Exhaust JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1359 of 3039

6 LH exhaust CMP sensor 7 LH MAFT sensor 8 LH front knock sensor 9 LH rear knock sensor 10 RH (right hand) rear knock sensor 11 RH front knock sensor 12 RH intake CMP sensor 13 RH exhaust CMP sensor 14 RH MAFT sensor CONTROL DIAGRAM SHEET 2 OF 2
Item Description 1 MAP sensor 2 ECT sensor (ECT 2)
Page 1365 of 3039
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The MAPT sensor allows the ECM to calculate the air charge density immediately before it enters the cylinders. This is used to adjust the ignition timing relative to the boost pressure, and to monitor the performance of the charge air coolers.
The MAPT sensor is installed in the rear of the LH intake manifold. The sensor is secured with a single screw and sealed with an O-ring. A four pin electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSORS
The TP (throttle position) sensors allow the ECM to determine the position and angular rate of change of the throttle blade. There are two TP sensors located in the electronic throttle. See below for details of the electronic throttle. If aTP sensor fails, the ECM:
Adopts a limp home mode where engine speed is limited to a maximum of approximately 2000 rev/min
Discontinues evaporative emissions control
Discontinues closed loop control of engine idle speed.
With a failed TP sensor, the engine will suffer from poor running and throttle response.
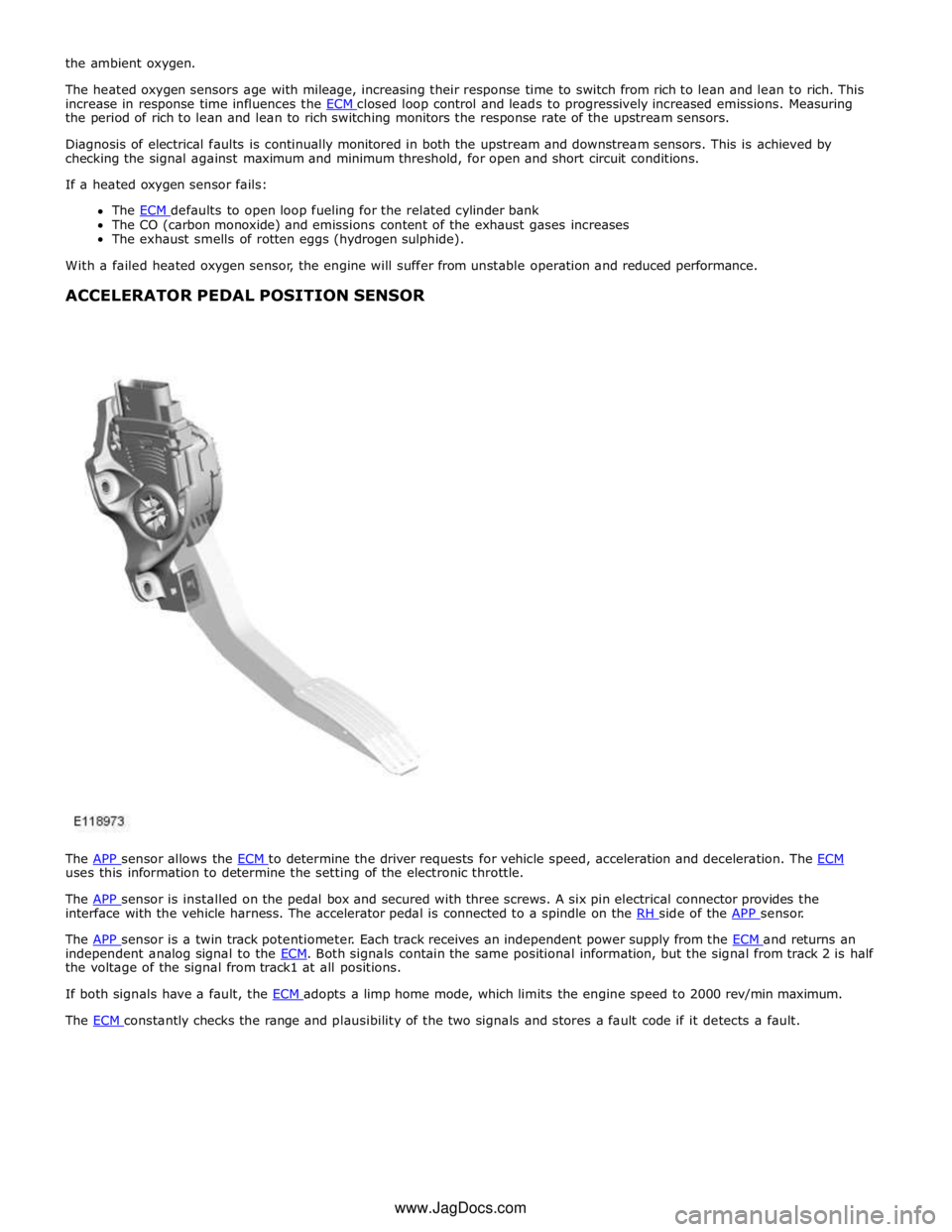
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS
Item Description A Upstream heated oxygen sensor B Downstream heated oxygen sensor The heated oxygen sensors allow the ECM to measure the oxygen content of the exhaust gases, for closed loop control of the fuel:air mixture and for catalytic converter monitoring.
An upstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in the outlet of each exhaust manifold, which enables independent control of
the fuel:air mixture for each cylinder bank. A downstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in each catalytic converter, which
enables the performance of the catalytic converters to be monitored.
Oxygen sensors need to operate at high temperatures in order to function correctly. To achieve the high temperatures required,
the sensors are fitted with heater elements that are controlled by a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM. The heater elements are operated immediately after each engine start and during low load conditions when the temperature of the
exhaust gases is insufficient to maintain the required sensor temperature. The PWM duty cycle is carefully controlled to prevent thermal shock to cold sensors. A non-functioning heater delays the sensor’s readiness for closed loop control and
increases emissions.
The upstream heated oxygen sensors produce a constant voltage, with a variable current that is proportional to the lambda
ratio. The downstream heated oxygen sensors produce an output voltage dependant on the ratio of the exhaust gas oxygen to
Page 1366 of 3039
the period of rich to lean and lean to rich switching monitors the response rate of the upstream sensors.
Diagnosis of electrical faults is continually monitored in both the upstream and downstream sensors. This is achieved by
checking the signal against maximum and minimum threshold, for open and short circuit conditions.
If a heated oxygen sensor fails:
The ECM defaults to open loop fueling for the related cylinder bank The CO (carbon monoxide) and emissions content of the exhaust gases increases
The exhaust smells of rotten eggs (hydrogen sulphide).
With a failed heated oxygen sensor, the engine will suffer from unstable operation and reduced performance.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
The APP sensor allows the ECM to determine the driver requests for vehicle speed, acceleration and deceleration. The ECM uses this information to determine the setting of the electronic throttle.
The APP sensor is installed on the pedal box and secured with three screws. A six pin electrical connector provides the interface with the vehicle harness. The accelerator pedal is connected to a spindle on the RH side of the APP sensor.
The APP sensor is a twin track potentiometer. Each track receives an independent power supply from the ECM and returns an independent analog signal to the ECM. Both signals contain the same positional information, but the signal from track 2 is half the voltage of the signal from track1 at all positions.
If both signals have a fault, the ECM adopts a limp home mode, which limits the engine speed to 2000 rev/min maximum. The ECM constantly checks the range and plausibility of the two signals and stores a fault code if it detects a fault. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1369 of 3039
Published: 16-Sep-2013
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Electronic Engine Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of electronic engine controls, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of the workshop
manual. REFER to: (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Engine oil level and condition
Cooling system coolant level
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Front End Accessory Drive (FEAD) belt
Air cleaner condition
Fuses
Wiring harness
Electrical connector(s)
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module
Transmission Control Module
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the customer concern and refer to the Symptom Chart below, alternatively,
check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine non-start Engine does not crank
Security system /Immobilizer
engaged
Engine in shut-down mode
ECM relay
Battery
Starting system
Engine seized
Check that the security system is disarmed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests
Ensure the battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition
For starting system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For engine system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual Engine cranks, but does not fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine controls
Ensure the engine breather system is free
from restriction and is correctly installed
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests Engine cranks and fires, but will not
start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
Ignition coil failure(s)
For purge valve tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Difficult to start Difficult cold start
Check engine coolant
level/anti-freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust gas recirculation
Check the engine coolant level and
condition. Refer to the relevant sections of
the workshop manual
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition. Refer to the battery
Page 1370 of 3039
Symptom Possible Cause Action (EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel pump
Evaporative emissions purge
valve care manual and the relevant sections of the
workshop manual.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections. Difficult hot start
Injector leak
Electronic engine controls
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out injector leak
tests, install new injectors as necessary.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections. Difficult to start after hot soak
(vehicle standing, engine off, after
engine has reached operating
temperature)
Injector leak
Electronic engine controls
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out injector leak
tests, install new injectors as necessary.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections. Engine cranks too fast/slow
Compressions high/low
Battery
Starting system
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out compression
tests.
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition. Refer to the battery
care manual and the relevant sections of the
workshop manual.
For starting system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Engine stalls Engine stalls soon after start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
ECM relay
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Air intake system restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines
Ensure the engine breather system is free
from restriction and is correctly installed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Check for blockage in air cleaner element
and air intake system
Check for leakage in air intake system
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Page 1371 of 3039
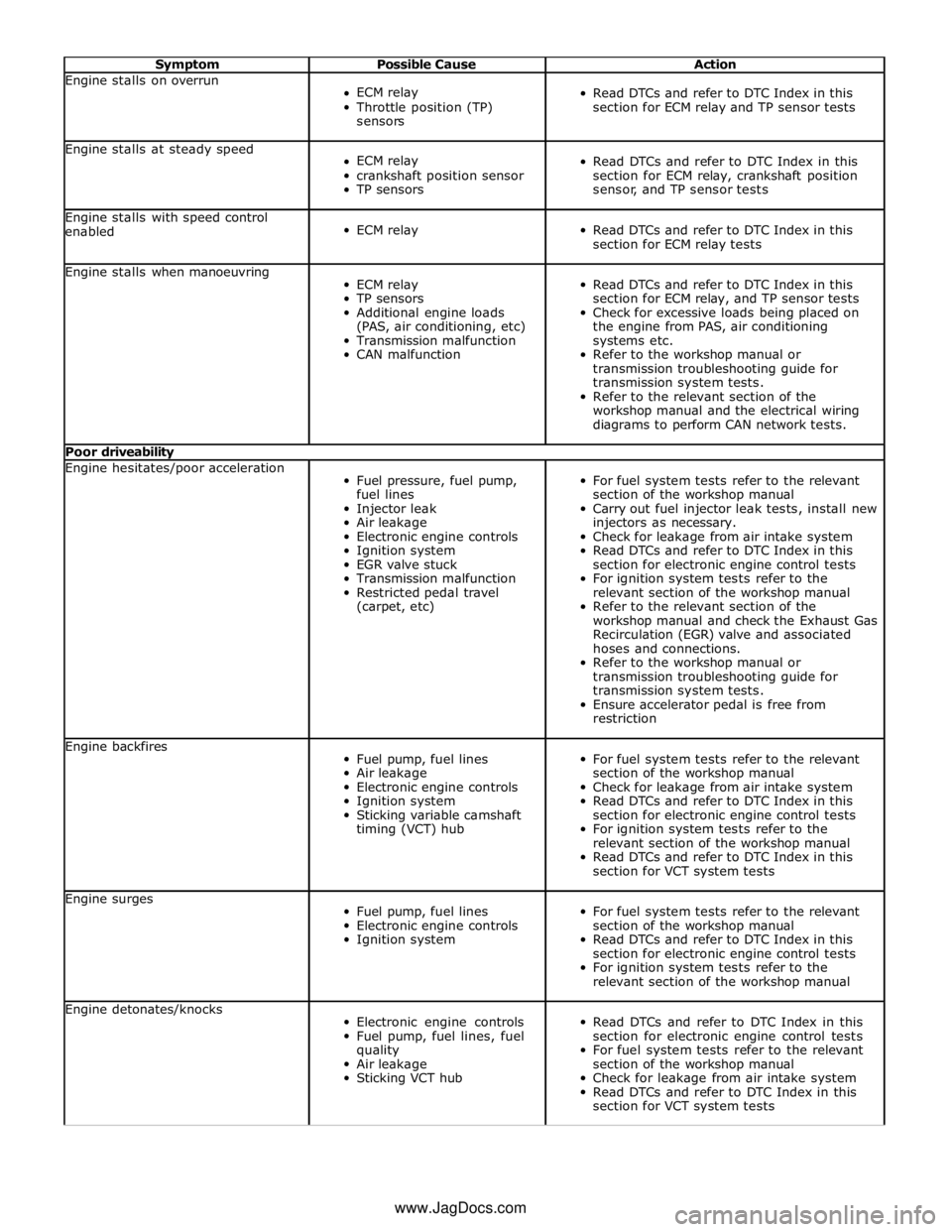
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine stalls on overrun
ECM relay
Throttle position (TP)
sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay and TP sensor tests Engine stalls at steady speed
ECM relay
crankshaft position sensor
TP sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, crankshaft position
sensor, and TP sensor tests Engine stalls with speed control
enabled
ECM relay
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests Engine stalls when manoeuvring
ECM relay
TP sensors
Additional engine loads
(PAS, air conditioning, etc)
Transmission malfunction
CAN malfunction
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, and TP sensor tests
Check for excessive loads being placed on
the engine from PAS, air conditioning
systems etc.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and the electrical wiring
diagrams to perform CAN network tests. Poor driveability Engine hesitates/poor acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck
Transmission malfunction
Restricted pedal travel
(carpet, etc)
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Carry out fuel injector leak tests, install new
injectors as necessary.
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from
restriction Engine backfires
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests Engine surges
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Engine detonates/knocks
Electronic engine controls
Fuel pump, fuel lines, fuel
quality
Air leakage
Sticking VCT hub
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests www.JagDocs.com
Page 1379 of 3039

Installation 5. CAUTION: Make sure that the mating faces are clean
and free of foreign material.
Torque: 48 Nm
1. CAUTIONS:
If accidentally dropped or knocked install a new sensor.
Make sure the catalyst monitor sensor wiring harness is not twisted
more than 180 degrees and is not in contact with either the exhaust or
driveshaft.
Make sure the anti-seize compound does not contact the catalyst
monitor sensor tip.
NOTE: If the original sensor is to be installed, apply lubricant
meeting specification ESE-M12A4-A to the thread of the sensor.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. NOTE: For NAS vehicles only.
If required, carry out a long drive cycle.
Refer to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Long Drive Cycle Self-Test (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General
Procedures).
Page 1381 of 3039

Installation
1. CAUTIONS:
Make sure the anti-seize compound does not contact the catalyst
monitor sensor tip.
If accidentally dropped or knocked install a new sensor.
Make sure the catalyst monitor sensor wiring harness is not twisted
more than 180 degrees and is not in contact with either the exhaust or
driveshaft.
NOTE: If the original sensor is to be installed, apply lubricant
meeting specification ESE-M12A4-A to the thread of the sensor.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. NOTE: For NAS vehicles only.
If required, carry out a long drive cycle.
Refer to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Long Drive Cycle Self-Test (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General
Procedures). www.JagDocs.com
Page 1387 of 3039

Published: 19-Aug-2013
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTES:
Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but the essential information is always correct.
Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Refer to: Cooling System Partial Draining, Filling and Bleeding (303-03B Engine Cooling - V6 3.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
3. Refer to: Catalytic Converter RH (309-00C Exhaust System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
4. Torque: 48 Nm
Page 1394 of 3039
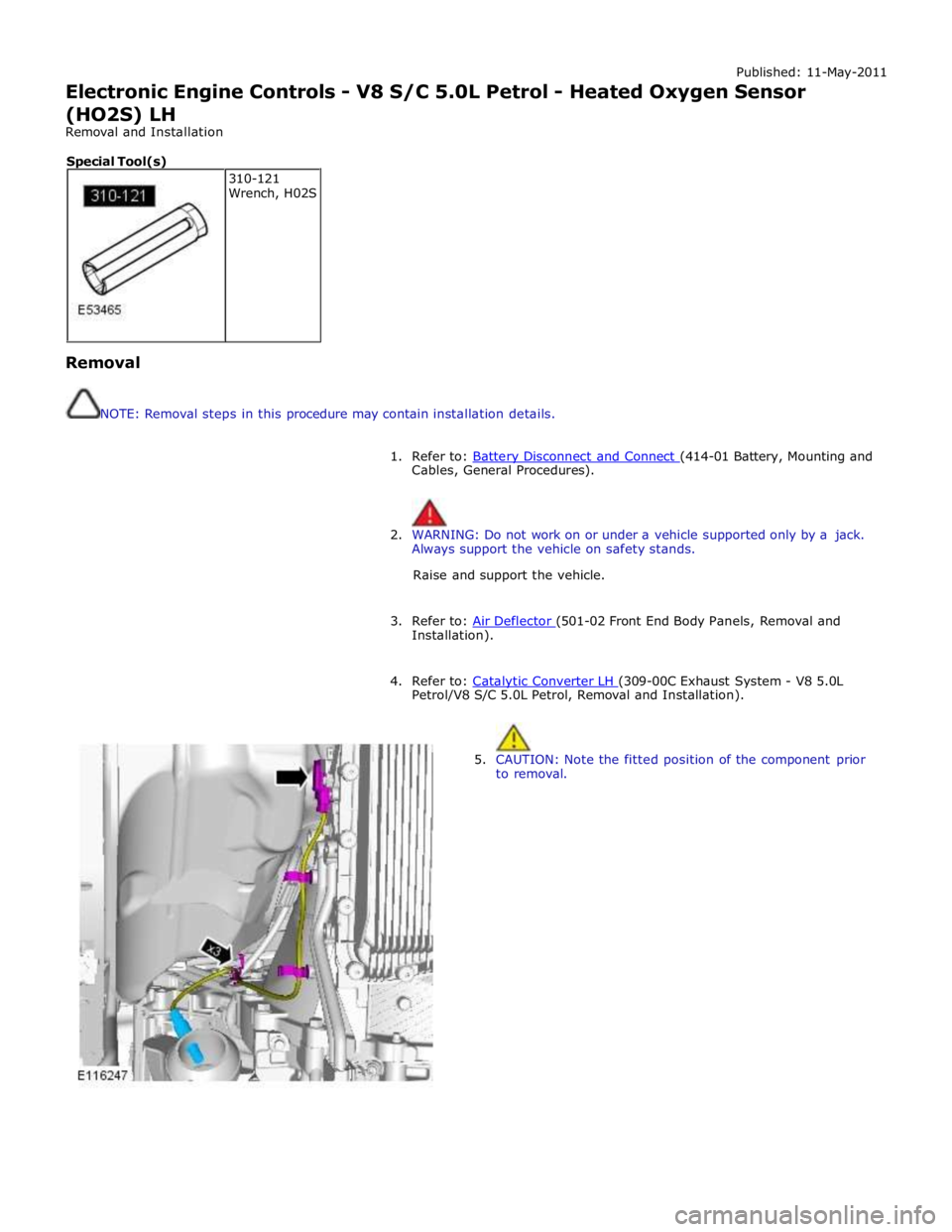
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S) LH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
2. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Air Deflector (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
4. Refer to: Catalytic Converter LH (309-00C Exhaust System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
5. CAUTION: Note the fitted position of the component prior
to removal. 310-121
Wrench, H02S Special Tool(s)