torque ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3867 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–81
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for
setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P0894 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
• The TCM cancels the DTC default actions when the ignition is off long enough to power down the TCM.
Diagnostic Aids
•
Bronze material found in the transmission oil pan may indicate stator shaft bushing wear. If bushing wear is
suspected, inspect the stator shaft and the input, turbine, shaft for damage.
• Perform the Torque Converter Diagnosis Procedure, refer to 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and
Mechanical Diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Checks the torque converter for slippage while in a commanded lock-up state.
4-12 Checks the mechanical components that cause the DTC and their state.
13 W hen the TAP cells are cleared the TCM needs to relearn the TAP cells for the transmission. As such, when the vehicle is first driven, the shifts may be harsh. The transmission shifts should become smoother the more the
vehicle is driven until the TCM has relearned all TAP cells.
DTC P0894 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.7 Diagnostic System Check
2 Inspect for correct transmission fluid level, refer to 7C4 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you perform the fluid checking procedure?
Go to Step 3 Check the
transmission fluid level, refer to
7C4 Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3868 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–82
Step Action Yes No
3 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Turn on the ignition, with the engine off.
NOTE
Before clearing the DTC, use the Tech 2 Freeze
Frame/Failure Record to record the transmission
parameters at the time the DTC set. Using Tech 2 to clear
the DTC(s) erases the Freeze Frame/Failure Record
records from the TCM.
3 On Tech 2 select: Transmission / Automatic Transmission / Diagnostic
Trouble Codes / Freeze Frame.
4 Select the relevant DTC and note the parameters at the time of the DTC setting.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
6 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear the DTCs.
NOTE
It may be necessary to allow multiple TCC cycles to occur
to verify a slipping condition. It may also be necessary to
ensure the transmission is warm before performing this
step.
7 On Tech 2 select: Automatic Transmission / Data Display / Transmission Data.
8 Drive the vehicle in 4th gear with the TCC commanded on.
On Tech 2, while TCC Solenoid status is On, is the TCC Slip Speed
within 130 – 800 RPM for 7 seconds?
Go to Step 4 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids within this Section
4 1 Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve for the
following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
2 Inspect the torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve for the following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3869 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–83
Step Action Yes No
5 1 Inspect the 1-2 shift solenoid (SS) valve for the following
conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
2 Inspect the 2-3 shift solenoid (SS) valve for the following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
3 Inspect the 3-2 shift solenoid valve assembly for the following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 6
6 Inspect the valve body assembly for the following conditions:
• stuck regulator apply valve, and
• scored regulator apply valve body, refer to 7C5 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – Unit Repair.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect the torque converter assembly for the following conditions:
• front stator shaft bushing for wear,
• stator roller clutch not holding, and
• external damage/leaks, refer to 7C5 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – Unit Repair.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
8 Inspect the oil pump assembly for the following conditions:
• a stuck converter clutch valve,
• the converter clutch valve is assembled backwards,
• a incorrectly position converter clutch valve retaining ring,
• a cocked converter clutch outer valve spring,
• a incorrectly positioned pump to case gasket,
• restricted orifice cup plugs,
• damaged orifice cup plugs, and
• over-tightened, or unevenly tightened pump body to cover bolts,
refer to 7C5 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Unit Repair.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3894 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–108
Step Action Yes No
13 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.33 DTC P2763 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2763 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
When the TCM detects a continuous short to voltage in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then DTC P2763
sets. DTC P2763 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2763 sets if the TCM commands the solenoid on and the voltage feedback remains high, battery voltage.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for
setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2763 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3897 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–111
4.34 DTC P2764 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2764 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
W hen the TCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then
DTC P2764 sets. DTC P2764 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2764 sets when either of the following conditions occurs for 5 seconds:
• The TCM detects an open in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PW M is commanded on.
• The TCM detects a short to ground in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PWM is
commanded on.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the Conditions for
Setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2764 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3901 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–115
Step Action Yes No
20 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.35 DTC P2769 – Torque Converter Clutch
Enable Solenoid Control Circuit Low
Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2769 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control Circuit Low
Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is an electrical device that is used with the torque converter clutch
pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve to control TCC apply and release. The TCC solenoid valve attaches
to the transmission case assembly extending into the pump cover. The TCC solenoid valve receives voltage through
ignition voltage circuit. The transmission control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing the ground path on the
TCC solenoid valve control circuit. The TCM monitors the throttle position (TP) voltage, the vehicle speed and other
inputs to determine when to energize the TCC solenoid valve.
NOTE
The TCC solenoid valve is part of the control
valve body wiring harness. To replace the
solenoid valve, the control valve body harness
must be replaced.
When the TCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the TCC solenoid valve control circuit, then DTC P2769
sets. DTC P2769 is a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2769 sets when either of the following conditions occurs for 5 seconds:
• The TCM detects an open in the TCC solenoid valve circuit when the TCC is commanded on.
• The TCM detects a short to ground in the TCC shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC is commanded on.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for
setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3905 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–119
16 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 On Tech 2 select: Miscellaneous Tests / TCC Solenoid.
4 Drive the vehicle in D4. With Tech 2 command the TCC solenoid valve On for 5 seconds and Off for 5 seconds
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P2769 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 17
17 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the
system for correct operation.
4.36 DTC P2770 – Torque Converter Clutch
Enable Solenoid Control Circuit High
Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2770 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control Circuit High
Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is an electrical device that is used with the torque converter clutch
pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve to control TCC apply and release. The TCC solenoid valve attaches
to the transmission case assembly extending into the pump cover. The TCC solenoid valve receives voltage through
ignition voltage circuit. The transmission control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing the ground path on the
TCC solenoid valve control circuit. The TCM monitors the throttle position (TP) voltage, the vehicle speed and other
inputs to determine when to energize the TCC solenoid valve.
NOTE
The TCC solenoid valve is part of the control
valve body wiring harness. To replace the
solenoid valve, the control valve body harness
must be replaced.
W hen the TCM detects a continuous short to voltage in the TCC solenoid valve control circuit, then DTC P2770 sets.
DTC P2770 is a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2770 sets if the TCM commands the solenoid on and the voltage feedback remains high, battery voltage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3915 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–2
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 24
3.10 Adaptor Housing, 4WD ........................................................................................................................................ 24
Remove and Reinstall .......................................................................................................................................... 24
3.11 Shift Solenoid Locations ..................................................................................................................................... 25
Location and Identification .................................................................................................... ............................. 25
3.12 1 – 2 Accumulator Assembly ..................................................................................................... ......................... 25
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Clean and Inspect ................................................................................................................................................ 26
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 26
3.13 Control Valve Body Harness ..................................................................................................... .......................... 26
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 26
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 28
3.14 Control Valve Body .............................................................................................................................................. 30
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 30
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 31
3.15 Spacer Plate, Check Balls, Filter Screens and 3 – 4 Accumulator ................................................................ .. 35
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 35
Clean and Inspect ................................................................................................................................................ 36
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 37
3.16 Filler Tube and Breather Hose .................................................................................................. .......................... 39
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 40
3.17 Transmission Cooler Line/Hose Assemblies ....................................................................................... ............. 41
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 41
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 42
3.18 Transmission Assembly...................................................................................................................................... 43
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 43
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 46
3.19 Transmission Control Module ............................................................................................................................ 47
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 47
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 48
TCM Programming Procedure ...................................................................................................... ...................... 48
4 Specifications .......................................................................................................................................50
5 Torque Wrench Specifications................................................................................................... .........51
6 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................52
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3916 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–3
1 General Information
This Section describes the removal and reinstallation procedures of the four speed 4L60E hydra-matic automatic
transmission as well as the service operations which can be performed with the transmission still fitted to the vehicle.
1.1 General Service Information
Description
The shift selector mechanism is linked to the transmission manual shaft with a selector cable. A heat protector is fitted
over the neutral start and back-up switch and manual shaft select lever.
For rear wheel drive (RWD) vehicles an extension housing is fitted to the rear of the transmission case.
Four wheel drive (4W D) vehicles have an adaptor housing and transfer case fitted to the rear of the transmission case,
for description and service operation refer to 7D Transfer Case and Adaptor Housing.
The four speed 4L60E hydra-matic automatic transmission is fitted with a filler tube, a breather hose and a vent pipe for
hot fluid overflow.
The transmission fluid is driven through a cooler within the radiator via the cooler line/hose assemblies to maintain
normal operating temperature.
Service Information
Throughout the service operations within this
Section, when handling retaining clips, using
compressed air or cleaning fluids, wear safety
equipment to avoid personal injury.
Refer to 7C1 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information for the following:
• information relating to mechanical and electrical operations,
• abbreviations, transmission specifications, special tools and torque wrench specifications,
• servicing, cleaning and inspection procedure recommendations.
It is essential to read and understand the General Information, W arnings, Cautions and Service Notes contained in that
same Section, before any service operation is performed on the four speed 4L60E hydra-matic automatic transmission or
any associated components.
Failure to comply with the procedures and service notes can affect the reliable and efficient operation of this automatic
transmission.
1.2 WARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to
diagnose and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard
to the technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3919 of 6020
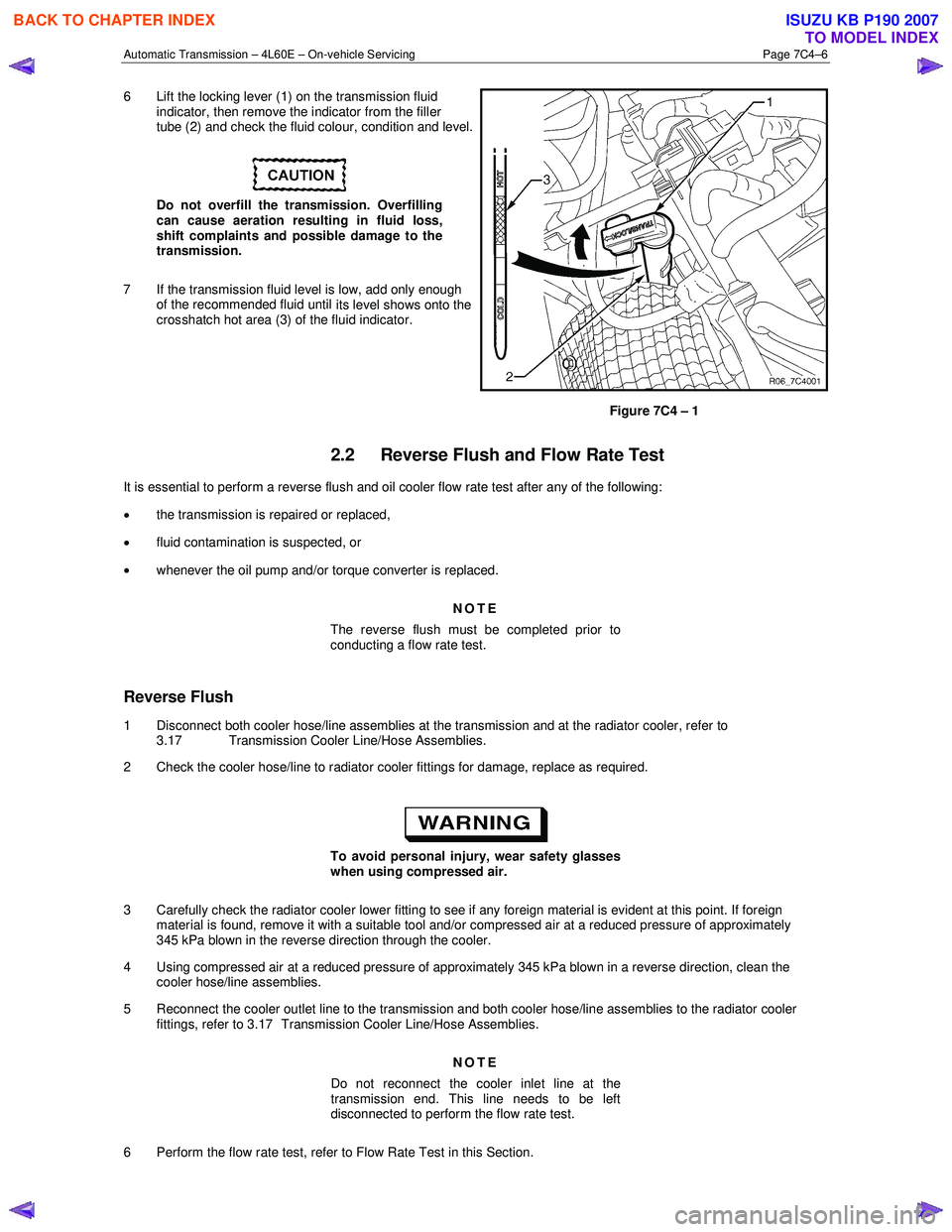
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–6
6 Lift the locking lever (1) on the transmission fluid
indicator, then remove the indicator from the filler
tube (2) and check the fluid colour, condition and level.
Do not overfill the transmission. Overfilling
can cause aeration resulting in fluid loss,
shift complaints and possible damage to the
transmission.
7 If the transmission fluid level is low, add only enough of the recommended fluid until
its level shows onto the
crosshatch hot area (3) of the fluid indicator.
Figure 7C4 – 1
2.2 Reverse Flush and Flow Rate Test
It is essential to perform a reverse flush and oil cooler flow rate test after any of the following:
• the transmission is repaired or replaced,
• fluid contamination is suspected, or
• whenever the oil pump and/or torque converter is replaced.
NOTE
The reverse flush must be completed prior to
conducting a flow rate test.
Reverse Flush
1 Disconnect both cooler hose/line assemblies at the transmission and at the radiator cooler, refer to 3.17 Transmission Cooler Line/Hose Assemblies.
2 Check the cooler hose/line to radiator cooler fittings for damage, replace as required.
To avoid personal injury, wear safety glasses
when using compressed air.
3 Carefully check the radiator cooler lower fitting to see if any foreign material is evident at this point. If foreign material is found, remove it with a suitable tool and/or compressed air at a reduced pressure of approximately
345 kPa blown in the reverse direction through the cooler.
4 Using compressed air at a reduced pressure of approximately 345 kPa blown in a reverse direction, clean the cooler hose/line assemblies.
5 Reconnect the cooler outlet line to the transmission and both cooler hose/line assemblies to the radiator cooler fittings, refer to 3.17 Transmission Cooler Line/Hose Assemblies.
NOTE
Do not reconnect the cooler inlet line at the
transmission end. This line needs to be left
disconnected to perform the flow rate test.
6 Perform the flow rate test, refer to Flow Rate Test in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007