head FORD FIESTA 2007 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2007, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 2007Pages: 1226, PDF Size: 61.26 MB
Page 27 of 1226

100-00-1 1 General Information 100-00-1 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
First Aid
Apart from meeting any legal requirements it is
desirable for someone in the workshop to be
trained in First Aid procedures.
Splashes in the eye should be flushed carefully
with clean water for at least ten minutes.
Soiled skin should be washed with soap and water.
In case of cold burns, from alternative fuels, place
affected area in cool to cold water.
Individuals affected by inhalation of gases and
fumes should be removed to fresh air immediately.
If effects persist, consult a doctor.
If liquids are swallowed inadvertently, consult a
doctor giving him the information on the container
or label. Do not induce vomiting unless this action
is indicated on the label.
Fluoroelastomer
See Viton.
Foams - Polyurethane
See also Fire.
Used in sound and noise insulation. Cured foams
used in seat and trim cushioning.
Follow manufacturers instructions.
Unreacted components are irritating and may be
harmful to the skin and eyes. Wear gloves and
goggles.
Individuals with chronic respiratory diseases,
asthma, bronchial medical problems, or histories
of allergic diseases should not work in or near
uncured materials.
The components, vapors or spray mists can cause
direct irritation, sensitivity reactions and may be
toxic or harmful.
Vapors and spray mists must not be inhaled. These
materials must be applied with adequate ventilation
and respiratory protection. Do not remove the
respirator immediately after spraying; wait until the
vapors/mists have cleared.
Burning of the uncured components and the cured
foams can generate toxic and harmful fumes.
Smoking, naked flames or the use of electrical
equipment during foaming operations and until
vapors/mists have cleared should not be allowed.
Any heat cutting of cured foams or partially cured foams
should be conducted with extraction
ventilation. See also the vehicle Body Repair
Manual.
Freon
See Air Conditioning Refrigerant.
Fuels
See also, Fire, Legal Aspects, Chemicals and
Solvents.
Avoid skin contact with fuel where possible. Should
contact occur, wash the affected skin with soap
and water.
Gasoline (Petrol)
Highly flammable - observe No Smoking policy.
Swallowing can result in mouth and throat irritation
and absorption from the stomach can result in
drowsiness and unconsciousness. Small amounts
can be fatal to children. Aspiration of liquid into the
lungs, through vomiting, is a very serious hazard.
Gasoline dries the skin and can cause irritation
and dermatitis on prolonged or repeated contact.
Liquid in the eye causes severe smarting.
Motor gasoline may contain appreciable quantities
of benzene, which is toxic upon inhalation, and the
concentration of gasoline vapors must be kept very
low. High concentrations will cause eye, nose and
throat irritation, nausea, headache, depression and
symptoms of drunkenness. Very high
concentrations will result in rapid loss of
CO~SC~OUS~~SS.
Make sure there is adequate ventilation when
handling and using gasoline. Great care must be
taken to avoid the serious consequences of
inhalation in the event of vapor build up arising
from spillages in confined spaces.
Special precautions apply to cleaning and
maintenance operations on gasoline storage tanks.
Gasoline should not be used as a cleaning agent.
It must not be siphoned by mouth. See First Aid.
Gasoil (Diesel Fuel)
Com busti ble.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 7372en
procarmanuals.com
Page 28 of 1226

100-00-12 General Information 100-00-12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Gross or prolonged skin contact with high boiling
point gas oils may also cause serious skin
disorders including skin cancer.
Kerosene (Paraffin)
Used also as heating fuel, solvent and cleaning
agent.
Flammable
- observe No Smoking policy.
Irritation of the mouth and throat may result from
swallowing. The main hazard from swallowing
arises if liquid aspiration into the lungs occurs.
Liquid contact dries the skin and can cause
irritation or dermatitis. Splashes in the eye may be
slightly irritating.
In normal circumstances the low volatility does not
give rise to harmful vapors. Exposure to mists and
vapors from kerosene at elevated temperature
should be avoided (mists may arise in dewaxing).
Avoid skin and eye contact and make sure there
is adequate ventilation.
Alternative Fuel
Highly flammable. Observe "NO SMOKING" signs.
Make sure there is adequate ventilation when
working on alternative fuelled vehicles. Great care
must be taken to avoid the serious consequences
of inhalation in the event of vapor build up in
confined spaces.
Inhalation in high concentrations may cause
dizziness, headache, nausea and loss of
co-ordination. Very high concentrations may result
in loss of consciousness.
Contact with liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) or
compressed natural gas (CNG) to the skin may
cause cold burns and frost bite.
Long sleeved cotton overalls, steel toe capped
safety boots and rubber neoprene gloves should
be worn during removal and installation of
LPGICNG fuel system components.
LPGICNG fuel leaks could cause a fire and be a
hazard to health that can lead to personal injury,
illness or even death.
If a leak is detected, under no circumstances
attempt to seal the leak by tightening the
unionlconnection until the fuel in the system or
component is depressurized. Once tightened the
system should be checked for integrity following
the specified procedures. If
the fuel tank is to be removed for service or repair
the fuel must be evacuated using dedicated
equipment and following the specified
procedures. (
Gas Cylinders
See also Fire.
Gases such as oxygen, acetylene, argon and
propane are normally stored in cylinders at
pressures of up to
138 bar (2000 psi) and great
care should be taken in handling these cylinders
to avoid mechanical damage to them or to the valve
gear attached. The contents of each cylinder
should be clearly identified by appropriate
markings.
Cylinders should be stored in well-ventilated
enclosures, and protected from ice and snow, or
direct sunlight. Fuel gases, for example acetylene
and propane, should not be stored in close
proximity to oxygen cylinders.
Care should be exercised to prevent leaks from
gas cylinders and lines, and to avoid sources of
ignition.
Only trained personnel should undertake work
involving gas cylinders.
Gases
See Gas Cylinders.
Gaskets (Fluoroelastomer)
See Viton.
General Workshop Tools and
Equipment
It is essential that all tools and equipment are
maintained in good condition and that the correct
safety equipment is used where required.
Never use tools or equipment for any purpose other
than that for which they were designed. Never
overload equipment such as hoists, jacks, axle and
chassis stands or
lifting slings. Damage caused by
overloading is not always immediately apparent
and may result in a fatal failure the next time that
the equipment is used.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 7372en
procarmanuals.com
Page 31 of 1226

General Information
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Two Pack
Can also contain harmful and toxic unreacted
resins and resin hardening agents. The
manufacturers instructions should be followed. See
also Resin-based Adhesives and
Isocyanate
Adhesives and Sealers under Adhesives and
Sealers.
Spraying should preferably be carried out in
exhausted ventilated booths removing vapor and
spray mists from the breathing zone. Individuals
working in booths should wear appropriate
respiratory protection. Those doing small-scale
repair work in the open workshop should wear
air-fed respirators.
Pressurized Equipment
See High Pressure Air, Lubrication and Oil Test
Equipment.
Solder
Solders are mixtures of metals such that the
melting point of the mixture is below that of the
constituent metals (normally lead and tin). Solder
application does not normally give rise to toxic lead
fumes, provided a
gaslair flame is used.
Oxy-acetylene flames should not be used, as they
are much hotter and will cause lead fumes to be
produced.
Some fumes may be produced by the application
of any flame to surfaces coated with grease, and
inhalation of these should be avoided.
Removal of excess solder should be undertaken
with care, to make sure that fine lead dust is not
produced, which can give toxic effects if inhaled.
Respiratory protection may be necessary.
Solder spillage and filings should be collected and
removed promptly to prevent general air
contamination by lead.
High standards of personal hygiene are necessary
in order to avoid ingestion of lead or inhalation of
solder dust from clothing.
Solvents
See also Chemical Materials, Fuels (Kerosene),
Fire.
For example acetone, white spirit, toluene, xylene,
trichloroethane.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006
Used in cleaning and dewaxing materials, paints,
plastics, resins and thinners.
Some may be highly flammable or flammable.
Skin contact will degrease the skin and may result
in irritation and dermatitis following repeated or
prolonged contact. Some can be absorbed through
the skin in toxic or harmful quantities.
Splashes in the eye may cause severe irritation
and could lead to loss of vision.
Brief exposure of high concentrations of vapors or
mists will cause eye and throat irritation,
drowsiness, dizziness, headaches and, in the worst
circumstances, unconsciousness.
Repeated or prolonged exposure to excessive but
lower concentrations of vapors or mists, for which
there might not be adequate warning indications,
can cause more serious toxic or harmful effects.
Aspiration into the lungs, for example through
vomiting, is the most serious consequence of
swallowing.
Avoid splashes to the skin, eyes and clothing. Wear
protective gloves, goggles and clothing if
necessary.
Make sure there is good ventilation when in use,
avoid breathing fumes, vapors and spray mists and
keep containers tightly sealed. Do not use in
confined spaces.
When spraying materials containing solvents, for
example paints, adhesive, coatings, use extraction
ventilation or personal respiratory protection in the
absence of adequate general ventilation.
Do not apply heat or flame except under specific
and detailed manufacturers instructions.
Sound Insulation
See Fibre Insulation, Foams.
Suspended Loads
A CAUTI0N:Never improvise lifting tackle.
There is always a danger when loads are lifted or
suspended. Never work under an unsupported,
suspended or raised load, for example a
suspended engine.
Always make sure that lifting equipment such as
jacks, hoists, axle stands and slings are adequate
and suitable for the job, in good condition and
regularly maintained.
procarmanuals.com
Page 40 of 1226

100-00-24 General Information 100-00-24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
- that the speedometer, coolant temperature - oil, coolant, hydraulic, air and fuel leaks.
gauge and tachometer (if equipped) register the - abnormal temperature of any moving
correct readings and operate correctly.
components or assemblies, for example wheel
(
- that the switches and controls operate smoothly hubs, transmission and axle, which might
and positively, warning and indicator lamps
indicate over tightness or lack of lubrication.
operate correctly and the direction indicator
control self cancels when the steering is
returned to the straight ahead position.
- that the heating and ventilation systems operate
correctly and effectively.
- the brake operation and efficiency.
Brake Testing
A WARNING:When brake testing, avoid
breathing the fumes from hot brakes, this
may contain asbestos dust which is
hazardous to health. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
For additional information, refer to: Health
and Safety Precautions
(1 00-00 General
Information, Description and Operation).
CAUTIONS:
A Avoid brake testing on busy roads where
it may cause inconvenience or danger to
other road users.
A Brake testing which includes heavy brake
applications should not be carried out with
new brake
padsldiscs or liningsldrums
until the components have bedded-in. New
brake friction components will not reach
full efficiency until the bedding-in process
is complete.
Test the brakes at several speeds within the normal
operating range using both light and heavy pedal
pressure. Note any tendency to snatch, pull or
drag, and any undue delay in application or
release.
Allow the vehicle to coast and note any tendency
to pull to one side, or evidence that the brakes are
binding.
After stopping the vehicle (not immediately after a
period of heavy braking), carefully check the brake
temperature.
A brake disc or brake drum that feels
hot or is appreciably hotter than the others,
indicates that the brake is binding.
After completion of the test, check for:
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 7375en
procarmanuals.com
Page 101 of 1226
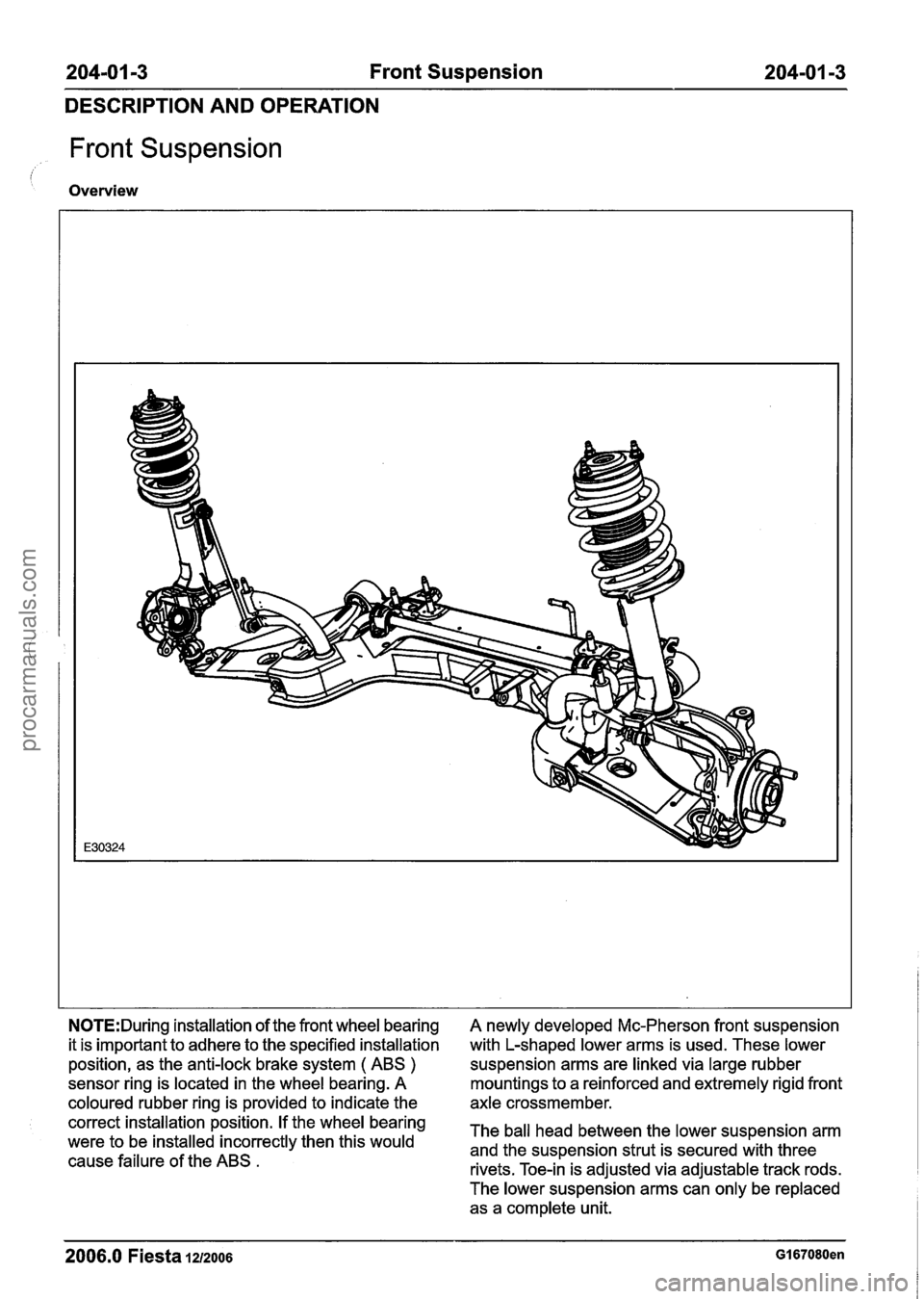
204-01 -3 Front Suspension 204-01 -3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Front Suspension
Overview
N0TE:During installation of the front wheel bearing
it is important to adhere to the specified installation
position, as the anti-lock brake system
( ABS )
sensor ring is located in the wheel bearing. A
coloured rubber ring is provided to indicate the
correct installation position. If the wheel bearing
were to be installed incorrectly then this would
cause failure of the ABS
.
A newly developed Mc-Pherson front suspension
with L-shaped lower arms is used. These lower
suspension arms are linked via large rubber
mountings to a reinforced and extremely rigid front
axle crossmember.
The ball head between the lower suspension arm
and the suspension strut is secured with three
rivets. Toe-in is adjusted via adjustable track rods.
The lower suspension arms can only be replaced as a complete unit.
2006.0 Fiesta IZIZOO~ GI 67080en
procarmanuals.com
Page 107 of 1226
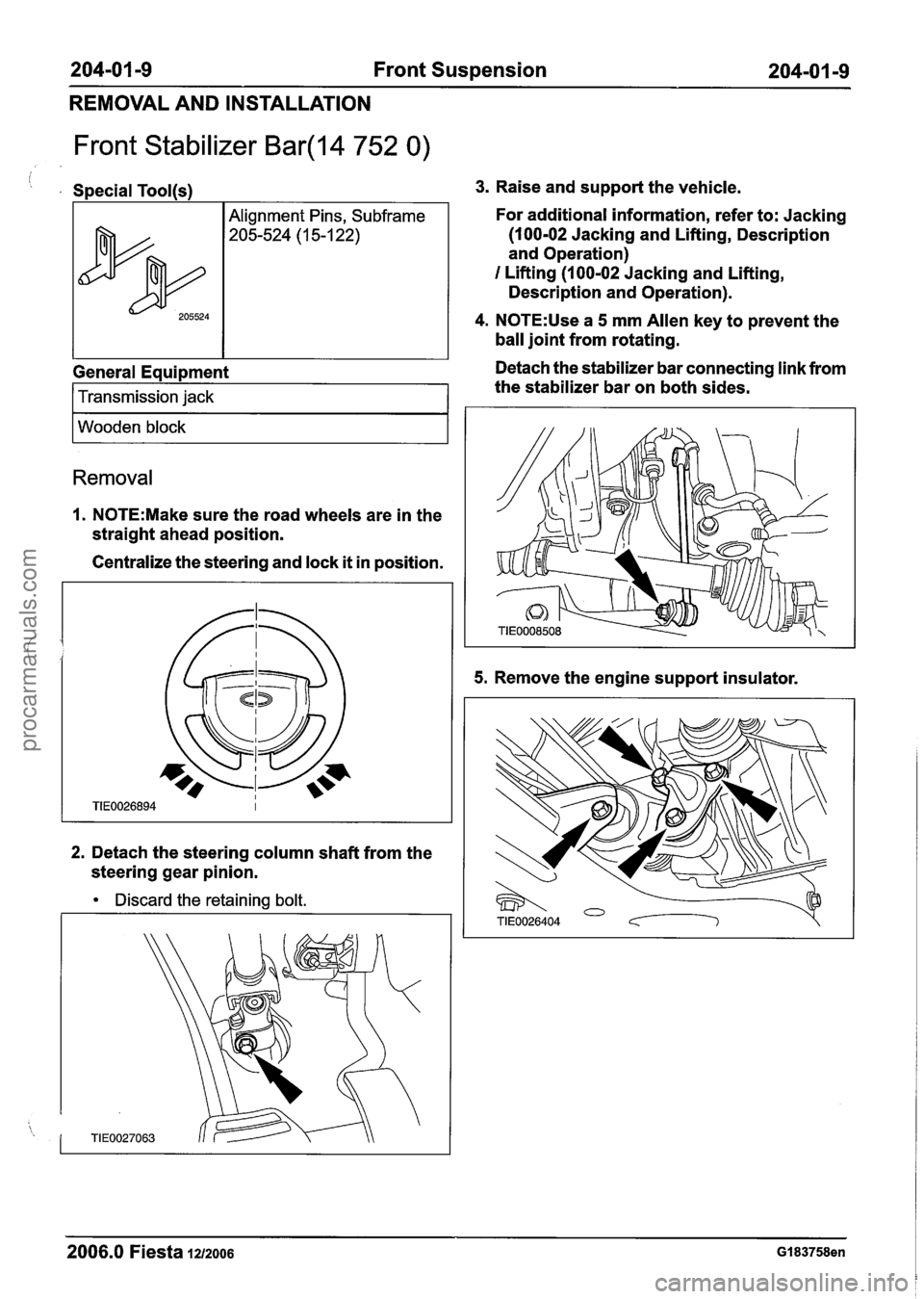
204-01 -9 Front Suspension 204-0 I -9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Front Stabilizer Bar(l4 752 0)
i , Special Tool(s1
General Equipment
205524
I Transmission jack 1
Alignment Pins, Subframe
205-524 (1 5-1 22)
I Wooden block I
Removal
1. N0TE:Make sure the road wheels are in the
straight ahead position.
Centralize the steering and lock
it in position.
2. Detach the steering column shaft from the
steering gear pinion.
Discard the retaining bolt.
3. Raise and support the vehicle.
For additional information, refer to: Jacking
(100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description
and Operation)
I Lifting (1 00-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
4. N0TE:Use a 5 mm Allen key to prevent the
ball joint from rotating.
Detach the stabilizer bar connecting link from
the stabilizer bar on both sides.
5. Remove the engine support insulator.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 83758en
procarmanuals.com
Page 267 of 1226

206-0713 Power Brake Actuation 206-0713
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Brake Booster
Emergency brake assistant (EBA) EBA operates purely mechanically, and is
completely integral with the brakeservo.
As ABS braking systems have become widespread,
it has emerged that because of incorrect use of the
Brake servo units with and without EBA are
brakes, many drivers are losing the safety benefit externally identical. For identification purposes,
which ABS
~rovides. brake servo units with EBA carry a white sticker I showing a large letter "A. Drivers are applying the brakes too timidly.
Because of this, the Anti-lock Braking System The tandem master cylinder
is the same for
(ABS) does not engage, and the maximum braking
vehicles with or without
effect is not achieved.
The EBA recognises from the driver's manner of
braking that an emergency situation is occurring,
and automatically applies full braking power.
This occurs in a matter of milliseconds, which is
faster than the driver could do it.
Furthermore, it was observed that after the first
heavy application of the brake pedal, the driver
releases the pressure on the pedal too early.
The EBA ensures that the ABS effect still continues
when the pedal pressure would normally lie below
the ABS range of control. The system is available
j as an option depending on market and vehicle
variant.
Function
In normal braking situations, the brake servo with
EBA operates in the same way as a conventional
brake servo unit. This means that the driver can
always modulate the brakes.
If an activation threshold defined by a characteristic
curve is exceeded during braking, the EBA
operates.
Determination of the activation threshold is based
on the pedal movement parameters, which are a
function of the pressure on the brake pedal and
the speed of movement of the pedal.
Depending on driving manner, EBA results in a The characteristic curve
is separately defined for
reduction in braking distance of 15% for each vehicle model.
experienced drivers, to over
40% for average The mechanical EBA uses the fact that in a brake
drivers. servo unit, the valve piston moves ahead of the
Because EBA decelerates the vehicle up to the control housing
when a braking operation starts.
wheel locking limit, emergency brake assist is only Because of this, there is a relative travel distance used in vehicles with ABS.
between the control housing and the valve piston
which can vary depending on the force applied to
Components the brake pedal and the pedal speed.
The relative travel distance is small when the pedal
moves slowly with low force applied to it. The
relative travel distance is larger when the pedal
moves faster with higher force applied to it.
Item Description
-
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 63289en
procarmanuals.com
Page 283 of 1226
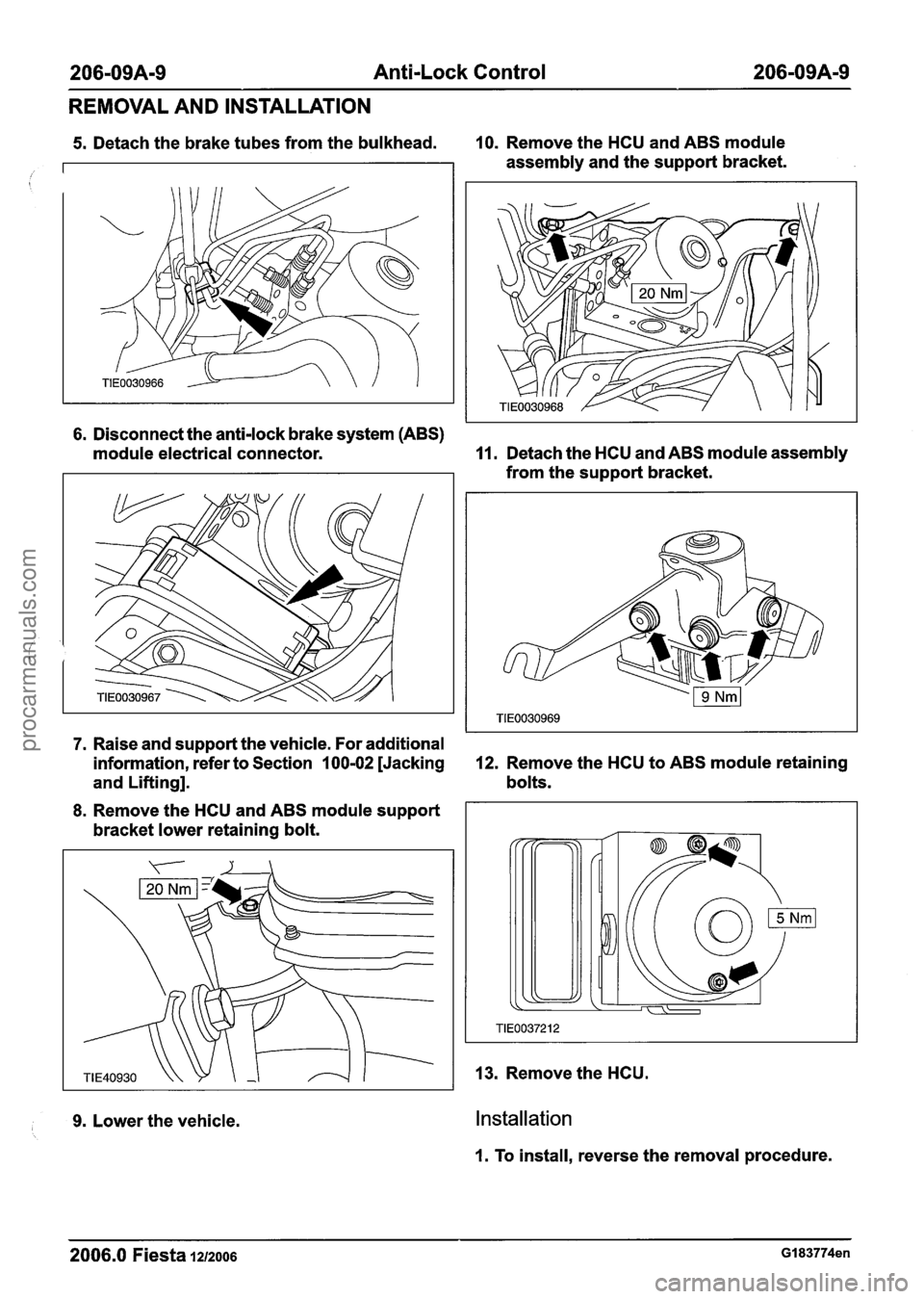
206-09A-9 Anti-Lock Control 206-09A-9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
6. Disconnect the anti-lock brake system (ABS)
module electrical connector.
11. Detach the HCU and ABS module assembly
from the support bracket.
5. Detach the brake tubes from the bulkhead. 10. Remove the HCU and ABS module
7. Raise and support the vehicle. For additional
information, refer to Section
100-02 [Jacking 12. Remove the HCU to ABS module retaining
and Lifting]. bolts.
/
8. Remove the HCU and ABS module support
bracket lower retaining bolt. assembly
and the support bracket.
9. Lower the vehicle.
13. Remove the HCU.
Installation
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 83774en
procarmanuals.com
Page 286 of 1226
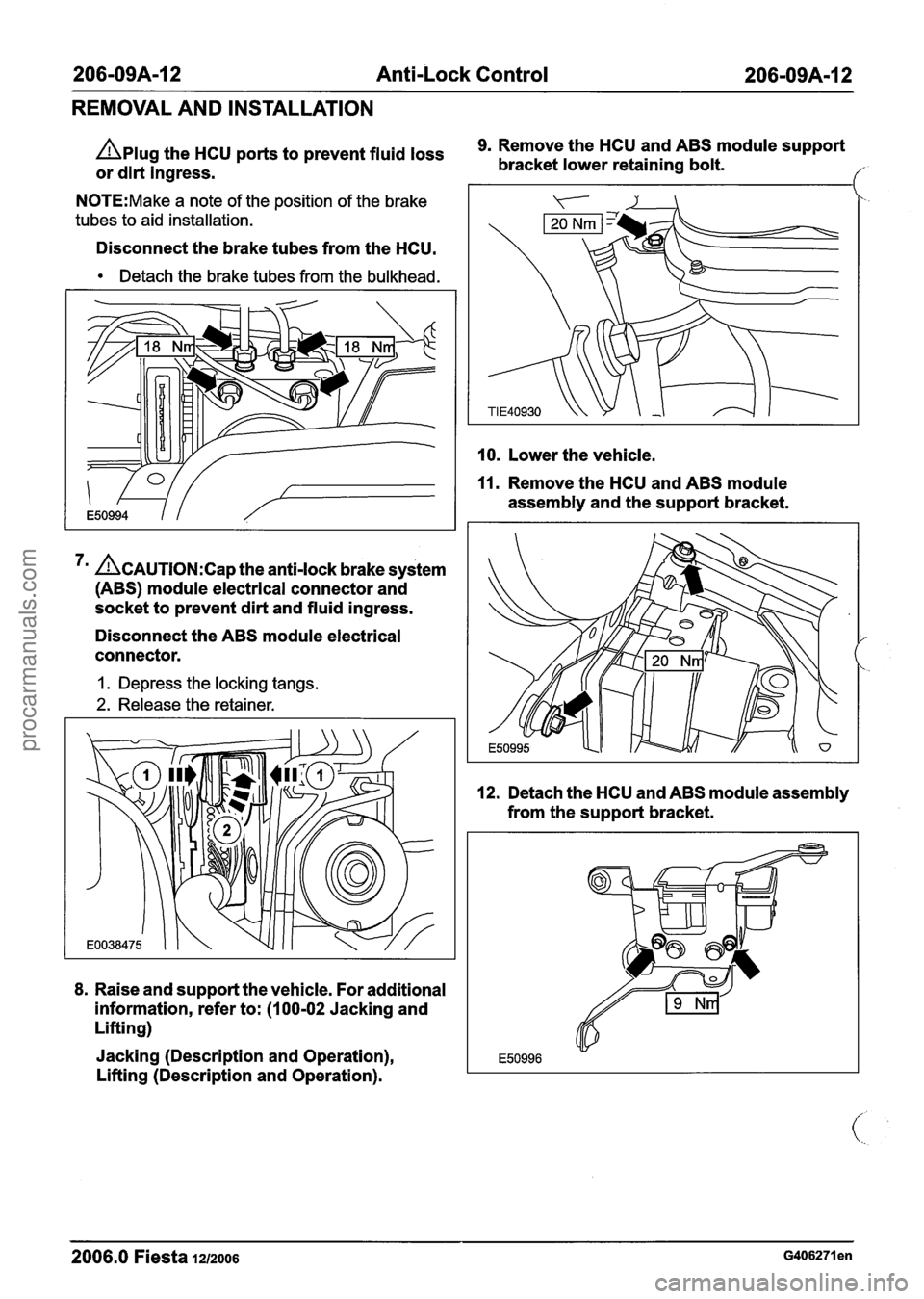
206-09A-I 2 Anti-Lock Control 206-0949-12
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Aplug the HCU ports to prevent fluid loss
or dirt ingress.
N0TE:Make a note of the position of the brake
tubes to aid installation.
Disconnect the brake tubes from the HCU.
Detach the brake tubes from the bulkhead.
7m &AUTION:C~~ the anti-lock brake system
(ABS) module electrical connector and
socket to prevent dirt and fluid ingress.
Disconnect the ABS module electrical
connector.
I. Depress the locking tangs.
2. Release the retainer.
8.
Raise and support the vehicle. For additional
information, refer to: (100-02 Jacking and
Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation),
Lifting (Description and Operation).
9. Remove the HCU and ABS module support
bracket lower retaining bolt.
f
10. Lower the vehicle.
11. Remove the HCU and ABS module
assembly and the support bracket.
12. Detach the HCU and ABS module assembly
from the support bracket.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 ~406271 en
procarmanuals.com
Page 289 of 1226
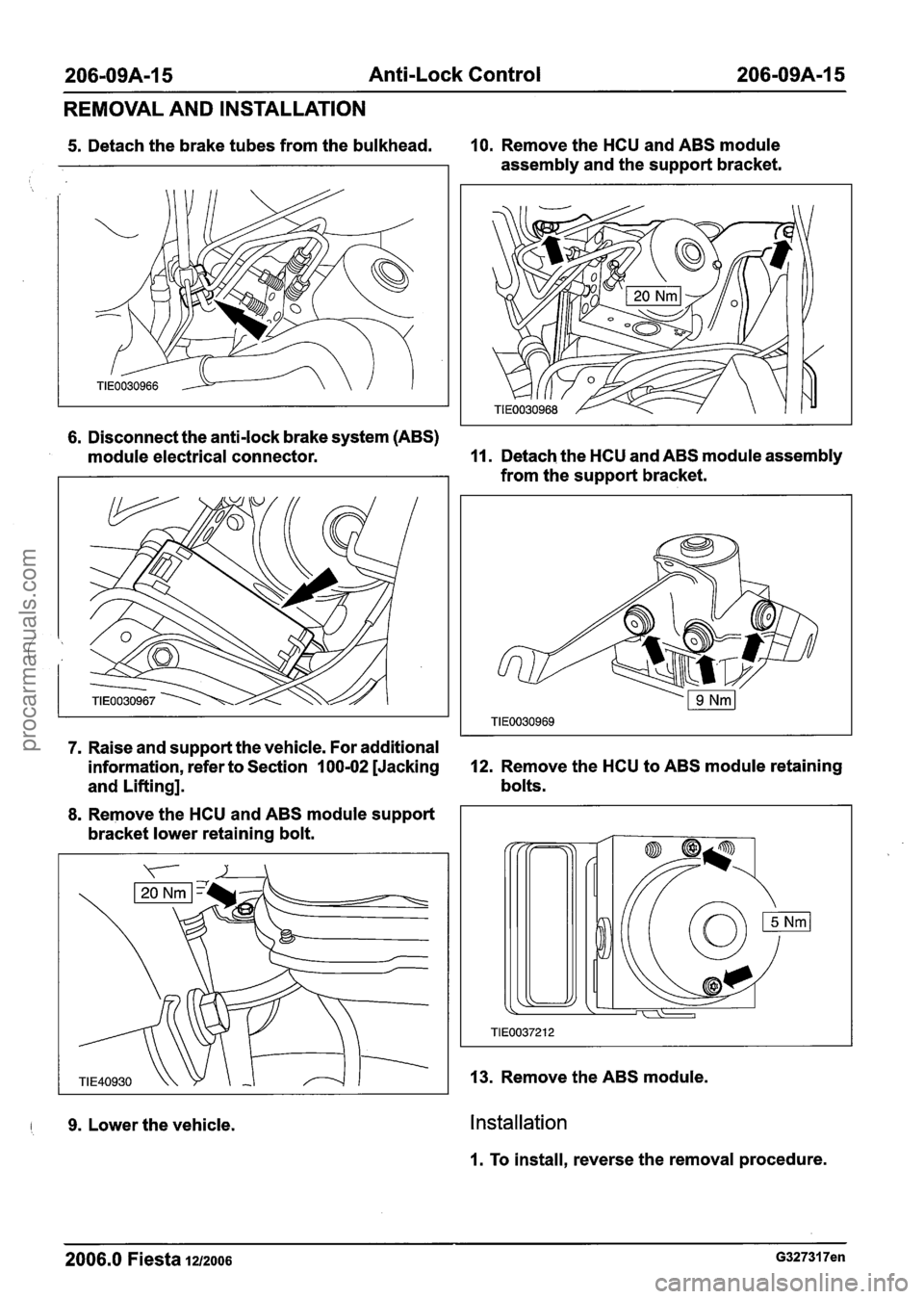
206-09A-I 5 Anti-Lock Control 206-09A-15
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
5. Detach the brake tubes from the bulkhead. 10. Remove the HCU and ABS module
assembly and the support bracket.
6. Disconnect the anti-lock brake system (ABS)
module electrical connector.
11. Detach the HCU and ABS module assembly
from the support bracket.
7. Raise and support the vehicle. For additional
information, refer to Section
100-02 [Jacking 12. Remove the HCU to ABS module retaining
and Lifting]. bolts.
8. Remove the HCU and ABS module support
bracket lower retaining bolt.
I 9. Lower the vehicle.
13. Remove the ABS module.
Installation
I. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G327317en
procarmanuals.com