heating ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3541 of 6020
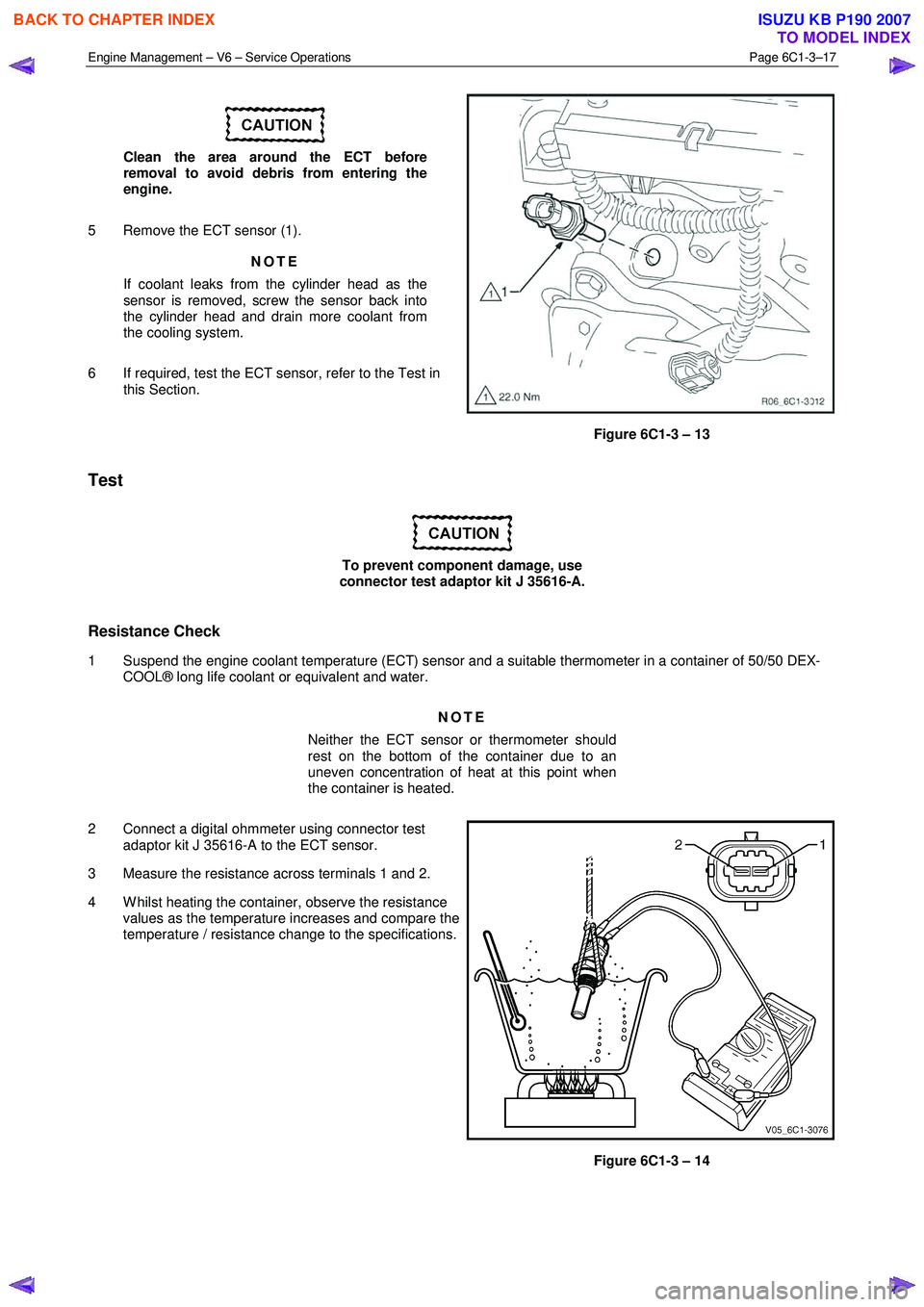
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–17
Clean the area around the ECT before
removal to avoid debris from entering the
engine.
5 Remove the ECT sensor (1). NOTE
If coolant leaks from the cylinder head as the
sensor is removed, screw the sensor back into
the cylinder head and drain more coolant from
the cooling system.
6 If required, test the ECT sensor, refer to the Test in this Section.
Figure 6C1-3 – 13
Test
To prevent component damage, use
connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A.
Resistance Check
1 Suspend the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and a suitable thermometer in a container of 50/50 DEX- COOL® long life coolant or equivalent and water.
NOTE
Neither the ECT sensor or thermometer should
rest on the bottom of the container due to an
uneven concentration of heat at this point when
the container is heated.
2 Connect a digital ohmmeter using connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A to the ECT sensor.
3 Measure the resistance across terminals 1 and 2.
4 W hilst heating the container, observe the resistance values as the temperature increases and compare the
temperature / resistance change to the specifications.
Figure 6C1-3 – 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3574 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–50
• plug/s overheating due to insufficient tightening (caused by combustion gases leaking past the threads).
Broken Insulator
Broken insulators are usually the result of improper installation or carelessness.
Breaks in the upper insulator can result from a poor fitting spark plug socket or impact. The cracked insulator may not
show up until oil or moisture penetrates the crack. The crack is often just below the crimped part of the shell and may not
be visible.
Breaks in the lower insulator often result from careless re-gapping and are usually visible.
This can also result from the plug operating too hot. For example, in periods of high speed operation or under heavy
loads.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3576 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–52
Oil Fouled (3)
W et, oily deposits with minor electrode wear possibly due to oil leaking past worn piston rings.
Breaking in a new or recently overhauled engine before the rings are fully seated may also result in this condition.
Deposit Fouling A (4)
Red brown, yellow and white coloured coatings on the insulator tip which are by-products of combustion. They come
from fuel and lubricating oil which generally contain additives. Most powdery deposits have no adverse effect on spark
plug operation, however, they may cause intermittent missing under severe operating conditions.
Deposit Fouling B (5)
Deposits similar to those identified in deposit fouling A (4). These are also by-products of combustion from fuel and
lubricating oil. Excessive valve stem clearances and / or defective intake valve seals allow too much oil to enter the
combustion chamber. The deposits will accumulate on the portion of the spark plug that projects into the chamber and
will be heaviest on the side facing the intake valve. If this condition is only detected in one or two cylinders, check the
valve stem seals.
Deposit Fouling C (6)
Most powdery deposits identified in deposit fouling A (4) have no adverse effect on the operation of the spark plug as
long as they remain powdery.
Under certain conditions of operation however, these deposits melt and form a shiny glaze coating on the insulator.
W hen hot, this acts as a good electrical conductor allowing the current to flow along the deposit instead of sparking
across the gap.
Detonation (7)
Commonly referred to as engine knock or pinging, detonation causes severe shocks inside the combustion chamber
causing damage to parts.
Pre-ignition (8)
Burnt or blistered insulator tip and badly eroded electrodes probably due to the excessive heat.
This is often caused by a cooling system blockage, sticking valves, improperly installed spark plugs or plugs that are the
wrong heat rating (too hot).
Sustained high speed with a heavy load can produce temperatures high enough to cause pre-ignition.
Heat Shock Failure (9)
A rapid increase in spark plug tip temperature under severe operating conditions can cause heat shock and result in
fractured insulators. This is a common cause of broken and cracked insulator tips.
Insufficient Installation Torque (10)
Poor contact between the spark plug and the cylinder head seat.
The lack of proper heat transfer that results from poor seat contact causes overheating of the spark plug. In many cases,
severe damage occurs. Dirty threads in the cylinder head can cause the plug to seize before it is seated.
Ensure the cylinder head and spark plug threads are free of deposits, burrs and scale before installation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3599 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-12
7 Reconnect the battery ground cable P-5.
8 Fit a loading device (7) across the battery terminals, e.g. an adjustable carbon pile.
The loading device must have a minimum
power consumption of 1000 W.
9 Record the voltage reading before starting the engine. (This reading should increase when the engine is running, indicating generator output.).
10 Start the engine.
11 Increase the engine speed to the value outlined in the chart below.
12 Using the reading from the multimeter set to measure current, adjust the loading device to apply a load within the range outlined in the chart below.
13 Using the multimeter set to measure voltage, check the generator output voltage against the specification.
Engine RPM ........................................................... 1300
Load ................................................................ 5.0 – 10 A
Output Voltage ........................................... 13.8 – 15.4 V
Load Regulation Test
NOTE
The decrease in the voltage recorded during this
test should not exceed 0.5 V from the readings
obtained for the Regulating Voltage Test. If the
decrease in the regulating voltage is greater than
0.5 V, the regulator is defective. Replace the
regulator.
14 Increase the engine speed to the value outlined in the chart below.
15 Using the reading from the multimeter set to measure current, adjust the loading device to apply a load of about 90% of the generator’s full output.
16 Using the multimeter set to measure voltage, check the generator output voltage against the specification.
Engine RPM............................................................ 1900
Load ......................................................................... 90 A
Output Voltage ........................................... 13.8 – 15.4 V
Full Load Output Test
Keep the time for this test to a minimum to
avoid undue heating and high engine speeds.
17 Increase the engine speed to the value outlined in the chart below .
18 Using the reading from the multimeter set to measure voltage, adjust the loading device to increase the load until the generator output voltage drops to 13.5 V. Full generator output, outlined in the chart below, is required.
19 Record the current reading displayed on the multimeter set to measure current.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3752 of 6020
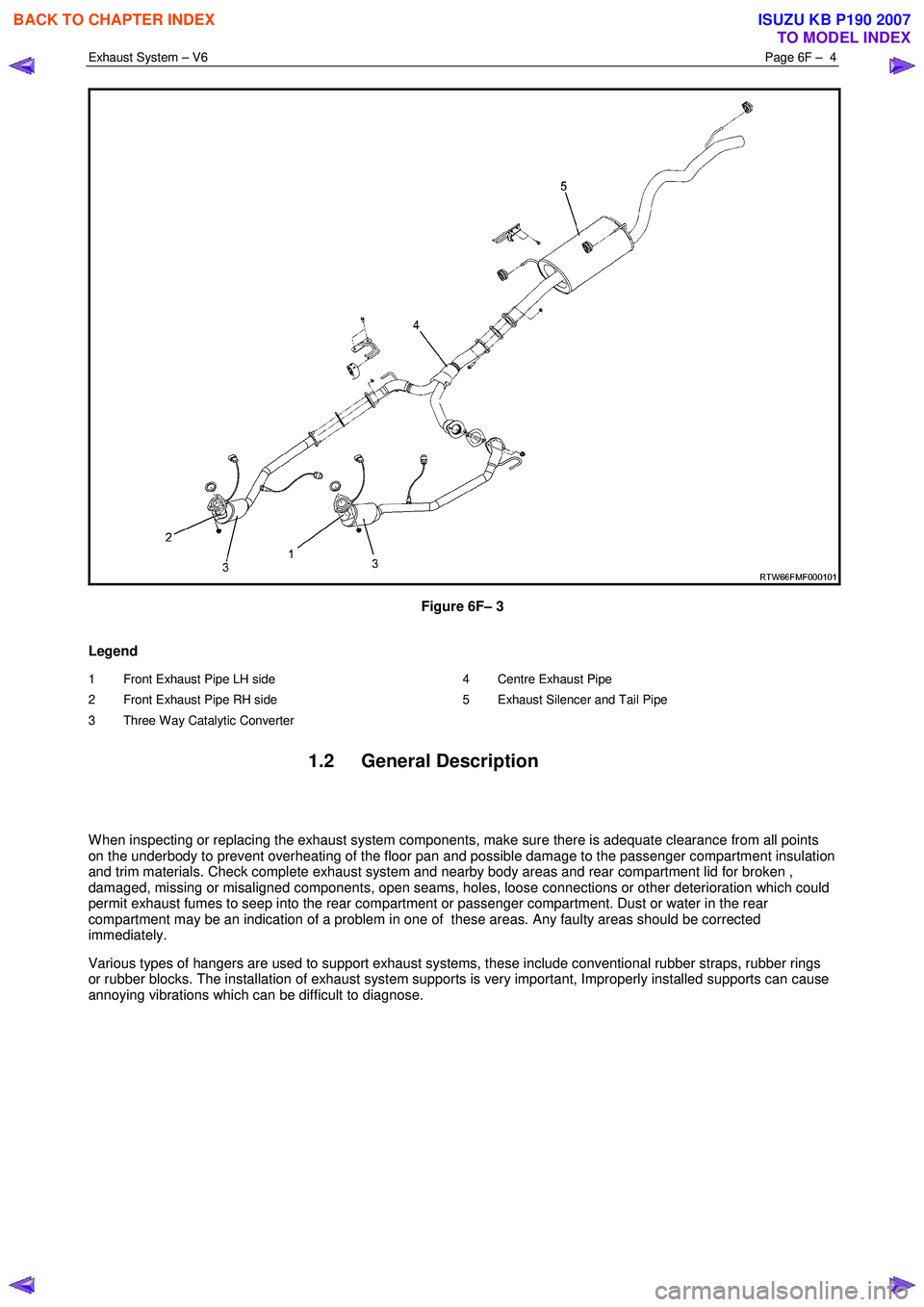
Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 4
Figure 6F– 3
Legend
1 Front Exhaust Pipe LH side
2 Front Exhaust Pipe RH side
3 Three Way Catalytic Converter 4 Centre Exhaust Pipe
5 Exhaust Silencer and Tail Pipe
1.2 General Description
W hen inspecting or replacing the exhaust system components, make sure there is adequate clearance from all points
on the underbody to prevent overheating of the floor pan and possible damage to the passenger compartment insulation
and trim materials. Check complete exhaust system and nearby body areas and rear compartment lid for broken ,
damaged, missing or misaligned components, open seams, holes, loose connections or other deterioration which could
permit exhaust fumes to seep into the rear compartment or passenger compartment. Dust or water in the rear
compartment may be an indication of a problem in one of these areas. Any faulty areas should be corrected
immediately.
Various types of hangers are used to support exhaust systems, these include conventional rubber straps, rubber rings
or rubber blocks. The installation of exhaust system supports is very important, Improperly installed supports can cause
annoying vibrations which can be difficult to diagnose.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3820 of 6020
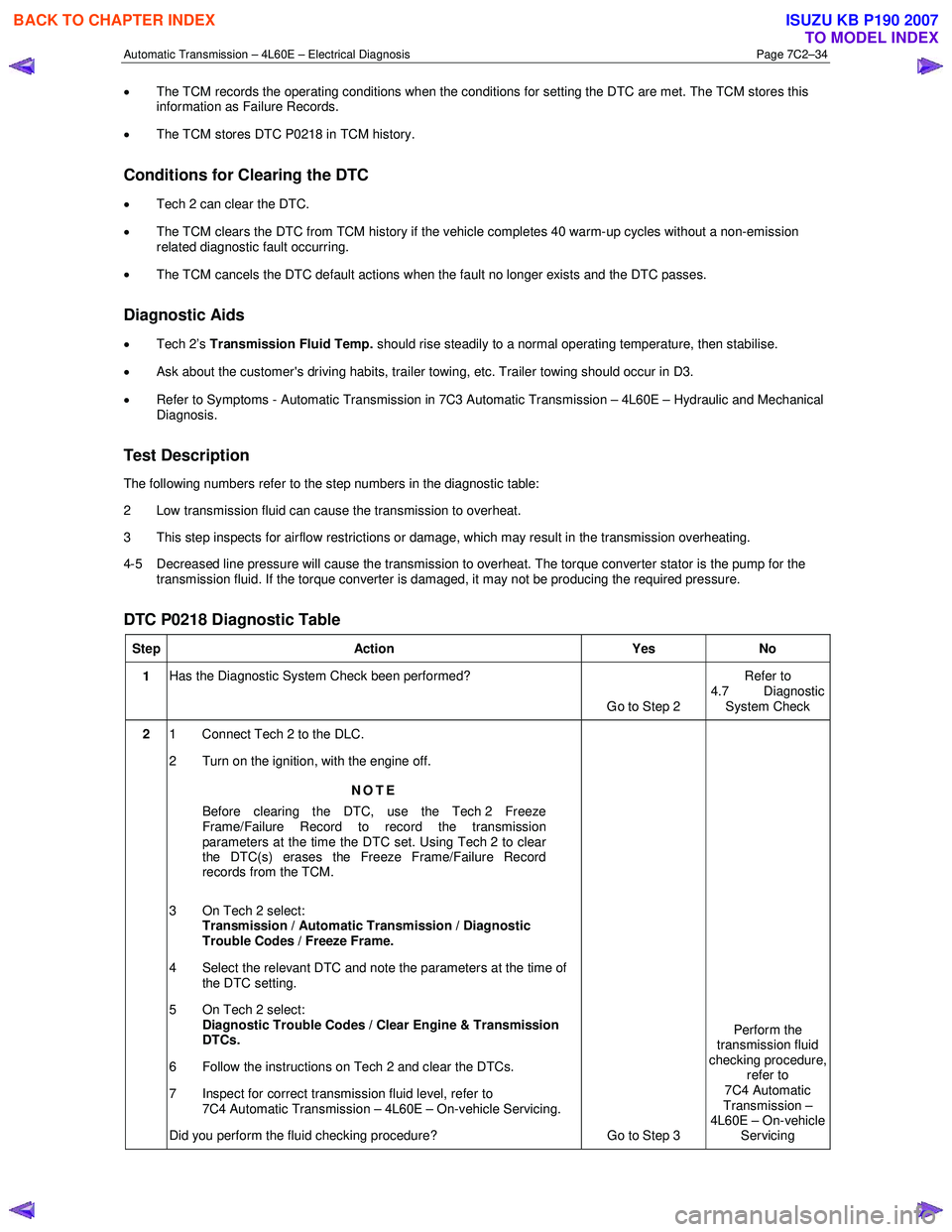
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–34
• The TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are met. The TCM stores this
information as Failure Records.
• The TCM stores DTC P0218 in TCM history.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
• The TCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the DTC passes.
Diagnostic Aids
• Tech 2’s Transmission Fluid Temp. should rise steadily to a normal operating temperature, then stabilise.
• Ask about the customer's driving habits, trailer towing, etc. Trailer towing should occur in D3.
• Refer to Symptoms - Automatic Transmission in 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical
Diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Low transmission fluid can cause the transmission to overheat.
3 This step inspects for airflow restrictions or damage, which may result in the transmission overheating.
4-5 Decreased line pressure will cause the transmission to overheat. The torque converter stator is the pump for the transmission fluid. If the torque converter is damaged, it may not be producing the required pressure.
DTC P0218 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.7 Diagnostic System Check
2 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Turn on the ignition, with the engine off.
NOTE
Before clearing the DTC, use the Tech 2 Freeze
Frame/Failure Record to record the transmission
parameters at the time the DTC set. Using Tech 2 to clear
the DTC(s) erases the Freeze Frame/Failure Record
records from the TCM.
3 On Tech 2 select: Transmission / Automatic Transmission / Diagnostic
Trouble Codes / Freeze Frame.
4 Select the relevant DTC and note the parameters at the time of the DTC setting.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
6 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear the DTCs.
7 Inspect for correct transmission fluid level, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you perform the fluid checking procedure? Go to Step 3 Perform the
transmission fluid
checking procedure, refer to
7C4 Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4310 of 6020

7A2-26 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Low & Reverse Brake Pressure Switch
This parameter displays the input state of the low &
reverse brake transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch
to the TCM. When the low & reverse brake fluid
pressure is generated, the scan tool displays On.
2-4 Brake Solenoid Command
This parameter displays the 2-4 brake solenoid valve
control duty ratio based on the command from the
TCM. The scan tool will display a lower percentage
when the 2-4 brake is controlled to engage (fluid
pressure is applied to the 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits).
The scan tool will display higher percentage when the
2-4 brake is controlled to disengage (fluid pressure is
drained from the 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits).
2-4 Brake Pressure Switch
This parameter displays the input state of the 2-4 brake
transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch to the TCM.
When the 2-4 brake fluid pressure is generated, the
scan tool displays On.
High Clutch Solenoid Command
This parameter displays the high clutch solenoid valve
control duty ratio based on the command from the
TCM. The scan tool will display a lower percentage
when the high clutch is controlled to engage (fluid
pressure is applied to the high clutch hydraulic circuits).
The scan tool will display higher percentage when the
high clutch is controlled to disengage (fluid pressure is
drained from the high clutch hydraulic circuits).
High Clutch Pressure Switch
This parameter displays the input state of the high
clutch transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch to the
TCM. When the high clutch fluid pressure is generated,
the scan tool displays On.
Low Clutch Solenoid Command
This parameter displays the low clutch solenoid valve
control duty ratio based on the command from the
TCM. The scan tool will display a lower percentage
when the low clutch is controlled to engage (fluid
pressure is applied to the low clutch hydraulic circuits).
The scan tool will display higher percentage when the
low clutch is controlled to disengage (fluid pressure is
drained from the low clutch hydraulic circuits).
TCC Solenoid (Torque Converter Clutch)
This parameter displays the torque converter clutch
(TCC) control duty ratio based on the command from
the TCM. The scan tool will display a lower percentage
when the TCC is controlled to disengage (fluid
pressure is drained from the TCC release hydraulic
circuits). The scan tool will display higher percentage
when the TCC is controlled to engage (fluid pressure is
applied to the TCC apply hydraulic circuits). Transmission Fluid Temperature
This parameter displays the temperature of the
automatic transmission fluid (ATF) temperature as
calculated by the TCM using the signal from the
transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor. The scan
tool will display a low temperature when the signal
voltage is high, and a high temperature when the signal
voltage is low.
Transmission Oil Temperature Lamp
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
transmission oil temperature lamp control circuit. The
lamp should be On when the scan tool indicates
command On.
TCM Status Temp. (Temperature Transmission
Control Module)
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
high temperature mode shift map. On indicates the
transmission fluid temperature is high and the high
temperature mode is selected to prevent an
overheating.
4 Wheel Drive Low
This parameter displays the input state of the 4WD low
gear signal from the transfer case control module
(TCCM). When the 4L mode is selected, the scan tool
displays On.
TCM Status Transfer (Transmission Control
Module)
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
shift map that is based on the transfer case position.
High indicates the high mode (2H or 4H) is inputted
from the transfer case control module (TCCM). Low
indicates the low mode (4L) is inputted from the TCCM.
TCM Status Down Slope (Transmission Control
Module)
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
down slope mode shift map. On indicates the down
slope mode is selected under certain driving conditions.
TCM Status Up Slope (Transmission Control
Module)
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
up slope mode shift map. On indicates the up slope
mode is selected under certin driving conditions.
3rd Start Switch
This parameter displays the input state of the 3rd start
switch to the TCM. When the switch is pressed, the
scan tool displays On.
3rd Start Lamp
This parameter displays the commanded state of the
3rd start lamp control circuit. The lamp should be On
when the scan tool indicates command On.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4424 of 6020

7A2-140 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
• Electrically Erasable Programmable Read OnlyMemory (EEPROM)
This type of memory allows selected portions of
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM,
such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/ calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory
Flash memory has increased memory storage capacity.
During programming, all information within this type of
memory is erased, and then replaced with entirely new
information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming a TCM are listed
below:
• Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming a TCM using one of
the methods listed above, refer to Service
Programming System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru
Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important: DO NOT program an existing TCM with the
identical software/ calibration package. This procedure
is not a short cut to correct the driveability condition.
This is an ineffective repair. An TCM should only be
programmed when the following occurs:
• When a service procedure instructs you to replace the TCM.
• An updated software/ calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming a TCM:
• The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
• The hardware key is plugged into the computer port.
• Vehicle system voltage:
- There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the TCM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the TCM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or TCM damage. - Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a
load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure:
- The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
TCM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the TCM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the TCM.
Performing the Remote Procedure 1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the TCM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the TCM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007