abs JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 1173 of 2490
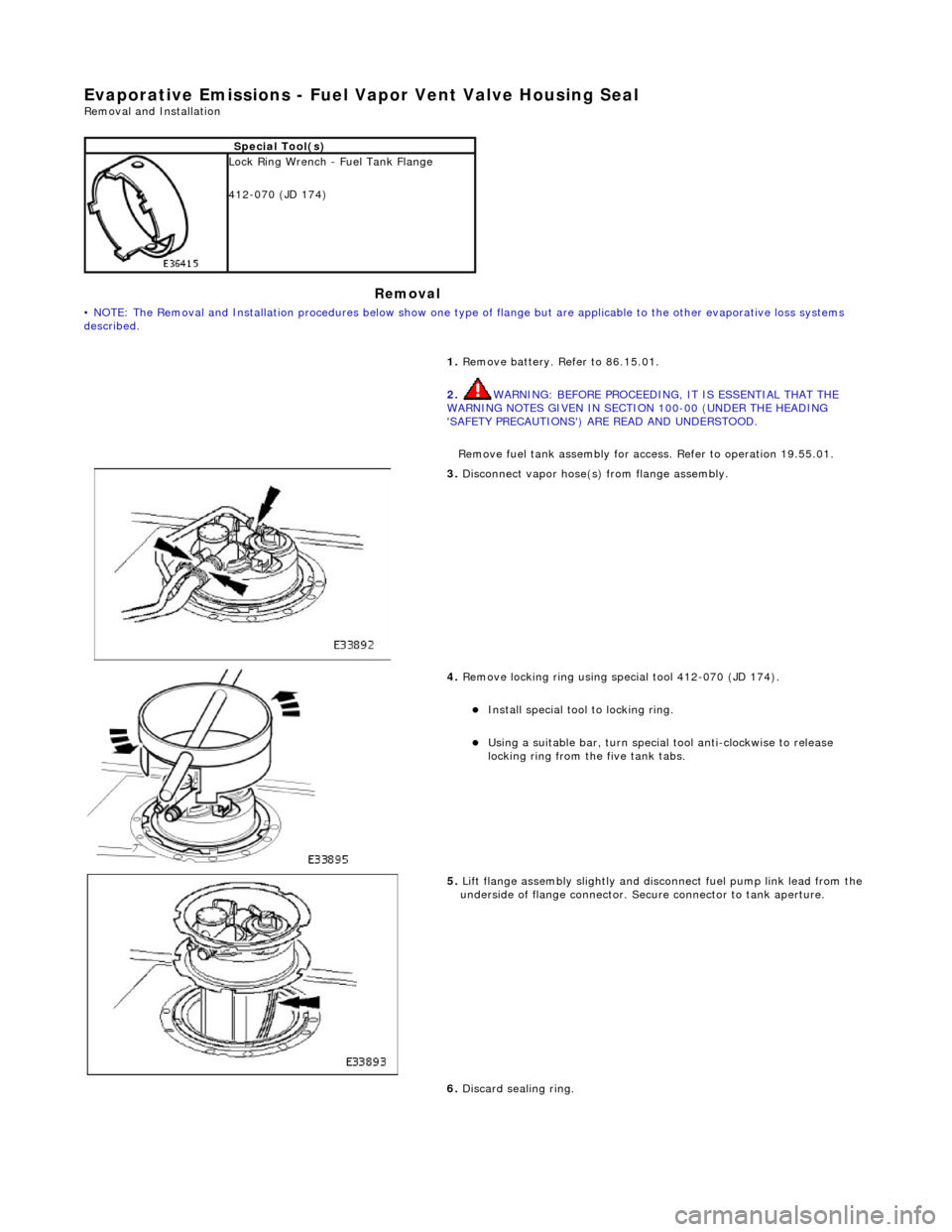
Evapor
ative Emissions - Fuel Va
por Vent Valve Housing Seal
Remov
al and Installation
Re
moval
• NO
TE: The Removal and Installation procedur
es below show one type of flange but are applicable to the other evaporative loss systems
described.
Special To
ol(s)
Lock
Ring Wrench - Fuel Tank Flange
412-070 (JD 174)
1. Remove battery. Refer to 86.15.01.
2. WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING, IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE
WARNING NOTES GIVEN IN SECTIO N 100-00 (UNDER THE HEADING
'SAFETY PRECAUTIONS') ARE READ AND UNDERSTOOD.
Remove fuel tank assembly for access. Refer to operation 19.55.01.
3. Discon
nect vapor hose(s) from flange assembly.
4. Remov
e locking ring using special tool 412-070 (JD 174).
Insta
ll special tool to locking ring.
Usi
ng a suitable bar, turn special tool anti-clockwise to release
locking ring from the five tank tabs.
5. Lift
flange assembly slightly and disconnect fuel pump link lead from the
underside of flange connector. Secure connector to tank aperture.
6. Discard sealing ring.
Page 1174 of 2490
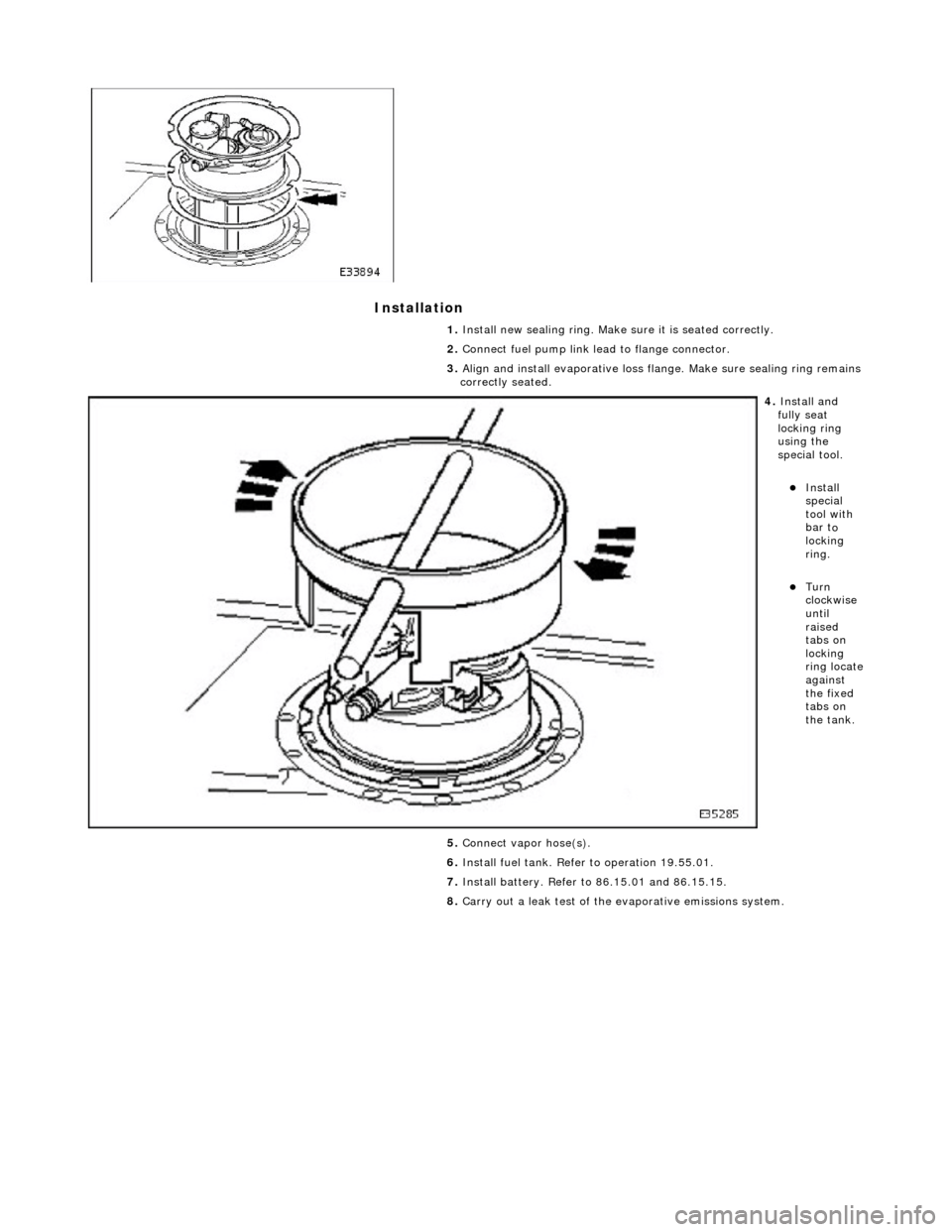
Installation
1.
Insta ll n
ew sealing ring. Make sure it is seated correctly.
2. Connect fuel pump link lead to flange connector.
3. Align and install evaporative loss flange. Make sure sealing ring remains
correctly seated.
4. Insta ll a
nd
fully seat
locking ring
using the
special tool.
Insta ll
special
tool with
bar t
o
locking
ring.
Turn
clock w
ise
until
raised
tabs on
locking
ring locate
against
the fixed
tabs on
the tank.
5. Connect vapor hose(s).
6. Install fuel tank. Refer to operation 19.55.01.
7. Install battery. Refer to 86.15.01 and 86.15.15.
8. Carry out a leak test of the evaporative emissions system.
Page 1207 of 2490
Pinpoint Tests
f
ailure
P1611Thr
ottle angle malfunction
TP sensor
circuit fault (refer to
P0121)
APP sensor circuit faul
t (refer to
P0121)
Throttl
e assembly failure
ECM failu
re
Se
e pinpoint tests for components
listed. For throttle body information,
REFER to Section 303
-04
Fuel
Charging and Con
trols
.
Contact deal
er technical support for
advice on possible ECM failure.
P1612Throttl
e offset malfunction
TP sensor
circuit fault (refer to
P0121)
APP sensor circuit faul
t (refer to
P0121)
Throttl
e assembly failure
ECM failu
re
Se
e pinpoint tests for components
listed. For throttle body information,
REFER to Section 303
-04
Fuel
Charging and Con
trols
.
Contact deal
er technical support for
advice on possible ECM failure.
P1637CAN AB
S/TCCM token missing
CAN
open circuit fault - ABS/TCCM
to ECM
CAN s
hort circuit fault
ABS/TCCM failu
re
ECM failu
re
F
or network circuit tests,
REFER to Section 418
-00
Module
Comm
unications Network
.
P1638CAN INST token missingCAN
open circuit fault - INST to
ECM
CAN s
hort circuit fault
INST
failure
ECM failu
re
F
or network circuit tests,
REFER to Section 418
-00
Module
Comm
unications Network
.
P1642CAN c
ircuit malfunction
CAN s
hort circuit fault
Control modul
e failure - check for
additional logged DTCs to locate
control module source
F
or network circuit tests,
REFER to Section 418
-00
Module
Comm
unications Network
.
P1643CAN TC
M token missing
CAN
open circuit fault - TCM to
ECM
CAN s
hort circuit fault
TCM failure
ECM failu
re
F
or network circuit tests,
REFER to Section 418
-00
Module
Comm
unications Network
.
P1646F
uel pump 2 relay malfunction.
NOTE: This DTC applies only to
the S/C fuel pump 2
F
uel pump 2 relay failure
F
uel pump 2 relay to ECM circuit
fault
F
uel pump 2 relay coil power
supply open circuit
ECM ground circuit faul
t (relay coil
drive)
F
or fuel pump 2 relay circuit tests,
REFER to Section 303
-04
Fuel
Charging and Con
trols
.
P
INPOINT TEST A : DTC P0101, P0102, P0103; MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
RANGE/PERFORMANCE, HIGH/LOW VOLTAGE
•
NOTE: Before commencing this
test, check the air filter for blockage, the engine air inta ke and breather systems for
leaks, and the TPS for additional DTCs.
TE
ST
CONDITIONS
D
ETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
A1: CHECK
THE MAF SENSOR SENS
E CIRCUIT FOR HIGH RESISTANCE
Di
sconnect the battery negative terminal.
1
D
isconnect the ECM electrical connector, EM12.
2
Di
sconnect the MAF sensor electrical connector, PI35.
3
Meas
ure the resistance between EM12, pin 13 (GY) and PI35, pin 02 (GY).
4
Is th
e resistance greater than 5 ohms?
Yes REPAIR the high resistance circuit. For additional information, refer to the wiring diagrams. CLEAR the
DTC. TEST the system for normal operation.
No GO to A2
.
A2: CHECK
THE MAF SENSOR SENSE CI
RCUIT FOR SHORT TO HIGH VOLTAGE
R
econnect the battery negative terminal.
1
Turn the ignition swi
tch to the ON
position.
2
M
easure the voltage between the MAF sensor electrical connector, PI35, pin 02 (GY) and GROUND.
3
Is th
e voltage greater than 3 volts?
Page 1239 of 2490
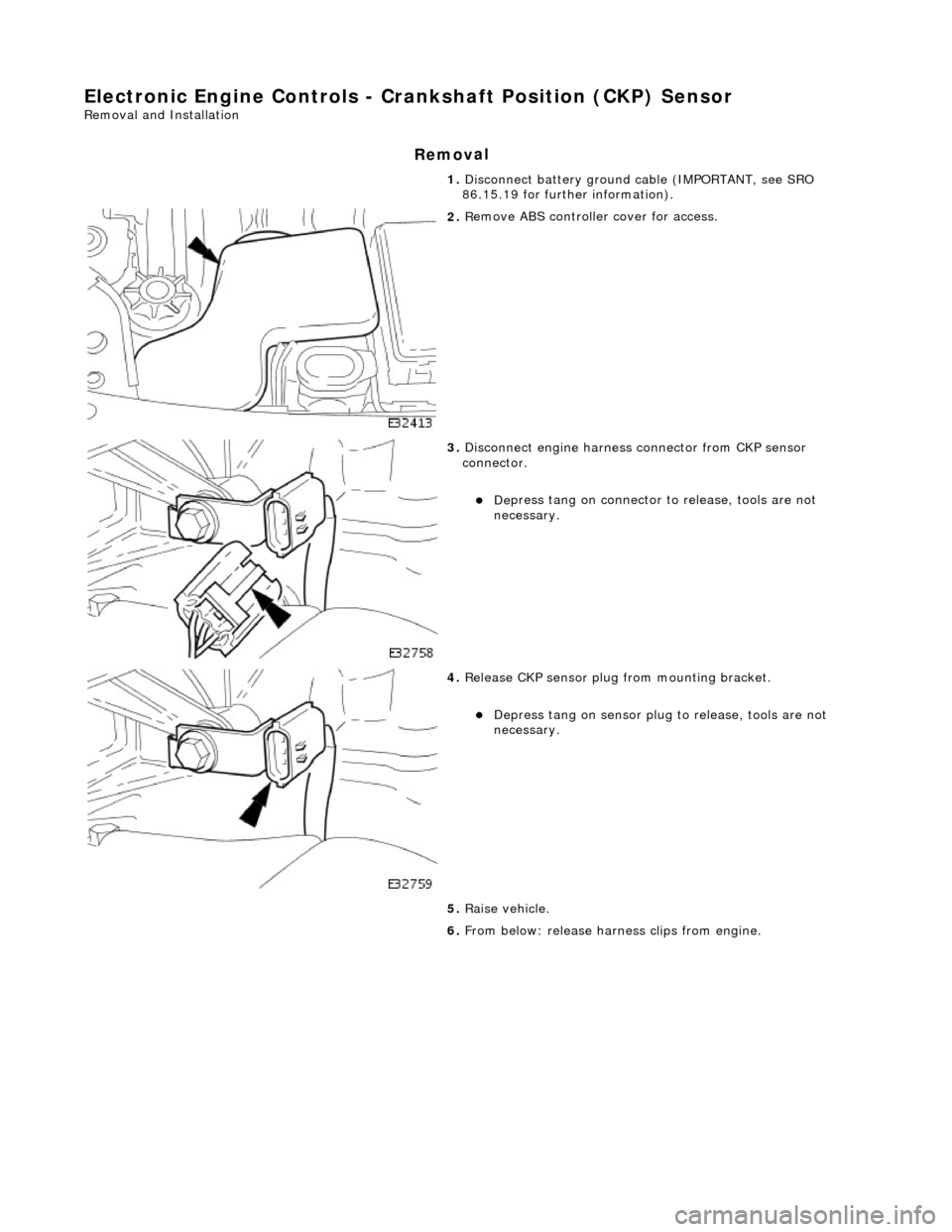
E
lectronic Engine Controls - Cr
ankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Re
moval and Installation
Remov
al
1.
Disc
onnect battery ground cable (IMPORTANT, see SRO
86.15.19 for further information).
2. R
emove ABS controller cover for access.
3. Di
sconnect engine harness connector from CKP sensor
connector.
De
press tang on connector to release, tools are not
necessary.
4. Re
lease CKP sensor plug from mounting bracket.
Depress tan
g on sensor plug
to release, tools are not
necessary.
5. Raise vehicle.
6. From below: release harn ess clips from engine.
Page 1268 of 2490
Input speed is monitored by the TCM with a rationality check being made against output speed. A fault will be flagged if the
indicated input speed exceeds 7400 rpm. Additionally, a failure judgement will be made if the indicated input speed is <160
rpm with engine speed >608 rpm and output speed >224 rpm
The procedure is similar for the output sp eed diagnostic. A fault (non OBDII) will be flagged if the indicated input speed
exceeds 6712 rpm. Additionally a failure judgement will be ma de if the indicated output speed is <160 rpm and the average
road wheel speed exceeds 100 rpm.
Under normal circumstance s after the output speed diagnost ic fault code has been set, the TCM uses rear wheel speed
information to compute its calculations, this has no effect on transmission operation. However, should a second fault occur,
in the ABS system, thus making rear wheel speed information unavailable, an additional fault code will be logged.
Control Systems
Introduction
Gear selection is achieved by controlling the flow of transmission fluid to internal multi-disc clutches.
The three solenoid valves direct the transmission fluid flow to the selected clutches and the pressure regulators control the
fluid pressure to each component. One pr essure regulator serves as a master pressure control for the entire system and a
second is used exclusively for torque converter clutch lock-up operation.
The TCM controls the internal components thus determining gear selection and shift pattern.
In the event of an electronic system fault the basic function s Park, Reverse Neutral and Drive Fourth are retained by the
hydraulic system.
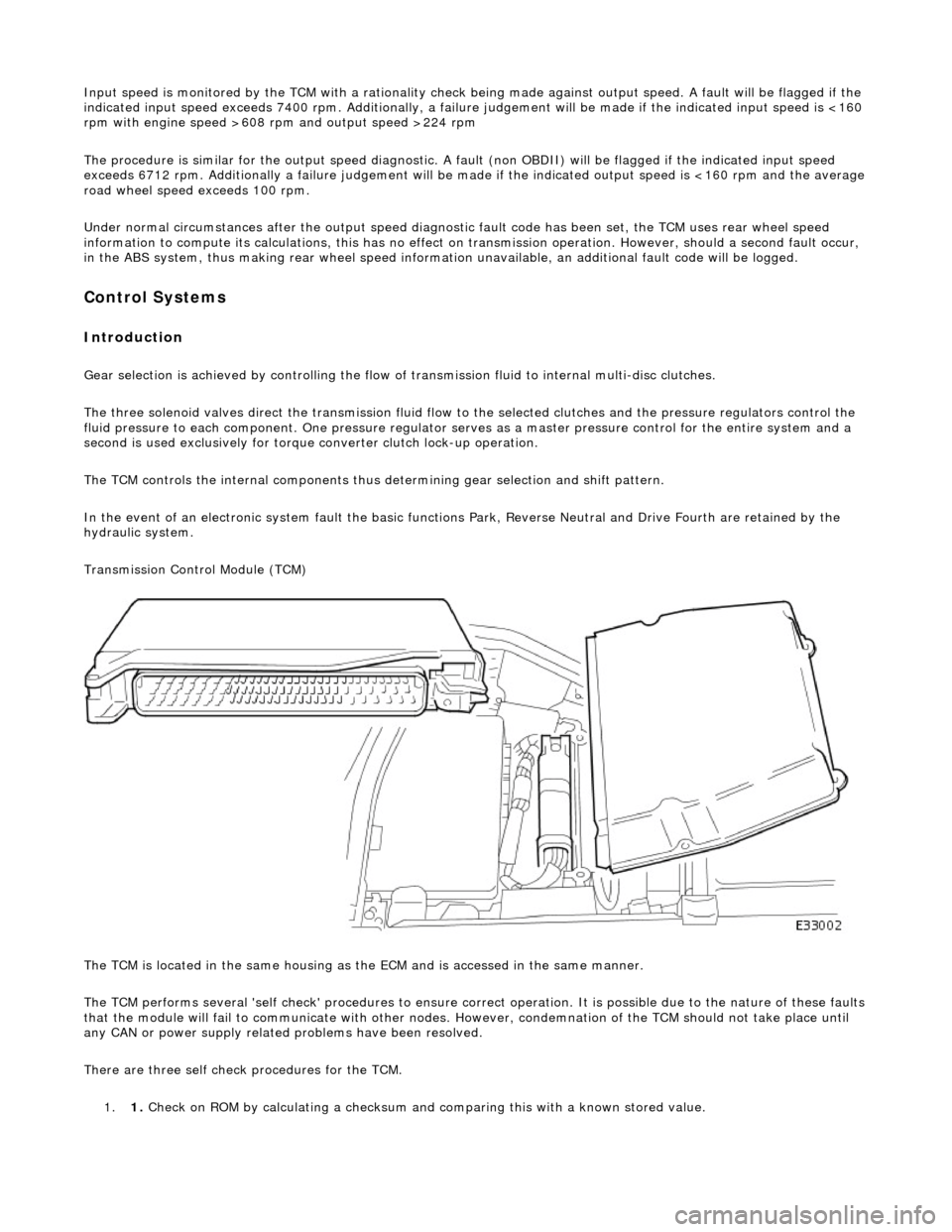
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is located in the same housing as th e ECM and is accessed in the same manner.
The TCM performs several 'self check' procedur es to ensure correct operation. It is possible due to the nature of these faults
that the module will fail to communicate with other nodes. However, condemnation of the TCM should not take place until
any CAN or power supply related problems have been resolved.
There are three self check procedures for the TCM. 1. 1. Check on ROM by calculatin
g a checksum and comparing this with a known stored value.
Page 1275 of 2490
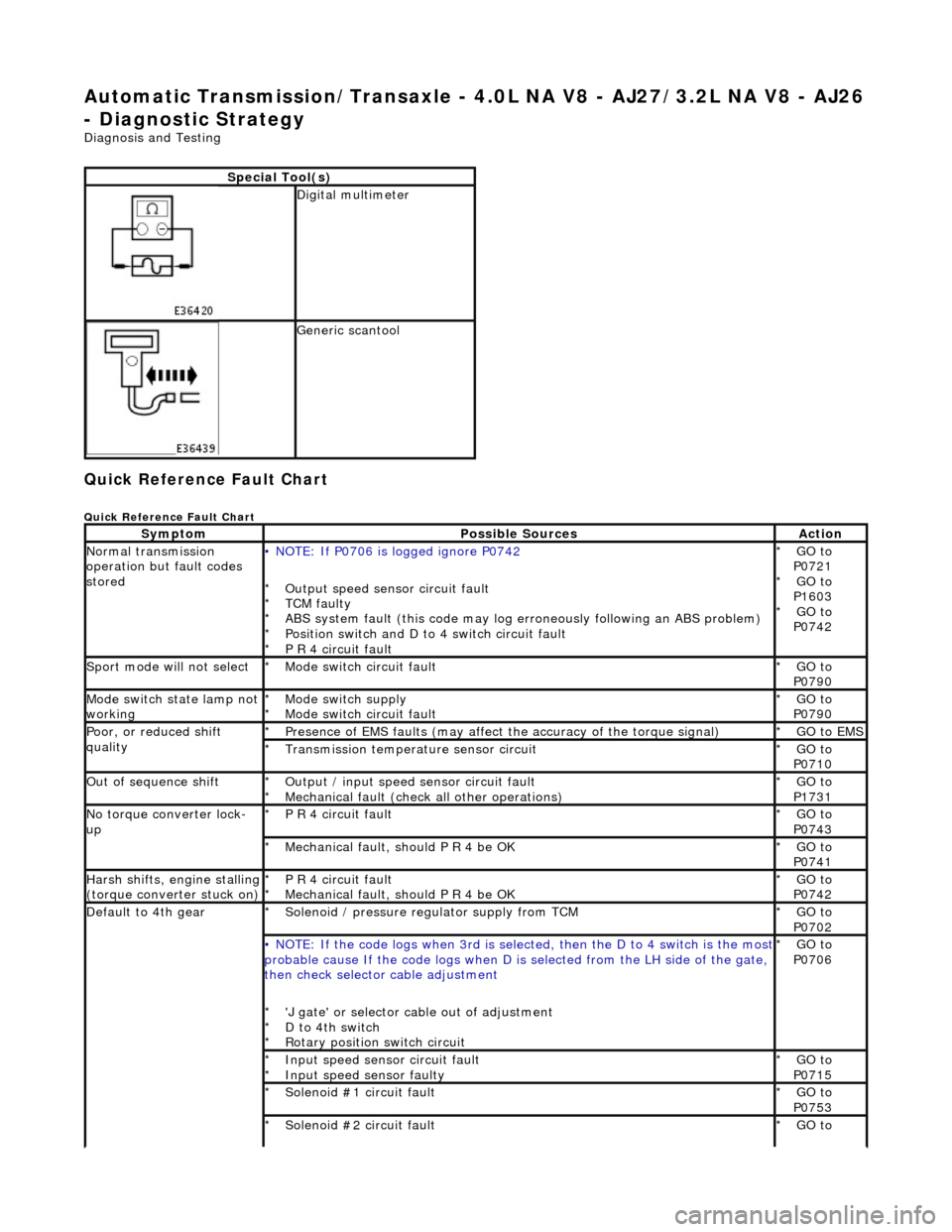
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - 4.0L NA V8 - AJ27/3.2L NA V8 - AJ26
- Diagnostic Strategy
Diagnosis and Testing
Quick Reference Fault Chart
Quick Reference Fault Chart
Special Tool(s)
Digital multimeter
Generic scantool
SymptomPossible SourcesAction
Normal transmission
operation but fault codes
stored• NOTE: If P0706 is logged ignore P0742
Output speed sensor circuit fault
TCM faulty
ABS system fault (this code may log er roneously following an ABS problem)
Position switch and D to 4 switch circuit fault
P R 4 circuit fault
*
*
*
*
*
GO to
P0721 GO to
P1603 GO to
P0742
*
*
*
Sport mode will not selectMode switch circuit fault
*GO to
P0790
*
Mode switch state lamp not
workingMode switch supply
Mode switch circuit fault
*
*GO to
P0790
*
Poor, or reduced shift
qualityPresence of EMS faults
(may affect the accuracy of the torque signal)
*GO to EMS *
Transmission temperature sensor circuit
*GO to
P0710
*
Out of sequence shiftOutput / input speed sensor circuit fault
Mechanical fault (check all other operations)
*
*GO to
P1731
*
No torque converter lock-
upP R 4 circuit fault
*GO to
P0743
*
Mechanical fault, should P R 4 be OK
*GO to
P0741
*
Harsh shifts, engine stalling (torque converter stuck on)P R 4 circuit fault
Mechanical fault, should P R 4 be OK
*
*GO to
P0742
*
Default to 4th gearSolenoid / pressure regulator supply from TCM
*GO to
P0702
*
• NOTE: If the code logs wh
en 3rd is selected, then the D to 4 switch is the most probable cause If the code logs when D is selected fro m the LH side of the gate,
then check selector cable adjustment
'J gate' or selector ca ble out of adjustment
D to 4th switch
Rotary position switch circuit
*
*
*GO to
P0706
*
Input speed sensor circuit fault
Input speed sensor faulty
*
*GO to
P0715
*
Solenoid #1 circuit fault
*GO to
P0753
*
Solenoid #2 circuit fault
*GO to
*
Page 1276 of 2490
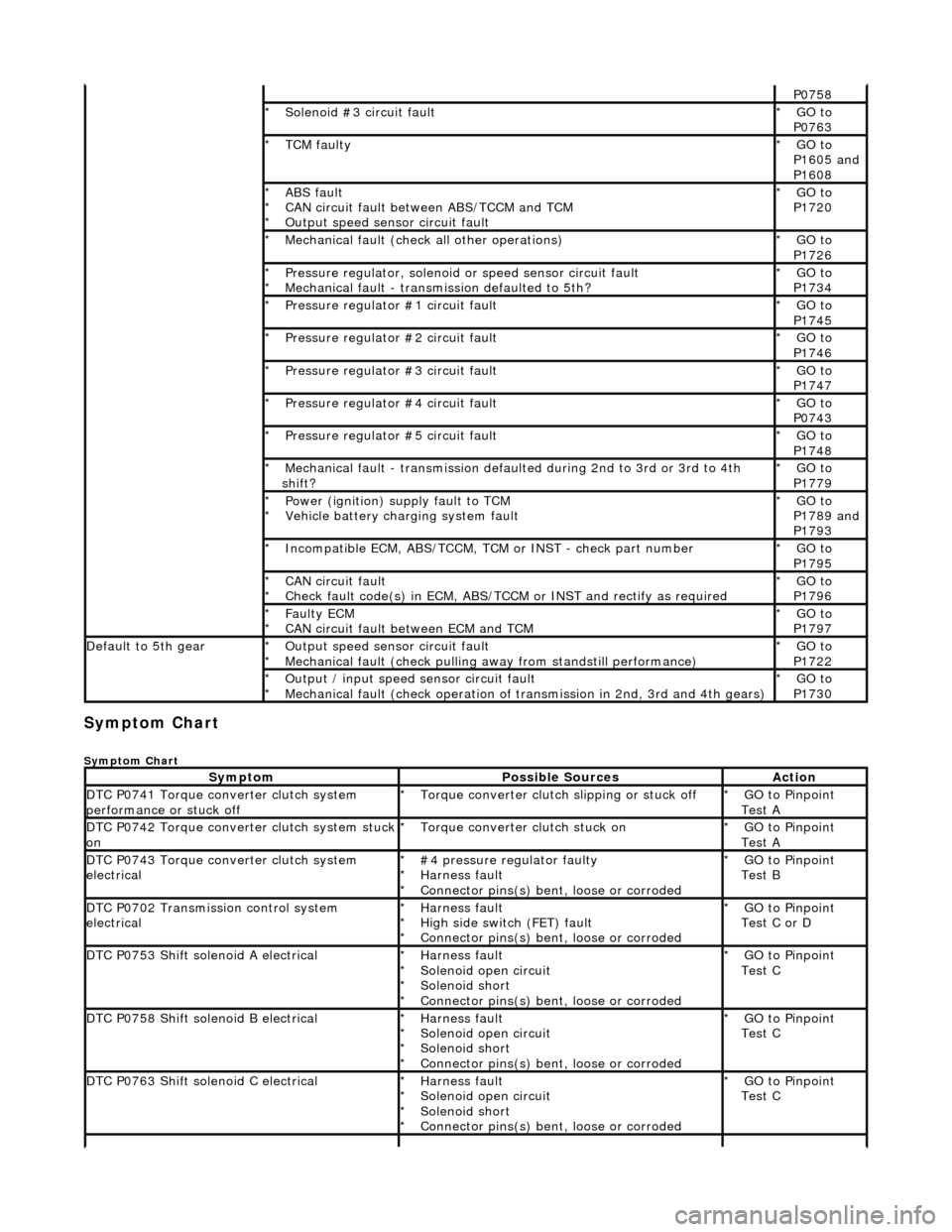
Symptom Chart
Symptom Chart
P0758
Solenoid #3 circuit fault
*GO to
P0763
*
TCM faulty
*GO to
P1605 and
P1608
*
ABS fault
CAN circuit fault between ABS/TCCM and TCM
Output speed sensor circuit fault
*
*
*GO to
P1720
*
Mechanical fault (check all other operations)
*GO to
P1726
*
Pressure regulator, solenoid
or speed sensor circuit fault
Mechanical fault - transmission defaulted to 5th?
*
*GO to
P1734
*
Pressure regulator #1 circuit fault
*GO to
P1745
*
Pressure regulator #2 circuit fault
*GO to
P1746
*
Pressure regulator #3 circuit fault
*GO to
P1747
*
Pressure regulator #4 circuit fault
*GO to
P0743
*
Pressure regulator #5 circuit fault
*GO to
P1748
*
Mechanical fault - transmission defaul
ted during 2nd to 3rd or 3rd to 4th
shift?
*GO to
P1779
*
Power (ignition) supply fault to TCM
Vehicle battery charging system fault
*
*GO to
P1789 and
P1793
*
Incompatible ECM, ABS/TCCM, TCM or INST - check part number
*GO to
P1795
*
CAN circuit fault
Check fault code(s) in ECM, ABS/TCCM or INST and rectify as required
*
*GO to
P1796
*
Faulty ECM
CAN circuit fault between ECM and TCM
*
*GO to
P1797
*
Default to 5th gearOutput speed sensor circuit fault
Mechanical fault (check pulling
away from standstill performance)
*
*GO to
P1722
*
Output / input speed sensor circuit fault
Mechanical fault (check operation of tr
ansmission in 2nd, 3rd and 4th gears)
*
*GO to
P1730
*
SymptomPossible SourcesAction
DTC P0741 Torque converter clutch system
performance or stuck offTorque converter clutch slipping or stuck off
*GO to Pinpoint
Test A
*
DTC P0742 Torque converter clutch system stuck onTorque converter clutch stuck on
*GO to Pinpoint
Test A
*
DTC P0743 Torque converter clutch system
electrical#4 pressure regulator faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test B
*
DTC P0702 Transmission control system
electricalHarness fault
High side switch (FET) fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test C or D
*
DTC P0753 Shift solenoid A electricalHarness fault
Solenoid open circuit
Solenoid short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test C
*
DTC P0758 Shift solenoid B electricalHarness fault
Solenoid open circuit
Solenoid short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test C
*
DTC P0763 Shift solenoid C electricalHarness fault
Solenoid open circuit
Solenoid short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test C
*
Page 1277 of 2490
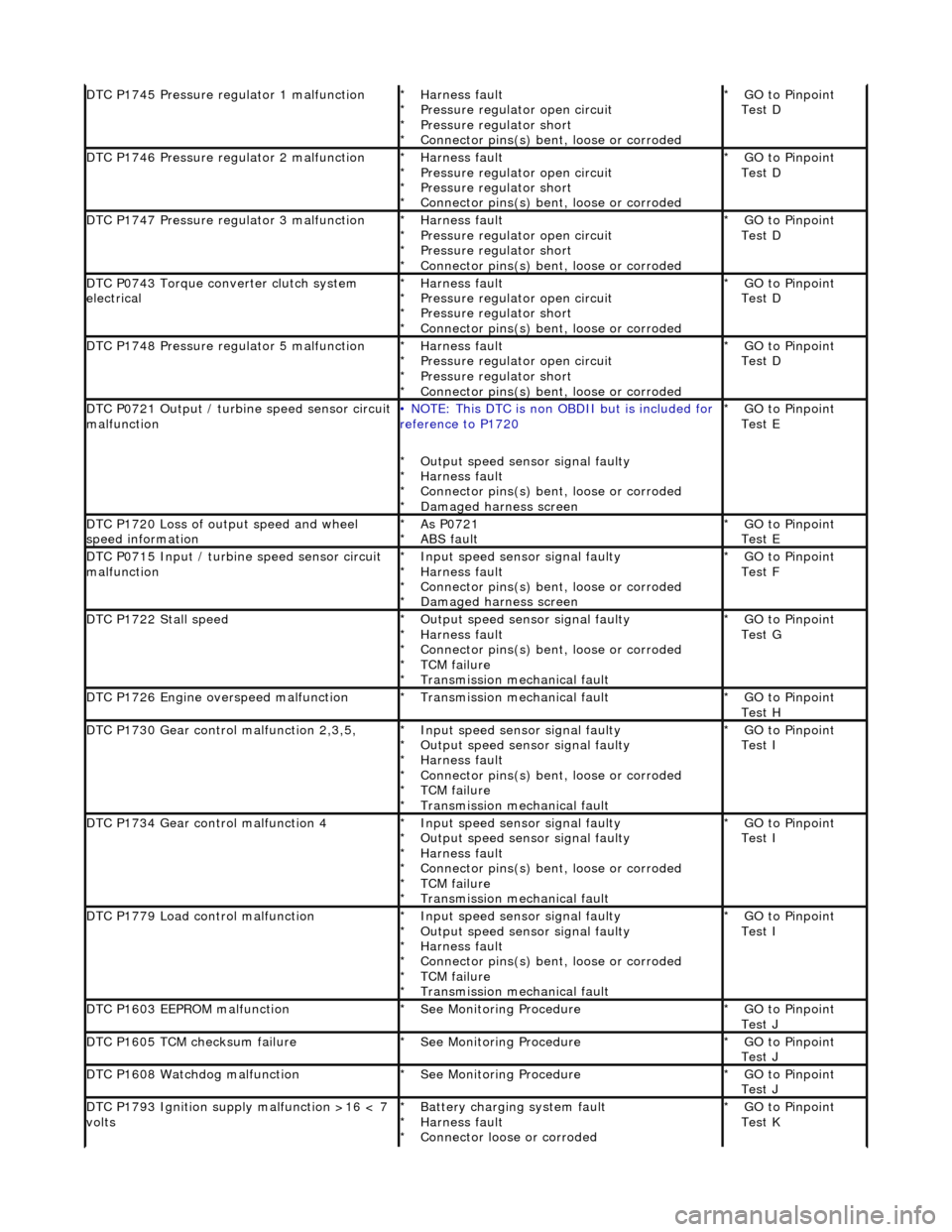
DTC P1745 Pressure regulator 1 malfunctionHarness fault
Pressure regulator open circuit
Pressure regulator short
Connector pins(s) bent, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test D
*
DTC P1746 Pressure regulator 2 malfunctionHarness fault
Pressure regulator open circuit
Pressure regulator short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test D
*
DTC P1747 Pressure regulator 3 malfunctionHarness fault
Pressure regulator open circuit
Pressure regulator short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test D
*
DTC P0743 Torque converter clutch system
electricalHarness fault
Pressure regulator open circuit
Pressure regulator short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test D
*
DTC P1748 Pressure regulator 5 malfunctionHarness fault
Pressure regulator open circuit
Pressure regulator short
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test D
*
DTC P0721 Output / turbine speed sensor circuit
malfunction• NOTE: This DTC is non OBDII but is included for
reference to P1720
Output speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent , loose or corroded
Damaged harness screen
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test E
*
DTC P1720 Loss of output speed and wheel
speed informationAs P0721
ABS fault
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test E
*
DTC P0715 Input / turbine speed sensor circuit
malfunctionInput speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
Damaged harness screen
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test F
*
DTC P1722 Stall speedOutput speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
TCM failure
Transmission mechanical fault
*
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test G
*
DTC P1726 Engine overspeed malfunctionTransmission mechanical fault
*GO to Pinpoint
Test H
*
DTC P1730 Gear control malfunction 2,3,5,Input speed sensor signal faulty
Output speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
TCM failure
Transmission mechanical fault
*
*
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test I
*
DTC P1734 Gear control malfunction 4Input speed sensor signal faulty
Output speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
TCM failure
Transmission mechanical fault
*
*
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test I
*
DTC P1779 Load control malfunctionInput speed sensor signal faulty
Output speed sensor signal faulty
Harness fault
Connector pins(s) bent
, loose or corroded
TCM failure
Transmission mechanical fault
*
*
*
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test I
*
DTC P1603 EEPROM malfunctionSee Monitoring Procedure
*GO to Pinpoint
Test J
*
DTC P1605 TCM checksum failureSee Monitoring Procedure
*GO to Pinpoint
Test J
*
DTC P1608 Watchdog malfunctionSee Monitoring Procedure
*GO to Pinpoint
Test J
*
DTC P1793 Ignition supply malfunction >16 < 7
voltsBattery charging system fault
Harness fault
Connector loose or corroded
*
*
*GO to Pinpoint
Test K
*
Page 1390 of 2490

Stator, intermediate and output shafts. Three epicyclic geartrains. Six multi-disc clutch/brake packs. Two freewheels (One-way clutches). Hydraulic pump. Parking lock assembly. Electro-hydraulic control unit. Internal harness and 13 pin connector with bayonet lock.
Hydraulic pump
This engine driven pump is located at the front of the transmission casing and provides pressure for the hydraulic
functions.
Supplies fluid under pressure to the torq ue converter, geartrain, electro-hydraulic control unit and the lubrication
circuit.
Draws fluid from the fluid pa n below the transmission casing, through a filter.
Parking lock
This component prevents movement of th e vehicle by engaging a fixed pawl with the parking lock gear located on the
output shaft. The pawl is engaged by movi ng the gear selector lever to the park (P) position.
Electro-hydraulic control unit
This unit, mounted in the transmission lower case, converts signals, mechanical from the J-gate and electrical from the
TCM, into hydraulic functions.
The following components ar e assembled to the unit:
Selector valve. Shift plate. Control valve - modulating pressure. Control valve - shift pressure. Solenoid valve 1 <-> 2 and 4 <-> 5 shift. Solenoid valve 3 <-> 4 shift. Solenoid valve 2 <-> 3 shift. Solenoid valve - converter lock-up. Speed sensors (2). Temperature sensor.
Speed sensors
There are two speed sensors within the transmission assembly which provide input to the TCM. These inputs, when used in
conjunction with CAN data relative to engine speed (from ECM) and road speed (from ABS), are used to electronically
control the transmission.
Temperature sensor
The output from this sensor allows the TCM to compensate for the affect of fluid temperature on shift time and quality
Control Systems
Hydraulic Control
The selector valve is operated directly by the J-gate and directs fluid flow for P R N D.
Of the four solenoid valves, 3 control shifts and 1 controls converter lock-up. One control valve controls modulating pressure
and the other shift pressure.
Regulating valves are used to maintain/control pressure for lu brication, normal operating functions, and the supply to the
control valves and shift valves.
Page 1392 of 2490

CAN Input Signals
Traction status ABS malfunction ABS status Engine torque status Throttle position Accelerator pedal position Engine torque reduction confirmation Engine speed Engine coolant temperature Cruise status OBDII fault code clear request Throttle malfunction warning RED or AMBER All road wheel speeds Token for network status ECM Token for network status INST Token for network status ABS Diagnostic data in from external device (PDU)
Output Signals
Solenoid valve 1 <-> 2 and 4 <-> 5 shift Solenoid valve 2 <-> 3 shift Solenoid valve 3 <-> 4 shift Solenoid valve converter lock-up clutch Control valve - modulating pressure Control valve - shift pressure
CAN Output Signals
Engine torque reduction request MIL status (whether present DTC should operate MIL) Transmission input speed Transmission output speed Converter slip Kickdown status Gear position (actual) Gear position (selected) Gear selection fault Converter lock-up status Current selected shift map Transmission oil temperature Transmission malfunction Pecus flag (state of current TCM program) Target for next gear position Gear shift torque transfer progress at shift MIL status (response to activate the MIL relevant to a DTC) OBDII fault code clear acknowledgement Transmission DTCs (P codes) Token for network status TCM Diagnostic data out to external device (PDU)
Emergency Running (elect ronic limp-home mode)
The TCM constantly monitors the transmissi on for faults. In the event of a problem the TCM will adopt the limp-home mode, in which the gear currently held remains engaged, until P is selected. The modulati ng and shift pressures will increase to
maximum and converter lock-up will be inhibited.
Following the selection of P , the only ratios available will be 2 (irrespective of forward ratio manual selection) and R .
With the vehicle at rest, the procedure to manually select is as follows:
1. 1. Select P .