relay ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3519 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fan relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the fan relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays
‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Level: This parameter displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in litres, as calculated by the ECM from data
received from the fuel level sensor.
Fuel Level Sensor: This parameter displays the voltage received from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank, by the ECM.
Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel pump relay control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel pump relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The
parameter displays ‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Pump Relay: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump relay control circuit.
Fuel Trim Learn: This parameter displays ‘Enabled’ when conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim
corrections. This indicates that the long term fuel trim is adapting continuing amounts of short term fuel trim. If Tech 2
displays ‘Disabled’, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short term fuel trim.
Ignition Accessory Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the
ignition ‘ACC’ terminal, X1-4 of the ignition switch.
Ignition On Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the ignition ‘IGN’
terminal X1-3 of the ignition switch.
Initial Brake Apply Signal: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. Before the cruise control can
be activated, this switch contact must be open circuit when the brake pedal is pressed.
Injection Time Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the amount of fuel injector On-time or pulse width as
commanded by the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the air entering the air induction system based on
input to the ECM from the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Knock Sensor Signal (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameters displays the voltage input to the control module from the
knock sensor (KS).
Knock Retard: This parameter indicates the amount of spark advance in crankshaft degrees, that the ECM removes
from the ignition control (IC) spark advance in response to the signal from the knock sensors.
Knock Retard Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the knock retard as commanded by the ECM for cylinders 1-6.
Each cylinder is controlled individually based on both knock sensor signal inputs.
Loop Status B1S1 / B2S1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the fuel control system
as commanded by the ECM. ‘Closed’ Loop operation indicates that the ECM is controlling the fuel delivery based on the
oxygen sensors input signal. In ‘Open’ Loop operation the ECM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and bases the
amount of fuel to be delivered on other sensor inputs.
LTFT Idle/Deceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for idle and deceleration conditions.
LTFT Cruise/Acceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for cruise and acceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator (MI): This parameter displays the commanded (‘On, ‘Off’ or ‘Flashing’) state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) control circuit by the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator (MI) Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the MIL control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the MIL control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This parameter displays
‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Mass Air Flow: This parameter displays the measured quantity (g/s) of air flowing into the engine during all operating
conditions.
Mass Air Flow Sensor: This parameter displays the signal voltage from the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to the ECM.
Misfire Current Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 200 counts. This parameter displays the number of
misfires that have been detected during the last 200 cylinder firing events. The counters may normally display some
activity, but the activity should be nearly equal for all of the cylinders, and in low numbers.
Misfire History Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 65,535 counts. The misfire history counters display the total
level of misfire that has been detected on each cylinder. The misfire history counters will not update or show any activity
until a misfire DTC P0300 has become active. The misfire history counters will update every 200 cylinder firing events.
Oil Level: W hen the ECM receives information from the engine oil level switch, where the engine oil level is within
preset parameters, Tech 2 will display ‘Normal’. If not within preset parameters, the display will show ‘Low’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3520 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–242
Oil Temperature Sensor: This parameter displays the engine oil temperature in degrees C.
Power Enrichment: This parameter displays the status of the operating mode of the ECM used to increase fuel delivery
during certain acceleration conditions.
Reduced Engine Power: This parameter displays when the ECM is commanding reduced engine power due to a
throttle actuator control (TAC) system condition.
Requested Torque: This parameter displays the calculated amount torque requested of the ECM by the Transmission
Control Module (TCM).
Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the short-term correction to the fuel delivery by the
ECM in response to oxygen sensor 1 or 2. If the oxygen sensor indicates a lean air/fuel mixture, the control module will
add fuel, increasing the short term fuel trim above 0. If the oxygen sensor indicates a rich air/fuel mixture, the control
module will reduce fuel decreasing the short term fuel trim below 0.
Spark Advance: This parameter displays the amount of spark advance the ECM is commanding on the ignition control
circuits. The ECM determines the desired advance.
Starter Relay: This parameter displays the Em’s commanded state of the starter motor relay control circuit.
Starter Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the starter relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the starter relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter
displays Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’. This parameter may not change if Tech 2
is used to command the relay control circuit ON.
Start Up ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the engine coolant on start
up based on input to the ECM from the ECT sensor.
Start Up IAT (Intake Air Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the intake air at start in the air
induction system based on input to the ECM from the IAT sensor.
Time Since Engine Off: This parameter displays the amount of time (hours:minutes:seconds) that has elapsed since
the engine was last cycled OFF.
Total Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the overall fuel trim from the idle/decel cell and the
cruise/accel cell.
Total Misfire: This parameter displays the total number of cylinder firing events that the control module detected as
misfires for the last 200 crankshaft revolution sample period.
TP Sensor 1 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 1 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 1 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 1 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 2 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 2 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 2 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 2 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 1-2 Correlation (Throttle Position): This parameter displays ‘Fault’ when the ECM detects that TP sensor 1
voltage signal is not within the correct relationship to TP sensor 2. Tech 2 displays ‘Okay’ under normal operating
conditions.
Transmission Gear: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is transmitted over the
serial data circuit from the TCM.
Transmission Gear Selector Signal: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is
transmitted over the serial data circuit from the TCM.
Vehicle Speed: This parameter displays the speed of the vehicle as calculated by the TCM from information received
from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
Volumetric Efficiency: This parameter displays the volumetric efficiency of the engine as calculated by the control
module.
8.5 OBD Data
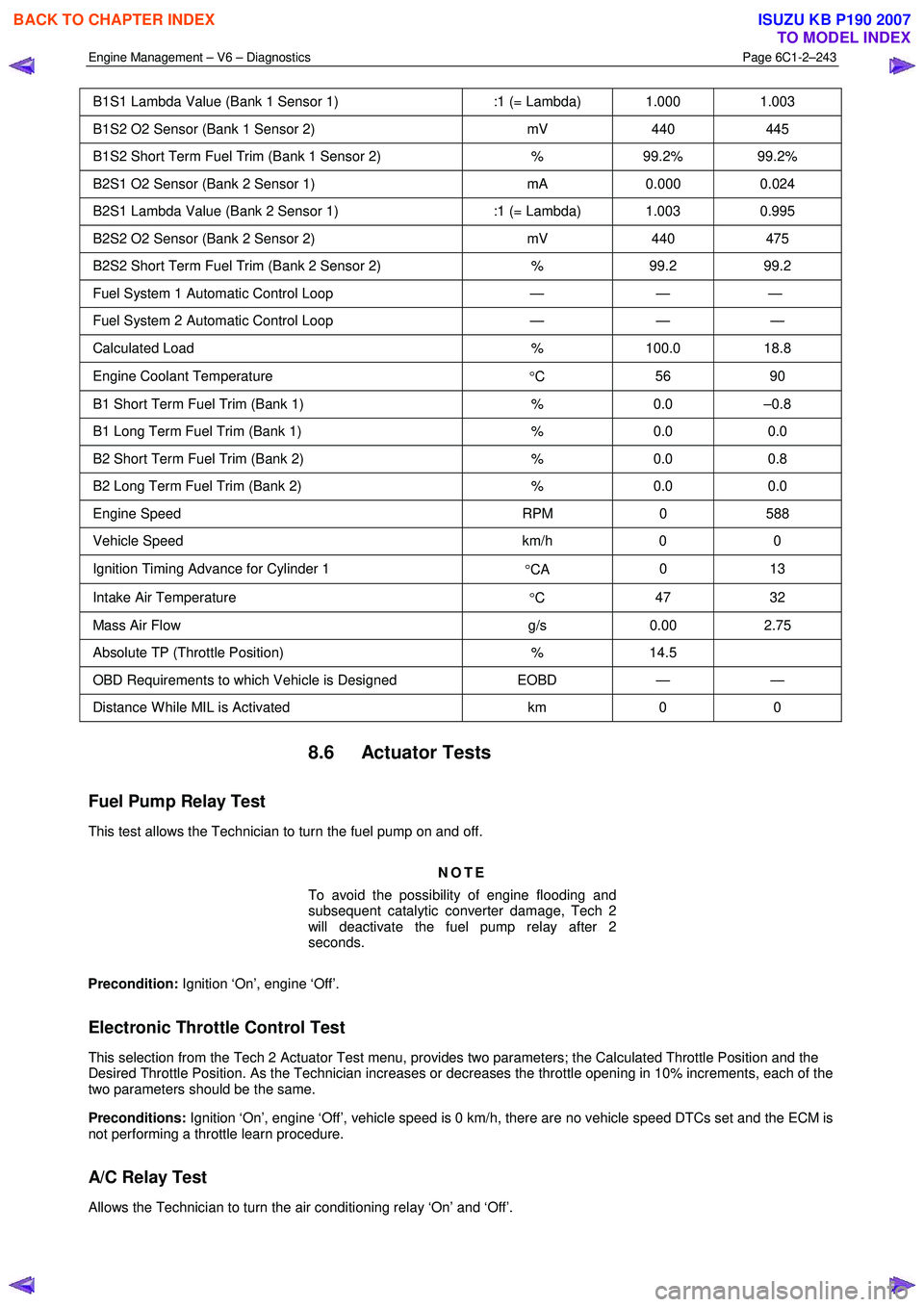
Typical Values Tech 2 Display Units Displayed
Ignition On Engine Running
B1S1 O2 Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) mA 0.008 0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3521 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–243
B1S1 Lambda Value (Bank 1 Sensor 1) :1 (= Lambda) 1.000 1.003
B1S2 O2 Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 2) mV 440 445
B1S2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1 Sensor 2) % 99.2% 99.2%
B2S1 O2 Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 1) mA 0.000 0.024
B2S1 Lambda Value (Bank 2 Sensor 1) :1 (= Lambda) 1.003 0.995
B2S2 O2 Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 2) mV 440 475
B2S2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2 Sensor 2) % 99.2 99.2
Fuel System 1 Automatic Control Loop — — —
Fuel System 2 Automatic Control Loop — — —
Calculated Load % 100.0 18.8
Engine Coolant Temperature
°C 56 90
B1 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1)
% 0.0 –0.8
B1 Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1) % 0.0 0.0
B2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2) % 0.0 0.8
B2 Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2) % 0.0 0.0
Engine Speed RPM 0 588
Vehicle Speed km/h 0 0
Ignition Timing Advance for Cylinder 1
°CA 0 13
Intake Air Temperature
°C 47 32
Mass Air Flow
g/s 0.00 2.75
Absolute TP (Throttle Position) % 14.5
OBD Requirements to which Vehicle is Designed EOBD — —
Distance W hile MIL is Activated km 0 0
8.6 Actuator Tests
Fuel Pump Relay Test
This test allows the Technician to turn the fuel pump on and off.
NOTE
To avoid the possibility of engine flooding and
subsequent catalytic converter damage, Tech 2
will deactivate the fuel pump relay after 2
seconds.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’.
Electronic Throttle Control Test
This selection from the Tech 2 Actuator Test menu, provides two parameters; the Calculated Throttle Position and the
Desired Throttle Position. As the Technician increases or decreases the throttle opening in 10% increments, each of the
two parameters should be the same.
Preconditions: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’, vehicle speed is 0 km/h, there are no vehicle speed DTCs set and the ECM is
not performing a throttle learn procedure.
A/C Relay Test
Allows the Technician to turn the air conditioning relay ‘On’ and ‘Off’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3523 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–245
Starter Motor Relay Test
The engine will crank and start during the
starter relay test.
Allows the Technician to turn the starter relay ‘On’, thereby activating the starter motor and cranking the engine.
Preconditions: Apply park brake, firmly apply foot brake, ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’, transmission in Park or Neutral.
Fuel Injector Balance
This test allows the Technician to check the fuel flow through each injector when the engine is not running. The
sequence of events are:
1 Install a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail.
2 Select ‘Fuel Injector Balance Test’, from the ‘Actuator Test’ menu on Tech 2
3 Activate the fuel injector balance test with Tech 2. This action activates the fuel pump and stabilises the fuel delivery system fuel pressure. The fuel pump is then turned off.
4 Note the stabilised fuel rail pressure.
5 W hen the pump is turned ‘Off’, the injector is activated for a pre-determined time.
6 The fuel pressure drop is then noted from the fuel pressure gauge.
NOTE
For a detailed procedure and analysis of fuel
injector condition, refer to 5.3 Fuel Injector
Balance Test.
8.7 Programming
F0: ICU Link to ECM/PIM : Should the ECM, PIM or ICU be replaced, the modules must be security linked to
each other. If this linking procedure is not performed, the vehicle will not crank nor run. For additional
information relating to Tech 2 and the linking procedure, refer to 11A – Immobiliser.
NOTE
After an ECU reset, the ignition switch must be
turned Off for at least 10 seconds and then
turned On for at least one minute, before
attempting communication between Tech 2 and
the ECU.
Preconditions: TIS approval (TIS 2000 Security Access) must be obtained, the four digit security number
entered into Tech 2 and the theft deterrent system disarmed. Then the ignition must be turned ‘On’, using a
programmed remote coded key.
F1: Reset ECU : This function erases the security link between the Engine Control Module (ECM) and the
Powertrain Interface Modules (PIM). If this procedure is performed, the engine will not crank nor run. A ICU
Link to ECM/PIM procedure will need to be performed. For additional information relating to the ICU Link to
ECM/PIM procedure, refer to 11A – Immobiliser.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3529 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–5
• Ensure the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting engine management system wiring connectors is
always followed.
• Ensure that all wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
• The engine management system wiring connectors are designed to fit only one way; there are indexing tabs and
slots on both halves of the connector. Forcing the connector into place is not necessary if it is being installed with
the correct orientation. Failure to take care to match the indexing tabs and slots correctly can cause damage to the
connector, the module, or other vehicle components or systems.
• Never touch the connector pins of any electronic component, such as an ECM, as electrostatic discharge (ESD)
damage may result.
• W hen steam or pressure cleaning engines, do not direct the cleaning nozzle at engine management system
components.
• Never subject the ECM to temperatures less than -40 ° C and greater than 125 ° C.
• Prior to disconnection or removal of any components associated with the fuel system, clean the area around any
connection points to avoid possible contamination of the fuel system.
• A depressurised fuel system contains fuel in the fuel system and fuel lines that can be spilled during service
operations. To reduce the chance of personal injury, cover the fittings with a shop towel to absorb any fuel spillage
prior to performing the service operation. Once the service operation has been completed, place the towel in an
approved container for disposal.
• To avoid accidental fuel discharge, it is advisable to disconnect the battery and remove the fuel pump relay if the
fuel line between the fuel pump and the fuel rail is to be disconnected / open for an indefinite period.
• Always tighten fasteners to the correct tightening torque, and where indicated in the service procedure, follow the
correct tightening sequence, precautions and recommendations to prevent premature failure of the fastener or
component.
• After removing components, such as the upper or lower intake manifold, front engine pipe, heated oxygen sensor,
etc. always plug any openings to prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering.
• Do not use silicone based assembly lubricants as damage to the heated oxygen sensors may result.
Use of incorrect electrical test equipment
when performing engine management service
procedures could result in incorrect results or
component damage.
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables. Use of other test equipment may either give
incorrect results or damage serviceable components, refer to, 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
• After completing the required service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct engine management
system operation.
Service Requirements
Basic Knowledge Required
A lack of basic understanding of electronics,
electrical wiring circuits and use of electrical
circuit testing tools when performing certain
service procedures could result in incorrect
results or damage to components.
In addition, a general understanding of the engine management system and its component operation is essential to
prevent misdiagnosis and component damage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3530 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–6
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing certain service
procedures could result in incorrect
diagnostic results or damage to components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section:
• Test lamp, refer to 8A Electrical – Body and Chassis for further information.
• Digital multimeter with 10 M Ω ohms impedance, refer to 8A Electrical – Body and Chassis for further information.
• Connector test adapter kit Tool No. J35616-A.
1.3 Service Operations Not Covered In This
Section
There are situations where components and/or procedures related to the powertrain management system are covered in
other Sections of the service documentation. To aid technicians in locating the necessary service procedures for these
components and/or procedures, refer to the stated references.
Air-conditioning System
For A/C pressure switch replacement procedure, refer to 2A Heater and Air-conditioning.
Electrical Components
For the following electrical system component replacement procedures, refer to the appropriate Sections as follows:
• Extended brake pedal travel switch and stop lamp switch service operations, refer to 5C Brakes.
• Fuse and relay locations, refer to 8A Electrical-Body and Chassis.
• Cruise control switch assembly service operations, refer to 8C Cruise Control – HFV6.
• Powertrain interface module PIM removal and installation procedure, refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
• Neutral start and back-up lamp switch, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
• Vehicle speed sensor service operations, refer to:
− 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing
− 7B1 Manual Transmission – V6
Fuel System
For the following fuel system component replacement procedures, refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
• Fuel system cleaning,
• Fuel system leak and pressure test,
• Fuel feed hose to fuel rail replacement,
• Fuel line quick connect fittings,
• Evaporative emission control canister,
• Fuel filter,
• Fuel hose / pipes layout,
• Fuel pump motor assembly and fuel pressure regulator assembly,
• Fuel sender assembly service operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3609 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–1
6D1-2
Starting System – V6
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property
damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................3
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES .................................................................................................... ................... 3
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 3
WARNING defined ............................................................................................................................................. 3
CAUTION defined .............................................................................................................................................. 3
NOTE defined..................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Components .......................................................................................................................................................... 4
Starting System Components ............................................................................................................................... 4
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components................................................................................... ............. 4
Solenoid Switch.................................................................................................................................................. 4
Planetary Drive Train.......................................................................................................... ................................ 4
Armature ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
Brushes .............................................................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 System Operation .................................................................................................................................................. 5
Operation ...................................................................................................................... ..................................... 5
Sequence of Operation .......................................................................................................... ............................ 6
2 Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................................7
2.1 Diagnostic General Information............................................................................................................................ 7
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required ......................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Tech 2 Data List ............................................................................................................... ...................................... 7
2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check ....................................................................................................... ............................ 7
2.4 Wiring Diagram ...................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.5 Starting System Inoperative / Malfunctioning ................................................................................... ................ 10
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................ 10
Diagnostic Table Notes ......................................................................................................... ........................... 10
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 10
Diagnostic Table – Slow Cranking, Solenoid Clicks or Chatters.................................................................. ..... 14
3 Minor Service Operations ....................................................................................................................15
3.1 Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2 Maintenance ......................................................................................................................................................... 15
Regular Checks ................................................................................................................. ................................... 15
3.3 On-Vehicle Testing ............................................................................................................. ................................. 15
Engine Compartment Relay And Fuse Panel ........................................................................................ ........... 16
Bad Connection Test ........................................................................................................................................ 16
Starter Motor Ground Test ...................................................................................................... ......................... 17
Switching Circuit Test ....................................................................................................................................... 17
Cranking Voltage Test .......................................................................................................... ............................ 18
Current Draw Test ............................................................................................................................................ 18
4 Major Service Operations ....................................................................................................................19
4.1 Starter Motor ........................................................................................................................................................ 19
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 19
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3612 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–4
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with greater
ease.
1.2 Components
Starting System Components
The main components of the starting system are:
• battery,
• wiring,
• ignition switch,
• theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor (a function of the theft deterrent system),
• park / neutral and back-up switch (on vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission),
• engine control module (ECM),
• start relay,
• solenoid switch, and
• starter motor.
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components
Solenoid Switch
The solenoid switch is used to activate the DC motor and has two windings; the pull-in winding and the hold-in winding.
The pull-in winding has heavier wire and is grounded through the DC motor winding and brushes. The hold-in winding is
grounded through the solenoid casing.
Planetary Drive Train
The planetary drive train consists of an internally toothed ring gear and three planetary gear wheels, which rotate on
sleeve bearings on the planetary drive shaft. The ring gear is keyed into the drive-end housing and is made from
high-grade polyamide with mineral additives.
W hen the starter motor operates, the armature turns the planetary gears inside the fixed planetary ring gear. This drives
the planetary shaft at a reduced speed ratio which turns the drive assembly. A fork lever in the drive-end housing forces
the drive assembly forward to engage with the flexplate / flywheel ring gear on the engine and transmit cranking torque.
An internal clutch allows the drive assembly pinion gear to rotate freely when the engine starts. This prevents the
armature from being driven at excessive speed by the engine.
Armature
The armature shaft is supported at each end by oil absorbent, sintered metal bushes; one in the commutator end shield
and one in the planetary drive shaft. The front end of the armature has a gear profile. This meshes with the three
planetary gear wheels. These in turn, mesh with the internal teeth of the ring gear.
Brushes
A brush plate supports four commutator brushes. This plate is fixed to the commutator end shield with two retaining
screws. Two negative brushes are grounded to the pole housing. The two positive brushes are insulated from the pole
housing and connected to the solenoid switch M terminal, refer to Figure 6D1-2 – 1.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3613 of 6020
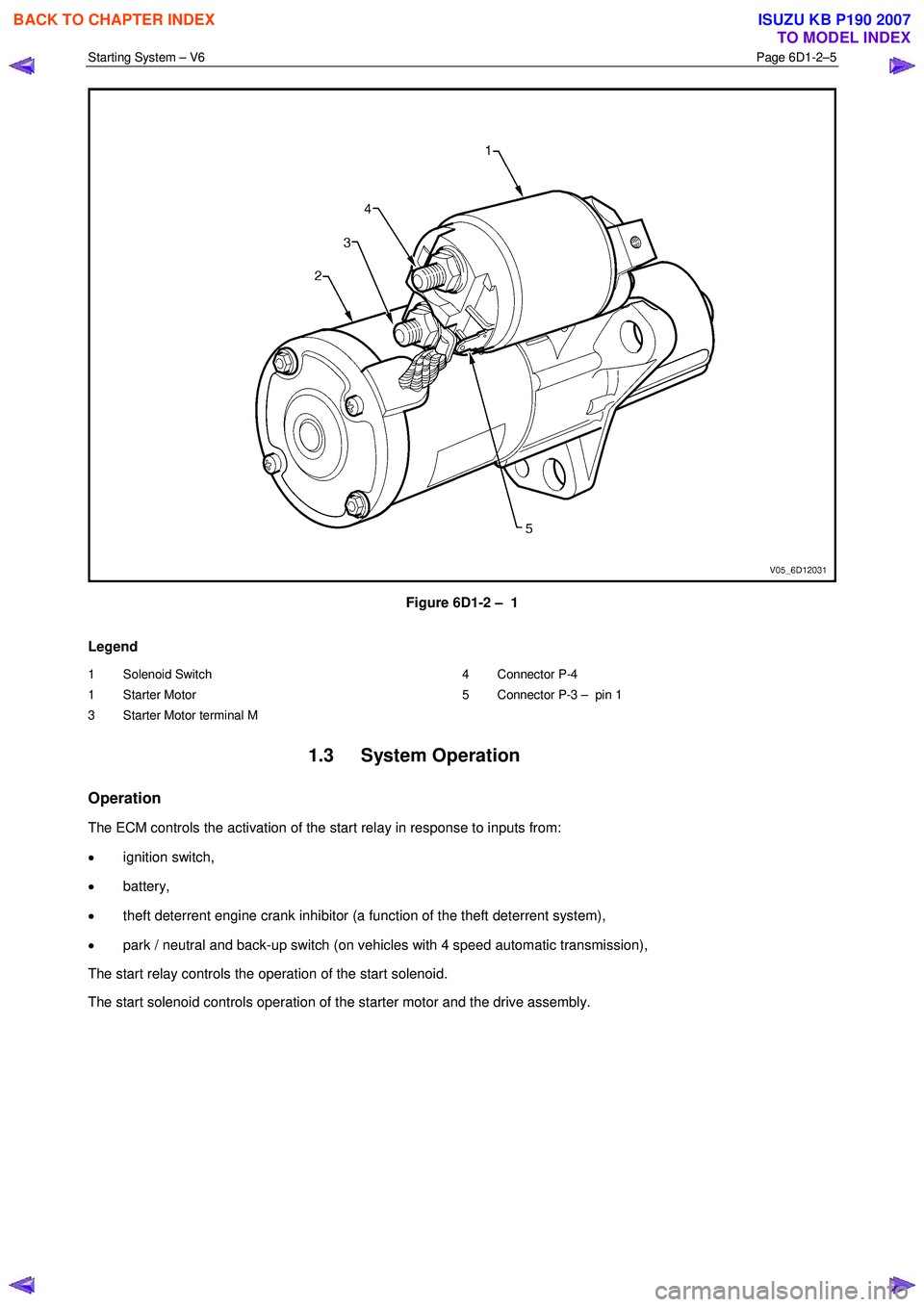
Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–5
Figure 6D1-2 – 1
Legend
1 Solenoid Switch
1 Starter Motor
3 Starter Motor terminal M 4 Connector P-4
5 Connector P-3 – pin 1
1.3 System Operation
Operation
The ECM controls the activation of the start relay in response to inputs from:
• ignition switch,
• battery,
• theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor (a function of the theft deterrent system),
• park / neutral and back-up switch (on vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission),
The start relay controls the operation of the start solenoid.
The start solenoid controls operation of the starter motor and the drive assembly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3614 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–6
Sequence of Operation
1 W hen the ignition switch is turned to the START position, a signal is also sent to the ECM to request the engine to
crank.
• For automatic vehicles the transmission must be in either park (P) or neutral (N) for the ECM to allow
cranking to commence.
• The ECM will only allow cranking if the battery voltage is above the minimum battery voltage threshold value,
refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for further information.
2 The ECM operates the start relay which provides power to the pull-in winding of the start solenoid.
3 Current flow to the pull-in winding develops powerful magnetism which pulls in the solenoid switch plunger.
4 The plunger closes the switch contacts connecting battery voltage to the DC motor and pivots the fork lever to engage the drive assembly to the flexplate / flywheel ring gear. Closing the solenoid switch contacts deactivates the
pull-in winding, the hold-in winding remains active.
5 W ith the solenoid switch contacts closed, current flows from the battery through the DC motor, which rotates the armature at high speed and provides cranking torque.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007