check engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2243 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–73
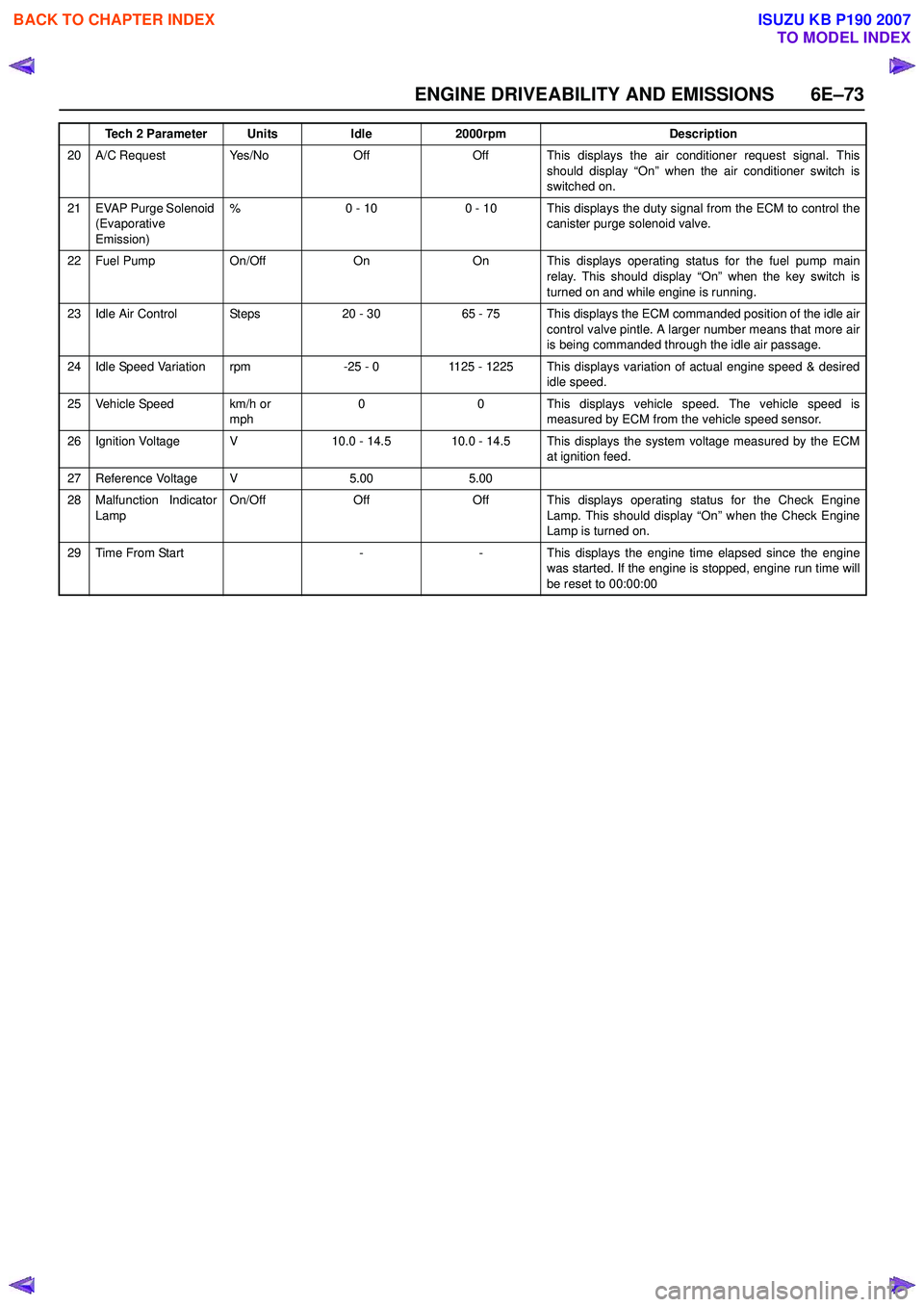
20 A/C Request Yes/NoOffOff This displays the air conditioner request signal. Thisshould display “On” when the air conditioner switch is
switched on.
21 EVAP Purge Solenoid (Evaporative
Emission) %0 - 100 - 10 This displays the duty signal from the ECM to control the
canister purge solenoid valve.
22 Fuel Pump On/OffOnOn This displays operating status for the fuel pump main
relay. This should display “On” when the key switch is
turned on and while engine is running.
23 Idle Air Control Steps20 - 3065 - 75 This displays the ECM commanded position of the idle air control valve pintle. A larger number means that more air
is being commanded through the idle air passage.
24 Idle Speed Variation rpm-25 - 01125 - 1225 This displays variation of actual engine speed & desired idle speed.
25 Vehicle Speed km/h or mph00This displays vehicle speed. The vehicle speed is
measured by ECM from the vehicle speed sensor.
26 Ignition Voltage V10.0 - 14.510.0 - 14.5 This displays the system voltage measured by the ECM at ignition feed.
27 Reference Voltage V5.005.00
28 Malfunction Indicator
Lamp On/OffOffOff This displays operating status for the Check Engine
Lamp. This should display “On” when the Check Engine
Lamp is turned on.
29Time From Start--This displays the engine time elapsed since the engine
was started. If the engine is stopped, engine run time will
be reset to 00:00:00
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2244 of 6020
6E–74 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
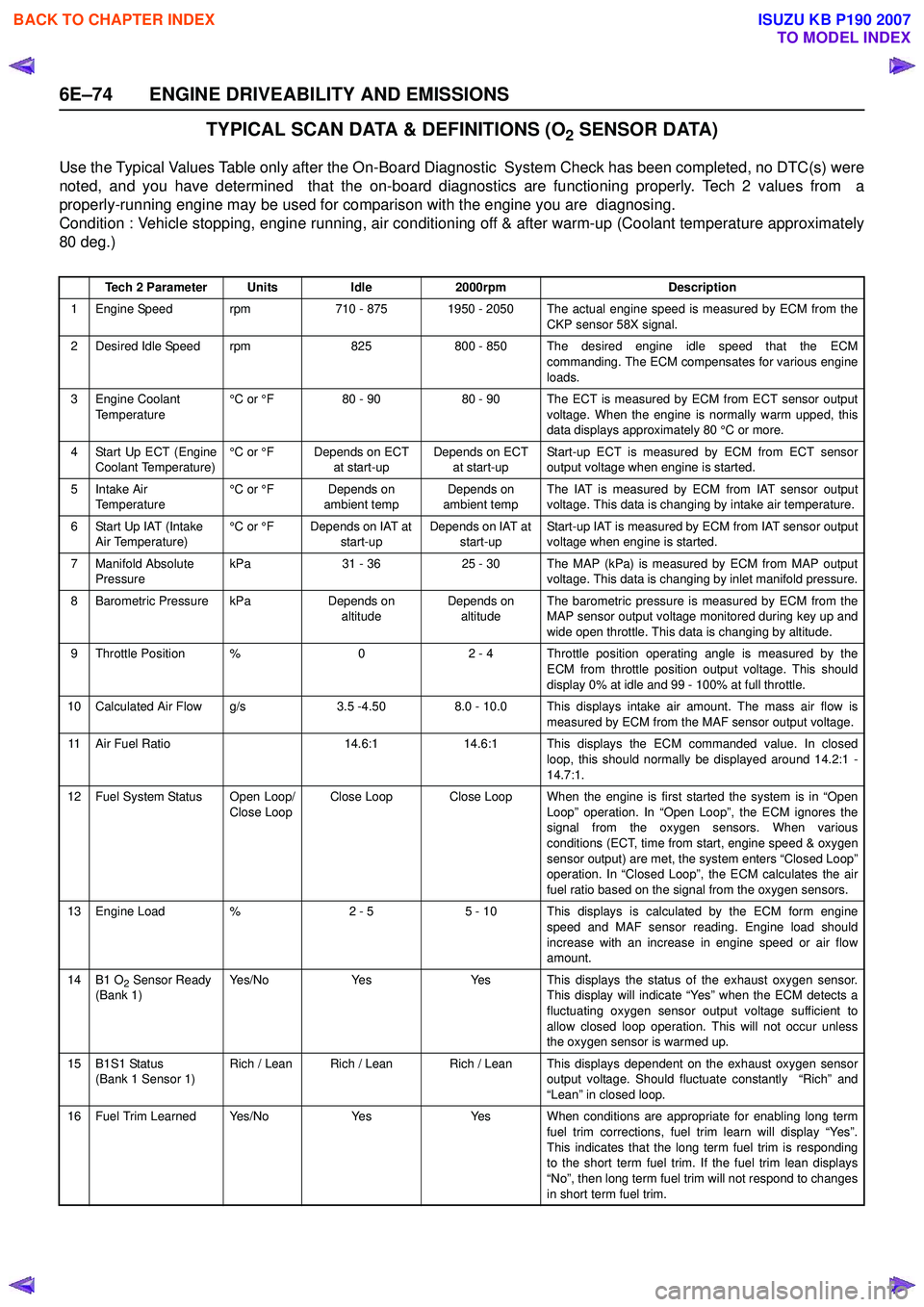
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (O2 SENSOR DATA)
Use the Typical Values Table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System Check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly. Tech 2 values from a
properly-running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approximately
80 deg.)
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
1 Engine Speed rpm710 - 8751950 - 2050 The actual engine speed is measured by ECM from the
CKP sensor 58X signal.
2 Desired Idle Speed rpm825800 - 850 The desired engine idle speed that the ECMcommanding. The ECM compensates for various engine
loads.
3 Engine Coolant Temperature °C or °F80 - 9080 - 90 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. When the engine is normally warm upped, this
data displays approximately 80 °C or more.
4 Start Up ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature) °C or °FDepends on ECT
at start-upDepends on ECT at start-up Start-up ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor
output voltage when engine is started.
5Intake Air
Temperature °C or °FDepends on
ambient tempDepends on
ambient temp The IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
6 Start Up IAT (Intake Air Temperature) °C or °FDepends on IAT at
start-upDepends on IAT at start-up Start-up IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage when engine is started.
7 Manifold Absolute Pressure kPa31 - 3625 - 30The MAP (kPa) is measured by ECM from MAP output
voltage. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
8 Barometric Pressure kPaDepends on altitudeDepends on altitude The barometric pressure is measured by ECM from the
MAP sensor output voltage monitored during key up and
wide open throttle. This data is changing by altitude.
9 Throttle Position %02 - 4 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the ECM from throttle position output voltage. This should
display 0% at idle and 99 - 100% at full throttle.
10 Calculated Air Flow g/s3.5 -4.508.0 - 10.0 This displays intake air amount. The mass air flow is measured by ECM from the MAF sensor output voltage.
11 Air Fuel Ratio14.6:114.6:1 This displays the ECM commanded value. In closedloop, this should normally be displayed around 14.2:1 -
14.7:1.
12 Fuel System Status Open Loop/ Close LoopClose LoopClose Loop When the engine is first started the system is in “OpenLoop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed & oxygen
sensor output) are met, the system enters “Closed Loop”
operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM calculates the air
fuel ratio based on the signal from the oxygen sensors.
13 Engine Load %2 - 55 - 10 This displays is calculated by the ECM form engine
speed and MAF sensor reading. Engine load should
increase with an increase in engine speed or air flow
amount.
14B1 O2 Sensor Ready
(Bank 1)Ye s / N oYe sYes This displays the status of the exhaust oxygen sensor. This display will indicate “Yes” when the ECM detects a
fluctuating oxygen sensor output voltage sufficient to
allow closed loop operation. This will not occur unless
the oxygen sensor is warmed up.
15B1S1 Status
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)Rich / LeanRich / LeanRich / Lean This displays dependent on the exhaust oxygen sensor output voltage. Should fluctuate constantly “Rich” and
“Lean” in closed loop.
16 Fuel Trim Learned Yes/NoYe sYes When conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim corrections, fuel trim learn will display “Yes”.
This indicates that the long term fuel trim is responding
to the short term fuel trim. If the fuel trim lean displays
“No”, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes
in short term fuel trim.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2246 of 6020

6E–76 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
MISCELLANEOUS TEST
The state of each circuit can be tested by using
miscellaneous test menus. Especially when DTC
cannot be detected, a faulty circuit can be diagnosed by
testing each circuit by means of these menus.
Even DTC has been detected, the circuit tests using
these menus could help discriminate between a
mechanical trouble and an electrical trouble.
Connect Tech 2 and select “Powertrain”, “2.XL L4
HV240” & “Miscellaneous Test”.
F0: Lamps
F0: Malfunction Indicator Lamp
When the Tech 2 is operated, “Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)” is turned on or off.
The circuit is normal if the “Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(Check Engine Lamp)” in the instrument panel is turned
on or off in accordance with this operation.
F1: Relays
F0: Fuel Pump Relay
When the Tech 2 is operated, fuel pump relay signal
turns ON or OFF.
The circuit is normal if fuel pump sound is generated in
accordance with this operation when key switch is
turned ON.
F1: A/C Clutch Relay
When the Tech 2 is operated, A/C clutch relay signal
turns ON or OFF.
The circuit is normal if A/C compressor clutch is
energized in accordance with this operation when the
engine is running.
F2: EVAP
F0: Purge Solenoid
When the Tech 2 is operated, duty ratio of EVAP purge
solenoid is changed 10%-by-10%.
• Press “Increase” key. Then, EVAP Purge Solenoid is increases 10%-by-
10%.
• Press “Quit” Key. F3: IAC System
F0: IAC Control
When the Tech 2 is operated, “Idle Air Control”
increases or decreases 5steps-by-5steps up to
150steps.
The circuit is normal if idle engine speed is changed in
accordance with this operation.
• Press “Increase” key. Then, Idle Air Control is increases 1osteps-by-
10steps up to 160steps. Engine speed is also
changed by this operation.
• Press “Quit” Key.
F1: IAC Reset
When the Tech 2 is operated, “Idle Air Control” resets.
The circuit is normal if idle engine speed is droped in
accordance with this operation.
• Press “Increase” key. Then, Desired Idle speed is increases 50rpm-by-
50rpm up to 1550rpm. Engine speed is also changed
by this operation.
• Press “Quit” Key.
Purge Solenoid
Engine Speed 800 RPM
Desired Idle Speed 762 RPM
Engine Coolant Temperature 80 °C
Start Up ECT 50 °C
Intake Air Temperature 30 °C
Start Up IAT 25 °C
Manifold Absolute Pressure 35kPa
EVAP Purge Solenoid 30%
IAC Control
Engine Speed 800 RPM
Desired Idle Speed 762 RPM
Engine Coolant Temperature 80 °C
Sta rt U p E C T 50 °C
Intake Air Temperature 30 °C
Start Up IAT25 °C
Manifold Absolute Pressure 35kPa
Idle Air Control 30 Steps
IAC Reset
Engine Speed 800 RPM
Desired Idle Speed 762 RPM
Engine Coolant Temperature 80 °C
Sta rt U p E C T 50 °C
Intake Air Temperature 30 °C
Start Up IAT 25 °C
Manifold Absolute Pressure 35kPa
Idle Air Control 30 Steps
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2251 of 6020
![ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–81
SNAPSHOT DISPLAY WITH TIS2000
Procedures for transferring and displaying Tech2
snapshot data by using TIS2000 [Snapshot Upload]
function is described below.
ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–81
SNAPSHOT DISPLAY WITH TIS2000
Procedures for transferring and displaying Tech2
snapshot data by using TIS2000 [Snapshot Upload]
function is described below.](/img/61/57177/w960_57177-2250.png)
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–81
SNAPSHOT DISPLAY WITH TIS2000
Procedures for transferring and displaying Tech2
snapshot data by using TIS2000 [Snapshot Upload]
function is described below.
Snapshot data can be displayed with [Snapshot Upload]
function included in TIS2000.
1. Record the snapshot data, in Tech2.
2. Transfer the snapshot data to PC. By analyzing these data in various methods, trouble
conditions can be checked.
Snapshot data is displayed by executing the three steps
below shown:
After recording the snapshot in Tech2, transfer the data
from Tech2 to PC by the below procedures.
1. Start TIS2000.
2. Select [Snapshot Upload] on the TIS2000 start screen.
3. Select [Upload from trouble diagnosis tool (transfer from diagnosis tester)] or click the corresponding
icon of the tool bar.
4. Select Tech2, and transfer the recorded snapshot information. 5. Select the transferred snapshot.
6. After ending transfer of the snapshot, data parameter list is displayed on the screen.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2254 of 6020

6E–84 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SERVICE PROGRAMMING SYSTEM (SPS)
The procedure to program the control unit by using the
Service Programming System (SPS) software contained
in TIS2000 is explained below.
NOTE:
• If the Engine Control Module (ECM) was programmed, the Immobilizer System must be
linked to the ECM: Refer to section 11
“Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for the
ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure.
• Should Tech2 display "SPS Procedure was not successful", engine will not start, but no DTCs
are present, low battery voltage or poor electrical
connections should be the primary suspects.
Perform the SPS procedure again after rectifying
the fault/s. IMPORTANT:
Perform the following checks before attempting to
program the control unit:
• The Tech2 PCMCIA card is programmed with The latest software release.
• The latest release of TIS2000 is loaded on the PC.
• The vehicle battery is fully charged.
• The control unit to be programmed is connected to the vehicle.
1. Preparations of TIS 2000 1. Connect Tech 2 to P/C.
2. Check to see if Hardware Key is plugged into Port.
3. Activate TIS 2000 by P/C.
4. On the activating screen of TIS2000, choose “Service Programming System”
5. On the screen of “Diagnostic Tester and Processing Program Selection”, choose the one that will comply
with the following.
• Tech-2 in use
• New programming by the existing module or new programming by the replaced/new module.
• Fixing position of the control unit. 6. Upon completion of the selection, push the button of
“Next”.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2255 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–85
2. Demand of Data1. Connect Tech-2 to the vehicle. When activated by turning on the power of Tech-2, push the “Enter”
switch.
2. Turn on the ignition switch (without starting the engine)
3. In the main menu of Diagnostic Tester, push “F1: Service Programming System (SPS)”.
4. Push “F0: Request Info” of Tech-2. 5. Where vehicle data has been already saved in Tech
2, the existing data come on display. In this
instance, as Tech-2 starts asking whether to keep
the data or to continue obtaining anew data from the
control unit, choose either of them
6. If you select “continue”, you have to select “Model Year”, “Vehicle Type”.
7. After that. then push button and turn Ignition switch tuned on, off, on following Tech-2 display. Tech-2
will read information from controller after this
procedure.
8. During obtaining information, Tech-2 is receiving information from the control unit ECM and TCM (A/T
only) at the same time. With VIN not being
programmed into the new control unit at the time of
shipment, "obtaining information" is not complete
(because the vehicle model, engine model and
model year are specified from VIN). For the
procedure get additional information on vehicles,
instruction will be provided in dialog form, when
TIS2000 is in operation.
9. Following instructions by Tech-2, push the “Exit” switch of Tech-2, turn off the ignition of the vehicle
and turn off the power of Tech-2, thereby removing
from the vehicle. 3. Data Exchange
1. Connect Tech-2 to P/C, turn on the power and click the “Next” button of P/C.
2. Check VIN of the vehicle and choose “Next”.
3. Select “System Type” for required control unit.
• Engine (Programming for ECM or PCM)
• Transmission (Programming for TCM)
4. When a lack of data is asked from among the following menu, enter accordingly.
Select following Menu
• Model Year
• Model
• Engine type
• Transmission type
• Destination code (vehicles for general export)*1
• Immobilizer
Etc.
* 1: How to read the destination code
Destination code can be read from ID Plate affixed on
vehicles, while on VIN plate the destination code is
described at the right-hand edge of Body Type line. In
the figure, the destination code can be read as "RR3"
(Australia).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2256 of 6020

6E–86 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
5. After choosing the data, click the “Next” button.
6. When all the necessary information is entered, the “details” of software within the database that match
the entered data will appear for confirmation. Click
the “Program” switch and then download the new
software onto Tech-2.
7. “Data Transfer” comes on display. The progress of downloading will be displayed on the screen in the
form of bar graph.
8. Upon finishing the data transfer, turn off the power of Tech-2, removing from P/C. 4. Programming of ECM
1. Check to see if batteries are fully charged, while ABS connectors shall be removed from the vehicle.
2. Connect Tech-2 to Vehicle Diagnostic Connectors.
3. Turn on the power of Tech-2 and the title screen comes on display.
4. Turn on the ignition (without allowing the engine to start)
5. On the title screen of Tech-2, push the “Enter” button.
6. Choose “F1: Service Programming System” on the main screen and then choose “Fl: Program ECU”.
7. While data is being transferred, “Programming in Progress” will be displayed on the Tech-2 screen.
8. Upon finishing the data transfer, Tech-2 will display “Reprogramming Was Successful”. Push the “Exit”
button to bring program to completion
9. Following “Procedure 2: Demand of Data”, try over again “Information Obtaining” and check to confirm
if the data has been correctly re-loaded.
10. Upon finishing confirmation, turn off the ignition of the vehicle and then turn off the power of Tech-2,
removing from the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2258 of 6020

6E–88 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Breaker Box Connection Type A
Breaker box connection type A, check for “open circuit”
and “short to ground circuit”.
51 43 2
(1) Engine Control Module (ECM)
(2) Harness Adapter
(3) Breaker Box (4) Digital Voltage Meter
(5) ECM - Harness Adapter Disconnection
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2259 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–89
Breaker Box Connection Type B
Breaker box connection type B, check for “short to
power supply circuit” and “power, signal voltage check”
between the engine control module (ECM) and
electrical components.
5 1
4 3 2
(1) Engine Control Module (ECM)
(2) Harness Adapter
(3) Breaker Box (4) Digital Voltage Meter
(5) ECM - Harness Adapter Connection
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2260 of 6020

6E–90 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK
Circuit Description
The on-board diagnostic system check is the starting
point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before
using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physical
check of the ECM and engine grounds for cleanliness
and tightness.
The on-board diagnostic system check is an organized
approach to identifying a problem created by an
electronic engine control system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for poor connections or a
damaged harness. Inspect the ECM harness and
connector for improper mating, broken locks, improperly
formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire
connection, and damaged harness.
Te s t D e s c r i p t i o n
Number(s) below refer the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The Check Engine Lamp (MIL) should be ON steady
with the ignition “On”, engine “Off”. If not, “No Check
Engine Lamp (MIL)” chart should be used to isolate the
malfunction.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that the
ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of
controlling the Check Engine Lamp (MIL) and the Check
Engine Lamp (MIL) driver circuit is not shorted to
ground circuit.
4. If the engine will not start, “Engine Cranks But Will
Not Run” chart should be used to diagnose the fault.
6. The Tech2 parameters which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing the
problem.
12. This vehicle is equipped with ECM which utilizes an
electrically erasable programmable read only memory
(EEPROM).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007