heating ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1963 of 6020

6E-346 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Engine Mechanical ChecksInspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper mechanical timing (timing gear and timing chain).
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
• Thermostat working (open stuck).
• Any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Electrical System Checks • Glow plug control (preheating) system operation. Refer to Glow Control System
Check in this section.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1967 of 6020

6E-350 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
• The hardware key is plugged into the computerport.
• Vehicle system voltage: - There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure: - The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
ECM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the ECM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the ECM. Performing the Remote Procedure
1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the ECM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the ECM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
d. If there is already stored in the scan tool, the existing data is displayed on the screen. The
scan tool asks user to keep existing data "Keep
Data" or "Continue" to request new vehicle
information from the ECM. If there is no data in
the scan tool, it will immediately start vehicle
identification.
e. Select the vehicle description by following the on-screen instructions based on stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
f. During obtaining information, the scan tool is receiving information from all modules at the
same time. But only ECM information is
displayed on the screen.
g. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Okay".
h. Verify that the correct VIN is displayed on the scan tool. If the VIN is incorrect or no VIN,
record the correct VIN.
2. Turn OFF the ignition.
3. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.
4. Transfer the data from the terminal to the scan tool using the following procedure:
Notice: The TIS supports service programming with
the Tech 2 scan tool only.
a. Connect the scan tool to the terminal.
b. Launch the TIS application.
c. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
d. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process
screen, then click "Next".
• Select Diagnostic Tool - Tech 2
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether an existing ECM is being
reprogrammed or an ECM is being replaced
with a new one
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
e. Verify the connections on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
f. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click
"Next".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1970 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-353
Description and Operation
Engine Control Module (ECM) Description
Engine Control Module (ECM) Service Precautions
Important:The symbol ! warns you of an electric shock
hazard. To avoid shock and possible serious injury, DO NOT
touch the terminals. When disconnecting the harness
connectors, always turn OFF the ignition switch or disconnect
the battery cable.
The engine control module (ECM) is designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. Avoid overloading any circuit. When testing
for opens and shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to
any of the ECM circuits unless instructed to do so. In
some cases, these circuits should only be tested using
a DMM. The ECM should remain connected to the
ECM harness.
The ECM is located inside of engine compartment via
mounting bracket and is behind air cleaner case. The
ECM mainly controls the following. • The fuel system control
• The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system control
• The preheating (glow) system control
• The A/C compressor control
• The immobilizer control
• On-board diagnostics for engine control
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. The ECM can
recognize operational problems, alert the driver
through the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), and store
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the
system faults to aid the technician in making repairs.
RTW56ESH000201
RTW56ESH004401
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2008 of 6020
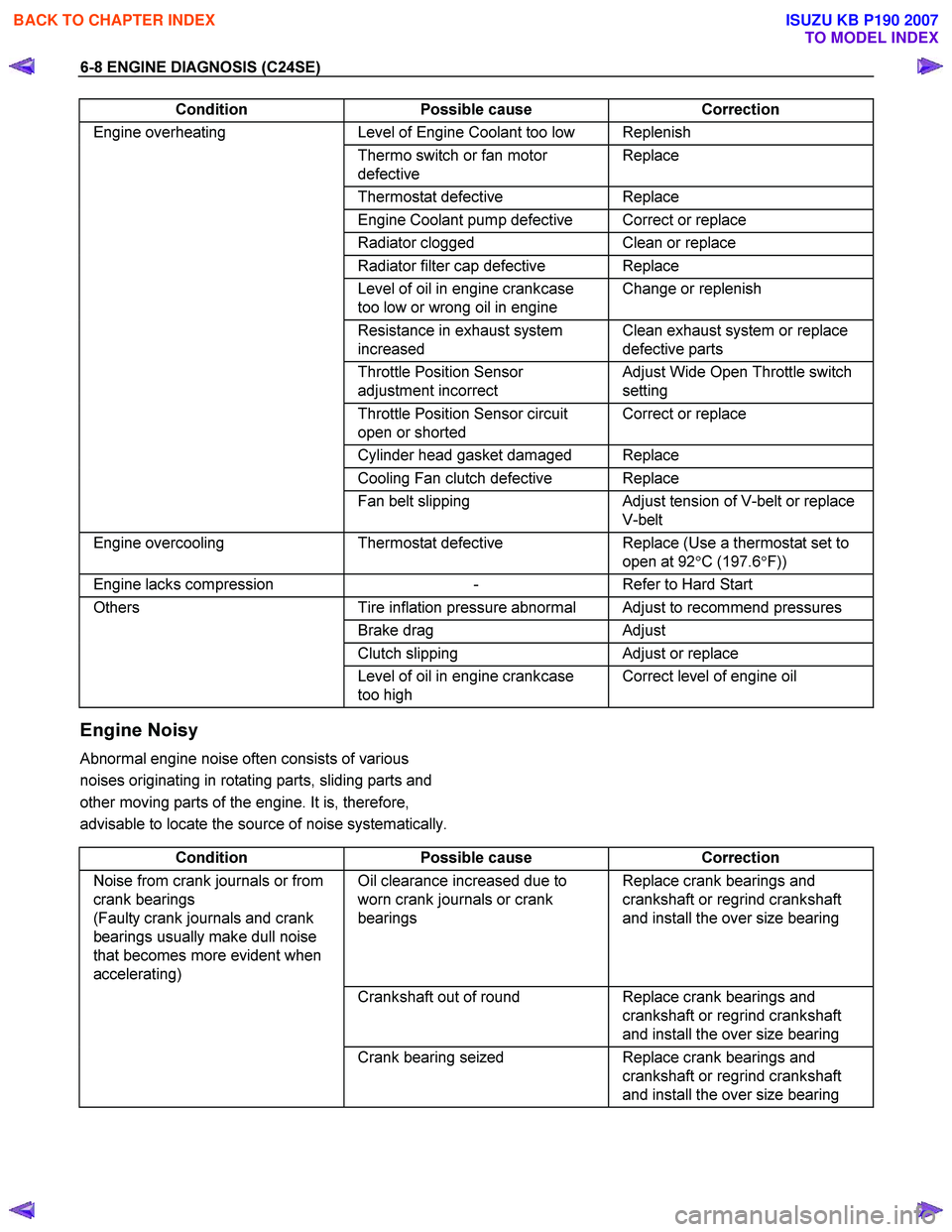
6-8 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine overheating Level of Engine Coolant too low Replenish
Thermo switch or fan motor
defective Replace
Thermostat
defective Replace
Engine Coolant pump defective Correct or replace
Radiator clogged Clean or replace
Radiator filter cap defective Replace
Level of oil in engine crankcase
too low or wrong oil in engine Change or replenish
Resistance in exhaust system
increased Clean exhaust system or replace
defective parts
Throttle Position Sensor
adjustment incorrect Adjust Wide Open Throttle switch
setting
Throttle Position Sensor circuit
open or shorted Correct or replace
Cylinder head gasket damaged Replace
Cooling Fan clutch defective Replace
Fan belt slipping Adjust tension of V-belt or replace
V-belt
Engine overcooling Thermostat defective Replace (Use a thermostat set to
open at 92 °C (197.6 °F))
Engine lacks compression - Refer to Hard Start
Others Tire inflation pressure abnormal Adjust to recommend pressures
Brake drag Adjust
Clutch slipping Adjust or replace
Level of oil in engine crankcase
too high Correct level of engine oil
Engine Noisy
Abnormal engine noise often consists of various
noises originating in rotating parts, sliding parts and
other moving parts of the engine. It is, therefore,
advisable to locate the source of noise systematically.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Noise from crank journals or from
crank bearings
(Faulty crank journals and crank
bearings usually make dull noise
that becomes more evident when
accelerating) Oil clearance increased due to
worn crank journals or crank
bearings Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
Crankshaft out of round Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
Crank bearing seized Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2010 of 6020
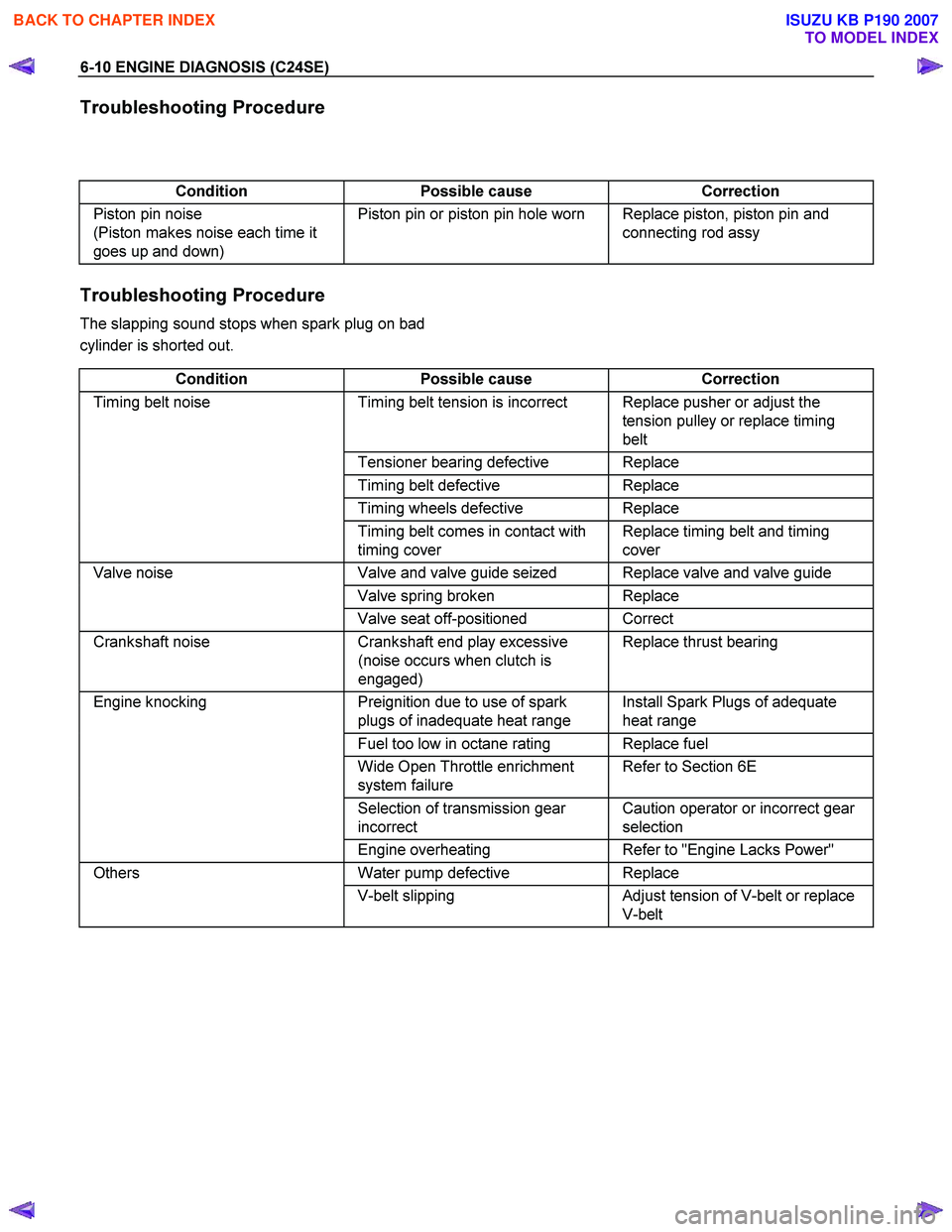
6-10 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Troubleshooting Procedure
Condition Possible cause Correction
Piston pin noise
(Piston makes noise each time it
goes up and down) Piston pin or piston pin hole worn Replace piston, piston pin and
connecting rod assy
Troubleshooting Procedure
The slapping sound stops when spark plug on bad
cylinder is shorted out.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Timing belt noise Timing belt tension is incorrect Replace pusher or adjust the
tension pulley or replace timing
belt
Tensioner bearing defective Replace
Timing belt defective Replace
Timing wheels defective Replace
Timing belt comes in contact with
timing cover Replace timing belt and timing
cover
Valve noise Valve and valve guide seized Replace valve and valve guide
Valve spring broken Replace
Valve seat off-positioned Correct
Crankshaft noise Crankshaft end play excessive
(noise occurs when clutch is
engaged) Replace thrust bearing
Engine knocking
Preignition due to use of spark
plugs of inadequate heat range Install Spark Plugs of adequate
heat range
Fuel too low in octane rating Replace fuel
Wide Open Throttle enrichment
system failure Refer to Section 6E
Selection of transmission gear
incorrect Caution operator or incorrect gear
selection
Engine overheating Refer to "Engine Lacks Power"
Others Water pump defective Replace
V-belt slipping Adjust tension of V-belt or replace
V-belt
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2109 of 6020
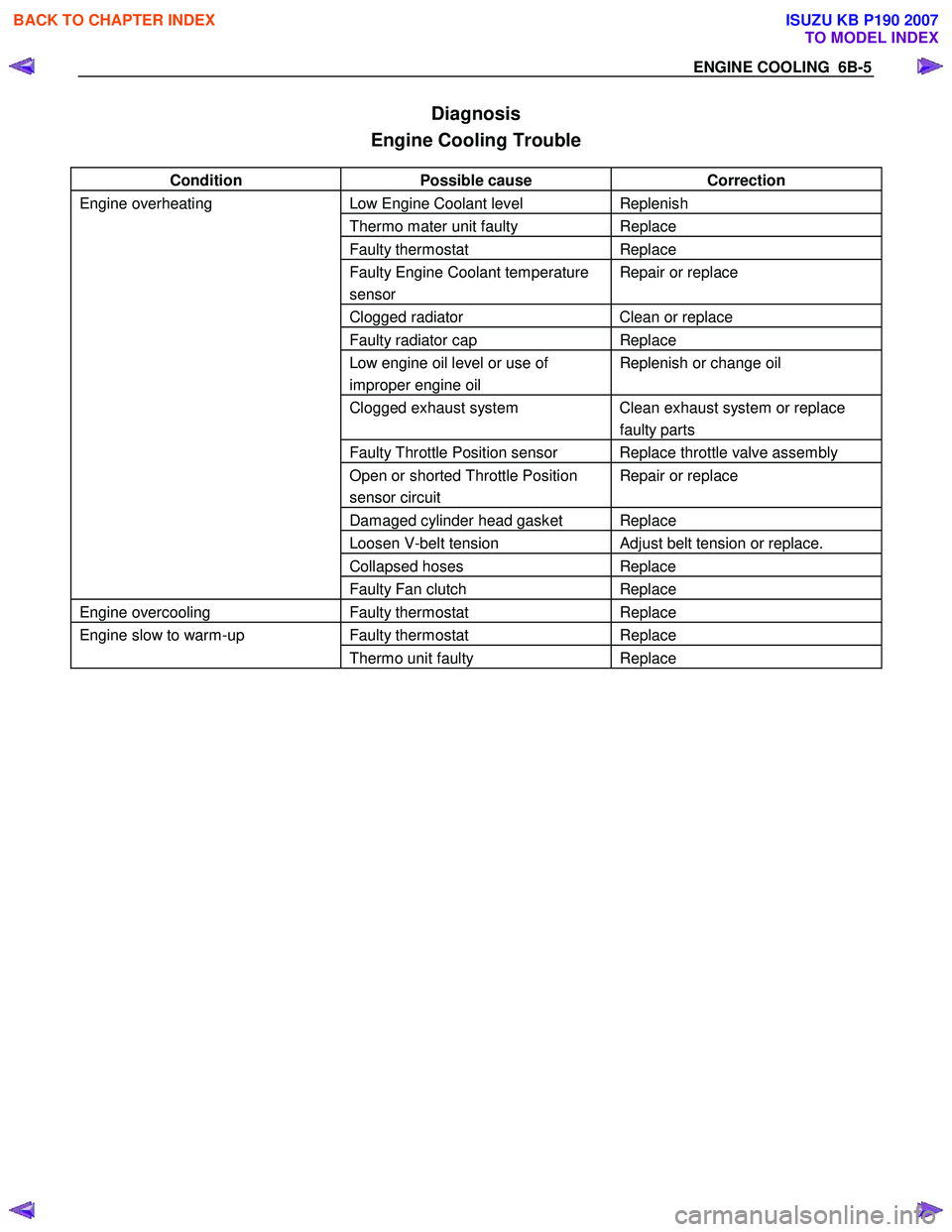
ENGINE COOLING 6B-5
Diagnosis
Engine Cooling Trouble
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine overheating Low Engine Coolant level Replenish
Thermo mater unit faulty Replace
Faulty thermostat Replace
Faulty Engine Coolant temperature
sensor Repair or replace
Clogged radiator Clean or replace
Faulty radiator cap Replace
Low engine oil level or use of
improper engine oil Replenish or change oil
Clogged exhaust system Clean exhaust system or replace
faulty parts
Faulty Throttle Position sensor Replace throttle valve assembly
Open or shorted Throttle Position
sensor circuit Repair or replace
Damaged cylinder head gasket Replace
Loosen V-belt tension Adjust belt tension or replace.
Collapsed hoses Replace
Faulty Fan clutch Replace
Engine overcooling Faulty thermostat Replace
Engine slow to warm-up Faulty thermostat Replace
Thermo unit faulty Replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2116 of 6020
6B-12 ENGINE COOLING
Inspection
Radiator Cap
Measure the valve opening pressure of the pressurizing valve
with a radiator filler cap tester.
Replace the cap if the valve opening pressure is outside the
standard range.
Valve opening pressure kPa (psi) 88.3 – 103.0
(13.5 – 15.7)
Cap tester: 5-8840-0277-0
Adapter: 5-8840-2603-0
Check the condition of the vacuum valve in the center of the
valve seat side of the cap. If considerable rust or dirt is found,
or if the valve seat cannot be moved by hand, clean or replace
the cap.
Valve opening vacuum kPa (psi) 1.9 - 4.9
(0.28 - 0.71)
Radiator Core
1. A bent fin may result in reduced ventilation and overheating
may occur. All bent fins must be straightened. Pay close
attention to the base of the fin when it is being straightened.
2. Remove all dust, bugs and other foreign material.
Flushing the Radiator
Thoroughly wash the inside of the radiator and the engine
coolant passages with cold water and mild detergent. Remove
all sign of scale and rust.
Cooling System Leakage Check
Use a radiator cap tester to force air into the radiator through
the filler neck at the specified pressure of 196 kPa (28.5 psi)
with a cap tester:
• Leakage from the radiator
• Leakage from the coolant pump
• Leakage from the water hoses
• Check the rubber hoses for swelling.
Cap tester: 5-8840-0277-0
Adapter: 5-8840-2603-0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2168 of 6020
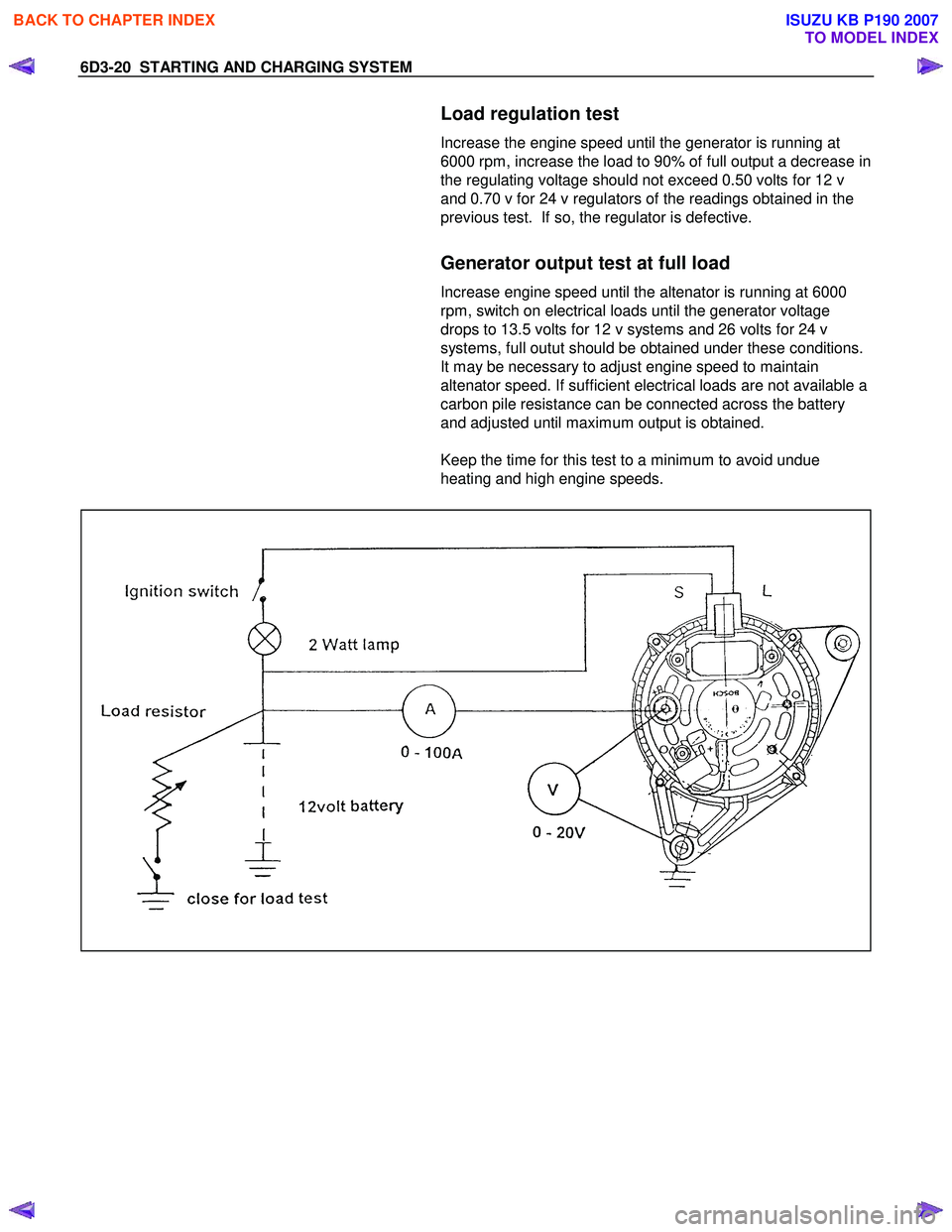
6D3-20 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Load regulation test
Increase the engine speed until the generator is running at
6000 rpm, increase the load to 90% of full output a decrease in
the regulating voltage should not exceed 0.50 volts for 12 v
and 0.70 v for 24 v regulators of the readings obtained in the
previous test. If so, the regulator is defective.
Generator output test at full load
Increase engine speed until the altenator is running at 6000
rpm, switch on electrical loads until the generator voltage
drops to 13.5 volts for 12 v systems and 26 volts for 24 v
systems, full outut should be obtained under these conditions.
It may be necessary to adjust engine speed to maintain
altenator speed. If sufficient electrical loads are not available a
carbon pile resistance can be connected across the battery
and adjusted until maximum output is obtained.
Keep the time for this test to a minimum to avoid undue
heating and high engine speeds.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2235 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–65
Step 3: Simulate the symptom and isolate the
problem
Simulate the symptom and isolate the system by
reproducing all possible conditions suggested in Step 1
while monitoring suspected circuits/components/
systems to isolate the problem symptom. Begin with the
most logical circuit/component.
Isolate the circuit by dividing the suspect system into
simpler circuits. Next, confine the problem into a smaller
area of the system. Begin at the most logical point (or
point of easiest access) and thoroughly check the
isolated circuit for the fault, using basic circuit tests.
Hints
You can isolate a circuit by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another
• If only component fails to operate, begin testing the component
• If a number of components do not operate, begin test at areas of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches, main connectors or major
components)
• Substitute a known good part from the parts department or the vehicle system
• Try the suspect part in a known good vehicle
See Symptom Simulation Tests on the next page for
problem simulation procedures. Refer to service manual
sections 6E and 8A for information about intermittent
diagnosis. Follow procedures for basic circuit testing in
service manual section 8A.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Bulletins
• Digital multimeter (with a MIN/MAX feature)
• Tech II and Tech II upload function
• Circuit testing tools (including connector kits/ harnesses and jumper wires)
• Experience
• Intermittent problem solving simulation methods
• Customer complaint check sheet
Symptom Simulation Tests
1. Vibration
This method is useful when the customer complaint
analysis indicates that the problem occurs when the
vehicle/system undergoes some form of vibration.
For connectors and wire harness, slightly shake
vertically and horizontally. Inspect the connector joint
and body for damage. Also, tapping lightly along a
suspected circuit may be helpful. For parts and sensors, apply slight vibration to the part
with a light tap of the finger while monitoring the system
for a malfunction.
2. Heat
This method is important when the complaint suggests
that the problem occurs in a heated environment. Apply
moderate heat to the component with a hair drier or
similar tool while monitoring the system for a
malfunction.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid overheating
the component.
3. Water and Moisture
This method may be used when the complaint suggests
that the malfunction occurs on a rainy day or under
conditions of high humidity. In this case, apply water in a
light spray on the vehicle to duplicate the problem.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid directly
exposing electrical connections to water.
4. Electrical loads
This method involves turning systems ON (such as the
blower, lights or rear window defogger) to create a load
on the vehicle electrical system at the same time you
are monitoring the suspect circuit/component.
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed
This condition refers to instances where a system
operating as designed is perceived to be unsatisfactory
or undesirable. In general, this is due to:
• A lack of understanding by the customer
• A conflict between customer expectations and vehicle design intent
• A system performance that is unacceptable to the customer
What you should do
You can verify that a system is operating as designed
by:
• Reviewing service manual functional/diagnostic checks
• Examining bulletins and other service information for supplementary information
• Compare system operation to an identical vehicle
If the condition is due to a customer misunderstanding
or a conflict between customer expectation and system
operation, you should explain the system operation to
the customer.
If the complaint is due to a case of unsatisfactory
system performance, you should contact Technical
Assistance for the latest information.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2424 of 6020
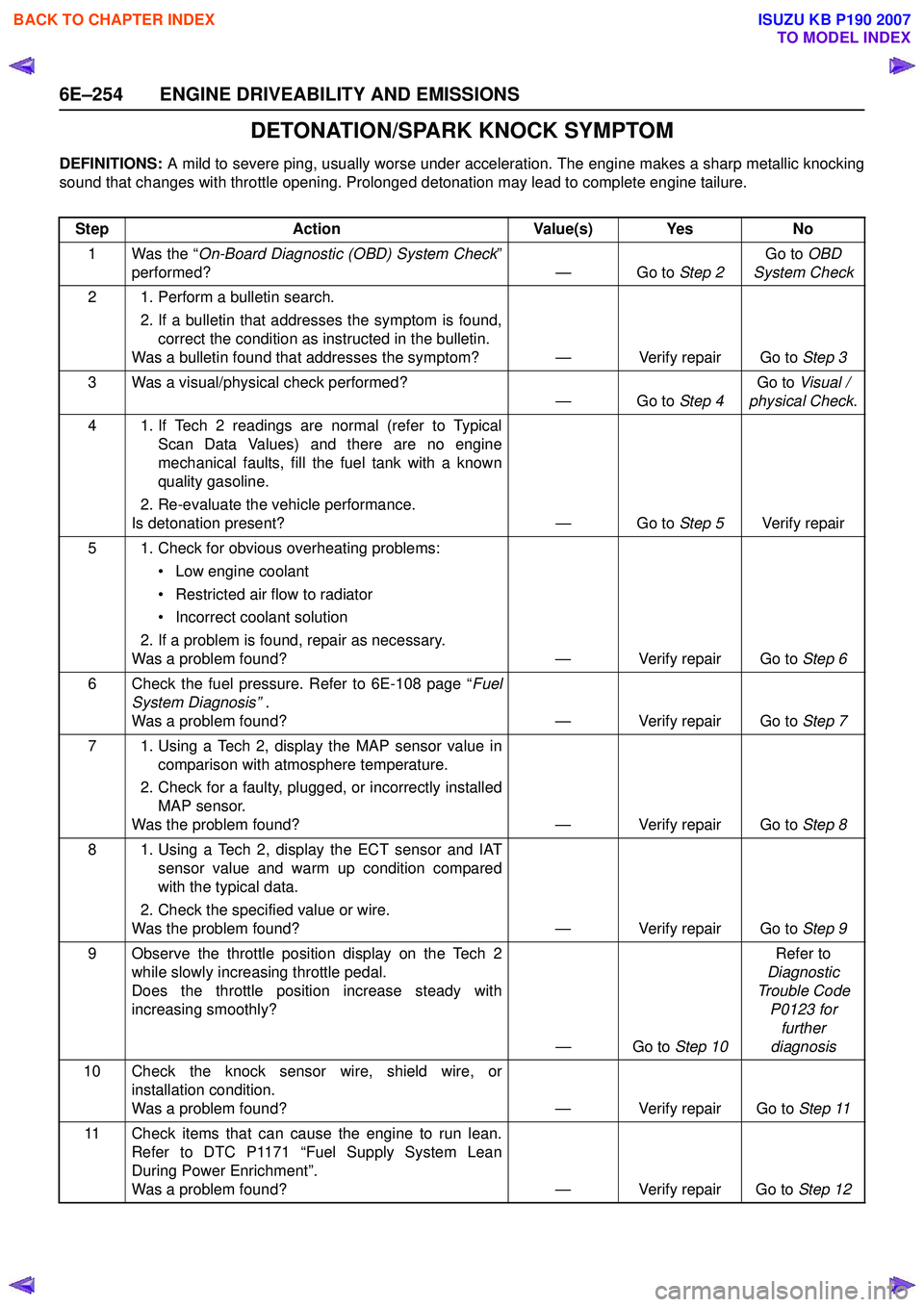
6E–254 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DETONATION/SPARK KNOCK SYMPTOM
DEFINITIONS: A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration. The engine makes a sharp metallic knocking
sound that changes with throttle opening. Prolonged detonation may lead to complete engine tailure.
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “ On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ”
performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Perform a bulletin search. 2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 Was a visual/physical check performed? —Go to Step 4Go to
Visual /
physical Check .
4 1. If Tech 2 readings are normal (refer to Typical Scan Data Values) and there are no engine
mechanical faults, fill the fuel tank with a known
quality gasoline.
2. Re-evaluate the vehicle performance.
Is detonation present? — Go to Step 5Verify repair
5 1. Check for obvious overheating problems: • Low engine coolant
• Restricted air flow to radiator
• Incorrect coolant solution
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Check the fuel pressure. Refer to 6E-108 page “ Fuel
System Diagnosis” .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 1. Using a Tech 2, display the MAP sensor value in comparison with atmosphere temperature.
2. Check for a faulty, plugged, or incorrectly installed MAP sensor.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 1. Using a Tech 2, display the ECT sensor and IAT sensor value and warm up condition compared
with the typical data.
2. Check the specified value or wire.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Observe the throttle position display on the Tech 2 while slowly increasing throttle pedal.
Does the throttle position increase steady with
increasing smoothly?
—Go to Step 10Refer to
Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0123 for further
diagnosis
10 Check the knock sensor wire, shield wire, or installation condition.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to DTC P1171 “Fuel Supply System Lean
During Power Enrichment”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007