key JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2126 of 3039

Anti-Theft - Active - Anti-Theft - Active
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 26-Feb-2014
For a detailed description of the anti-theft - active system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (419-01A Anti-Theft - Active)
Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation), Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation), Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Door latch micro switches
Hood ajar switch
Passive anti-theft alarm horn (if installed)
Battery backed sounder (if installed) or battery backed sounder with tilt sensor (if
installed)
Vehicle horns
Fuse(s)
Electrical
connector(s)
Wiring Harness
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the relevant DTC Index. For
additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop
manual
REFER to: Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) Module (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Index
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing electrical voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal
places, and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads
into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Page 2128 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10EE-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear door passenger side double
locking motor control circuit -
short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear door passenger side double locking
motor control circuit for short ground B10EE-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear door passenger side double
locking motor control circuit -
short to power, open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test rear door
passenger side double locking motor control
circuit for short power, open circuit B10F1-11
Key In Switch - Circuit
short to ground
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check keyless vehicle
module, key IN status circuit for short to
ground B10F1-12
Key In Switch - Circuit
short to battery
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check keyless vehicle module, key IN status
circuit for short to power B10F1-13
Key In Switch - Circuit
open
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check keyless vehicle module, key IN status
circuit for open circuit B1108-11
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Driver door central locking motor
control circuit - short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test driver door central locking motor control
circuit for short ground B1108-15
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Driver door central locking motor
control circuit - short to power,
open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test driver door central
locking motor control circuit for short to
power, open circuit B1109-11
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to ground B1109-15
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to power or open circuit B110A-11
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to ground
Rear driver door central locking
motor control circuit - short to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear driver door central locking motor
control circuit for short ground B110A-15
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Rear driver door central locking
motor control circuit - short to
power, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear driver door central locking motor
control circuit for short to power, open circuit B110B-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short circuit
to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B110B-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short circuit
to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B1163-11
Left Mirror Heater
Output Short To Ground
- Circuit short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test left mirror heater output circuit for short
to ground
Page 2133 of 3039
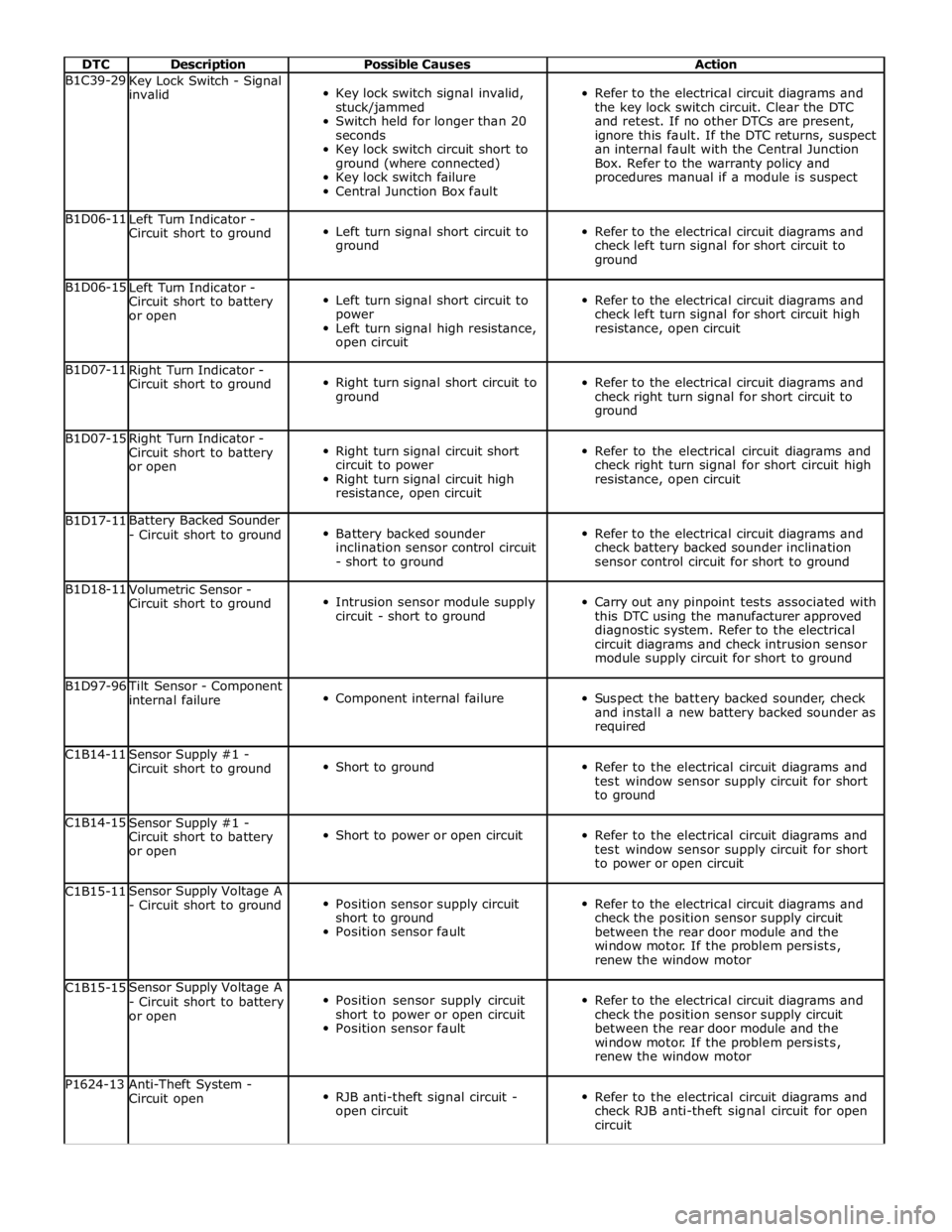
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1C39-29
Key Lock Switch - Signal
invalid
Key lock switch signal invalid,
stuck/jammed
Switch held for longer than 20
seconds
Key lock switch circuit short to
ground (where connected)
Key lock switch failure
Central Junction Box fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
the key lock switch circuit. Clear the DTC
and retest. If no other DTCs are present,
ignore this fault. If the DTC returns, suspect
an internal fault with the Central Junction
Box. Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual if a module is suspect B1D06-11
Left Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to ground
Left turn signal short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check left turn signal for short circuit to
ground B1D06-15
Left Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Left turn signal short circuit to
power
Left turn signal high resistance,
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check left turn signal for short circuit high
resistance, open circuit B1D07-11
Right Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to ground
Right turn signal short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check right turn signal for short circuit to
ground B1D07-15
Right Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Right turn signal circuit short
circuit to power
Right turn signal circuit high
resistance, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check right turn signal for short circuit high
resistance, open circuit B1D17-11 Battery Backed Sounder
- Circuit short to ground
Battery backed sounder
inclination sensor control circuit
- short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check battery backed sounder inclination
sensor control circuit for short to ground B1D18-11
Volumetric Sensor -
Circuit short to ground
Intrusion sensor module supply
circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check intrusion sensor
module supply circuit for short to ground B1D97-96 Tilt Sensor - Component
internal failure
Component internal failure
Suspect the battery backed sounder, check
and install a new battery backed sounder as
required C1B14-11
Sensor Supply #1 -
Circuit short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test window sensor supply circuit for short
to ground C1B14-15
Sensor Supply #1 -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test window sensor supply circuit for short
to power or open circuit C1B15-11 Sensor Supply Voltage A
- Circuit short to ground
Position sensor supply circuit
short to ground
Position sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the position sensor supply circuit
between the rear door module and the
window motor. If the problem persists,
renew the window motor C1B15-15 Sensor Supply Voltage A
- Circuit short to battery
or open
Position sensor supply circuit
short to power or open circuit
Position sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the position sensor supply circuit
between the rear door module and the
window motor. If the problem persists,
renew the window motor P1624-13
Anti-Theft System -
Circuit open
RJB anti-theft signal circuit -
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check RJB anti-theft signal circuit for open
circuit
Page 2140 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
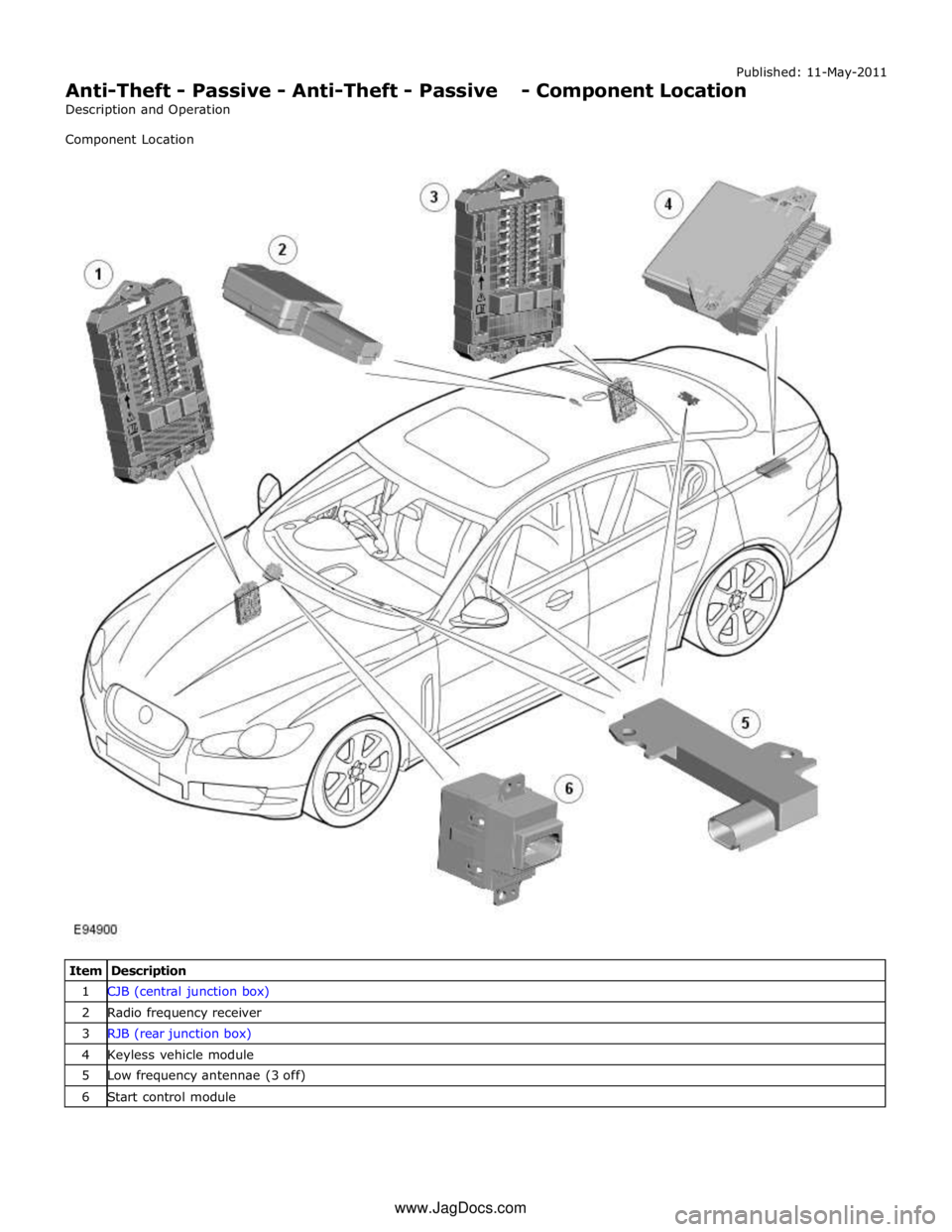
Anti-Theft - Passive - Anti-Theft - Passive - Component Location
Description and Operation
Component Location
Item Description 1 CJB (central junction box) 2 Radio frequency receiver 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 Keyless vehicle module 5 Low frequency antennae (3 off) 6 Start control module www.JagDocs.com
Page 2141 of 3039

Anti-Theft - Passive - Anti-Theft - Passive - Overview
Description and Operation
Overview Published: 11-May-2011
The PATS (passive anti-theft system) prevents the vehicle's engine from being started by unauthorized persons.
Engine starting is prevented by inhibiting the fuel, engine (spark, injectors and crank) and ignition systems from operating.
This is achieved by using a uniquely coded Smart Key and an encoded data exchange between multiple control modules.
The system is automatic and requires no input from the driver.
The engine start system is initiated when the encoded data between the Smart Key and vehicle control modules is verified.
The engine can then be started when the drive selector is in the 'Park' position, and the start/stop switch and the brake pedal
are pressed simultaneously.
Page 2142 of 3039
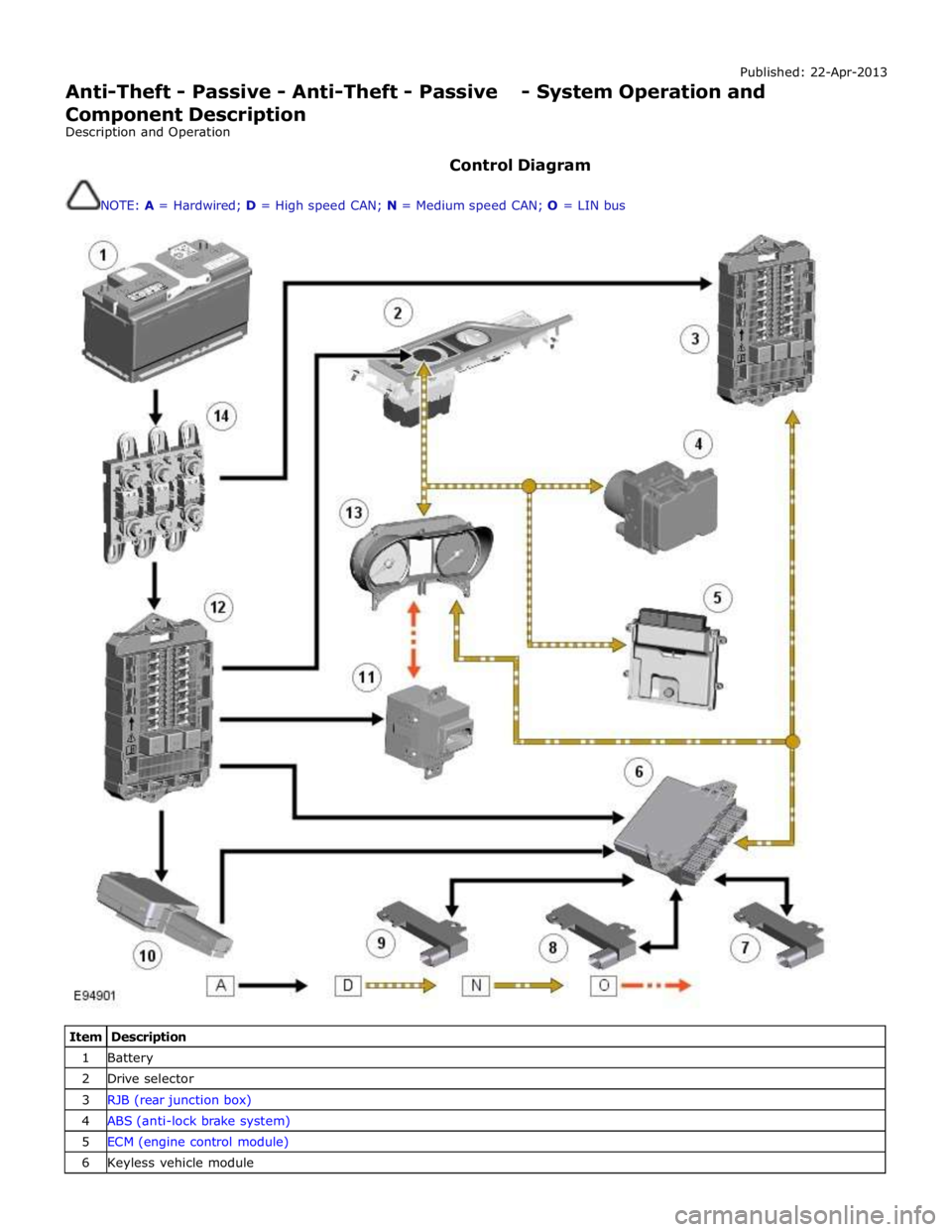
Published: 22-Apr-2013
Anti-Theft - Passive - Anti-Theft - Passive - System Operation and
Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN; N = Medium speed CAN; O = LIN bus
Item Description 1 Battery 2 Drive selector 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 ABS (anti-lock brake system) 5 ECM (engine control module) 6 Keyless vehicle module
Page 2143 of 3039

7 Low frequency antenna - front 8 Low frequency antenna - center 9 Low frequency antenna - rear 10 Radio frequency receiver 11 Start control module 12 CJB (central junction box) 13 Instrument cluster 14 Megafuse (250 amp)
System Operation
The passive start function prevents the vehicle from being started by unauthorized persons. It does this by immobilizing the
ignition, fuel and engine crank functions. The system is automatic and requires no input from the driver.
At the request of the CJB, the keyless vehicle module prompts each of the Low Frequency (LF) antennae to output a signal. When the Smart Key is in the vehicle cabin, it detects the LF signals and responds with a Radio Frequency (RF)
data-identification signal back to the keyless vehicle module via the RF receiver.
If the data received matches that stored in the keyless vehicle module it continues the passive start process by
communicating a 'Smart Key valid’ signal to the CJB via the medium speed CAN (controller area network) bus.
Once the CJB receives the authorization and confirms a response with an internal calculation, it passes the result to the
instrument cluster on the medium speed CAN bus.
Before the instrument cluster sends a mobilization signal to the ECMit will exchange encrypted data with: The electric steering lock mechanism to authorize unlocking the steering column.
The RJB to authorize fuel pump operation. Once the RJB receives the authorization and confirms the response with an internal calculation, it will enable the FPDM (fuel pump driver module).
The CJB to authorize the ignition status. If the drive selector is in the park position and the driver presses the brake
pedal and simultaneously presses the start/stop switch, the CJB interprets this as an engine crank request. Before the
engine crank request is allowed, the CJB compares a brake pressure signal received from the ABS module. The brake pressure signal is compared to an internally stored threshold value within the CJB. If the signal is greater than the
stored threshold value, a crank request signal is sent to the ECM on the high speed CAN bus.
Once these factors have been confirmed, and the vehicle is in 'Park', the engine can be started by pressing the brake pedal and
the Stop/Start button simultaneously.
NOTES:
If the keyless vehicle module fails to locate the Smart Key, the message 'SMART KEY NOT FOUND PLEASE INSERT IN
SLOT' will appear in the instrument cluster message center. When inserted the start control module will read the transponder
within the Smart Key. If the transponder identification is valid, authorization will be transmitted to the instrument cluster on
the LIN (local interconnect network) bus.
When the vehicle is delivered from the factory the passive start function is inhibited. In this condition the vehicle can
only be started by placing the Smart Key in the start control module. The system should be switched on during the Pre-Delivery
Inspection (PDI) using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system. For additional information, refer to the PDI Manual.
To ensure optimum long term reliability of the smart key the battery must be replaced with a brand new, unused battery. If a
used battery is installed the "SMART KEY BATTERY LOW" message may not be cleared. To avoid contamination of the contacts
the battery should be removed from its packaging and installed into the smart key while wearing gloves. To confirm that the
replacement battery is working correctly press the unlock button twice while holding the smart key outside the vehicle, then
enter the vehicle with the smart key, press the start button and confirm that the "SMART KEY BATTERY LOW" message is not
displayed.
Start Control Module Component Description
The start control module is used if the keyless vehicle module is unable to authorise the Smart Key.
If the keyless vehicle module is unable to identify the Smart Key, for example if the Smart Key battery voltage is low or there
is local RF interference, the transponder within the Smart Key can be read in the conventional manner. The driver will be
alerted to this by a chime and a message in the instrument cluster message center 'SMART KEY NOT FOUND PLEASE INSERT IN
SLOT'.
Once inserted the start control module will read the transponder within the Smart Key. If the transponder identification is
valid, authorization will be transmitted to the instrument cluster on the LIN bus.
NOTE: Inserting the Smart Key into the start control module will not charge the Smart Key battery. The battery is
non-chargeable and must be replaced if defective.
Page 2144 of 3039

A message 'REMOVE SMART KEY' will be displayed if the Smart Key is still in the start control module and the driver's door is
opened.
Low Frequency Antenna
Three Low Frequency (LF) antennae for the passive start system are positioned in specific locations in the vehicle; refer to
Component Location graphic.
NOTE: On vehicles with the passive entry system, five additional antennae are used; one integrated into the rear bumper
and one in each door handle assembly. These are only used by the passive entry system and have no function in the passive
start system.
The keyless vehicle module transmits an LF signal via the antennae which is received by the Smart Key. The Smart Key then
responds by transmitting a Radio Frequency (RF) signal which is received by the RF receiver and passed to the keyless vehicle
module for authorization.
Keyless Vehicle Module
The keyless vehicle module controls signal transmissions to and from the Smart Key and provides authorization to allow the
vehicle to be started. The module has a medium speed CAN connection to the CJB for authorizing vehicle starting.
Radio Frequency Receiver
The Radio Frequency (RF) receiver transmission is received from the Smart Key to enable key identification.
Page 2145 of 3039
Anti-Theft - Passive (Description and Operation), Anti-Theft - Passive (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
Anti-theft - Passive
The best method to confirm the correct operation of the Passive Anti-Theft System (PATS) is to check the LED (located in the
center of the instrument panel). The LED should illuminate solid for 3 seconds, when the ignition status is set to ON, and then
extinguish. This validates all PATS functions (i.e. the key transponder matches a stored key code, the challenge/response
sequence between the respective modules was successful resulting in the EMS being enabled).
Ignition fails to operate
Check that the smart key is located within the vehicle interior, and that it is the correct one for the vehicle.
Insert the smart key into the start control unit (located at out board side of driver instrument panel lower panel), this is an
alternative method to allow Ignition On/Engine Start.
Check that the start button circuit to the CJB is not open circuit or short circuit to power.
Check that the Low Speed CAN network is not malfunctioning, i.e. open circuit or short circuit. This would mean that the
remote keyless entry module, Central Junction Box (CJB) and instrument cluster would be unable to communicate.
Engine fails to crank
If a PATS fault is detected, the LED will flash for 60 seconds at 4Hz with a 50% duty cycle. At the end of this period, the LED
will flash a 2 digit code; this code is repeated 10 times. The meaning of these fault codes along with the frequency of flashing
is given in the accompanying table. As a general rule a fault code of 16 or less will cause the vehicle not to crank. Additionally,
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system should be used to check the instrument cluster, CJB & ECM for Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs).
One potential occurrence for failing to crank could be due to the P & N start switch (input to the ECM).
Check the Crank Request output from the CJB to ECM is not short circuit to ground or open circuit. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2146 of 3039

Check the Starter Relay circuit.
NOTE: On petrol engine variants, due to Smart Start, both sides of Relay Coil are switched directly from ECM (If
conditions correct). On diesel engine variants the low side only is switched directly from the ECM.
Check that the Steering Column Lock correctly operates and the steering wheel can turn freely.
Check that the High Speed CAN network is not malfunctioning, i.e. the CAN circuit is open or short circuit. This would mean
that the instrument cluster and ECM would be unable to communicate resulting in no Challenge being performed to enable the
ECM. This would be supported by LED Flash Code 24, see PATS Fault Code Table.
Also check the CAN network between the ABS module and the CJB. The CJB uses the CAN_BrakePressureTMC signal to
determine if the brake pedal has been pressed in order to allow an engine crank. The CJB uses a value of 0x05, if the CJB sees
a value less than this, it will not enable the Crank Request Output.
Engine cranks but will not start
If the Engine is cranking it means that the ECM has passed the authorisation required with the Instrument Cluster. If this
authorisation failed, the ECM would not engage the starter relay. This could be confirmed by verifying the PATS LED prove out
(illuminated solid for 3 seconds) or by reading DTCs from the instrument cluster and ECM.
In this case, the fuel pump circuit should be verified. The Fuel Pump Delivery Module (FPDM), which is supplied via the RJB
(authentication required with the instrument cluster) and controlled by the ECM, supplies the fuel pump.
In all cases of suspected non-start issues, the most logical failure modes should be eliminated first. i.e.
1. Check all relevant supplies and grounds to the relevant modules listed herein.
2. Note any unusual behaviour from other systems/functionality.
3. Note any functions that are not operating as expected.
PATS Fault Codes
For the various PATS modes/faults listed in the table , the instrument cluster will store a DTC and indicate this to the customer
during the detection period defined in the 'when logged' column, by illuminating the indicator as described for 60 seconds and
then flashing the LED 10 times as appropriate. The indication will stop immediately the ignition status is set to OFF any time
during the fault indication sequence. Up to 4 DTCs could be stored per key read sequence (1-10 read attempts). No DTCs will be
stored until all retry attempts are complete. Only the highest priority fault code will be flashed.
To determine the fault code from the LED: The LED will flash initially ten times with 1.5 seconds between. The LED will remain
OFF for 2.5 seconds then flash a number of times with 0.5 seconds between (the number of times the LED flashes represents
the first digit of the code), the LED will remain OFF for 1.5 seconds then flash a number of times with 1.5 seconds between
(the number of times the LED flashes represents the second digit of the code).
The PATS LED will be commanded on as shown under 'indication'. Normal PATS operations are complete within 400ms of the
ignition switch transition from OFF to ON or START, worst case for ECM communication problems will be less than 2 seconds. If
PATS is not complete during the 2 seconds the ECM will terminate PATS and await the next ignition ON or START event. PATS
faults will be indicated via the LED as soon as possible and will terminate the LED prove out. At ignition OFF all previous
flashing will cease and the perimeter anti-theft system will control the LED when the vehicle is locked and armed.
PATS Fault Code Table
Mode of Operation/Fault
When Logged
Ignition
Status
DTC LED
Fault
Code
Indication Prove out N/A Transition
from OFF to
ON N/A N/A
3 Seconds of steady
illumination Perimeter Anti-theft Control N/A OFF -
Vehicle
locked and
armed N/A N/A
Off or 0.5Hz flashing
at 5% duty cycle ±
20% until Off Start Control Unit already programmed Key Insert Any B1B0105 N/A No Indication Start Control Unit status = invalid response Key Insert Any B1B0167 N/A No Indication Start Control Unit programming error Key Insert Any B1B0151 N/A No Indication Start Control Unit challenge response error Key Insert OFF B1B0162 N/A No Indication Key Programming timer expired or Key Auth Timer expired Key Insert Any B1B0187 N/A No Indication Transponder challenge response error Key Insert Any B1B0164 N/A No Indication Transponder keys stored below minimum number required B&A/Dealer Any B1B0100 N/A No Indication Transponder not programmed B&A/Dealer Any B1B0155 N/A No Indication If the instrument cluster sends a 'theft' key status
to the ECM or the ECM returns a status message
containing the data 'Disabled/Theft', the instrument
cluster will set this DTC EMS CAN
communication OFF to ON B1B3364 16
60 seconds of 4Hz
flashing at 50% duty
cycle followed by fault
code 16 flashing 10
times