torque ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3807 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–21
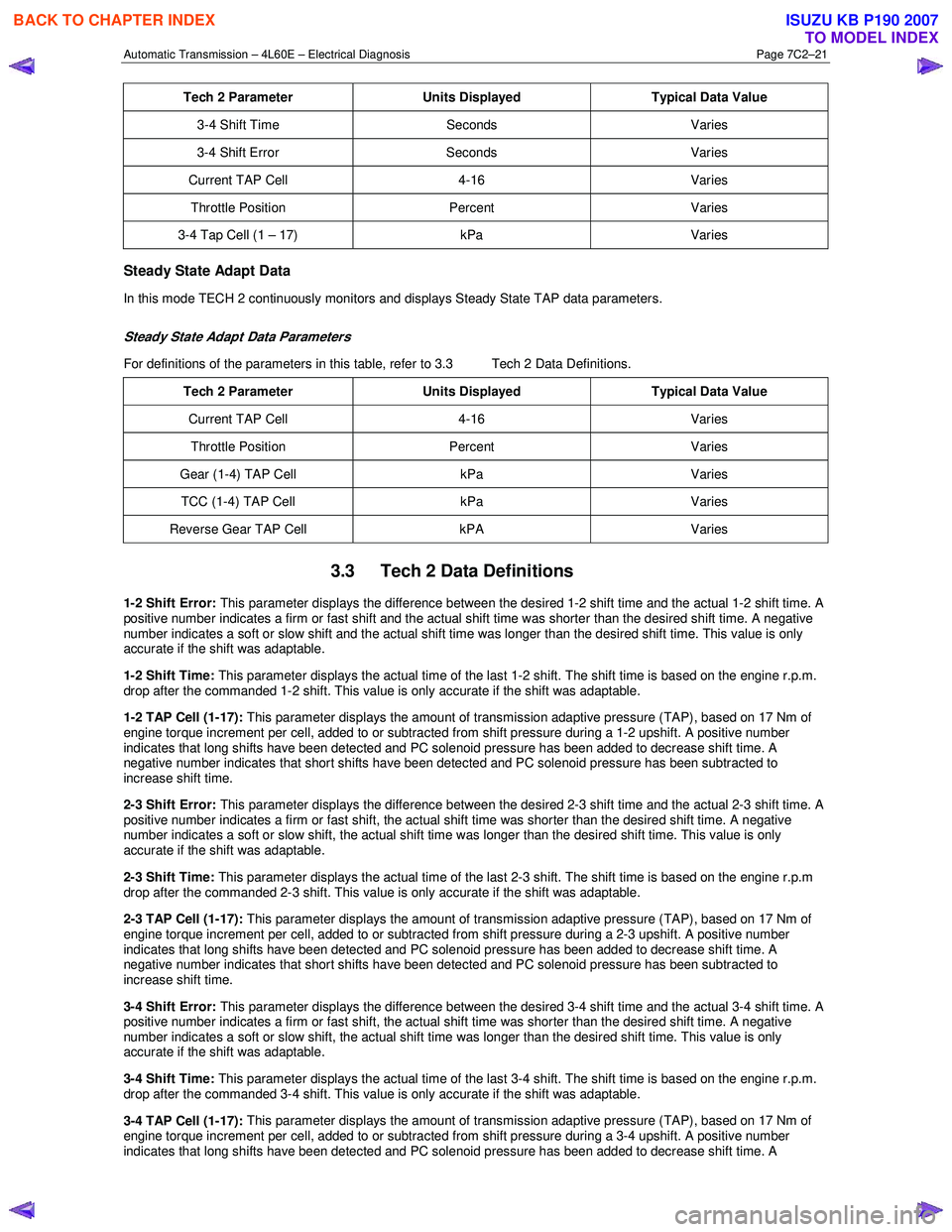
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Data Value
3-4 Shift Time Seconds Varies
3-4 Shift Error Seconds Varies
Current TAP Cell 4-16 Varies
Throttle Position Percent Varies
3-4 Tap Cell (1 – 17) kPa Varies
Steady State Adapt Data
In this mode TECH 2 continuously monitors and displays Steady State TAP data parameters.
Steady State Adapt Data Parameters
For definitions of the parameters in this table, refer to 3.3 Tech 2 Data Definitions.
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Data Value
Current TAP Cell 4-16 Varies
Throttle Position Percent Varies
Gear (1-4) TAP Cell kPa Varies
TCC (1-4) TAP Cell kPa Varies
Reverse Gear TAP Cell kPA Varies
3.3 Tech 2 Data Definitions
1-2 Shift Error: This parameter displays the difference between the desired 1-2 shift time and the actual 1-2 shift time. A
positive number indicates a firm or fast shift and the actual shift time was shorter than the desired shift time. A negative
number indicates a soft or slow shift and the actual shift time was longer than the desired shift time. This value is only
accurate if the shift was adaptable.
1-2 Shift Time: This parameter displays the actual time of the last 1-2 shift. The shift time is based on the engine r.p.m.
drop after the commanded 1-2 shift. This value is only accurate if the shift was adaptable.
1-2 TAP Cell (1-17): This parameter displays the amount of transmission adaptive pressure (TAP), based on 17 Nm of
engine torque increment per cell, added to or subtracted from shift pressure during a 1-2 upshift. A positive number
indicates that long shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been added to decrease shift time. A
negative number indicates that short shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been subtracted to
increase shift time.
2-3 Shift Error: This parameter displays the difference between the desired 2-3 shift time and the actual 2-3 shift time. A
positive number indicates a firm or fast shift, the actual shift time was shorter than the desired shift time. A negative
number indicates a soft or slow shift, the actual shift time was longer than the desired shift time. This value is only
accurate if the shift was adaptable.
2-3 Shift Time: This parameter displays the actual time of the last 2-3 shift. The shift time is based on the engine r.p.m
drop after the commanded 2-3 shift. This value is only accurate if the shift was adaptable.
2-3 TAP Cell (1-17): This parameter displays the amount of transmission adaptive pressure (TAP), based on 17 Nm of
engine torque increment per cell, added to or subtracted from shift pressure during a 2-3 upshift. A positive number
indicates that long shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been added to decrease shift time. A
negative number indicates that short shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been subtracted to
increase shift time.
3-4 Shift Error: This parameter displays the difference between the desired 3-4 shift time and the actual 3-4 shift time. A
positive number indicates a firm or fast shift, the actual shift time was shorter than the desired shift time. A negative
number indicates a soft or slow shift, the actual shift time was longer than the desired shift time. This value is only
accurate if the shift was adaptable.
3-4 Shift Time: This parameter displays the actual time of the last 3-4 shift. The shift time is based on the engine r.p.m.
drop after the commanded 3-4 shift. This value is only accurate if the shift was adaptable.
3-4 TAP Cell (1-17): This parameter displays the amount of transmission adaptive pressure (TAP), based on 17 Nm of
engine torque increment per cell, added to or subtracted from shift pressure during a 3-4 upshift. A positive number
indicates that long shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been added to decrease shift time. A
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3808 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–22
negative number indicates that short shifts have been detected and PC solenoid pressure has been subtracted to
increase shift time.
A/C Clutch: This parameter displays the condition of the sirconditioning compressor as either On or Off .
AT Output Speed: This parameter displays the rotational speed of the transmission output shaft. Tech 2 displays output
shaft speed as revolutions per minute (RPM).
Commanded Gear: This parameter displays the current commanded state of the shift solenoid valves. Tech 2 displays 1,
2 , 3 or 4.
Current TAP Cell: This parameter displays the current transmission adaptive pressure (TAP) cell in use for transmission
line pressure adaptation. The cells are based on 17 Nm of engine torque. The higher the engine torque, the higher the
current TAP cell. The last cell used will remain displayed until the next adaptable upshift occurs.
Engine Coolant Temperature: This parameter displays the input signal from the engine coolant temperate (ECT)
sensor. ECT is high at 151°C when the signal voltage is low, 0 V. ECT is low at -40°C when the signal voltage is high,
5 V.
Engine Speed: This parameter displays the rotational speed of the engine expressed as revolutions per minute.
Engine Torque: This parameter displays the calculated value based on engine load, throttle position, mass air flow, and
other engine inputs. This parameter is accurate to within 20 Nm of actual measured engine torque.
Estimated Gear Ratio: This parameter displays the estimated turbine speed divided by the transmission output speed.
Estimated turbine speed is calculated from engine speed and engine torque.
Ignition Voltage: This parameter displays the
system voltage measured at the ignition feed.
Latest Shift: This parameter displays the actual time of the last upshift. This value is only accurate if the shift was
adaptable.
PCS Actual Current: This parameter displays the current flow through the pressure control solenoid circuit, which is
measured by the control module. High current flow results in low line pressure. Low current flow results in high line
pressure.
PCS Duty Cycle: This parameter displays the commanded state of the pressure control solenoid, expressed as a
percentage of energised on time. A reading of low percent indicates zero on time, non-energised, or no current flow. A
high percent at idle indicates maximum on time, energised, or high current flow.
PCS Desired Current: This parameter displays the commanded current of the pressure control solenoid circuit. High
current results in low line pressure. Low current results in high line pressure.
Shift Pattern: This parameter displays Normal, Power or Cruise depending on what mode the transmission is in.
Shift Solenoid A: This parameter displays the commanded state of the 1-2 shift solenoid valve. W hen the transmission
is in 1
st and 4th gear, the display should indicate On; current is flowing through the solenoid. When the transmission is in
2nd and 3rd gear, the display should indicate Off; current is not flowing through the solenoid.
Shift Solenoid A Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the 1-2 shift solenoid valve feedback signal. The 1-2 shift solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
Shift Solenoid B: This parameter displays the commanded state of the 2-3 shift solenoid valve. W hen the transmission
is in 1
st and 4th gear, the display should indicate On; current is flowing through the solenoid. When the transmission is in
2nd and 3rd gear, the display should indicate Off; current is not flowing through the solenoid.
Shift Solenoid B Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the 2-3 shift solenoid valve feedback signal. The 2-3 shift solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
Speed Ratio: This parameter displays the calculated speed ratio of the transmission.
TCC Duty Cycle Circuit: This parameter displays whether an open or a short to ground, short to battery or the circuit is
okay in the TCC PW M solenoid valve feedback signal. The TCC PW M solenoid valve must be commanded off and on.
TCC Solenoid: This parameter displays the commanded sate of the TCC solenoid. On indicates a commanded
energised state; current is flowing through the solenoid. Off indicates a commanded non-energised state; current is not
flowing through the solenoid. This commanded state occurs at various vehicle speeds between applications.
TCC Slip Speed: This parameter displays the difference between transmission output speed and engine speed. A
negative value indicates the engine speed is less than the output speed, deceleration. A positive value indicates the
engine speed is greater than the output speed, acceleration. A value of zero indicates the engine speed is equal to the
output speed, TCC applied.
TCC PWM Solenoid: This parameter displays the commanded percentage of on time for the TCC PWM solenoid. A high
percentage represents an on, energised, commanded state.0 percent represents an off, non-energised, commanded
state.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3809 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–23
TFP Gear: This parameter displays Park/Neutral, Reverse , Drive4 , Drive3 , Drive2 , Drive1 or Invalid . This parameter
is the decoded status of the three A/B/C inputs from the automatic transmission fluid pressure manual valve position
switch. If a valid combination of inputs is not detected, invalid will be displayed.
TFP Swi A/B/C: This parameter displays Open 12 V / Closed 0 V for each switch. This parameter indicates the statues
of the three inputs from the automatic transmission fluid pressure manual valve position switch assembly.
Throttle Position: This parameter displays a calculated value, which is determined by the accelerator pedal position and
the actual throttle position, used to optimise transmission controls. It represents the driver’s intended requested for
torque or acceleration. The range is 0-100%, 0% represents an idle or coast request and 100% represents a request for
wide open throttle (WOT).
Torque Converter Efficiency: This parameter displays a ratio of 0.00:1 to 2:1. The ratio is calculates by multiplying the
speed ratio by a value related to the ‘K factor’ of the torque converter. The ‘K factor’ is the looseness or tightness of the
torque converter for a given torque. The nearer the torque converter is to full coupling, i.e. 1:1, the closer the torque
converter efficiency number will be to 1.
TR Switch A/B/C/P: This parameter displays the status of the four inputs from the transmission range switch. Tech 2
displays Open 12V / Closed 0 V . Open 12 V indicates an ignition voltage input to the control module. Closed 0 V
indicates a zero voltage input to the control module.
Transmission Fluid Temperature: This parameter displays the input signal of the transmission fluid temperature sensor.
Transmission fluid temperature is high, 151°C, when signal voltage is low, 0 V. Transmission fluid temperature is low, -
40°C, when signal voltage is high, 5 V.
Transmission Hot Mode: This parameter displays the automatic transmission fluid temperature (TFT) and displays On
or Off . Off indicates the TFT has not exceeded 130°C. On indicates the TFT has exceeded 130°C and has not cooled to
120°C for greater than 5 seconds. These numbers are approximate and differ with transmissions.
Vehicle Speed: This parameter displays the speed at which the vehicle is travelling. Tech 2 displays vehicle speed as
kilometres per hour (km/h). The vehicle speed is calculates based on the input signal from the automatic transmission
output shaft speed sensor.
3.4 Miscellaneous Tests
Tech 2
Miscellaneous Tests Description
Shift Solenoid A •
The TCM commands the 1-2 shift solenoid valve on and off. Tech 2’s Shift Solenoid A
Parameter should match the commanded state. Tech 2’s Commanded Gear
parameter should correspond with the shift solenoid combination. Refer to
5.6 Shift Solenoid Valve State and Gear Ratio.
• When the ignition is on, and the engine is off, there no limits to this control. The
solenoid remains on until commanded off, and vice versa. W hen the test is exited, the
solenoid state is determined by the TCM.
• W hen the engine is running, the following control limits apply:
• Only sequential gear changes are allowed. For example, 1
st to 3rd is not allowed.
If a non-sequential gear change is attempted, the message Non-sequential
gear changes not allowed . Gear changes must be made in order appears
on Tech 2.
• The vehicle speed must be below a calibrated value. If the vehicle speed is too
high, the message Vehicle speed too high appears on Tech 2.
• The engine speed must be below a calibrated value. If the engine speed is too
high, the message Engine speed too high appears on Tech 2.
• Downshifts are allowed only when the vehicle speed is below a calibrated value.
If the vehicle speed is too high, the message Eng. is on and veh. speed to hi
for 3-2 or 2-1 downshift appears on Tech 2.
• The gear requested may not be greater than the current selected transmission
range (PRNDL). For example, 3
rd gear is not allowed if the transmission range is
D2. If the gear requested is greater than the current selected transmission
range, the message Eng. running and gear request is greater than the
current TR appears on Tech 2.
• The solenoid remains on until commanded off, and vice versa. W hen the test is
exited, the solenoid state is determined by the TCM.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3818 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–32
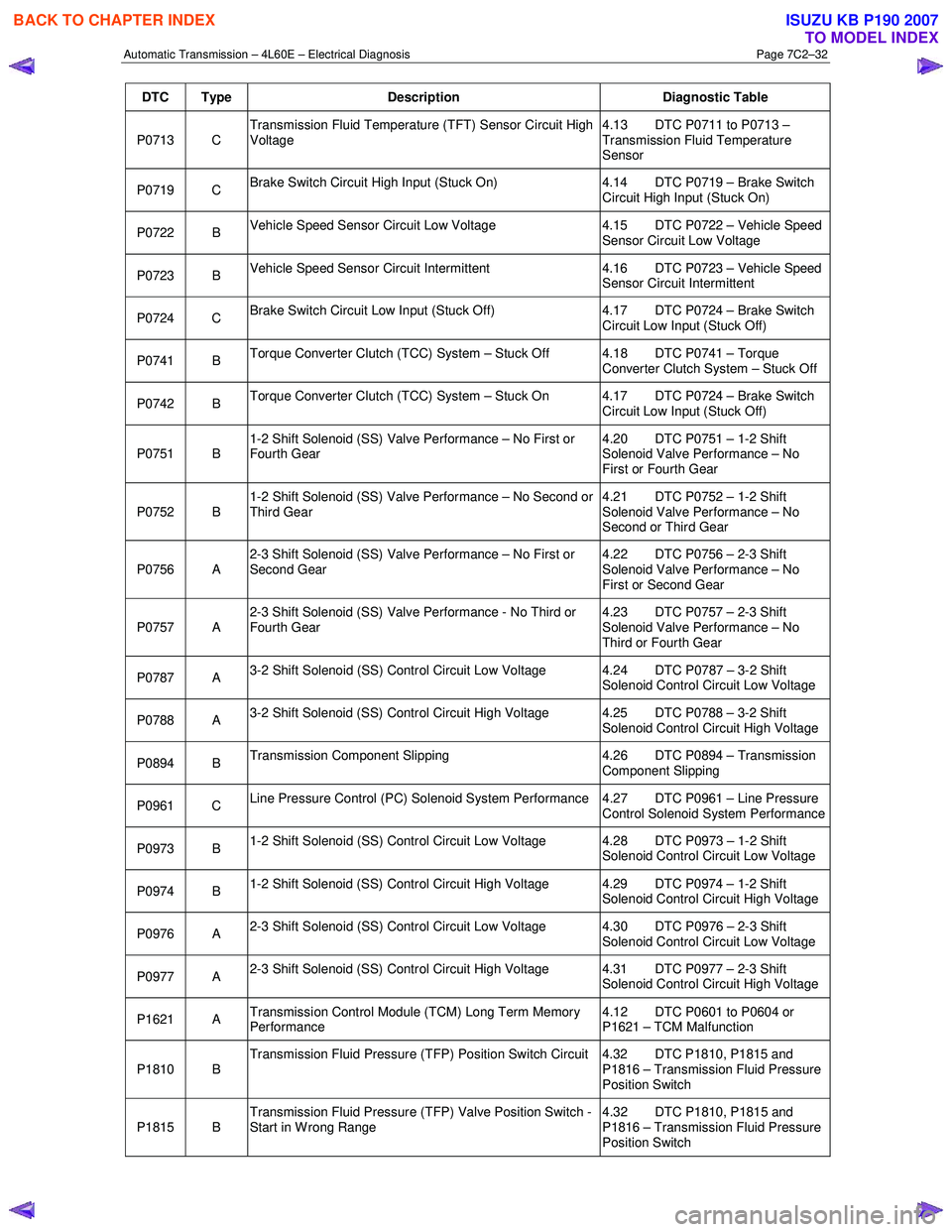
DTC Type Description Diagnostic Table
P0713 C Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High
Voltage 4.13 DTC P0711 to P0713 –
Transmission Fluid Temperature
Sensor
P0719 C Brake Switch Circuit High Input (Stuck On) 4.14 DTC P0719 – Brake Switch
Circuit High Input (Stuck On)
P0722 B Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 4.15 DTC P0722 – Vehicle Speed
Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
P0723 B Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent 4.16 DTC P0723 – Vehicle Speed
Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0724 C Brake Switch Circuit Low Input (Stuck Off) 4.17 DTC P0724 – Brake Switch
Circuit Low Input (Stuck Off)
P0741 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) System – Stuck Off 4.18 DTC P0741 – Torque
Converter Clutch System – Stuck Off
P0742 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) System – Stuck On 4.17 DTC P0724 – Brake Switch
Circuit Low Input (Stuck Off)
P0751 B 1-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Performance – No First or
Fourth Gear 4.20 DTC P0751 – 1-2 Shift
Solenoid Valve Performance – No
First or Fourth Gear
P0752 B 1-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Performance – No Second or
Third Gear 4.21 DTC P0752 – 1-2 Shift
Solenoid Valve Performance – No
Second or Third Gear
P0756 A 2-3 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Performance – No First or
Second Gear 4.22 DTC P0756 – 2-3 Shift
Solenoid Valve Performance – No
First or Second Gear
P0757 A 2-3 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Performance - No Third or
Fourth Gear 4.23 DTC P0757 – 2-3 Shift
Solenoid Valve Performance – No
Third or Fourth Gear
P0787 A 3-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit Low Voltage 4.24 DTC P0787 – 3-2 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage
P0788 A 3-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit High Voltage 4.25 DTC P0788 – 3-2 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage
P0894 B Transmission Component Slipping 4.26 DTC P0894 – Transmission
Component Slipping
P0961 C Line Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid System Performance 4.27 DTC P0961 – Line Pressure
Control Solenoid System Performance
P0973 B 1-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit Low Voltage 4.28 DTC P0973 – 1-2 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage
P0974 B 1-2 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit High Voltage 4.29 DTC P0974 – 1-2 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage
P0976 A 2-3 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit Low Voltage 4.30 DTC P0976 – 2-3 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage
P0977 A 2-3 Shift Solenoid (SS) Control Circuit High Voltage 4.31 DTC P0977 – 2-3 Shift
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage
P1621 A Transmission Control Module (TCM) Long Term Memory
Performance 4.12 DTC P0601 to P0604 or
P1621 – TCM Malfunction
P1810 B Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Position Switch Circuit 4.32 DTC P1810, P1815 and
P1816 – Transmission Fluid Pressure
Position Switch
P1815 B Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Valve Position Switch -
Start in W rong Range 4.32 DTC P1810, P1815 and
P1816 – Transmission Fluid Pressure
Position Switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3819 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–33
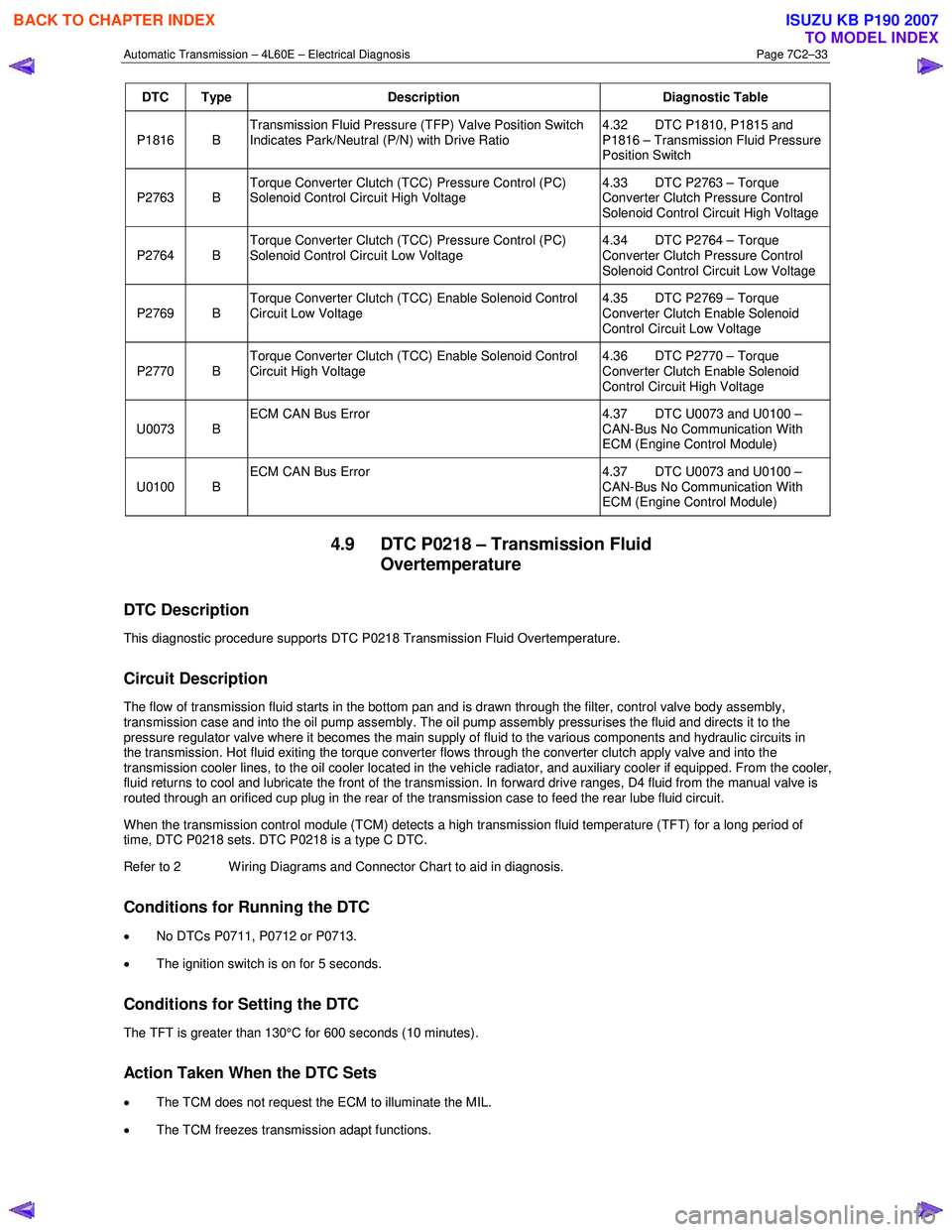
DTC Type Description Diagnostic Table
P1816 B Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Valve Position Switch
Indicates Park/Neutral (P/N) with Drive Ratio 4.32 DTC P1810, P1815 and
P1816 – Transmission Fluid Pressure
Position Switch
P2763 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC)
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage 4.33 DTC P2763 – Torque
Converter Clutch Pressure Control
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage
P2764 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC)
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage 4.34 DTC P2764 – Torque
Converter Clutch Pressure Control
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage
P2769 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage 4.35 DTC P2769 – Torque
Converter Clutch Enable Solenoid
Control Circuit Low Voltage
P2770 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage 4.36 DTC P2770 – Torque
Converter Clutch Enable Solenoid
Control Circuit High Voltage
U0073 B ECM CAN Bus Error
4.37 DTC U0073 and U0100 –
CAN-Bus No Communication With
ECM (Engine Control Module)
U0100 B ECM CAN Bus Error
4.37 DTC U0073 and U0100 –
CAN-Bus No Communication With
ECM (Engine Control Module)
4.9 DTC P0218 – Transmission Fluid Overtemperature
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Overtemperature.
Circuit Description
The flow of transmission fluid starts in the bottom pan and is drawn through the filter, control valve body assembly,
transmission case and into the oil pump assembly. The oil pump assembly pressurises the fluid and directs it to the
pressure regulator valve where it becomes the main supply of fluid to the various components and hydraulic circuits in
the transmission. Hot fluid exiting the torque converter flows through the converter clutch apply valve and into the
transmission cooler lines, to the oil cooler located in the vehicle radiator, and auxiliary cooler if equipped. From the cooler ,
fluid returns to cool and lubricate the front of the transmission. In forward drive ranges, D4 fluid from the manual valve is
routed through an orificed cup plug in the rear of the transmission case to feed the rear lube fluid circuit.
When the transmission control module (TCM) detects a high transmission fluid temperature (TFT) for a long period of
time, DTC P0218 sets. DTC P0218 is a type C DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• No DTCs P0711, P0712 or P0713.
• The ignition switch is on for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TFT is greater than 130°C for 600 seconds (10 minutes).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
•
The TCM does not request the ECM to illuminate the MIL.
• The TCM freezes transmission adapt functions.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3820 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–34
• The TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are met. The TCM stores this
information as Failure Records.
• The TCM stores DTC P0218 in TCM history.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
• The TCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the DTC passes.
Diagnostic Aids
• Tech 2’s Transmission Fluid Temp. should rise steadily to a normal operating temperature, then stabilise.
• Ask about the customer's driving habits, trailer towing, etc. Trailer towing should occur in D3.
• Refer to Symptoms - Automatic Transmission in 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical
Diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Low transmission fluid can cause the transmission to overheat.
3 This step inspects for airflow restrictions or damage, which may result in the transmission overheating.
4-5 Decreased line pressure will cause the transmission to overheat. The torque converter stator is the pump for the transmission fluid. If the torque converter is damaged, it may not be producing the required pressure.
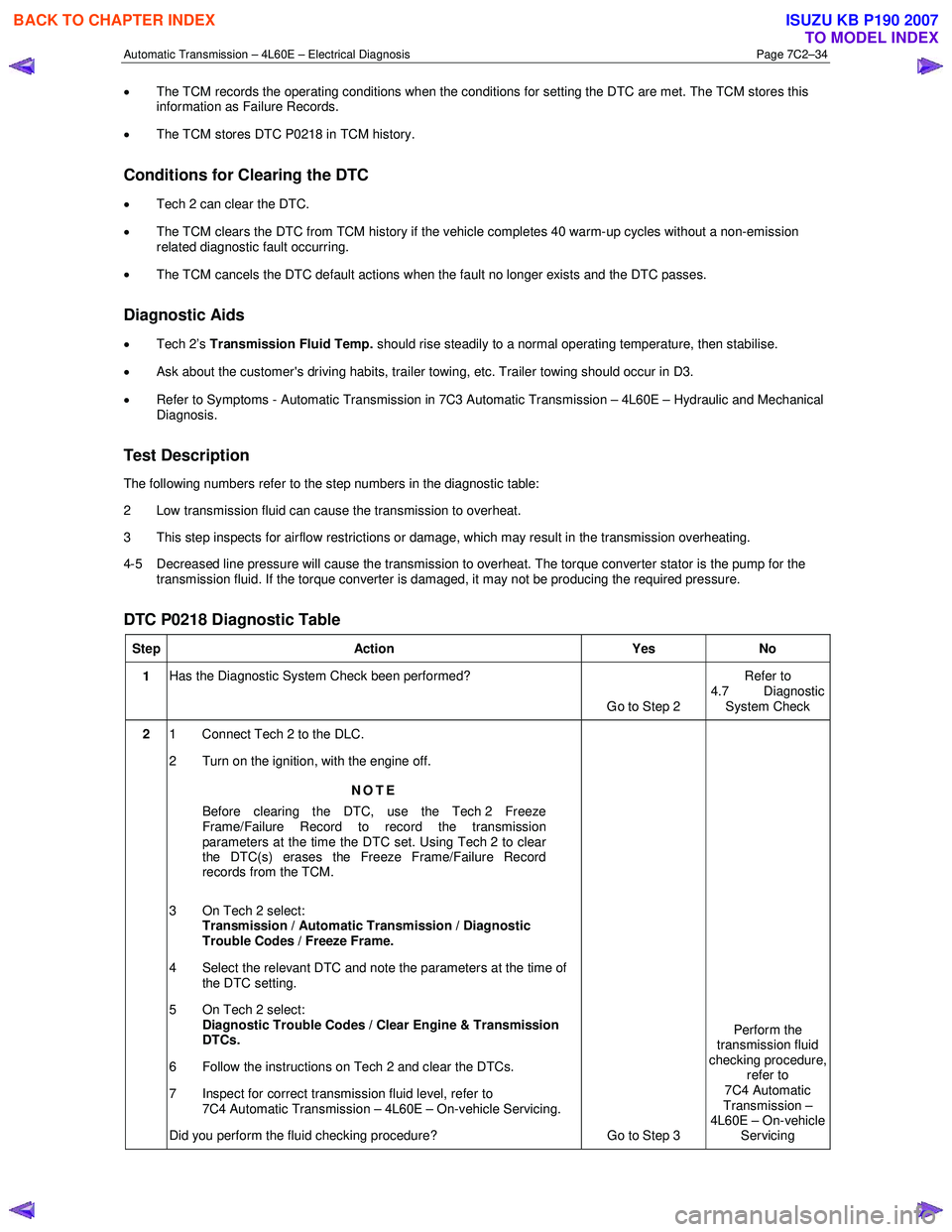
DTC P0218 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.7 Diagnostic System Check
2 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Turn on the ignition, with the engine off.
NOTE
Before clearing the DTC, use the Tech 2 Freeze
Frame/Failure Record to record the transmission
parameters at the time the DTC set. Using Tech 2 to clear
the DTC(s) erases the Freeze Frame/Failure Record
records from the TCM.
3 On Tech 2 select: Transmission / Automatic Transmission / Diagnostic
Trouble Codes / Freeze Frame.
4 Select the relevant DTC and note the parameters at the time of the DTC setting.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
6 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear the DTCs.
7 Inspect for correct transmission fluid level, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you perform the fluid checking procedure? Go to Step 3 Perform the
transmission fluid
checking procedure, refer to
7C4 Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3821 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–35
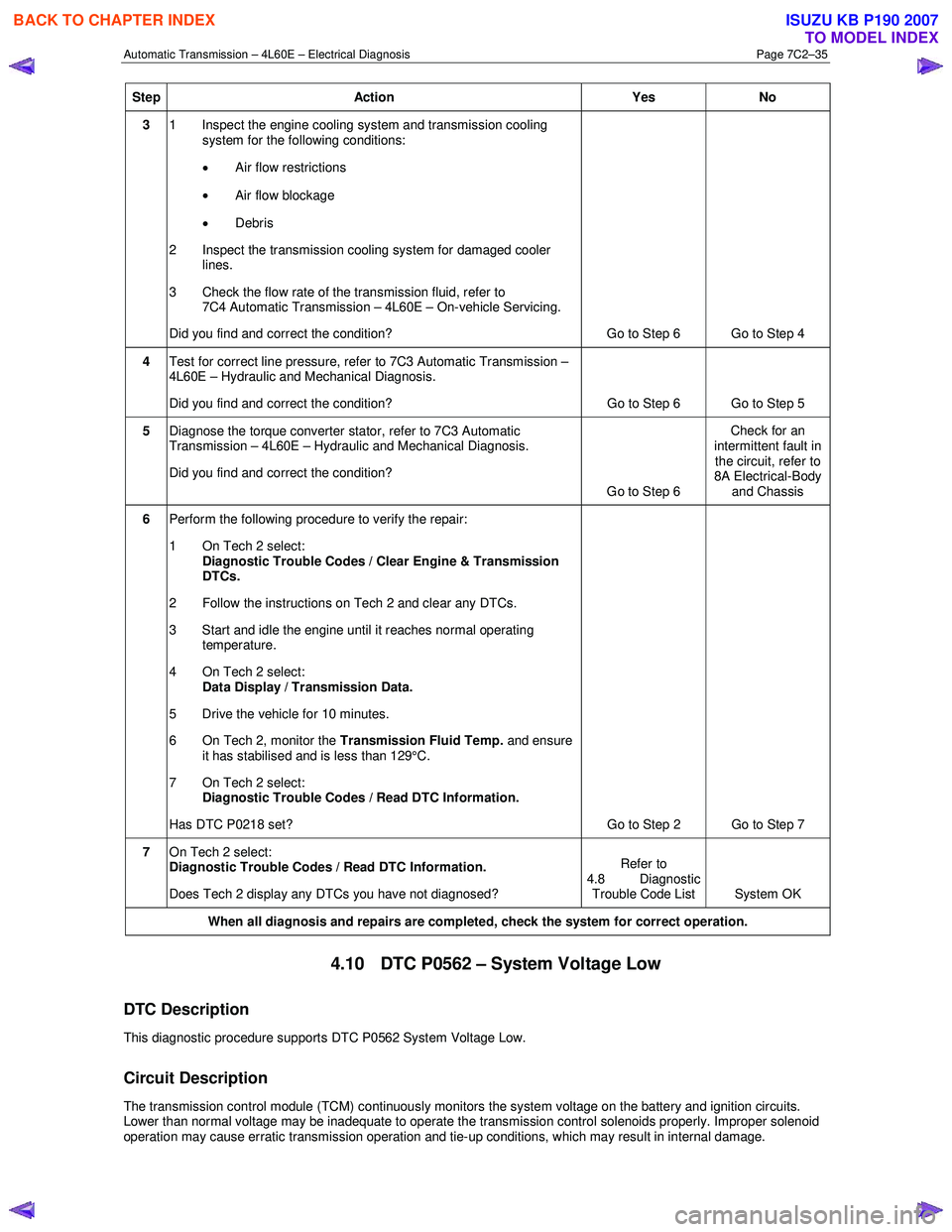
Step Action Yes No
3 1 Inspect the engine cooling system and transmission cooling
system for the following conditions:
• Air flow restrictions
• Air flow blockage
• Debris
2 Inspect the transmission cooling system for damaged cooler lines.
3 Check the flow rate of the transmission fluid, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4 Test for correct line pressure, refer to 7C3 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Diagnose the torque converter stator, refer to 7C3 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 6 Check for an
intermittent fault in the circuit, refer to
8A Electrical-Body
and Chassis
6 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 Start and idle the engine until it reaches normal operating temperature.
4 On Tech 2 select: Data Display / Transmission Data.
5 Drive the vehicle for 10 minutes.
6 On Tech 2, monitor the Transmission Fluid Temp. and ensure
it has stabilised and is less than 129°C.
7 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0218 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the
system for correct operation.
4.10 DTC P0562 – System Voltage Low
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0562 System Voltage Low.
Circuit Description
The transmission control module (TCM) continuously monitors the system voltage on the battery and ignition circuits.
Lower than normal voltage may be inadequate to operate the transmission control solenoids properly. Improper solenoid
operation may cause erratic transmission operation and tie-up conditions, which may result in internal damage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3832 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–46
Step Action Yes No
3 Inspect the transmission and related components for the following:
• transmission fluid level,
• transmission fluid cooling system restrictions / blockages,
• debris in the transmission fluid,
• incorrect line pressure,
• torque converter stator operation, and
• transmission overload.
W as a fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Check for an
intermittent fault in
the circuit, refer to
8A Electrical-Body and Chassis
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect connector E-95 from the transmission.
3 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, probe between harness connector E-95 pin 16 and a known ground.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Test the TFT sensor signal circuit (between connectors E-95 pin 16
and C-96 pin 35) for a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or
short to voltage fault condition.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove the TCM fuses C-8 and EB-4, refer to 8A Electrical- Body and Chassis.
3 Using a multimeter set to measure resistance, probe between connector E95 pin 15 and a known ground.
Does the multimeter display less than 5 Ω? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
7 Using a multimeter, test between E-95 pin 15 and C-96 pin 30 for high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 —
8 Replace the TFT sensor, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
NOTE
Check for damaged wiring (short to ground, short to
voltage, high resistance or open circuit) or poor
connections inside the transmission assembly before
replacing the TFT sensor.
Was the repair complete? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10
—
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3835 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–49
Step Action Yes No
6 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
• Turn on the ignition, with the engine off for at least
2 seconds.
• Start the vehicle and idle for 5 seconds.
• Drive in D4 from 0 – 60 km/h 8 times in 1 ignition cycle.
4 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0719 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the
system for correct operation.
4.15 DTC P0722 – Vehicle Speed Sensor
Circuit Low Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0722 Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Low Voltage.
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) provides vehicle speed information to the transmission control module (TCM). The VSS
is a permanent magnet generator. The sensor is mounted in the extension housing facing the rear internal gear which is
splined to the output shaft assembly. As the output shaft and internal gear rotate, the toothed rotor of the internal gear
produces AC voltage as the rotor teeth pass through the magnetic field of the sensor. The AC voltage level and the
number of pulses increase as the speed of the vehicle increases. The TCM converts the voltage to vehicle speed. The
TCM uses the output shaft speed signal to determine shift timing and torque converter clutch (TCC) scheduling.
If the TCM detects no vehicle speed when there is engine speed in a drive gear range, then DTC P0722 sets.
DTC P0722 is a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• No DTCs P0723, P1810, P1815 or P1816.
• Ignition voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• TFT is -40°C – 150°C.
• The engine run time is greater than 5 seconds.
• The throttle position is greater than 12 percent.
• The engine torque is 108 – 882 Nm.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The transmission output shaft speed is less than 50 r.p.m. for 3 seconds.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3836 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–50
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM illuminates the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the Conditions for Setting the DTC are
met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM calculates vehicle speed from the automatic transmission engine r.p.m. and commanded gear.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P0722 in TCM history.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the sixth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without an emission related
diagnostic fault occurring.
• The TCM cancels the default actions when the ignition is off long enough to power down the TCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the rear internal gear teeth for damage.
• Visually inspect the VSS for cracks or damage.
• Ensure the VSS is properly torqued to the extension housing.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Disable the traction control system when performing this step. W hen the ignition key is cycled off and then cycled back on, the traction control system defaults to on.
3 Checks the VSS for correct resistance.
4 Checks if the VSS and associated circuits are shorted to ground.
5 Checks the VSS produces an AC voltage when the output shaft is rotated.
6 Checks the integrity of the circuits between the TCM and the VSS.
DTC P0722 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.7 Diagnostic System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007