ABS JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 414 of 521

in these areas indicates the onset of wear.
Hold the inner race between the fingers and thumb of one hand, spin the outer race and checkthat
it revolves absolutely
smoothly. Rotate the outer ring with a reciprocating motion, while holding the inner ring; feel for any obstruction to
rotation and reject the bearing if the action is not perfectly smooth. Lubricate the bearing generously with lubricant
appropriate to the installation. Inspect the shaft and bearing housing for discolouration or other marking which may
suggest that movement has taken place between the bearing and bearing seat.
If markings are found, use Loctite when
installing the replacement bearing.
Ensure that the shaft and housing
are clean and free from
burrs before fitting the bearing. If one bearing of a pair
shows an imperfection, it is generally advisable to renew
both bearings: an exception could be made only if the bear- ings had covered a low mileage and it could be established
that damage was confined to the one bearing.
- In the case of bearings which are lubricated with grease (e.g.
hub bearings) the space between the bearings should be
smeared with a recommended grade of grease, and the
bearings and seal should be re
-packed. When fitting the
bearing to the shaft, apply force only to the inner ring of
bearing (Fig.
1A). When fitting the bearing to the housing,
apply force only to outer ring (Fig. 1B).
Always mark components of separable bearings (e.g taper
roller bearings) when dismantling, to ensure correct
reassembly. Never
fit a new inner roller assembly to a used
outer track.
A3.2.6 Oil Seals
Always fit new oil seals when rebuilding an assembly.
Examine the seal before fitting to ensure that it is clean and
undamaged. Smear sealing lips with clean grease, pack
dust excluder seals with grease and pack grease into the
cavity between the sealing lips of duplex seals. Ensure that
the seal spring,
if provided, is correctly fitted.
Place the lip
of the seal towards the fluid to be sealed and
slide it into position on the shaft, using a fitting sleeve (Fig. 2) when possible to protect the sealing lip from damage by
threads, splines or sharp edges on the end of the shaft. If a fitting sleeve is not available, use plastic tube or adhesive
tape to prevent damage to the sealing lip.
Grease the outside diameter of the seal, place it square to the
housing recess and press it into position, using great care
and, where available, a seal installer (Fig. 3) to ensure that
the seal does not tilt. In some cases it may be preferable to
fit the seal to the housing before fitting it to the shaft. Never
let the weight of an unsupported shaft rest in a seal. If the
correct service tool is not available, use a piece of tube which
is approximately 0,4 mm (0.015 in) smaller than the outside
diameter of the seal. Use a press to install the seal or use a
hammer VERY GENTLY on the tubular drift if a press is un-
suitable or not available.
,107 001 A B
I Fig. 1
A3.2.5 Ball And Roller Bearings
CAUTION: Never replace a ball or roller bearing without first ensuring that it is in as-new condition.
Remove
all traces of lubricant from the bearing by washing it in petrol or a suitable degreaser. Maintain absolute
cleanliness throughout the operations. Inspect visually for markings of any form on rolling elements, bearing tracks,
outer surface of outer rings or inner surface of inner rings. Reject any bearings found to be marked, since any markings
Fig.
2
307 002
i
Fig. 3
Issue 1 August 1994 3 X300 VSM
Page 415 of 521
General Fitting Instructions
Pressordrifttheseal in tothefull depthofthe housing ifthe housing is shouldered,orflush withthefaceofthe housing
where no shoulder is provided.
Note: Careless fitting of oil seals, which can result in damage to the seal and sealing surfaces, accounts for most
cases of failure of seals. Care in fitting is essential
if good results are to be obtained.
A3.2.7 joints And joint Faces
Remove all traces of old jointing materials prior to reassembly. Inspect joint faces for scratches or burrs and remove
with a fine file or oilstone; do not allow swarf or dirt to enter tapped holes or enclosed parts. Blow out any pipes, chan- nels or crevices with compressed air, refitting or renewing any 0-rings or seals which have been displaced by the com- pressed air.
Always use the specified gaskets. Use jointing compound only when recommended, otherwise fit joints dry. When
jointing compound is used, apply in
a thin film to metal surfaces; take great care to prevent it from entering oilways, pipes or blind tapped holes.
A3.2.8
Before removing a hose from the brake or power steering systems, thoroughly clean the end fittings and the area sur- rounding them. Obtain blanking caps beforedetaching hosefittings,sothat portscan becovered to excludedirt. Clean
the hose externally and blow through with compressed air. Examine the hose carefully for cracks, separation of plies,
security of end fittings and external damage. Reject any hose found to be faulty. When refitting the hose, ensure that
no unnecessary bends are introduced and that the hose is not twisted before or during tightening of union nuts.
Do not store hydraulic fluid in an unsealed container because it will absorb water. Fluid in this condition would be dan- gerous to use due to a lowering of its boiling point. Do not allow hydraulic fluid to be contaminated with mineral oil,
or use a container which has previously contained mineral oil.
Do not re-use fluid bled from the system. Always use clean brake fluid, or a recommended alternative, to clean the
hydraulic components. Fit a blanking cap to the hydraulic union and
a plug to its mating socket, after removal from
the vehicle, to prevent ingress of dirt. Absolute cleanliness must be observed with hydraulic components at all times.
After any work has been performed on hydraulicsystems, inspect carefully for leaks underneath the car while a second
operator applies maximum pressure to the brakes (with the engine running) and operates the steering.
Hydraulic Flexible Pipes And Hoses
A3.2.9 Metric
Bolt Identification
An IS0 metric bolt or screw, made of steel and larger than
6mm in diameter can be identified by the symbols ISOM or M embossed on top of the head (Fig. 1 ). In addition to marks
to identify the manufacturer, the head is also marked with
symbols to indicate the strength grade eg
8.8, 10.9, 12.9 or 14.9. The first figure gives the minimum strength of the bolt
material in tens of kgf / mm2. Zinc plated IS0 metric bolts
and nuts are chromate passivated and coloured greenish- khaki to gold-bronze.
A3.2.10 Metric Nut Identification
A nut with an IS0 metricthread is marked on one face (1 Fig. 2) or on one of the flats (2 Fig. 2) of the hexagon with the
strength grade symbol 8, 12 or 14. Some nuts with a
strength 4,5 or 6 are also marked and some have the metric
symbol M on the flat which is opposite to the strength grade
marking.
Aclockfacesystem is used as an alternative method of indi
- cating the strength grade (3 Fig. 2). The external chamfers
or a face of the nut is marked in a position relative to the ap-
propriate hour mark on a clock face to indicate the strength
grade. A dot is used to locate the 12 o’clock position and a dash to indicate the strength grade. If the grade is above 12,
two dots identify the 12 o’clock position. Fig.
1
I I
Fig. 2
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 4
Page 432 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
Term
ABS
ABS
/ PA
ABS
/ PC
ABS / PBT
A#. 1.6 PLASTICS - EXPLANATORY NOTES
A#. 1.6.1 Plastic component and trim materials.
This table, in conjunction with the illustrations on the following pages will enable rapid identification of the particular
material of any major plastic part.
Material Name
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
& Polyamide (nylon) blend
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
& Polycarbonate blend
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate
& Polybutylene Terephthalate
PC
PE
PMMA
POM
PP
PPO
PUR
PVC
SMA
I PA 1 Polyamide (nylon) I
Polycarbonate
Polyethylene
Polymethyl
Methacrylate
Polyoxymethylene (acetal)
Polypropylene
Modified Polyphenylene Oxide
Polyurethane
Polyvinylchloride
Styrene Maleic Anhydride
w: Not all plastic components are nominated, only those suitable for economic reclamation.
A#. 1.6.2 Plastics - Handling Notes
w: With reference to the following conditions, consider the properties of those plastic components which may
be affected by a repair or rectification procedure.
0 As mentioned elsewhere, the exterior panel temperature of the vehicle must not exceed 95OC at any time and
may only be held at this upper limit for a maximum of 2 (two) hours.
0 Interior vehicle temperature must not exceed 86OC, the time limit being 2 (two) hours.
0 Temperatures above those specified in 1 and 2, may result in distorted or permanently damaged components. If there is any doubt whatsoever, remove those components which may be affected by the application of heat.
0 Certain items may be manufactured from 'blended' materials; these must NOT be recycled with pure materials.
For example do not mix PC/ABS (wheel trim) with ABS ('B' pillar upper trim).
0 Should plastic components become greasy, they may be cleaned with an 'SBP 3' spirit wipe, or equivalent.
A4.1.6.3 Recycled Materials
Any of the materials listed in A4.1.6.1 may be recycled provided that they are not contaminated by other incompatible
plastics or metals. For instance, the air conditioning unit case, manufactured from PP (polypropylene), must be separ- ated from the heater matrix, evaporator, control devices (electronic and mechanical) and all fixings before it can be
considered for recycling.
After disassembly, the case must be placed for disposal only
with materials of the same generic type.
w: The bumper cover assemblies have side armatures (non-eerviceable items) rivetted to them; because they
are dissimilar materials the armatures and fixings must be removed prior to recycling.
In the bumper cover intake aperture there is a cosmetic 'black-out' piece; a similar component may be found
on the fog lamp blanks (where fitted). These items should be separated from the major component for recycl- ing.
Issue 1 August 1994 5 X300 VSM
Page 441 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
A4.2.3 ZINC COATED PANELS
A4.2.3.1
Description
Approximately 65% of the 'body in white' (BIW) mass is made up of zinc coated panels.
All exterior skin panels, with the exception of the roof, are double side zinc plated and this coating (nominally
7,5 mi- crons) provides corrosion protection in two ways.
1. Should the outer layer of paint become chipped but the zinc coating remain intact, the zinc will oxidize on contact
with air. This coat of oxidation is impermeable and will prevent corrosion damage to the base metal.
2. If both the outer layer of paint and the zinc coating become damaged, the zinc will react with the air and 'sacrifice'
itself to corrosion, rather than the base metal. In this process the zinc is known as a 'sacrificial anode'.
Iynpp: To maintain the protective qualities of the zinc treatment, repairs to any damaged coated area MUST be made as soon as possible after the damage has occurred.
A4.2.3.2 Wdding Preparation
Where 'resistance spot welding' is employed, the zinc coating should be lightly abraded away on the mating surfaces
and those in contact with the electrode tips. Do not remove more of the zinc coating than is absolutely necessary.
Before welding,
a weld-through primer or inter-weld sealer should be applied, as detailed in the Body Sealing and
Preservation man ua I.
Contamination of the weld will occur ifthe plating is not removed, thus making the joint less strong; another side effect
of this will be a greater need for electrode tip dressing and increased tool down time.
In exceptional cases where the plating must remain intact, increase the tip pressure and welding current by 10 to
20%.
Where MIG welding is used as an alternative to resistance spot welding for plug, butt welds, or limited access, the prob- lems caused by the presence of zinc coating are much the same as those previously mentioned. There may also be
the added problems of increased weld spatter and nozzle contamination.
0
A4.2.3.3 Body Fillers
Conventional polyester fillers do not adhere satisfactorily to zinc plated panels. Therefore, it is important to use only
those products specifically designed for this application and follow the manufacturers recommendations.
A4.2.3.4 Refinishing
Use only those products approved by Jaguar Cars Ltd and take special care with zinc coated panels.
Replacement panels are supplied ready primed
so there should be no need for bare metal to be exposed, other than
those areas prepared for welding etc (see 'Welding Preparation' sub section 4.2.3.2).
Where any part of a panel is dressed backto a bare surface, it should be treated with a zinc rich primer compatible with
the chosen paint application system, please refer to section A4.4.1.1.
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 14
Page 444 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
A4.2.5.2 PANELS, ALIGN AND WELD
. Observe all appropriate safety procedures.
. Apply appropriate sealer or joint preparation.
. Align the replacement panel with associated panels and clamp in position; with certain panels it may be necessary
. Recheck alignment and panel contours and readjust as necessary.
= Select the correct 'arms' for resistance spot welding and ensure that tips are correctly trimmed.
w:
0 SRO 77.10.05 di77.10.06
to MIG tack weld (A Fig. 1) or use 'PK screws.
It is recommended that 'arms' of not more than 300 mm (12 in.) long are used and test the equipment for satis-
factory operation by producing test coupons (B Fig. 1). In the absence of test equipment, a satisfactory weld
can be verified by pulling the test coupons apart and viewing the welded condition.
Resistance spot weld where required (C Fig. 1).
. Note the presence of zinc coated panels and treat as detailed in the previous sections.
. Dress back all MIG tack welds.
. MIG seam weld the butt joints (D Fig. 1).
. As required, dress all welds.
. Final braze and fill as necessary prior to paint preparation.
//
C
Fig. 1
B
D
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 17
Page 459 of 521
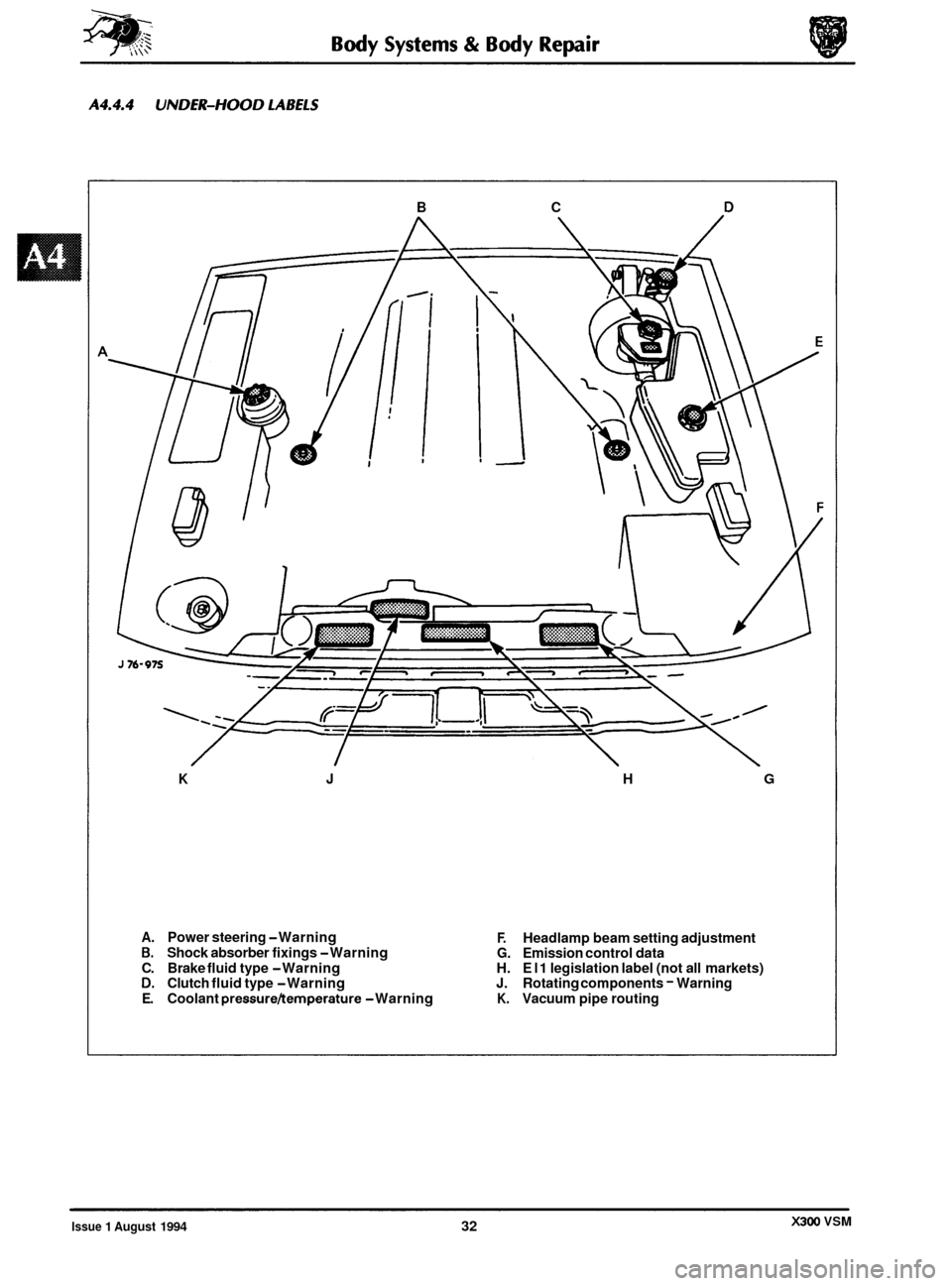
B C D
K J H G
A. Power steering -Warning F. Headlamp beam setting adjustment B. Shock absorber fixings -Warning G. Emission control data
C. Brake fluid type -Warning H. El 1 legislation label (not all markets) D. Clutch fluid type -Warning J. Rotating components - Warning
E. Coolant pressureltemperature -Warning K. Vacuum pipe routing
0
0
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 32