coolant level ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2109 of 6020
ENGINE COOLING 6B-5
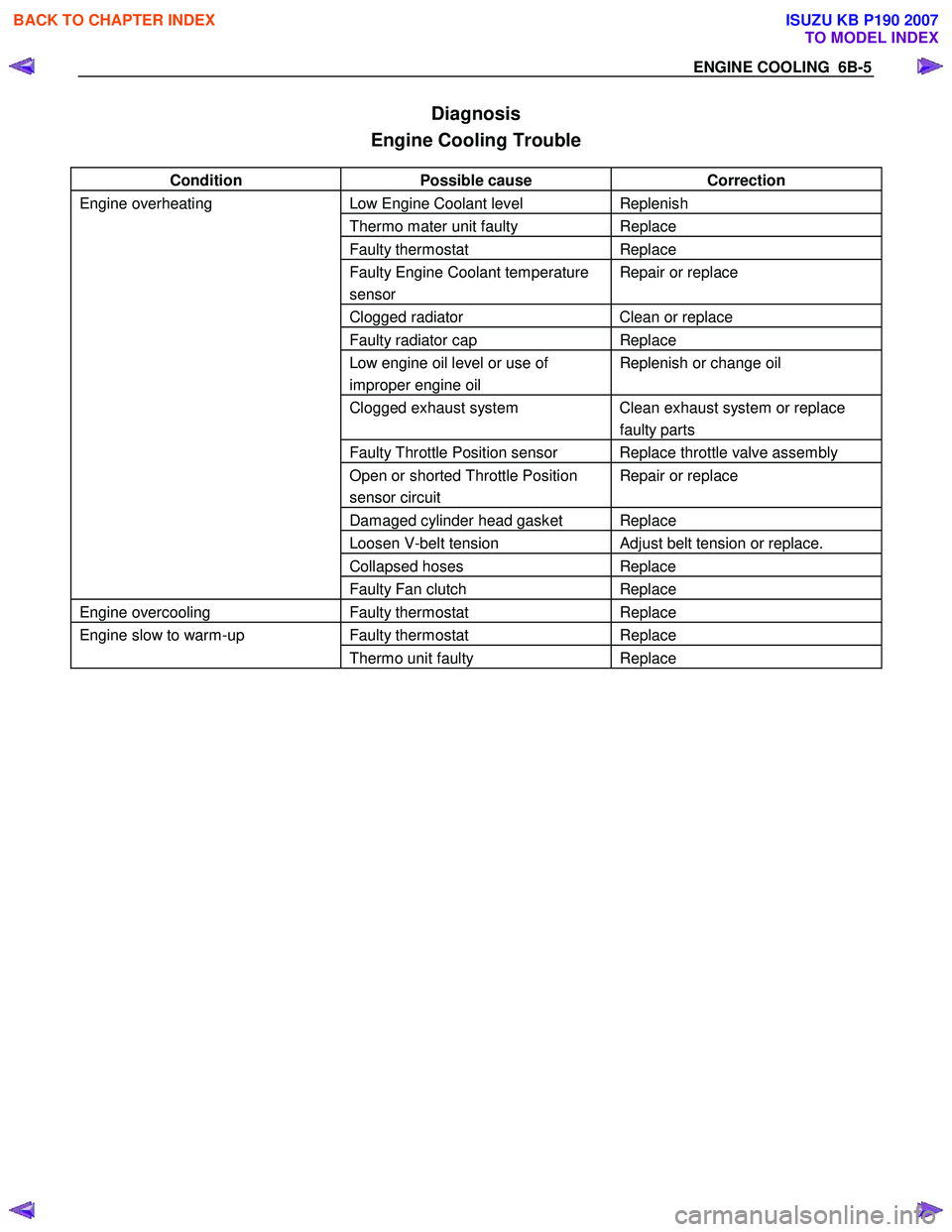
Diagnosis
Engine Cooling Trouble
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine overheating Low Engine Coolant level Replenish
Thermo mater unit faulty Replace
Faulty thermostat Replace
Faulty Engine Coolant temperature
sensor Repair or replace
Clogged radiator Clean or replace
Faulty radiator cap Replace
Low engine oil level or use of
improper engine oil Replenish or change oil
Clogged exhaust system Clean exhaust system or replace
faulty parts
Faulty Throttle Position sensor Replace throttle valve assembly
Open or shorted Throttle Position
sensor circuit Repair or replace
Damaged cylinder head gasket Replace
Loosen V-belt tension Adjust belt tension or replace.
Collapsed hoses Replace
Faulty Fan clutch Replace
Engine overcooling Faulty thermostat Replace
Engine slow to warm-up Faulty thermostat Replace
Thermo unit faulty Replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2110 of 6020

6B-6 ENGINE COOLING
Draining and Refilling Cooling
System
Before draining the cooling system, inspect the system and
perform any necessary service to ensure that it is clean, does
not leak and is in proper working order. The engine coolant
level should be between the "MIN" and "MAX" lines of reserve
tank when the engine is cold. If low, check for leakage and add
engine coolant up to the "MAX" line. There should not be any
excessive deposit of rust or scales around the radiator cap or
radiator filler hole, and the engine coolant should also be free
from oil.
Replace the engine coolant if excessively dirty.
1. Completely drain the cooling system by opening the drain
plug at the bottom of the radiator.
2. Remove the radiator cap.
WARNING: TO AVOID THE DANGER OF BEING BURNED,
DO NOT REMOVE THE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE AND
RADIATOR ARE STILL HOT. SCALDING FLUID AND
STEAM CAN BE BLOWN OUT UNDER PRESSURE.
3. Disconnect all hoses from the engine coolant reserve tank.
Scrub and clean the inside of the reserve tank with soap and water. Flush it well with clean water, then drain it. Install
the reserve tank and hoses.
4. Refill the cooling system with the engine coolant using a solution that is at least 50 percent antifreeze.
5. Fill the radiator to the base of the filler neck.
Fill the engine coolant reserve tank to "MAX" line when the engine is cold.
6. Block the drive wheels and firmly apply the parking brake and place the shift lever in the "NEUTRAL" position.
7. Remove the radiator cap. Start the engine and warm it up at 2,500 - 3,000 rpm for about 30 minutes.
8. W hen the air comes out from the radiator filler neck and the engine coolant level has gone down, replenish with the
engine coolant. Repeat this procedure until the engine
coolant level does not go down. Then stop the engine and
install the radiator cap. Let the engine cool down.
9. After the engine has cooled, replenish with engine coolant up to the "MAX" line of the reserve tank.
10. Start the engine. W ith the engine running at 3,000 rpm, make sure there is no running water sound from the heate
r
core (behind the center console).
11. If the running water sound is heard, repeat steps 8 to 10.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2117 of 6020

ENGINE COOLING 6B-13
Installation
1. Install radiator assembly, taking care not to damage theradiator core.
2. Install the radiator assembly.
3. Connect reserve tank hose.
4. Connect radiator inlet hose and outlet hose.
5. Pour engine coolant up to filler neck of radiator, and up to MAX mark of reserve tank.
Important operation (in case of 100% engine coolant change) procedure for filling with engine coolant.
• Remove radiator cap.
• Fill with engine coolant to the radiator filler neck.
• Fill with EC to the "MAX" line on the reservoir tank.
• Start the engine with the radiator cap removed and bring to
operating temperature by running engine at 2,500 - 3,000
rpm for 30 minutes.
• By engine coolant temperature gauge reading make sure
that the thermostat is open.
• If air bubbles come up to the radiator filler neck, replenish
with engine coolant. Repeat until the EC level does not drop
any further. Install the radiator cap and stop the engine.
• Replenish engine coolant to the "MAX" line on the reservoi
r
tank and leave as it is until the engine gets cool.
•
After the engine gets cool, start the engine and make sure
there is no water running noise heard from the heater core
while the engine runs at 3000 rpm.
• Should water running noise be heard, repeat the same
procedure from the beginning.
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Cooling system Engine Coolant forced circulation
Radiator Tube type corrugated (2 tube in row)
Heat radiation capacity 66.3 kcal/h
Heat radiation area 7.08 m2
Radiator front area 028 m2
Radiator dry (weight) 3.1 kg
Radiator cap valve opening pressure 93.3 – 122.7 kpa
Engine coolant capacity 3.4L
Engine coolant pump Centrifugal type
Thermostat Bypass type
Engine coolant total capacity 8lit
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2227 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–57
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose
The basic evaporative emission control system used on
the charcoal canister storage method. The method
transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated
carbon (charcoal) storage devise to hold the vapors
when the vehicle is not operating.
The canister is located on the rear axle housing by the
frame cross-member.
When the engine is running, the fuel vapor is purged
from the carbon element by intake air flow and
consumed in the normal combustion process.
EVAP Emission Control System Operation
The EVAP canister purge is controlled by a solenoid
valve that allows the manifold vacuum to purge the
canister. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a
ground to energize the solenoid valve (purge on). The
EVAP purge solenoid control is pulse-width modulated
(PWM) (turned on and off several times a second). The
duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine
operating conditions including load, throttle position,
coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty
cycle is calculated by the ECM. the output is
commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met. These conditions are:
• The engine is fully warmed up.
• The engine has been running for a specified time.
• The IAT reading is above 10°C (50°F).
• Purge/Vacuum Hoses. Made of rubber compounds, these hoses route the gasoline fumes from their
sources to the canister and from the canister to the
intake air flow.
• EVAP Canister. Mounted on a bracket ahead of the fuel tank, the canister stores fuel vapors until the
ECM determined that engine conditions are right for
them to be removed and burned.
Poor idle, stalling and Poor driveability can be caused
by:
• A malfunctioning purge solenoid.
• A damaged canister.
• Hoses that are split, cracked, or not connected properly.
System Fault Detection
The EVAP leak detection strategy is based on applying
vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring vacuum
decay. At an appropriate time, the EVAP purge solenoid
is turned “ON,” allowing the engine vacuum to draw a
small vacuum on the entire evaporative emission
system.
After the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the
EVAP purge solenoid is turned “OFF,” sealing the
system. A leak is detected by monitoring for a decrease
in vacuum level over a given time period, all other
variables remaining constant.
If the desired vacuum level cannot be achieved in the
test described above, a large leak or a faulty EVAP
purge control solenoid valve is indicated.
Leaks can be caused by the following conditions:
• Missing or faulty fuel cap
• Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked EVAP purge line
• Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked fuel tank vapor line
• Disconnected or faulty EVAP purge control solenoid valve
• Open ignition feed circuit to the purge solenoid
(1) Purge Solenoid Valve
(2) From Canistor to Purge Solenoid
(3) From Purge Solenoid to Intake
(1) Canistor
(2) Air Separator
132
12
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2228 of 6020

6E–58 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
• Damaged EVAP canister
• Leaking fuel sender assembly O-ring
• Leaking fuel tank or fuel filler neck
The ECM supplies a ground to energize the purge
control solenoid valve (purge “ON” ). The EVAP purge
control is turned “ON” and “OFF,” several times a
second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by
engine operating conditions including load, throttle
position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature.
The duty cycle is calculated by the ECM and the output
is commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met.
The system checks for conditions that cause the EVAP
system to purge continuously by commanding the EVAP
purge solenoid “OFF”, EVAP purge solenoid duty ratio
“0%”. If fuel tank vacuum level increases during the test,
a continuous purge flow condition is indicated. This can
be caused by the following conditions:
• EVAP purge solenoid leaking
• EVAP purge and engine vacuum lines switched at the EVAP purge control solenoid valve
• EVAP purge control solenoid valve driver circuit grounded
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2344 of 6020

6E–174 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0325 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) MODULE CIRCUIT
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation. The knock sensor produced an AC voltage
signal. The knock sensor sends this signal to the ECM.
The amplitude and the frequency of the AC voltage
signal depends upon the knock level being detected.
The ECM will then retard the spark timing based on the signals from the Knock Sensor.Diagnostic Aids
Correct any abnormal engine noise before using the
diagnostic table.
Check for an open circuit.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325 Knock Sensor Module Circuit
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0325 B Knock Sensor Module Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor filter module integrated cir- cuit malfunction. ECM retards ignition timing 4 deg. C
.
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2347 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–177
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The ECM uses the Knock Sensor (KS) in order to detect
engine detonation. This allows the ECM to retard the
Ignition Control (IC) spark timing based on the KS signal
the ECM receives. The knock sensors produce an AC
signal that rides on the 1.3 volts DC. The signal’s
amplitude and frequency are dependent upon the
amount of the knock being experienced.
The ECM determines whether the knock is occurring by
comparing the signal level on the KS circuit with a
voltage level on the noise channel. The normal engine
noise varies depending on the engine speed and load.
Then the ECM determines that an abnormally high
noise channel voltage level is being experienced, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0327 sets.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
A poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the knock
sensor and the ECM connectors for: , broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals.
• Backed out terminals
• Broken locks
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals
Also, check the wiring harness for: shorts to ground,
shorts to battery positive, and open circuits.
• A misrouted harness. Inspect the knock sensor harness in order to ensure that it is not routed too
close to high voltage wires such as spark plug leads.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0327 A Knock Sensor Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor harness short to ground or short to voltage circuit. ECM retards ignition timing 4 deg. C
.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2426 of 6020
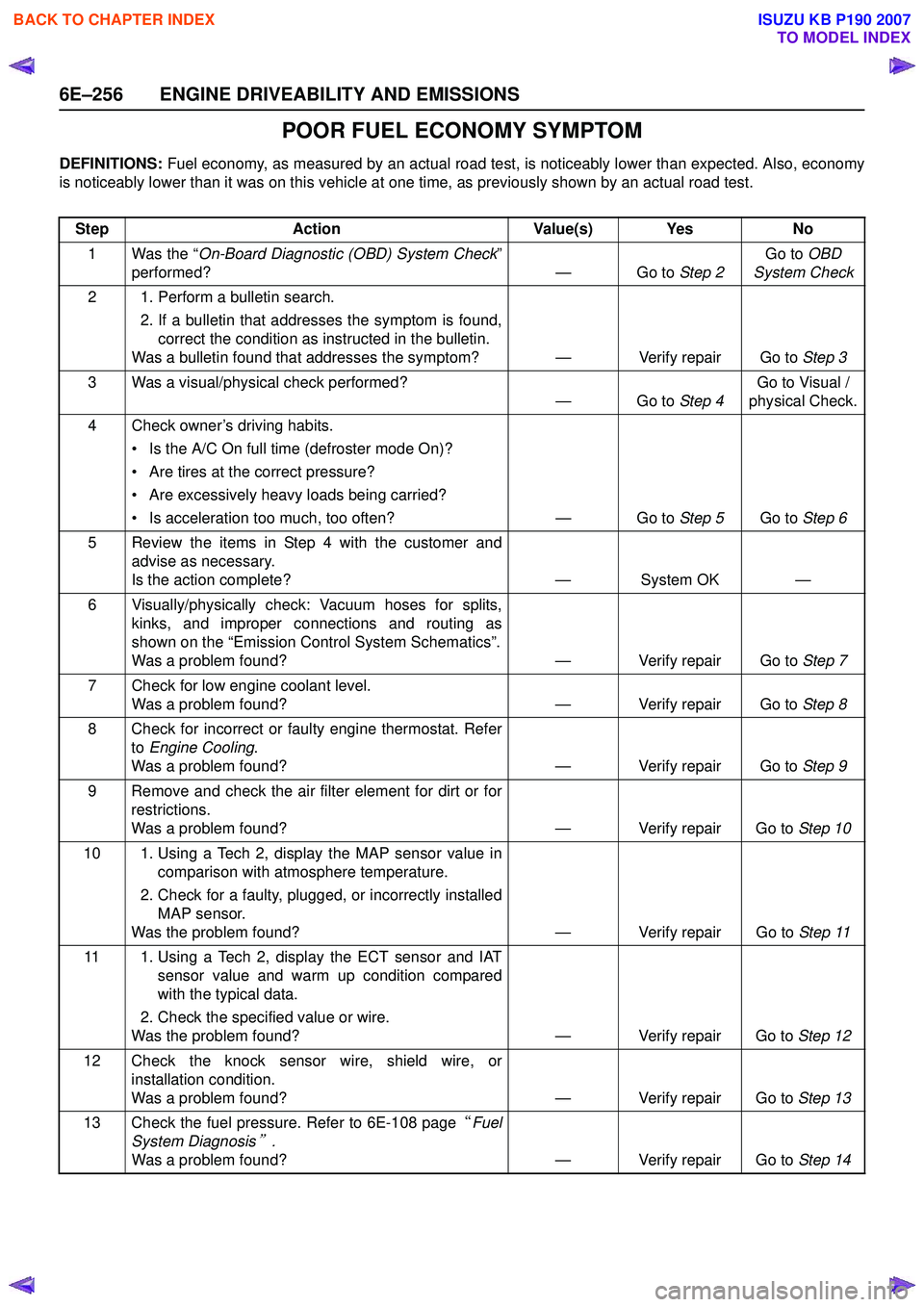
6E–256 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
POOR FUEL ECONOMY SYMPTOM
DEFINITIONS: Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy
is noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time, as previously shown by an actual road test.
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “ On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ”
performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Perform a bulletin search. 2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 Was a visual/physical check performed? —Go to Step 4Go to Visual /
physical Check.
4 Check owner’s driving habits. • Is the A/C On full time (defroster mode On)?
• Are tires at the correct pressure?
• Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
• Is acceleration too much, too often? — Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5 Review the items in Step 4 with the customer and advise as necessary.
Is the action complete? — System OK —
6 Visually/physically check: Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and improper connections and routing as
shown on the “Emission Control System Schematics”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Check for low engine coolant level. Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 Check for incorrect or faulty engine thermostat. Refer to Engine Cooling .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or for restrictions.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 1. Using a Tech 2, display the MAP sensor value in comparison with atmosphere temperature.
2. Check for a faulty, plugged, or incorrectly installed MAP sensor.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Using a Tech 2, display the ECT sensor and IAT sensor value and warm up condition compared
with the typical data.
2. Check the specified value or wire.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check the knock sensor wire, shield wire, or installation condition.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check the fuel pressure. Refer to 6E-108 page “Fuel
System Diagnosis
” .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2435 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–265
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR
Location
Installed to the thermostat housing.
Removal Procedure 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain enough engine coolant so that the coolant level will be below the ECT sensor.
3. Disconnect connector from the ECT sensor.
4. Loosen and remove the ECT sensor from the thermostat housing.
NOTE: Cool down the engine before above procedures
are carried out.
Installation Procedure
1. Apply sealer to threads of screw at the ECT sensor.
2. Tighten the ECT sensor with specified tightening torque.
Tightening Torque
• Bolt: 13N·m (1.3kgf·m)
3. Connect a ECT sensor connector to the ECT sensor.
4. Fill the engine coolant.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
NOTE: Verify any DTCs (diagnosis Trouble Code) are
not stored after replacement.
Verify no engine coolant leaking from the sensor
threads after replacement.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
Location
Installed to the intake duct housing.
Removal Procedure 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect a IAT sensor connector from the IAT sensor.
3. Remove the IAT sensor from the intake duct.
Installation Procedure 1. Install the IAT sensor into intake air duct.
2. Connect a IAT sensor connector to the IAT sensor.
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
NOTE: Verify any DTCs (diagnosis Trouble Code) are
not stored after replacement.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2516 of 6020
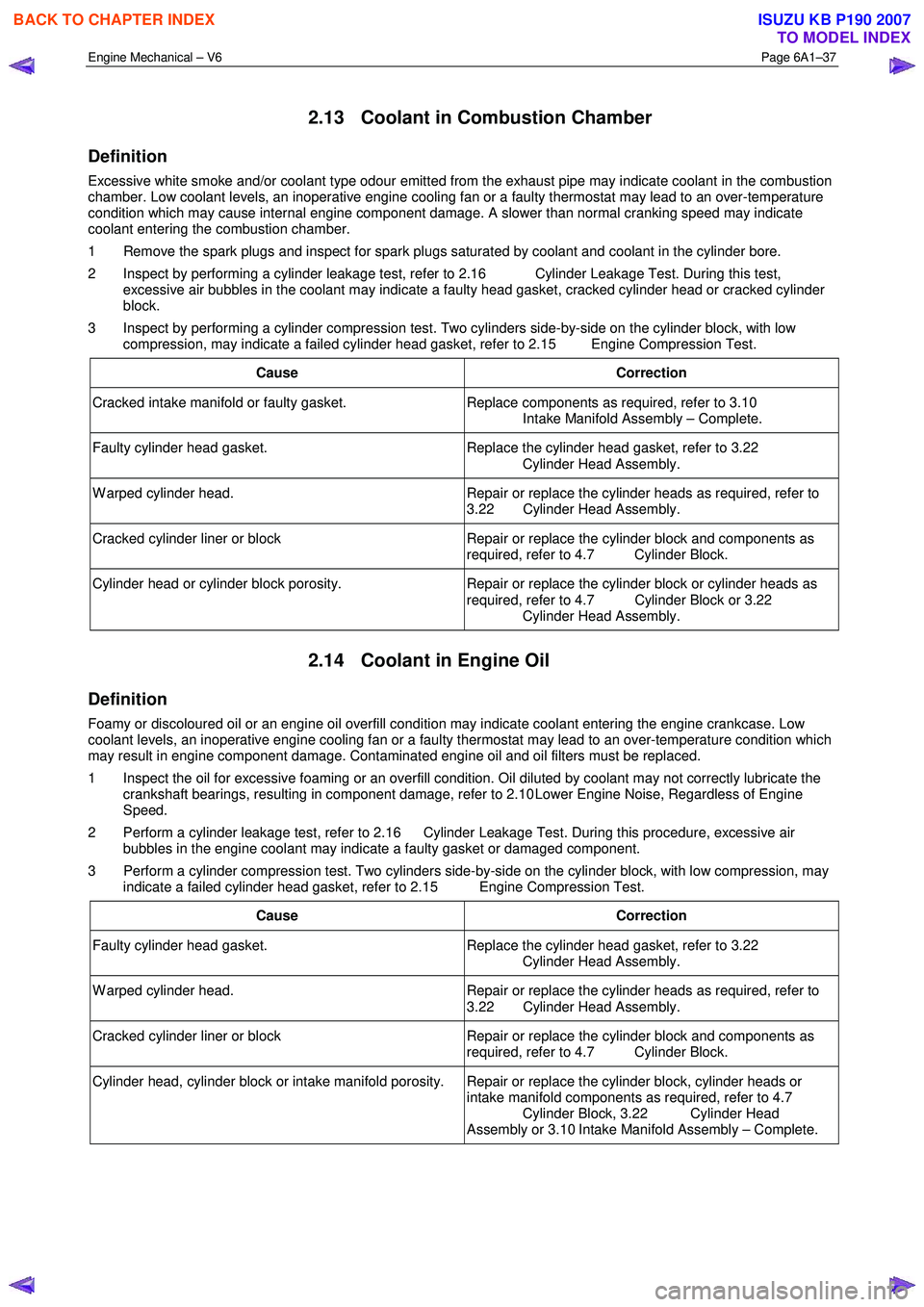
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–37
2.13 Coolant in Combustion Chamber
Definition
Excessive white smoke and/or coolant type odour emitted from the exhaust pipe may indicate coolant in the combustion
chamber. Low coolant levels, an inoperative engine cooling fan or a faulty thermostat may lead to an over-temperature
condition which may cause internal engine component damage. A slower than normal cranking speed may indicate
coolant entering the combustion chamber.
1 Remove the spark plugs and inspect for spark plugs saturated by coolant and coolant in the cylinder bore.
2 Inspect by performing a cylinder leakage test, refer to 2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test. During this test, excessive air bubbles in the coolant may indicate a faulty head gasket, cracked cylinder head or cracked cylinder
block.
3 Inspect by performing a cylinder compression test. Two cylinders side-by-side on the cylinder block, with low compression, may indicate a failed cylinder head gasket, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
Cause Correction
Cracked intake manifold or faulty gasket. Replace components as required, refer to 3.10
Intake Manifold Assembly – Complete.
Faulty cylinder head gasket. Replace the cylinder head gasket, refer to 3.22
Cylinder Head Assembly.
W arped cylinder head. Repair or replace the cylinder heads as required, refer to
3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
Cracked cylinder liner or block Repair or replace the cylinder block and components as
required, refer to 4.7 Cylinder Block.
Cylinder head or cylinder block porosity. Repair or replace the cylinder block or cylinder heads as
required, refer to 4.7 Cylinder Block or 3.22
Cylinder Head Assembly.
2.14 Coolant in Engine Oil
Definition
Foamy or discoloured oil or an engine oil overfill condition may indicate coolant entering the engine crankcase. Low
coolant levels, an inoperative engine cooling fan or a faulty thermostat may lead to an over-temperature condition which
may result in engine component damage. Contaminated engine oil and oil filters must be replaced.
1 Inspect the oil for excessive foaming or an overfill condition. Oil diluted by coolant may not correctly lubricate the crankshaft bearings, resulting in component damage, refer to 2.10 Lower Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine
Speed.
2 Perform a cylinder leakage test, refer to 2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test. During this procedure, excessive air bubbles in the engine coolant may indicate a faulty gasket or damaged component.
3 Perform a cylinder compression test. Two cylinders side-by-side on the cylinder block, with low compression, may indicate a failed cylinder head gasket, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket. Replace the cylinder head gasket, refer to 3.22
Cylinder Head Assembly.
W arped cylinder head. Repair or replace the cylinder heads as required, refer to
3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
Cracked cylinder liner or block Repair or replace the cylinder block and components as
required, refer to 4.7 Cylinder Block.
Cylinder head, cylinder block or intake manifold porosity. Repair or replace the cylinder block, cylinder heads or intake manifold components as required, refer to 4.7
Cylinder Block, 3.22 Cylinder Head
Assembly or 3.10 Intake Manifold Assembly – Complete.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007