ECU ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 962 of 6020
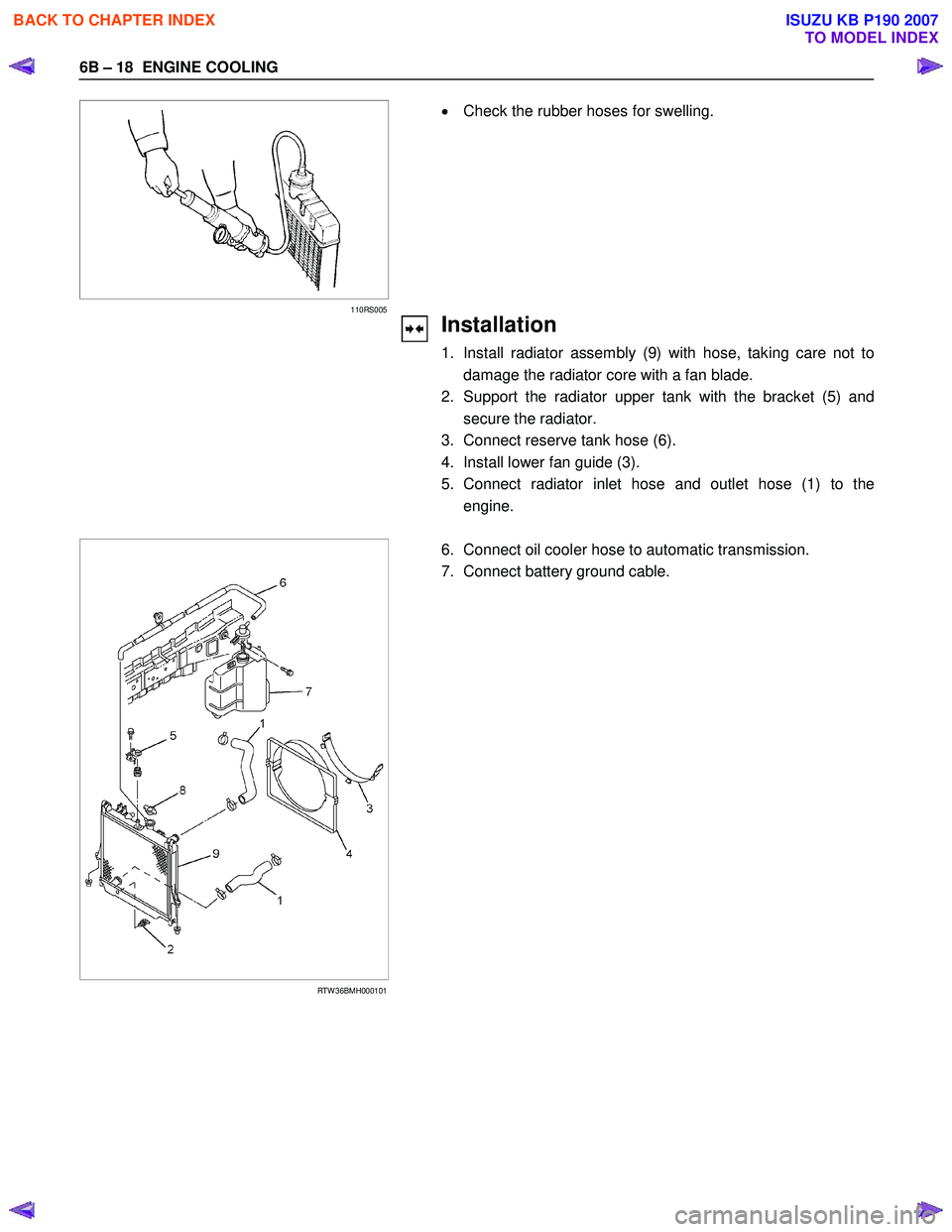
6B – 18 ENGINE COOLING
110RS005
• Check the rubber hoses for swelling.
Installation
1. Install radiator assembly (9) with hose, taking care not to damage the radiator core with a fan blade.
2. Support the radiator upper tank with the bracket (5) and secure the radiator.
3. Connect reserve tank hose (6).
4. Install lower fan guide (3).
5. Connect radiator inlet hose and outlet hose (1) to the engine.
RTW 36BMH000101
6. Connect oil cooler hose to automatic transmission.
7. Connect battery ground cable.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 979 of 6020

FUEL SYSTEM 6C – 15
140R100037
2. For removal of the quick connector, hold the quick
connector in one hand, and pull out the connector with the
other hand while pressing the square relieve button of the
connector, as illustrated.
NOTE: Do not use tools of any kind. Only use bare hands
when disconnecting the connector. Use a lubricant (light oil)
and/or push and pull the connector until the pipe is
disconnected.
140R100028
Cover the connectors that was removed with a plastic bag,
to prevent dust or rain water from entering.
140R100036
Reuse of Quick–Connector
• Replace the port and connector if scratch, dent or crack is
found.
• Remove any dirt build up on the port when installing the
connector. Replace the connector, if there is any forms o
f
rust, dent, scratch.
• After cleaning the port, insert it straight into the connecto
r
until it clicks. After it clicks, try pulling at 49N (5kgf) it out to
make sure that it is not drawn and is securely locked.
Assembling Advice
By applying engine oil or light oil to the pipe, port makes pipe
assembly easier. The pipe assembly should take place
immediately after applying oil (to prevent dust from sticking to
the pipe surface – which may decrease sealing ability). Test/Inspection After Assembling
1. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Start the engine and observe the engine idle speed. The presence of dirt in the fuel system may affect the fuel
injection system.
3. Check for fuel leakage from the connector.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 995 of 6020
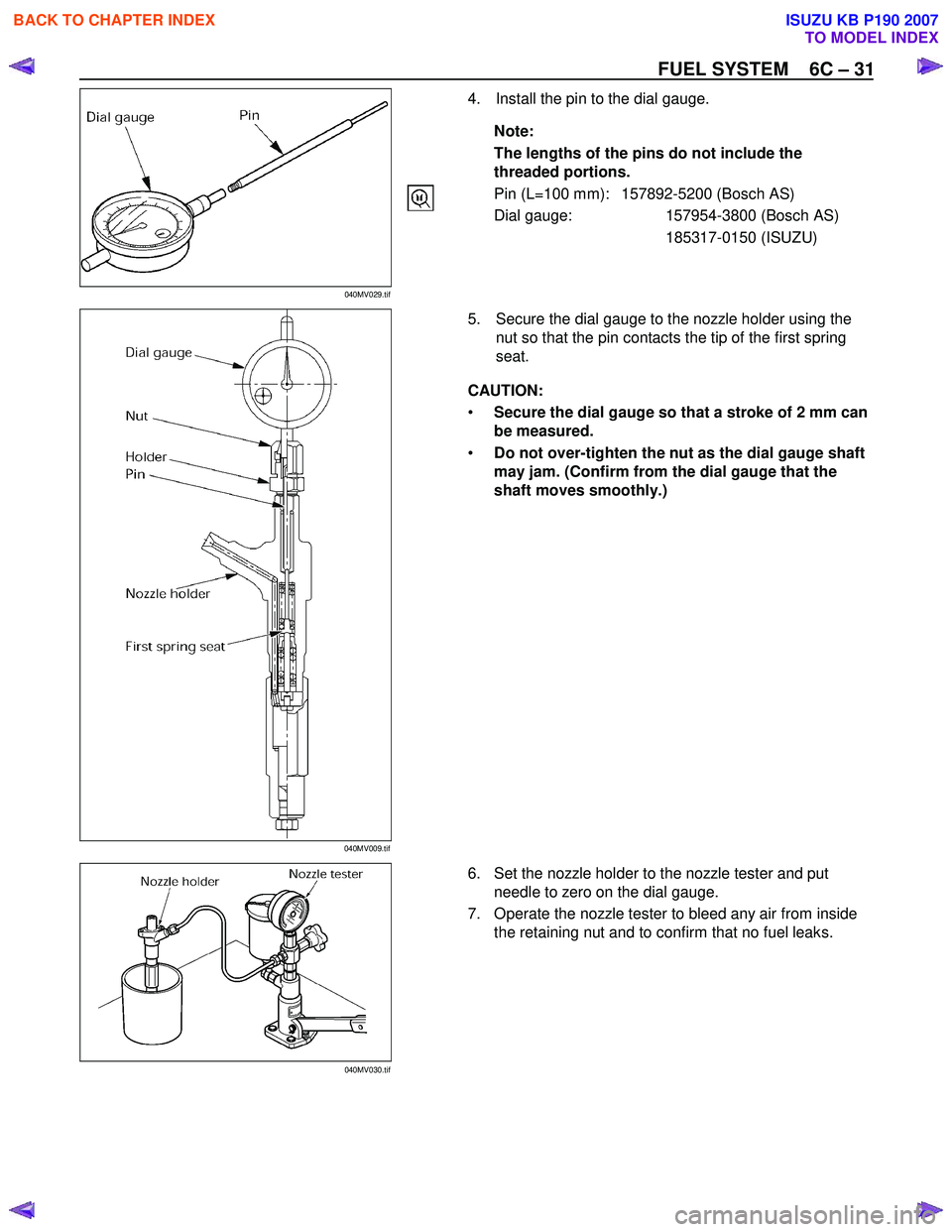
FUEL SYSTEM 6C – 31
4. Install the pin to the dial gauge.
Note:
The lengths of the pins do not include the threaded portions.
Pin (L=100 mm): 157892-5200 (Bosch AS)
Dial gauge: 157954-3800 (Bosch AS)
185317-0150 (ISUZU)
5. Secure the dial gauge to the nozzle holder using the nut so that the pin contacts the tip of the first spring
seat.
CAUTION:
• Secure the dial gauge so that a stroke of 2 mm can
be measured.
• Do not over-tighten the nut as the dial gauge shaft
may jam. (Confirm from the dial gauge that the
shaft moves smoothly.)
6. Set the nozzle holder to the nozzle tester and put needle to zero on the dial gauge.
7. Operate the nozzle tester to bleed any air from inside the retaining nut and to confirm that no fuel leaks.
040MV029.tif
040MV009.tif 040MV030.tif
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1096 of 6020
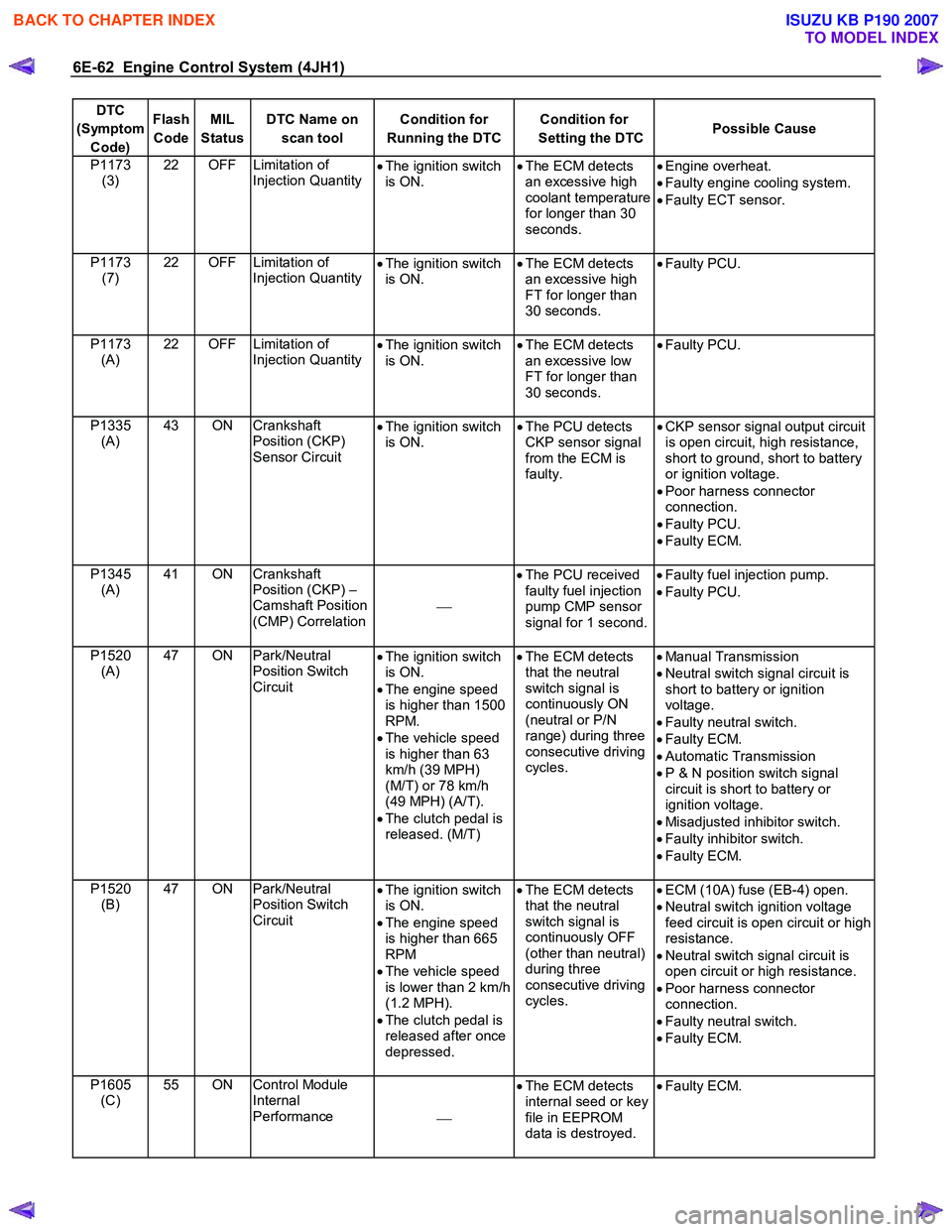
6E-62 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC
(Symptom Code) Flash
Code MIL
Status DTC Name on
scan tool Condition for
Running the DTC Condition for
Setting the DTC Possible Cause
P1173
(3) 22 OFF Limitation of
Injection Quantity •
The ignition switch
is ON. •
The ECM detects
an excessive high
coolant temperature
for longer than 30
seconds.
•
Engine overheat.
• Faulty engine cooling system.
• Faulty ECT sensor.
P1173 (7) 22 OFF Limitation of
Injection Quantity
•
The ignition switch
is ON. •
The ECM detects
an excessive high
FT for longer than
30 seconds.
•
Faulty PCU.
P1173 (A) 22 OFF Limitation of
Injection Quantity
•
The ignition switch
is ON. •
The ECM detects
an excessive low
FT for longer than
30 seconds.
•
Faulty PCU.
P1335 (A) 43 ON Crankshaft
Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit •
The ignition switch
is ON. •
The PCU detects
CKP sensor signal
from the ECM is
faulty.
•
CKP sensor signal output circuit
is open circuit, high resistance,
short to ground, short to battery
or ignition voltage.
• Poor harness connector
connection.
• Faulty PCU.
• Faulty ECM.
P1345 (A) 41 ON Crankshaft
Position (CKP) –
Camshaft Position
(CMP) Correlation
•
The PCU received
faulty fuel injection
pump CMP sensor
signal for 1 second.
•
Faulty fuel injection pump.
• Faulty PCU.
P1520 (A) 47 ON Park/Neutral
Position Switch
Circuit •
The ignition switch
is ON.
• The engine speed
is higher than 1500
RPM.
• The vehicle speed
is higher than 63
km/h (39 MPH)
(M/T) or 78 km/h
(49 MPH) (A/T).
• The clutch pedal is
released. (M/T)
•
The ECM detects
that the neutral
switch signal is
continuously ON
(neutral or P/N
range) during three
consecutive driving
cycles.
•
Manual Transmission
• Neutral switch signal circuit is
short to battery or ignition
voltage.
• Faulty neutral switch.
• Faulty ECM.
• Automatic Transmission
• P & N position switch signal
circuit is short to battery or
ignition voltage.
• Misadjusted inhibitor switch.
• Faulty inhibitor switch.
• Faulty ECM.
P1520 (B) 47 ON Park/Neutral
Position Switch
Circuit •
The ignition switch
is ON.
• The engine speed
is higher than 665
RPM
• The vehicle speed
is lower than 2 km/h
(1.2 MPH).
• The clutch pedal is
released after once
depressed.
•
The ECM detects
that the neutral
switch signal is
continuously OFF
(other than neutral)
during three
consecutive driving
cycles.
•
ECM (10A) fuse (EB-4) open.
• Neutral switch ignition voltage
feed circuit is open circuit or high
resistance.
• Neutral switch signal circuit is
open circuit or high resistance.
• Poor harness connector
connection.
• Faulty neutral switch.
• Faulty ECM.
P1605 (C) 55 ON Control Module
Internal
Performance •
The ECM detects
internal seed or key
file in EEPROM
data is destroyed.
•
Faulty ECM.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1097 of 6020
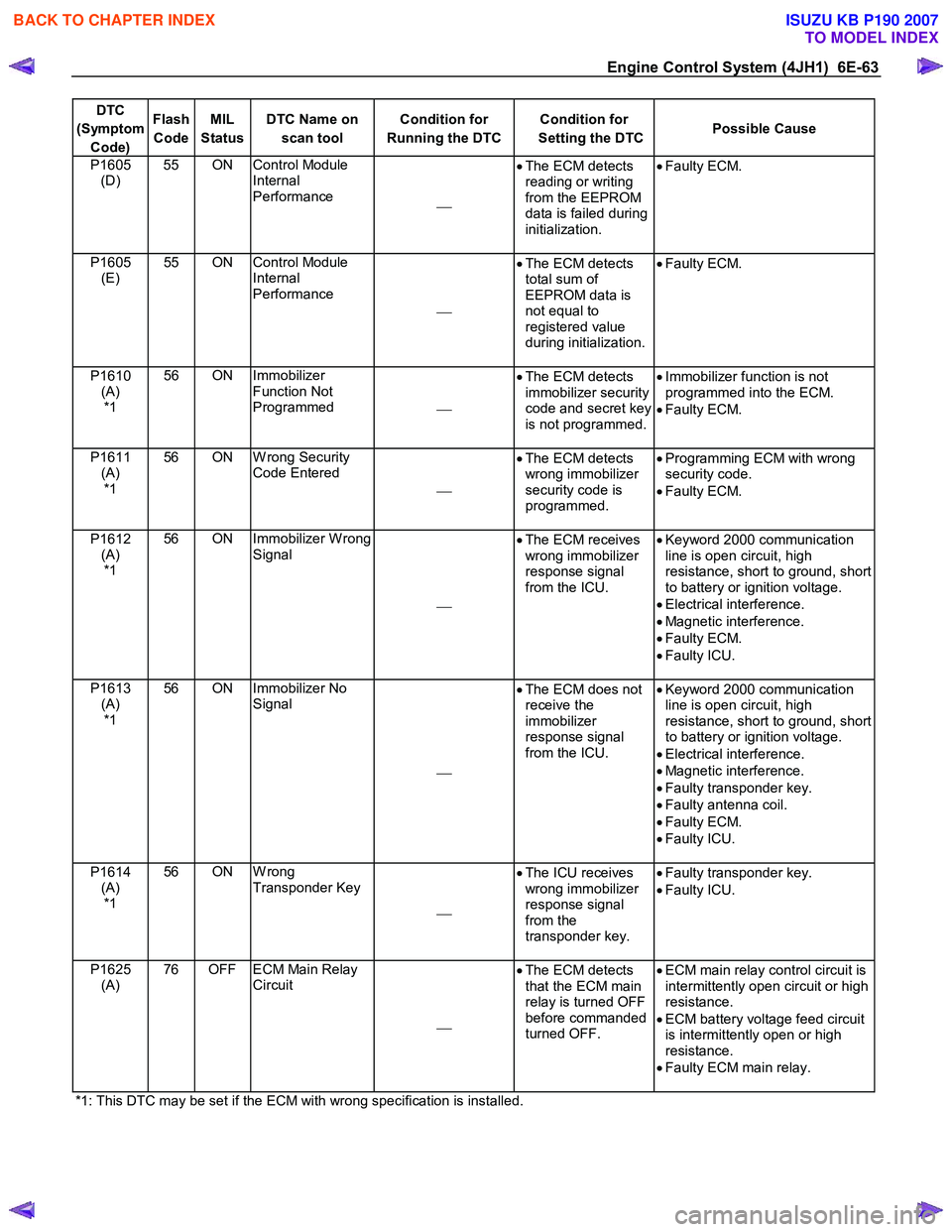
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-63
DTC
(Symptom Code) Flash
Code MIL
Status DTC Name on
scan tool Condition for
Running the DTC Condition for
Setting the DTC Possible Cause
P1605
(D) 55 ON Control Module
Internal
Performance •
The ECM detects
reading or writing
from the EEPROM
data is failed during
initialization.
•
Faulty ECM.
P1605
(E) 55 ON Control Module
Internal
Performance
•
The ECM detects
total sum of
EEPROM data is
not equal to
registered value
during initialization.
•
Faulty ECM.
P1610
(A) *1 56 ON Immobilizer
Function Not
Programmed •
The ECM detects
immobilizer security
code and secret key
is not programmed.
•
Immobilizer function is not
programmed into the ECM.
• Faulty ECM.
P1611 (A) *1 56 ON W rong Security
Code Entered
•
The ECM detects
wrong immobilizer
security code is
programmed.
•
Programming ECM with wrong
security code.
• Faulty ECM.
P1612 (A) *1 56 ON Immobilizer W rong
Signal
•
The ECM receives
wrong immobilizer
response signal
from the ICU.
•
Keyword 2000 communication
line is open circuit, high
resistance, short to ground, short
to battery or ignition voltage.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty ECM.
• Faulty ICU.
P1613 (A) *1 56 ON Immobilizer No
Signal
•
The ECM does not
receive the
immobilizer
response signal
from the ICU.
•
Keyword 2000 communication
line is open circuit, high
resistance, short to ground, short
to battery or ignition voltage.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty transponder key.
• Faulty antenna coil.
• Faulty ECM.
• Faulty ICU.
P1614 (A) *1 56 ON W rong
Transponder Key
•
The ICU receives
wrong immobilizer
response signal
from the
transponder key.
•
Faulty transponder key.
• Faulty ICU.
P1625 (A) 76 OFF ECM Main Relay
Circuit
•
The ECM detects
that the ECM main
relay is turned OFF
before commanded
turned OFF.
•
ECM main relay control circuit is
intermittently open circuit or high
resistance.
• ECM battery voltage feed circuit
is intermittently open or high
resistance.
• Faulty ECM main relay.
*1: This DTC may be set if the ECM with wrong specification is installed.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1100 of 6020

6E-66 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 7) (Flash Code 65)
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that
measures the amount of air that enters the engine. It is
fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. A small
quantity of air that enters the engine indicates
deceleration or idle speed. A large quantity of air that
enters the engine indicates acceleration or a high load
condition. The MAF sensor has the following circuits.
• Ignition voltage circuit
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• MAF sensor signal circuit
The engine control module (ECM) provides 5 volts
reference voltage through the reference circuit to the
MAF sensor. The ECM monitors the voltage on the 5
volts reference circuit. If the ECM detects an
excessively high MAF sensor 5 volts reference voltage,
this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects that the MAF sensor 5 volts
reference circuit voltage is more than 5.2 volts fo
r
0.5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM uses a MAF substitution of 1600 mg/strk
for engine control.
• The ECM uses an EGR solenoid valve control
substitution of 10%.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Notice: • The MAF Sensor parameter on the scan tool will
only update with engine running.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
3. If the MAF sensor 5 volts reference circuit between
the ECM and the sensor is normal, the sensor signal
voltage low DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) will set.
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 7) (Flash Code 65)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor harness connector.
3. Start the engine and let idle for 30 seconds.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Does DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) set, but not
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 7)?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1102 of 6020

6E-68 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 9) (Flash Code 65)
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that
measures the amount of air that enters the engine. It is
fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. A small
quantity of air that enters the engine indicates
deceleration or idle speed. A large quantity of air that
enters the engine indicates acceleration or a high load
condition. The MAF sensor has the following circuits.
• Ignition voltage circuit
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• MAF sensor signal circuit
The engine control module (ECM) provides 5 volts
reference voltage through the reference circuit to the
MAF sensor. The ECM monitors the voltage on the 5
volts reference circuit. If the ECM detects an
excessively low MAF sensor 5 volts reference voltage,
this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects that the MAF sensor 5 volts
reference circuit voltage is less than 4.6 volts fo
r
0.5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
•
The ECM uses a MAF substitution of 1600 mg/strk
for engine control.
• The ECM uses an EGR solenoid valve control
substitution of 10%.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Notice: • The MAF Sensor parameter on the scan tool will
only update with engine running.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
3. If the MAF sensor 5 volts reference circuit between
the ECM and the sensor is normal, the sensor signal
voltage low DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) will set.
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 9) (Flash Code 65)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor harness connector.
3. Start the engine and let idle for 30 seconds.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Does DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) set, but not
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code 9)?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 1. Test the 5 volts reference circuit between the engine control module (ECM) (pin 83 of C-57
connector) and the MAF sensor (pin 4 of C-116
connector) for the following conditions: • A short to ground
• A short to the low reference circuit
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1104 of 6020

6E-70 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) (Flash Code 65)
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that
measures the amount of air that enters the engine. It is
fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. A small
quantity of air that enters the engine indicates
deceleration or idle speed. A large quantity of air that
enters the engine indicates acceleration or a high load
condition. The MAF sensor has the following circuits.
• Ignition voltage circuit
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• MAF sensor signal circuit
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the MAF
sensor signal for voltage outside the normal range o
f
the MAF sensor. If the ECM detects an excessively low
MAF sensor signal voltage, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM calculated MAF is lower than -18.6 kg/h
for 5 seconds. This indicates the ECM detects that
the MAF sensor signal voltage is smaller than a
predetermined range during engine run.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM uses a MAF substitution of 1600 mg/strk
for engine control.
• The ECM uses an EGR solenoid valve control
substitution of 10%.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL that the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Notice: • W rong direction of MAF sensor installation will
cause this DTC to set.
• Contaminated or restricted MAF sensor will cause
this DTC to set.
• The MAF Sensor parameter on the scan tool will
only update with engine running.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
7. If the MAF sensor signal circuit between the ECM
and the sensor is short to ground or any low reference
circuits, the sensor 5 volts reference voltage low DTC
P0100 (Symptom Code 9) will set.
8. If the MAF sensor signal circuit between the ECM
and the sensor is normal, the sensor signal voltage high
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code C) will set.
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) (Flash Code 65)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine and let idle for 30 seconds.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Inspect the ECM (10A) fuse (EB-4) in the engine room fuse block.
Is the ECM (10A) fuse (EB-4) open?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Replace the ECM (10A) fuse (EB-4). If the fuse continues to open, repair the short to ground on one
of the circuits that is fed by the ECM (10A) fuse (EB-
4) or replace the shorted attached component fed by
the ECM (10A) fuse (EB-4).
Did you complete the repair?
Go to Step 17
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1107 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-73
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code C) (Flash Code 65)
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that
measures the amount of air that enters the engine. It is
fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. A small
quantity of air that enters the engine indicates
deceleration or idle speed.
A large quantity of air that
enters the engine indicates acceleration or a high load
condition. The MAF sensor has the following circuits.
• Ignition voltage circuit
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• MAF sensor signal circuit
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the MAF
sensor signal for voltage outside the normal range o
f
the MAF sensor. If the ECM detects an excessively high
MAF sensor signal voltage, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM calculated MAF is higher than 984 kg/h
for 10 seconds. This indicates the ECM detects
that the MAF sensor signal voltage is higher than a
predetermined range during engine run.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM uses a MAF substitution of 1600 mg/strk
for engine control.
• The ECM uses an EGR solenoid valve control
substitution of 10%.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Notice: • The MAF Sensor parameter on the scan tool will
only update with engine running.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
3. If the MAF sensor signal circuit between the ECM
and the sensor is normal, the sensor signal voltage lo
w
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) will set.
DTC P0100
(Symptom Code C) (Flash Code 65)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine and let idle for 30 seconds.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor harness connector.
3. Start the engine and let idle for 30 seconds.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Does DTC P0100 (Symptom Code B) set, but not
DTC P0100 (Symptom Code C)?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1109 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-75
DTC P0105 (Symptom Code 1) (Flash Code 34)
Circuit Description
The vacuum pressure sensor is installed to the
turbocharger wastegate control hose and it detects the
regulated vacuum pressure to the turbocharge
r
wastegate valve. The vacuum pressure sensor is a
transducer that varies voltage according to changes in
the vacuum pressure inside the vacuum hose. The
vacuum pressure sensor has the following circuits.
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• Vacuum pressure sensor signal circuit
The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to
the vacuum pressure sensor on the 5 volts reference
circuit. The ECM also provides a ground on the lo
w
reference circuit. The vacuum pressure sensor provides
a signal to the ECM on the vacuum pressure signal
circuit which is relative to the vacuum pressure changes
in the turbocharger wastegate valve control hose. The
ECM should detect a low signal voltage at a high
vacuum pressure and high signal voltage at a lo
w
vacuum pressure. The ECM monitors the vacuum
pressure sensor signal for voltage outside the normal
range of the vacuum pressure sensor. If the ECM
detects an excessively high vacuum pressure senso
r
signal voltage, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects that the vacuum pressure
sensor signal voltage is more than 4.4 volts for 3
seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM uses a barometric pressure of 615 hPa
for turbocharger wastegate valve control.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
3. If the vacuum pressure sensor signal circuit between
the ECM and the sensor is normal, the sensor signal
voltage low DTC P0105 (Symptom Code 2) will set.
DTC P0105 (Symptom Code 1) (Flash Code 34)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the vacuum pressure sensor harness connector.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Does DTC P0105 (Symptom Code 2) set, but not
DTC P0105 (Symptom Code 1)?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Connect a test lamp between the low reference circuit of the vacuum pressure sensor harness
(pin 2 of C-124 connector) and battery voltage.
Does the test lamp illuminate?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007