
withdraw the unit.
18The distributor drive is by means of an
offset dog no special procedure is required to
refit it. Providing the dog engages in its slot
and the distributor body is turned to align the
marks made before removal, the timing will
automatically be correct.
19If a new distributor is being fitted (body
unmarked), set No. 4 piston at TDC (0º) by
turning the crankshaft pulley bolt until the
timing marks on the crankshaft pulley and
engine front cover are in alignment.
20Align the drive dog and fit the distributor
then turn the distributor body until the contact
end of the rotor is aligned with the arrow on
the distributor dust shield.
21Tighten the distributor clamp nuts. Refit the
cap and disconnected components and then
check ignition timing using a stroboscope.
Distributor (breakerless
type) - overhaul#
22It is recommended that a worn out or
faulty distributor is renewed. However,
individual components such as the cap, rotor,
reluctor, magnet/stator/baseplate assembly,
vacuum diaphragm unit, and drive gear or dog
are available separately.
Breakerless
ignition system
components - testing
ª
23A voltmeter and an ohmmeter will be
required for this work.
Primary circuit voltage
24Turn on the ignition, and using a voltmeter
check the voltage at the ignition coil LT
terminals. Any deviation from battery voltage
will indicate a faulty connection, or if these are
satisfactory, then the coil is unserviceable.
Magnetic impulse generator winding
25Remove the distributor and ECU and
disconnect their connecting leads.
26Connect an ohmmeter to the impulse
generator terminals and note the reading. The
resistance should be as given in the Specifi-
cations at the beginning of this Chapter.
27Now check between one of the impulse
generator terminals and the metal body of the
distributor. Infinity should be indicated on the
ohmmeter. If it is not, renew the impulse
generator carrier plate. Note: When carrying out
this test it is imperative that the connections are
remade as originally observed. Also ensure that
there is no possibility of the ECU supply (red)
cable and earth cable making contact in service.
Ignition coil winding resistance
28Check the resistance using an ohmmeter
between the coil LT terminals. Refer to the
Specifications for the expected coil resistance.
29Check the resistance between the LT lead
socket on the coil and each of the LT
terminals. Refer to the Specifications for the
expected coil resistance.
30The rotor arm resistance should be
approximately 5000 ohms.
Microplex ignition system -
description
31This system is fitted to the 1301 and
1372 cc Turbo ie models, and comprises the
following components.
Electro-magnetic sensors
32Two sensors are used to pick up engine
speed and TDC position directly from the
crankshaft.
Pressure and vacuum sensor
33This converts inlet manifold vacuum
pressure into an electrical signal for use by
the electronic control unit (ECU).
Anti-knock sensor
34This converts “pinking” detonations which
occur within the combustion chambers into
an electrical signal for use by the ECU (photo).
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
35This computes the optimum ignition
advance angle from the sensor signals
received, and controls the action of the
ignition unit (photo).
13•86 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.72 Rotor aligned with arrow on
distributor dust shield - 999 and 1108 cc
engines (Sec 10)
1 ECU
2 Ignition coil
3 Distributor
4 Vacuum advance
unit5 Pick-up filter with
calibrated opening
for atmospheric
pressure
Fig. 13.71 Location of electronic ignition
components on early models with
breakerless ignition (Sec 10)
10.16 Distributor LT lead connecting plug