ECO mode FIAT UNO 1983 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 97 of 303

20 Interior lamps-
bulb renewal
1
Courtesy lamp
1The lamp lenses, whether roof or pillar
mounted, are removed by prising off using a
screwdriver inserted under one end (photo).
2The festoon type bulb is pulled from its
spring contacts.
Instrument panel lamps
3Remove the instrument panel hood cover
as described in the next Section. The panel
lighting bulbs may be renewed without further
dismantling, but access to the warning and
indicator bulbs can only be obtained if the
instrument panel is partially withdrawn as
described in the next Section (photo). 4Pull out the appropriate bulbholder and
withdraw the wedge base type bulb.
5Fit the new bulb, the holder, instrument
panel and hood cover.
21 Instrument panel-
removal and refitting
1
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the instrument panel hood cover.
The easiest way to do this is to insert the
fingers at the sides, and pull the hood sharply
upwards off its retaining clips.
3Extract the two fixing screws from the
instrument panel and pull it towards you until the
speedometer drive cable can be disconnected
by squeezing its plastic retaining ring (photo).
4Disconnect the wiring plugs and record
their exact locations. 5Remove the instrument panel upwards
(photo).
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
22 Instrument panel-
dismantling
1
1With the instrument panel removed from
the car, individual instruments may be
removed in the following way.
2Pull off the speedometer trip device knob.
3Remove the instrument hood cover by
gently releasing the plastic clips (Fig. 9.4).
4The speedometer is secured by two screws
for its metal casing and one screw for its
plastic casing. Other instruments are held to
the panel by nuts (photo).
5On models equipped with a check control
system (see Section 34), the speedometer
cannot be removed until the control unit has
first been withdrawn.
6On ES versions, the speedometer cannot
be removed until the economy gauge control
unit has been removed.
23 Speedometer drive cable-
renewal
1
1Remove the instrument panel hood cover
as described in Section 21.
2Disconnect the speedometer cable from
the speedometer by squeezing the plastic
retaining ring (photo).
9•8 Electrical system
23.2 Speedometer cable connector at
head22.4 Rear view of instrument panel21.5 Instrument panel and steering wheel
removed
21.3 Removing instrument panel screw21.2 Removing instrument panel hood
cover
Fig. 9.4 Instrument hood cover (1) (Sec 21)20.3 Instrument panel warning lamp20.1 Interior roof lamp withdrawn
Page 99 of 303

27 Tailgate wiper motor-
removal and refitting
1
1Remove the blade and arm as previously
described. Unscrew the drive spindle bezel
nut.
2Open the tailgate fully.
3Unclip and remove the wiper motor cover.
4Unscrew the mounting screws, withdraw
the motor and disconnect the wiring plug
(photo).
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
28 Washer system
1
1The washer system for the windscreen and
the tailgate operates from a bag type fluid
reservoir within the engine compartment
(photo).
2The reservoir bag is fitted with two pumps,
one for each system (photo).
3Use screen cleaning fluid mixed in the
recommended proportion in the washer fluid
reservoir and in very cold weather add a small
quantity of methylated spirit.
4To clear a blocked washer jet nozzle or to
adjust the wash jet glass-striking pattern,
insert a pin part way into the jet nozzle.
29 Heated tailgate window-
precautions and repair
2
1The heater element inside the tailgate glass
should be treated with care.
2Clean only with a damp cloth and wipe in
the direction in which the filaments run. Avoid
scratching with rings on the fingers, or by
allowing luggage to rub on the glass. Never
stick adhesive labels over the heater element.
3Should one of the heater filaments be
broken it can be repaired using one of the
special silver paints available, but follow the
manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
30 Radio/cassette- fitting
2
1In-car entertainment equipment is not
provided as standard on the models covered
by this Manual.
2However, the centre console is designed to
receive a radio set after removing the blanking
plate behind which a power lead is already
provided.
3The ignition system and other electrical
components are suppressed during
production of the car and further suppression
should not be required other than earthing the
wiper motor.
Receiver
4Fit the radio/cassette using the installation
kit supplied with the equipment.
5On Comfort models, fit an in-line fuse in the
power feed. On Super models the radio
supply is protected by fuse number 12.
6Make sure that the radio is well earthed to a
metal body component.
Aerial
7The recommended locations for the aerial
are towards the rear of the right-hand front
wing or on the windscreen pillar.
8Fitting instructions for Fiat aerials are
supplied with them, but the following general
advice will help if using non-Fiat equipment.9Motorised automatic aerials rise when the
equipment is switched on and retract at
switch-off. They require more fitting space
and supply leads, and can be a source of
trouble.
10There is no merit in choosing a very long
aerial as, for example, the type about three
metres in length which hooks or clips on to
the rear of the car, since part of this aerial will
inevitably be located in an interference field.
For VHF/FM radios the best length of aerial is
about one metre. Active aerials have a
transistor amplifier mounted at the base and
this serves to boost the received signal. The
aerial rod is sometimes rather shorter than
normal passive types.
11A large loss of signal can occur in the
aerial feeder cable, especially over the Very
High Frequency (VHF) bands. The design of
feeder cable is invariably in the co-axial form,
ie a centre conductor surrounded by a flexible
copper braid forming the outer (earth)
conductor. Between the inner and outer
conductors is an insulator material which can
be in solid or stranded form. Apart from
insulation, its purpose is to maintain the
correct spacing and concentricity. Loss of
signal occurs in this insulator, the loss usually
being greater in a poor quality cable. The
quality of cable used is reflected in the price
of the aerial with the attached feeder cable.
12The capacitance of the feeder should be
within the range 65 to 75 picofarads (pF)
approximately (95 to 100 pF for Japanese and
American equipment), otherwise the
adjustment of the car radio aerial trimmer may
not be possible. An extension cable is
necessary for a long run between aerial and
receiver. If this adds capacitance in excess of
the above limits, a connector containing a
series capacitor will be required, or an
extension which is labelled as
“capacity-compensated”.
13Fitting the aerial will normally involve
making a 7/8 in (22 mm) diameter hole in the
bodywork, but read the instructions that come
with the aerial kit. Once the hole position has
been selected, use a centre punch to guide
the drill. Use sticky masking tape around the
area for this helps with marking out and drill
location, and gives protection to the
9•10 Electrical system
Fig. 9.8 Radio housing and power lead (A)
(Sec 30)
28.2 Washer pumps28.1 Washer fluid reservoir27.4 Tailgate wiper motor
Page 100 of 303

paintwork should the drill slip. Three methods
of making the hole are in use:
a) Use a hole saw in the electric drill. This is,
in effect, a circular hacksaw blade
wrapped round a former with a centre
pilot drill.
b) Use a tank cutter which also has cutting
teeth, but is made to shear the metal by
tightening with an Allen key.
c) The hard way of drilling out the circle is
using a small drill, say 1/8 in (3 mm), so
that the holes overlap. The centre metal
drops out and the hole is finished with
round and half-round files.
14Whichever method is used, the burr is
removed from the body metal and paint
removed from the underside. The aerial is fitted
tightly ensuring that the earth fixing, usually a
serrated washer, ring or clamp, is making a
solid connection. This earth connection is
important in reducing interference. Cover any
bare metal with primer paint and topcoat, and
follow by underseal if desired.
15Aerial feeder cable routing should avoid
the engine compartment and areas where
stress might occur, eg under the carpet where
feet will be located.Loudspeakers
16A mono speaker may be located under
the facia panel beneath the glovebox.
17Provision is made for twin speakers within
the door tidy bins or under the rear shelf
mountings.
18Speakers should be matched to the
output stage of the equipment, particularly as
regards the recommended impedance. Power
transistors used for driving speakers are
sensitive to the loading placed on them.
31 Electrically-operated front
door windows
3
1The electrically-operated front door
windows are controlled by switches on the
centre console or in the door armrest
(depending on model). The regulator motor
and cable are located within the door cavity.
2To gain access to the assembly, remove
the door trim panel as described in Chap-
ter 12.
3Disconnect the wiring plug (1) (Fig. 9.11).4Release the bolts which connect the power
lift to the glass mounting.
5Remove the bolts which hold the lift
assembly to the door.
6The motor and glass mounting may be
disconnected from the cable guide and sleeve
and any faulty components renewed.
7When refitting the assembly to the door,
make sure that the window glass slides
smoothly before fully tightening the cable
guide bolts. Refer to Section 10 for details of
system fuses and relays.
32 Central door locking system
1
1The doors are locked simultaneously from
the outside by turning the key in either
direction.
2The doors can be locked from inside the car
in the following ways:
All doors locked or unlocked - depress or lift
a front door lock plunger knob.
One rear door locked or unlocked - depress
or lift a rear door lock plunger knob.
Electrical system 9•11
Fig. 9.9 Door speaker mounting (Sec 30)Fig. 9.10 Rear speaker mounting (Sec 30)
Fig. 9.13 Central door locking system
components (Sec 32)Fig. 9.12 Power operated window
components (Sec 31)Fig. 9.11 Power-operated window motor
(Sec 31)
1 Connector plug
1 Electric motor
2 Glass mounting
3 Cable guide4 Cable
5 Cable sleeve1 Solenoid
2 Lock relay lever
3 Link rod4 Exterior handle
lever
9
Page 101 of 303

3The centralised door locking system can
operate independently of the key.
4To gain access to the lock solenoid and
linkage, remove the front door trim panel as
described in Chapter 12.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Disconnect the electrical wiring plugs from
the solenoid within the door cavity.
7Disconnect the solenoid from the lock lever
by removing the clip.
8Unscrew the two bolts which secure the
solenoid to the door and remove it.
9Renew the solenoid or switch as necessary.
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
11Refer to Section 10 for details of system
fuses and relays.
33 Economy gauge
(Econometer)
2
1This device is fitted to ES (energy saving)
models and indicates to the driver the fuel
consumption (in litres per 100 km) coupled
with a needle which moves over coloured
sections of a dial to make the driver aware
that his method of driving is either conducive
to high or low fuel consumption. Refer to
Chapter 3, Section 16.
2The device is essentially a vacuum gauge
which also incorporates a warning lamp to
indicate to the driver when a change of gear is
required.
3A fuel cut-out valve (see Chapter 3, Sec-
tion 11) is used in conjunction with the
economy gauge so that when the accelerator
pedal is released during a pre-determined
engine speed range, fuel supply to the engine
is stopped, but resumes when the engine
speed falls below the specified range.
LED (light emitter diode)
4The gearchange indicator will only light up
at engine speeds in excess of 2000 rev/min
for vacuum pressures up to 600 mm Hg in 1st,
2nd and 3rd speed gears and for vacuum
pressures up to 676 mm Hg in 4th speedgear. The light will not come on if 5th speed
gear is engaged or if the coolant temperature
is below 55ºC.
5There is a two second delay in the light
coming on to prevent it operating during rapid
acceleration in a low gear.
6If the LED light comes on during
deceleration it should be ignored.
Fault finding
7A faulty economy gauge should be checked
in the following way.
8Refer to Section 21 and remove the
instrument panel.
9Disconnect the economy gauge L
connector and then connect a test lamp
between the BN cable contact and earth. If
the lamp comes on then the gauge supply
circuit is not open. If the lamp does not come
on, check all connections in the supply cable
which comes from the interconnecting unit of
the electrical system, also Fuse No 12.
10Now connect a voltmeter between the
white cable and earth. Check the voltage with
the engine not running, but the ignition
switched on. It should be between 0.7 and
0.9 volt. If the reading varies considerably
from that specified, check the connections
between the economy gauge and the fuel
cut-out device control unit. If the fault cannot
be rectified, renew the ignition control unit
(Digiplex system, see Chapter 4).
11Now check the closed throttle valve plate
switch by connecting a voltmeter between the
brown and BN cables of the L connector. With
the valve plate open, there should be no
reading, but with it open, voltage should be
indicated.
12Failure to conform as described will be
due to a faulty earth in the switch or a faulty
fuel cut-out device control unit.
13A further test of the throttle valve plate
switch may be carried out by disconnecting
the multi-plug from the fuel cut-out device
control unit.
14Connect a test lamp to contact 4 (positive
battery terminal). The lamp should come on,
when the engine is idling or the accelerator
released. If it does not, renew the throttle
valve plate switch.15Connect a tachometer to the brown/white
cable contact in the L connector and record
the engine speed with the engine running. If
no reading is obtained, renew the Digiplex
ignition control unit which must be faulty.
34 Check control (warning
module) system
2
1This is fitted into the instrument panel of
certain models to provide a means of
checking the operation of many electrical
circuits and other systems in the interest of
safety. Sensors are used where appropriate.
2The following components are not
monitored by the system, but have separate
warning lamps:
Handbrake “on”
Choke in use
Low engine oil pressure
Battery charge indicator
3The multi-functional electronic device
automatically checks the following functions
whether the engine is running or not:
Coolant level
Disc pad wear
Door closure
Engine oil level
Front parking lamps
Rear foglamps
Stop lamps
4The check information is stored by the
system monitor until the engine is started
when the display panel then indicates the
situation by means of the LEDs (light emitter
diodes) and the general lamp.
5If all functions are in order, the green panel
lamp will come on when the ignition key is
turned and will go out after two to three
seconds.
6If some functions are not in order, then the
red panel lamp will come on also the
appropriate LED.
Sensors - checking
7If a fault signal occurs which is
subsequently found to be incorrect, first
check the wiring connections between the
9•12 Electrical system
Fig. 9.15 Check system control panel (Sec 34)
A Parking lamps
B Coolant levelC Engine oil level
D Door closureE Brake fluid level
F Disc pad wearFig. 9.14 Location of control units (Sec 33)
A Digiplex ignition system control unit
B Fuel cut-out valve control unit
Page 102 of 303
sensors, lamp circuits and the control unit.
Corrosion at the terminals may also be a
contributory cause.
8Never short circuit a sensor supply wire or
the electronic module will be damaged.
Check control unit and monitor -
removal and refitting
9Remove the instrument panel as described
in Section 21.
10Unbolt the control unit housing from the
instrument panel.
11Access to the monitor can only be
obtained after removing the tachometer andthe red and green general warning lamps.
Unscrew the two monitor fixing bolts.
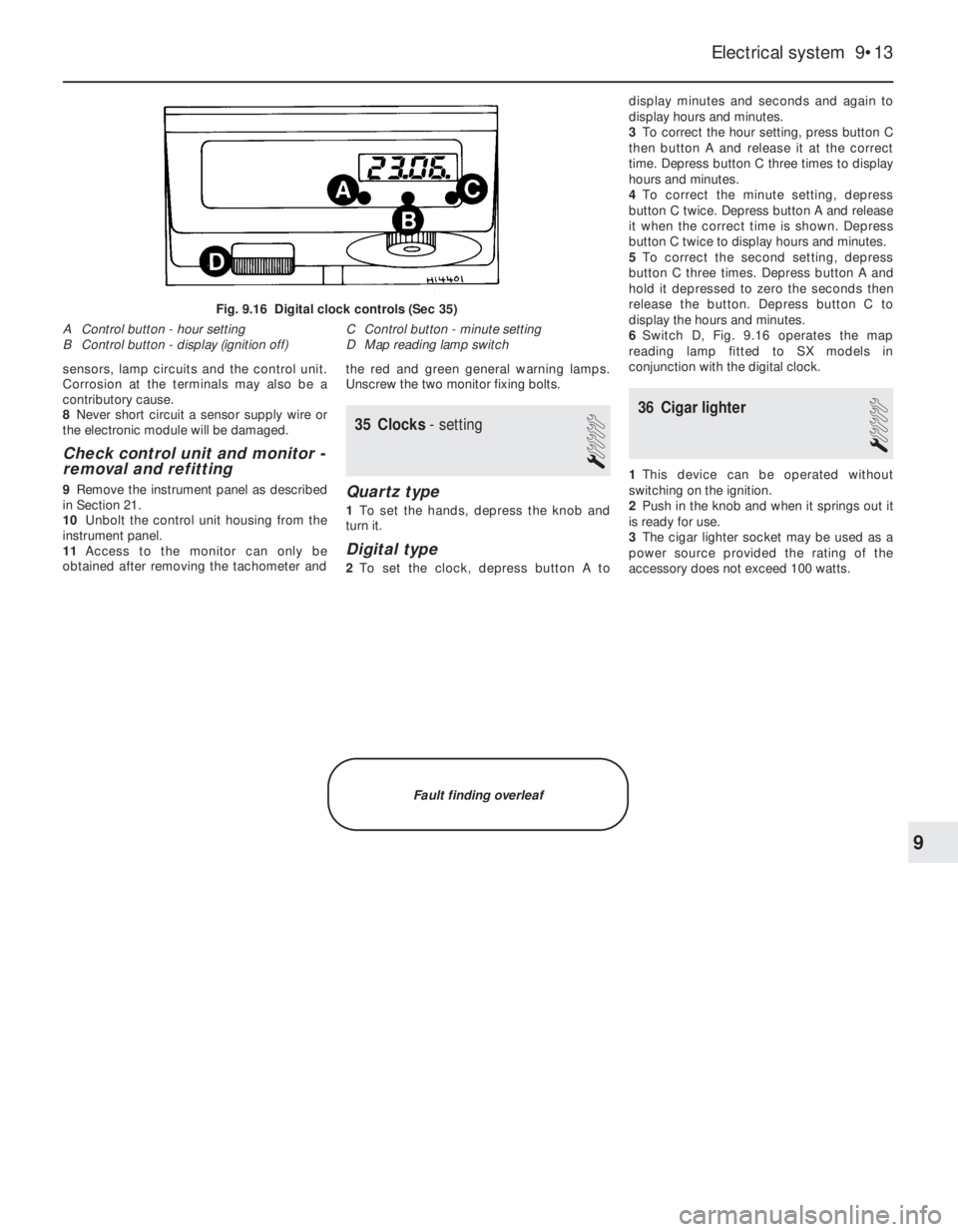
35 Clocks- setting
1
Quartz type
1To set the hands, depress the knob and
turn it.
Digital type
2To set the clock, depress button A todisplay minutes and seconds and again to
display hours and minutes.
3To correct the hour setting, press button C
then button A and release it at the correct
time. Depress button C three times to display
hours and minutes.
4To correct the minute setting, depress
button C twice. Depress button A and release
it when the correct time is shown. Depress
button C twice to display hours and minutes.
5To correct the second setting, depress
button C three times. Depress button A and
hold it depressed to zero the seconds then
release the button. Depress button C to
display the hours and minutes.
6Switch D, Fig. 9.16 operates the map
reading lamp fitted to SX models in
conjunction with the digital clock.
36 Cigar lighter
1
1This device can be operated without
switching on the ignition.
2Push in the knob and when it springs out it
is ready for use.
3The cigar lighter socket may be used as a
power source provided the rating of the
accessory does not exceed 100 watts.
Electrical system 9•13
Fig. 9.16 Digital clock controls (Sec 35)
A Control button - hour setting C Control button - minute setting
B Control button - display (ignition off) D Map reading lamp switch
9
Fault finding overleaf
Page 106 of 303

13Stake the lower end of the tube to retain
the bush.
14Reassembly is a reversal of removal,
noting that the universal joint coupling
pinch-bolts should pass smoothly through the
grooves in the steering shaft.
15Fit the steering wheel when the
roadwheels are in the straight-ahead position.
16Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specified
torque. Reconnect the battery.
6 Steering rack-
removal and refitting
4
1Set the steering in the straight-ahead
mode.
2Working inside the car, disconnect thesteering shaft lower coupling by unscrewing
and removing the pinch-bolt (photo).
3Disconnect the tie-rod end balljoints from
the steering arms as described earlier in this
Chapter.
4Unscrew and remove the rack clamp
mounting bolts and withdraw the steering
gear from the car crossmember (photo).
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion check the front wheel alignment
as described in Section 8.
7 Steering gear- overhaul
4
1A worn steering gear should not be
overhauled, but a new or factory
reconditioned unit fitted.
2After a high mileage, the following
adjustment may be needed however.
Rack damper - adjustment
3The slipper in the rack housing presses the
rack into mesh with the pinion. This cuts out
any backlash between the gears. Also, due to
its pressure, it introduces some stiffness into
the rack, which cuts out excessive reaction
from the road to the steering wheel.
4In due course, wear reduces the pressures
exerted by the slipper. The pressure is
controlled by the cover plate and a spring.
5The need for resetting of the slipper is not
easy to detect. On bumpy roads, the shockinduced through the steering will give a feeling
of play, and sometimes faint clonking can be
heard. In extreme cases, free play in the
steering may be felt, though this is rare. If the
steering is compared with that of a new rack
on another car, the lack of friction damping is
quite apparent in the ease of movement of the
steering wheel of the worn one.
6Centralise the steering rack. Do this by
counting the number of turns lock-to-lock and
then turning the steering wheel from one lock
through half the number of turns counted.
7Take the cover plate off the damping
slipper, remove the spring and shims, and refit
the cover plate.
8Screw in the cover plate bolts just enough
to hold the slipper against the rack.
9Measure the gap between the cover plate
and the rack housing using feeler blades.
10Select shims from the thicknesses
available (0.10, 0.125 and 0.30 mm) to provide
a shim pack thicker than the gap by between
0.05 and 0.13 mm.
11Remove the cover plate, fit the spring and
bolt on the cover plate with the selected shims.
8 Steering angles and front
wheel alignment
4
1Accurate front wheel alignment is essential
to provide good steering and roadholding char-
acteristics and to ensure slow and even tyre
Steering 10•3
Fig. 10.4 Renewing steering shaft bushes
(Sec 5)Fig. 10.3 Unscrewing combination switch
clamp nuts (Sec 5)Fig. 10.2 Removing steering column
shroud screws (Sec 5)
Fig. 10.6 Camber angle (Sec 8)
A Vertical line B Camber angle (positive)Fig. 10.5 Sectional view of rack damper
(Sec 7)6.4 Steering rack housing at pinion end
10
6.2 Steering shaft coupling
Page 114 of 303

12
For dimensions, weights etc. refer to the Introductory Section of this Manual.
Chapter 12 Bodywork
For modifications, and information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Bonnet - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Bonnet - lock and release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Centre console - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Door - dismantling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Door - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Door trim panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Facia panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Fixed side window (five-door) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Front bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Front seat - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Front wing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Grab handles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Maintenance - bodywork and underframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2Maintenance - upholstery and carpets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Major body damage - repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Minor body damage - repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Opening side window (three-door) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 18
Radiator grille - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Rear bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Rear seat - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Rear view mirrors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Roof rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Seat belts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Sunroof - operation and maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Tailgate - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Tailgate glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Windscreen glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
12•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General description
The Uno is an all steel, welded Hatchback
of unitary construction available in three- or
five-door versions.
Various levels of trim and equipment are
available depending upon model.
Factory fitted options include a sunroof,
central door locking and electrically-operated
front windows.
2 Maintenance-
bodywork and underframe
1
The general condition of a vehicle’s
bodywork is the one thing that significantly
affects its value. Maintenance is easy, but
needs to be regular. Neglect, particularly after
minor damage, can lead quickly to further
deterioration and costly repair bills. It is
important also to keep watch on those parts
of the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheel
arches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam-cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam-cleaning is available at
many garages, and is necessary for the
removal of the accumulation of oily grime,
which sometimes is allowed to become thick
in certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-applied; the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
Note that these methods should not be used
on vehicles with wax-based underbody
protective coating, or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just prior to Winter, when
the underbody should be washed down, and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc, as an additional safeguard against rust
damage, where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish
will give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen
has dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish. Always check that
the door and ventilator opening drain holes
and pipes are completely clear, so that water
Page 121 of 303

speakers, central door locking or power
operated windows, the electrical leads must be
disconnected and withdrawn through the
flexible duct before the door hinges are
unbolted. Disconnection will require removal of
the door trim panel as described in Section 11.
5It is recommended that the door is unbolted
from the hinge, leaving the hinge attached to
the body pillar.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but leave
the bolts finger tight until the door has been
gently closed and its alignment checked.
7The door can be moved up and down or
sideways using the travel provided by the
elongated bolt holes.
8If the door is not flush with the adjacent
body panels then shims should be inserted
under the hinges.9Adjust the striker to provide smooth
positive closure (photo).
14 Tailgate-
removal and refitting
1
1Open the tailgate and have an assistant
support it.
2From the upper ends of the struts, prise out
the locking wedges from the ball cups and
disconnect the struts (photo).
3Disconnect the washer tube.
4Unscrew the hinge mounting bolts from the
tailgate and lift the tailgate from the car
(photo).
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ifre-alignment is required, then the rear section
of the roof lining will have to be removed and
the hinge to body bolts released.
6Adjust the position of the lock striker to
provide smooth positive closure. The rubber
buffers should be screwed in or out in
conjunction with the adjustment of the striker
(photos).
7On some models, a remote control tailgate
opening release lever is fitted. Removal and
refitting of the cable is similar to that
described in Section 8 (photo).
15 Windscreen glass-
removal and refitting
5
1Remove the interior rear view mirror, the tax
disc and the wiper blade and arm.
2If the glass is intact, go inside the car and
pull the lip of the weatherseal downwards off
the body metal all along the top edge.
3Push the glass outwards while an assistant
stands outside ready to catch it.
4Clean the body flange and fit the
weatherstrip to the glass.
5Insert a length of strong cord in the body
flange groove of the weatherseal so that the
ends of the cord cross over at the centre of
the bottom run and hang out a few inches.
6Brush soapy water onto the edge of the
body flange and then offer the glass to the
12•8 Bodywork
14.7 Tailgate remote control release lever14.6C Tailgate rubber buffer14.6B Tailgate striker
14.6A Tailgate lock14.4 Tailgate hinge
14.2 Tailgate strut ball cup13.9 Door lock striker13.3 Door lower hinge
Page 126 of 303

13
Chapter 13 Supplement:
Revisions and information on later models
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Routine maintenance - all models from June 1991 . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Engine 903 and 1299/1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Sump pan sealing strips (903 cc engine) - modification
1299 cc engine - description
Rocker cover (903 cc engine) - removal
Cylinder head (903 cc engine) - refitting
Engine - 999 and 1108 cc (FIRE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Part A: General
Description
Part B: Operations possible with engine in car
Valve clearances - adjustment
Timing belt - renewal
Camshaft - removal and refitting
Cylinder head - removal and refitting
Sump pan - removal and refitting
Oil pump - removal, checking and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - removal and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - separation and piston ring renewal
Engine/transmission mountings - renewal
Part C: Engine removal and dismantling
Method of removal - general
Engine/transmission - removal and separation
Dismantling - general
Complete dismantling
Examination and renovation
Part D: Engine reassembly and refitting
Reassembly - general
Complete reassembly
Engine/transmission - reconnection and refitting
Initial start-up after major overhaul
Engine 1301 cc Turbo ie.................................................................. 6
Part A: General
Description
Lubrication system - description
Part B: Operations possible with engine in car
Camshaft and camshaft carrier - removal and refitting
Cylinder head - removal and refitting
Piston rings
Engine mountings - renewal
Timing belt - renewal
Oil pump drivegear cover plate
Engine oil cooler - removal and refittingPart C: Engine removal, dismantling, reassembly and refitting
Engine/transmission - removal and separation
Engine - dismantling and reassembly
Engine/transmission - reconnection and refitting
Initial start-up after major overhaul
Engine 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie......................................... 7
Part A: General
Description
Maintenance
Part B: Operations possible with the engine in car
Valve clearances - checking and adjustment
Timing belt, tensioner and sprockets - removal and refitting
Camshaft front oil seal - renewal
Camshaft, housing and followers - removal and refitting
Camshaft housing, camshaft and cam followers - dismantling,
inspection and reassembly
Cylinder head (1372 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Cylinder head (1372 cc Turbo ie engine) - removal and refitting
Cylinder head - inspection and renovation
Crankshaft front oil seal - removal and renewal
Crankshaft rear oil seal - removal and renewal
Flywheel - removal, inspection and refitting
Sump - removal and refitting
Oil pump - removal, checking and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - removal and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - examination and renovation
Engine/transmission mountings - renewal
Part C: Engine removal and dismantling
Method of removal - general
1372 cc ie engine/transmission - removal and separation
1372 cc Turbo ie engine/transmission - removal and separation
Engine dismantling - general
Auxiliary shaft - removal, inspection and refitting
Engine - complete dismantling
Crankshaft and main bearings - removal
Engine components - examination and renovation
Part D: Engine reassembly
Reassembly - general
Crankshaft and main bearings - refitting
Pistons and connecting rods - refitting
Oil pump - refitting
Sump - refitting
Flywheel - refitting
Auxiliary shaft - refitting
Cylinder head - refitting
Timing belt and covers - refitting
Engine/transmission - reconnection and refitting
Initial start-up after major overhaul
13•1
Contents
Page 128 of 303

Braking system................................................................................. 14
Part A: Braking system general
Front brake pads all later models
Part B: Braking system - Turbo ie models
Description
Front disc pads - renewal
Front disc caliper - removal and refitting
Front disc caliper - overhaul
Front brake disc - inspection, renovation or renewal
Rear disc pads - renewal
Rear disc caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting
Rear brake disc - inspection, renovation and renewal
Pressure regulating valve
Brake pedal - removal and refitting
Vacuum servo unit and master cylinder - general
Antiskid system - description
Electrical system.............................................................................. 15
Alternator (999 cc models) - removal and refitting
Alternator (later models) - removal and refitting
Alternator brushes - renewal
Starter motor (999 cc models) - removal and refitting
Starter motor (1301 cc Turbo ie, 1372 cc ie, 1372 cc Turbo ie)
- removal and refitting
Starter motor brushes (later models) - renewal
Fuses - later models
Relays (Turbo ie models) - general
Headlamps - later models
Headlamp beam adjusters for load compensation - later models
Headlamp unit removal - later models
Headlamp dim-dip system - description
Front fog lamps bulb/unit - removal and refitting and beam
adjustment
Horn - relocation
Steering column combination switches (later models) - removal
and refittingInstrument panel (Turbo ie models) - removal and refitting
Facia-mounted switches (1301 cc Turbo ie model) - removal
and refitting
Instrument panel (later models) - removal and refitting
Auxiliary control panel (later models) - removal and refitting
Heater control panel (later models) - removal and refitting
Trip master
Interior roof mounted spotlamp, switch and/or clock - removal
and refitting
Central door locking system
Cigar lighter (later models) - removal and refitting
Electrically operated window switches - removal and refitting
Windscreen wiper motor (later models) - removal and refitting
Windscreen washer reservoir (Turbo) - removal and refitting
Tailgate wiper motor (later models) - removal and refitting
Radio Check control system sensors - description
Check control system sensors - testing
Suspension....................................................................................... 16
Front anti-roll bar - removal and refitting
Suspension strut later models
Bodywork.......................................................................................... 17
Plastic components
Rear view mirrors
Door armrest
Tailgate (Turbo ie model) - component removal and refitting
Radiator grille (1301 cc Turbo ie model) - removal and
refitting
Radiator grille (1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie models) -
removal and refitting
Bumpers (1301 cc Turbo ie, 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie
models) - removal and refitting
Rear hinged windows - removal and refitting
Door trim panel (Turbo ie model) - removal and refitting
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•3
13
1 Introduction
Since its introduction in 1983, the FIAT Uno
has had a number of modifications and
improvements including the fitting of a twin
choke carburettor, low profile tyres, tinted
windows and remotely-controlled central door
locking.
The major mechanical change was the
introduction of the FIRE (Fully Integrated
Robotised Engine) on 45 and 45S models to
be followed by a new 1108 cc “FIRE” engine
on the 60S model from 1989 on.
A 1301 cc Turbo ie engine model wasavailable for a short period. This model had a
Bosch LE2 Jetronic electronic fuel injection
(ie) and a turbocharger to give added
performance. To uprate the braking to suit,
disc brakes were fitted to the rear in place of
the original drum type brakes.
A 1372 cc engine model was introduced in
1989. Two versions were initially available. A
Bosch Mono-Jetronic single-point fuel
injection (SPi) system, as found on the 70 SX
model and Bosch L3.1 or L3.2 Jetronic
multi-point fuel injection (MPi) systems were
fitted to Turbo models. L3.2 MPi system
models were equipped with catalytic
converters, to improve exhaust emission. All
fuel injection engines are fitted with electroni-
cally controlled engine management systems.
A new style instrument panel, switchgearand a revised facia layout was introduced in
1989.
During 1992, SPi fuel systems were fitted to
the 999 cc and 1108 cc engines, along with
catalytic converters for improved exhaust
emissions.
Five speed transmissions were introduced
to 999 cc models in 1993.
It is recommended that this Supplement is
always referred to before the main Chapters
of the Manual.
Project vehicles
The vehicles used in the preparation of this
supplement, and appearing in many of the
photographic sequences were a 1986 Uno
45S FIRE, a 1988 1301 cc Uno Turbo ie and a
1991 1372 cc Uno SXie.
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321