check INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: M35, Model: INFINITI M35 2006Pages: 5621, PDF Size: 65.56 MB
Page 3493 of 5621

GI-30
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
UNDER SEATING AREAS
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by seat components (such as slide guides)
during vehicle vibration. If the wiring runs under seating areas, inspect wire routing for possible damage or
pinching.
Heat Sensitive
The customer's concern may occur during hot weather or after car
has sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a
heat sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60
C (140F). If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the compo-
nent.
Freezing
The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freezing
somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked outside
overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis of
those electrical components which could be affected.
The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair or
replace the component.
Water Intrusion
The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water intru-
sion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the car
or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
Electrical Load
The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis with
all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio, fog
lamps) turned on.
SGI842
SGI843
SGI844
SGI845
Page 3494 of 5621
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-31
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
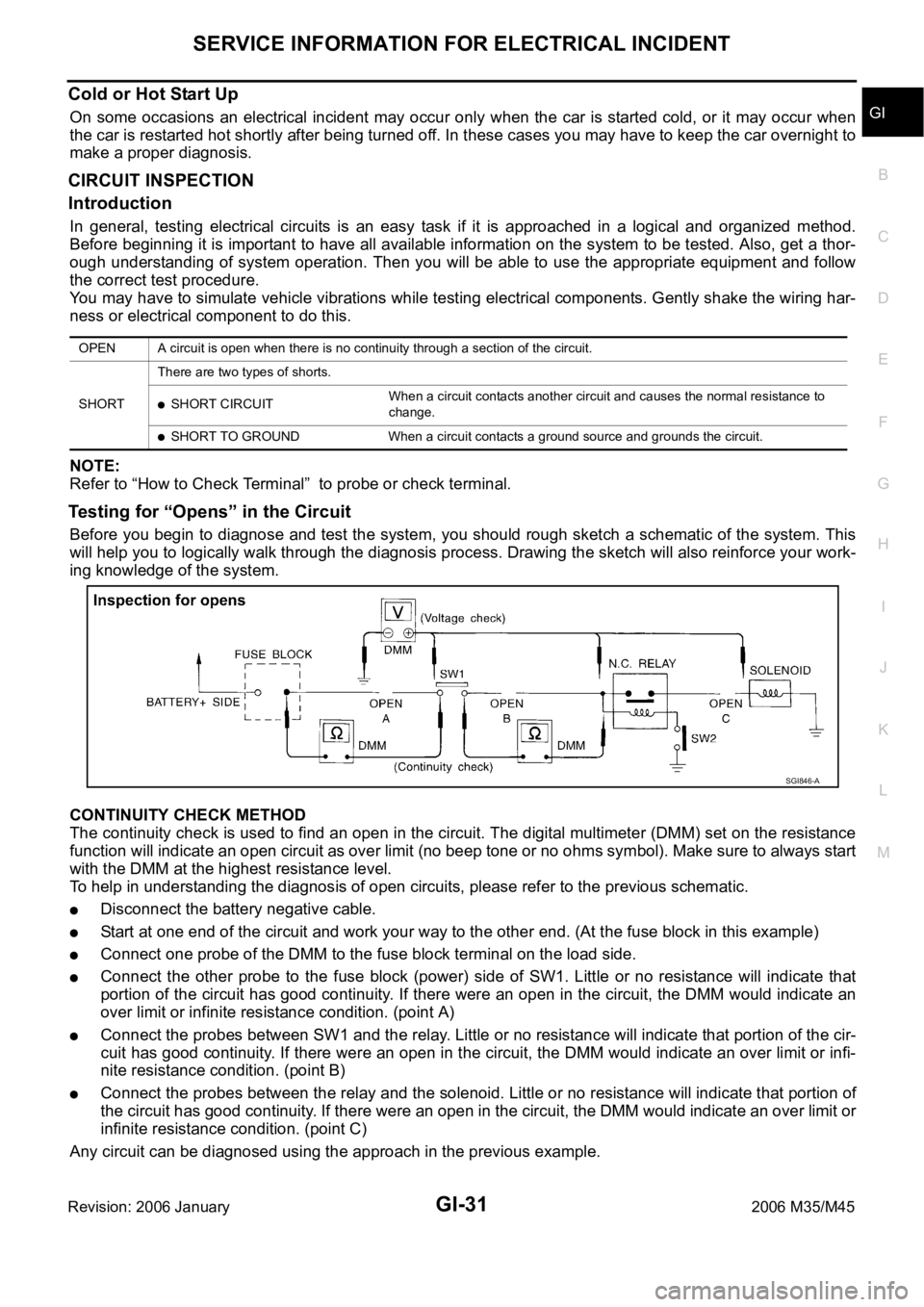
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORTThere are two types of shorts.
SHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Page 3495 of 5621
GI-32
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
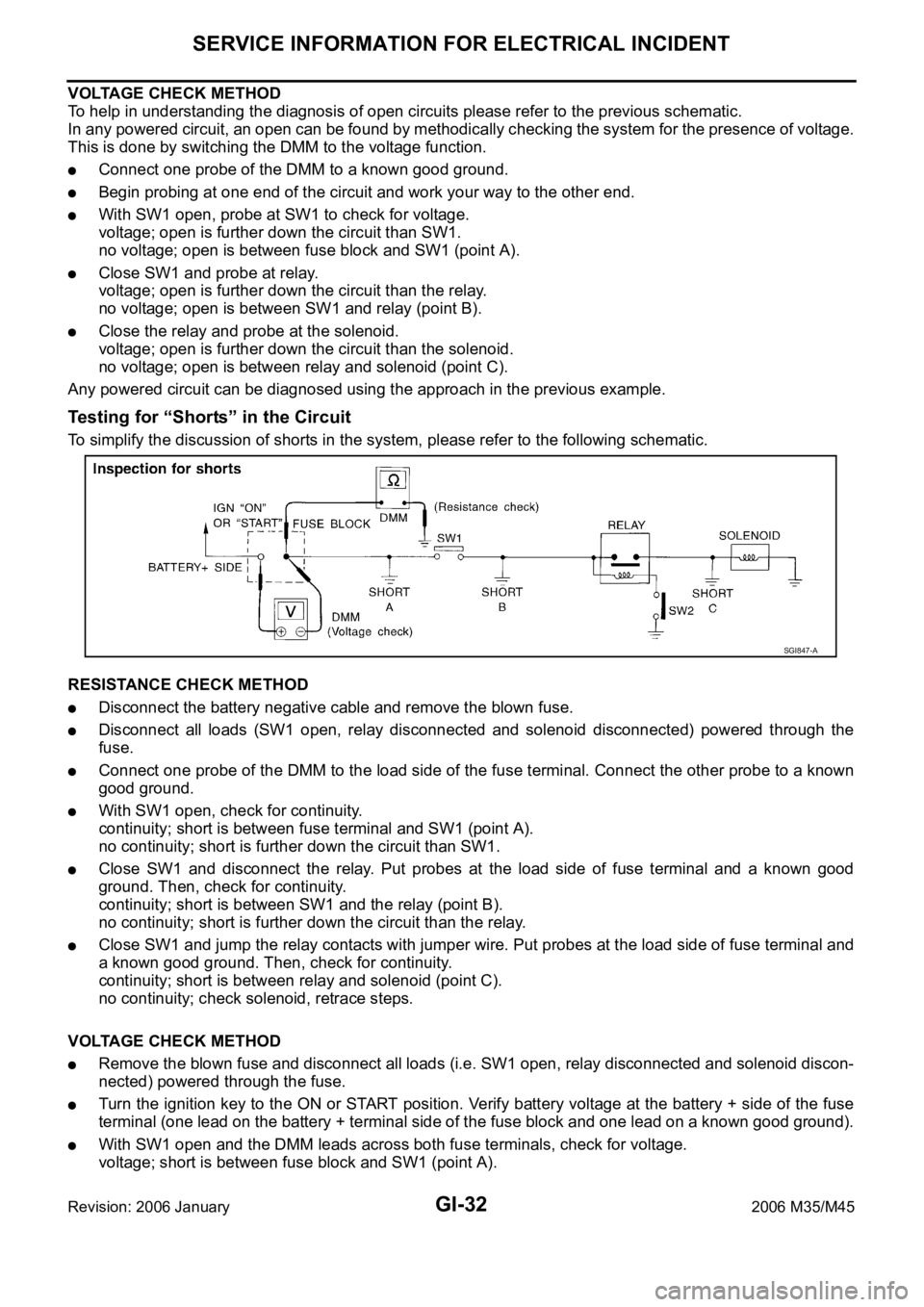
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse
terminal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
SGI847-A
Page 3496 of 5621
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-33
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
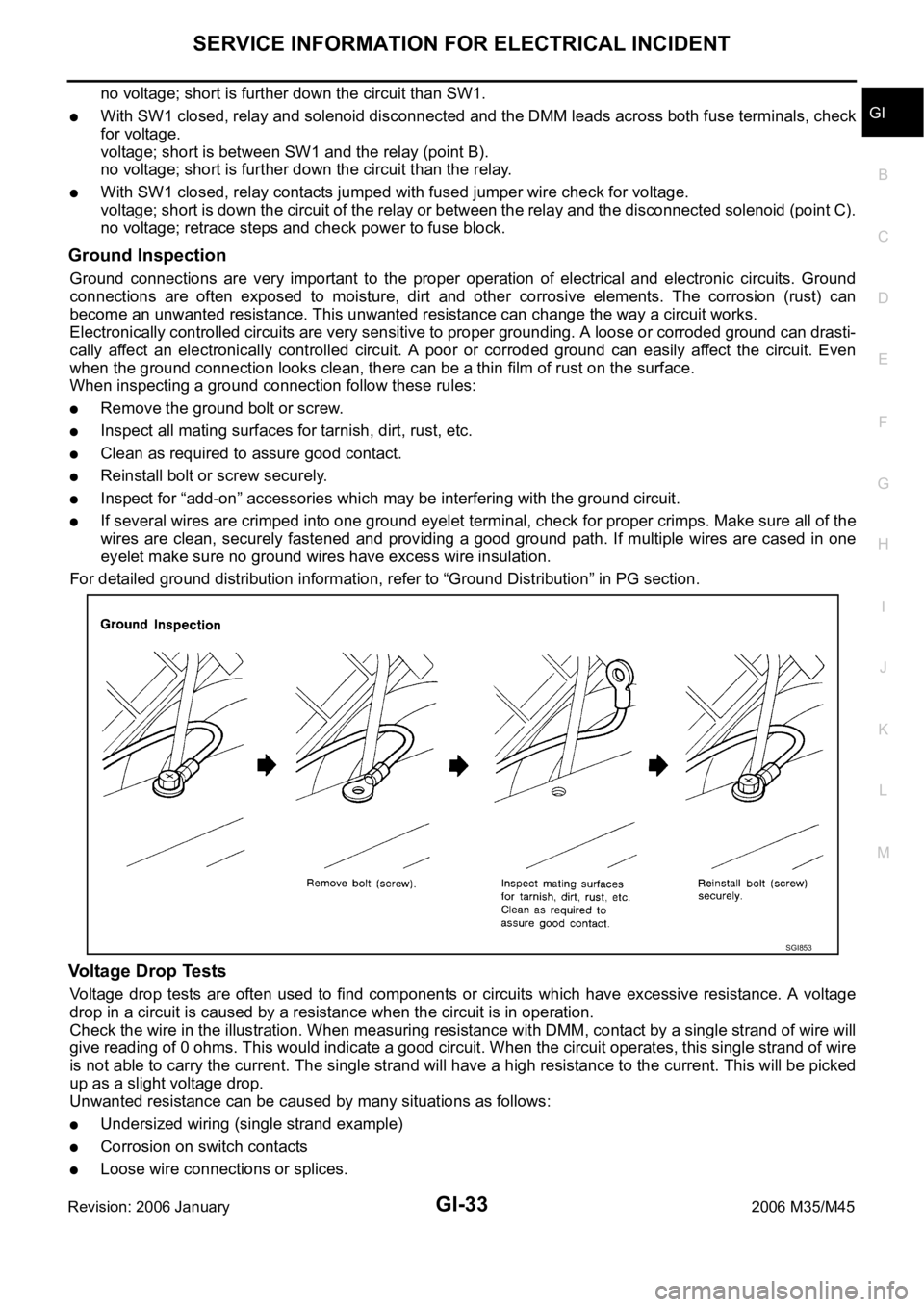
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
Remove the ground bolt or screw.
Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
Clean as required to assure good contact.
Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
Inspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 3497 of 5621

GI-34
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — ACCUMULATED METHOD
Connect the DMM across the connector or part of the circuit you want to check. The positive lead of the
DMM should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
Operate the circuit.
The DMM will indicate how many volts are being used to “push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — STEP-BY-STEP
The step-by-step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those in
“Computer Controlled Systems”).
Circuits in the “Computer Controlled System” operate on very low amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in the
system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper wire
gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
SGI974
SAIA0258E
Page 3499 of 5621

GI-36
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Control Units and Electrical PartsNAS0008L
PRECAUTIONS
Never reverse polarity of battery terminals.
Install only parts specified for a vehicle.
Before replacing the control unit, check the input and output and
functions of the component parts.
Do not apply excessive force when disconnecting a connector.
If a connector is installed by tightening bolts, loosen bolt mount-
ing it, then take it out by hand.
Before installing a connector, make sure the terminal is not bent
or damaged, and then correctly connect it.
When installing a connector by tightening bolts, fix it by tighten-
ing the mounting bolt until the painted projection of the connec-
tor becomes even with the surface.
For removal of the lever type connector, pull the lever up to the
direction pointed to by the arrow A in the figure, and then
remove the connector.
For installation of the lever type connector, pull down the lever to
the direction pointed by the arrow B in the figure, and then push
the connector until a clicking noise is heard.
SAIA0251E
SAIA0252E
SAIA0253E
SAIA0254E
Page 3500 of 5621

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-37
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Do not apply excessive shock to the control unit by dropping or
hitting it.
Be careful to prevent condensation in the control unit due to
rapid temperature changes and do not let water or rain get on it.
If water is found in the control unit, dry it fully and then install it in
the vehicle.
Be careful not to let oil to get on the control unit connector.
Avoid cleaning the control unit with volatile oil.
Do not disassemble the control unit, and do not remove the
upper and lower covers.
When using a DMM, be careful not to let test probes get close to
each other to prevent the power transistor in the control unit
from damaging battery voltage because of short circuiting.
When checking input and output signals of the control unit, use
the specified check adapter.
SAIA0255E
SEF348N
Page 3501 of 5621

GI-38
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEMPFP:00000
DescriptionNAS0007S
CONSULT-II is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the
vehicle side, it will communicate with the control unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various
kinds of diagnostic tests.
Refer to “CONSULT-II Software Operation Manual” for more information.
Function and System Application NAS0007T
x: Applicable
*: NISSAN Anti-Theft System (INFINITI/NISSAN Vehicle Immobilizer System) Diagnostic test
modeFunction
ENGINE
A/T
AIR BAG
METER A/C AMP
BCM
AUTO DRIVE POS.
ABS (Including VDC)
NATS (IVIS/NATS) *
IPDM E/R
ICC
ALL MODE AWD/4WD
INTELLIGENT KEY
LDW
AIR PRESSURE MONITOR
RAS/HICAS
ADAPTIVE LIGHT
PRECRASH SEATBELT
MULTI AV
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust
some devices faster and more accurately by
following the indications on CONSULT-II.x - - - xxx -- x- xxx- x- -
Self-diagnostic
resultsSelf-diagnostic results can be read and
erased quickly.xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Trouble diagnos-
tic recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble
diagnostic records previously stored can be
read.--x---------------
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. x x - x x x x - x xxxxxxxxx
CAN diagnosis
support monitorThe condition of CAN communication line
can be read.xx- xxxx- xxxxxxxxxx
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-II
drives some actuators apart from the ECUs
and also shifts some parameters in a speci-
fied range.x- - - xxx -xxxxxxxx- -
DTC & SRT con-
firmationThe results of SRT (System Readiness Test)
and the self-diagnosis status/result can be
confirmed.x- ----------------
DTC work sup-
portThe operating condition to confirm Diagnosis
Trouble Codes can be selected.xx----------------
ECU (ECM/TCM)
part numberECU (ECM/TCM) part number can be read. xx - - xxx -- xxxxxxxxx
ECU discrimi-
nated No.Classification number of a replacement ECU
can be read to prevent an incorrect ECU from
being installed.-- x---------------
Function testThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis
of ECU with either 'OK' or 'NG'. For engines,
more practical tests regarding sensors/
switches and/or actuators are available.xxx---x-----------
Control unit ini-
tializationAll registered ignition key IDs in NATS com-
ponents can be initialized and new IDs can
be registered.-- -----x----------
AV COMM moni-
torThe condition of AV communication can be
Indicated.------------ ---- -x
Page 3502 of 5621
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-39
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement NAS0007U
CONSULT-II contains a nickel metal hydride battery. When replacing the battery obey the following:
WAR NING :
Replace the nickel metal hydride battery with Genuine CONSULT-II battery only. Use of another bat-
tery may present a risk of fire or explosion. The battery may present a fire or chemical burn hazard if
mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble or dispose of in fire.
Keep the battery out of reach of children and discard used battery conforming to the local regulations.
Checking Equipment NAS0007V
When ordering the following equipment, contact your NISSAN/INFINITI distributor.
NOTE:
The CONSULT-II must be used in conjunction with a program card.
CONSULT-II does not require loading (Initialization) procedure.
Be sure the CONSULT-II is turned off before installing or removing a program card.
CAUTION:
If CONSULT-II is used with no connection of CONSULT-II CONVERTER, malfunctions might be
detected in self-diagnosis depending on control unit which carry out CAN communication.
If CONSULT-II CONVERTER is not connected with CONSULT-II, vehicle occur the “FAIL SAFE
MODE” which is “LIGHT UP the HEAD LIGHT” and/or “COOLING FAN ROTAT I N G ” w h e n C O N -
SULT-II is started.
Previous CONSULT-II “I” and “Y” DLC-I and DLC-II cables should NOT be used anymore because
their DDL connector pins can be damaged during cable swapping.
CONSULT-II Start ProcedureNAS0007W
NOTE:
Turning ignition switch off when performing CAN diagnosis could cause CAN memory to be erased.
1. Connect CONSULT-II and CONSULT-II CONVERTER to the
data link connector.
Tool nameDescription
NISSAN CONSULT-II
1. CONSULT-II unit (Tester internal soft: Resident
version 3.3.0) and accessories
2. Program card UED05B and AEN04A-1 (For
NATS)
3. CONSULT-II CONVERTER
4. “CONSULT-II Pigtail” Cable
SAIA0363E
PAIA0070E
Page 3503 of 5621

GI-40
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
2. If necessary, turn on the ignition switch.
3. Touch “START (NISSAN BASED VHCL)” or “System Shortcut”
(eg: ENGINE) on the screen.
4. Touch necessary system on "SELECT SYSTEM" screen.
If necessary system is not indicated, check power supply and
ground of system control unit. If it is normal, refer to GI-40,
"CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit" .
5. Select the desired part to be diagnosed on the "SELECT DIAG
MODE" screen.
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) CircuitNAS0007X
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT-II cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
NOTE:
The DDL1 and DDL2 circuits from DLC pins 12, 13, 14 and 15 may be connected to more than one system. A
short in a DDL circuit connected to a control unit in one system may affect CONSULT-II access to other sys-
tems.
SAIA0450E
BCIA0030E
BCIA0031E
Symptom Check item
CONSULT-II cannot access
any system.
CONSULT-II DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 8) and ground circuit (Terminal 4) (For detailed
circuit, refer to “MIL & Data Link Connectors Wiring Diagram” in EC section.)
CONSULT-II DLC cable and CONSULT-II CONVERTER
CONSULT-II cannot access
individual system. (Other sys-
tems can be accessed.)
CONSULT-II program card (Check the appropriate CONSULT-II program card for the system.
Refer to "Checking Equipment".)
Power supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system (For detailed circuit, refer to wir-
ing diagram for each system.)
Open or short circuit between the system and CONSULT-II DLC (For detailed circuit, refer to wiring
diagram for each system.)
Open or short circuit CAN communication line. Refer to LAN-7, "Precautions When Using CON-
SULT-II" .