coolant level ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3159 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–24
12 Open the coolant reservoir tank cap.
13 Top up the radiator coolant recovery reservoir to the MAX line.
14 Reinstall the coolant recovery reservoir cap.
NOTE
This condition only applies when the cooling
system is first being filled after a major loss of
coolant. The level of coolant in the reservoir
will then drop, once the engine is started and
normal operating temperature is reached. The
coolant level should then be maintained at the
correct level (between the MAX and MIN
Lines).
Figure 6B1 – 21
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3167 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–32
4 Attach coolant filler cap (2) to a commercially
available cooling system pressure tester (1), using
the pressure cap adaptor.
5 Slowly pressurise cap to 120 – 130 kPa. The cap is serviceable if it unloads slightly above this pressure
range and holds pressure at 120 kPa.
NOTE
Should the cap fail to reach or hold the
specified pressure, replace the cap.
Figure 6B1 – 30
6 Prior to installing coolant filler cap ensure that the coolant filler neck cap seating surface is clean and
free from obstruction.
Figure 6B1 – 31
Cooling System Pressure Testing
Refer to 3.1 Service Notes in this Section, for
important safety items.
1 Allow the engine to cool to ambient temperature (less than 50 ° C), then remove coolant filler cap.
2 Ensure that the coolant level is correct.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3191 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–56
Reinstall
Installation of the radiator is the reverse of removal procedures, noting the following points:
1 Before installing radiator, inspect core to ensure that there is no foreign matter in core fins. Clean out between core fins with compressed air, blowing from rear to front.
2 If the vehicle is fitted with an automatic transmission, remove plugs from the removed cooling pipe ends and the two quick connect fittings.
3 After wiping cooler line ends and smearing clean automatic transmission fluid over each flared line end, push into the quick connect fitting to engage. As a security check, tug on each line to ensure correct engagement.
4 Check the transmission fluid level. Refer to the following references as required:
• 7C4 Automatic Transmission
• 4L60E On-vehicle Servicing
5 Install the following hoses:
a. Lower radiator hose, securing with the hose clamp.
b. Upper radiator hose, securing with the hose clamp.
6 Install the radiator cooling fan and shroud assembly. Refer to 3.13Cooling Fan and Shroud Assembly in this Section. Ensure that electrical connectors and the transmission cooler lines are seated correctly in the integral
retainer clips before install upper radiator shroud.
7 Refill cooling system. Refer to 3.3 Draining and Filling Cooling System in this Section.
8 Check for coolant leaks. Refer to 3.7 Pressure Testing in this Section.
9 Reconnect battery ground lead. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
10 Check cooling fan operation. Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management Diagnostics. Also check for correct rotational direction of cooling fan.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3196 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–61
4 Engine Cooling System
Diagnosis
4.1 Poor Heater Operation
Little or no heat coming from the heater, especially at idle could be an indication of a cooling system problem.
As the coolant level begins to get lower than normal, air enters the system to replace the missing coolant. The heater
core is one of the highest parts of the cooling system and therefore, the first area to lose coolant circulation.
At first, with a small amount of coolant loss, lack of heat will be most noticeable at idle. As driving speed increases, the
engine pumps more coolant and more heat is now able to pass through the heater core.
If coolant level drops even lower, heater operation will become less effective, even during normal driving. Cooling and
engine systems can be adversely affected if problem is not corrected before overheating occurs.
4.2 Leaking Cylinder Head Gasket
Combustion gases leaking past the cylinder head gasket can pressurise the cooling system, forcing coolant out of the
system and into the coolant recovery reservoir.
Indications are air bubbles in the coolant or an overflow condition of the recovery reservoir.
4.3 Question the Customer
To avoid needless time and cost in diagnosing cooling system complaints, the customer should be questioned about
driving conditions that place abnormal loads on the cooling system.
1 Is overheating occurring after prolonged idle, in gear, with air conditioning system operating?
If answer is YES – instruct owner on driving techniques that would avoid overheating such as:
• Idle in neutral as much as possible – increase engine rpm to get higher air flow (due to an increase in voltage
to the fan) and coolant flow through the radiator
• Turn air conditioning system off during extended idling periods if overheating is indicated on temperature
gauge. Further diagnostic checks should not be required
2 Is overheating occurring after prolonged driving in slow city traffic, traffic jams, parades, etc?
If answer is YES, explain driving technique to the customer, that would avoid overheating – same as for prolonged idle – No.1. Further diagnostic checks should not be required.
4.4 Diagnostic Chart
If none of the above conditions apply, refer to the following Diagnosis Chart.
To effectively use this chart, question the customer to determine which of the following three categories apply to the
complaint:
1 If complaint is hot indication on temperature gauge.
W as temperature reading accompanied by boiling?
• If answer is YES, go to overheating on diagnosis chart
• If answer is NO, check temperature gauge and sender
2 If complaint is boiling – go to overheating on diagnosis chart.
3 If complaint is coolant loss. Determine if customer is filling the system correctly.
4 If incorrect filling is not the problem, go to coolant loss in the diagnosis chart.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3197 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–62
Refer to 3.1 Service Notes in this Section, for
important safety items before removing the
coolant filler pressure cap or servicing the
system.
The cooling system is designed to operate at
120 –
––
–
130 kPa and a maximum temperature
not above 130 °
°°
°
C.
Cooling System Diagnosis
Step Action Result Yes No
1
Check Temperature gauge reading High Temp.
Low Temp. Go to Step 2
Go to Step 6 –
2
Check drive belt condition and tension. Refer to 6A1
Engine Mechanical. To Specification Go to Step 3 Replace drive
belt or
tensioner.
3 Check coolant Boiling Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Check coolant level. Refer to 3.2 Coolant
Maintenance in this Section. Low Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
5
Check coolant filler cap. Refer to 3.7 Pressure
Testing – Coolant Filler Cap Pressure Testing in this
Section OK? Go to Step 8
Replace
Coolant filler
cap
6 Check thermostat. Refer to 3.8 Thermostat in this
Section. OK? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 13
7
Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
Refer to 6C1 Engine Management General Information. Faulty Replace Go to Step 12
8
Check cooling fan operation. Refer to 6C1 Engine
Management General Information. Operational Go to Step 10 Repair
9
Check for collapsed upper or lower radiator hose. Collapsed Replace Go to Step 13
10 Visual system check Leaks Go to Step 13 Go to Step 11
11 Check coolant concentration. Refer to 3.2 Coolant
Maintenance. To Specification Go to Step 12 Correct
Concentration Level
12 Check radiator core for bent fins, dirt, bugs or other
obstructions. Obstructed Clean or
straighten Go to Step 14
13
Pressure Test cooling system. Refer to 3.7 Pressure
Testing in this Section. Leaks Repair System OK
14
If none of the above require repair, the problem is
complex or of a major nature.
Refer to 4.5 Problems Not Requiring Disassembly of
Cooling System or 4.6 Problems Requiring Disassembly
of Cooling System. – – –
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3202 of 6020
Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–67
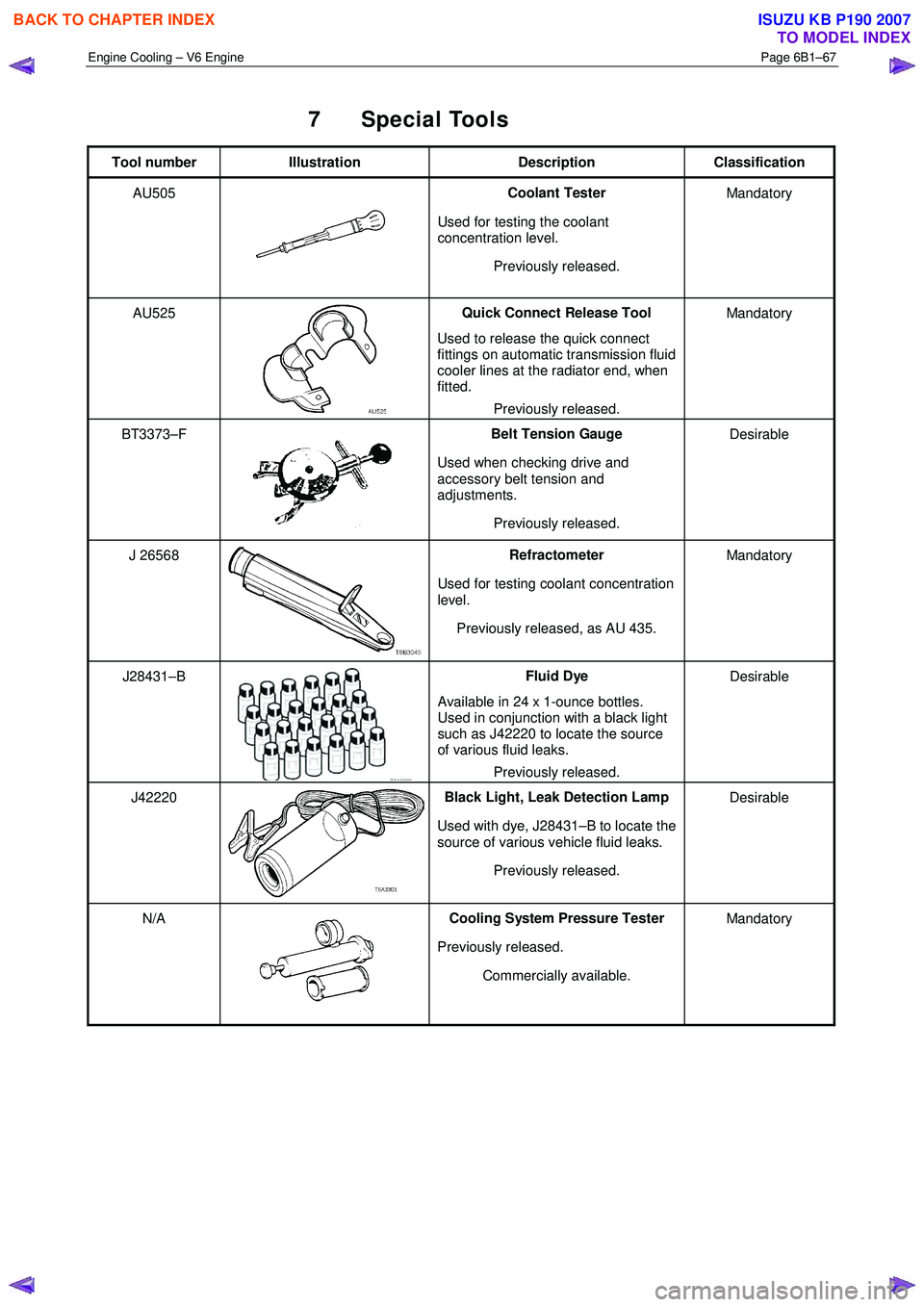
7 Special Tools
Tool number Illustration Description Classification
AU505
Coolant Tester
Used for testing the coolant
concentration level.
Previously released. Mandatory
AU525
Quick Connect Release Tool
Used to release the quick connect
fittings on automatic transmission fluid
cooler lines at the radiator end, when
fitted.
Previously released. Mandatory
BT3373–F
Belt Tension Gauge
Used when checking drive and
accessory belt tension and
adjustments.
Previously released. Desirable
J 26568 Refractometer
Used for testing coolant concentration
level.
Previously released, as AU 435. Mandatory
J28431–B Fluid Dye
Available in 24 x 1-ounce bottles.
Used in conjunction with a black light
such as J42220 to locate the source
of various fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
J42220 Black Light, Leak Detection Lamp
Used with dye, J28431–B to locate the
source of various vehicle fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
N/A Cooling System Pressure Tester
Previously released. Commercially available. Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3244 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–2
3.9 Serial Data Communication System ................................................................................................................... 17
3.10 Self Diagnostics System ..................................................................................................................................... 17
3.11 Service Programming System ..................................................................................................... ....................... 17
3.12 Immobiliser System ............................................................................................................................................. 18
4 Component Description and Operation ............................................................................................ .19
4.1 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor ....................................................................................................................... 19
4.2 Brake Pedal Switch Assembly ............................................................................................................................ 19
Stop Lamp and Initial Brake Apply Switch ....................................................................................... ................. 19
Stop Lamp Switch ............................................................................................................................................ 19
Initial Brake Apply Switch ..................................................................................................... ............................ 19
4.3 Barometric Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... .......................... 20
4.4 Camshaft Position Sensor .................................................................................................................................. 20
4.5 Crankshaft Position Sensor ................................................................................................................................ 21
4.6 Clutch Pedal Switch Assembly – Manual Vehicles Only ............................................................................ ...... 22
4.7 Engine Control Module........................................................................................................................................ 22
4.8 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor .............................................................................................. ................... 23
4.9 Electric Cooling Fans .......................................................................................................................................... 23
4.10 Engine Oil Level and Temperature Sensor ........................................................................................ ................ 24
Engine Oil Temperature Sensor ......................................................................................................................... 24
Engine Oil Level Sensor ...................................................................................................................................... 25
4.11 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... ........................... 25
4.12 Fuel Injectors........................................................................................................................................................ 26
4.13 Fuel Rail Assembly ............................................................................................................. ................................. 27
4.14 Heated Oxygen Sensors .......................................................................................................... ............................ 27
LSF 4.2 Two-step Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors .................................................................................. ......... 27
LSU 4.2 Wide-band Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors ................................................................................. ....... 29
4.15 Ignition Coil and Spark Plug ............................................................................................................................... 31
4.16 Intake Air Temperature Sensor .................................................................................................. ......................... 32
4.17 Knock Sensor ....................................................................................................................................................... 32
4.18 Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Air Intake System ................................................................................................................................................. 33
Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Construction ..................................................................................................................................................... 34
Operation ......................................................................................................................................................... 34
5 Abbreviations and Glossary of Terms ............................................................................................ ...35
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3249 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–7
Figure 6C1-1 – 4
Legend
1 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
2 Fuel Rail Assembly
3 Fuel Injector (six places)
4 Evaporative Canister Purge (EVAP) Valve 5 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
6 Engine Oil Level / Temperature Sensor
7 Knock (KS) Sensor (two places)
8 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3339 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–61
• DTCs P0341, P0342, P0343, ran and passed:
• The engine is running.
• The ECM has learned the camshafts position.
DTC P0016
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0335, P0336, P0338, P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed:
• The calculated engine oil temperature is less than 95 °C.
• The engine coolant temperature is 20 – 90 °C.
• The engine is running for greater than 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0008
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 1 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0009
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 2 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0016
The ECM detects the following deviation in the correlation between the camshaft position and the crankshaft position for
greater than 10 minutes:
• a camshaft position is too advanced in relationship to the crankshaft, or
• a camshaft position is too retarded in relationship to the crankshaft.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CKP / CMP sensor correlation DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CMP system operation.
• Inspect the engine for recent engine mechanical repairs. Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain
installation will trigger these DTCs.
• The engine oil condition has a major impact on the operation of the camshaft actuator.
• A low oil level may set these DTCs.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in any of the listed sensors will trigger these DTCs.
5 Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain installation will trigger these DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3362 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–84
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250ºC – 800ºC.
• The engine coolant temperature is less than 40ºC at start-up and greater than 60ºC when the ignition was turned
off last ignition cycle.
• The fuel tank level is greater than 25 percent.
DTC P0138 and P0158
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is operating for longer than two minutes.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The HO2S is at operating temperature.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250ºC – 800ºC.
DTC P0140 and P0160
Run continuously once the following conditions are met for longer than 90 seconds:
• The engine is operating.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250º C – 800º C.
DTC P0141 and P0161
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0036, P0037, P0038, P0056, P0057, and P0058 ran and passed.
• DTCs P0137, P0138, P0140, P0157, P0158, or P0160 are not set.
• The engine is operating.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance is valid.
• The fuel system is not in decel fuel shut-off.
• The intake air temperature is greater than -7ºC.
• If the engine is operating and the ignition is turned off, the engine must be off for at least 5 minutes for this DTC to
run.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 360ºC – 500ºC.
DTC P2243 and P2247
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051 and P0052 ran and passed.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance is greater than 570 Ω.
• The HO2S is at operating temperature.
DTC P2270 and P2272
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0036, P0037, P0038, P0056, P0057, P0058, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P0342, P0343, P0443, P0458 and P0459 ran and passed.
• The engine is running.
• The HO2S 2 are at operating temperature for longer than 10 seconds.
• The long term fuel control is enabled.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007