check engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2232 of 6020

6E–62 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Thought Process
As you follow a diagnostic plan, every box on the
Strategy Based Diagnostics chart requires you to use
the diagnostic thought process. This method of thinking
optimizes your diagnosis in the following ways:
• Improves your understanding and definition of the customer complaint
• Saves time by avoiding testing and/or replacing good parts
• Allows you to look at the problem from different perspectives
• Guides you to determine what level of understanding about system operation is needed:
– Owner’s manual level
– Service manual level
– In-depth (engineering) level – Owner’s manual level
– Service manual level
– In-depth (engineering) level
1. Verify the Complaint
What you should do
To verify the customer complaint, you need to know the
correct (normal) operating behavior of the system and
verify that the customer complaint is a valid failure of the
system.
The following information will help you verify the
complaint:
• WHAT the vehicle model/options are
• WHAT aftermarket and dealer-installed accessories exist
• WHAT related system(s) operate properly
• WHEN the problem occurs
• WHERE the problem occurs
• HOW the problem occurs
• HOW LONG the condition has existed (and if the system ever worked correctly)
• HOW OFTEN the problem occurs
• Whether the severity of the problem has increased, decreased or stayed the same
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to assist you in verifying the complaint:
• Service manual Theory or Circuit Description sections
• Service manual “System Performance Check”
• Owner manual operational description
• Technician experience
• Identical vehicle for comparison • Circuit testing tools
• Vehicle road tests
• Complaint check sheet
• Contact with the customer
2. Perform Preliminary Checks
NOTE: An estimated 10 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You perform preliminary checks for several reasons:
• To detect if the cause of the complaint is VISUALLY OBVIOUS
• To identify parts of the system that work correctly
• To accumulate enough data to correctly and accurately search for a ISUZU Service Bulletin on
ISUZU Web site.
The initial checks may vary depending on the
complexity of the system and may include the following
actions:
• Operate the suspect system
• Make a visual inspection of harness routing and accessible/visible power and ground circuits
• Check for blown fuses
• Make a visual inspection for separated connectors
• Make a visual inspection of connectors (includes checking terminals for damage and tightness)
• Check for any DTCs stored by the on-board computers
• Sense unusual noises, smells, vibrations or movements
• Investigate the vehicle service history (call other dealerships, if appropriate)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources for assistance in performing preliminary
checks:
• Tech II or other technical equipment for viewing DTCs
• Service manual information: – Component locations
– Harness routing
– Wiring schematics
– Procedures for viewing DTCs
• Dealership service history file
• Vehicle road test
• Identical vehicle or system for comparison
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2233 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–63
3. Check Bulletins and Troubleshooting Hints
NOTE: As estimated 30 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You should have enough information gained from
preliminary checks to accurately search for a bulletin
and other related service information. Some service
manual sections provide troubleshooting hints that
match symptoms with specific complaints.
What resources you should use
You should use the following resources for assistance in
checking for bulletins and troubleshooting hints:
• Printed bulletins
• Access ISUZU Bulletin Web site.
• Videotapes
• Service manual
4. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Checks
What you should do
The “System Checks” in most service manual sections
and in most cells of section 8A (electrical) provide you
with:
• A systematic approach to narrowing down the possible causes of a system fault
• Direction to specific diagnostic procedures in the service manual
• Assistance to identify what systems work correctly
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual checks:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for viewing DTCs and analyzing data)
• Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
• Other tools as needed
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Procedures
NOTE: An estimated 40 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with these steps!
What you should do
When directed by service manual diagnostic checks,
you must then carefully and accurately perform the
steps of diagnostic procedures to locate the fault related to the customer complaint.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual diagnostic
procedures:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for analyzing diagnostic data)
• Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
• Essential and special tools
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses
When there is no DTC stored and no matching
symptom for the condition identified in the service
manual, you must begin with a thorough understanding
of how the system(s) operates. Efficient use of the
service manual combined with you experience and a
good process of elimination will result in accurate
diagnosis of the condition.
What you should do
Step 1: Identify and understand the suspect
circuit(s)
Having completed steps 1 through 4 of the Strategy
Based Diagnostics chart, you should have enough
information to identify the system(s) or sub-system(s)
involved. Using the service manual, you should
determine and investigate the following circuit
characteristics:
• Electrical: – How is the circuit powered (power distributioncharts and/or fuse block details)?
– How is the circuit grounded (ground distribution charts)?
– How is the circuit controlled or sensed (theory of operation):
– If it is a switched circuit, is it normally open or normally closed?
– Is the power switched or is the ground switched?
– Is it a variable resistance circuit (ECT sensor or TP sensor, for example)?
– Is it a signal generating device (MAF sensor of VSS, for example)?
– Does it rely on some mechanical/vacuum device to operate?
•Physical:
– Where are the circuit components (componentlocators and wire harness routing diagrams):
– Are there areas where wires could be chafed or pinched (brackets or frames)?
– Are there areas subjected to extreme temperatures?
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2234 of 6020

6E–64 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
– Are there areas subjected to vibration ormovement (engine, transmission or
suspension)?
– Are there areas exposed to moisture, road salt or other corrosives (battery acid, oil or other
fluids)?
– Are there common mounting areas with other systems/components?
– Have previous repairs been performed to wiring, connectors, components or mounting areas
(causing pinched wires between panels and
drivetrain or suspension components without
causing and immediate problem)?
– Does the vehicle have aftermarket or dealer- installed equipment (radios, telephone, etc.)
Step 2: Isolate the problem
At this point, you should have a good idea of what could
cause the present condition, as well as could not cause
the condition. Actions to take include the following:
• Divide (and separate, where possible) the system or circuit into smaller sections
• Confine the problem to a smaller area of the vehicle (start with main harness connections while removing
panels and trim as necessary in order to eliminate
large vehicle sections from further investigation)
• For two or more circuits that do not share a common power or ground, concentrate on areas where
harnesses are routed together or connectors are
shared (refer to the following hints)
Hints
Though the symptoms may vary, basic electrical failures
are generally caused by:
• Loose connections: – Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,connectors or grounds
• Incorrect connector/harness routing (usually in new vehicles or after a repair has been made):
– Open/high resistance in terminals, splices, connectors of grounds
• Corrosion and wire damage:
– Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,connectors of grounds
• Component failure: – Opens/short and high resistance in relays,modules, switches or loads
• Aftermarket equipment affecting normal operation of other systems
You may isolate circuits by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another part
• Operating shared circuits and eliminating those that function normally from the suspect circuit
• If only one component fails to operate, begin testing at the component
• If a number of components do no operate, begin tests at the area of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches or major connectors)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for data analysis)
• Experience
• Technical Assistance
• Circuit testing tools
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis
By definition, an intermittent problem is one that does
not occur continuously and will occur when certain
conditions are met. All these conditions, however, may
not be obvious or currently known. Generally,
intermittents are caused by:
• Faulty electrical connections and wiring
• Malfunctioning components (such as sticking relays, solenoids, etc.)
• EMI/RFI (Electromagnetic/radio frequency interference)
• Aftermarket equipment
Intermittent diagnosis requires careful analysis of
suspected systems to help prevent replacing good
parts. This may involve using creativity and ingenuity to
interpret customer complaints and simulating all
external and internal system conditions to duplicate the
problem.
What you should do
Step 1: Acquire information
A thorough and comprehensive customer check sheet
is critical to intermittent problem diagnosis. You should
require this, since it will dictate the diagnostic starting
point. The vehicle service history file is another
source for accumulating information about the
complaint.
Step 2: Analyze the intermittent problem
Analyze the customer check sheet and service history
file to determine conditions relevant to the suspect
system(s).
Using service manual information, you must identify,
trace and locate all electrical circuits related to the
malfunctioning system(s). If there is more than one
system failure, you should identify, trace and locate
areas of commonality shared by the suspect circuits.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2235 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–65
Step 3: Simulate the symptom and isolate the
problem
Simulate the symptom and isolate the system by
reproducing all possible conditions suggested in Step 1
while monitoring suspected circuits/components/
systems to isolate the problem symptom. Begin with the
most logical circuit/component.
Isolate the circuit by dividing the suspect system into
simpler circuits. Next, confine the problem into a smaller
area of the system. Begin at the most logical point (or
point of easiest access) and thoroughly check the
isolated circuit for the fault, using basic circuit tests.
Hints
You can isolate a circuit by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another
• If only component fails to operate, begin testing the component
• If a number of components do not operate, begin test at areas of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches, main connectors or major
components)
• Substitute a known good part from the parts department or the vehicle system
• Try the suspect part in a known good vehicle
See Symptom Simulation Tests on the next page for
problem simulation procedures. Refer to service manual
sections 6E and 8A for information about intermittent
diagnosis. Follow procedures for basic circuit testing in
service manual section 8A.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Bulletins
• Digital multimeter (with a MIN/MAX feature)
• Tech II and Tech II upload function
• Circuit testing tools (including connector kits/ harnesses and jumper wires)
• Experience
• Intermittent problem solving simulation methods
• Customer complaint check sheet
Symptom Simulation Tests
1. Vibration
This method is useful when the customer complaint
analysis indicates that the problem occurs when the
vehicle/system undergoes some form of vibration.
For connectors and wire harness, slightly shake
vertically and horizontally. Inspect the connector joint
and body for damage. Also, tapping lightly along a
suspected circuit may be helpful. For parts and sensors, apply slight vibration to the part
with a light tap of the finger while monitoring the system
for a malfunction.
2. Heat
This method is important when the complaint suggests
that the problem occurs in a heated environment. Apply
moderate heat to the component with a hair drier or
similar tool while monitoring the system for a
malfunction.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid overheating
the component.
3. Water and Moisture
This method may be used when the complaint suggests
that the malfunction occurs on a rainy day or under
conditions of high humidity. In this case, apply water in a
light spray on the vehicle to duplicate the problem.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid directly
exposing electrical connections to water.
4. Electrical loads
This method involves turning systems ON (such as the
blower, lights or rear window defogger) to create a load
on the vehicle electrical system at the same time you
are monitoring the suspect circuit/component.
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed
This condition refers to instances where a system
operating as designed is perceived to be unsatisfactory
or undesirable. In general, this is due to:
• A lack of understanding by the customer
• A conflict between customer expectations and vehicle design intent
• A system performance that is unacceptable to the customer
What you should do
You can verify that a system is operating as designed
by:
• Reviewing service manual functional/diagnostic checks
• Examining bulletins and other service information for supplementary information
• Compare system operation to an identical vehicle
If the condition is due to a customer misunderstanding
or a conflict between customer expectation and system
operation, you should explain the system operation to
the customer.
If the complaint is due to a case of unsatisfactory
system performance, you should contact Technical
Assistance for the latest information.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2236 of 6020

6E–66 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
• Vehicle service information (service manual, etc.)
• ISUZU field support
• Experience
• Identical vehicle or system for comparison
6. Re-examine the complaint
When you do not successfully find/isolate the problem
after executing a diagnostic path, you should re-
examine the complaint.
What you should do
In this case, you will need to backtrack and review
information accumulated from step 1 through 4 of
Strategy Based Diagnostics. You also should repeat any
procedures that require additional attention.
A previous path may be eliminated from consideration
only if you are certain that all steps were executed as
directed. You must then select another diagnostic path
(step 5a, 5b, 5c or 5d). If all possible options have been
explored, you may call or seek ISUZU field support.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Accumulated information form a previous diagnostic path
• Service information and publications
• ISUZU field support
7. Repair and Verify Fix
What you should do
After you have located the cause of the problem, you
must execute a repair by following recommended
service manual procedures.
When the repair is completed, you should verify the fix
by performing the system checks under the conditions
listed in the customer complaint.
If applicable, you should carry out preventive measures
to avoid a repeat complaint.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the repair process:
• Electrical repair procedures
• Service manual information and publications
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2237 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–67
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after it leaves the factory. No allowances
have been made in the vehicle design for this type of
equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle's electrical system at the
battery (power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the electric system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any electric problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction.
• An example of charging by friction is a person sliding across a vehicle seat.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with well- insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentarily touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components. Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold
sensor or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis
and turns on the check engine lamp.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the check
engine lamp.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the check
engine lamp to turn on if the vehicle is not maintained
properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and crankcase
deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper oil
viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics,
vehicle maintenance schedules must be more closely
followed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any
diagnostic procedure or diagnosing the cause of an
emission test failure. This can often lead to repairing a
problem without further steps. Use the following
guidelines when performing a visual/physical
inspection:
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts, disconnects, and correct routing.
• Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other components.
• Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched
wires, contact with sharp edges or contact with hot
exhaust manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in
an incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2238 of 6020

6E–68 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which
is a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive.
When a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the
diagnostic executive records the following data:
• The diagnostic test has been completed since the last ignition cycle.
• The diagnostic test has passed during the current ignition cycle.
• The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the
diagnostic executive records the following data:
• The diagnostic test has been completed since the last ignition cycle.
• The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently active.
• The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
• The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
• Commanding the check engine lamp on and off
• DTC logging and clearing
• Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are
designed to locate a faulty circuit or component through
a process of logical decisions. The charts are prepared
with the requirement that the vehicle functioned
correctly at the time of assembly and that there are not
multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented
by the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual.
The language of communicating the source of the
malfunction is a system of diagnostic trouble codes.
When a malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the check engine
lamp is illuminated.
Check Engine Lamp
The check engine lamp looks the same as the check
engine lamp you are already familiar with, the “Check
Engine” lamp.
Basically, the check engine lamp is turned on when the
ECM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.
• When the check engine lamp remains “ON” while the engine is running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a driveability or emissions problem,
a Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check must be performed. The procedures for these
checks are given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check. These checks will expose faults
which may not be detected if other diagnostics are
performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the contorl
module is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located
behind the lower front instrument panel. The DLC is
used to connect to a Tech 2. Some common uses of the
Tech 2 are listed below:
• Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
• Clearing DTCs.
• Reading serial data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps is very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2239 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–69
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using a
Te c h 2
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is
to used a diagnostic Tech 2. When reading DTC(s),
follow instructions supplied by Tech 2 manufacturer.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), use the
Tech 2 “clear DTCs” or “clear information” function.
When clearing DTCs follow instructions supplied by the
Tech 2 manufacturer.
Diagnosis With Tech 2
If no codes are set:
•Refer to F1: Data Display and identify the electrical
faults that are not indicated by trouble code.
• Refer to “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS ”.
If codes are set: 1. Record all trouble codes displayed by Tech 2 and check id the codes are intermittent.
2. Clear the codes.
3. Drive the vehicle for a test to reproduce the faulty status.
4. Check trouble codes again using the Tech 2.
5. If no codes is displayed by test driving, the fault is intermittent. In this case, refer to “DIAGNOSIS
AIDS”.
6. If a code is present, refer to DTC Chart for diagnosis.
7. Check trouble codes again using the Tech 2.
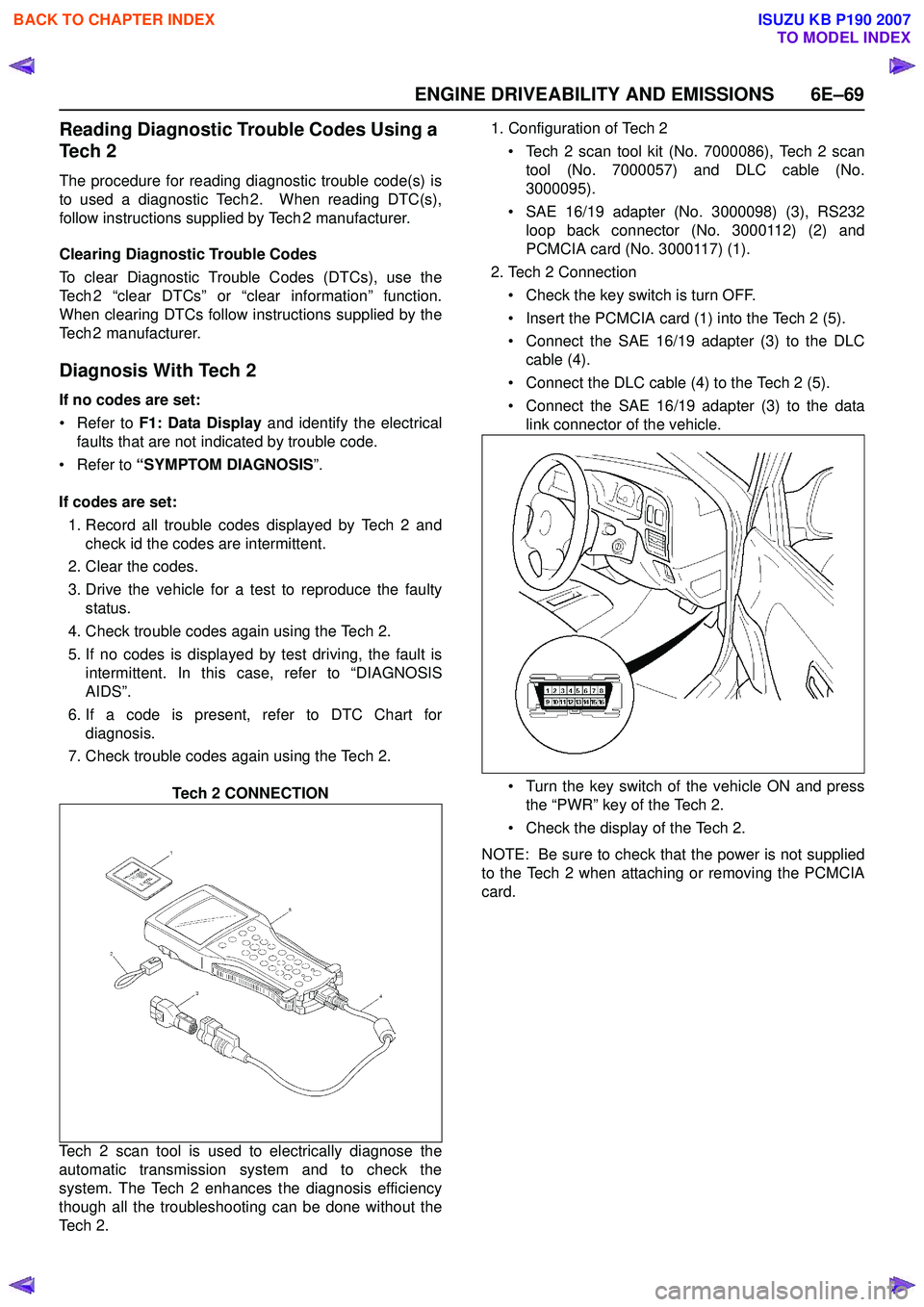
Tech 2 CONNECTION
Tech 2 scan tool is used to electrically diagnose the
automatic transmission system and to check the
system. The Tech 2 enhances the diagnosis efficiency
though all the troubleshooting can be done without the
Te c h 2 . 1. Configuration of Tech 2
• Tech 2 scan tool kit (No. 7000086), Tech 2 scan tool (No. 7000057) and DLC cable (No.
3000095).
• SAE 16/19 adapter (No. 3000098) (3), RS232 loop back connector (No. 3000112) (2) and
PCMCIA card (No. 3000117) (1).
2. Tech 2 Connection
• Check the key switch is turn OFF.
• Insert the PCMCIA card (1) into the Tech 2 (5).
• Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC cable (4).
• Connect the DLC cable (4) to the Tech 2 (5).
• Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the data link connector of the vehicle.
• Turn the key switch of the vehicle ON and press the “PWR” key of the Tech 2.
• Check the display of the Tech 2.
NOTE: Be sure to check that the power is not supplied
to the Tech 2 when attaching or removing the PCMCIA
card.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2241 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
The purpose of the “Diagnostic Trouble Codes” mode is
to display stored trouble code in the ECM.
When “Clear DTC Information” is selected, a “Clear
DTC Information”, warning screen appears.
This screen informs you that by cleaning DTC's “all
stored DTC information in the ECM will be erased”.
After clearing codes, confirm system operation by test
driving the vehicle.
Use the “DTC Information” mode to search for a specific
type of stored DTC information.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in
the ECM's history memory. It will not display Type B
DTCs that have not requested the MIL (“Check Engine Lamp”). It will display all type A and B DTCs that
requested the MIL and have failed within the last 40
warm-up cycles. In addition, it will display all type C and
D DTCs that have failed within the last 40 warm-up
cycles.
MIL SVC or Message Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and Type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using the MIL. Type C and D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option.
This selection will report type B DTCs only after the MIL
has been requested.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test run. The last test may have run during
a previous ignition cycle of a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as last test fail.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
The selection will display all active and history DTCs
that have reported a test failure since the last time
DTCs were cleared. DTCs that last failed more that 40
warm-up cycles before this option is selected will not be
displayed.
No Run Since Code Cleared
This selection will display up to DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Failed This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed
during the present ignition cycle.
F1: Data Display
The purpose of the “Data Display” mode is to
continuously monitor data parameters.
The current actual values of all important sensors and
signals in the system are display through F1 mode.
See the “Typical Scan Data” section.
F2: Snapshot
“Snapshot” allows you to focus on making the condition
occur, rather than trying to view all of the data in
anticipation of the fault.
The snapshot will collect parameter information around
a trigger point that you select.
F3: Miscellaneous Test:
The purpose of “Miscellaneous Test” mode is to check
for correct operation of electronic system actuators.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority
F1: Clear DTC Information
F2: DTC Information
F0: History
F1: MIL SVS or Message Requested
F2: Last Test Failed
F3: Test Failed Since Code Cleared
F4: Not Run Since Code Cleared
F5: Failed This Ignition
F1: Data Display
F0: Engine Data
F1: O2 Sensor Data
F2: Snapshot
F3: Miscellaneous Test
F0: Lamps
F0: Malfunction Indicator Lamps
F1: Relays
F0: Fuel Pump Relay
F1: A/C Clutch Relay
F2: EVAP
F0: Purge Solenoid
F3: IAC System
F0: IAC Control
F1: IAC Reset
F4: Injector Balance Test
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2242 of 6020
6E–72 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
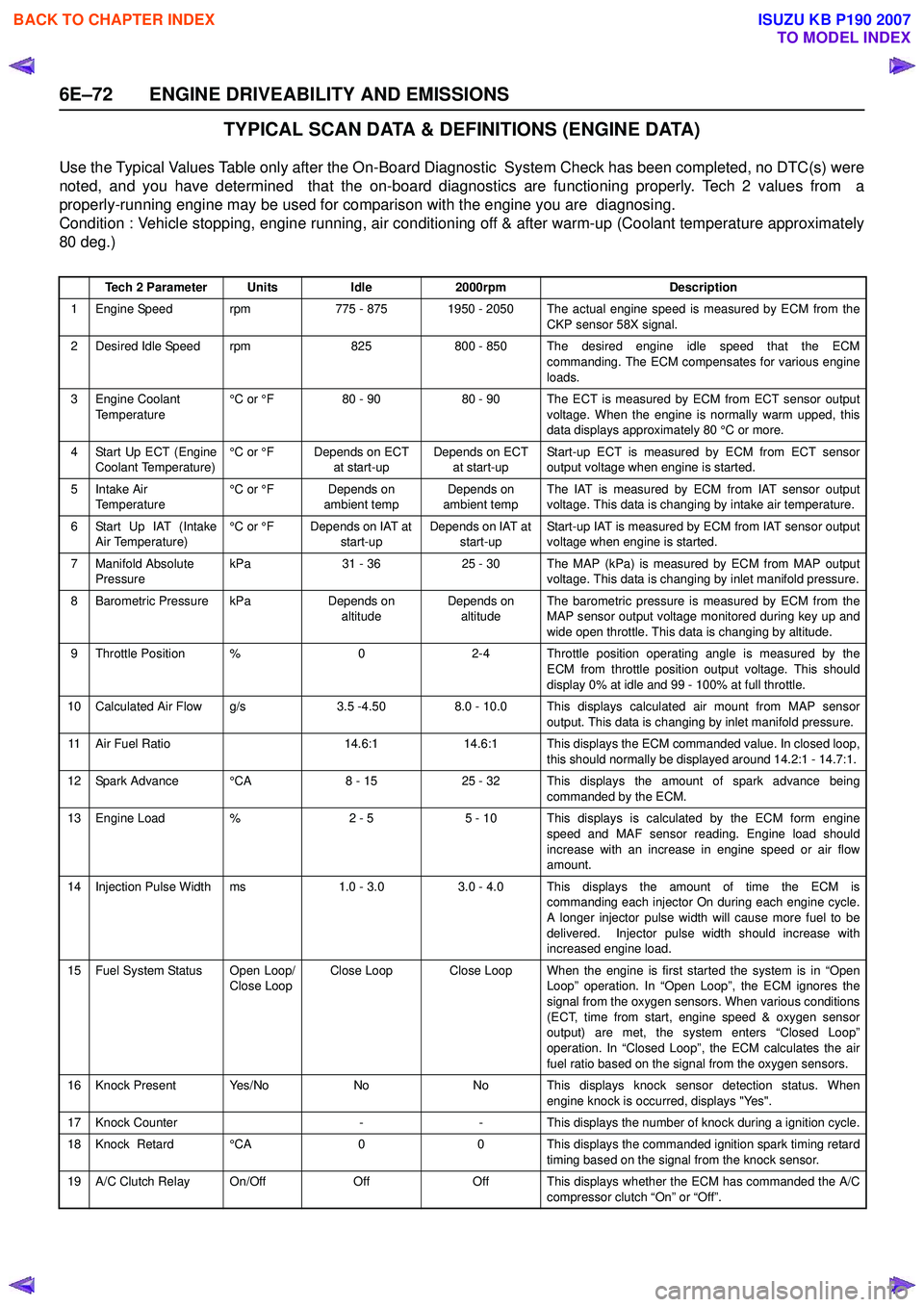
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA)
Use the Typical Values Table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System Check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly. Tech 2 values from a
properly-running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approximately
80 deg.)
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
1 Engine Speed rpm775 - 8751950 - 2050 The actual engine speed is measured by ECM from the
CKP sensor 58X signal.
2 Desired Idle Speed rpm825800 - 850 The desired engine idle speed that the ECMcommanding. The ECM compensates for various engine
loads.
3 Engine Coolant Temperature °C or °F80 - 9080 - 90 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. When the engine is normally warm upped, this
data displays approximately 80 °C or more.
4 Start Up ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature) °C or °FDepends on ECT
at start-upDepends on ECT at start-up Start-up ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor
output voltage when engine is started.
5Intake Air
Temperature °C or °FDepends on
ambient tempDepends on
ambient temp The IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
6 Start Up IAT (Intake Air Temperature) °C or °FDepends on IAT at
start-upDepends on IAT at start-up Start-up IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage when engine is started.
7 Manifold Absolute Pressure kPa31 - 3625 - 30The MAP (kPa) is measured by ECM from MAP output
voltage. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
8 Barometric Pressure kPaDepends on altitudeDepends on altitude The barometric pressure is measured by ECM from the
MAP sensor output voltage monitored during key up and
wide open throttle. This data is changing by altitude.
9 Throttle Position %02-4 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the ECM from throttle position output voltage. This should
display 0% at idle and 99 - 100% at full throttle.
10 Calculated Air Flow g/s3.5 -4.508.0 - 10.0 This displays calculated air mount from MAP sensor output. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
11 Air Fuel Ratio14.6:114.6:1 This displays the ECM commanded value. In closed loop,this should normally be displayed around 14.2:1 - 14.7:1.
12 Spark Advance °CA8 - 1525 - 32 This displays the amount of spark advance being commanded by the ECM.
13 Engine Load %2 - 55 - 10 This displays is calculated by the ECM form engine
speed and MAF sensor reading. Engine load should
increase with an increase in engine speed or air flow
amount.
14 Injection Pulse Width ms1.0 - 3.0 3.0 - 4.0 This displays the amount of time the ECM is commanding each injector On during each engine cycle.
A longer injector pulse width will cause more fuel to be
delivered. Injector pulse width should increase with
increased engine load.
15 Fuel System Status Open Loop/ Close LoopClose LoopClose Loop When the engine is first started the system is in “OpenLoop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various conditions
(ECT, time from start, engine speed & oxygen sensor
output) are met, the system enters “Closed Loop”
operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM calculates the air
fuel ratio based on the signal from the oxygen sensors.
16 Knock Present Yes/NoNoNo This displays knock sensor detection status. When engine knock is occurred, displays "Yes".
17 Knock Counter--This displays the number of knock during a ignition cycle.
18 Knock Retard °CA00 This displays the commanded ignition spark timing retard
timing based on the signal from the knock sensor.
19 A/C Clutch Relay On/OffOffOff This displays whether the ECM has commanded the A/C compressor clutch “On” or “Off”.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007