instrument cluster JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1423 of 3039

The TCM can be reprogrammed using a Jaguar approved diagnostic system using a flash code. The TCM processor has a 440 kb internal flash memory. Of this capacity, approximately 370 kb are used by the basic transmission program. The remainder,
approximately 70 kb is used to store vehicle-specific application data.
Engine Stall
If the vehicle stalls it will coast down in gear, with the transmission providing drive to the engine. A restart can be attempted
at this point and the engine may start and the driver can continue.
If the coast down speed reduces such that the speed of the engine is less than 600 rev/min, the transmission will go to
neutral, D illumination will flash in the instrument cluster. The driver needs to select neutral or park and then press the brake
pedal to restart the engine.
If the start/stop button is pressed when driving, the message ENGINE STOP BUTTON PRESSED is displayed in the message
center but there will be no change to the ignition state. If the driver requires to switch off the engine, the start/stop button
must be pressed for a second time. The engine will be stopped and will be back driven by the transmission as the vehicle
coasts down. When the engine speed is less than 600 rev/min the transmission engages neutral (flashing D illumination in the
instrument cluster). When vehicle speed is less than 2 km/h (1.2 mph) Park is engaged. The JaguarDrive selector automatically
rotates back to its lowered P position and the vehicle ignition is switched off.
The park engagement is prevented in a stall case as the ignition power is on and D was the last selected gear. The park
engagement speed at ignition off is from the least value of the wheel speeds (CAN signal) and transmission output speed (internal signal).
TRANSMISSION Component Description
The transmission comprises the main casing which houses all of the transmission components. The main casing also
incorporates an integral bell housing.
A fluid pan is attached to the lower face of the main casing and is secured with bolts. The fluid pan is sealed to the main
casing with a gasket. Removal of the fluid pan allows access to the Mechatronic valve block. The fluid pan has a magnet
located around the drain plug which collects any metallic particles present in the transmission fluid.
A fluid filter is located inside the fluid pan. If the transmission fluid becomes contaminated or after any service work, the fluid
pan with integral filter must be replaced.
The integral bell housing provides protection for the torque converter assembly and also provides the attachment for the
gearbox to the engine cylinder block. The torque converter is a non-serviceable assembly which also contains the lock-up clutch
mechanism. The torque converter drives a crescent type pump via drive tangs. The fluid pump is located in the main casing,
behind the torque converter.
The main casing contains the following major components:
Input shaft
Output shaft
Mechatronic valve block which contains the solenoids, speed sensors and the TCM Three rotating multiplate drive clutches
Two fixed multiplate brake clutches
A single planetary gear train and a double planetary gear train.
Page 1441 of 3039
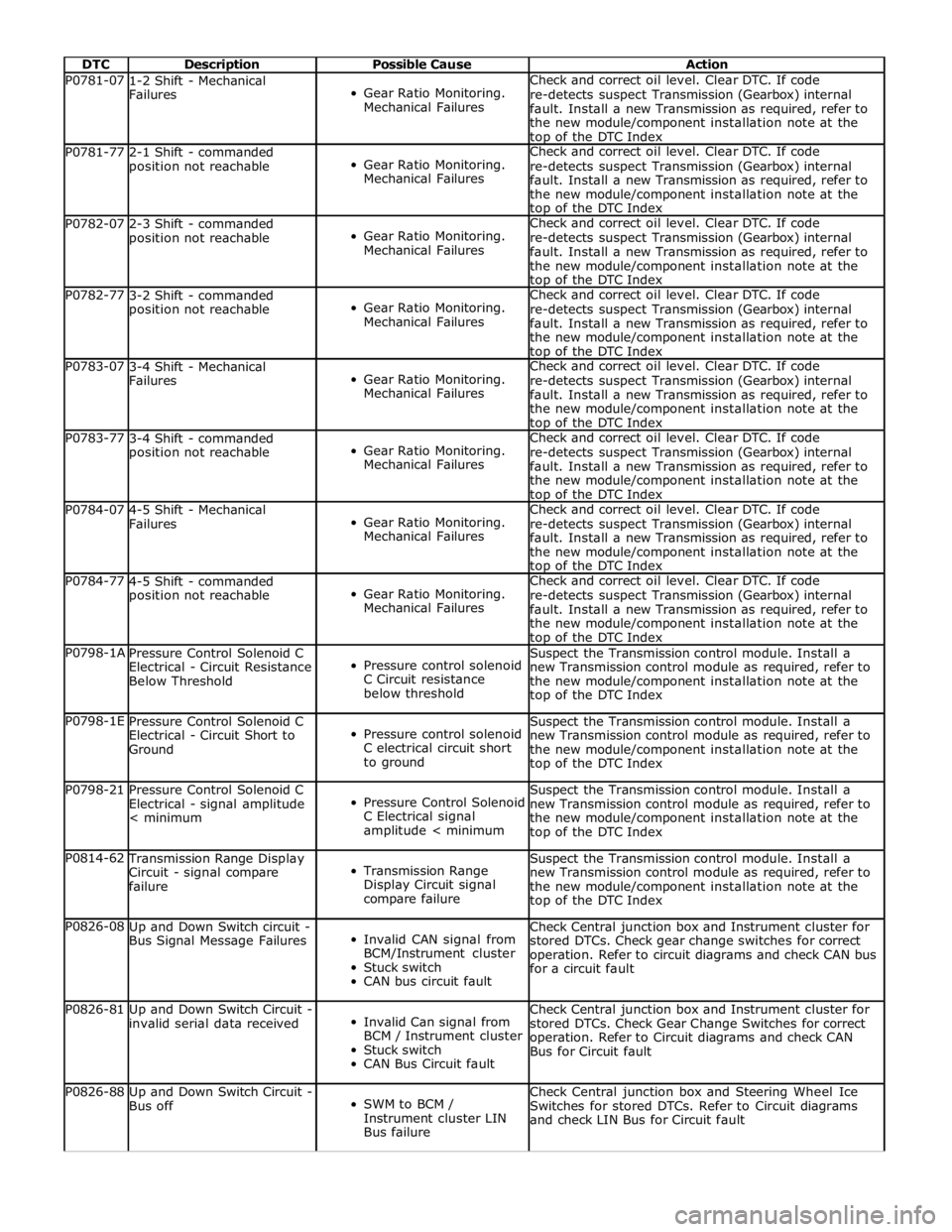
DTC Description Possible Cause Action P0781-07
1-2 Shift - Mechanical
Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0781-77
2-1 Shift - commanded
position not reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0782-07
2-3 Shift - commanded
position not reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0782-77
3-2 Shift - commanded
position not reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0783-07
3-4 Shift - Mechanical
Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0783-77
3-4 Shift - commanded
position not reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0784-07
4-5 Shift - Mechanical
Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0784-77
4-5 Shift - commanded
position not reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (Gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0798-1A
Pressure Control Solenoid C
Electrical - Circuit Resistance
Below Threshold
Pressure control solenoid
C Circuit resistance
below threshold Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0798-1E
Pressure Control Solenoid C
Electrical - Circuit Short to
Ground
Pressure control solenoid
C electrical circuit short
to ground Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0798-21
Pressure Control Solenoid C
Electrical - signal amplitude
< minimum
Pressure Control Solenoid
C Electrical signal
amplitude < minimum Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0814-62 Transmission Range Display
Circuit - signal compare
failure
Transmission Range
Display Circuit signal
compare failure Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0826-08
Up and Down Switch circuit -
Bus Signal Message Failures
Invalid CAN signal from
BCM/Instrument cluster
Stuck switch
CAN bus circuit fault Check Central junction box and Instrument cluster for
stored DTCs. Check gear change switches for correct
operation. Refer to circuit diagrams and check CAN bus
for a circuit fault P0826-81
Up and Down Switch Circuit -
invalid serial data received
Invalid Can signal from
BCM / Instrument cluster
Stuck switch
CAN Bus Circuit fault Check Central junction box and Instrument cluster for
stored DTCs. Check Gear Change Switches for correct
operation. Refer to Circuit diagrams and check CAN
Bus for Circuit fault P0826-88
Up and Down Switch Circuit -
Bus off
SWM to BCM /
Instrument cluster LIN
Bus failure Check Central junction box and Steering Wheel Ice
Switches for stored DTCs. Refer to Circuit diagrams
and check LIN Bus for Circuit fault
Page 1447 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Cause Action U0103-82
Lost Communication With
Gear Shift Control Module
A-alive / sequence counter
incorrect / not updated
Alive counter fault Check Transmission shift module for stored DTCs.
Check CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0103-83
Lost Communication With
Gear Shift Control Module A
- value of signal protection
calculation incorrect
Checksum fault Check Transmission shift module for stored DTCs.
Check CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0103-87
Lost Communication With
Gear Shift Control Module A
- missing message
CAN Timeout Check Transmission shift module for stored DTCs.
Check CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0122-82
Lost Communication With
Vehicle Dynamics Control
Module - alive / sequence
counter incorrect / not updated
Alive counter fault Check Anti-lock braking system for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0122-83
Lost Communication With
Vehicle Dynamics Control
Module - value of signal
protection calculation
incorrect
Checksum fault Check Anti-lock braking system for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0122-87
Lost Communication With
Vehicle Dynamics Control
Module - missing message
CAN Timeout Check Anti-lock braking system for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0126-00
Lost Communication With
Steering Angle Sensor
Module - no sub type
information
Lost Communication
With Steering Angle
Sensor Module Check Steering angle sensor for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0128-87
Lost Communication With
Park Brake Control Module -
missing message
CAN timeout electronic
parking brake module Check Electronic Parking Brake Module for stored DTCs.
Check CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0140-82
Lost Communication With
Body Control Module - alive / sequence counter incorrect / not updated
Alive counter fault Check Central junction box for stored DTCs. Check CAN
Bus Circuit for fault U0140-83
Lost Communication With
Body Control Module - value
of signal protection
calculation incorrect
Checksum fault Check Central junction box for stored DTCs. Check CAN
Bus Circuit for fault U0140-87
Lost Communication With
Body Control Module - missing message
CAN Timeout Check Central junction box for stored DTCs. Check CAN
Bus Circuit for fault U0155-87
Lost Communication With
Instrument Panel Cluster
(Instrument cluster) Control
Module - missing message
CAN timeout instrument
cluster Check Instrument cluster for stored DTCs. Check CAN
Bus Circuit for fault U0300-68
Control Module - event
information
Transmission software
does not match vehicle
network Check Central junction box software level, Check
Transmission control module Software level, Update
software as required using the manufacturer approved
process U0401-08
Invalid Data Received From
Engine control module/PCM
A - Bus Signal Message
Failures
Inaccurate engine speed,
torque information Check Engine control module for stored DTCs, Check
CAN Bus circuit for faults U0401-68
Invalid Data Received from
Engine control module/PCM
A - event information
Inaccurate engine speed,
torque information Check Engine control module for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0401-86
Invalid Data Received from
Engine control module/PCM
A - Signal Invalid
Inaccurate engine speed,
torque information Check Engine control module for stored DTCs. Check
CAN Bus Circuit for fault U0404-68
Invalid Data Received from
Gear Shift Control Module A
- event information
Incorrect CAN data
received from
Transmission shift
module Check Transmission Shift Module for stored DTCs.
Refer to Circuit diagrams and check CAN and LIN Bus
for Circuit fault U0404-81
Invalid Data Received from
Gear Shift Control Module A
- Invalid Serial Data
Received
Incorrect LIN data
received from
Transmission shift
module Check Transmission Shift Module for stored DTCs.
Refer to Circuit diagrams and check CAN and LIN Bus
for Circuit fault www.JagDocs.com
Page 1530 of 3039

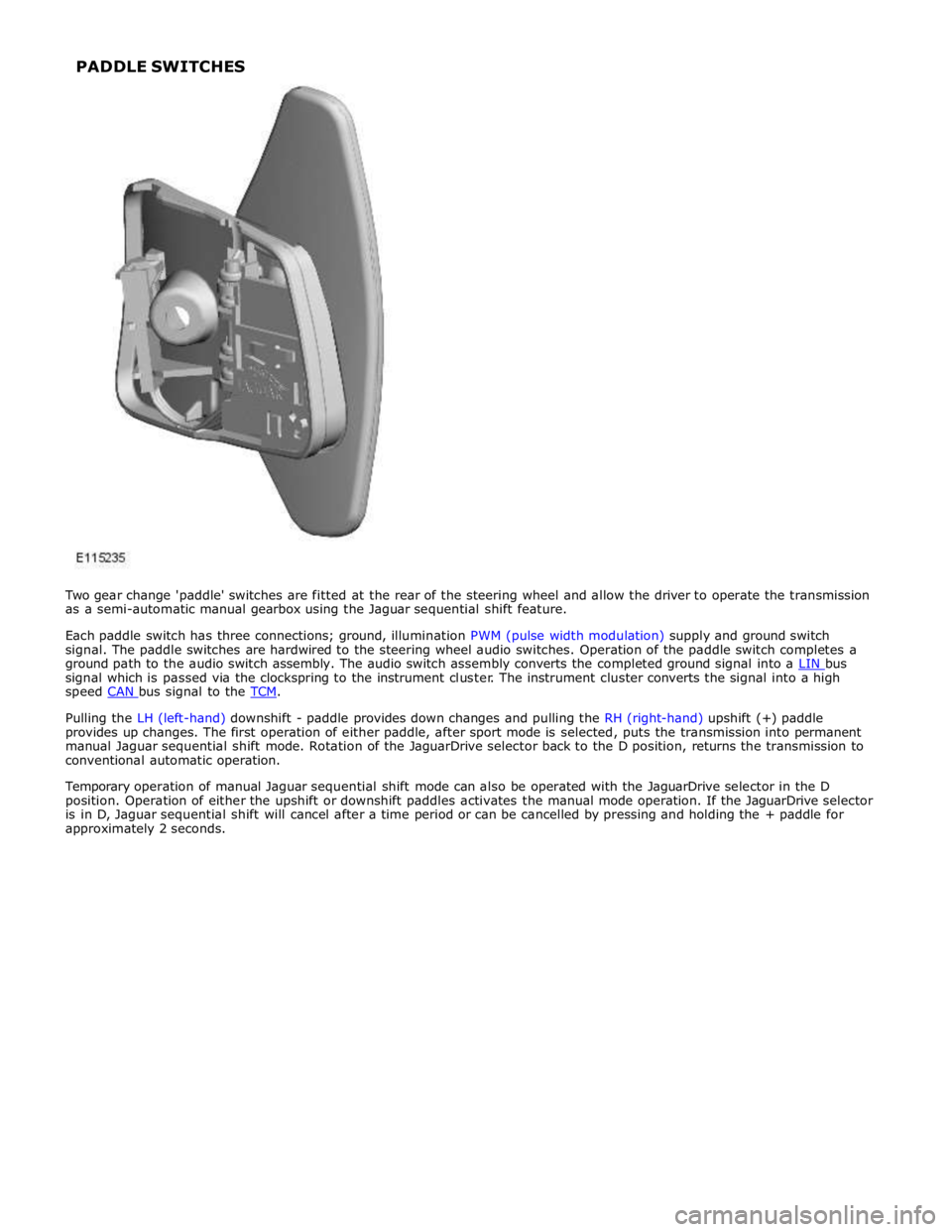
6 Clockspring 7 Steering wheel audio switches 8 Upshift paddle switch 9 Downshift paddle switch 10 Instrument cluster 11 JaguarDrive selector
JAGUARDRIVE SELECTOR System Operation
Rotation of the JaguarDrive selector to any of the five positions is sensed by the TCM (transmission control module) via the
high speed CAN bus. A LIN bus connection is also provided, but is only used in the event of a CAN bus failure as a back-up. The TCM then reacts according to the selected position. The JaguarDrive selector is a magnetic system using Hall effect sensors to determine the position of the selector.
The S (sport) position selection allows the TCM to operate the transmission using the semi-automatic Jaguar sequential shift. Gear selections are sensed by the TCM when the driver operates the steering wheel paddle switches. Once the JaguarDrive selector position is confirmed, the TCM outputs appropriate information on the high speed CAN bus which is received by the instrument cluster to display the gear selection information in the message center.
Refer to: Information and Message Center (413-08 Information and Message Center, Description and Operation).
The paddles can also be used on a temporary basis when the JaguarDrive selector is in the D (drive) position to override the
automatic gear selection if required.
PARK INTERLOCK AND NEUTRAL LOCK
Neutral lock is a requirement for the JaguarDrive selector. The selector is always locked at ignition on when the engine is not
running, except after an engine stall when the selector is not in P (park) or N (neutral).
If, when driving with the JaguarDrive selector in S, D or R (reverse) at a speed of more than 5 km/h (3 mph), the driver selects
P or N:
Without the brake pedal pressed, the JaguarDrive selector will be immediately locked once the vehicle speed falls to
below 5 km/h (3 mph).
With the brake pedal pressed, the JaguarDrive selector will remain locked for as long as the brake pedal remains
pressed, regardless of vehicle speed.
The transmission will only engage park once the vehicle speed is less than 2 km/h (1 mph).
If the driver selects N and releases the brake pedal with a vehicle speed of less than 5 km/h (3 mph), the JaguarDrive selector
will be locked 2 seconds after N is selected. The selector will remain locked until the driver presses the brake pedal again.
To ensure that a driver request to change from a non-driving range (N for example) to a driving range (D for example), the park
interlock and neutral lock features are used in conjunction with the intermediate position.
If the transmission receives a range change request without the brake pedal pressed, the TCM initiates a soft lock function. The transmission will remain in park or neutral, depending on the starting position.
If a transmission position letter is flashing in the message center and the vehicle has no drive, the driver must:
Press the brake pedal.
Reselect N or P on the JaguarDrive selector.
Select the required driving range, ensuring that the brake pedal is pressed.
Rocking Function
The rocking function compliments the neutral lock function. For all changes from a non-driving range to a driving range, it is
necessary to press the brake pedal (to release either the park interlock or neutral lock).
In situations where the driver will require to change the gear selection from R to D, or from D to R, without brake pedal input
(car park maneuvering, 3 point turns or 'rocking' the vehicle from a slippery surface for example), the rocking function gives a 2
second lock delay when N is selected on the JaguarDrive selector and the brake pedal is not pressed.
Intermediate Position
If the JaguarDrive selector is rotated slowly from P to S and back to position P with the brake pedal pressed, the R or D
position display letter in the message center will flash and the transmission will remain in park or neutral depending on the
previous starting position of the selector.
If the brake pedal is released when R or D is flashing in the message center and the JaguarDrive selector is rotated to the R or
D position, the required range will not be selected and the transmission will remain in park or neutral, depending on the
previous starting position. This feature is known as soft lock.
If the driving range letter in the message center is flashing and the vehicle has no drive, the driver should depress the brake
pedal to reselect N or P, and then select the required driving range while the brake pedal remains pressed.
Page 1532 of 3039
signal which is passed via the clockspring to the instrument cluster. The instrument cluster converts the signal into a high
speed CAN bus signal to the TCM.
Pulling the LH (left-hand) downshift - paddle provides down changes and pulling the RH (right-hand) upshift (+) paddle
provides up changes. The first operation of either paddle, after sport mode is selected, puts the transmission into permanent
manual Jaguar sequential shift mode. Rotation of the JaguarDrive selector back to the D position, returns the transmission to
conventional automatic operation.
Temporary operation of manual Jaguar sequential shift mode can also be operated with the JaguarDrive selector in the D
position. Operation of either the upshift or downshift paddles activates the manual mode operation. If the JaguarDrive selector
is in D, Jaguar sequential shift will cancel after a time period or can be cancelled by pressing and holding the + paddle for
approximately 2 seconds. PADDLE SWITCHES
Page 1591 of 3039
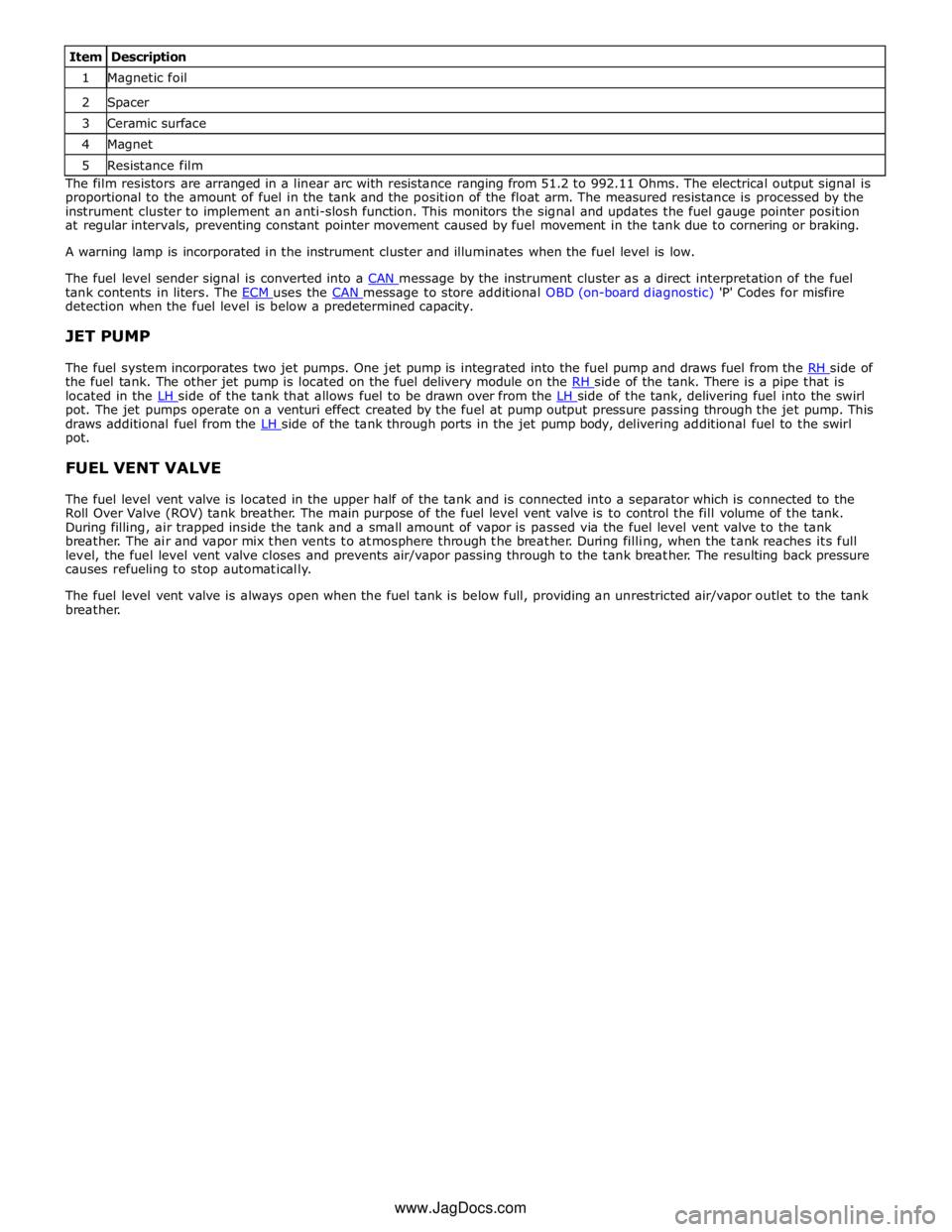
1 Magnetic foil 2 Spacer 3 Ceramic surface 4 Magnet 5 Resistance film The film resistors are arranged in a linear arc with resistance ranging from 51.2 to 992.11 Ohms. The electrical output signal is
proportional to the amount of fuel in the tank and the position of the float arm. The measured resistance is processed by the
instrument cluster to implement an anti-slosh function. This monitors the signal and updates the fuel gauge pointer position
at regular intervals, preventing constant pointer movement caused by fuel movement in the tank due to cornering or braking.
A warning lamp is incorporated in the instrument cluster and illuminates when the fuel level is low.
The fuel level sender signal is converted into a CAN message by the instrument cluster as a direct interpretation of the fuel tank contents in liters. The ECM uses the CAN message to store additional OBD (on-board diagnostic) 'P' Codes for misfire detection when the fuel level is below a predetermined capacity.
JET PUMP
The fuel system incorporates two jet pumps. One jet pump is integrated into the fuel pump and draws fuel from the RH side of the fuel tank. The other jet pump is located on the fuel delivery module on the RH side of the tank. There is a pipe that is located in the LH side of the tank that allows fuel to be drawn over from the LH side of the tank, delivering fuel into the swirl pot. The jet pumps operate on a venturi effect created by the fuel at pump output pressure passing through the jet pump. This
draws additional fuel from the LH side of the tank through ports in the jet pump body, delivering additional fuel to the swirl pot.
FUEL VENT VALVE
The fuel level vent valve is located in the upper half of the tank and is connected into a separator which is connected to the
Roll Over Valve (ROV) tank breather. The main purpose of the fuel level vent valve is to control the fill volume of the tank.
During filling, air trapped inside the tank and a small amount of vapor is passed via the fuel level vent valve to the tank
breather. The air and vapor mix then vents to atmosphere through the breather. During filling, when the tank reaches its full
level, the fuel level vent valve closes and prevents air/vapor passing through to the tank breather. The resulting back pressure
causes refueling to stop automatically.
The fuel level vent valve is always open when the fuel tank is below full, providing an unrestricted air/vapor outlet to the tank
breather.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1597 of 3039
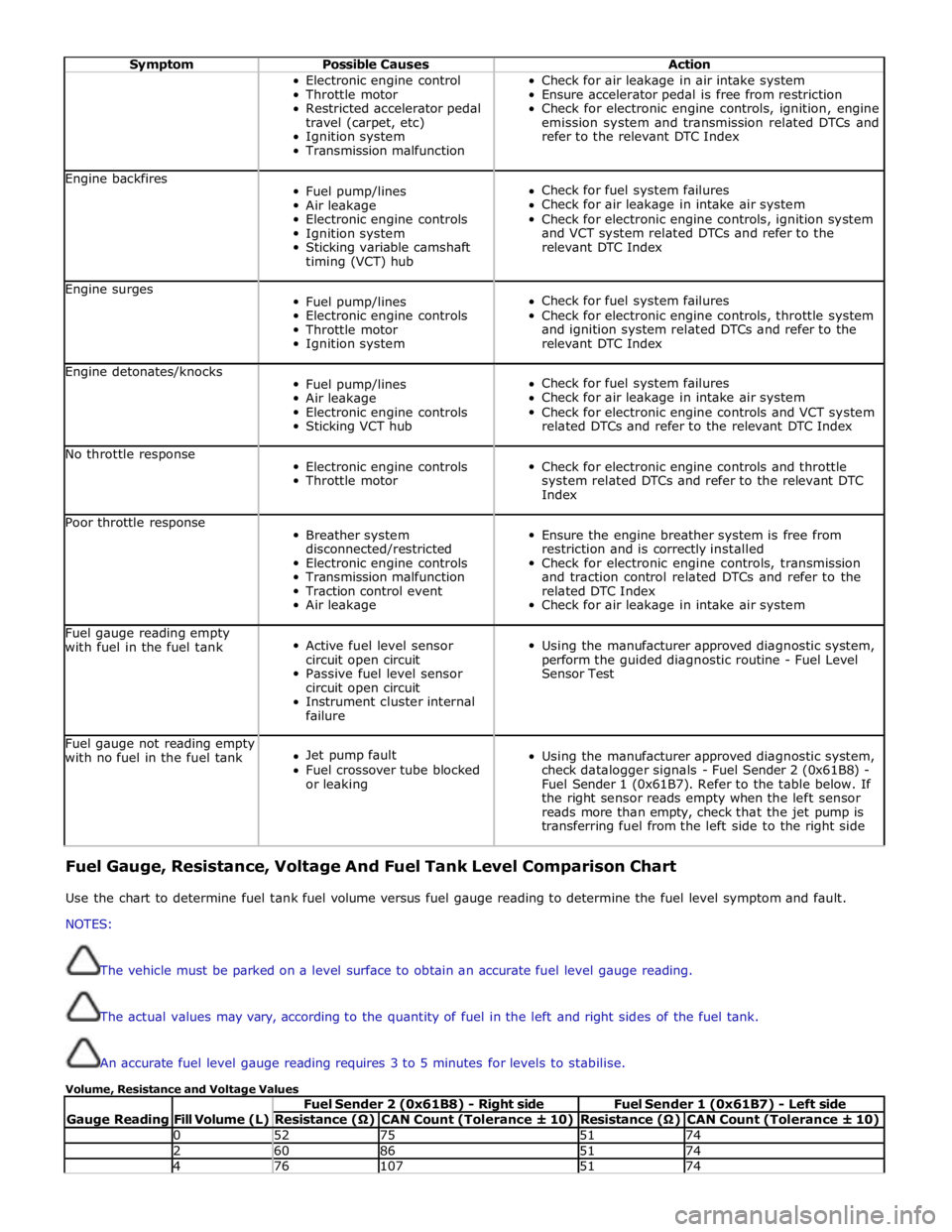
Symptom Possible Causes Action Electronic engine control
Throttle motor
Restricted accelerator pedal
travel (carpet, etc)
Ignition system
Transmission malfunction Check for air leakage in air intake system
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from restriction
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition, engine
emission system and transmission related DTCs and
refer to the relevant DTC Index Engine backfires
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition system
and VCT system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine surges
Fuel pump/lines
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Ignition system
Check for fuel system failures
Check for electronic engine controls, throttle system
and ignition system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine detonates/knocks
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Sticking VCT hub
Check for fuel system failures
Check for air leakage in intake air system
Check for electronic engine controls and VCT system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Check for electronic engine controls and throttle
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine controls
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event
Air leakage
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for electronic engine controls, transmission
and traction control related DTCs and refer to the
related DTC Index
Check for air leakage in intake air system Fuel gauge reading empty
with fuel in the fuel tank
Active fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Passive fuel level sensor
circuit open circuit
Instrument cluster internal
failure
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
perform the guided diagnostic routine - Fuel Level
Sensor Test Fuel gauge not reading empty
with no fuel in the fuel tank
Jet pump fault
Fuel crossover tube blocked
or leaking
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
check datalogger signals - Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) -
Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7). Refer to the table below. If
the right sensor reads empty when the left sensor
reads more than empty, check that the jet pump is
transferring fuel from the left side to the right side Fuel Gauge, Resistance, Voltage And Fuel Tank Level Comparison Chart
Use the chart to determine fuel tank fuel volume versus fuel gauge reading to determine the fuel level symptom and fault.
NOTES:
The vehicle must be parked on a level surface to obtain an accurate fuel level gauge reading.
The actual values may vary, according to the quantity of fuel in the left and right sides of the fuel tank.
An accurate fuel level gauge reading requires 3 to 5 minutes for levels to stabilise.
Volume, Resistance and Voltage Values
Gauge Reading
Fill Volume (L) Fuel Sender 2 (0x61B8) - Right side Fuel Sender 1 (0x61B7) - Left side Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) Resistance (Ω) CAN Count (Tolerance ± 10) 0 52 75 51 74 2 60 86 51 74 4 76 107 51 74
Page 1637 of 3039
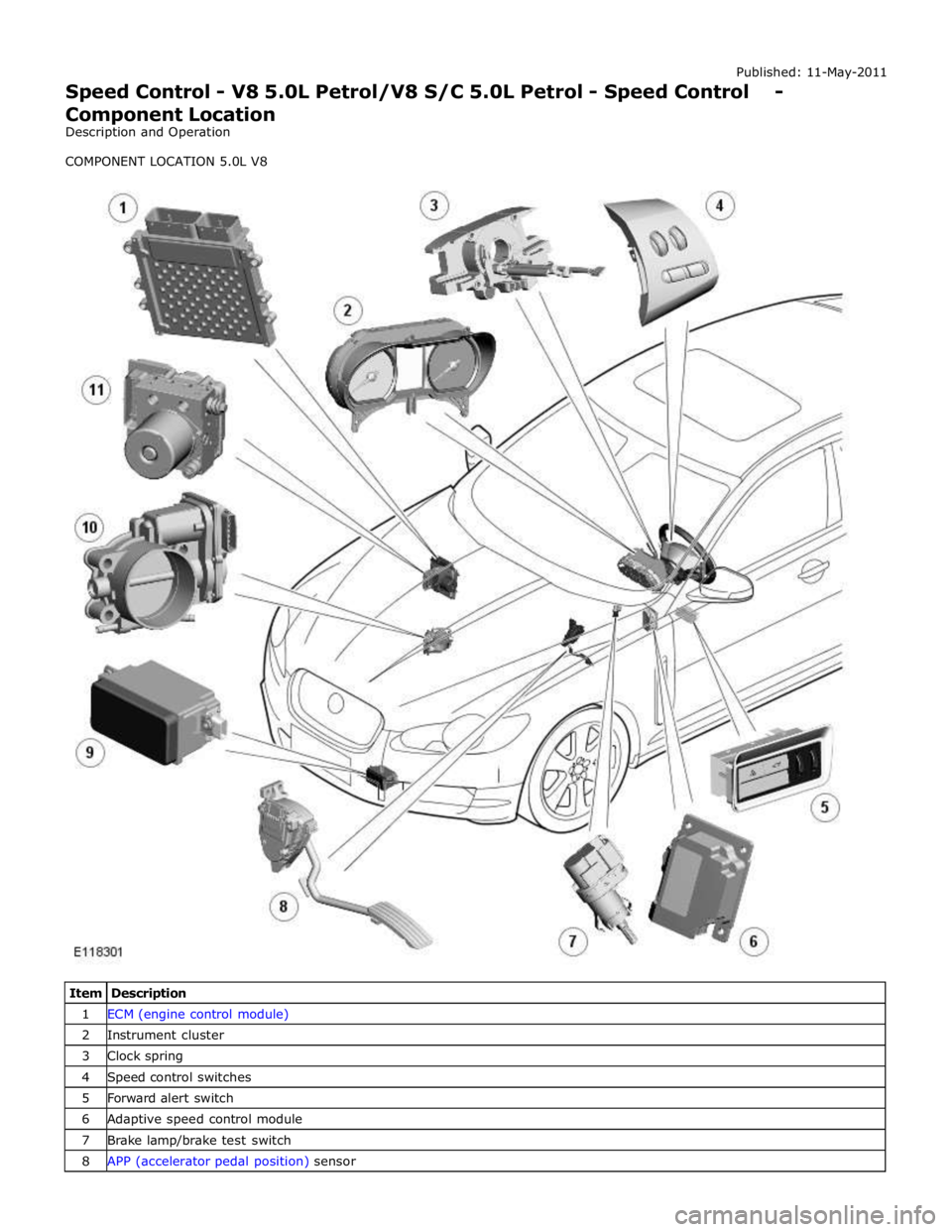
1 ECM (engine control module) 2 Instrument cluster 3 Clock spring 4 Speed control switches 5 Forward alert switch 6 Adaptive speed control module 7 Brake lamp/brake test switch 8 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor
Page 1639 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Speed Control
The speed control system is integrated with the engine management system and uses fueling intervention to automatically
maintain a set vehicle speed. Once engaged, the system can also be used to accelerate the vehicle without using the
accelerator pedal.
The speed control system comprises the following components:
On/Off/Suspend switch
'+' and '-' (set/accelerate and decelerate) steering wheel switches
Resume switch
Clock spring
Speed control warning indicator.
Adaptive Speed Control
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained.
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM (engine control module)
Electric throttle actuator
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module and pump
Adaptive speed control warning indicator (in the instrument cluster).
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the