sensor JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 486 of 3039
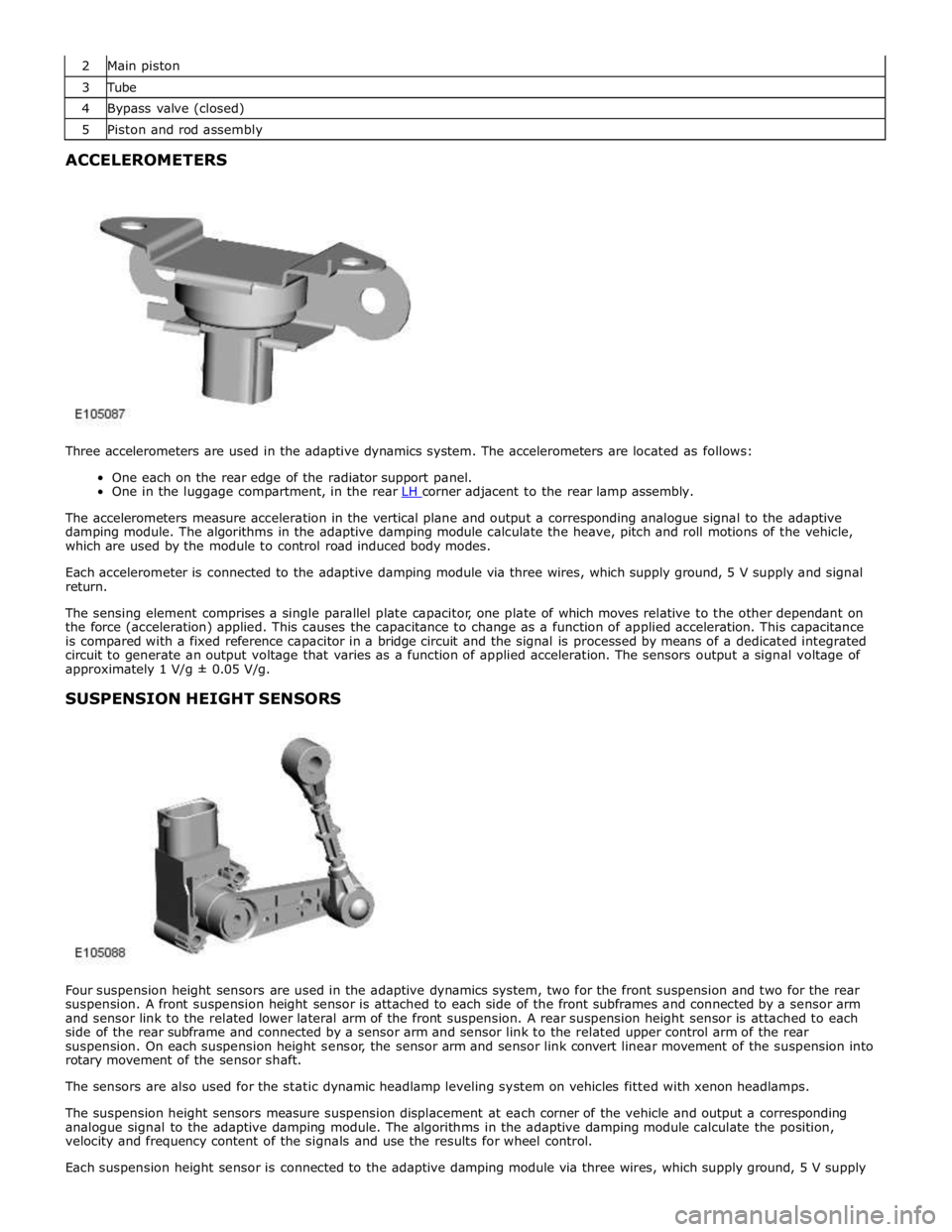

2 Main piston 3 Tube 4 Bypass valve (closed) 5 Piston and rod assembly ACCELEROMETERS
Three accelerometers are used in the adaptive dynamics system. The accelerometers are located as follows:
One each on the rear edge of the radiator support panel.
One in the luggage compartment, in the rear LH corner adjacent to the rear lamp assembly.
The accelerometers measure acceleration in the vertical plane and output a corresponding analogue signal to the adaptive
damping module. The algorithms in the adaptive damping module calculate the heave, pitch and roll motions of the vehicle,
which are used by the module to control road induced body modes.
Each accelerometer is connected to the adaptive damping module via three wires, which supply ground, 5 V supply and signal
return.
The sensing element comprises a single parallel plate capacitor, one plate of which moves relative to the other dependant on
the force (acceleration) applied. This causes the capacitance to change as a function of applied acceleration. This capacitance
is compared with a fixed reference capacitor in a bridge circuit and the signal is processed by means of a dedicated integrated
circuit to generate an output voltage that varies as a function of applied acceleration. The sensors output a signal voltage of
approximately 1 V/g ± 0.05 V/g.
SUSPENSION HEIGHT SENSORS
Four suspension height sensors are used in the adaptive dynamics system, two for the front suspension and two for the rear
suspension. A front suspension height sensor is attached to each side of the front subframes and connected by a sensor arm
and sensor link to the related lower lateral arm of the front suspension. A rear suspension height sensor is attached to each
side of the rear subframe and connected by a sensor arm and sensor link to the related upper control arm of the rear
suspension. On each suspension height sensor, the sensor arm and sensor link convert linear movement of the suspension into
rotary movement of the sensor shaft.
The sensors are also used for the static dynamic headlamp leveling system on vehicles fitted with xenon headlamps.
The suspension height sensors measure suspension displacement at each corner of the vehicle and output a corresponding
analogue signal to the adaptive damping module. The algorithms in the adaptive damping module calculate the position,
velocity and frequency content of the signals and use the results for wheel control.
Each suspension height sensor is connected to the adaptive damping module via three wires, which supply ground, 5 V supply
Page 487 of 3039
System Fault Message
The adaptive damping module has a high speed CAN connection to the instrument cluster. If a fault is detected by the adaptive damping module, a message is sent to the instrument cluster and the message 'ADAPTIVE DYNAMICS FAULT' is
displayed. The adaptive damping module also logs an appropriate DTC. The adaptive damping module can be interrogated using an approved Jaguar diagnostic system.
When a fault is detected, the adaptive damping module implements a strategy based on the type of fault. If there is an
electrical power fault, or the adaptive damping module cannot control the dampers, they default to the firm condition. If a
sensor fails that only affects one or more control modes then an intermediate damper setting is used as the lower threshold
and the remaining working modes can demand higher damping as required.
Page 488 of 3039

Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - Vehicle Dynamic Suspension
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 09-Jul-2014
For a detailed description of the adaptive damping system operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of
the workshop manual. REFER to: (204-05 Vehicle Dynamic Suspension)
Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (Description and Operation),
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Coil spring(s)
Shock absorber(s)
Accelerometer(s) installation
Height sensor(s) installation
Fuse(s)
Wiring harness/electrical connectors
Accelerometer(s)
Adaptive Damping Control Module
Height sensor(s)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check the system for any logged Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the
DTC index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Adaptive Damping Module (SUMB) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Page 532 of 3039

6 Oil temperature sensor 7 High speed CAN from suspension control module 8 CJB (central junction box)
System Operation
ELECTRONIC
DIFFERENTIAL
-
5.0L
SUPERCHARGER
VEHICLES
FROM
2010MY
The
multi-plate
clutch
prevents
excessive
differential
slip and
therefore
maximizes
the
traction
performance
of
the
vehicle.
This
is
fundamentally
different
from
'braked'
traction
control
systems,
which
can
only
counteract
differential
slip when it
occurs.
A
certain
amount
of
differential
slip is
required
to
allow
the
vehicle
to
turn
corners
and
to
remain
stable
under
control
of
the
ABS
(anti-lock
brake
system).
The
system
is
completely
automatic and
does
not
require
any
special
driver
input.
The
multi-plate
clutch
actively
controls
the
torque
flow
through
the
differential
and
optimizes
the
torque
distribution in
the
driveline.
The
clutch
biases
the
torque
from
the
differential
to
the
wheel
with the
higher
grip
and prevents
the
wheel
with the
lower
grip
from
spinning.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 533 of 3039
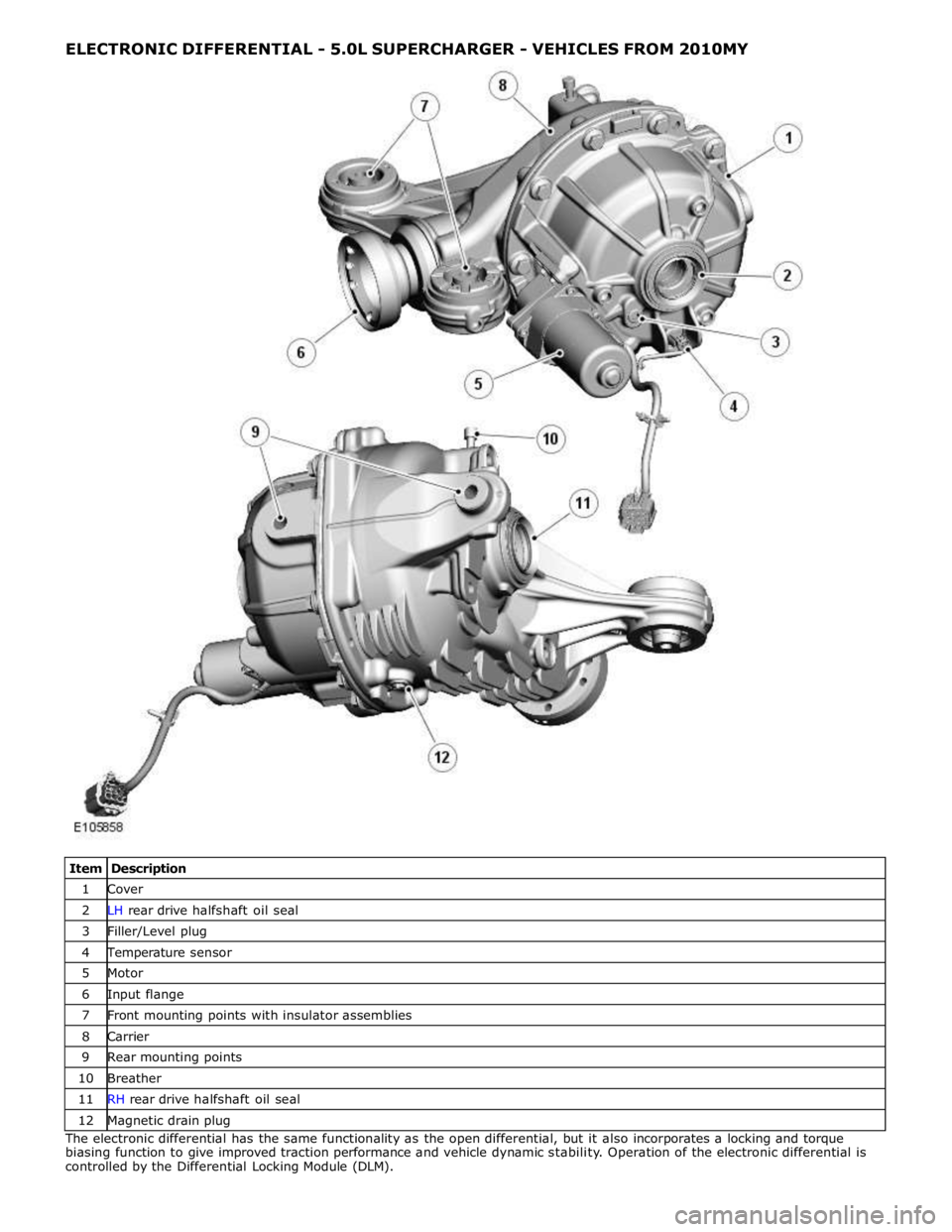
ELECTRONIC DIFFERENTIAL - 5.0L SUPERCHARGER - VEHICLES FROM 2010MY
Item Description 1 Cover 2 LH rear drive halfshaft oil seal 3 Filler/Level plug 4 Temperature sensor 5 Motor 6 Input flange 7 Front mounting points with insulator assemblies 8 Carrier 9 Rear mounting points 10 Breather 11 RH rear drive halfshaft oil seal 12 Magnetic drain plug The electronic differential has the same functionality as the open differential, but it also incorporates a locking and torque
biasing function to give improved traction performance and vehicle dynamic stability. Operation of the electronic differential is
controlled by the Differential Locking Module (DLM).
Page 534 of 3039
A motor and reduction gearbox, attached to the cover.
A temperature sensor installed in the cover.
The DLM (differential locking module) operates the motor of the electronic differential under the control of the ADM (adaptive
damping module).
Exploded View of Electronic Differential
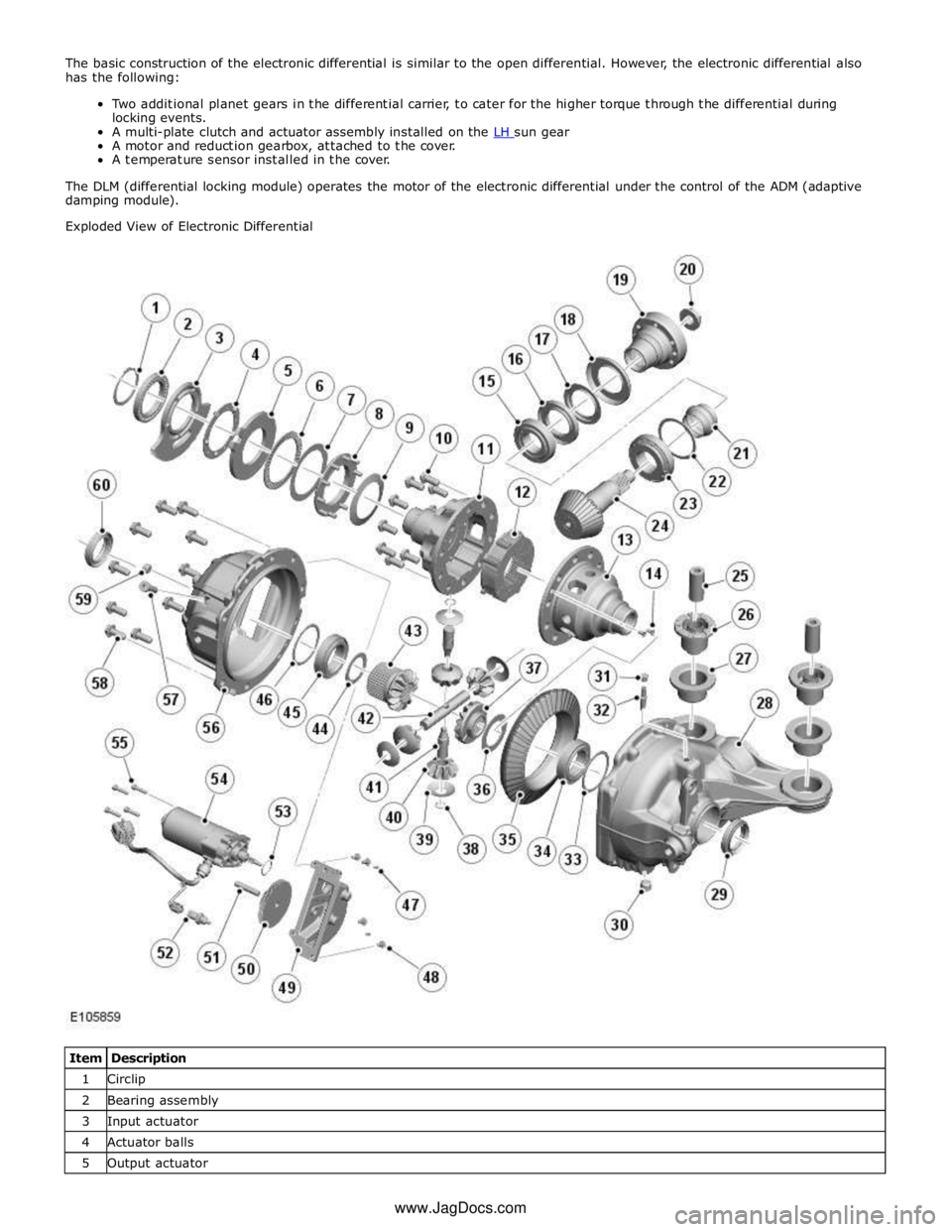
Item Description 1 Circlip 2 Bearing assembly 3 Input actuator 4 Actuator balls 5 Output actuator www.JagDocs.com
Page 535 of 3039

Thrust race 7 Shim 8 Thrust plate 9 Dished washer 10 Bolt (10 off) 11 Clutch basket 12 Multi-plate clutch and pressure disc 13 Differential case 14 Screw (2 off) 15 Bearing assembly 16 Oil seal 17 Oil slinger inner 18 Oil slinger outer 19 Input flange 20 Pinion nut 21 Collapsible spacer 22 Shim 23 Bearing assembly 24 Pinion shaft 25 Mounting insulator inner (2 off) 26 Mounting insulator rubber (2 off) 27 Mounting insulator outer (2 off) 28 Carrier 29 Oil seal 30 Drain plug 31 Vent 32 Breather cap 33 Shim 34 Bearing assembly 35 Drive gear 36 Shim 37 RH sun gear 38 Circlip 39 Thrust washer (4 off) 40 Planet gear (4 off) 41 Pin (2 off) 42 Shaft 43 LH sun gear 44 Shim 45 Bearing assembly 46 Shim 47 Dowel (2 off) 48 Bolt (4 off) 49 Reduction gear casing 50 Reduction gear 51 Shaft 52 Temperature sensor 53 O-ring seal 54 Motor 55 Screw (4 off) 56 Cover 57 Output actuator locking pin 58 Bolt (9 off)
Page 536 of 3039
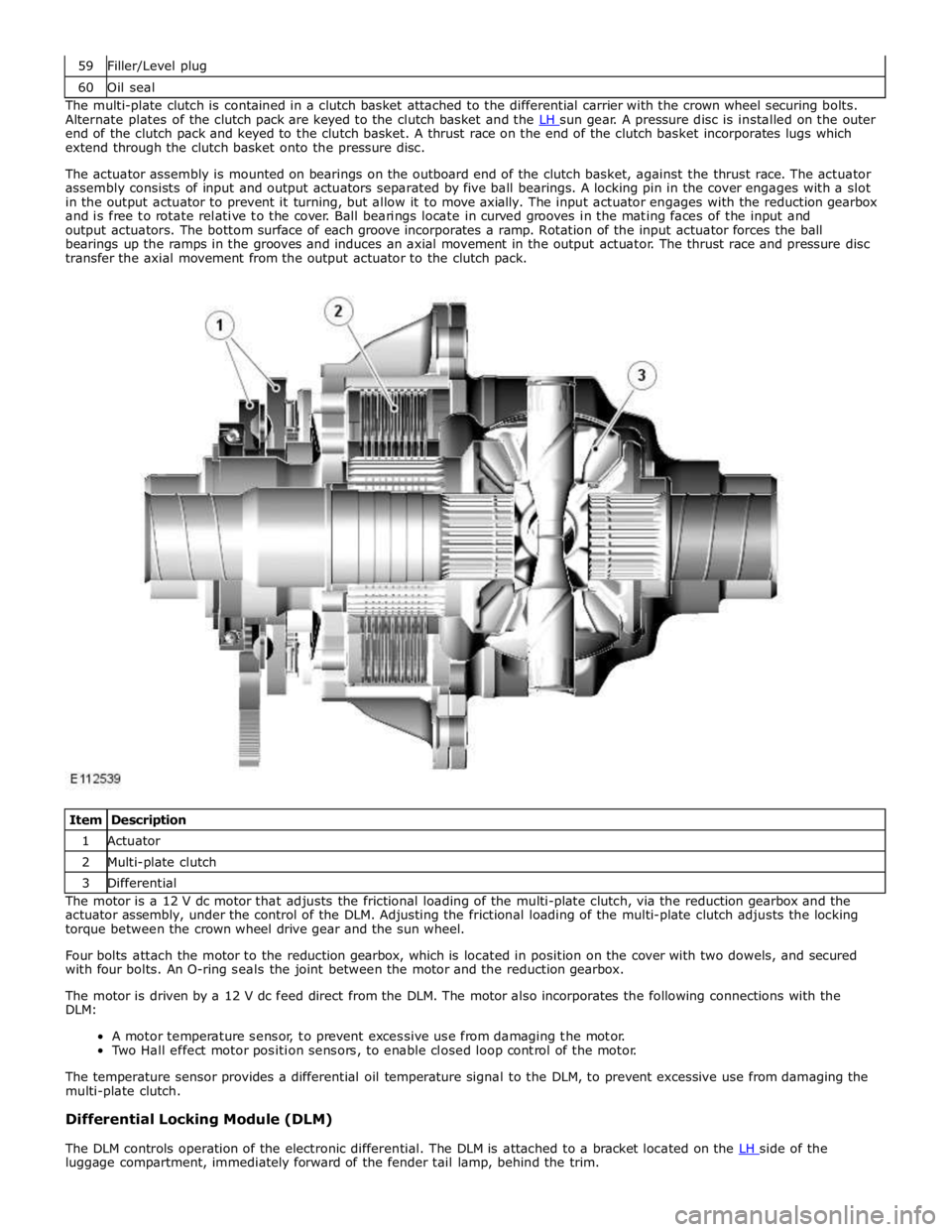
60 Oil seal The multi-plate clutch is contained in a clutch basket attached to the differential carrier with the crown wheel securing bolts.
Alternate plates of the clutch pack are keyed to the clutch basket and the LH sun gear. A pressure disc is installed on the outer end of the clutch pack and keyed to the clutch basket. A thrust race on the end of the clutch basket incorporates lugs which
extend through the clutch basket onto the pressure disc.
The actuator assembly is mounted on bearings on the outboard end of the clutch basket, against the thrust race. The actuator
assembly consists of input and output actuators separated by five ball bearings. A locking pin in the cover engages with a slot
in the output actuator to prevent it turning, but allow it to move axially. The input actuator engages with the reduction gearbox
and is free to rotate relative to the cover. Ball bearings locate in curved grooves in the mating faces of the input and
output actuators. The bottom surface of each groove incorporates a ramp. Rotation of the input actuator forces the ball
bearings up the ramps in the grooves and induces an axial movement in the output actuator. The thrust race and pressure disc
transfer the axial movement from the output actuator to the clutch pack.
Item Description 1 Actuator 2 Multi-plate clutch 3 Differential The motor is a 12 V dc motor that adjusts the frictional loading of the multi-plate clutch, via the reduction gearbox and the
actuator assembly, under the control of the DLM. Adjusting the frictional loading of the multi-plate clutch adjusts the locking
torque between the crown wheel drive gear and the sun wheel.
Four bolts attach the motor to the reduction gearbox, which is located in position on the cover with two dowels, and secured
with four bolts. An O-ring seals the joint between the motor and the reduction gearbox.
The motor is driven by a 12 V dc feed direct from the DLM. The motor also incorporates the following connections with the
DLM:
A motor temperature sensor, to prevent excessive use from damaging the motor.
Two Hall effect motor position sensors, to enable closed loop control of the motor.
The temperature sensor provides a differential oil temperature signal to the DLM, to prevent excessive use from damaging the
multi-plate clutch.
Differential Locking Module (DLM)
The DLM controls operation of the electronic differential. The DLM is attached to a bracket located on the LH side of the luggage compartment, immediately forward of the fender tail lamp, behind the trim.
Page 583 of 3039
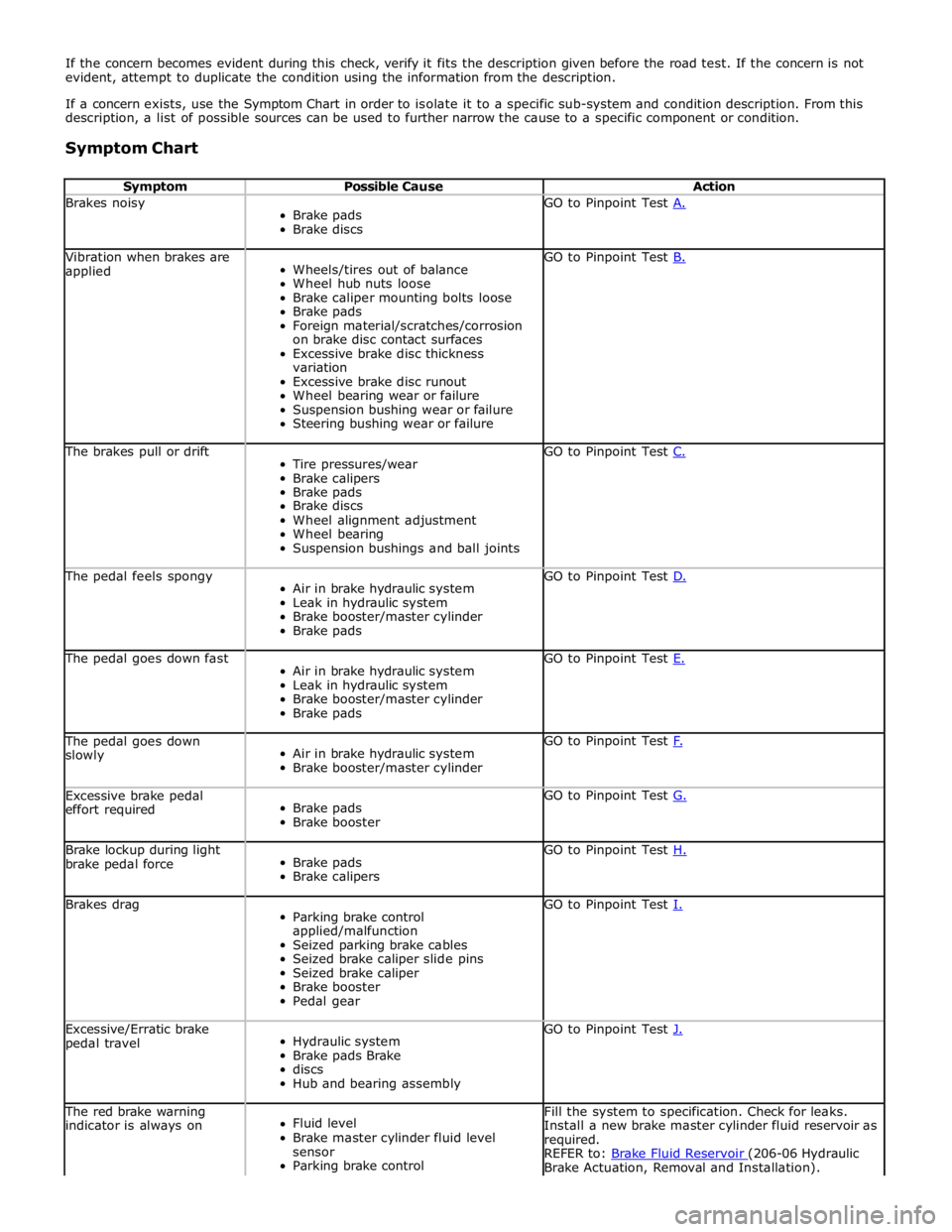
If the concern becomes evident during this check, verify it fits the description given before the road test. If the concern is not
evident, attempt to duplicate the condition using the information from the description.
If a concern exists, use the Symptom Chart in order to isolate it to a specific sub-system and condition description. From this
description, a list of possible sources can be used to further narrow the cause to a specific component or condition.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action Brakes noisy
Brake pads
Brake discs GO to Pinpoint Test A. Vibration when brakes are
applied
Wheels/tires out of balance
Wheel hub nuts loose
Brake caliper mounting bolts loose
Brake pads
Foreign material/scratches/corrosion
on brake disc contact surfaces
Excessive brake disc thickness
variation
Excessive brake disc runout
Wheel bearing wear or failure
Suspension bushing wear or failure
Steering bushing wear or failure GO to Pinpoint Test B. The brakes pull or drift
Tire pressures/wear
Brake calipers
Brake pads
Brake discs
Wheel alignment adjustment
Wheel bearing
Suspension bushings and ball joints GO to Pinpoint Test C. The pedal feels spongy
Air in brake hydraulic system
Leak in hydraulic system
Brake booster/master cylinder
Brake pads GO to Pinpoint Test D. The pedal goes down fast
Air in brake hydraulic system
Leak in hydraulic system
Brake booster/master cylinder
Brake pads GO to Pinpoint Test E. The pedal goes down
slowly
Air in brake hydraulic system
Brake booster/master cylinder GO to Pinpoint Test F. Excessive brake pedal
effort required
Brake pads
Brake booster GO to Pinpoint Test G. Brake lockup during light
brake pedal force
Brake pads
Brake calipers GO to Pinpoint Test H. Brakes drag
Parking brake control
applied/malfunction
Seized parking brake cables
Seized brake caliper slide pins
Seized brake caliper
Brake booster
Pedal gear GO to Pinpoint Test I. Excessive/Erratic brake
pedal travel
Hydraulic system
Brake pads Brake
discs
Hub and bearing assembly GO to Pinpoint Test J. The red brake warning
indicator is always on
Fluid level
Brake master cylinder fluid level
sensor
Parking brake control Fill the system to specification. Check for leaks.
Install a new brake master cylinder fluid reservoir as
required.
REFER to: Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
Page 590 of 3039

Does the brake pedal return to its original position? Yes
No action required, vehicle is OK.
No
GO to K2. K2: CHECK FOR BRAKE PEDAL BINDING 1 Disconnect the brake booster from the brake pedal. Check the brake pedal to ensure free operation. Is the brake pedal operating freely? Yes
Install a new brake booster as required. REFER to:
Brake Booster (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation), Brake Booster - RHD (206-07, Removal and Installation).
Re-test the system for normal operation.
No
Repair or install new brake pedal. Re-test the system for normal operation. Component Tests
Brake Booster
1. Check all hoses and connections. All unused vacuum connectors should be capped. Hoses and their connections should
be correctly secured and in good condition with no holes and no collapsed areas. Inspect the valve on the brake booster
for damage.
2. Check the hydraulic brake system for leaks or low fluid.
3. With the automatic transmission in PARK, stop the engine and apply the parking brake. Pump the brake pedal several
times to exhaust all vacuum in the system. With the engine switched off and all vacuum in the system exhausted,
apply the brake pedal and hold it down. Start the engine. If the vacuum system is operating, the brake pedal will tend
to move downward under constant foot pressure. If no motion is felt, the vacuum booster system is not functioning.
4. Remove the vacuum hose from the brake booster. Manifold vacuum should be available at the brake booster end of the
hose with the engine at idle speed and the automatic transmission in PARK. Make sure that all unused vacuum outlets
are correctly capped, hose connectors are correctly secured and vacuum hoses are in good condition. When it is
established that manifold vacuum is available to the brake booster, connect the vacuum hose to the brake booster and
repeat Step 3. If no downward movement of the brake pedal is felt, install a new brake booster.
5. Operate the engine for a minimum of 10 seconds at a fast idle. Stop the engine and allow the vehicle to stand for 10
minutes. Then, apply the brake pedal with approximately 89 N (20lb) of force. The pedal feel (brake application) should
be the same as that noted with the engine running. If the brake pedal feels hard (no power assist), install a new valve
and then repeat the test. If the brake pedal still feels hard, install a new brake booster. If the brake pedal movement
feels spongy, bleed the brake system.
REFER to: Brake System Bleeding (206-00 Brake System - General Information, General Procedures). Brake Master Cylinder
Usually, the first and strongest indicator of anything wrong in the brake system is a feeling through the brake pedal. In
diagnosing the condition of the brake master cylinder, check pedal feel as evidence of a brake concern. Check for brake warning
lamp illumination and the brake fluid level in the brake master cylinder reservoir.
Normal Conditions
The following conditions are considered normal and are not indications that the brake master cylinder is in need of repair.
Modern brake systems are designed to produce a pedal effort that is not as hard as in the past. Complaints of light
pedal efforts should be compared to the pedal efforts of another vehicle of the same model and year.
The fluid level will fall with brake pad wear.
Abnormal Conditions
Changes in the brake pedal feel or brake pedal travel are indicators that something could be wrong in the brake system. The
diagnostic procedure and techniques use brake pedal feel, warning indicator illumination and low brake fluid level as indicators
to diagnosing brake system concerns. The following conditions are considered abnormal and indicate that the brake master
cylinder is in need of repair:
NOTE: Prior to carrying out any diagnosis, make sure the brake system warning indicator is functional.
Brake pedal goes down fast. This could be caused by an external or internal leak.
Brake pedal goes down slowly. This could be caused by an internal or external leak.
Brake pedal is low or feels spongy. This condition may be caused by no fluid in the brake master cylinder, reservoir cap
vent holes clogged or air in the hydraulic system.
Brake pedal effort is excessive. This may be caused by a bind or obstruction in the pedal/linkage, a faulty non-return
valve, booster or insufficient booster vacuum.
Rear brakes lock up during light pedal force. This may be caused by damaged brake pads, a partially applied parking
brake, a damaged ABS sensor or bearing failure.
Brake pedal effort erratic. This condition could be caused by the brake booster or incorrectly installed brake pads.
Brake warning indicator is on. This may be caused by low fluid level or float assembly damaged. www.JagDocs.com