wheel JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 227 of 521
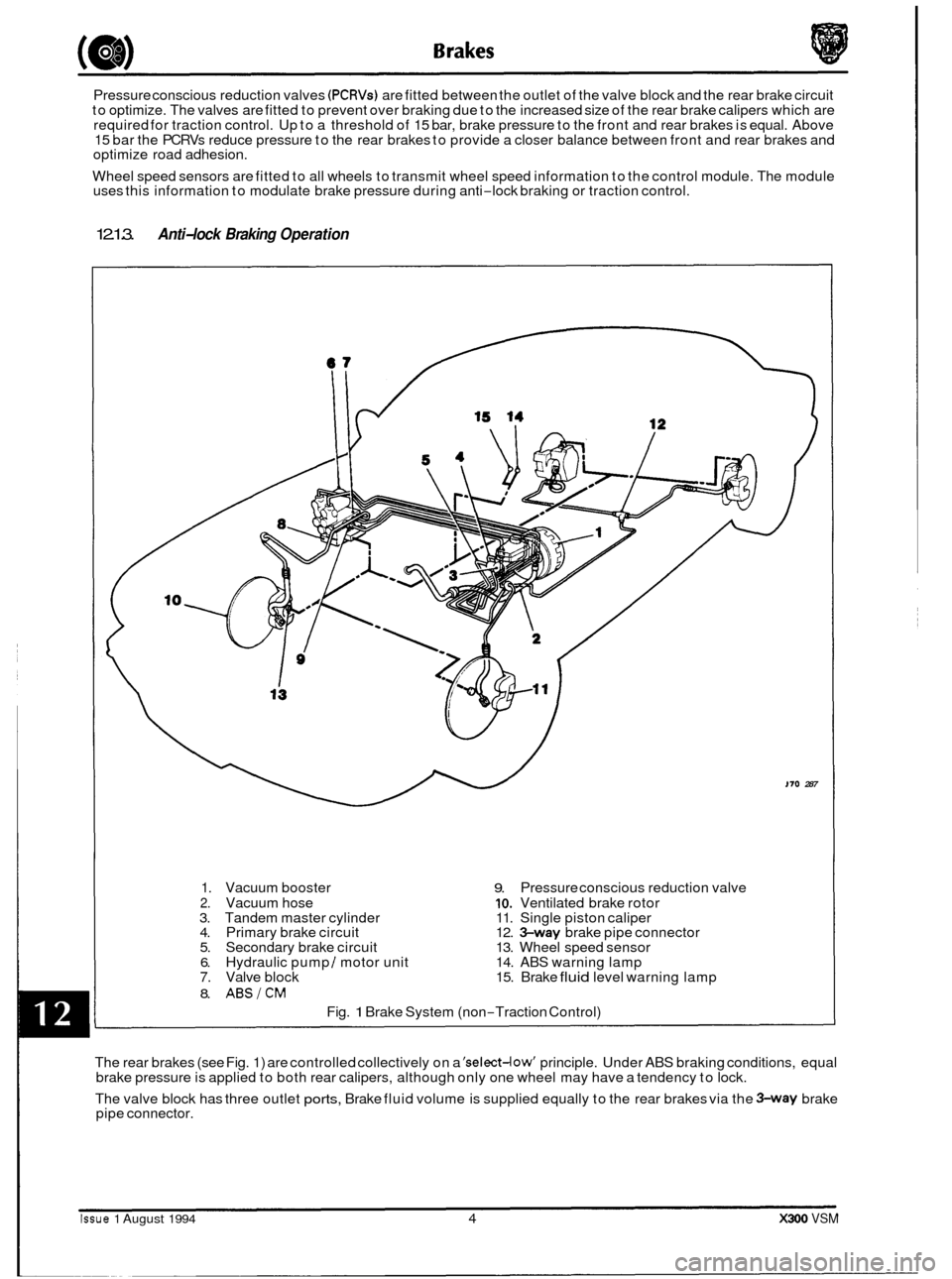
Pressure conscious reduction valves (PCRVs) are fitted between the outlet of the valve block and the rear brake circuit
to optimize. The valves are fitted to prevent over braking due to the increased size of the rear brake calipers which are
required for traction control. Up to a threshold of 15 bar, brake pressure to the front and rear brakes is equal. Above
15 bar the PCRVs reduce pressure to the rear brakes to provide a closer balance between front and rear brakes and
optimize road adhesion.
Wheel speed sensors are fitted to all wheels to transmit wheel speed information to the control module. The module
uses this information to modulate brake pressure during anti
-lock braking or traction control.
12.1.3. Anti-lock Braking Operation
170 287
1. Vacuum booster 9. Pressure conscious reduction valve
2. Vacuum hose 10. Ventilated brake rotor
3. Tandem master cylinder 11. Single piston caliper
4. Primary brake circuit 12.
%way brake pipe connector
5. Secondary brake circuit 13. Wheel speed sensor
6. Hydraulic pump I motor unit 14. ABS warning lamp 7. Valve block 15. Brake fluid level warning lamp
8. ABSICM
Fig. 1 Brake System (non-Traction Control)
The rear brakes (see Fig. 1) are controlled collectively on a
'select-low' principle. Under ABS braking conditions, equal
brake pressure is applied to both rear calipers, although only one wheel may have a tendency to lock.
The valve block has three outlet
ports, Brake fluid volume is supplied equally to the rear brakes via the %way brake
pipe connector.
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 229 of 521
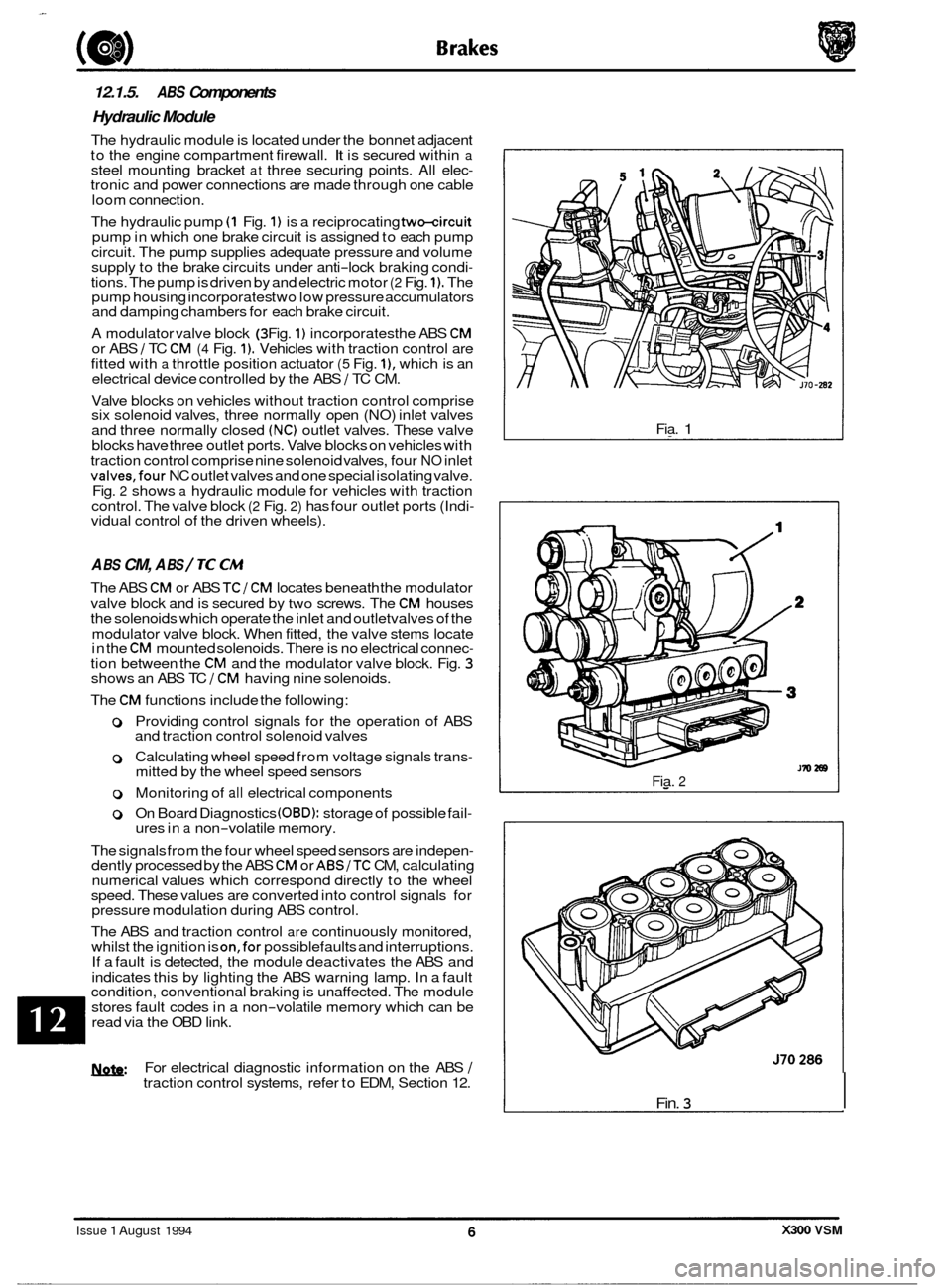
12.1.5. ABS Components
Hydraulic Module
The hydraulic module is located under the bonnet adjacent
to the engine compartment firewall. It is secured within a steel mounting bracket at three securing points. All elec- tronic and power connections are made through one cable
loom connect ion.
The hydraulic pump
(1 Fig. 1) is a reciprocating two-circuit pump in which one brake circuit is assigned to each pump
circuit. The pump supplies adequate pressure and volume
supply to the brake circuits under anti
-lock braking condi- tions. The pump is driven by and electric motor (2 Fig. 1). The
pump housing incorporates two low pressure accumulators
and damping chambers for each brake circuit.
A modulator valve block
(3 Fig. 1) incorporates the ABS CM or ABS / TC CM (4 Fig. 1). Vehicles with traction control are
fitted with a throttle position actuator (5 Fig. I), which is an
electrical device controlled by the ABS 1 TC CM.
Valve blocks on vehicles without traction control comprise
six solenoid valves, three normally open (NO) inlet valves
and three normally closed
(NC) outlet valves. These valve
blocks have three outlet ports. Valve blocks on vehicles with
traction control comprise nine solenoid valves, four
NO inlet valves,four NC outlet valves and one special isolating valve.
Fig. 2 shows a hydraulic module for vehicles with traction
control. The valve block (2 Fig. 2) has four outlet ports (Indi- vidual control of the driven wheels).
A BS CM, A BS / TC CM
The ABS CM or ABS TCI CM locates beneath the modulator
valve block and is secured by
two screws. The CM houses
the solenoids which operate the inlet and outletvalves of the
modulator valve block. When fitted, the valve stems locate
in the
CM mounted solenoids. There is no electrical connec- tion between the CM and the modulator valve block. Fig. 3 shows an ABS TC 1 CM having nine solenoids.
The
CM functions include the following:
0 Providing control signals for the operation of ABS
and traction control solenoid valves
0 Calculating wheel speed from voltage signals trans- mitted by the wheel speed sensors
0 Monitoring of all electrical components
0 On Board Diagnostics (OBD): storage of possible fail- ures in a non-volatile memory.
The signals from the four wheel speed sensors are indepen
- dently processed by the ABS CM or ABSITC CM, calculating
numerical values which correspond directly to the wheel
speed. These values are converted into control signals for
pressure modulation during ABS control.
The ABS and traction control
are continuously monitored,
whilst the ignition is on,for possiblefaults and interruptions.
If a fault is detected, the module deactivates the ABS and
indicates this by lighting the ABS warning lamp. In a fault
condition, conventional braking is unaffected. The module
stores fault codes in a non
-volatile memory which can be
read via the OBD link.
U: For electrical diagnostic information on the ABS I traction control systems, refer to EDM, Section 12. Fia.
1
Fia. 2
Fin. 3 I
J70286
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM
Page 232 of 521
Brakes (e#
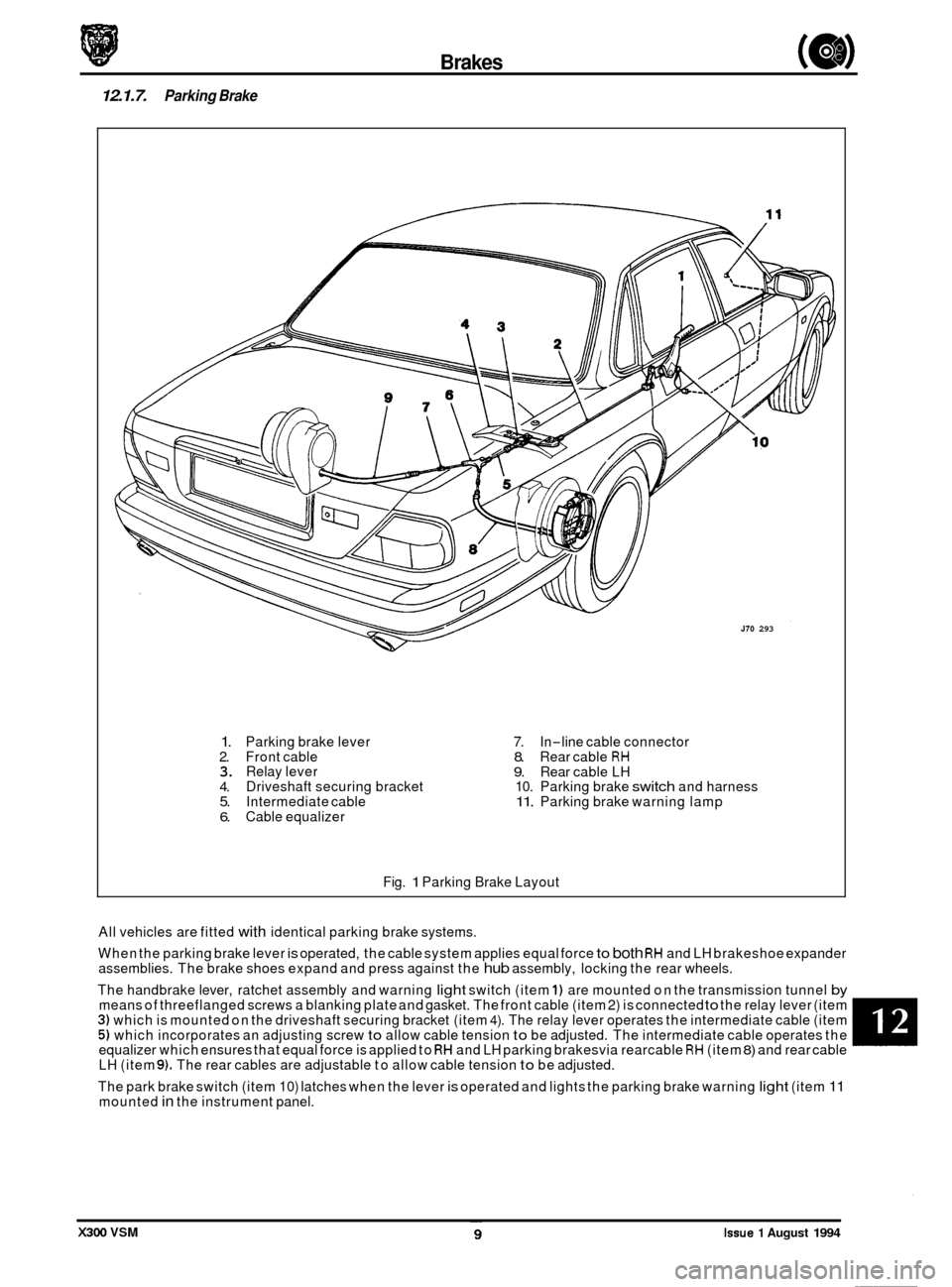
12.1.7. Parking Brake
J70 293
W
1. Parking brake lever 2. Front cable 3. Relay lever 4. Driveshaft securing bracket 5. Intermediate cable 6. Cable equalizer
7. In-line cable connector 8. Rear cable RH 9. Rear cable LH
10. Parking brake switch and harness 11. Parking brake warning lamp
Fig.
1 Parking Brake Layout
All vehicles are fitted with identical parking brake systems.
When the parking brake lever
is operated, the cable system applies equal force to both RH and LH brakeshoe expander
assemblies. The brake shoes expand and press against the hub assembly, locking the rear wheels.
The handbrake lever, ratchet assembly and warning
light switch (item 1) are mounted on the transmission tunnel by means of threeflanged screws a blanking plate and gasket. The front cable (item 2) is connected to the relay lever (item 3) which is mounted on the driveshaft securing bracket (item 4). The relay lever operates the intermediate cable (item 5) which incorporates an adjusting screw to allow cable tension to be adjusted. The intermediate cable operates the
equalizer which ensures that equal force is applied to RH and LH parking brakesvia rearcable RH (item 8) and rear cable
LH (item 9). The rear cables are adjustable to allow cable tension to be adjusted.
The park brake switch (item 10) latches when the lever
is operated and lights the parking brake warning light (item 11 mounted in the instrument panel.
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994
Page 234 of 521
Brakes
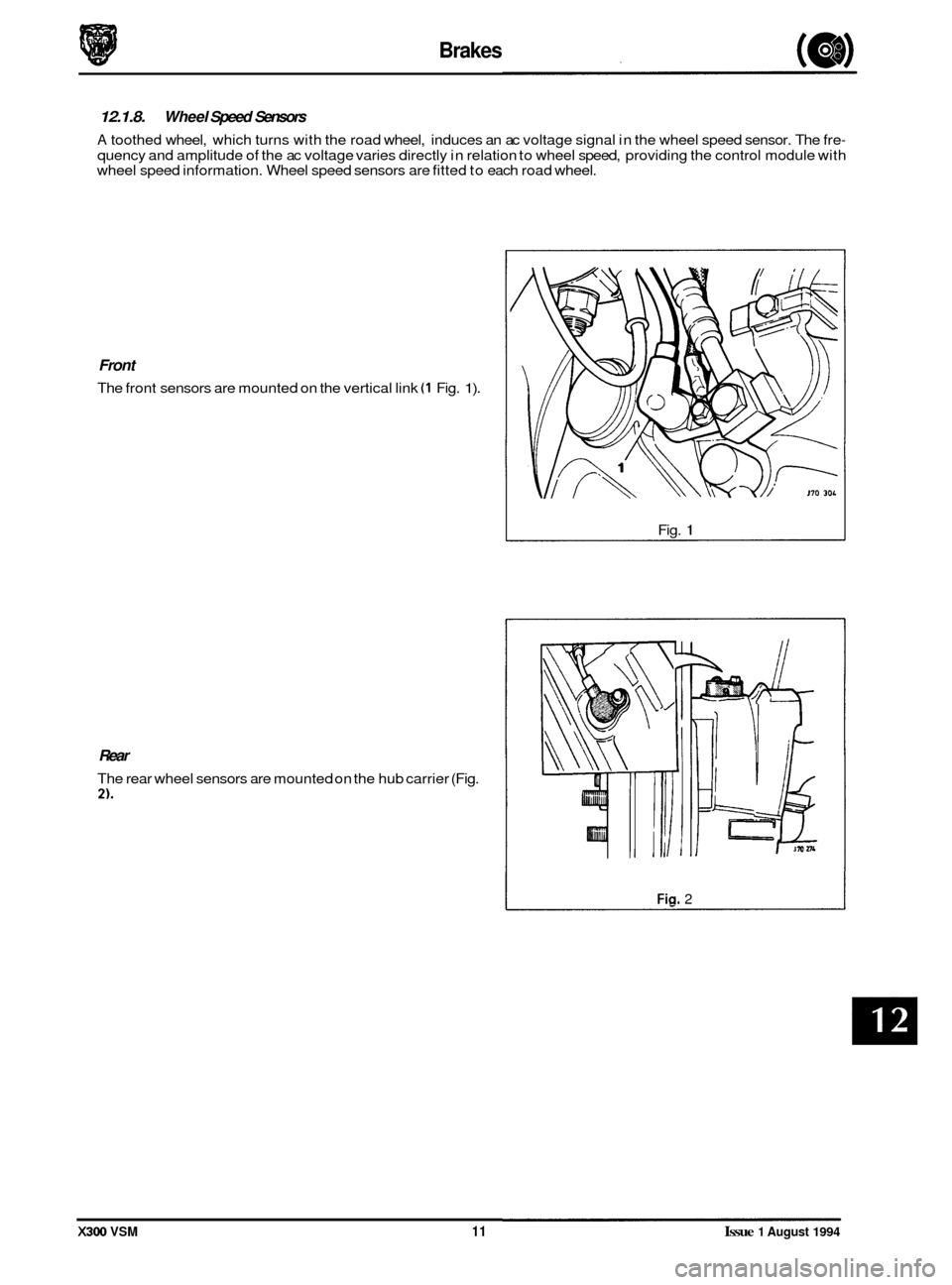
12.1.8. Wheel Speed Sensors
A toothed wheel, which turns with the road wheel, induces an ac voltage signal in the wheel speed sensor. The fre-
quency and amplitude of the ac voltage varies directly in relation to wheel speed, providing the control module with
wheel speed information. Wheel speed sensors are fitted to each road wheel.
Front
The front sensors are mounted on the vertical link (1 Fig. 1).
Fig. 1
Rear
The rear wheel sensors are mounted on the hub carrier (Fig.
2).
Fin. 2
X300 VSM 11 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 235 of 521
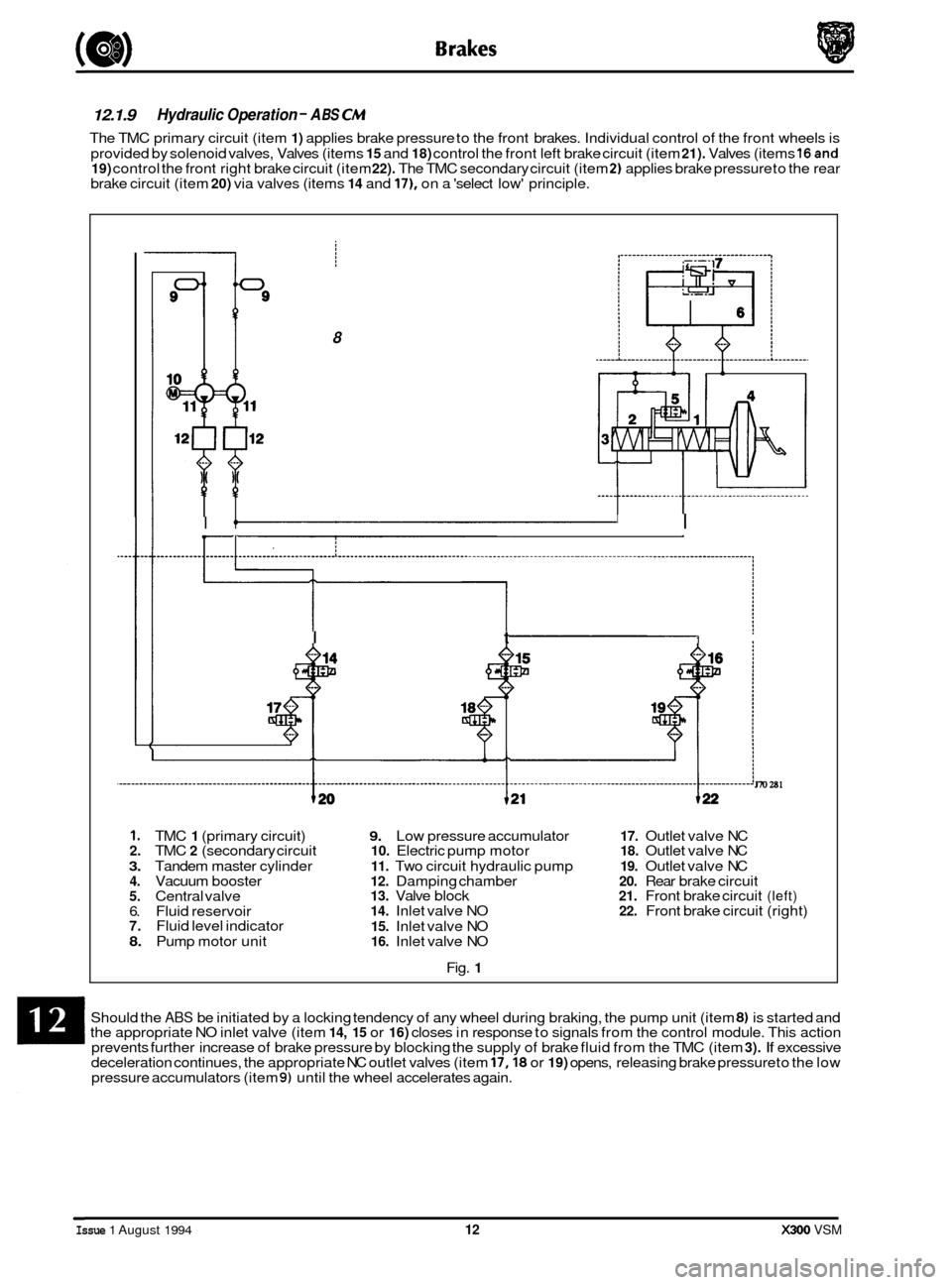
12.1.9
The TMC primary circuit (item 1) applies brake pressure to the front brakes. Individual control of the front wheels is
provided by solenoid valves, Valves (items
15 and 18) control the front left brake circuit (item 21). Valves (items 16and 19) control the front right brake circuit (item 22). The TMC secondary circuit (item 2) applies brake pressure to the rear
brake circuit (item 20) via valves (items 14 and 17), on a 'select low' principle.
Hydraulic Operation - A BS CM
8
I I + I
I t 1
'0281
1. TMC 1 (primary circuit) 9. Low pressure accumulator 17. Outlet valve NC 2. TMC 2 (secondary circuit 10. Electric pump motor 18. Outlet valve NC
3. Tandem master cylinder 11. Two circuit hydraulic pump 19. Outlet valve NC 4. Vacuum booster 12. Damping chamber 20. Rear brake circuit 5. Central valve 13. Valve block 21. Front brake circuit (left)
6. Fluid reservoir 14. Inlet valve NO 22. Front brake circuit (right) 7. Fluid level indicator 15. Inlet valve NO 8. Pump motor unit 16. Inlet valve NO
Fig.
1
Should the ABS be initiated by a locking tendency of any wheel during braking, the pump unit (item 8) is started and
the appropriate NO inlet valve (item 14, 15 or 16) closes in response to signals from the control module. This action
prevents further increase of brake pressure by blocking the supply of brake fluid from the TMC (item 3). If excessive
deceleration continues, the appropriate NC outlet valves (item 17,18 or 19) opens, releasing brake pressure to the low
pressure accumulators (item 9) until the wheel accelerates again.
Issue 1 August 1994 12 X300 VSM
Page 237 of 521
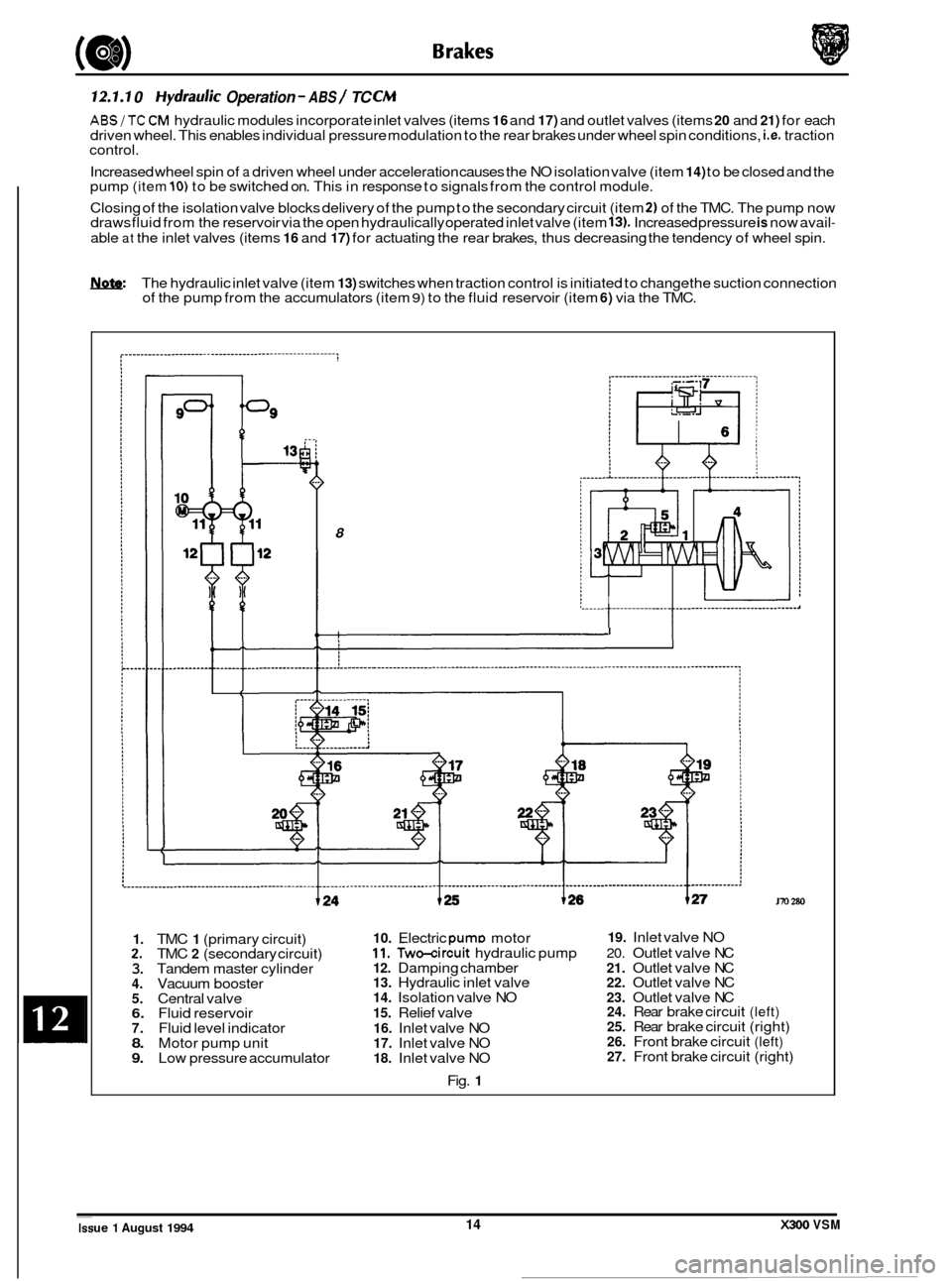
12.1.1 0 Hydrauric Operation - ABS 1 TC CM
ABS/TC CM hydraulic modules incorporate inlet valves (items 16 and 17) and outlet valves (items 20 and 21) for each
driven wheel. This enables individual pressure modulation to the rear brakes under wheel spin conditions, i.e. traction
control.
Increased wheel spin of
a driven wheel under acceleration causes the NO isolation valve (item 14) to be closed and the
pump (item 10) to be switched on. This in response to signals from the control module.
Closing of the isolation valve blocks delivery of the pump to the secondary circuit (item
2) of the TMC. The pump now
draws fluid from the reservoir via the open hydraulically operated inlet valve (item 13). Increased pressure is now avail-
able at the inlet valves (items 16 and 17) for actuating the rear brakes, thus decreasing the tendency of wheel spin.
The hydraulic inlet valve (item
13) switches when traction control is initiated to change the suction connection
of the pump from the accumulators (item 9) to the fluid reservoir (item 6) via the TMC.
1. TMC 1 (primary circuit)
8
I 1-
I
10. Electric DumD motor 19. Inlet valve NO
170 280
2. TMC 2 (secondary circuit) 11. Two-cirh hydraulic pump 20. Outlet valve NC
3. Tandem master cylinder 12. Damping chamber 21. Outlet valve NC
4. Vacuum booster 13. Hydraulic inlet valve 22. Outlet valve NC
5. Central valve 14. Isolation valve NO 23. Outlet valve NC
6. Fluid reservoir 15. Relief valve 7. Fluid level indicator 16. Inlet valve NO 8. Motor pump unit 17. Inlet valve NO 9. Low pressure accumulator 18. Inlet valve NO
Fig.
1 24.
Rear
brake circuit (left) 25. Rear brake circuit (right) 26. Front brake circuit (left) 27. Front brake circuit (right) ~
Issue 1 August 1994 14 X300 VSM
Page 238 of 521

Brakes
The pressure at the inlet valves corresponds to the opening pressure of the relief valve (item 15) incorporated in the
isolation valve. Excess brake fluid is drained to the suction side of the pump via the relief valve and returns either to
the TMC secondary circuit and on to the
fluid reservoir, or is directly drawn on by the pump.
As soon as the spinning wheel has been braked down into the normal range of wheel spin, the NO valves (items
16 or 17) close to prevent any further increase in brake pressure. Depending upon the acceleration of the wheel, the NC
valve (item
20 or 21) may open to decrease thesecondary circuit brake pressure. NCvalves (item 17 or 18) may remain
closed in orderto achieve a brake pressure holding phase. If the pressure in the secondarycircuit needs to be increased
again, the NC valve closes again (if open) and the NO valve opens, diverting the necessary volume flow. This control
action, keeps the wheel in the range of optimum slip until the spinning tendency ceases.
The NO isolation valve
(14) remains closed throughout the traction control cycle.
An actuation of the brake, sensed by the control module, causes the traction control mode to be terminated and the
isolation valve (item
14) to be opened. The TMC pressure simultaneously closes the hydraulic inlet valve (item 13) so that the pump can no longer draw fluid from it. The ABS / TC CM now operates in normal ABS mode.
m: When traction control is initiated, speed control is deactivated (if in operation) and requires re-setting after
the traction control mode has terminated. Gear shift is inhibited on automatic transmission vehicles; no down- shifts are allowed and upshifts occur at 4800 RPM.
X300 VSM 15 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 239 of 521
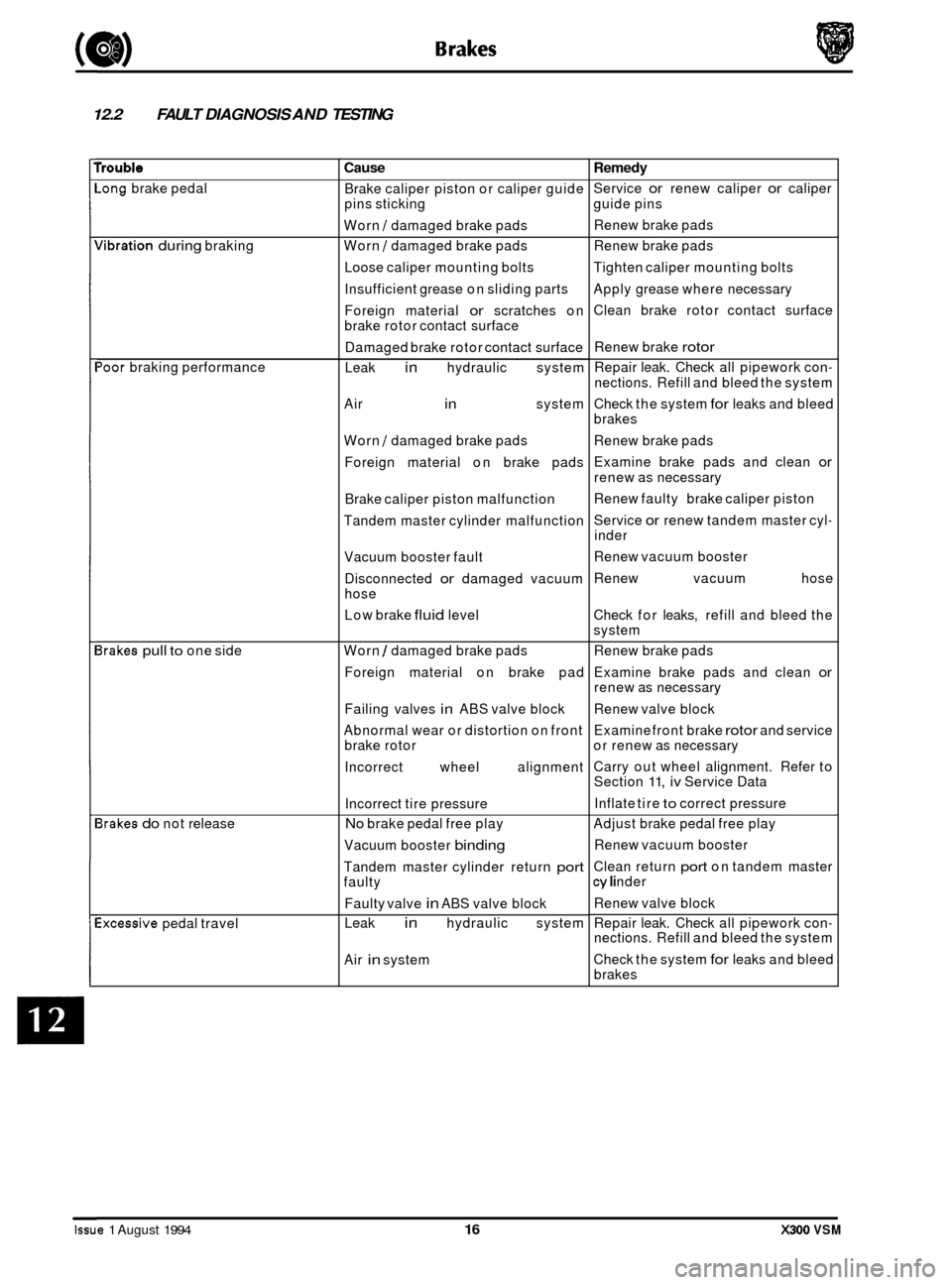
12.2 FAULT DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
rrouble
-ong brake pedal
dibration during braking
'oor braking performance
3rakes pull to one side
3rakes do not release
ixcessive pedal travel
Cause
Brake caliper piston or caliper guide
pins sticking
Worn
I damaged brake pads
Worn
1 damaged brake pads
Loose caliper mounting bolts
Insufficient grease on sliding parts
Foreign material
or scratches on
brake rotor contact surface
Damaged brake rotor contact surface
Leak
in hydraulic system
Air
in system
Worn
I damaged brake pads
Foreign material on brake pads
Brake caliper piston malfunction
Tandem master cylinder malfunction
Vacuum booster fault
Disconnected
or damaged vacuum
hose
Low brake
fluid level
Worn
I damaged brake pads
Foreign material on brake pad
Failing valves
in ABS valve block
Abnormal wear or distortion on front
brake rotor
Incorrect wheel alignment
Incorrect tire pressure
No brake pedal free play
Vacuum booster
binding
Tandem master cylinder return port faulty
Faulty valve
in ABS valve block
Leak
in hydraulic system
Air
in system
Remedy
Service or renew caliper or caliper
guide pins
Renew brake pads
Renew brake pads
Tighten caliper mounting bolts
Apply grease where necessary
Clean brake rotor contact surface
Renew brake
rotor
Repair leak. Check all pipework con-
nections. Refill and bleed the system
Check the system
for leaks and bleed
brakes
Renew brake pads
Examine brake pads and clean
or
renew as necessary
Renew faulty brake caliper piston
Service
or renew tandem master cyl- inder
Renew vacuum booster
Renew vacuum hose
Check for leaks, refill and bleed the
system
Renew brake pads
Examine brake pads and clean
or renew as necessary
Renew valve block
Examine front brake
rotor and service
or renew as necessary
Carry out wheel alignment. Refer to
Section
11, iv Service Data
Inflate tire
to correct pressure
Adjust brake pedal free play
Renew vacuum booster
Clean return
port on tandem master cy I i nder
Renew valve block
Repair leak. Check all pipework con
- nections. Refill and bleed the system
Check the system
for leaks and bleed
brakes
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 16 X300 VSM
Page 240 of 521
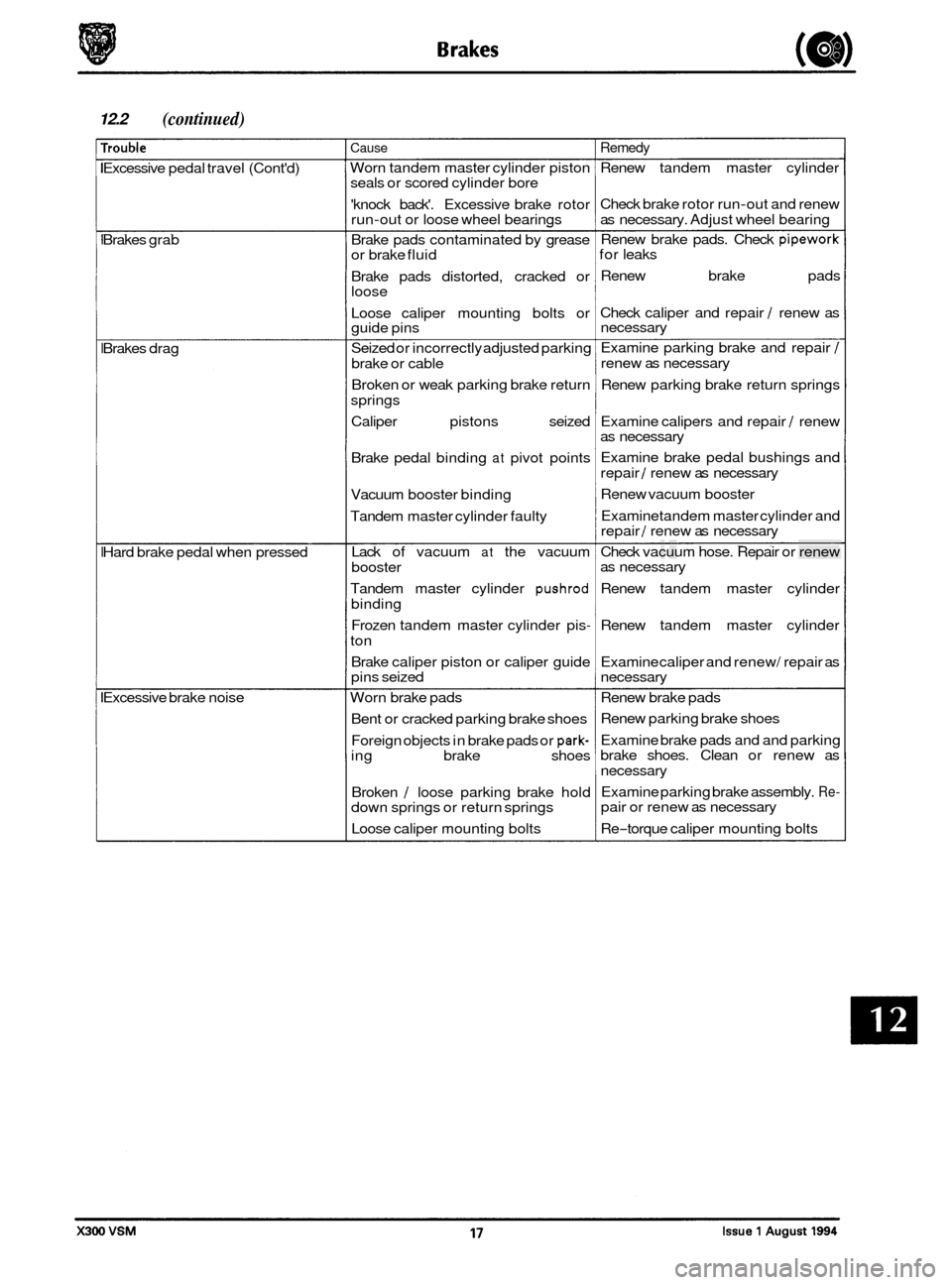
12.2 (continued)
rrouble
Excessive pedal travel (Cont'd)
Brakes grab
Brakes drag
Hard brake pedal when pressed
Excessive brake noise
Cause
Worn tandem master cylinder piston
seals or scored cylinder bore
'knock back'. Excessive brake rotor
run
-out or loose wheel bearings
Brake pads contaminated by grease
or brake fluid
Brake pads distorted, cracked or
loose
Loose caliper mounting bolts or
guide pins
Seized or incorrectly adjusted parking
brake or cable
Broken or weak parking brake return
springs
Caliper pistons seized
Brake pedal binding
at pivot points
Vacuum booster binding
Tandem master cylinder faulty
Lack of vacuum
at the vacuum
booster
Tandem master cylinder
pushrod
binding
Frozen tandem master cylinder pis
-
ton
Brake caliper piston or caliper guide
pins seized
Worn brake pads
Bent or cracked parking brake shoes
Foreign objects in brake pads or
park- ing brake shoes
Broken
/ loose parking brake hold
down springs or return springs
Loose caliper mounting bolts
Remedy
Renew tandem master cylinder
Check brake rotor run
-out and renew
as necessary. Adjust wheel bearing
Renew brake pads. Check
pipework for leaks
Renew brake pads
Check caliper and repair
/ renew as
necessary
Examine parking brake and repair
/
renew as necessary
Renew parking brake return springs
Examine calipers and repair
/ renew
as necessary
Examine brake pedal bushings and
repair
/ renew as necessary
Renew vacuum booster
Examine tandem master cylinder and
repair
/ renew as necessary
Check vacuum hose. Repair or renew
as necessary
Renew tandem master cylinder
Renew tandem master cylinder
Examine caliper and renew/ repair as
necessary
Renew brake pads
Renew parking brake shoes
Examine brake pads and and parking
brake shoes. Clean or renew as
necessary
Examine parking brake assembly.
Re- pair or renew as necessary
Re
-torque caliper mounting bolts
Page 245 of 521
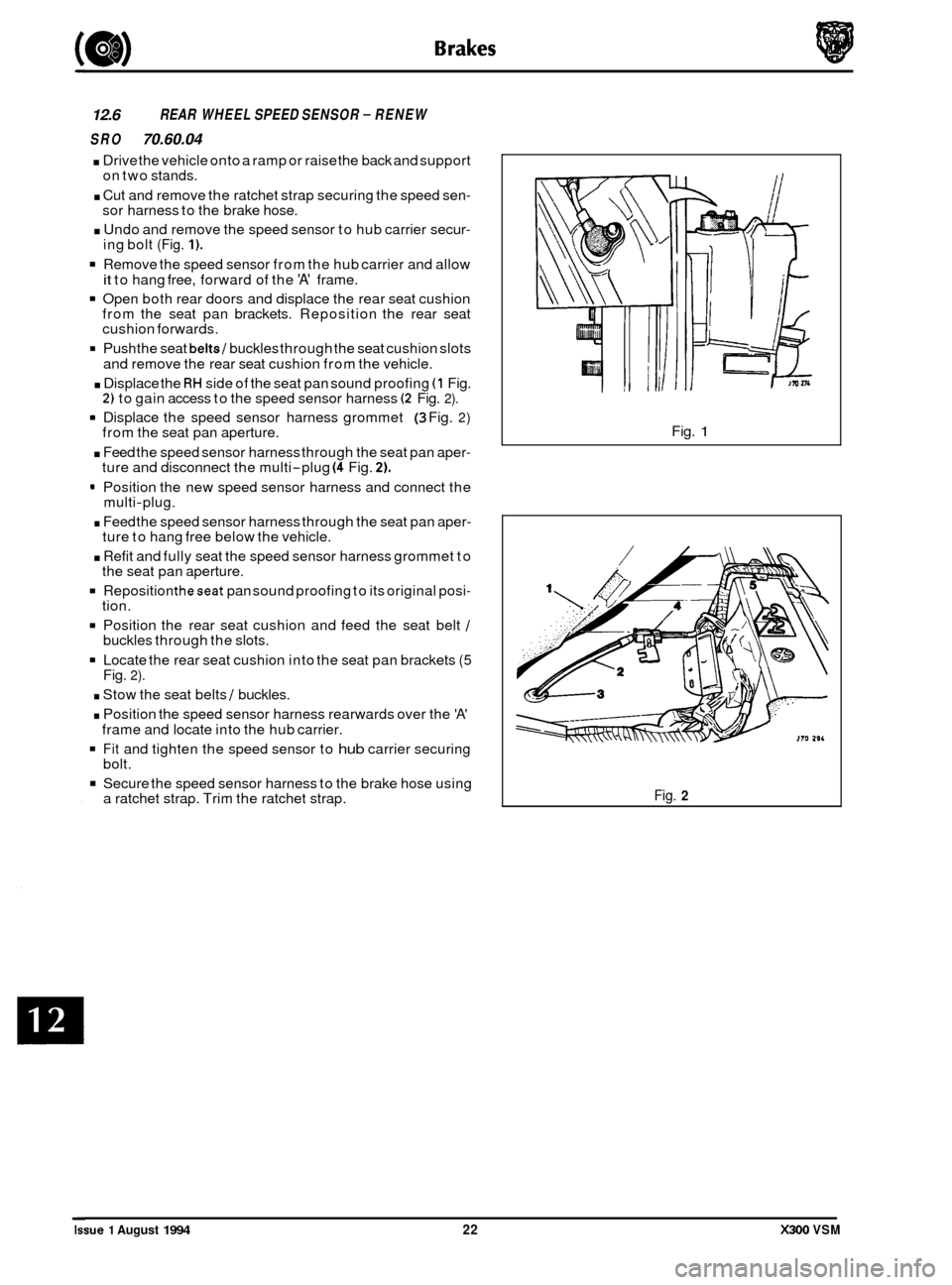
12.6 REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - RENEW
SRO
70.60.04
. Drive the vehicle onto a ramp or raise the back and support
on two stands.
. Cut and remove the ratchet strap securing the speed sen- sor harness to the brake hose.
. Undo and remove the speed sensor to hub carrier secur- ing bolt (Fig. 1).
Remove the speed sensor from the hub carrier and allow
it to hang free, forward of the 'A' frame.
Open both rear doors and displace the rear seat cushion
from the seat pan brackets. Reposition the rear seat
cushion forwards.
9 Push the seat belts/ buckles through the seat cushion slots
and remove the rear seat cushion from the vehicle.
. Displace the RH side of the seat pan sound proofing (1 Fig. 2) to gain access to the speed sensor harness (2 Fig. 2).
9 Displace the speed sensor harness grommet (3 Fig. 2) from the seat pan aperture.
. Feed the speed sensor harness through the seat pan aper- ture and disconnect the multi-plug (4 Fig. 2).
9 Position the new speed sensor harness and connect the
multi-plug.
. Feed the speed sensor harness through the seat pan aper- ture to hang free below the vehicle.
. Refit and fully seat the speed sensor harness grommet to
the seat pan aperture.
Reposition theseat pan sound proofing to its original posi- tion.
Position the rear seat cushion and feed the seat belt / buckles through the slots.
Locate the rear seat cushion into the seat pan brackets (5 Fig. 2).
. Stow the seat belts / buckles.
. Position the speed sensor harness rearwards over the 'A'
Fit and tighten the speed sensor to hub carrier securing
Secure the speed sensor harness to the brake hose using
frame
and locate into the hub carrier.
bolt.
a ratchet strap. Trim the ratchet strap. Fig.
1
Fig. 2
Issue 1 August 1994 22 X300 VSM
0
0
0