change wheel FORD MUSTANG 1969 Volume One Chassis
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1969, Model line: MUSTANG, Model: FORD MUSTANG 1969Pages: 413, PDF Size: 75.81 MB
Page 19 of 413
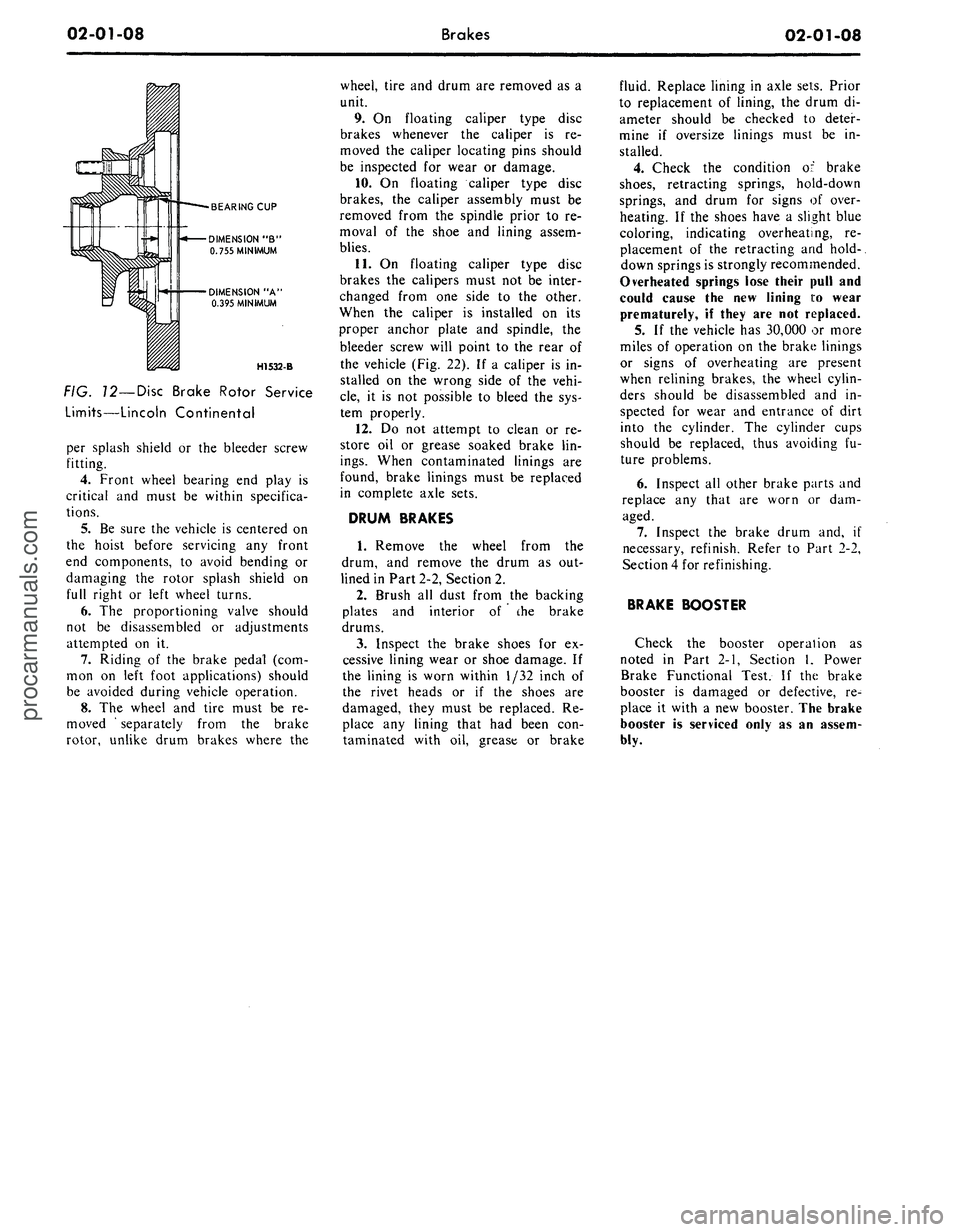
02-01-08
Brakes
02-01-08
BEARING CUP
DIMENSION "B"
0.755 MINIMUM
DIMENSION "A'
0.395 MINIMUM
H1532-B
FIG. 12—Disc Brake Rotor Service
Limits—Lincoln Continental
per splash shield or the bleeder screw
fitting.
4.
Front wheel bearing end play is
critical and must be within specifica-
tions.
5.
Be sure the vehicle is centered on
the hoist before servicing any front
end components, to avoid bending or
damaging the rotor splash shield on
full right or left wheel turns.
6. The proportioning valve should
not be disassembled or adjustments
attempted on it.
7.
Riding of the brake pedal (com-
mon on left foot applications) should
be avoided during vehicle operation.
8. The wheel and tire must be re-
moved ' separately from the brake
rotor, unlike drum brakes where the
wheel, tire and drum are removed as a
unit.
9. On floating caliper type disc
brakes whenever the caliper is re-
moved the caliper locating pins should
be inspected for wear or damage.
10.
On floating caliper type disc
brakes, the caliper assembly must be
removed from the spindle prior to re-
moval of the shoe and lining assem-
blies.
11.
On floating caliper type disc
brakes the calipers must not be inter-
changed from one side to the other.
When the caliper is installed on its
proper anchor plate and spindle, the
bleeder screw will point to the rear of
the vehicle (Fig. 22). If a caliper is in-
stalled on the wrong side of the vehi-
cle,
it is not possible to bleed the sys-
tem properly.
12.
Do not attempt to clean or re-
store oil or grease soaked brake lin-
ings.
When contaminated linings are
found, brake linings must be replaced
in complete axle sets.
DRUM BRAKES
1.
Remove the wheel from the
drum, and remove the drum as out-
lined in Part 2-2, Section 2.
2.
Brush all dust from the backing
plates and interior of the brake
drums.
3.
Inspect the brake shoes for ex-
cessive lining wear or shoe damage. If
the lining is worn within 1/32 inch of
the rivet heads or if the shoes are
damaged, they must be replaced. Re-
place any lining that had been con-
taminated with oil, grease or brake
fluid. Replace lining in axle sets. Prior
to replacement of lining, the drum di-
ameter should be checked to deter-
mine if oversize linings must be in-
stalled.
4.
Check the condition of brake
shoes,
retracting springs, hold-down
springs, and drum for signs of over-
heating. If the shoes have a slight blue
coloring, indicating overheating, re-
placement of the retracting and hold-.
down springs is strongly recommended.
Overheated springs lose their pull and
could cause the new lining i:o wear
prematurely, if they are not replaced.
5. If the vehicle has 30,000 or more
miles of operation on the brake linings
or signs of overheating are present
when relining brakes, the wheel cylin-
ders should be disassembled and in-
spected for wear and entrance of dirt
into the cylinder. The cylinder cups
should be replaced, thus avoiding fu-
ture problems.
6. Inspect all other brake parts and
replace any that are worn or dam-
aged.
7.
Inspect the brake drum and, if
necessary, refinish. Refer to Part 2-2,
Section 4 for refinishing.
BRAKE BOOSTER
Check the booster operation as
noted in Part 2-1, Section 1, Power
Brake Functional Test. If the brake
booster is damaged or defective, re-
place it with a new booster. The brake
booster is serviced only as an assem-
bly.procarmanuals.com
Page 25 of 413
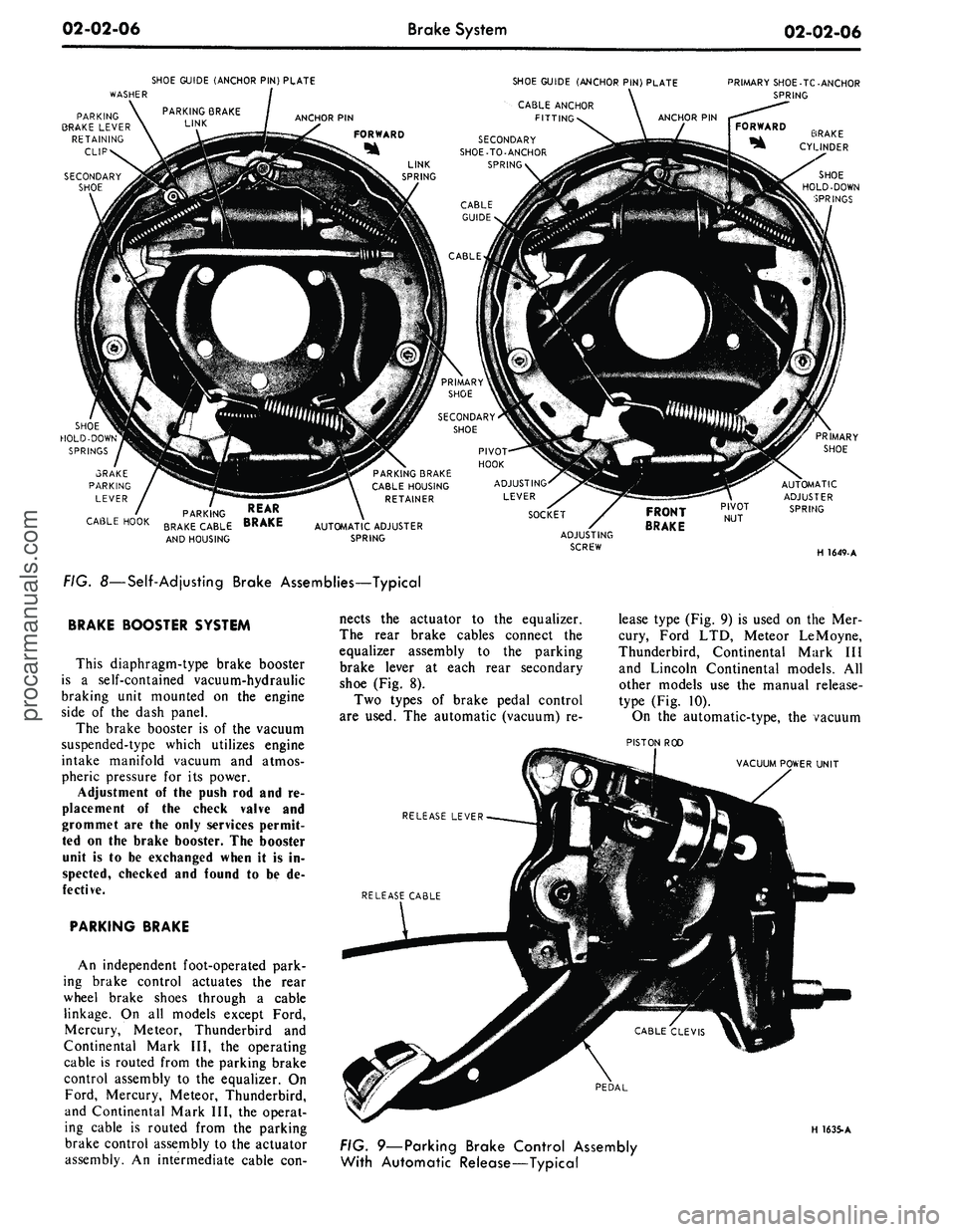
02-02-06
Brake
System
02-02-06
SHOE GUIDE (ANCHOR
PIN)
PLATE
SHOE GUIDE (ANCHOR
PIN)
PLATE
WASHER
PRIMARY SHOE
-TC
-ANCHOR
SPRING
PARKING
BRAKE LEVER
RETAINING
CLIP
SECONDARY
SHOE
PRIMARY
SHOE
CABLE HOOK
PARKING
BRAKE CABLE
AND HOUSING
PIVOT
NUT
AUTOMATIC
ADJUSTER
SPRING
H
1649-
A
FIG. 8—Self-Adjusting Brake Assemblies—Typical
BRAKE BOOSTER SYSTEM
This diaphragm-type brake booster
is
a
self-contained vacuum-hydraulic
braking unit mounted
on the
engine
side
of the
dash panel.
The brake booster
is of the
vacuum
suspended-type which utilizes engine
intake manifold vacuum
and
atmos-
pheric pressure
for its
power.
Adjustment
of the
push
rod and re-
placement
of the
check valve
and
grommet
are the
only services permit-
ted
on the
brake booster.
The
booster
unit
is to be
exchanged when
it is in-
spected, checked
and
found
to be de-
fective.
PARKING BRAKE
An independent foot-operated park-
ing brake control actuates
the
rear
wheel brake shoes through
a
cable
linkage.
On all
models except Ford,
Mercury, Meteor, Thunderbird
and
Continental Mark
III, the
operating
cable
is
routed from
the
parking brake
control assembly
to the
equalizer.
On
Ford, Mercury, Meteor, Thunderbird,
and Continental Mark
III, the
operat-
ing cable
is
routed from
the
parking
brake control assembly
to the
actuator
assembly.
An
intermediate cable
con-
nects
the
actuator
to the
equalizer.
The rear brake cables connect
the
equalizer assembly
to the
parking
brake lever
at
each rear secondary
shoe
(Fig. 8).
Two types
of
brake pedal control
are used.
The
automatic (vacuum)
re-
lease type
(Fig. 9) is
used
on the Mer-
cury, Ford
LTD,
Meteor LeMoyne,
Thunderbird, Continental Mark
III
and Lincoln Continental models.
All
other models
use the
manual release-
type
(Fig. 10).
On
the
automatic-type,
the
vacuum
PISTON
ROD
VACUUM POWER UNIT
RELEASE LEVER
PEDAL
H 1635-A
FIG. 9—Parking Brake Control Assembly
With Automatic Release—Typicalprocarmanuals.com
Page 26 of 413
02-02-07
Brake System
02-02-07
ANTI-SKID CONTROL SYSTEM
RELEASE PAWL CAM PIN
RELEASE PAWL CAM LEVER
RELEASE CABLE
H
1636-
A
FIG. 10—Parking Brake Control Assembly
With Manual Release—Typical
power unit with mounting bracket is
riveted to the control assembly. The
vacuum actuated piston within the
unit is connected by a rod to the
upper end of the release lever (Fig. 9).
The lower end of the release lever ex-
tends out for alternate manual release
in the event of vacuum power failure
or for optional manual release at any
time.
Hoses connect the power unit and
the engine manifold to a vacuum re-
lease valve in the transmission neutral
safety switch.
The anti-skid control system con-
sists of three major components (Fig.
39).
Mechanically driven electromag-
netic sensors at each rear wheel; an
electronic control module mounted
under the glove box; a vacuum pow-
ered actuator attached to a bracket on
the inside of the right front frame rail
under the toe board.
The sensors consist of steel rings
having teeth on their outer diameters,
pressed on each axle shaft just out-
board of the wheel bearing. The teeth
rotate past corresponding teeth on the
inside diameter of stationary steel
rings mounted in the bearing retain-
ers.
Also mounted in the retainers, are
ring-shaped permanent magnets and
coils of wire. Two wires from each
sensor connect the sensors to the con-
trol module.
The control module consists of solid
state electronic components sealed in
a container. It is connected to the sen-
sors and to a solenoid on the actuator.
The actuator is similar to a vacuum
brake booster and consists of three
parts.
A chamber divided by a vacuum
suspended diaphragm; a hydraulic cyl-
inder connected to the diaphragm; and
a solenoid connected electrically to the
control module.
IN-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS AND REPAIRS
After any brake service work, ob-
tain a firm brake pedal before moving
the vehicle. Riding the brake pedal
(common on left foot application)
should be avoided when driving the
vehicle.
BRAKE SHOE ADJUSTMENTS—
DRUM BRAKES
The hydraulic drum brakes are
self-adjusting and require a manual
adjustment only after the brake shoes
have been relined, replaced, or when
the length of the adjusting screw has
been changed while performing some
other service operation. The manual
adjustment is performed with the
drums removed, using the tool and the
procedure detailed below.
When adjusting the rear brake
shoes,
check the parking brake cables
for proper adjustment. Make sure that
the equalizer operates freely.
To adjust the brake shoes:
1.
Use Rotunda Tool HRE 8650,
(Fig. 11) to determine the inside diam-
eter of the drum braking surface.
2.
Reverse the tool as shown in Fig.
11 and adjust the brake shoe diameter
to fit the gauge. Hold the automatic
adjusting lever out of engagement
while rotating the adjusting screw, to
prevent burring the screw slots. Make
sure the adjusting screw rotates freely.
If necessary, lubricate the adjusting
screw threads with a thin, uniform
coating of MIC-100-A.
3.
Rotate Tool HRE 8650 around
the brake shoes to be sure of the set-
ting.
4.
Apply a small quantity of high
temperature grease to the points
where the shoes contact the backing
plate, being careful not to get the lu-
bricant on the linings.
5. Install the drums. Install Tinner-
man nuts and tighten securely.
6. Install the wheels on the drums
and tighten the nuts to specification.
7.
Complete the adjustment by
applying the brakes several times with
a minimum of 50 lbs pressure on the
pedal while backing the vehicle. After
each stop the vehicle must be moved
forward.
8. After the brake shoes have been
properly adjusted, check the operation
of the brakes by making several stops
while operating in a forward direction.
WHEEL CYLINDER REPAIR-
DRUM BRAKE
Wheel cylinders should not be di-
sassembled unless they are leaking or
unless new cups and boots are to be
installed. It is not necessary to remove
the brake cylinder from the backing
plate to disassemble, inspect, or hone
and overhaul the cylinder. Removal is
necessary only when the cylinder is
damaged or scored beyond repair.procarmanuals.com
Page 70 of 413

03-01-05
Suspension — Steering, Wheels And Tires — General Service
03-01-05
type of equipment is used, follow the
installation and inspection instructions
provided by the equipment manufactu-
rer.
CASTER
Check the caster angle at each front
wheel.
The caster is the forward or rear-
ward tilt of the top of the wheel
spindle (Fig. 12). If the spindle tilts to
the rear, caster is positive. If the
spindle tilts to the front, caster is neg-
ative. The correct caster angle, or tilt,
is specified in Part 3-13.
On Mustang, Cougar, Fairlane,
Falcon and Montego vehicles, the
maximum caster difference for check-
ing purposes must not exceed one de-
gree.
If setting is necessary, then the
maximum difference must not exceed
1/2 degree. On all other vehicles, the
maximum caster difference must never
exceed 1/2 degree.
CAMBER
Check the camber angle at each
front wheel.
Camber is the amount the front
wheels are tilted at the top (Fig. 12).
If a wheel tilts outward, camber is
positive. If a wheel tilts inward, cam-
ber is negative. The correct camber
angle, or outward (positive) tilt is
specified in Part 3-13.
On Mustang, Cougar, Fairlane,
Falcon and Montego vehicles, the
maximum camber difference for
checking purposes must not exceed
one degree. If setting is necessary,
then the maximum difference must
not exceed 1/2 degree. On all other
vehicles, the maximum camber differ-
ence must never exceed 1/2 degree.
TOE-IN
Alignment height spacers should not
be used to check and adjust toe-in.
Toe-in should only be checked and ad-
justed after the caster and camber
have been adjusted to specifications.
Check the toe-in with the front
wheels in the straight-ahead position.
Run the engine so that the power
steering control valve will be in the
center (neutral) position (if so
equipped). Measure the distance be-
tween the extreme front and also be-
tween the extreme rear of both front
wheels. The difference between these
two distances is the toe-in or toe-out.
Correct toe-in, or inward pointing
of both front wheels at the front is
specified in Part 3-13.
FRONT WHEEL
TURNING ANGLE
When the inside wheel is turned 20
degrees, the turning angle of the out-
side wheel should be as specified in
Part 3-13. The turning angle cannot
be adjusted directly, because it is a re-
sult of the combination of caster,
camber, and toe-in adjustments and
should, therefore, be measured only
after these adjustments have been
made. If the turning angle does not
measure to specifications, check the
spindle or other suspension parts for a
bent condition.
ALIGNMENT
MARKS
G-1496-A
FIG. I?—Straight Ahead Position
Marks—Typical
POSITIVE
CAMBER
• •
NEGATIVE-*!
| ^*—
CASTER
ICL
OF TIRE
POSITIVE
CASTER
5r\
CA&U
ANGlE
F1216-A
FIG. 72—Caster and Camber
Angles
COMMON ADJUSTMENTS AND REPAIRS
After front wheel alignment factors
have been checked, make the neces-
sary adjustments. Do not attempt to
adjust front wheel alignment by bend-
ing the suspension or steering parts.
CASTER AND CAMBER
ADJUSTMENTS
FORD, MERCURY, METEOR,
THUNDERBIRDAND
CONTINENTAL MARK III
Caster and camber is adjusted by
loosening the bolts that attach the
upper suspension arm inner shaft to
the frame side rail, and moving the
inner shaft in or out in the elongated
bolt holes with the tool shown in Fig.
13.
The tool should be installed with
the tool pins in the frame holes and
the hooks over the upper arm inner
shaft. Then, tighten the tool hook nuts
snug before loosening the upper arm
inner shaft attaching bolts.
Caster
To adjust the caster angle, tighten
the tool front hook nut or loosen the
rear hook nut (Fig. 14) as required to
increase caster to the desired angle.
To decrease caster, tighten the tool
rear hook nut or loosen the front
hook nut as required (Fig. 14). The
caster angle can be checked without
tightening the inner shaft attaching
bolts.
Check the camber adjustment to
be sure it did not change during the
caster adjustment and adjust if neces-
FIG. 73—Camber and Caster
Adjusting Toolprocarmanuals.com
Page 71 of 413
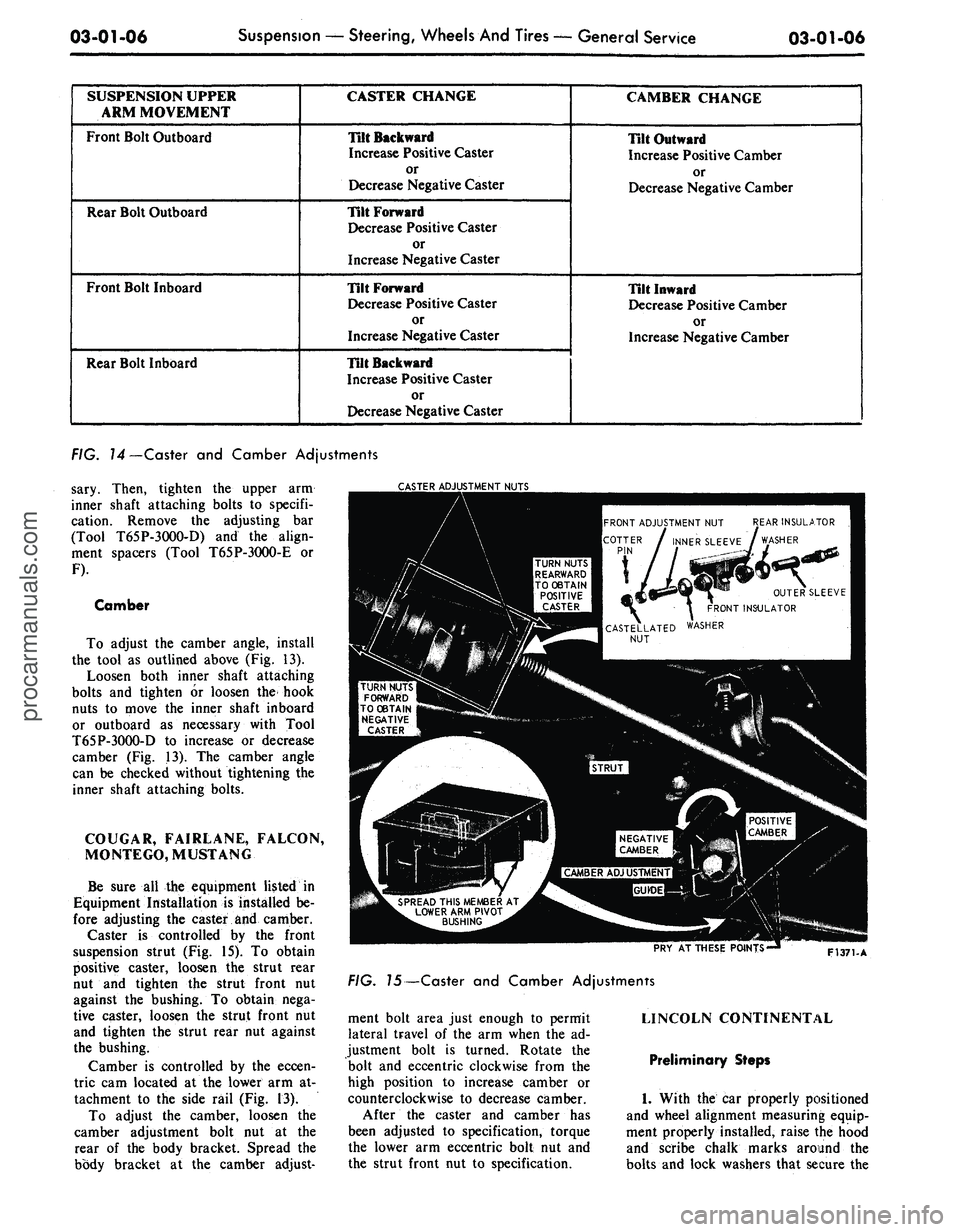
03-01-06
Suspension — Steering, Wheels And Tires — General Service
03-01-06
SUSPENSION UPPER
ARM MOVEMENT
Front Bolt Outboard
Rear Bolt Outboard
Front Bolt Inboard
Rear Bolt Inboard
CASTER CHANGE
Tilt Backward
Increase Positive Caster
or
Decrease Negative Caster
Tilt Forward
Decrease Positive Caster
or
Increase Negative Caster
Tilt Forward
Decrease Positive Caster
or
Increase Negative Caster
Tilt Backward
Increase Positive Caster
or
Decrease Negative Caster
CAMBER CHANGE
Tilt Outward
Increase Positive Camber
or
Decrease Negative Camber
Tilt Inward
Decrease Positive Camber
or
Increase Negative Camber
FIG. 14—Caster and Camber Adjustments
sary. Then, tighten the upper arm
inner shaft attaching bolts to specifi-
cation. Remove the adjusting bar
(Tool T65P-3OOO-D) and the align-
ment spacers (Tool T65P-3O00-E or
F).
Camber
To adjust the camber angle, install
the tool as outlined above (Fig. 13).
Loosen both inner shaft attaching
bolts and tighten or loosen the hook
nuts to move the inner shaft inboard
or outboard as necessary with Tool
T65P-3OOO-D to increase or decrease
camber (Fig. 13). The camber angle
can be checked without tightening the
inner shaft attaching bolts.
COUGAR, FAIRLANE, FALCON,
MONTEGO, MUSTANG
Be sure all the equipment listed in
Equipment Installation is installed be-
fore adjusting the caster and camber.
Caster is controlled by the front
suspension strut (Fig. 15). To obtain
positive caster, loosen the strut rear
nut and tighten the strut front nut
against the bushing. To obtain nega-
tive caster, loosen the strut front nut
and tighten the strut rear nut against
the bushing.
Camber is controlled by the eccen-
tric cam located at the lower arm at-
tachment to the side rail (Fig. 13).
To adjust the camber, loosen the
camber adjustment bolt nut at the
rear of the body bracket. Spread the
body bracket at the camber adjust-
TER ADJUSTMENT NUTS
EAR INSULATOR
WASHER
FRONT ADJUSTMENT NUT
INNER SLEEVE
TURN NUTS
REARWARD
TO OBTAIN
POSITIVE
CASTER
OUTER SLEEVE
RONT INSULATOR
WASHER
CASTELLATED
NUT
TURN NUTS
FORWARD
TO OBTAIN
NEGATIVE
CASTER
NEGATIVE
CAMBER
SPREAD THIS MEMBER AT
LOWER ARM PIVOT
BUSHING
PRY AT THESE POINTS'
F1371-A
FIG. J5—Caster and Camber Adjustments
ment bolt area just enough to permit
lateral travel of the arm when the ad-
justment bolt is turned. Rotate the
bolt and eccentric clockwise from the
high position to increase camber or
counterclockwise to decrease camber.
After the caster and camber has
been adjusted to specification, torque
the lower arm eccentric bolt nut and
the strut front nut to specification.
LINCOLN CONTINENTAL
Preliminary Steps
1.
With the car properly positioned
and wheel alignment measuring equip-
ment properly installed, raise the hood
and scribe chalk marks around the
bolts and lock washers that secure theprocarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 413
03-01-07
Suspension — Steering, Wheels And Tires — General Service
03-01-07
upper arm shaft to the frame member
(Fig. 3, Part 3-2).
2.
Loosen the arm shaft attaching
bolts,
raise the front end of the vehicle
and lower it again. This will break the
arm shaft loose from the frame mem-
ber.
3.
With a pry bar, move the arm
shaft back into alignment with the
chalk marks made in Step 1, and
tighten the shaft attaching bolts. The
bolts should be tightened just enough
to hold the shaft in position without
preventing its being moved with the
pry bar.
Caster
1.
With the aid of a pry bar, move
the shaft in or out, as required, to
meet specifications. A movement of
approximately 3 /32 inch at either the
front or rear bolt location will change
the caster 1/2 degree. Inboard move-
ment of the front bolt, or outboard
movement of the rear bolt, will change
caster in the negative direction. Out-
board movement of the front bolt, or
inboard movement of the rear bolt,
will change caster in the positive di-
rection.
2.
When the caster is correct, tor-
que the shaft attaching bolts to speci-
fication and recheck the caster and
camber to insure that the readings
have not changed.
Camber
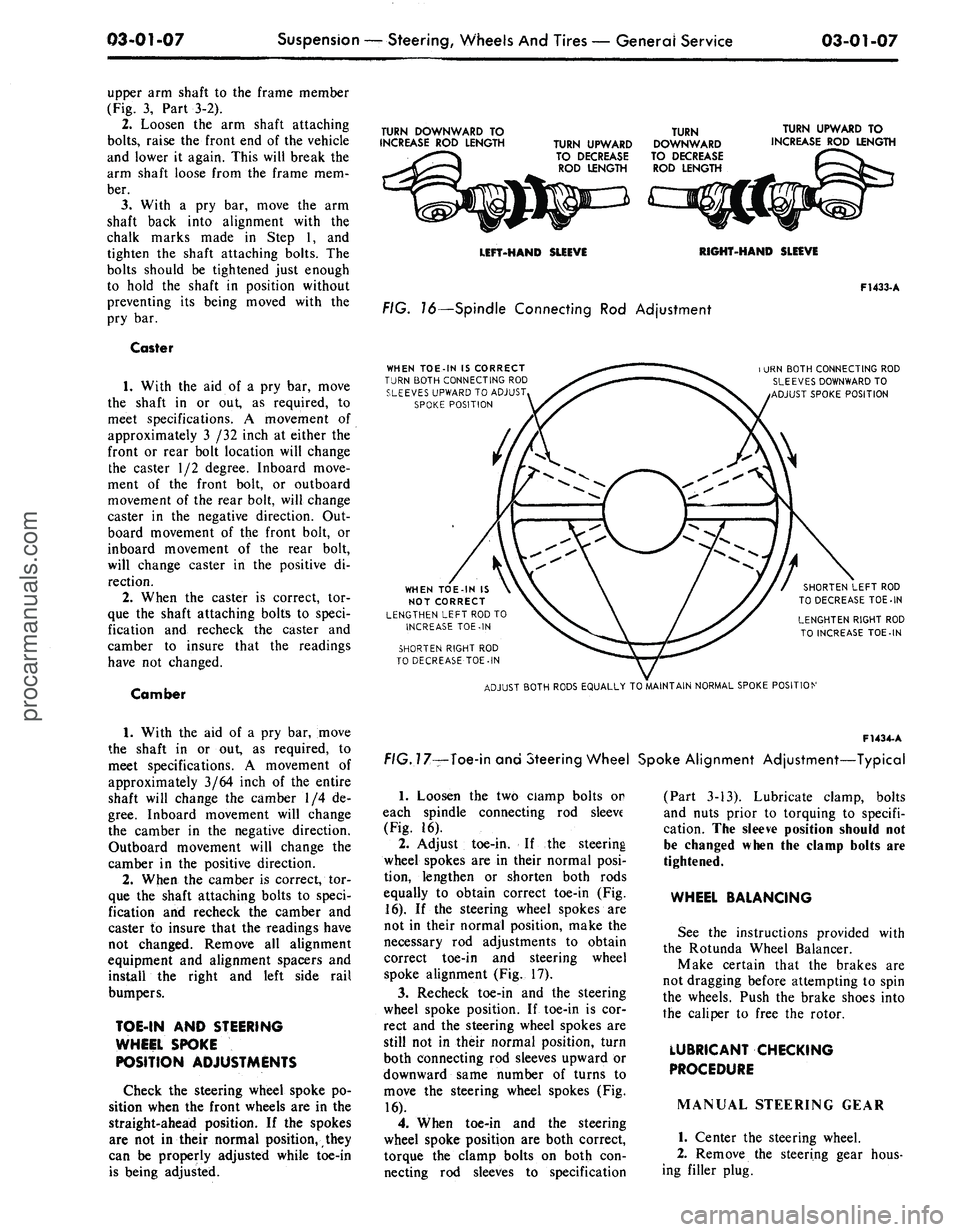
TURN DOWNWARD TO
INCREASE ROD LENGTH
TURN UPWARD
TO DECREASE
ROD LENGTH
TURN
DOWNWARD
TO DECREASE
ROD LENGTH
TURN UPWARD TO
INCREASE ROD LENGTH
LEFT-HAND SLEEVE
RIGHT-HAND SLEEVE
FIG. 16—Spindle Connecting Rod Adjustment
WHEN TOE-IN IS CORRECT
TURN BOTH CONNECTING ROD
SLEEVES UPWARD TO ADJUST
SPOKE POSITION
F1433-A
i URN BOTH CONNECTING ROD
SLEEVES DOWNWARD TO
ADJUST SPOKE POSITION
WHEN TOE-IN IS
NOT CORRECT
LENGTHEN LEFT ROD TO
INCREASE TOE-IN
SHORTEN RIGHT ROD
TO DECREASE TOE-IN
SHORTEN LEFT ROD
TO DECREASE TOE-IN
LENGHTEN RIGHT ROD
TO INCREASE TOE-IN
ADJUST BOTH RODS EQUALLY TO MAINTAIN NORMAL SPOKE POSITION
1.
With the aid of a pry bar, move
the shaft in or out, as required, to
meet specifications. A movement of
approximately 3/64 inch of the entire
shaft will change the camber 1/4 de-
gree.
Inboard movement will change
the camber in the negative direction.
Outboard movement will change the
camber in the positive direction.
2.
When the camber is correct, tor-
que the shaft attaching bolts to speci-
fication and recheck the camber and
caster to insure that the readings have
not changed. Remove all alignment
equipment and alignment spacers and
install the right and left side rail
bumpers.
TOE-IN AND STEERING
WHEEL SPOKE
POSITION ADJUSTMENTS
Check the steering wheel spoke po-
sition when the front wheels are in the
straight-ahead position. If the spokes
are not in their normal position, they
can be properly adjusted while toe-in
is being adjusted.
F1434-
A
f/G.77—Toe-in and Steering Wheel Spoke Alignment Adjustment—Typical
1.
Loosen the two ciamp bolts or
each spindle connecting rod sleeve
(Fig. 16).
2.
Adjust toe-in. If the steering
wheel spokes are in their normal posi-
tion, lengthen or shorten both rods
equally to obtain correct toe-in (Fig.
16).
If the steering wheel spokes are
not in their normal position, make the
necessary rod adjustments to obtain
correct toe-in and steering wheel
spoke alignment (Fig. 17).
3.
Recheck toe-in and the steering
wheel spoke position. If toe-in is cor-
rect and the steering wheel spokes are
still not in their normal position, turn
both connecting rod sleeves upward or
downward same number of turns to
move the steering wheel spokes (Fig.
16).
4.
When toe-in and the steering
wheel spoke position are both correct,
torque the clamp bolts on both con-
necting rod sleeves to specification
(Part 3-13). Lubricate clamp, bolts
and nuts prior to torquing to specifi-
cation. The sleeve position should not
be changed when the clamp bolts are
tightened.
WHEEL BALANCING
See the instructions provided with
the Rotunda Wheel Balancer.
Make certain that the brakes are
not dragging before attempting to spin
the wheels. Push the brake shoes into
the caliper to free the rotor.
LUBRICANT CHECKING
PROCEDURE
MANUAL STEERING GEAR
1.
Center the steering wheel.
2.
Remove the steering gear hous-
ing filler plug.procarmanuals.com
Page 115 of 413

03-05-02
Steering Columns
And
Linkage
03-05-02
which also will shear away during
im-
pact.
TILT STEERING COLUMNS
The steering column
is of the col-
lapsible type
to
lessen
the
possibility
of injury
to the
driver
of the
vehicle
should
he
become involved
in an
acci-
dent.
The
lower
end of the
steering
column tube
at the
bellows area will
collapse approximately
six
inches
upon
a
hard impact.
The shift tube
and the
steering shaft
are provided with plastic dowels
and
will shear
and
allow them
to
collapse
in proportion
to the
outer tube upon
impact.
Once
the
steering column
has
been
collapsed,
a
complete
new
column
must
be
installed.
The tilt column features nine driv-
ing positions (four
up and
four down
from
a
center position).
The
.column
also features
a
turn signal switch with
a lane-changer position turn indicating
position
and
emergency warning flash-
er control.
TILT-AWAY STEERING COLUMNS
The tilt-away steering column
fea-
tures nine driving positions (four
up
and four down from
a
center position)
and
a
tilt-away position that
is
auto-
matically accomplished
on
Mustang
and Cougar models when
the
ignition
key
is
turned
to the
OFF
position
and
the left door
is
opened.
On
Thunder-
bird models,
the
tilt-away occurs when
the shift lever
is
placed
in
PARK
and
the driverns door
is
opened.
The steering column
is of the col-
lapsible type
to
lessen
the
possibility
of injury
to the
driver
of the
vehicle
should
he
become involved
in an
acci-
dent.
The
lower
end of the
steering
column tube
at the
bellows area will
collapse approximately
six
inches
upon
a
hard impact.
The shift tube
and the
steering shaft
are provided with plastic dowels
and
will shear
and
allow them
to
collapse
in proportion
to the
outer tube upon
impact.
Once
the
steering column
has
been
collapsed,
a
complete
new
column
must
be
installed along with mounting
brackets which will also shear away
during impact.
IN-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS
AND
REPAIRS
STEERING WHEEL SPOKE
POSITION ADJUSTMENT
When
the
steering gear
is on the
high point,
the
front wheels should
be
in
the
straight-ahead position
and the
steering wheel spokes should
be in
their normal position with
the
Pitman
arm pointing directly forward.
If the
spokes
are not in
their normal posi-
tion, they
can be
adjusted without
dis-
turbing
the
toe-in adjustment (Part
3-1).
STEERING WHEEL
REPLACEMENT
1.
Disconnect
the
negative cable
from
the
battery.
2.
Working from
the
underside
of
the steering wheel spoke, remove
the
crash
pad
attaching screws. Lift
the
crash
pad
from
the
wheel.
(On
Conti-
nental Mark
III
models,
pry out the
crash
pad
insert
and
remove
the two
screws that secure
the
crash
pad. Re-
move
the
crash
pad. On
models
equipped with steering wheel mounted
speed controls, refer
to
Group
16 for
removal instructions). Remove
the
horn ring
(if so
equipped)
by
turning
it counterclockwise.
3.
Remove
the
steering wheel
nut,
and then remove
the
steering wheel
with tool T67L-3600-A
(Fig. 1). Do
not
use a
knock-off type steering
wheel puller
or
strike
the end of the
steering shaft with
a
hammer. Striking
the puller
or
shaft will damage
the
bearing
or the
collapsible column.
4.
Transfer
all
serviceable parts
to
the
new
steering wheel.
5.
Position
the
steering wheel
on
the shaft
so
that
the
alignment mark
on
the hub of the
wheel
is
adjacent
to
the
one on the
shaft. Install
a new
locknut
and
torque
it to
specifications.
6. Install
the
horn ring
(if so
equipped)
and
crash
pad.
STEERING COLUMN UPPER
BEARING REPLACEMENT
STATIONARY COLUMNS
Removal
1. Disconnect
the
horn wire
and the
turn indicator wires
at the
connector.
2.
Working from
the
underside
of
the steering wheel spoke, remove
the
two crash
pad
attaching screws. Lift
the crash
pad
from
the
wheel.
(On
Continental Mark
III
models,
pry out
the crash
pad
insert
and
remove
the
two screws that secure
the
crash
pad.
Remove
the
crash
pad. On
models
equipped with steering wheel mounted
speed controls, refer
to
Group
16 for
7oo/-T67L-3600-A
removal instructions). Remove
the
horn ring
(if so
equipped)
by
turning
it counterclockwise.
3.
Remove
the
steering wheel
at-
taching
nut.
Remove
the
steering
wheel using tool T67L-3600-A
(Fig.
1).
Do not use a
knock-off type steer-
ing wheel puller
or
strike
the end of
the steering shaft with
a
hammer.
Striking
the
puller
or
shaft will
dam-
age
the
bearing
or the
collapsible
col-
umn.
4.
Remove
the
turn indicator lever.
5.
Remove
the
turn signal switch
attaching screws. Lift
the
switch over
the
end of the
steering shaft
and
place
it
to one
side.
6. Remove
the
snap ring from
the
top
of the
steering shaft.
7.
Loosen
the two
flange-to-steering
column tube attaching bolts
to
disen-
gage them from
the
tube.
8. Raise
the
flange upward while
BEARING
AND
INSULATOR
Spacer
G 1502 -B
FIG.
1—Removing
Steering Wheel
G 1497-A
FIG. 2—Installing Upper Bearingprocarmanuals.com
Page 145 of 413
03-08-01
Ford Design Integral Power Steering Gear
03-08-01
PART
3-8
Ford Design Integral Power
Steering Gear
COMPONENT INDEX
STEERING GEAR
Adjustments
Cleaning
and
Inspection
(See
Part 03-01)
Description
Disassembly
and
Assembly
Overhaul
Removal
and
Installation
VALVE CENTERING SHIM
Removal
and
Installation
VALVE SPOOL CENTERING CHECK
MODEL APPLICATION
All Models
Ford
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
Mercury
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
Meteor
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
Cougar
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Fairlane
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Falcon
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Montego
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Mustang
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Lincoln-
Continental
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
Thunderbird
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
Continental-
Mark
III
08-02
08-01
08-05
08-06
08-03
08-03
08-02
DESCRIPTION
The Ford integral power steering
unit
(Fig. 1) is a
torsion-bar type
of
hydraulic assisted system. This system
furnishes power
to
reduce
the
amount
of turning effort required
at the
steer-
ing wheel.
It
also reduces road shock
and vibrations.
The torsion
bar
power steering unit
includes
a
worm
and
one-piece rack
piston, which
is
meshed
to the
gear
teeth
on the
steering sector shaft.
The
unit also includes
a
hydraulic valve,
valve actuator, input shaft
and
torsion
bar assembly which
are
mounted
on
the
end of the
worm shaft
and
operat-
ed
by the
twisting action
of the tor-
sion
bar.
The torsion-bar type
of
power steer-
ing gear
is
designed with
the one
piece
rack-piston, worm
and
sector shaft
in
one housing
and the
valve spool
in an
attaching housing
(Fig. 1).
This makes
possible internal fluid passages
bet-
ween
the
valve
and
cylinder, thus
eli-
minating
all
external lines
and
hoses,
except
the
pressure
and
return hoses
between
the
pump
and
gear assembly.
The power cylinder
is an
integral
part
of the
gear housing.
The
piston
is
double acting,
in
that fluid pressure
may
be
applied
to
either side
of the
piston.
A selective metal shim located
in
the valve housing
of the
gear
is for the
purpose
of
tailoring steering gear
ef-
forts.
If
efforts
are not
within specifi-
cations they
can be
changed
by in-
creasing
or
decreasing shim thickness
as follows:
Efforts heavy
to the
left—Increase
shim thickness.
Efforts light
to the
left—Decrease
shim thickness.
A change
of one
shim size will
in-
crease
or
decrease steering efforts
ap-
proximately
1 1/2
in-lbs.
Shims
are
available
in the
following
thicknesses
and are
notched
on the
outside diameter
for
identification:
0.0057-0.0063 inch—0 notch
0.0077-0.0083 inch—1 notch
0.0097-0.0103 inch—2 notches
0.0117-0.0123 inch—3 notches
0.0137-0.0143 inch—4 notches
Do
not use
more than
one
shim.
procarmanuals.com
Page 147 of 413

03-08-03
Ford Design Integral Power Steering Gear
03-08-03
factory adjustments will change. These
changes in adjustment do not neces-
sarily affect the satisfactory operation
of the steering gear assembly, and
therefore ordinarily do not require
readjustment unless there is excessive
lash or other malfunctioning.
ADJUSTMENT IN
VEHICLE
The only adjustment which can be
performed is the total over center
position load, to eliminate excessive
lash between the sector and rack
teeth.
1.
Disconnect the pitman arm from
the sector shaft.
2.
Disconnect the fluid return line
at the reservoir, at the same time cap
the reservoir return line pipe.
3.
Place the end of the return line
in a clean container and cycle the
INPUT SHAFT
SECTOR SHAFT
ADJUSTMENT SCREW
C1547- A
FIG.
2—Adjusting Mesh Load
steering wheel in both directions as re-
quired, to discharge the fluid from the
gear.
4.
Remove the ornamental cover
from the steering wheel hub and turn
the steering wheel to 45 degrees from
the left stop.
5.
Using an in-lb torque wrench on
the steering wheel nut, determine the
torque required to rotate the shaft
slowly through an approximately 1/8
turn from the 45 degree position.
6. Turn the steering gear back to
center, then determine the torque re-
quired to rotate the shaft back and
forth across the center position. Loos-
en the adjuster nut, and turn the ad-
juster screw in (Fig. 2) until the read-
ing is 8-9 in-lb greater than the torque
45 degrees from the stop.
Tighten the lock nut while holding
the screw in place.
7.
Recheck the readings and replace
pitman arm and steering wheel hub
cover.
8. Connect the fluid return line to
the reservoir and fill the reservoir with
specified lubricant to the proper level.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
REMOVAL
1.
Disconnect the pressure and the
return lines from the steering gear.
Plug the lines and the ports in the
gear to prevent entry of dirt.
2.
Remove the two bolts that secure
the flex coupling to the steering gear
and to the column.
3.
Raise the vehicle and remove the
sector shaft attaching nut.
4.
Remove the Pitman arm from
the sector shaft with Tool T64P-
3590-F.
Remove the tool from the
Pitman arm. Do not damage the
seals.
5.
If working on a vehicle equipped
with a standard transmission, remove
the clutch release lever retracting
spring to provide clearance for remov-
ing the steering gear.
6. Support the steering gear then
remove the three steering gear attach-
ing bolts.
7.
Work steering gear free of the
flex coupling and remove it from the
vehicle.
8. If the flex coupling stayed on the
input shaft, lift if off the shaft at this
time.
INSTALLATION
1.
Slide the flex coupling into place
on the steering shaft. Turn the steer-
ing wheel so that the spokes are in the
horizontal position.
2.
Center the steering gear input
shaft.
3.
Slide the steering gear input
shaft into the flex coupling and into
place on the frame side rail. Install
the three attaching bolts and torque
them to specification.
4.
Make sure that the wheels are in
the straight ahead position, then in-
stall the Pitman arm on the sector
shaft. Install and tighten the sector
shaft and install and tighten the at-
taching bolts to specification.
5.
Move the flex coupling into
place on the input and steering co-
lumn shaft and install and tighten the
attaching bolts to specification.
6. Connect and tighten the fluid
pressure and the return line to the
steering gear.
7.
Fill the power steering pump and
cycle the steering gear. Check for
leaks and again check the fluid level.
Add fluid as required.
MAJOR REPAIR OPERATIONS
In most cases, complete disassembly
of the power steering gear will not be
necessary. It is suggested that only
those assemblies that are faulty be dis-
assembled. Disassembly and reassem-
bly of the unit and the subassemblies
must be made on a clean workbench.
As in repairing any hydraulically op-
erated unit, cleanliness is of utmost
importance. Therefore, the bench,
tools,
and parts must be kept clean at
all times. Thoroughly clean the exter-
ior of the unit with a suitable solvent
and when necessary, drain as much of
the hydraulic oil as possible. Handle
all parts very carefully to avoid nicks,
burrs,
scratches and dirt, which could
make the parts unfit for use. Do not
clean, wash or soak seals in cleaning
solvent.
VALVE CENTERING
SHIM REPLACEMENT
1.
Hold the steering gear over a
drain pan in an inverted position and
cycle the input shaft several times to
drain the remaining fluid from the
gear.
2.
Mount the gear in a soft-jawed
vise.procarmanuals.com
Page 153 of 413
03-09-01
Saginaw Design Integral Power Steering Gear
03-09-01
PART 3-9 Saginaw Design
Integral Power Steering Gear
COMPONENT INDEX
STEERING GEAR
Cleaning and Inspection (See Page 03-01)
Description
Disassembly and Assembly
Mesh Load Adjustment
Removal and Installation
Overhaul
MODEL APPLICATION
All
Models
Ford
09-01
09-03
09-01
09-02
09-04
Mercury
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Meteor
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Cougar
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Fairlane
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Falcon
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Montego
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Mustang
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Lincoln-
Continental
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Thunderbird
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/\
N/A
Continental-
Mark III
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
A page number indicates that the item is for the vehicle listed at the head of the column.
N/A indicates that the item is not applicable to the vehicle listed.
DESCRIPTION
The Rotary Valve Safety power
steering gear operates entirely on dis-
placing fluid to provide hydraulic fluid
pressure assists only when turning. As
the entire gear assembly is always full
of fluid, all internal components of the
gear are immersed in fluid making
periodic lubrication unnecessary. In
addition, this fluid acts as a cushion
to absorb road shocks that may be
transmitted to the driver. All fluid
passages are internal except the pres-
sure and return hoses between the
gear and pump.
The rotary valve provides a smooth
transmission through the driving range
of steering wheel effort. A torsion bar
transmits the road feel to the driver.
Response of the steering gear to effort
applied to the steering wheel has been
greatly increased.
The rack-piston nut is one piece and
is geared to the sector shaft. Lash be-
tween the sector shaft and rack-piston
nut is maintained by an adjusting
screw which is retained in the end o\'
the shaft uear (Eiiz.l).
IN-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS AND REPAIRS
During the breaking in period of
the vehicle, it is probable that some
of the factory adjustments will change.
These changes in adjustment do not
necessarily affect the satisfactory op-
eration of the steering gear assembly
and ordinarily do not require re-ad-
justment unless there is excessive lash
or other malfunctioning. The only ad-
justment that should be performed in
the vehicle is the total over center
position load (mesh load) to eliminate
excessive lash between the sector shaft
and rack teeth.
MESH LOAD ADJUSTMENT
1.
Disconnect the Pitman arm from
the sector shaft and remove the steer-
ing wheel hub.
2.
Disconnect the fluid return line
at the reservoir; at the same time cap
the reservoir return line pipe.
3.
Place the end of the return line
in a clean container and cycle the
steering wheel in both directions as
required, to discharge the fluid from
the gear.
4.
Turn the gear 1/2 turn off cen-
ter (either direction). Using a 24 in-
lb torque wrench on the steering wheel
nut, determine the torque required to
rotate the shaft slowly through a 20
degree arc.
5.
Turn the sear back to center and
repeating the method of reading tor-
que as in Step 4, above, loosen the
adjuster lock nut, turn the screw in-
ward with a 7/32-inch Allen wrench
until the reading is equal to 6 in-lbs
in excess of Step 4 above, and retigh-
ten the lock nut while holding the
screw in place.
6. Recheck the readings and re-
place the Pitman arm and the steering
wheel hub.
7.
Connect the fluid return line to
the reservoir and fill the reservoir
with C1AZ-I9582-A Fluid to the
proper level.
procarmanuals.com