OBD port ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2237 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–67
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after it leaves the factory. No allowances
have been made in the vehicle design for this type of
equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle's electrical system at the
battery (power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the electric system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any electric problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction.
• An example of charging by friction is a person sliding across a vehicle seat.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with well- insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentarily touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components. Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold
sensor or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis
and turns on the check engine lamp.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the check
engine lamp.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the check
engine lamp to turn on if the vehicle is not maintained
properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and crankcase
deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper oil
viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics,
vehicle maintenance schedules must be more closely
followed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any
diagnostic procedure or diagnosing the cause of an
emission test failure. This can often lead to repairing a
problem without further steps. Use the following
guidelines when performing a visual/physical
inspection:
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts, disconnects, and correct routing.
• Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other components.
• Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched
wires, contact with sharp edges or contact with hot
exhaust manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in
an incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2238 of 6020

6E–68 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which
is a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive.
When a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the
diagnostic executive records the following data:
• The diagnostic test has been completed since the last ignition cycle.
• The diagnostic test has passed during the current ignition cycle.
• The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the
diagnostic executive records the following data:
• The diagnostic test has been completed since the last ignition cycle.
• The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently active.
• The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
• The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
• Commanding the check engine lamp on and off
• DTC logging and clearing
• Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are
designed to locate a faulty circuit or component through
a process of logical decisions. The charts are prepared
with the requirement that the vehicle functioned
correctly at the time of assembly and that there are not
multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented
by the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual.
The language of communicating the source of the
malfunction is a system of diagnostic trouble codes.
When a malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the check engine
lamp is illuminated.
Check Engine Lamp
The check engine lamp looks the same as the check
engine lamp you are already familiar with, the “Check
Engine” lamp.
Basically, the check engine lamp is turned on when the
ECM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.
• When the check engine lamp remains “ON” while the engine is running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a driveability or emissions problem,
a Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check must be performed. The procedures for these
checks are given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check. These checks will expose faults
which may not be detected if other diagnostics are
performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the contorl
module is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located
behind the lower front instrument panel. The DLC is
used to connect to a Tech 2. Some common uses of the
Tech 2 are listed below:
• Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
• Clearing DTCs.
• Reading serial data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps is very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2270 of 6020

6E–100 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Injector Coil Test Procedure (Steps 1-6) and Injector Balance Test Procedure (Steps 7-11)
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Turn the engine OFF. NOTE: In order to prevent flooding of a single cylinder
and possible engine damage, relieve the fuel pressure
before performing the fuel injector coil test procedure.
2. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to Test Description Number 2.
3. Connect the 5-8840-2618-0 Fuel Injector Tester to B+ and ground, and to the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector
Adapter Cable.
4. Remove the harness connector of the Fuel Injector and connect the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector
Adapter Cable for F/I check.
5. Set the amperage supply selector switch on the fuel injector tester to the “Coil Test” 0.5 amp
position.
6. Connect the leads from the 5-8840-2392-0 Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to the fuel injector tester. Refer
to the illustrations associated with the test
description.
7. Set the DVM to the tenths scale (0.0).
8. Observe the engine coolant temperature.
Is the engine coolant temperature within the specified
values? 10°C (50°F)
to
35°C (95°F) Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
3 1. Set the injector adapter cable to injector #1. 2. Press the “Push to Start Test” button on the fuelinjector tester.
3. Observe the voltage reading on the DVM.
Important: The voltage reading may rise during the
test.
4. Record the lowest voltage observed after the first second of the test.
5. Set the injector adapter cable to the next injector and repeat steps 2, 3, and 4.
Did any fuel injector have an erratic voltage reading
(large fluctuations in voltage that did not stabilize) or a
voltage reading outside of the specified values? 5.7-6.6V Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
4 Replace the faulty fuel injector(S). Refer to Fuel
Injector .
Is the action complete? — Go to Step 7—
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2272 of 6020

6E–102 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
9 1. Connect the 5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Injector Testerand 5-8840-2589-0 Injector Adapter Cable to the
fuel injector harness connector.
2. Set the amperage supply selector switch on the fuel injector tester to the “Balance Test” 0.5-2.5
amp position.
3. Using the Scan Tool turn the fuel pump ON then OFF in order to pressurize the fuel system.
4. Record the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge after the fuel pressure stabilizes.
This is the first pressure reading.
5. Energize the fuel injector by depressing the “Push to Start Test” button on the fuel injector tester.
6. Record the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge after the fuel pressure gauge
needle has stopped moving. This is the second
pressure reading.
7. Repeat steps 1 through 6 for each fuel injector.
8. Subtract the second pressure reading from the first pressure reading for one fuel injector. The
result is the pressure drop value.
9. Obtain a pressure drop value for each fuel injector.
10. Add all of the individual pressure drop values. This is the total pressure drop.
11. Divide the total pressure drop by the number of fuel injectors. This is the average pressure drop.
Does any fuel injector have a pressure drop value that
is either higher than the average pressure drop or
lower than the average pressure drop by the specified
value? 10kPa
(1.5psi) Go to Step 10Go to
OBD
System Check
10 Re-test any fuel injector that does not meet the specification. Refer to the procedure in Step 11.
NOTE: Do not repeat any portion of this test before
running the engine in order to prevent the engine from
flooding.
Does any fuel injector still have a pressure drop value
that is either higher than the average pressure drop or
lower than the average pressure drop by the specified
value? 10kPa
(1.5psi) Go to Step 11Go to
Symptoms
11 1. Replace the faulty fuel injector(s). Refer to Fuel
Injector .
2. Disconnect the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector Adapter Cable for F/I check and re-connect the original F/I
check connector.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2326 of 6020
6E–156 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Fuel System Diagnosis.
• Perform “Injector Balance Test” - Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis.
• Check the EVAP canister for fuel saturation - If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses. Refer to
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission Control System.
• Check for a leak in the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the
regulator for the presence of fuel. • An intermittent TPS output will cause the system to
go rich due to a false indication of the engine
accelerating.
• Silicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is
indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion
of the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If
contamination is noticed, replace the affected HO2S.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132
O
2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(S) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0132 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0132 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
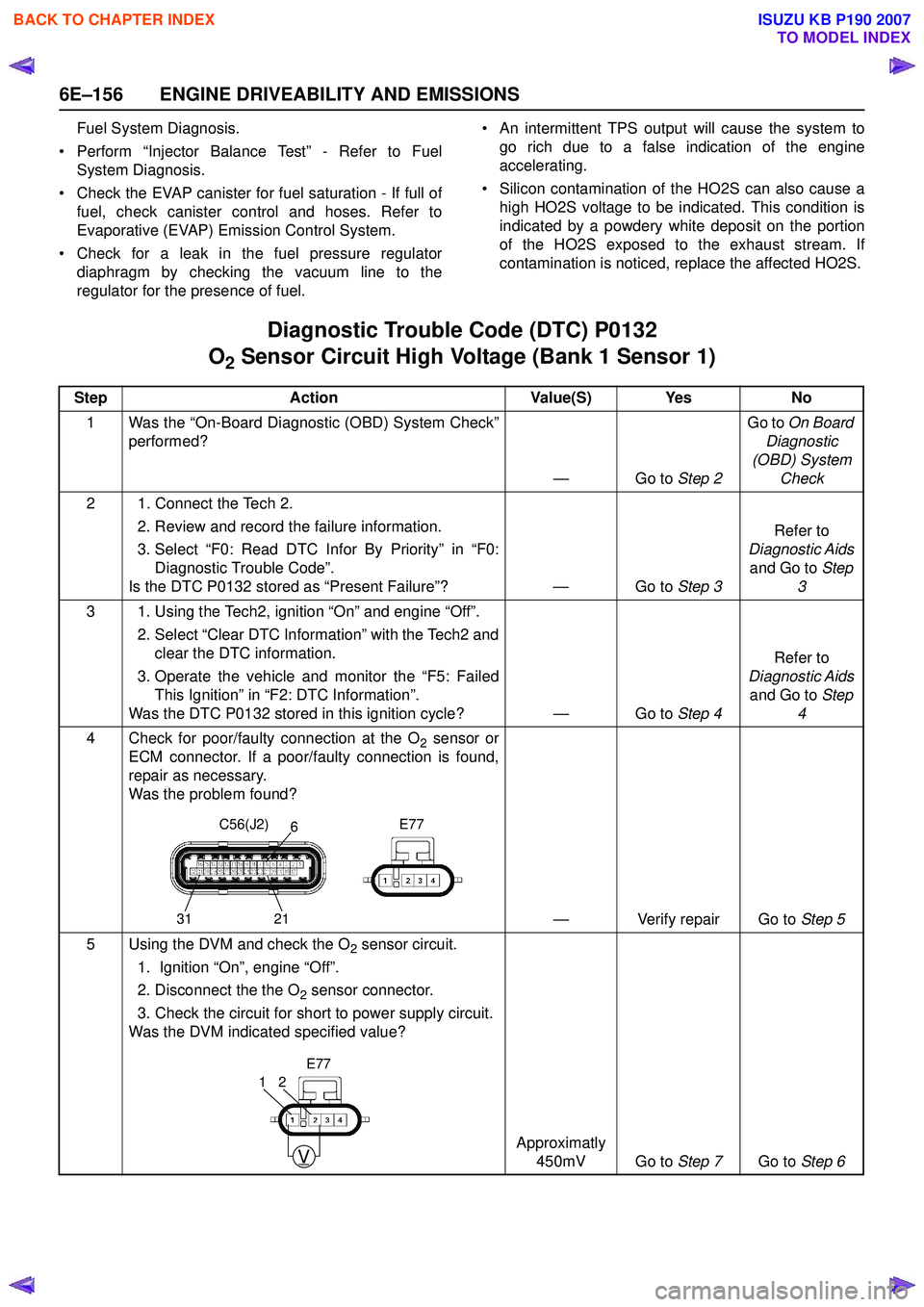
4 Check for poor/faulty connection at the O
2 sensor or
ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found,
repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to power supply circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
Approximatly 450mV Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
C56(J2) E77
31 216
V
21
E77
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2376 of 6020

6E–206 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0601 ECM MEMORY CHECKSUM
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) used in this vehicle
utilizes an electrically erasable programmable read-only
memory (EEPROM). The EEPROM contains program
information and the calibrations required for engine,
transmission, and powertrain diagnostics operation.
Unlike the PROM used in past applications, the
EEPROM is not replaceable. When the ECM is
replaced or a calibration update is required, the ECM must be programmed using a Tech 2.Diagnostic Aids
• Diagnostic Trouble Code P0601 indicates that the
contents of the EEPROM have changed since the
ECM was programmed. The only possible repair is
ECM reprogramming or replacement. Check service
bulletins to program the replacement ECM with the
correct software and calibration for the vehicle.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601 ECM Memory Checksum
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0601 A ECM Memory Checksum ECM memory area error.Engine control disabled.
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0601 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0601 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
4 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2382 of 6020
6E–212 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
• Perform “Injector Balance Test” - Refer to Fuel
System Diagnosis .
• Check the EVAP canister for fuel saturation - If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses. Refer to
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission Control System .
• Check for a leak in the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to toe
regulator for the presence of fuel. • An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the
system to go rich due to a false indication of the
engine accelerating.
• Silicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is
indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion
of the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If
contamination is noticed, replace the affected HO2S.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1167
Fuel Supply System Rich During Deceleration Fuel Cutoff
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1167 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1167 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to S tep
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Monitor the “Throttle Position” in the data display.
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct “Throttle Position” in
accordance with accelerator pedal operation? — Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5 Check for the following conditions. • Objects blocking the throttle valve.
• Incorrectly installed.
If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
6 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Manifold Absolute Pressure” in thedata display.
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct “Manifold Absolute
Pressure” in accordance with engine speed or
acceleration? — Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
7 Remove the MAP sensor and check for the following conditions.
• Objects blocking the air cleaner.
• Objects blocking the MAP sensor.
• Objects blocking the throttle valve.
• Vacuum leaking at intake duct.
• Vacuum leaking at throttle body.
If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2387 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–217
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1625 ECM SYSTEM RESET
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors unexpected
ECM reset. This will not turn on MIL light on, only
records code DTC P1625.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the follwing conditions:
• P1625 alone stored does not need diagnosis. Clear DTC code.
NOTE: DTC P1625 is a DTC to record a ECM reset
history. If DTC P1625 is not reset and no engine
abnormality occurs after learing the DTC, no farther
diagnostic procedures are required.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1625 ECM System Reset
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1625 B ECM System Reset ECM reset has occurred other than “On”. Engine control disabled.
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1625 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1625 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 Is the Immobilizer function programmed in the ECM? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2393 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–223
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1631 Immobilizer Wrong Signal
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1631 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1631 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Immobilizer” in the system selection menu“Body”.
3. Select “Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority” in the “Diagnositic Trouble Code”.
Was the DTC B0007 stored in this ignition cycle? —Refer to
“Immobilizer Workshop
Manual” & Go to DTC Chart B0007 Go to Step 5
5 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2395 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–225
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1648 Wrong Security Code Entered
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1648 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1648 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Immobilizer” in the system selection menu“Body”.
3. Select “Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority” in the “Diagnositic Trouble Code”.
Was the DTC B0007 stored in this ignition cycle? —Refer to
“Immobilizer Workshop
Manual” & Go to DTC Chart B0007 Go to Step 5
5 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007