transmission fluid ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 4435 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-151
The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor is part
of the harness assembly. The sensor is a variable
resistor and it measures the temperature of the
transmission fluid. When the TFT sensor is cold, the
sensor resistance is high. When the transmission fluid
temperature increases, the sensor resistance
decreases. With high sensor resistance, the TCM
detects a high voltage on the signal circuit. With lower
sensor resistance, the TCM detects a lower voltage on
the signal circuit.
If the fluid temperature increases to 135 °C (275 °F), the
TCM illuminates A/T Oil Temp lamp on the instrument
panel cluster. When the fluid temperature deceases
below 125 °C (257 °F), the lamp goes off.
Transmission Range (TR) Switch
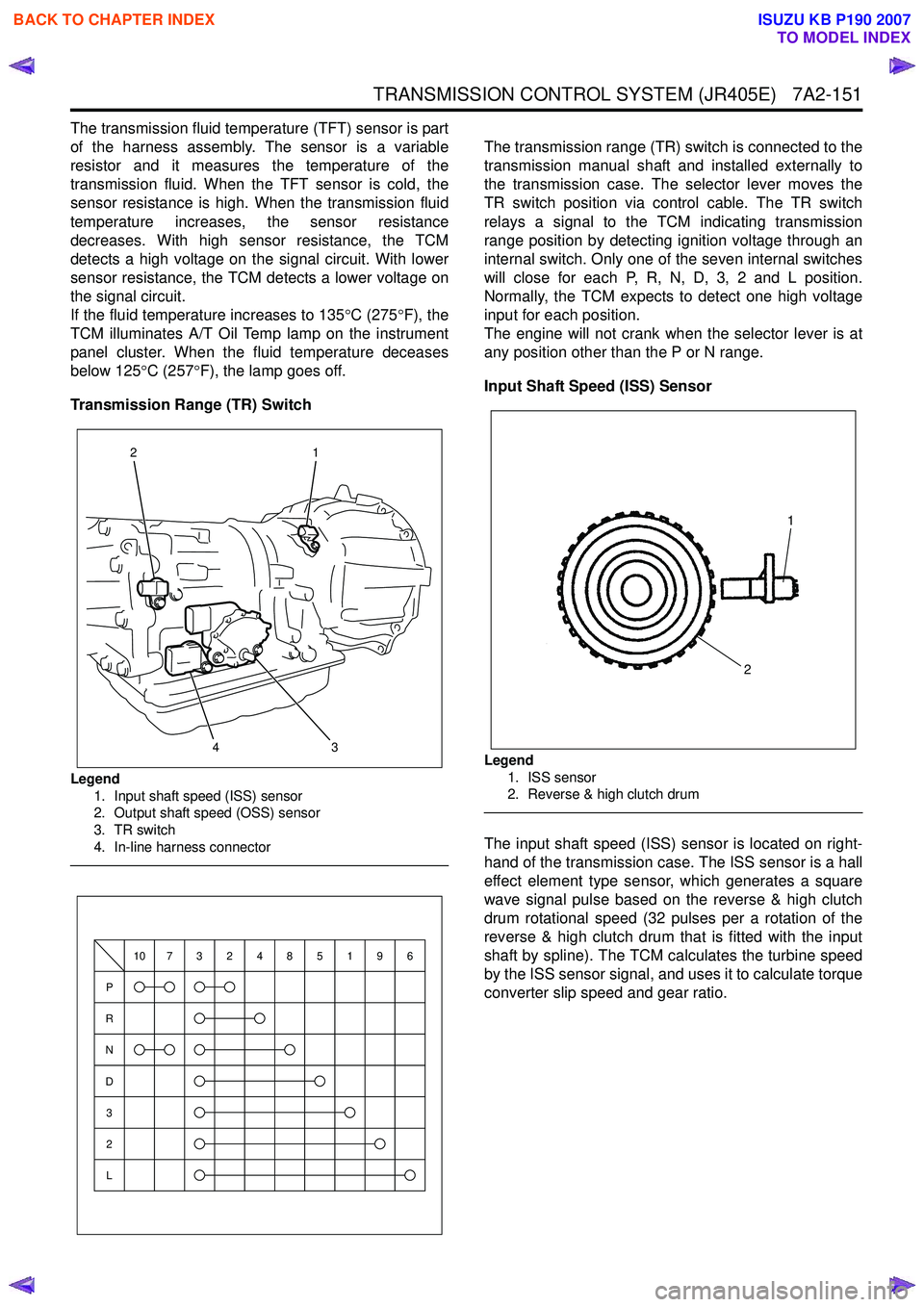
Legend 1. Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
2. Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
3. TR switch
4. In-line harness connector
The transmission range (TR) switch is connected to the
transmission manual shaft and installed externally to
the transmission case. The selector lever moves the
TR switch position via control cable. The TR switch
relays a signal to the TCM indicating transmission
range position by detecting ignition voltage through an
internal switch. Only one of the seven internal switches
will close for each P, R, N, D, 3, 2 and L position.
Normally, the TCM expects to detect one high voltage
input for each position.
The engine will not crank when the selector lever is at
any position other than the P or N range.
Input Shaft Speed (ISS) Sensor
Legend 1. ISS sensor
2. Reverse & high clutch drum
The input shaft speed (ISS) sensor is located on right-
hand of the transmission case. The ISS sensor is a hall
effect element type sensor, which generates a square
wave signal pulse based on the reverse & high clutch
drum rotational speed (32 pulses per a rotation of the
reverse & high clutch drum that is fitted with the input
shaft by spline). The TCM calculates the turbine speed
by the ISS sensor signal, and uses it to calculate torque
converter slip speed and gear ratio.
3
1
24
P
R
N
D
3
2
L
10732485196
1
2
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4437 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-153
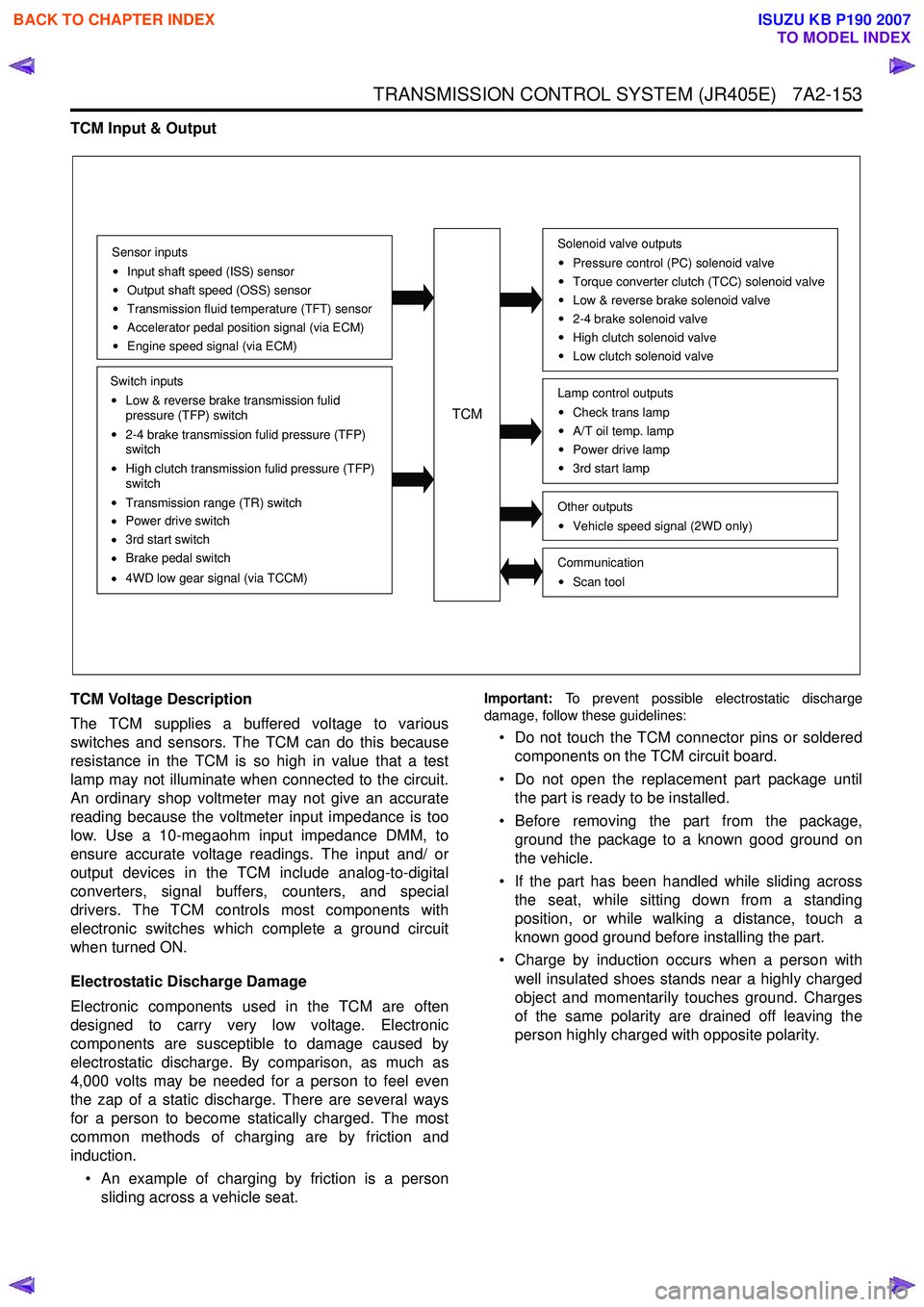
TCM Input & Output
TCM Voltage Description
The TCM supplies a buffered voltage to various
switches and sensors. The TCM can do this because
resistance in the TCM is so high in value that a test
lamp may not illuminate when connected to the circuit.
An ordinary shop voltmeter may not give an accurate
reading because the voltmeter input impedance is too
low. Use a 10-megaohm input impedance DMM, to
ensure accurate voltage readings. The input and/ or
output devices in the TCM include analog-to-digital
converters, signal buffers, counters, and special
drivers. The TCM controls most components with
electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned ON.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the TCM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. By comparison, as much as
4,000 volts may be needed for a person to feel even
the zap of a static discharge. There are several ways
for a person to become statically charged. The most
common methods of charging are by friction and
induction.
• An example of charging by friction is a person sliding across a vehicle seat.
Important: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
• Do not touch the TCM connector pins or soldered components on the TCM circuit board.
• Do not open the replacement part package until the part is ready to be installed.
• Before removing the part from the package, ground the package to a known good ground on
the vehicle.
• If the part has been handled while sliding across the seat, while sitting down from a standing
position, or while walking a distance, touch a
known good ground before installing the part.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with well insulated shoes stands near a highly charged
object and momentarily touches ground. Charges
of the same polarity are drained off leaving the
person highly charged with opposite polarity.
Sensor inputs
Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Switch inputs
Low & reverse brake transmission fulid
pressure (TFP) switch
2-4 brake transmission fulid pressure (TFP)
switch
High clutch transmission fulid pressure (TFP)
switch
Transmission range (TR) switch
Power drive switch
3rd start switch
Brake pedal switch
4WD low gear signal (via TCCM)
TCM
Solenoid valve outputs
Pressure control (PC) solenoid valve
Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
Low & reverse brake solenoid valve
2-4 brake solenoid valve
High clutch solenoid valve
Low clutch solenoid valve
Other outputsVehicle speed signal (2WD only)
CommunicationScan tool
Lamp control outputsCheck trans lamp
A/T oil temp. lamp
Power drive lamp
3rd start lamp
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4439 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-155
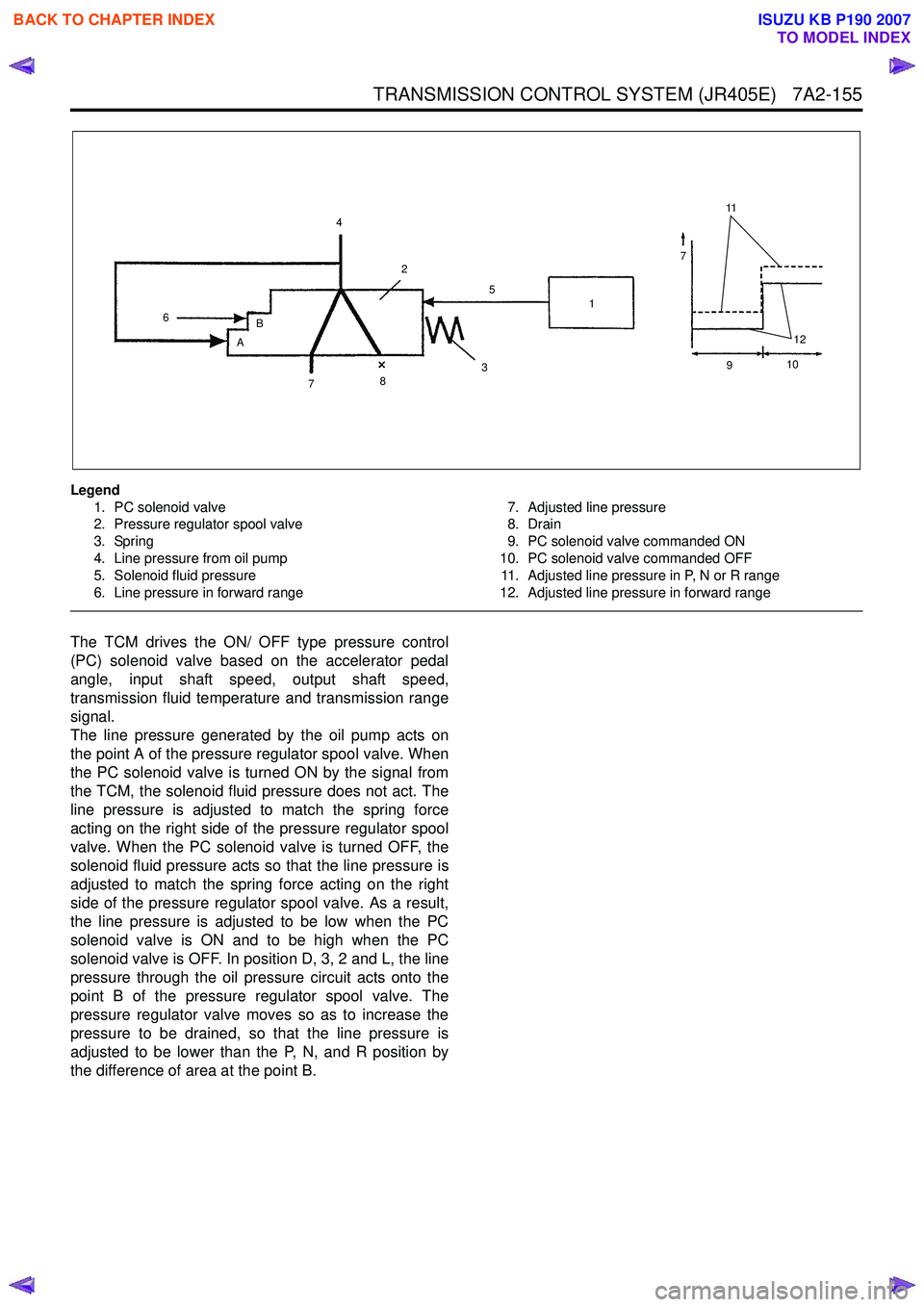
Legend1. PC solenoid valve
2. Pressure regulator spool valve
3. Spring
4. Line pressure from oil pump
5. Solenoid fluid pressure
6. Line pressure in forward range 7. Adjusted line pressure
8. Drain
9. PC solenoid valve commanded ON
10. PC solenoid valve commanded OFF 11. Adjusted line pressure in P, N or R range
12. Adjusted line pressure in forward range
The TCM drives the ON/ OFF type pressure control
(PC) solenoid valve based on the accelerator pedal
angle, input shaft speed, output shaft speed,
transmission fluid temperature and transmission range
signal.
The line pressure generated by the oil pump acts on
the point A of the pressure regulator spool valve. When
the PC solenoid valve is turned ON by the signal from
the TCM, the solenoid fluid pressure does not act. The
line pressure is adjusted to match the spring force
acting on the right side of the pressure regulator spool
valve. When the PC solenoid valve is turned OFF, the
solenoid fluid pressure acts so that the line pressure is
adjusted to match the spring force acting on the right
side of the pressure regulator spool valve. As a result,
the line pressure is adjusted to be low when the PC
solenoid valve is ON and to be high when the PC
solenoid valve is OFF. In position D, 3, 2 and L, the line
pressure through the oil pressure circuit acts onto the
point B of the pressure regulator spool valve. The
pressure regulator valve moves so as to increase the
pressure to be drained, so that the line pressure is
adjusted to be lower than the P, N, and R position by
the difference of area at the point B.
11
7
12
4
6 B
A 2
7 8 3 1
5
910
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4440 of 6020
7A2-156 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Gearshift Control & Shift Map Selection
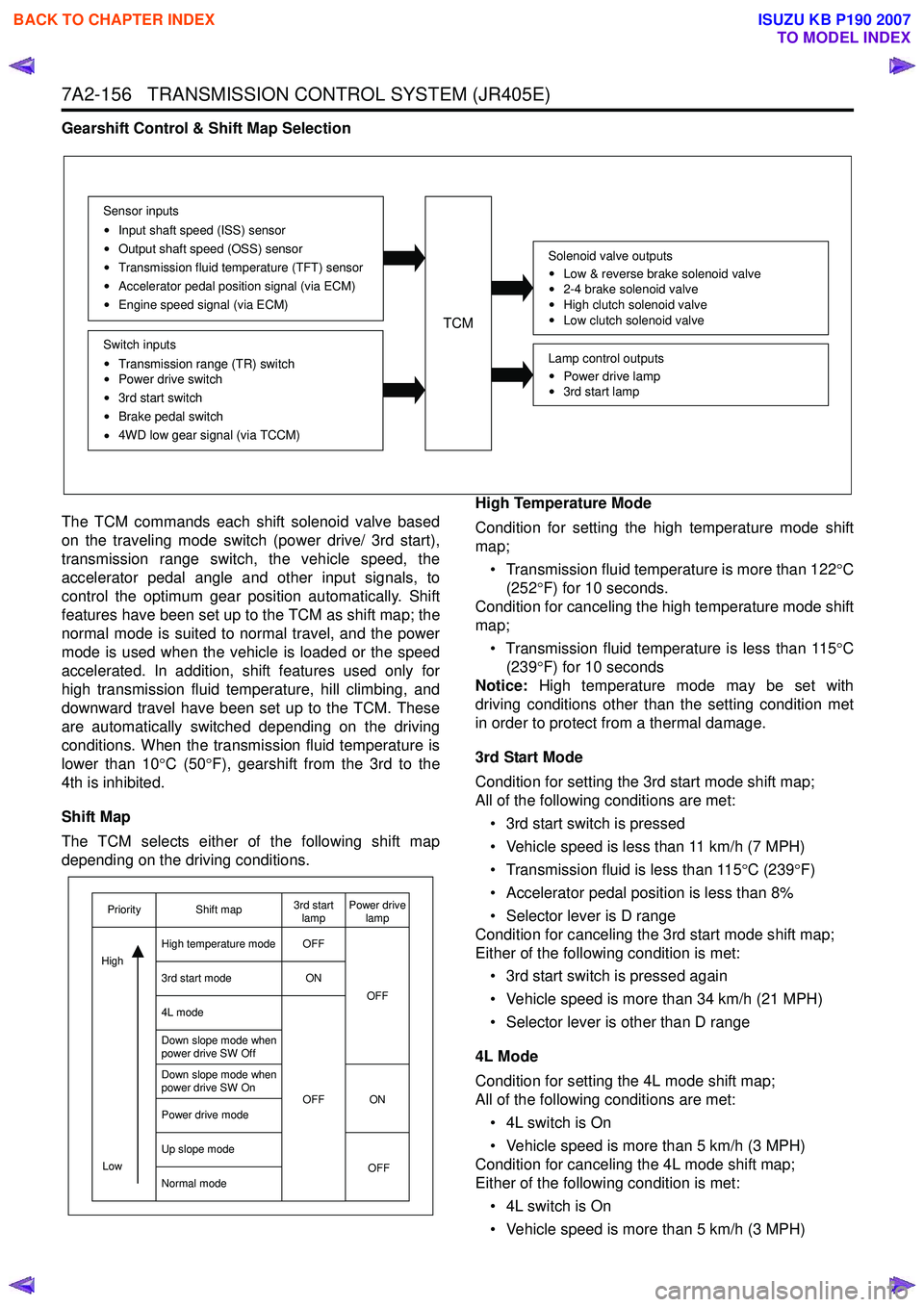
The TCM commands each shift solenoid valve based
on the traveling mode switch (power drive/ 3rd start),
transmission range switch, the vehicle speed, the
accelerator pedal angle and other input signals, to
control the optimum gear position automatically. Shift
features have been set up to the TCM as shift map; the
normal mode is suited to normal travel, and the power
mode is used when the vehicle is loaded or the speed
accelerated. In addition, shift features used only for
high transmission fluid temperature, hill climbing, and
downward travel have been set up to the TCM. These
are automatically switched depending on the driving
conditions. When the transmission fluid temperature is
lower than 10 °C (50 °F), gearshift from the 3rd to the
4th is inhibited.
Shift Map
The TCM selects either of the following shift map
depending on the driving conditions. High Temperature Mode
Condition for setting the high temperature mode shift
map;
• Transmission fluid temperature is more than 122 °C
(252 °F) for 10 seconds.
Condition for canceling the high temperature mode shift
map;
• Transmission fluid temperature is less than 115 °C
(239 °F) for 10 seconds
Notice: High temperature mode may be set with
driving conditions other than the setting condition met
in order to protect from a thermal damage.
3rd Start Mode
Condition for setting the 3rd start mode shift map;
All of the following conditions are met:
• 3rd start switch is pressed
• Vehicle speed is less than 11 km/h (7 MPH)
• Transmission fluid is less than 115 °C (239 °F)
• Accelerator pedal position is less than 8%
• Selector lever is D range
Condition for canceling the 3rd start mode shift map;
Either of the following condition is met:
• 3rd start switch is pressed again
• Vehicle speed is more than 34 km/h (21 MPH)
• Selector lever is other than D range
4L Mode
Condition for setting the 4L mode shift map;
All of the following conditions are met:
• 4L switch is On
• Vehicle speed is more than 5 km/h (3 MPH)
Condition for canceling the 4L mode shift map;
Either of the following condition is met:
• 4L switch is On
• Vehicle speed is more than 5 km/h (3 MPH)
TCM
Sensor inputs
Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Switch inputs
Transmission range (TR) switch
Power drive switch
3rd start switch
Brake pedal switch
4WD low gear signal (via TCCM)
Solenoid valve outputs
Low & reverse brake solenoid valve
2-4 brake solenoid valve
High clutch solenoid valve
Low clutch solenoid valve
Lamp control outputs
Power drive lamp
3rd start lamp
OFF
ON
OFF ON OFF
OFF
Low
Priority Shift map 3rd start
lamp Power drive
lamp
High temperature mode
3rd start mode
4L mode
Down slope mode when
power drive SW Off
Down slope mode when
power drive SW On
Power drive mode
Up slope mode
Normal mode
High
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4441 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-157
Down Slope Mode
Condition for setting the down slope mode shift map;
All of the following conditions are met:
• Brake pedal switch is depressed
• Accelerator pedal is released
• Vehicle speed is more than 60 km/h (36 MPH)
• Increment of vehicle speed is more than 1 km/h (1 MPH) per second
• Selector lever is D or 3 range
Condition for canceling the down slope mode shift map;
Either of the following condition is met:
• Accelerator pedal is depressed
• Selector lever is other than D or 3 range Power Drive Mode
When the power drive switch is ON, the TCM switches
shift map to the power drive mode map and performs
gearshift control from 1st to 4th to gain more
acceleration compared with normal mode.
Up Slope Mode
Up slope reasoning value is calculated from the
averaged accelerator pedal angle and the averaged
acceleration. Otherwise, up slope reasoning value is
calculated from the vehicle speed. The TCM selects a
up slope mode when the former is bigger than the
latter.
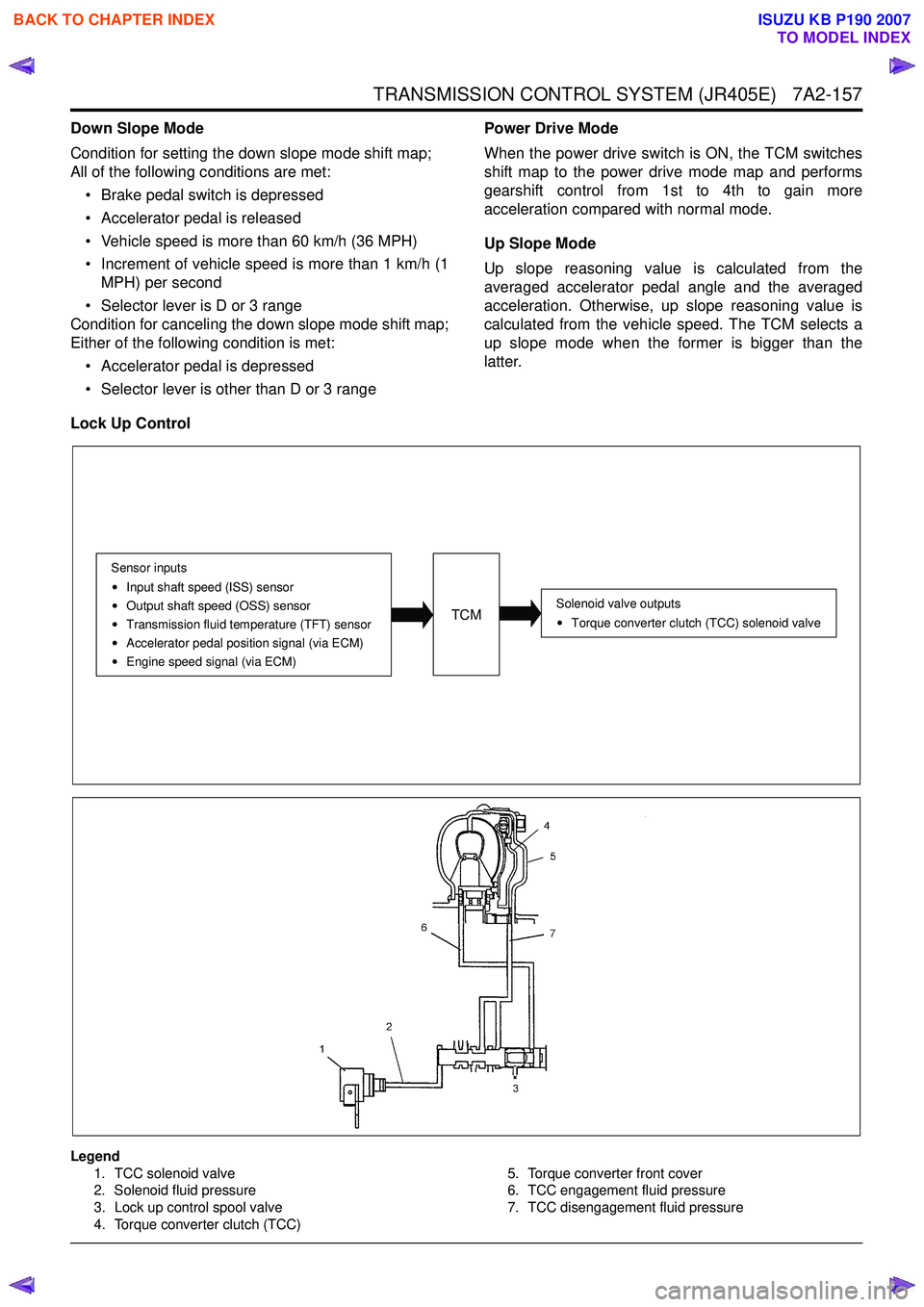
Lock Up Control
Legend 1. TCC solenoid valve
2. Solenoid fluid pressure
3. Lock up control spool valve
4. Torque converter clutch (TCC) 5. Torque converter front cover
6. TCC engagement fluid pressure
7. TCC disengagement fluid pressure
TCM
Sensor inputs
Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Solenoid valve outputsTorque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4442 of 6020

7A2-158 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
The TCM controls the torque converter clutch (TCC)
solenoid valve based on the accelerator pedal angle,
input shaft speed, output shaft speed and transmission
fluid temperature.
Smooth lock up control is employed to engage or
disengage the TCC smoothly at the time of lock up On
or Off. When the TCM determines the TCC
engagement, the solenoid valve control duty cycle
(pulse width modulation [PWM]) signal is gradually
increased (5% to 95%) and the transmission fluid
between the TCC piston and torque converter front
cover is gradually drained. As a result, the TCC piston
is fitted slowly to the torque converter front cover under
fluid pressure securing smooth lock up engagement. The lock up control does not start when the
transmission fluid temperature is less than 20 °C (68 °F)
even though the vehicle is at the lock up control speed
area. The lock up control disengages when the
accelerator pedal angle is released.
Direct Electronic Shift Control (DECS)
Legend 1. Oil pump
2. Pressure regulator spool valve
3. ON/ OFF type solenoid valve (pressure control [PC]
solenoid valve 4. Duty cycle type solenoid valve (shift solenoid valve)
5. Amplifier (AMP) valve
6. Clutch
Solenoid valve outputs
Pressure control (PC) solenoid valve
Low & reverse brake solenoid valve
2-4 brake solenoid valve
High clutch solenoid valve
Low clutch solenoid valve
TCM
Sensor inputsInput shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Switch inputs
Low & reverse brake transmission fluid
pressure (TFP) switch
2-4 brake transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch
High clutch transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4443 of 6020

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-159
Based on each transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch signal and each speed sensor signal and the
accelerator pedal angle, the duty cycle type shift
solenoid valve adjusts the clutch pressure to match the
engine load and vehicle running conditions. Controlling
the engagement and disengagement of the clutch and
brake pressure is directly and accurately controlled via
TCM, which is different to the conventional accumulator
type. Instead of the conventional system (On/ Off type
shift solenoid valve and shift valve), the combination of
the duty cycle type solenoid valve and the amplifier
(AMP) valve are used to adjust the clutch pressure to
match the engine load and vehicle driving conditions,
based on the signal from the TCM. Also, the TFP
switch provided in the fluid passage of the control valve
transmits to TCM, enabling the engagement and
disengagement control of the clutch and brake to be
directly and finely. When the gear is shifted from the
2nd to 3rd, 3rd to 4th, 4th to 3rd and 3rd to 2nd, the
clutch pressures on the engagement side and
disengagement side are simultaneously controlled. As
a result, engine racing or clutch drag is prevented
which enables a smooth and quick shift response.
Learning Control
Solenoid valve outputs
Low & reverse brake solenoid valve
2-4 brake solenoid valve
High clutch solenoid valve
Low clutch solenoid valve
TCM
Sensor inputs Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Switch inputs
Low & reverse brake transmission fluid
pressure (TFP) switch
2-4 brake transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch
High clutch transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4444 of 6020
7A2-160 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
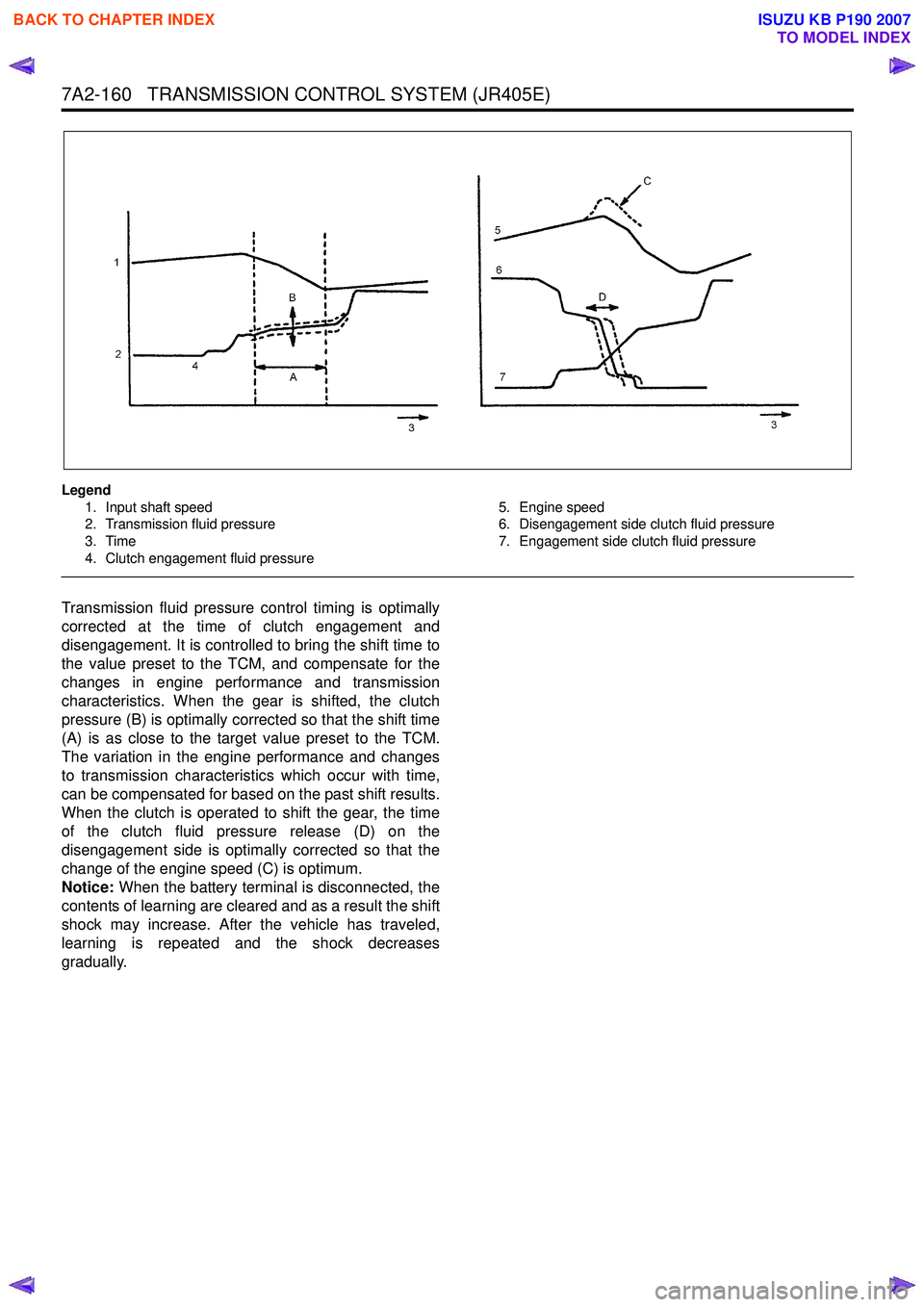
Legend1. Input shaft speed
2. Transmission fluid pressure
3. Time
4. Clutch engagement fluid pressure 5. Engine speed
6. Disengagement side clutch fluid pressure
7. Engagement side clutch fluid pressure
Transmission fluid pressure control timing is optimally
corrected at the time of clutch engagement and
disengagement. It is controlled to bring the shift time to
the value preset to the TCM, and compensate for the
changes in engine performance and transmission
characteristics. When the gear is shifted, the clutch
pressure (B) is optimally corrected so that the shift time
(A) is as close to the target value preset to the TCM.
The variation in the engine performance and changes
to transmission characteristics which occur with time,
can be compensated for based on the past shift results.
When the clutch is operated to shift the gear, the time
of the clutch fluid pressure release (D) on the
disengagement side is optimally corrected so that the
change of the engine speed (C) is optimum.
Notice: When the battery terminal is disconnected, the
contents of learning are cleared and as a result the shift
shock may increase. After the vehicle has traveled,
learning is repeated and the shock decreases
gradually.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4455 of 6020

ON-VEHICLE SERVICE (JR405E) 7A3-1
SECTION 7A3
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE (JR405E)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Description ................................................................................................................... ... 7A3 – 2
Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF) ............................................................................ 7A3 – 2
ATF Level ..................................................................................................................... .... 7A3 – 2
ATF Change .................................................................................................................... . 7A3 – 3
Transmission Control Module (TCM) ............................................................................ 7A3 – 5
Inhibitor Switch .............................................................................................................. . 7A3 – 6
Speed Sensor .................................................................................................................. 7A3 – 8
Turbine Sensor ............................................................................................................... 7A3 – 9
Power and 3rd Start Switch ........................................................................................... 7A3 – 9
Select Lever .................................................................................................................. ... 7A3 –10
Shift Cable ................................................................................................................... .... 7A3 –13
Solenoids, Oil Pressure Switch and Oil Temperature Sensor .................................... 7A3 –16
Control Valve Assembly ................................................................................................. 7A3 –1 8
Flushing the Transmission Fluid Cooler and Line ...................................................... 7A3 –19
Transmission Assembly ................................................................................................. 7A3 –20
Special Service Tool ....................................................................................................... 7A 3 –23
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4456 of 6020

7A3-2 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE (JR405E)
DESCRIPTION
Before performing on-vehicle service on the automatic
transmission, check that the engine idling speed and
general engine condition are normal.
For shift interlock function, if the ignition key is out of
“LOCK” position, the shift lever select button can not be
pushed. (shift lever can not be operated.)
RTW 77ASH000901
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID (ATF)
Inspect
Remove the transmission dipstick to check the condition
of the ATF.
Check the color and smell of the ATF.
If the ATF is abnormal color or smells burnt, replace it
and investigate the cause of trouble.
Coloor of ATF Condition Clear red Normality
Blackish discoloration Defects of power train
parts (clutches)
W hite turbidity Include water
Discoloration of red brown Deterioration of ATF
ATF LEVEL
Inspect
Hot Level
1. W arm up the engine and the transmission by driving
the vehicle on the road so that the temperature
reaches around 80 °C (176 °F).
Do not turn the engine off.
2. Park the vehicle on a level surface.
3. Apply the parking brake firmly.
4. Let the engine run at idle.
Move the select lever slowly through all the gea
r
positions.
Stop in each gear position just long enough for the transmission to engage.
5. Return the select lever to either “P” or “N”.
6. Remove the ATF level dipstick.
7. W ipe the dipstick clean with a paper towel.
8. Reinsert the dipstick and wait several seconds.
9. Remove the dipstick.
The ATF level should be inside the “H” range on the dipstick.
242R300001
If the ATF level is below the “H” range, ATF must be added.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007