light ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3217 of 6020
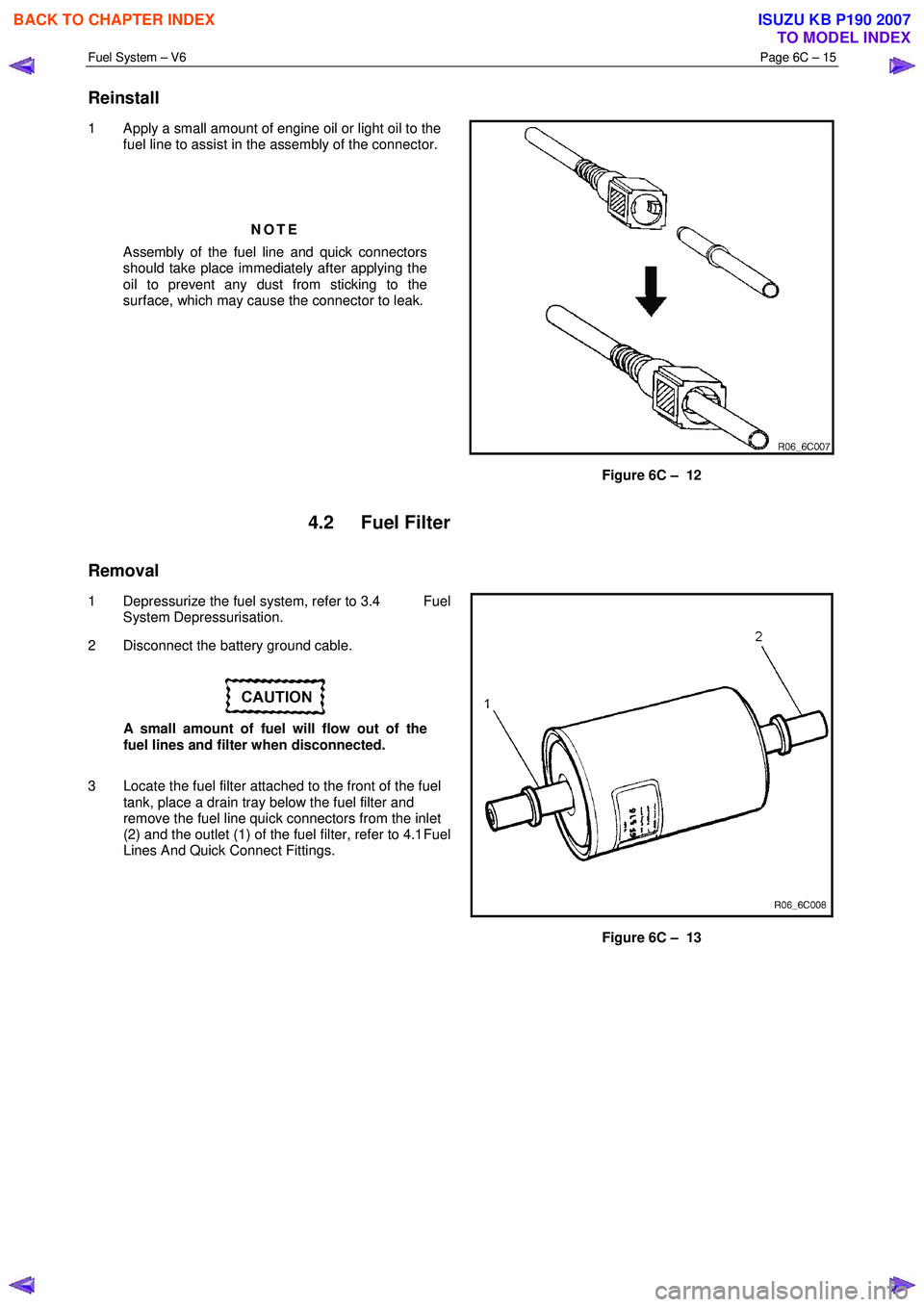
Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 15
Reinstall
1 Apply a small amount of engine oil or light oil to the
fuel line to assist in the assembly of the connector.
NOTE
Assembly of the fuel line and quick connectors
should take place immediately after applying the
oil to prevent any dust from sticking to the
surface, which may cause the connector to leak.
Figure 6C – 12
4.2 Fuel Filter
Removal
1 Depressurize the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel
System Depressurisation.
2 Disconnect the battery ground cable.
A small amount of fuel will flow out of the
fuel lines and filter when disconnected.
3 Locate the fuel filter attached to the front of the fuel tank, place a drain tray below the fuel filter and
remove the fuel line quick connectors from the inlet
(2) and the outlet (1) of the fuel filter, refer to 4.1 Fuel
Lines And Quick Connect Fittings.
Figure 6C – 13
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3246 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–4
ADR 37/01 (Petrol) 2.1 0.26 2 0.63 Not Applicable
ADR 79/01 (Petrol,
LPG, CNG) 2.3 0.2 2 0.15 0.05
1.3 Warning Caution and Notes
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM Holden LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM Holden LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3277 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–35
5 Abbreviations and Glossary of
Te r m s
Abbreviations and terms used in this Section are listed below in alphabetical order with an explanation of the
abbreviation or term.
Abbreviation Description
A/C Air-conditioning
AC Alternating Current – An electrical current where the polarity is constantly changing between positive and
negative
A/F Air / Fuel (A/F Ratio)
Analogue Signal An electrical signal that constantly varies in voltage within a given parameter
Barometric Pressure Barometric absolute pressure (atmospheric pressure)
CAN Controller Area Network – A type of serial data for communication between electronic devices.
Catalytic Converter
A muffler-shaped device fitted in the exhaust system, usually close to the engine. Through chemical reaction,
a catalytic converter converts harmful gases produced by the combustion process such as HC, CO, and NOx,
into environmentally safe water vapour, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
CKT Circuit
Closed Loop A fuel control mode of operation that uses the signal from the exhaust oxygen sensor(s), to control the air / fuel
ratio precisely at a 14.7 to 1 ratio. This allows maximum efficiency of the catalytic converter.
CO Carbon Monoxide. One of the gases produced by the engine combustion process.
DC Direct Current
Digital Signal An electrical signal that is either on or off.
DLC
Data Link Connector. Used at the assembly plant to evaluate the engine management system. For service, it
allows the use of Tech 2 in performing system checks.
DLC Data Stream An output from the ECM initiated by Tech 2 and transmitted via the Data Link Connector(DLC).
DMM (10 M Ω) Digital Multimeter. A multipurpose meter that has capability of measuring voltage, current flow and resistance.
A digital multimeter has an input impedance of 10 M Ω (megohms), which means they draw very little power
from the device under test, they are very accurate and will not damage delicate electronic components
Driver An electronic device, usually a power transistor, that operates as an electrical switch.
DTC
Diagnostic Trouble Code. If a fault occurs in the engine management system, the ECM may set a four digit
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) which represents the fault condition. Tech 2 is used to interface with the ECM
and access the DTC(s). The ECM may also operate the malfunction indicator lamp in the instrument cluster.
Duty Cycle The time, in percentage, that a circuit is on versus off.
ECT Sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the
temperature of the engine coolant.
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. A type of read only memory (ROM) that can be
electrically programmed, erased and reprogrammed using Tech 2. Also referred to as Flash Memory
EMI or Electrical
Noise An unwanted signal interfering with a required signal. A common example is the effect of high voltage power
lines on an AM radio.
Engine Braking A condition where the engine is used to slow the vehicle on closed throttle or low gear.
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. A type of Read Only Memory (ROM) that can be erased with
ultraviolet light and then reprogrammed.
ESD Electrostatic Discharge. The discharge of static electricity which has built up on an insulated material
EVAP
Evaporative emission control system. Used to prevent fuel vapours from the fuel tank from entering into the
atmosphere. The vapours are stored in a canister that contains an activated charcoal element. The fuel
vapours are purged from the canister into the manifold to be burned in the engine.
GM LAN General Motors Local Area Network - A type of serial data for communication between electronic devices.
Fuse
A thin metal strip which melts when excessive current flows through it, creating an open circuit and protecting
a circuit from damage.
HC Hydrocarbon. Result of unburned fuel produced by incomplete combustion.
Heavy Throttle Approximately 3/4 of accelerator pedal travel (75% throttle position)
IAT Sensor
Intake Air Temperature sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the
temperature of air entering the intake system.
Ideal Mixture The air / fuel ratio which provides the best performance, while maintaining maximum conversion of exhaust
emissions, typically 14.7 to 1 on spark ignition engines
IGN Ignition
Inputs Information from sensors (MAF, TP, etc.) and switches (A/C request, etc.) used by the ECM to determine how
to control its outputs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3278 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–36
Intermittent
An electrical signal that occurs now and then; not continuously. In electrical circuits, refers to occasional open,
short, or ground in a circuit
Light Throttle Approximately 1/4 of accelerator pedal travel (25% throttle position)
Low
A voltage less than a specific threshold. Operates the same as a ground and may, or may not, be connected
to chassis ground.
MAF Sensor Mass Air Flow Sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the amount of air flow
entering in the intake system.
Medium Throttle Approximately 1/2 of accelerator pedal travel (50% throttle position)
N.C Normally Closed. Switch contacts that are closed when they are in the normal operating position
N.O Normally Open. Switch contacts that are normally open when in the normal operating position
NOx
Nitrogen Oxide. One of the pollutants found in spark ignition engine exhaust that is formed from normal
combustion and increases in severity with combustion temperature.
O2 Sensor Oxygen Sensor. A device located in the exhaust system that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on
the oxygen content of exhaust gas.
May also include a heating circuit to provide faster initial warm-up (HO2 sensor).
OBD On Board Diagnostic
Open Loop ECM control of the fuel control system without the use of the oxygen sensor signal.
Output Functions that are controlled by the ECM, typically these can include solenoids and relays, etc.
ECM Engine Control Module. An electronic device which controls the engine management system.
ECU Electronic Control Unit. An electronic device which controls specific system functions
PCV
Positive Crankcase Ventilation. Method of reburning crankcase fumes rather than passing them directly into
the atmosphere
PIM Powertrain Interface Module – The PIM acts as a communication translator between the ECM and other on-
board controllers that use a different serial data protocol.
PM Permanent Magnet
PWM
Pulse Width Modulated. A digital signal turned on and off for a percentage of available cycle time. A signal that
is 30% on and 70% of would be termed a 30% on PWM signal.
Quad Driver A transistor in the ECM capable of operating four separate outputs. Outputs can be either on-off or pulse width
modulated.
RAM Random Access Memory. A microprocessor can write into or read from this memory as needed. This memory
is volatile and needs a constant power supply to be retained. If the power is lost or removed, RAM data is lost.
r.p.m. Revolutions Per Minute
Serial Data
Serial data is a series of rapidly changing voltage signals pulsed from high to low. These signals are typically
transmitted through a wire often referred to as the Serial Data Circuit.
SFI Sequential Fuel Injection. Method of injecting fuel into the engine one cylinder at a time in relation to the
engines firing order.
Solenoid An electromagnetic coil which creates a magnetic field when current is applied, causing a plunger or ball to
move.
Switch Device to opens and close a circuit, thereby controlling current flow.
Tech 2
Tech 2 is a peripheral device that aids in the diagnosis and repair of electronic systems such as engine
management, transmission control etc. Tech 2 connects to the vehicle’s Data Link Connector (DLC).
TP Sensor Throttle Position sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the position of the
throttle plate.
Vacuum – manifold Vacuum sourced downstream of the throttle plate.
Vacuum – ported Vacuum sourced upstream of the throttle plate.
VSS Vehicle Speed Sensor. A permanent magnet type device that provides a digital voltage to the ECM.
WOT Wide Open Throttle – Full travel of the accelerator pedal (100% throttle position).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3285 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–7
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3297 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–19
• Do not start the engine if the battery terminal is not properly secured to the battery.
• Do not disconnect or reconnect the following while the ignition is switched on or when the engine is running:
− Any engine management system component electrical wiring connector, or
− Battery terminal leads.
• Ensure the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting engine management system electrical wiring
connectors is always followed. For information on the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting specific
wiring connectors, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are fitted correctly.
• W hen steam or pressure cleaning engines, do not direct the cleaning nozzle at engine management system
components.
• Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
• The fault must be present when using the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) diagnostic tables. Otherwise,
misdiagnosis or replacement of good parts may occur.
• Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered components on the ECM circuit board to prevent ECM
Electrostatic Discharge damage. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on Electrostatic
Discharge.
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables as other test equipment may give incorrect results or
damage good components.
• The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draw associated with vehicle operations. However, the following
fault conditions or incorrect test procedure may overload the ECM internal circuit and damage the ECM:
− A short to voltage fault condition in any of the ECM low reference circuits may cause internal ECM and / or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to voltage fault condition in the ECM low reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
− A short to ground fault condition in any of the ECM 5 V reference circuits may cause internal ECM and / or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to ground fault condition in the ECM 5 V reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
− W hen using a test lamp to test an electrical circuit, do not use any of the ECM low reference circuits or 5 V
reference circuits as a reference point. Otherwise, excessive current draw from the test lamp may damage
the ECM.
• Disregard DTCs that set while performing the following diagnostic Steps:
− Using Tech 2 actuator tests, or
− Disconnecting an engine management system sensor connector then switching on the ignition.
• After completing the required diagnostics and service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct engine
management system operation.
4.3 Preliminary Checks
The preliminary checks are a set of visual and physical checks or inspections that may quickly identify engine
management system fault condition.
• Refer to the appropriate Service Techlines for relevant information regarding the fault condition.
• Ensure the battery is fully charged.
• Inspect the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
• Ensure that all engine management system related fuses are serviceable.
• Inspect for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent devices, lights or mobile phone installation.
• Ensure there is no speaker magnet positioned too close to any electronic module that contains relays.
• Inspect the engine wiring harness for proper connections, pinches or cuts.
• Ensure that all engine management related electrical wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
• Inspect the ECM ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or incorrect position.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3301 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–23
• there is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary
• Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check the immobiliser
system. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Tech 2 Tests The following are lists of Tech 2 diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose
intermittent faults:
• W riggle test the suspected wiring harness and connectors while observing Tech 2
operating parameters. If Tech 2 read-out fluctuates during this procedure, check
the tested wiring harness circuit for a loose connection.
• Observe the freeze frame / failure records for the suspected history DTC and then
operate the vehicle in the conditions that triggers the intermittent fault while an
assistant observes the suspected Tech 2 operating parameter data.
• Capture and store data in the snapshot mode when the fault occurs. The stored
data may be played back at a slower rate to aid diagnostics. Refer to Tech 2 User
Instructions for further information on the Snapshot function.
• Compare the engine operating parameters of the engine being diagnosed to the
engine operating parameters of a known good engine.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• ECM grounds are loose.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3302 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–24
Checks Actions
Temperature Related Temperature related intermittent fault condition occurs only when the engine or ambient
temperature is hot, or only when it is cold.
• If the intermittent fault is heat related, review Tech 2 data in relationship to the
following:
• high ambient temperature,
• engine generated heat,
• circuit generated heat due to a poor electrical connection or high electrical
load, and
• higher than normal load conditions (towing, etc.).
• If the intermittent fault is related to cold ambient or engine temperature, review
Tech 2 data in relationship to the following:
• low ambient temperature, and
• the fault condition that occurs only on a cold start situation.
Additional Tests
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid or switch. The fault is triggered when the relay or solenoid is activated.
• Test the A/C compressor clutch and some relays that contain a clamping diode or
resistor for an open circuit.
• Test the generator for a faulty rectifier bridge that may allow the A/C noise into the
ECM electrical circuit.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.3 Backfire
Description
The air / fuel mixture in the intake manifold or in the exhaust system ignites which produces a loud popping noise.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the Preliminary Checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
Sensor / System • Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3324 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–46
6.5 Alcohol / Contaminants in Fuel
Diagnosis
Description
W ater contamination in the fuel system may cause driveability conditions such as hesitation, stalling, no start, or
misfires in one or more cylinders. W ater may collect near a single fuel injector at the lowest point in the fuel rail, and
cause a misfire in that cylinder. If the fuel system is contaminated with water, inspect the fuel system components for
rust, or deterioration.
Alcohol (e.g. Ethanol) concentrations more than 10% in the fuel can be detrimental to fuel system components. Alcohol
contamination may cause fuel system corrosion, deterioration of rubber components, and subsequent fuel filter
restriction. Fuel contaminated with alcohol may cause driveability conditions such as hesitation, lack of power, stalling,
or no start. Some types of alcohol are more detrimental to fuel system components than others.
Alcohol in Fuel Testing Procedure
NOTE
The procedures detailed are not intended to be
accurate but rather, indicative of a contamination
situation.
The fuel sample should be drawn from the bottom of the tank so that any water present in the tank will be detected. The
sample should be bright and clear. If alcohol contamination is suspected, then use the following procedure to test the
fuel quality.
• Using a 100 ml graduated cylinder with 1 ml marks, fill the cylinder with fuel to the 90 ml mark.
• Add 10 ml of water to bring the total fluid volume to 100 ml and install a stopper.
• Shake the cylinder vigorously for 10 – 15 seconds.
• Carefully loosen the stopper to release the pressure.
• Re-install the stopper and shake the cylinder vigorously again for 10 – 15 seconds.
• Put the cylinder on a level surface for approximately 5 minutes to allow adequate liquid separation.
If alcohol is present in the fuel, the volume of the lower layer, that now contains both alcohol and water, will be more
than 10 ml. For example, if the volume of the lower layer is increased to 15 ml, this indicates at least 5 percent alcohol in
the fuel. The actual amount of alcohol may be somewhat more because this procedure does not extract all of the
alcohol from the fuel. To obtain an accurate determination of the amount of alcohol contamination in a given fuel sample,
then professional analysis should be sought.
Particulate Contaminants in Fuel Testing Procedure
The fuel sample should be drawn from the bottom of the tank so that any contaminants present in the tank will be
detected. The sample should be bright and clear. If the sample appears cloudy or contaminated with water as indicated
by a water layer at the bottom of the sample, use the following procedure to diagnose the fuel.
• Using an approved fuel container, draw approximately 0.5 litre of fuel.
• Place the cylinder on a level surface for approximately 5 minutes to allow settling of the particulate contamination.
Particulate contamination will show up in various shapes and colours. Sand will typically be identified by a white or light
brown crystals. Rubber will appear as black and irregular particles. If particles are found, clean the entire fuel system
thoroughly. Refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
6.6 Crankshaft Position (CKP) System
Variation Learn Procedure
Description
The crankshaft position system variation learn feature is carried out automatically on the HFV6 engine under decel with
fuel cut. The road speed and duration of the self-learn process varies with different vehicle equipment levels such as
transmission, final drive ratio etc.
The variation learn procedure cannot be over-written, nor can it be accessed with Tech 2.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3448 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–170
Step Action Yes
No
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.46 DTC P2096 or P2098
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2096 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 1)
• DTC P2098 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor 1 measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and provides more
information than the switching style HO2S2. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen
pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the
pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to
the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the
oxygen pumping cell, maintaining a constant voltage in the oxygen sensing cell. The ECM monitors the voltage variation
in the sensing cell and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow, or
oxygen ion flow, to the pumping cell. By measuring the amount of current required to maintain the voltage in the sensing
cell, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. The HO2S voltage is displayed as a lambda
value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the
lambda value will remain around 1. W hen the fuel system is lean, the oxygen level will be high and the lambda signal
will be high or more than 1. W hen the fuel system is rich, the oxygen level will be low, and the lambda signal will be low
or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the correct air / fuel ratio.
Fuel trim biasing is used by the ECM to keep the post catalyst HO2S voltage within a range of 580 – 665 mV as
possible. This allows optimal catalyst efficiency under light load conditions, such as at idle or a steady cruise. The ECM
constantly monitors how lean or rich the fuel trim bias is commanded. If the ECM detects that the fuel trim bias is
commanded lean for more than a calibrated amount, DTC P2096 or P2098 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2096 or P2098 failed, DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0041, P0050, P0051,
P0052, P0101, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0151, P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2231, P2234, P2237, P2240, P2243, P2247, P2251, P2254, P2270, P2271, P2273, P2626, and
P2629 must run and pass.
• The engine is operating for more than 2 seconds.
• The post catalyst fuel trim control is enabled.
• The front and rear HO2S are in Closed Loop.
• DTCs P2096and P2098 run continuously once the above conditions are met for more than 40 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The post catalyst fuel trim correction factor is biased lean by more than 3 percent of the HO2S lambda value for more
than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM activates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the
diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the
control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second
consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The
control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007