differential ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 538 of 6020

4C1-34 FRONT WHEEL DRIVE
12. Flange Nut and Washer
(1) Apply lubricant to the pinion threads.
(2) Tighten the nut to the specified torque using the pinion flange holder.
Pinion flange holder : 5-8840-0133-0
Torque N ⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅ft
)
177 - 275 (18 - 28/130 - 202)
Discard used flange nut and install new one.
(3) Pinion bearing preload
(a) Measure the bearing preload by using a torque meter. Note the scale reading required to rotate the flange.
(b) continue tightening until the specified starting torque is obtained.
Starting Torque N⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅in
)
0.63 - 1.13 (0.06 – 0.12/5 - 10)
13. Adjust Shim
(1)
Attach the side bearing to the differential assembly without
shims. Support the opposite side using a pilot to prevent
bearing damage.
1 Installer : 9-8522-1164-0
2 Drive handle : 5-8840-0007-0
3 Pilot : 9-8521-1743-0
(2) Insert the differential cage assembly with bearing oute
r
races into the side bearing bores of the carrier.
(3) Using two sets of feeler gauges, insert a feeler stock o
f
sufficient thickness between each bearing outer race and
the carrier to remove all end plat. Make certain the feele
r
stock is pushed to the bottom of the bearing bores.
Mount the dial indicator on the carrier so that the indicato
r
stem is at right angles to a tooth on the ring gear.
Dial indicator : 5-8840-0126-0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 541 of 6020
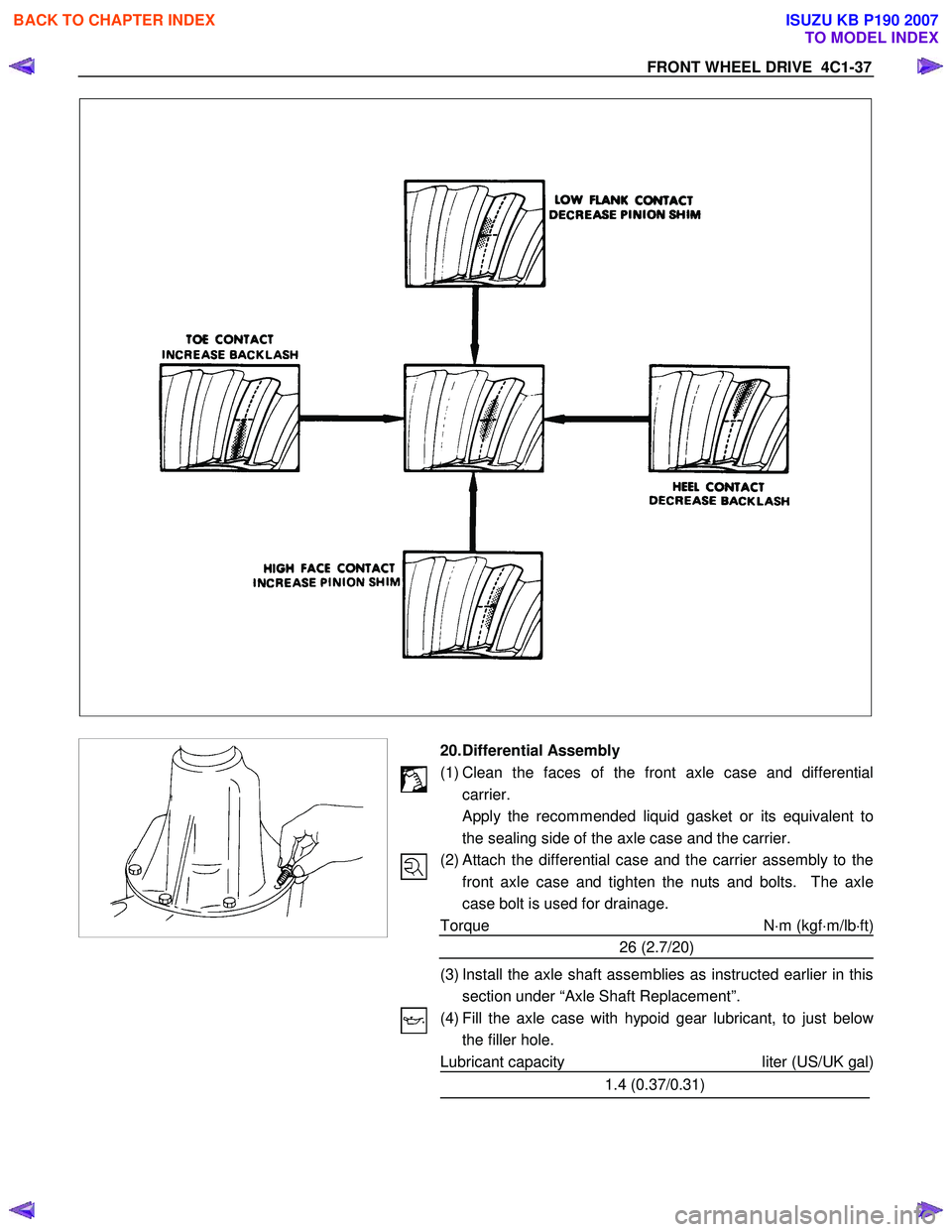
FRONT WHEEL DRIVE 4C1-37
20. Differential Assembly
(1) Clean the faces of the front axle case and differential carrier.
Apply the recommended liquid gasket or its equivalent to
the sealing side of the axle case and the carrier.
(2)
Attach the differential case and the carrier assembly to the
front axle case and tighten the nuts and bolts. The axle
case bolt is used for drainage.
Torque N ⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅ft)
26 (2.7/20)
(3) Install the axle shaft assemblies as instructed earlier in this section under “Axle Shaft Replacement”.
(4) Fill the axle case with hypoid gear lubricant, to just belo
w
the filler hole.
Lubricant capacity liter (US/UK gal)
1.4 (0.37/0.31)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 571 of 6020
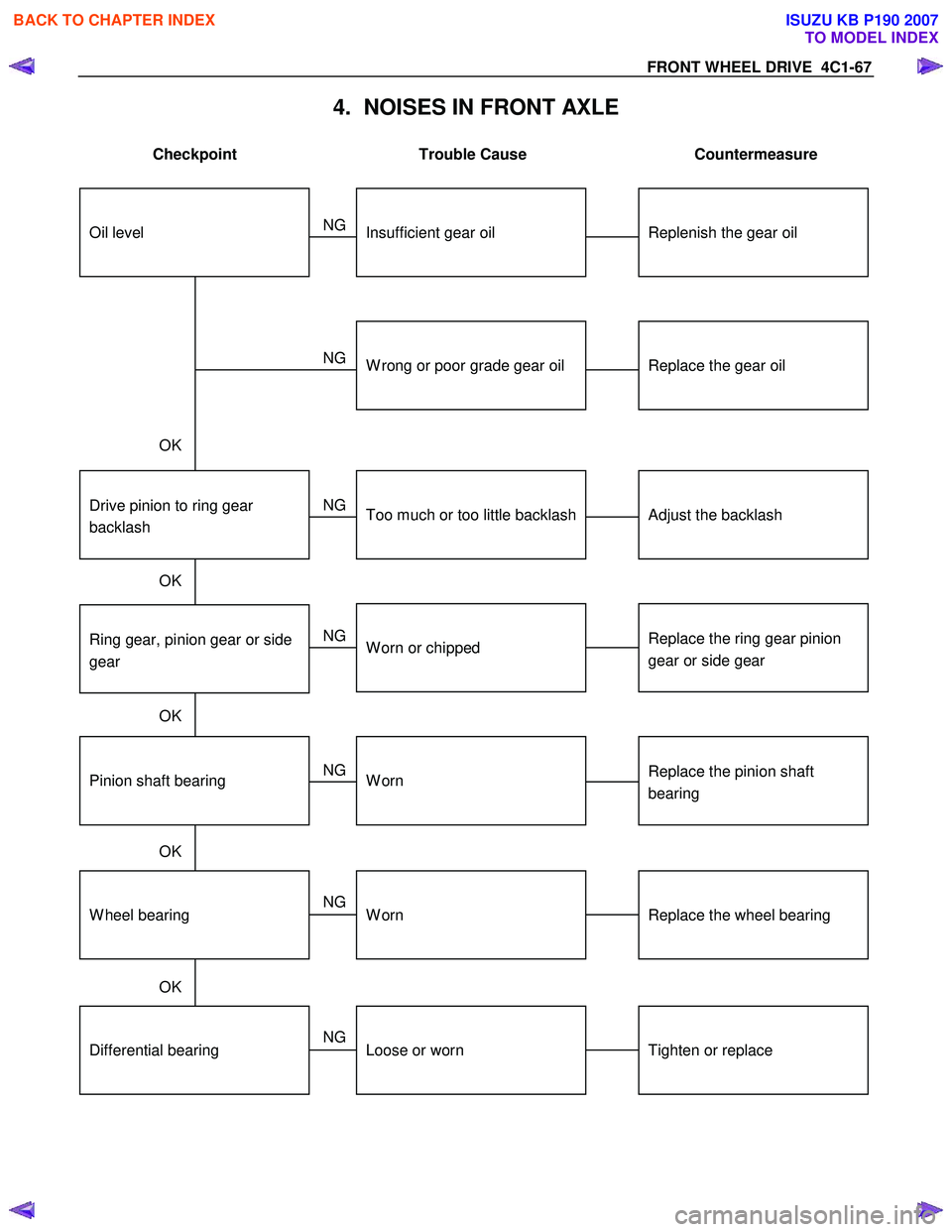
FRONT WHEEL DRIVE 4C1-67
4. NOISES IN FRONT AXLE
Checkpoint Trouble Cause Countermeasure
Replenish the gear oilInsufficient gear oil
NG
Replace the wheel bearing
Replace the pinion shaft
bearing
Replace the ring gear pinion
gear or side gear
Replace the gear oil
W heel bearingWorn
Pinion shaft bearingWorn
W orn or chipped
W rong or poor grade gear oil
Ring gear, pinion gear or side
gear
Adjust the backlashDrive pinion to ring gear
backlashToo much or too little backlash
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
OK
OK
OK
OK
Oil level
Tighten or replaceDifferential bearingLoose or worn
NG
OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 587 of 6020

SHIFT ON THE FLY SYSTEM 4C2-9
RTW 440SH000601
RTW 440SH000801
Dimension Check
Measure illustration sized A, B, and C
Limit mm (in)
A 64.3 (2.53)
B 6.7 (0.26)
C 6.7 (0.26)
RTW 440SH000701
Reassembly
15. Oil seal
Install the new oil seal which has been immersed in
differential gear oil, by using an oil seal installer.
Installer 5-8840-2407-0
Grip 5-8840-0007-0
412RS051
14. Needle Bearing
Force a new needle bearing into inner shaft by using a
special tool.
Installer : 5-8840-2408-0
Grip : 5-8840-0007-0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 588 of 6020

4C2-10 SHIFT ON THE FLY SYSTEM
412RS044
13. Inner Shaft Bearing
• Place a new snap ring in inner shaft.
• Force a new inner shaft bearing into the inner shaft.
Installer : 5-8840-2197-0
12. Snap Ring
NOTE;
Be careful not to damage the inner shaft.
11.inner Shaft • Clean the housing contact surface of the front axle
case.
• Insert inner shaft assembly into the front axle case.
NOTE:
Be careful not to damage oil seal.
412RW 017
10. Snap Ring
Install snap ring in the groove of front axle case.
NOTE:
Be sure to install the snap ring properly.
9. Clutch Gear Apply differential gear oil to clutch oil.
8. Sleeve Apply differential gear oil to sleeve.
412RW 023
7. Housing
• Clean contact surface with the front axle and actuato
r
mounting surface.
•
Apply liquid gasket to the contact surface on the front
axle case and install in the housing.
6. Bolt
Tighten bolts to specified tightening torque.
Housing Bolt Torque N⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅ft)
75 (7.6/55)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 589 of 6020
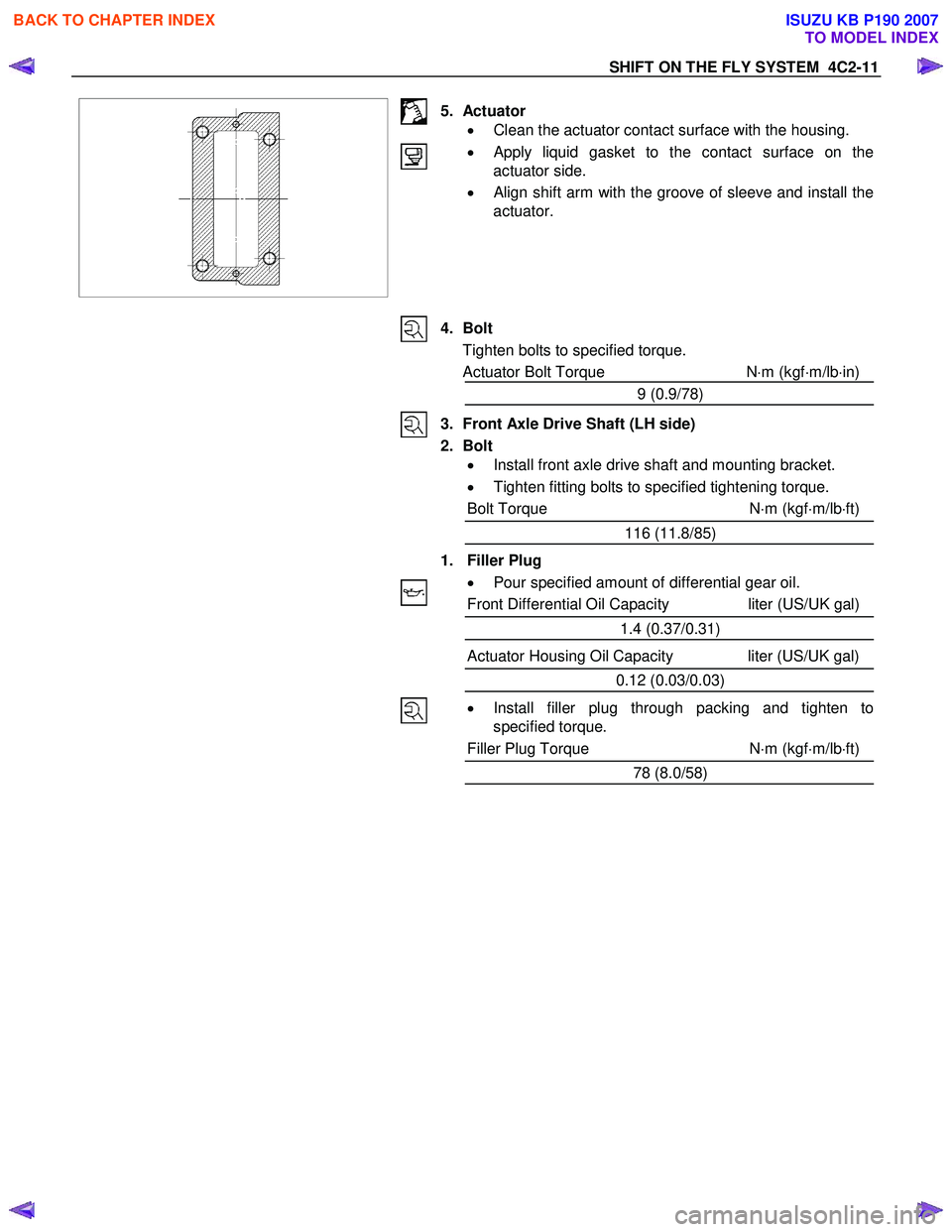
SHIFT ON THE FLY SYSTEM 4C2-11
5. Actuator • Clean the actuator contact surface with the housing.
•
Apply liquid gasket to the contact surface on the
actuator side.
• Align shift arm with the groove of sleeve and install the
actuator.
4. Bolt
Tighten bolts to specified torque.
Actuator Bolt Torque N⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅in)
9 (0.9/78)
3. Front Axle Drive Shaft (LH side)
2. Bolt • Install front axle drive shaft and mounting bracket.
• Tighten fitting bolts to specified tightening torque.
Bolt Torque N⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅ft)
116 (11.8/85)
1. Filler Plug • Pour specified amount of differential gear oil.
Front Differential Oil Capacity liter (US/UK gal)
1.4 (0.37/0.31)
Actuator Housing Oil Capacity liter (US/UK gal) 0.12 (0.03/0.03)
• Install filler plug through packing and tighten to
specified torque.
Filler Plug Torque N⋅m (kgf ⋅m/lb ⋅ft)
78 (8.0/58)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 657 of 6020
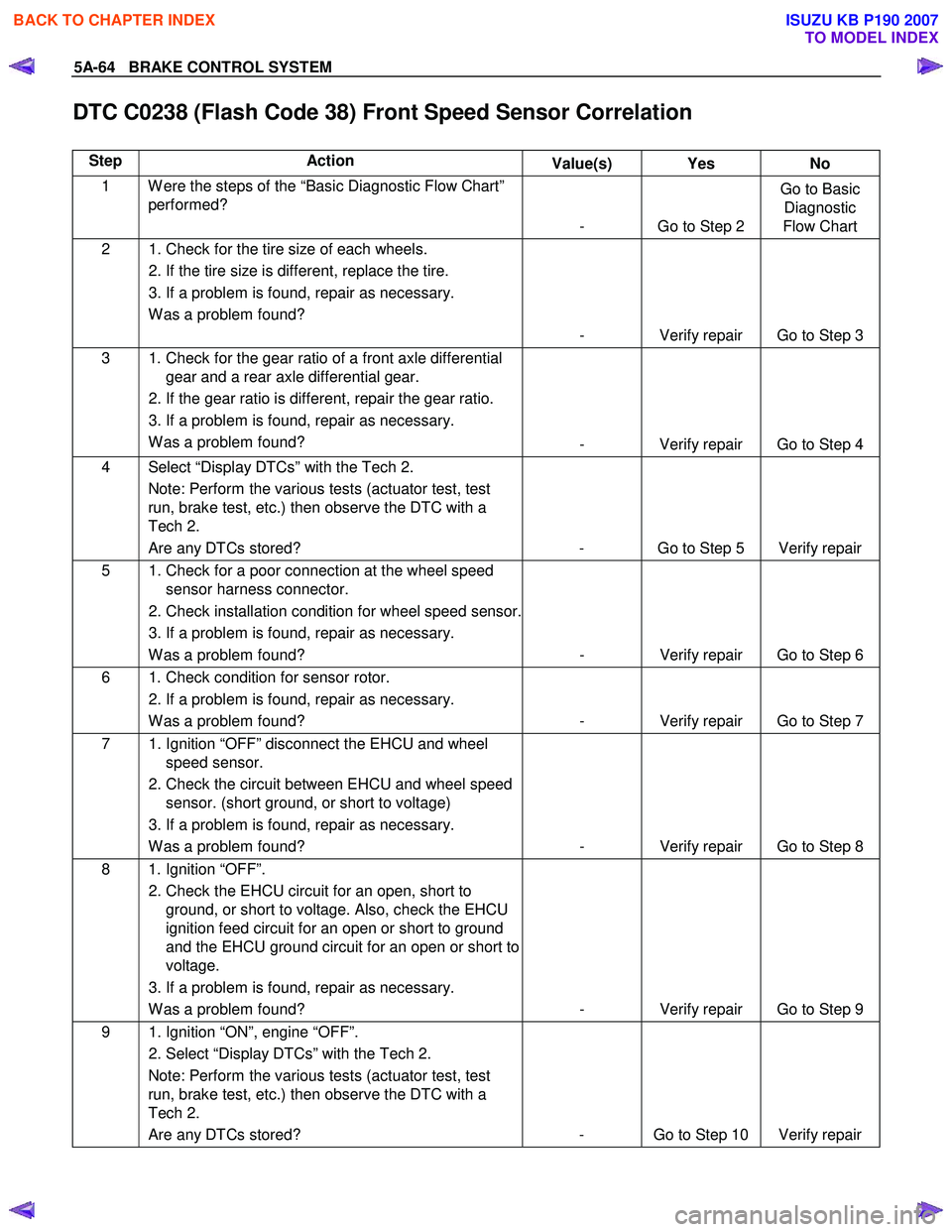
5A-64 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
DTC C0238 (Flash Code 38) Front Speed Sensor Correlation
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 W ere the steps of the “Basic Diagnostic Flow Chart”
performed?
- Go to Step 2 Go to Basic
Diagnostic
Flow Chart
2 1. Check for the tire size of each wheels.
2. If the tire size is different, replace the tire.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 1. Check for the gear ratio of a front axle differential gear and a rear axle differential gear.
2. If the gear ratio is different, repair the gear ratio.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 4
4 Select “Display DTCs” with the Tech 2.
Note: Perform the various tests (actuator test, test
run, brake test, etc.) then observe the DTC with a
Tech 2.
Are any DTCs stored? - Go to Step 5 Verify repair
5 1. Check for a poor connection at the wheel speed sensor harness connector.
2. Check installation condition for wheel speed sensor.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 1. Check condition for sensor rotor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 1. Ignition “OFF” disconnect the EHCU and wheel
speed sensor.
2. Check the circuit between EHCU and wheel speed sensor. (short ground, or short to voltage)
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 1. Ignition “OFF”.
2. Check the EHCU circuit for an open, short to ground, or short to voltage. Also, check the EHCU
ignition feed circuit for an open or short to ground
and the EHCU ground circuit for an open or short to
voltage.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. W as a problem found? - Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 1. Ignition “ON”, engine “OFF”.
2. Select “Display DTCs” with the Tech 2. Note: Perform the various tests (actuator test, test
run, brake test, etc.) then observe the DTC with a
Tech 2.
Are any DTCs stored? - Go to Step 10 Verify repair
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 842 of 6020
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 37
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Read this section carefully before performing any removal and installation procedure. This section gives
you important points as well as the order of operation. Be sure that you understand everything in this section before
you begin.
Removal
P1010011
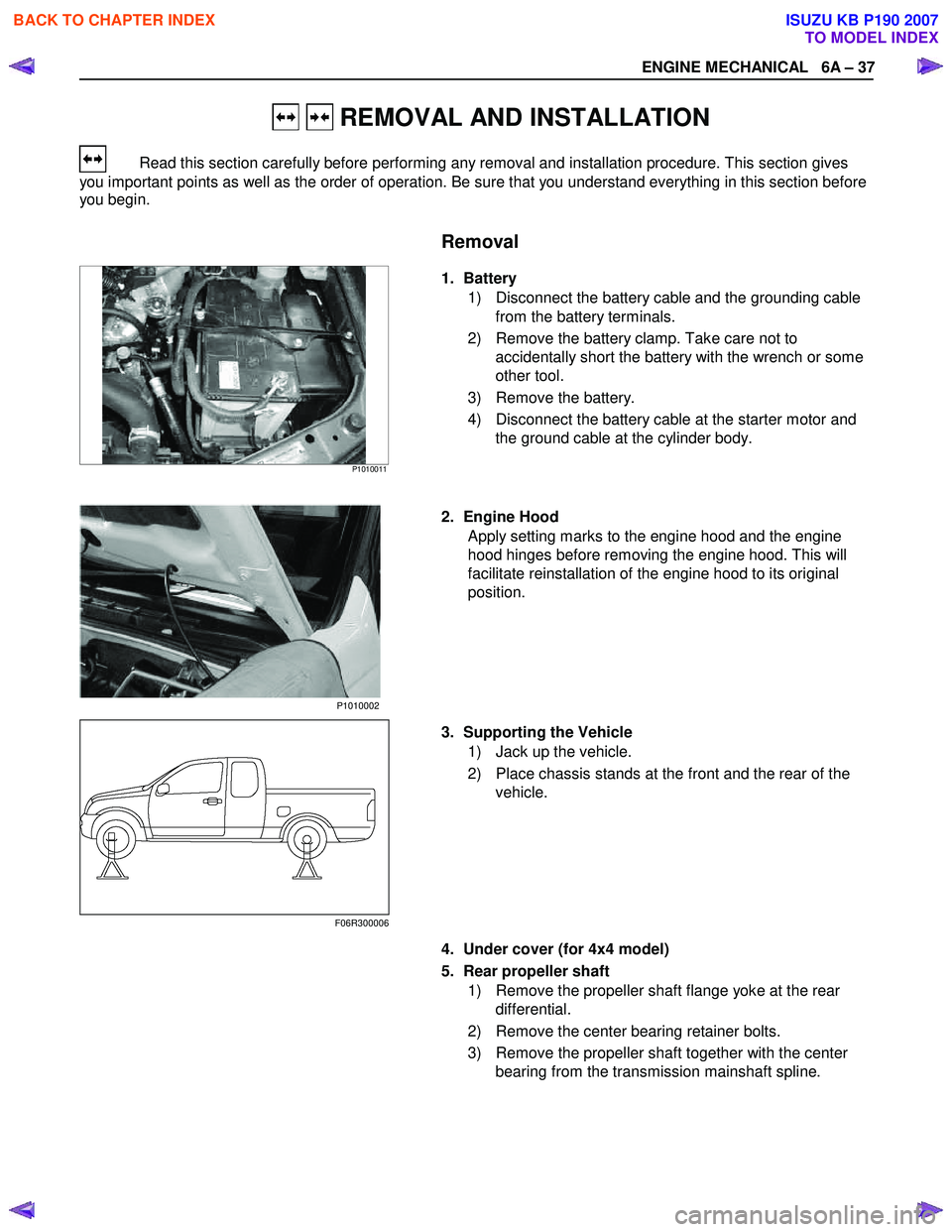
1. Battery
1) Disconnect the battery cable and the grounding cable from the battery terminals.
2) Remove the battery clamp. Take care not to accidentally short the battery with the wrench or some
other tool.
3) Remove the battery.
4) Disconnect the battery cable at the starter motor and the ground cable at the cylinder body.
2. Engine Hood Apply setting marks to the engine hood and the engine
hood hinges before removing the engine hood. This will
facilitate reinstallation of the engine hood to its original
position.
3. Supporting the Vehicle 1) Jack up the vehicle.
2) Place chassis stands at the front and the rear of the vehicle.
4. Under cover (for 4x4 model) 5. Rear propeller shaft 1) Remove the propeller shaft flange yoke at the rear differential.
2) Remove the center bearing retainer bolts.
3) Remove the propeller shaft together with the center bearing from the transmission mainshaft spline.
F06R300006 P1010002
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1672 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-55
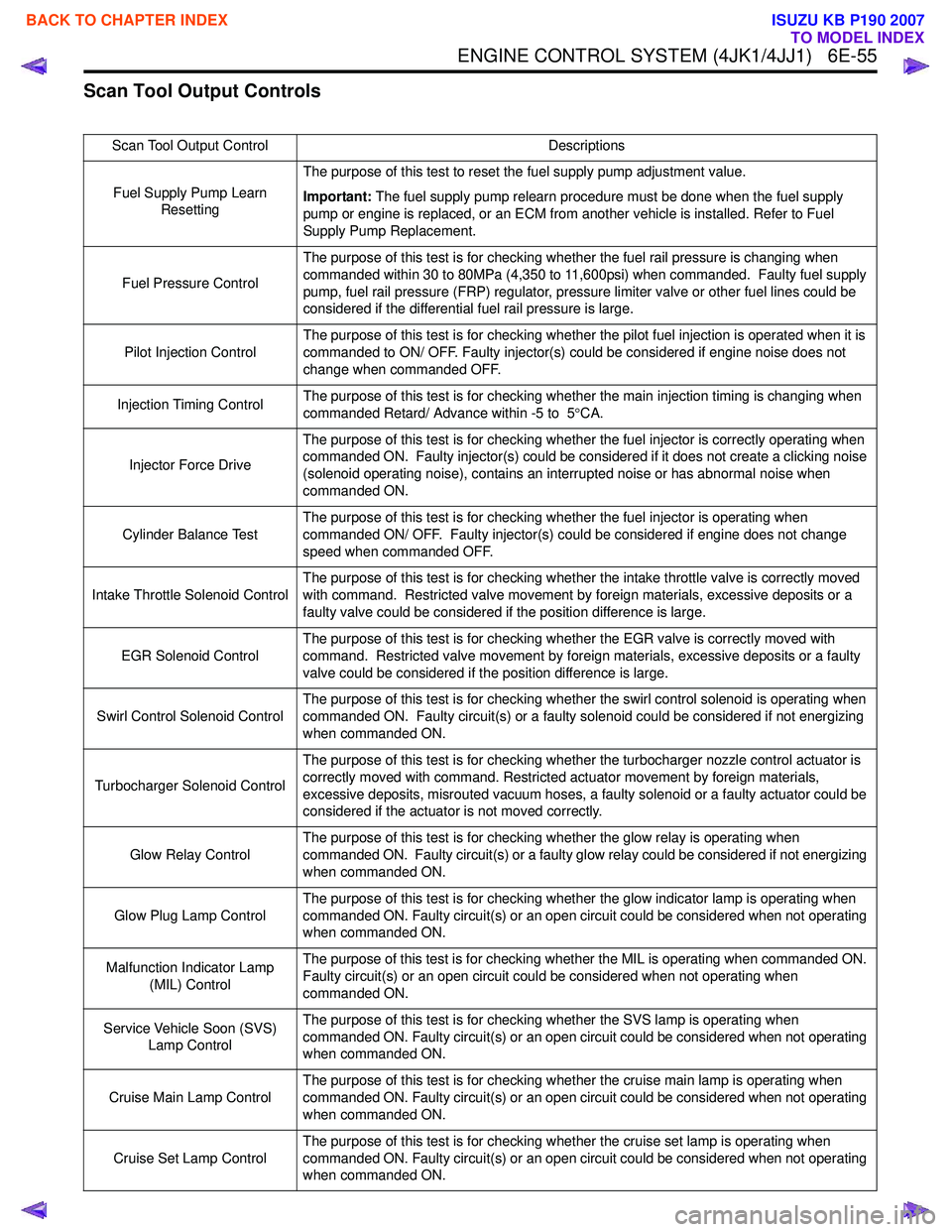
Scan Tool Output Controls
Scan Tool Output ControlDescriptions
Fuel Supply Pump Learn Resetting The purpose of this test to reset the fuel supply pump adjustment value.
Important: The fuel supply pump relearn procedure must be done when the fuel supply
pump or engine is replaced, or an ECM from another vehicle is installed. Refer to Fuel
Supply Pump Replacement.
Fuel Pressure Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the fuel rail pressure is changing when
commanded within 30 to 80MPa (4,350 to 11,600psi) when commanded. Faulty fuel supply
pump, fuel rail pressure (FRP) regulator, pressure limiter valve or other fuel lines could be
considered if the differential fuel rail pressure is large.
Pilot Injection Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the pilot fuel injection is operated when it is
commanded to ON/ OFF. Faulty injector(s) could be considered if engine noise does not
change when commanded OFF.
Injection Timing Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the main injection timing is changing when
commanded Retard/ Advance within -5 to 5 °CA.
Injector Force Drive The purpose of this test is for checking whether the fuel injector is correctly operating when
commanded ON. Faulty injector(s) could be considered if it does not create a clicking noise
(solenoid operating noise), contains an interrupted noise or has abnormal noise when
commanded ON.
Cylinder Balance Test The purpose of this test is for checking whether the fuel injector is operating when
commanded ON/ OFF. Faulty injector(s) could be considered if engine does not change
speed when commanded OFF.
Intake Throttle Solenoid Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the intake throttle valve is correctly moved
with command. Restricted valve movement by foreign materials, excessive deposits or a
faulty valve could be considered if the position difference is large.
EGR Solenoid Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the EGR valve is correctly moved with
command. Restricted valve movement by foreign materials, excessive deposits or a faulty
valve could be considered if the position difference is large.
Swirl Control Solenoid Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the swirl control solenoid is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or a faulty solenoid could be considered if not energizing
when commanded ON.
Turbocharger Solenoid Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the turbocharger nozzle control actuator is
correctly moved with command. Restricted actuator movement by foreign materials,
excessive deposits, misrouted vacuum hoses, a faulty solenoid or a faulty actuator could be
considered if the actuator is not moved correctly.
Glow Relay Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the glow relay is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or a faulty glow relay could be considered if not energizing
when commanded ON.
Glow Plug Lamp Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the glow indicator lamp is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or an open circuit could be considered when not operating
when commanded ON.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the MIL is operating when commanded ON.
Faulty circuit(s) or an open circuit could be considered when not operating when
commanded ON.
Service Vehicle Soon (SVS) Lamp Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the SVS lamp is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or an open circuit could be considered when not operating
when commanded ON.
Cruise Main Lamp Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the cruise main lamp is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or an open circuit could be considered when not operating
when commanded ON.
Cruise Set Lamp Control The purpose of this test is for checking whether the cruise set lamp is operating when
commanded ON. Faulty circuit(s) or an open circuit could be considered when not operating
when commanded ON.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1907 of 6020

6E-290 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
DTC P2227 (Flash Code 71)
Circuit Description
The barometric pressure (BARO) sensor is located on
the intake manifold. The BARO sensor is a transducer
that varies voltage according to changes the barometric
pressure. Within the ECM, the diagnostic compares the
BARO sensor input to the boost pressure sensor input.
If the ECM detects that the inputs are not within a
specified amount of each other, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0500,
P0501, P0638, P0652, P0653, P0698, P0699,
P2100, P2101, P2103, P2228 and P2229 are not
set.
AND following conditions are met for longer than 3
seconds.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine coolant temperature is more than 5 °C
(41 °F).
• The engine speed is less than 800 RPM.
• The fuel injection quantity is less than a predetermined value.
• The accelerator pedal is not depressed.
• The vehicle is not running.
• The engine run time is longer than 5 seconds. Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects that the differential pressure between the barometric pressure and the boost
pressure is more than 10 kPa (1.5 psi) for 10
seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits EGR control.
• The ECM inhibits cruise control.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
Diagnostic Aids • If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P2227
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0107, P0108, P2228 or P2229 also set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 3
3 1. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
2. Compare the Boost Pressure parameter to the Barometric Pressure (BARO) parameter with
a scan tool.
Are both parameter within the range specified of
each other? 10 kPa (1.5
psi)
Go to Diagnostic Aids Go to Step 4
4 Determine the outside barometric pressure from
your location specified in the altitude vs barometric
pressure table. Refer to Altitude vs Barometric
Pressure.
Is the BARO parameter on the scan tool close to
the outside barometric pressure? —
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007