warning light JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 84 of 227
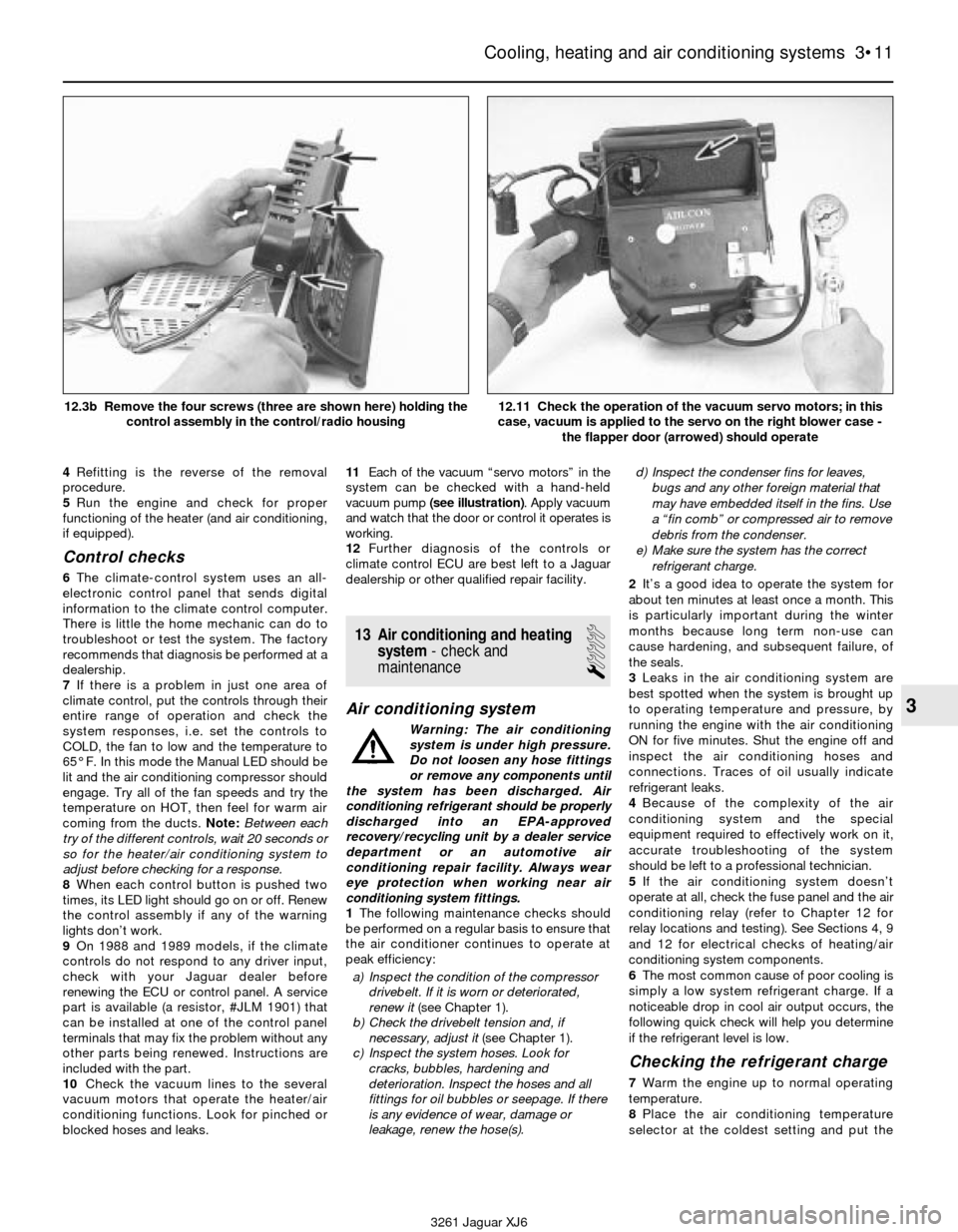
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
5Run the engine and check for proper
functioning of the heater (and air conditioning,
if equipped).
Control checks
6The climate-control system uses an all-
electronic control panel that sends digital
information to the climate control computer.
There is little the home mechanic can do to
troubleshoot or test the system. The factory
recommends that diagnosis be performed at a
dealership.
7If there is a problem in just one area of
climate control, put the controls through their
entire range of operation and check the
system responses, i.e. set the controls to
COLD, the fan to low and the temperature to
65° F. In this mode the Manual LED should be
lit and the air conditioning compressor should
engage. Try all of the fan speeds and try the
temperature on HOT, then feel for warm air
coming from the ducts. Note:Between each
try of the different controls, wait 20 seconds or
so for the heater/air conditioning system to
adjust before checking for a response.
8When each control button is pushed two
times, its LED light should go on or off. Renew
the control assembly if any of the warning
lights don’t work.
9On 1988 and 1989 models, if the climate
controls do not respond to any driver input,
check with your Jaguar dealer before
renewing the ECU or control panel. A service
part is available (a resistor, #JLM 1901) that
can be installed at one of the control panel
terminals that may fix the problem without any
other parts being renewed. Instructions are
included with the part.
10Check the vacuum lines to the several
vacuum motors that operate the heater/air
conditioning functions. Look for pinched or
blocked hoses and leaks.11Each of the vacuum “servo motors” in the
system can be checked with a hand-held
vacuum pump (see illustration). Apply vacuum
and watch that the door or control it operates is
working.
12Further diagnosis of the controls or
climate control ECU are best left to a Jaguar
dealership or other qualified repair facility.
13 Air conditioning and heating
system- check and
maintenance
1
Air conditioning system
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any hose fittings
or remove any components until
the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an EPA-approved
recovery/recycling unit by a dealer service
department or an automotive air
conditioning repair facility. Always wear
eye protection when working near air
conditioning system fittings.
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis to ensure that
the air conditioner continues to operate at
peak efficiency:
a) Inspect the condition of the compressor
drivebelt. If it is worn or deteriorated,
renew it (see Chapter 1).
b) Check the drivebelt tension and, if
necessary, adjust it (see Chapter 1).
c) Inspect the system hoses. Look for
cracks, bubbles, hardening and
deterioration. Inspect the hoses and all
fittings for oil bubbles or seepage. If there
is any evidence of wear, damage or
leakage, renew the hose(s).d) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves,
bugs and any other foreign material that
may have embedded itself in the fins. Use
a “fin comb” or compressed air to remove
debris from the condenser.
e) Make sure the system has the correct
refrigerant charge.
2It’s a good idea to operate the system for
about ten minutes at least once a month. This
is particularly important during the winter
months because long term non-use can
cause hardening, and subsequent failure, of
the seals.
3Leaks in the air conditioning system are
best spotted when the system is brought up
to operating temperature and pressure, by
running the engine with the air conditioning
ON for five minutes. Shut the engine off and
inspect the air conditioning hoses and
connections. Traces of oil usually indicate
refrigerant leaks.
4Because of the complexity of the air
conditioning system and the special
equipment required to effectively work on it,
accurate troubleshooting of the system
should be left to a professional technician.
5If the air conditioning system doesn’t
operate at all, check the fuse panel and the air
conditioning relay (refer to Chapter 12 for
relay locations and testing). See Sections 4, 9
and 12 for electrical checks of heating/air
conditioning system components.
6The most common cause of poor cooling is
simply a low system refrigerant charge. If a
noticeable drop in cool air output occurs, the
following quick check will help you determine
if the refrigerant level is low.
Checking the refrigerant charge
7Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature.
8Place the air conditioning temperature
selector at the coldest setting and put the
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•11
3
3261 Jaguar XJ6 12.3b Remove the four screws (three are shown here) holding the
control assembly in the control/radio housing
12.11 Check the operation of the vacuum servo motors; in this
case, vacuum is applied to the servo on the right blower case -
the flapper door (arrowed) should operate
Page 85 of 227

blower at the highest setting. Open the doors
(to make sure the air conditioning system
doesn’t cycle off as soon as it cools the
passenger compartment).
9With the compressor engaged - the clutch
will make an audible click and the centre of
the clutch will rotate. After the system reaches
operating temperature, feel the two pipes
connected to the evaporator at the bulkhead
(see illustration).
10The pipe (thinner tubing) leading from the
condenser outlet to the evaporator should be
cold, and the evaporator outlet line (the
thicker tubing that leads back to the
compressor) should be slightly colder (3 to
10° F). If the evaporator outlet is considerably
warmer than the inlet, the system needs a
charge. Insert a thermometer in the centre air
distribution duct while operating the air
conditioning system - the temperature of the
output air should be 35 to 40° F below the
ambient air temperature (down to approxi-
mately 40° F). If the ambient (outside) air
temperature is very high, say 110° F, the duct
air temperature may be as high as 60° F, but
generally the air conditioning is 30 to 50° F
cooler than the ambient air. If the air isn’t as
cold as it used to be, the system probably
needs a charge. Further inspection or testing
of the system is beyond the scope of the
home mechanic and should be left to a
professional.
11Inspect the sight glass (see illustration).
If the refrigerant looks foamy when running,
it’s low. When ambient temperatures are very
hot, bubbles may show in the sight glass even
with the proper amount of refrigerant. With the
proper amount of refrigerant, when the air
conditioning is turned off, the sight glass
should show refrigerant that foams, then
clears. Note:1993 and 1994 models are
equipped with R-134a refrigerant systems and
do not have a sight glass.Heating systems
12If the air coming out of the heater vents
isn’t hot, the problem could stem from any of
the following causes:
a) The thermostat is stuck open, preventing
the engine coolant from warming up
enough to carry heat to the heater core.
Renew the thermostat (see Section 3).
b) A heater hose is blocked, preventing the
flow of coolant through the heater core.
Feel both heater hoses at the bulkhead.
They should be hot. If one of them is cold,
there is an obstruction in one of the hoses
or in the heater core, or the heater control
valve is shut. Detach the hoses and back
flush the heater core with a water hose. If
the heater core is clear but circulation is
impeded, remove the two hoses and flush
them out with a water hose.
c) If flushing fails to remove the blockage
from the heater core, the core must be
renewed.(see Section 11).
13If the blower motor speed does not
correspond to the setting selected on the
blower switch, the problem could be a badfuse, circuit, control panel or climate control
computer (see Sections 10 and 12).
14If there isn’t any air coming out of the
vents:
a) Turn the ignition ON and activate the fan
control. Place your ear at the heating/air
conditioning register (vent) and listen.
Most motors are audible. Can you hear
the motor running?
b) If you can’t (and have already verified that
the blower switch and the blower motor
resistor are good), the blower motor itself
is probably bad (see Section 10).
15If the carpet under the heater core is
damp, or if antifreeze vapour or steam is
coming through the vents, the heater core is
leaking. Remove it (see Section 11) and refit a
new unit (most radiator shops will not repair a
leaking heater core).
16Inspect the drain hose from the heat/AC
assembly at the right side of the bulkhead,
make sure it is not clogged (see illustration).
If there is a humid mist coming from the
system ducts, this hose may be plugged. In
some early models, the hose may have been
pinched during assembly or blocked with
insulation or underseal.
14 Air conditioning
receiver/drier-
removal and refitting
4
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any hose fittings
or remove any components until
the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an EPA-approved recovery/
recycling unit by a dealer service depart-
ment or an automotive air conditioning
3•12 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
13.16 This drain hose (arrowed) from the
heater/air conditioning unit should be kept
clear to allow drainage of condensation
3261 Jaguar XJ6 13.9 Feel the inlet (small arrow) and outlet (large arrow) pipes at
the bulkhead leading to the air conditioning evaporator (battery
removed here for clarity only)
13.11 The sight glass (arrowed) is located on the top of the
receiver/drier, to the right of the radiator
Page 90 of 227
special electrical device that provides circuit
protection by switching off the ignition and
fuel pump upon impact in the event of vehicle
collision. Later Jaguar models are equipped
with an additional specialised inertia switch.
This later device switches OFF all ignition fed
circuits, locks the fuel filler cap, locks the boot
(only if doors are locked) and unlocks the
doors if they are locked during the accident.
All these functions are directed by the inertia
switch. The inertia switch is located behind
the left kick panel. Refer to Chapter 12 for
more information.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system includes an exhaust
manifold equipped with an exhaust oxygen
sensor, a catalytic converter, an exhaust pipe,
and a silencer.
The catalytic converter is an emission
control device added to the exhaust system to
reduce pollutants. A single-bed converter is
used in combination with a three-way
(reduction) catalyst. See Chapter 6 for more
information regarding the catalytic converter.
2 Fuel pressure relief
1
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs near the work area, and don’t
work in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or a
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
Since petrol is carcinogenic, wear latex
gloves when there’s a possibility of being
exposed to fuel, and, if you spill any fuel on
your skin, rinse it off immediately with soap
and water. Mop up any spills immediately
and do not store fuel-soaked rags wherethey could ignite. The fuel system is under
constant pressure, so, if any fuel lines are
to be disconnected, the fuel pressure in
the system must be relieved first. When
you perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses and have a
Class B type fire extinguisher on hand.
1Before servicing any fuel system
component, you must relieve the fuel pressure
to minimise the risk of fire or personal injury.
2Remove the fuel filler cap - this will relieve
any pressure built up in the tank.
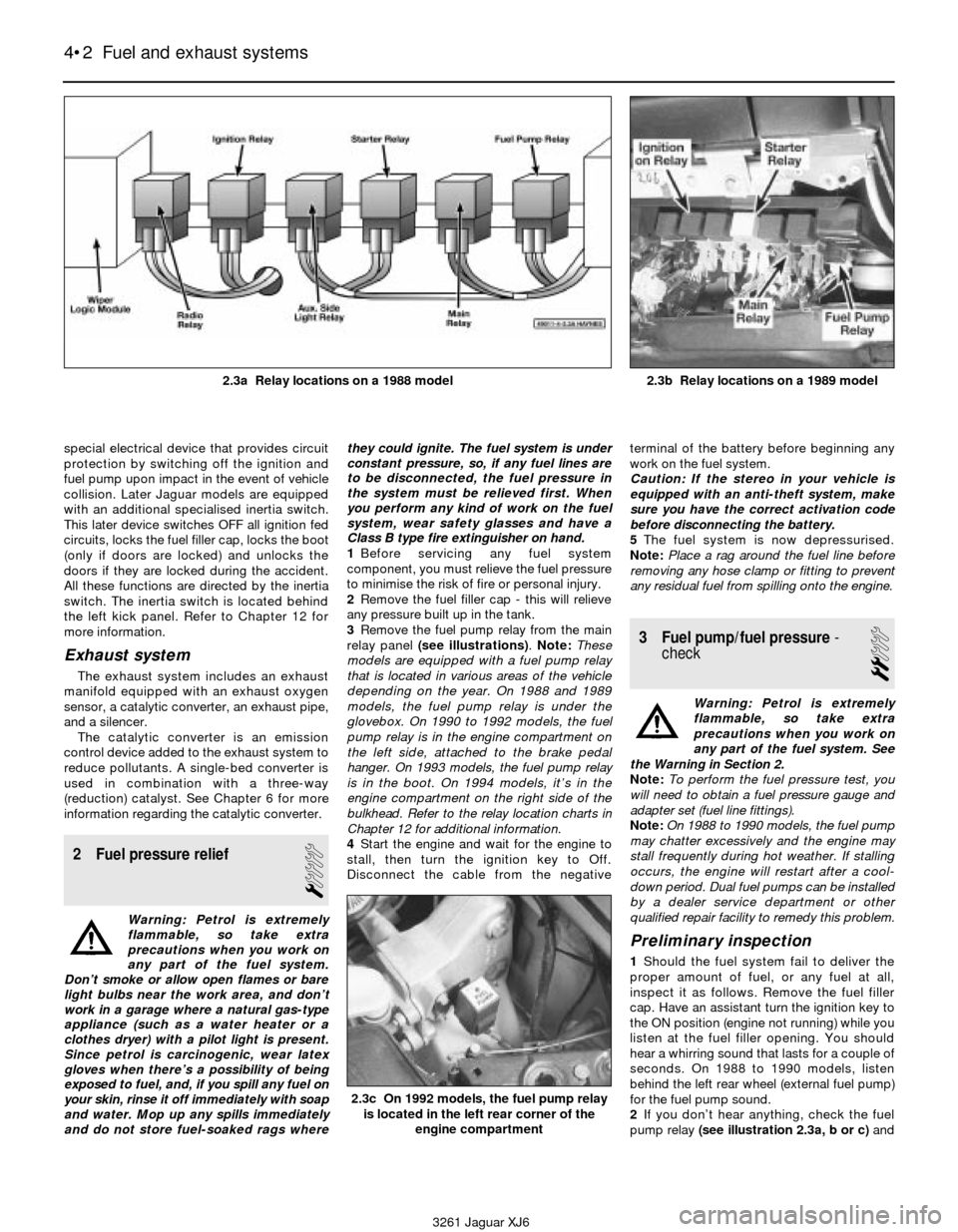
3Remove the fuel pump relay from the main
relay panel (see illustrations). Note:These
models are equipped with a fuel pump relay
that is located in various areas of the vehicle
depending on the year. On 1988 and 1989
models, the fuel pump relay is under the
glovebox. On 1990 to 1992 models, the fuel
pump relay is in the engine compartment on
the left side, attached to the brake pedal
hanger. On 1993 models, the fuel pump relay
is in the boot. On 1994 models, it’s in the
engine compartment on the right side of the
bulkhead. Refer to the relay location charts in
Chapter 12 for additional information.
4Start the engine and wait for the engine to
stall, then turn the ignition key to Off.
Disconnect the cable from the negativeterminal of the battery before beginning any
work on the fuel system.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
5The fuel system is now depressurised.
Note:Place a rag around the fuel line before
removing any hose clamp or fitting to prevent
any residual fuel from spilling onto the engine.
3 Fuel pump/fuel pressure-
check
2
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. See
the Warning in Section 2.
Note: To perform the fuel pressure test, you
will need to obtain a fuel pressure gauge and
adapter set (fuel line fittings).
Note: On 1988 to 1990 models, the fuel pump
may chatter excessively and the engine may
stall frequently during hot weather. If stalling
occurs, the engine will restart after a cool-
down period. Dual fuel pumps can be installed
by a dealer service department or other
qualified repair facility to remedy this problem.
Preliminary inspection
1Should the fuel system fail to deliver the
proper amount of fuel, or any fuel at all,
inspect it as follows. Remove the fuel filler
cap. Have an assistant turn the ignition key to
the ON position (engine not running) while you
listen at the fuel filler opening. You should
hear a whirring sound that lasts for a couple of
seconds. On 1988 to 1990 models, listen
behind the left rear wheel (external fuel pump)
for the fuel pump sound.
2If you don’t hear anything, check the fuel
pump relay (see illustration 2.3a, b or c)and
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
2.3c On 1992 models, the fuel pump relay
is located in the left rear corner of the
engine compartment
3261 Jaguar XJ6 2.3a Relay locations on a 1988 model
2.3b Relay locations on a 1989 model
Page 93 of 227
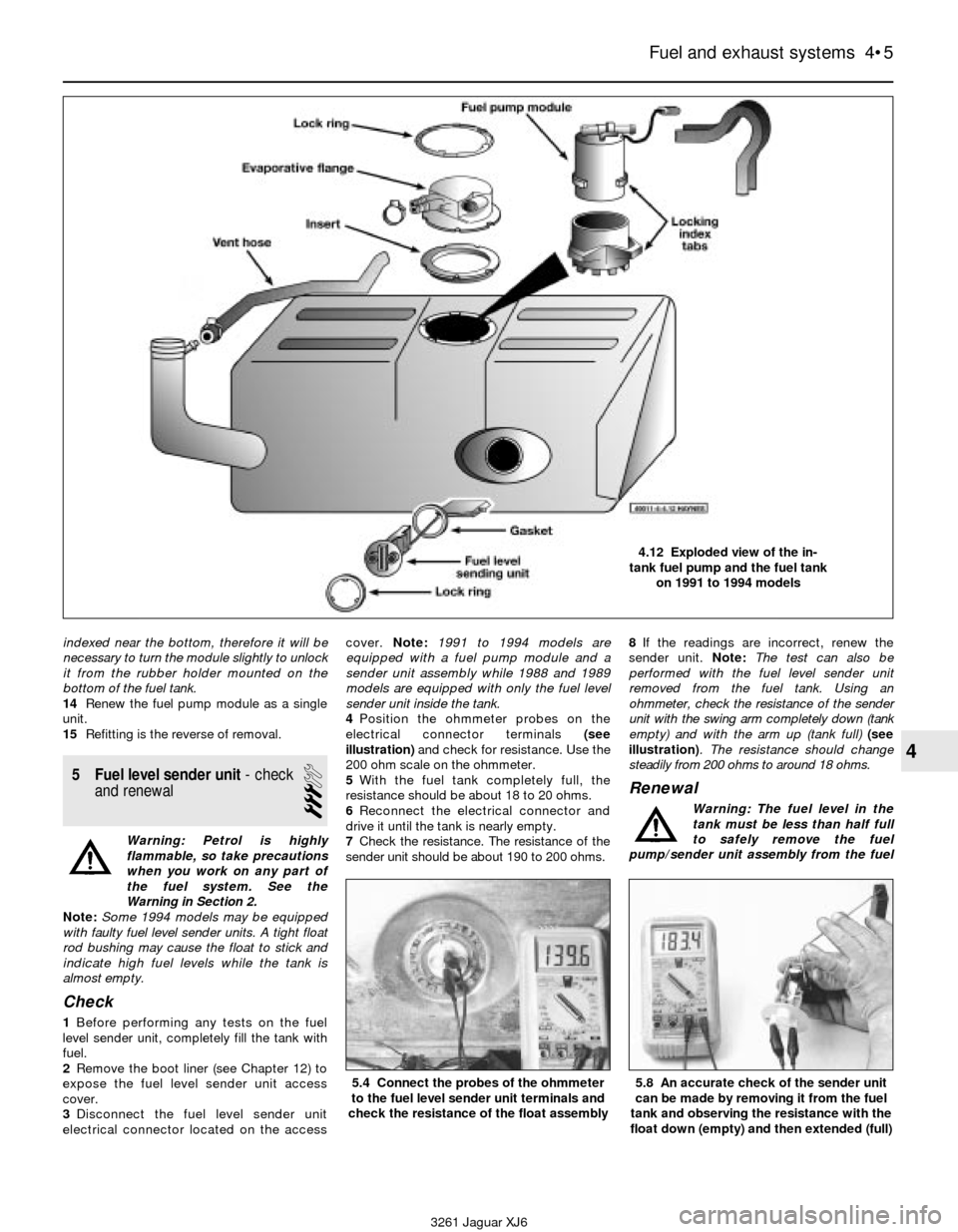
indexed near the bottom, therefore it will be
necessary to turn the module slightly to unlock
it from the rubber holder mounted on the
bottom of the fuel tank.
14Renew the fuel pump module as a single
unit.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5 Fuel level sender unit- check
and renewal
3
Warning: Petrol is highly
flammable, so take precautions
when you work on any part of
the fuel system. See the
Warning in Section 2.
Note:Some 1994 models may be equipped
with faulty fuel level sender units. A tight float
rod bushing may cause the float to stick and
indicate high fuel levels while the tank is
almost empty.
Check
1Before performing any tests on the fuel
level sender unit, completely fill the tank with
fuel.
2Remove the boot liner (see Chapter 12) to
expose the fuel level sender unit access
cover.
3Disconnect the fuel level sender unit
electrical connector located on the accesscover.Note:1991 to 1994 models are
equipped with a fuel pump module and a
sender unit assembly while 1988 and 1989
models are equipped with only the fuel level
sender unit inside the tank.
4Position the ohmmeter probes on the
electrical connector terminals (see
illustration)and check for resistance. Use the
200 ohm scale on the ohmmeter.
5With the fuel tank completely full, the
resistance should be about 18 to 20 ohms.
6Reconnect the electrical connector and
drive it until the tank is nearly empty.
7Check the resistance. The resistance of the
sender unit should be about 190 to 200 ohms.8If the readings are incorrect, renew the
sender unit. Note:The test can also be
performed with the fuel level sender unit
removed from the fuel tank. Using an
ohmmeter, check the resistance of the sender
unit with the swing arm completely down (tank
empty) and with the arm up (tank full) (see
illustration). The resistance should change
steadily from 200 ohms to around 18 ohms.
Renewal
Warning: The fuel level in the
tank must be less than half full
to safely remove the fuel
pump/sender unit assembly from the fuel
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4
5.4 Connect the probes of the ohmmeter
to the fuel level sender unit terminals and
check the resistance of the float assembly5.8 An accurate check of the sender unit
can be made by removing it from the fuel
tank and observing the resistance with the
float down (empty) and then extended (full)
3261 Jaguar XJ6
4.12 Exploded view of the in-
tank fuel pump and the fuel tank
on 1991 to 1994 models
Page 98 of 227

of these sensors and their corresponding
ECU-controlled relays are not contained
within EFI components, but are located
throughout the engine compartment. For
further information regarding the ECU and its
relationship to the engine electrical and
ignition system, see Chapter 6.
12 Electronic Fuel Injection
(EFI) system- check
2
1Check the earth wire connections for
tightness. Check all wiring and electrical
connectors that are related to the system.
Loose electrical connectors and poor grounds
can cause many problems that resemble
more serious malfunctions.
2Check to see that the battery is fully
charged, as the control unit and sensors
depend on an accurate supply voltage in
order to properly meter the fuel.
3Check the air filter element - a dirty or
partially blocked filter will severely impede
performance and economy (see Chapter 1).
4If a blown fuse is found, renew it and see if
it blows again. If it does, search for a shorted
wire in the harness related to the system.
5Check the air intake duct from the MAF
sensor to the intake manifold for leaks, which
will result in an excessively lean mixture. Also
check the condition of the vacuum hoses
connected to the intake manifold.
6Remove the air intake duct from the throttle
body and check for carbon and residue build-
up. If it’s dirty, clean with aerosol carburettor
cleaner (make sure the can says it’s safe for
use with oxygen sensors and catalytic
converters) and a toothbrush.
7With the engine running, place a
stethoscope against each injector, one at a
time, and listen for a clicking sound, indicating
operation (see illustration).8If there is a problem with an injector,
purchase a special injector test light (noid
light) and refit it into the injector electrical
connector (see illustration). Start the engine
and make sure that each injector connector
flashes the noid light. This will test for the
proper voltage signal to the injector.Caution:
If the engine will not start and the noid
light indicates that each injector is
receiving the proper signal, there is a good
possibility that the injector(s) is stuck open
and allowing fuel into the combustion
chamber in excessive amounts. If the spark
plugs are fouled, detach the primary (low
voltage) wires from the ignition coil, disable
the fuel pump by removing the fuel pump
relay (see Section 2), remove the spark plugs
and crank the engine over. If fuel sprays from
the spark plug holes, the engine is flooded
and the fuel must be removed from the
combustion chambers.
9With the engine OFF and the fuel injector
electrical connectors disconnected, measure
the resistance of each injector (see
illustration). Each injector should measure
about 2.0 to 3.0 ohms. If not, the injector is
probably faulty.10The remainder of the system checks
should be left to a Jaguar service department
or other qualified repair workshop, as there is
a chance that the control unit may be
damaged if not performed properly.
13 Electronic Fuel Injection
(EFI) system- component
check and renewal
3
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. See
the Warning in Section 2.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Throttle body
Check
1Verify that the throttle linkage operates
smoothly.
2Start the engine, detach each vacuum hose
and, using your finger, check the vacuum at
each port on the throttle body with the engine
at idle and above idle. The vacuum available
from the throttle body is ported. Raise the
engine rpm and watch as vacuum increases.
It may be necessary to use a vacuum gauge.
Refer to Chapter 2B for additional information
concerning vacuum checks.
Renewal
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before
beginning this procedure.
3Detach the cable from the negative terminal
of the battery (see the Cautionat the
beginning of this Section).
4Drain the radiator (see Chapter 1).
4•10 Fuel and exhaust systems
12.9 Using an ohmmeter, measure the
resistance across both terminals
of the injector
3261 Jaguar XJ6 12.7 Use a stethoscope or a screwdriver to determine if the
injectors are working properly - they should make a steady
clicking sound that rises and falls with engine speed changes
12.8 Refit the “noid” light into the fuel injector electrical
connector and check to see that it blinks with the engine running
Page 104 of 227

same dimensions, amperage rating, cold
cranking rating, etc. as the original.
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
4 Battery cables-
check and renewal
1
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
1Periodically inspect the entire length of
each battery cable for damage, cracked or
burned insulation and corrosion. Poor battery
cable connections can cause starting
problems and decreased engine performance.
2Check the cable-to-terminal connections at
the ends of the cables for cracks, loose wire
strands and corrosion. The presence of white,
fluffy deposits under the insulation at the
cable terminal connection is a sign that the
cable is corroded and should be renewed.
Check the terminals for distortion, missing
mounting bolts and corrosion.
3When removing the cables, always
disconnect the negative cable first and hook it
up last or the battery may be shorted by the
tool used to loosen the cable clamps. Even if
only the positive cable is being renewed, be
sure to disconnect the negative cable from
the battery first (see Chapter 1 for further
information regarding battery cable removal).
4Disconnect the cables from the battery,
then trace each of them to their opposite ends
and detach them from the starter solenoid
and earth terminals. Note the routing of each
cable to ensure correct refitting.
5If you are replacing either or both of the old
cables, take them with you when buying new
items. It is vitally important that you replace
the cables with identical parts. Cables have
characteristics that make them easy to
identify: positive cables are usually red, larger
in cross-section and have a larger diameter
battery post clamp; earth cables are usually
black, smaller in cross-section and have a
slightly smaller diameter clamp for the
negative post.
6Clean the threads of the solenoid or earth
connection with a wire brush to remove rust
and corrosion. Apply a light coat of battery
terminal corrosion inhibitor, or petroleum jelly,
to the threads to prevent future corrosion.
7Attach the cable to the solenoid or earth
connection and tighten the mounting nut/bolt
securely.
8Before connecting a new cable to the
battery, make sure that it reaches the battery
post without having to be stretched.
9Connect the positive cable first, followed by
the negative cable.
5 Ignition system- general
information and precautions
1All models are equipped with a computerised
ignition system. The ignition system consists of
the ignition coil, the crankshaft position sensor,
the amplifier and the electronic control unit
(ECU). The ignition ECU controls the ignition
timing and advance characteristics for the
engine. The ignition timing is not adjustable,
therefore, changing the position of the distributor
will not change the timing in any way. Note:In
the event the distributor must be removed from
the engine, be sure to follow the precautions
described in Section 9 and mark the engine and
distributor with paint to ensure correct refitting. If
the distributor is not marked and Ihe crankshaft is
turned while the distributor is out of the engine,
have the distributor installed by a dealer service
department. The distributor must be installed
using a special alignment tool.
2The distributor is driven by the intermediate
shaft which also drives the power steering pump.
The crankshaft position sensor is located on the
front timing cover. It detects crank position by
pulsing an electronic signal to the ECU. This
signal is sent to the ECU to provide ignition
timing specifications.
3The computerised ignition system provides
complete control of the ignition timing by
determining the optimum timing in response to
engine speed, coolant temperature, throttle
position and vacuum pressure in the intake
manifold. These parameters are relayed to the
ECU by the crankshaft position sensor, throttle
potentiometer, coolant temperature sensor and
MAF sensor. Ignition timing is altered during
warm-up, idling and warm running conditions by
the ECU. This electronic ignition system also
consists of the ignition switch, battery, coil,
distributor, spark plug leads and spark plugs.
4Refer to a dealer parts department or car
accessory outlet for any questions concerning
the availability of the distributor parts and
assemblies. Testing the crankshaft position
sensor is covered in Chapter 6.
5When working on the ignition system, take
the following precautions:
a) Do not keep the ignition switch on for
more than 10 seconds if the engine will
not start.
b) Always connect a tachometer in
accordance with the manufacturer’s
instructions. Some tachometers may be
incompatible with this ignition system.
Consult a dealer service department
before buying a tachometer for use with
this vehicle.
c) Never allow the ignition coil terminals to
touch earth. Earthing the coil could result
in damage to the igniter and/or the
ignition coil.
d) Do not disconnect the battery when the
engine is running.
6 Ignition system- check
2
Warning: Because of the high
voltage generated by the
ignition system, extreme care
should be taken when working
on the ignition components. This not only
includes the amplifier, coil, distributor and
spark plug leads, but related components
such as connectors, tachometer and other
test equipment also.
1With the ignition switch turned to the “ON”
position, a “Battery” light or an “Oil Pressure”
light is a basic check for ignition and battery
supply to the ECU.
2Check all ignition wiring connections for
tightness, cuts, corrosion or any other signs of a
bad connection.
3Use a calibrated ignition tester to verify
adequate secondary voltage (25,000 volts) at
each spark plug (see illustration). A faulty or
poor connection at that plug could also result in a
misfire. Also, check for carbon deposits inside
the spark plug boot.
4Check for carbon tracking on the coil. If
carbon tracking is evident, renew the coil and be
sure the secondary wires related to that coil are
clean and tight. Excessive wire resistance or
faulty connections could damage the coil.
5Check for battery voltage to the ignition coil
(see illustration). If battery voltage is available,
check the ignition coil primary and secondary
resistance (see Section 8).
6Check the distributor cap for any obvious
signs of carbon tracking, corroded terminals or
cracks (see Chapter 1).
7Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance of
the spark plug leads. Each wire should measure
less than 25,000 ohms.
8Check for battery voltage to the ignition
amplifier (see Section 7). If battery voltage does
not exist, check the circuit from the ignition
switch (refer to the wiring diagrams at the end of
Chapter 12).
5•2 Engine electrical systems
6.3 To use a calibrated ignition tester
(available at most car accessory outlets),
remove a plug lead from a cylinder,
connect the spark plug boot to the tester
and clip the tester to a good earth - if there
is enough voltage to fire the plug, sparks
will be clearly visible between the
electrode tip and the tester body
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 105 of 227
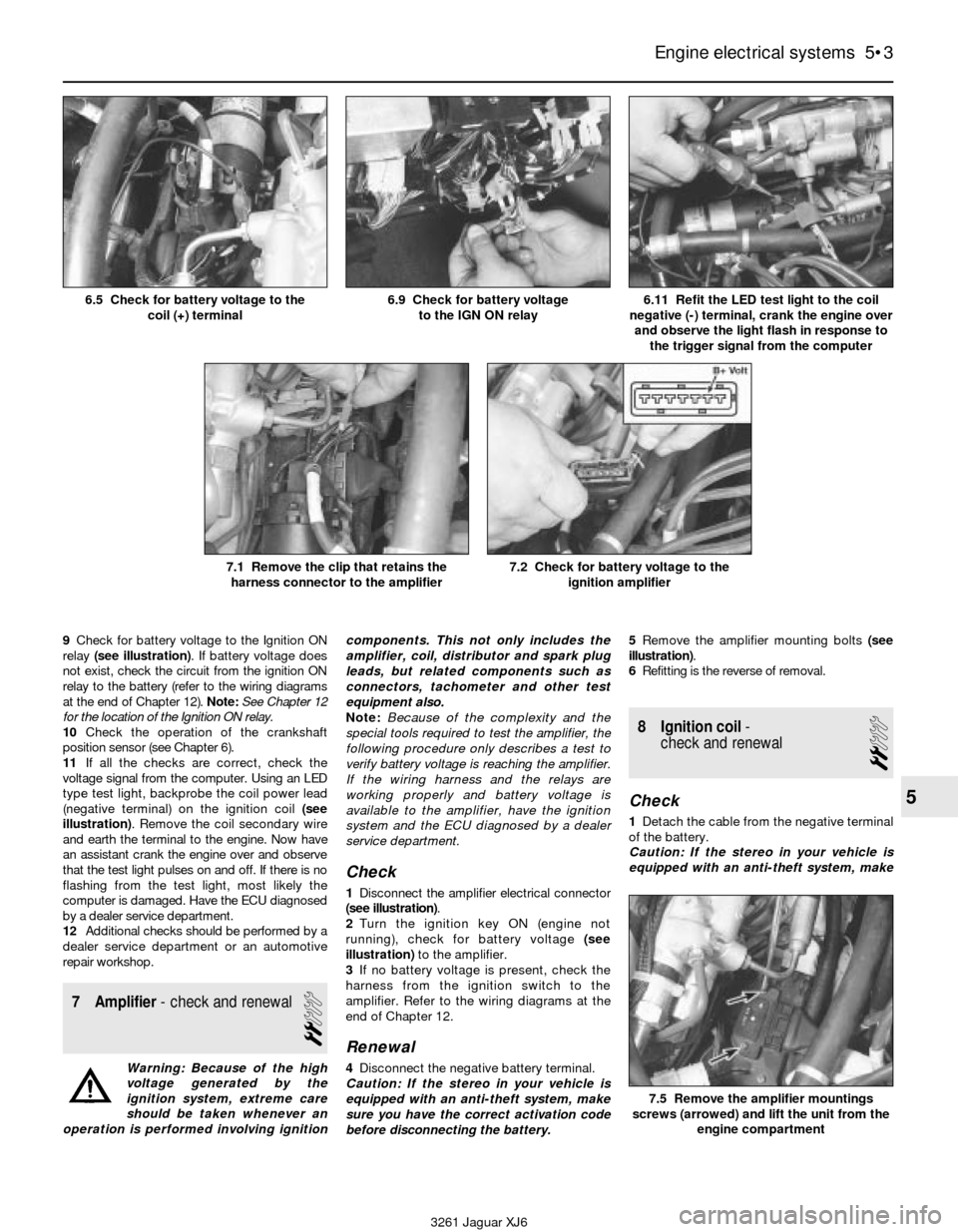
9Check for battery voltage to the Ignition ON
relay (see illustration). If battery voltage does
not exist, check the circuit from the ignition ON
relay to the battery (refer to the wiring diagrams
at the end of Chapter 12). Note:See Chapter 12
for the location of the Ignition ON relay.
10Check the operation of the crankshaft
position sensor (see Chapter 6).
11If all the checks are correct, check the
voltage signal from the computer. Using an LED
type test light, backprobe the coil power lead
(negative terminal) on the ignition coil (see
illustration). Remove the coil secondary wire
and earth the terminal to the engine. Now have
an assistant crank the engine over and observe
that the test light pulses on and off. If there is no
flashing from the test light, most likely the
computer is damaged. Have the ECU diagnosed
by a dealer service department.
12Additional checks should be performed by a
dealer service department or an automotive
repair workshop.
7 Amplifier- check and renewal
2
Warning: Because of the high
voltage generated by the
ignition system, extreme care
should be taken whenever an
operation is performed involving ignitioncomponents. This not only includes the
amplifier, coil, distributor and spark plug
leads, but related components such as
connectors, tachometer and other test
equipment also.
Note:Because of the complexity and the
special tools required to test the amplifier, the
following procedure only describes a test to
verify battery voltage is reaching the amplifier.
If the wiring harness and the relays are
working properly and battery voltage is
available to the amplifier, have the ignition
system and the ECU diagnosed by a dealer
service department.
Check
1Disconnect the amplifier electrical connector
(see illustration).
2Turn the ignition key ON (engine not
running), check for battery voltage (see
illustration) to the amplifier.
3If no battery voltage is present, check the
harness from the ignition switch to the
amplifier. Refer to the wiring diagrams at the
end of Chapter 12.
Renewal
4Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.5Remove the amplifier mounting bolts (see
illustration).
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
8 Ignition coil-
check and renewal
2
Check
1Detach the cable from the negative terminal
of the battery.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
6.5 Check for battery voltage to the
coil (+) terminal6.9 Check for battery voltage
to the IGN ON relay6.11 Refit the LED test light to the coil
negative (-) terminal, crank the engine over
and observe the light flash in response to
the trigger signal from the computer
7.1 Remove the clip that retains the
harness connector to the amplifier7.2 Check for battery voltage to the
ignition amplifier
7.5 Remove the amplifier mountings
screws (arrowed) and lift the unit from the
engine compartment
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 107 of 227
Refitting
7Insert the distributor into the engine in
exactly the same relationship to the block that
it was in when removed.
8If the distributor does not seat completely,
recheck the alignment marks between the
distributor base and the block to verify that
the distributor is in the same position it was in
before removal. Also check the rotor to see if
it’s aligned with the mark you made on the
edge of the distributor base.
9Refit the distributor hold-down bolt(s).
10The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
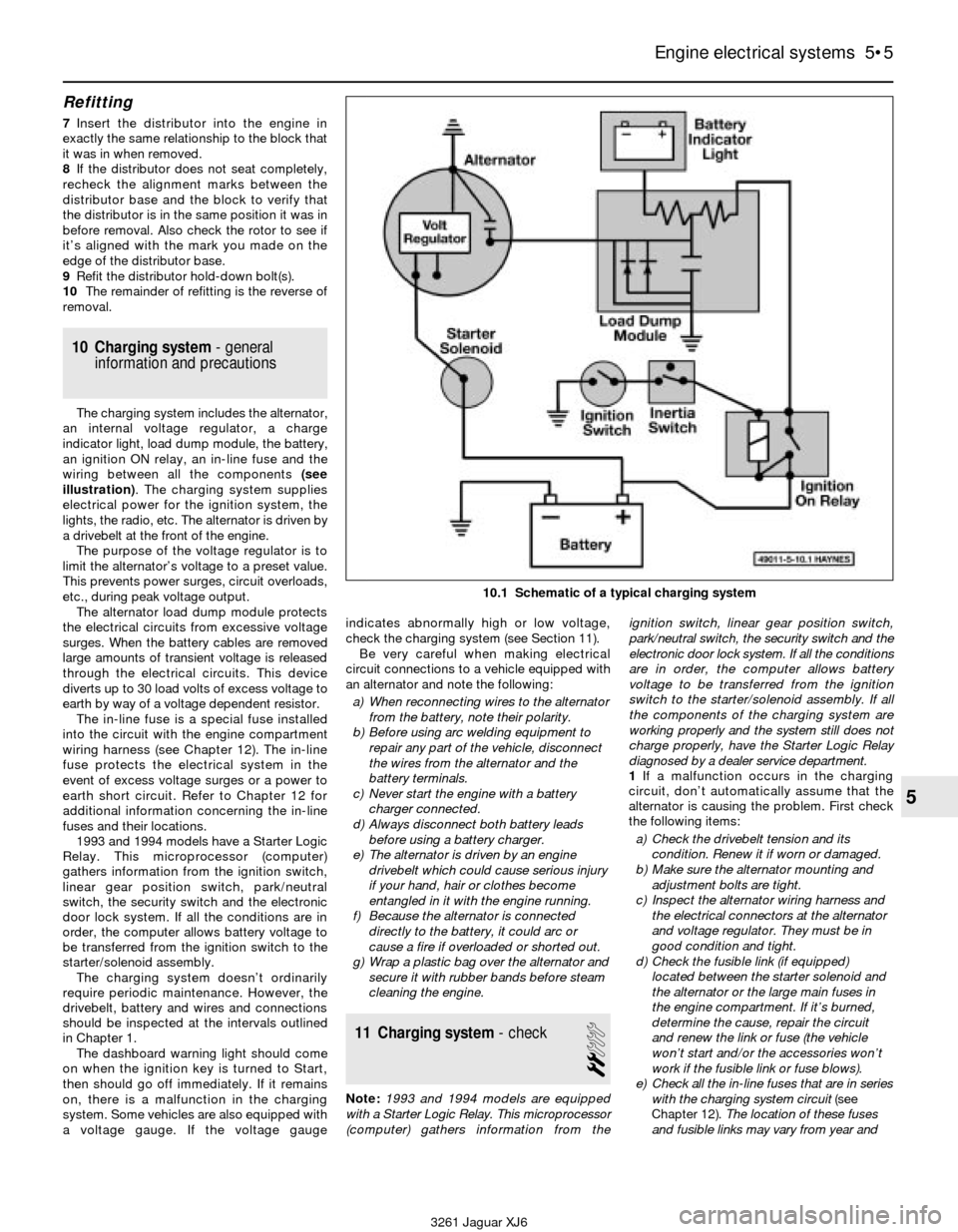
10 Charging system- general
information and precautions
The charging system includes the alternator,
an internal voltage regulator, a charge
indicator light, load dump module, the battery,
an ignition ON relay, an in-line fuse and the
wiring between all the components (see
illustration). The charging system supplies
electrical power for the ignition system, the
lights, the radio, etc. The alternator is driven by
a drivebelt at the front of the engine.
The purpose of the voltage regulator is to
limit the alternator’s voltage to a preset value.
This prevents power surges, circuit overloads,
etc., during peak voltage output.
The alternator load dump module protects
the electrical circuits from excessive voltage
surges. When the battery cables are removed
large amounts of transient voltage is released
through the electrical circuits. This device
diverts up to 30 load volts of excess voltage to
earth by way of a voltage dependent resistor.
The in-line fuse is a special fuse installed
into the circuit with the engine compartment
wiring harness (see Chapter 12). The in-line
fuse protects the electrical system in the
event of excess voltage surges or a power to
earth short circuit. Refer to Chapter 12 for
additional information concerning the in-line
fuses and their locations.
1993 and 1994 models have a Starter Logic
Relay. This microprocessor (computer)
gathers information from the ignition switch,
linear gear position switch, park/neutral
switch, the security switch and the electronic
door lock system. If all the conditions are in
order, the computer allows battery voltage to
be transferred from the ignition switch to the
starter/solenoid assembly.
The charging system doesn’t ordinarily
require periodic maintenance. However, the
drivebelt, battery and wires and connections
should be inspected at the intervals outlined
in Chapter 1.
The dashboard warning light should come
on when the ignition key is turned to Start,
then should go off immediately. If it remains
on, there is a malfunction in the charging
system. Some vehicles are also equipped with
a voltage gauge. If the voltage gaugeindicates abnormally high or low voltage,
check the charging system (see Section 11).
Be very careful when making electrical
circuit connections to a vehicle equipped with
an alternator and note the following:
a) When reconnecting wires to the alternator
from the battery, note their polarity.
b) Before using arc welding equipment to
repair any part of the vehicle, disconnect
the wires from the alternator and the
battery terminals.
c) Never start the engine with a battery
charger connected.
d) Always disconnect both battery leads
before using a battery charger.
e) The alternator is driven by an engine
drivebelt which could cause serious injury
if your hand, hair or clothes become
entangled in it with the engine running.
f) Because the alternator is connected
directly to the battery, it could arc or
cause a fire if overloaded or shorted out.
g) Wrap a plastic bag over the alternator and
secure it with rubber bands before steam
cleaning the engine.
11 Charging system- check
2
Note:1993 and 1994 models are equipped
with a Starter Logic Relay. This microprocessor
(computer) gathers information from theignition switch, linear gear position switch,
park/neutral switch, the security switch and the
electronic door lock system. If all the conditions
are in order, the computer allows battery
voltage to be transferred from the ignition
switch to the starter/solenoid assembly. If all
the components of the charging system are
working properly and the system still does not
charge properly, have the Starter Logic Relay
diagnosed by a dealer service department.
1If a malfunction occurs in the charging
circuit, don’t automatically assume that the
alternator is causing the problem. First check
the following items:
a) Check the drivebelt tension and its
condition. Renew it if worn or damaged.
b) Make sure the alternator mounting and
adjustment bolts are tight.
c) Inspect the alternator wiring harness and
the electrical connectors at the alternator
and voltage regulator. They must be in
good condition and tight.
d) Check the fusible link (if equipped)
located between the starter solenoid and
the alternator or the large main fuses in
the engine compartment. If it’s burned,
determine the cause, repair the circuit
and renew the link or fuse (the vehicle
won’t start and/or the accessories won’t
work if the fusible link or fuse blows).
e) Check all the in-line fuses that are in series
with the charging system circuit (see
Chapter 12).The location of these fuses
and fusible links may vary from year and
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
10.1 Schematic of a typical charging system
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 112 of 227

components identified. When servicing the
engine or emissions systems, the VECI label
in your particular vehicle should always be
checked for up-to-date information.
2 Electronic control system
and ECU
General description
Note: These models are susceptible to ECU
damage if water is allowed to build up in the
front cowl drain and overspill into the dash
area near the computer. Inspect and clear the
front cowl drain as a regular maintenance item
to keep the water draining properly. Remove
the duckbill-type rubber hose and inspect it
for clogging, collapsing or deterioration.
1The Lucas LH Engine Management system
controls the fuel injection system by means of
a microcomputer known as the Electronic
Control unit (ECU).
2The ECU receives signals from various
sensors which monitor changing engine
operating conditions such as intake air mass,
intake air temperature, coolant temperature,
engine rpm, acceleration/deceleration,
exhaust oxygen content, etc. These signals
are utilised by the ECU to determine the
correct injection duration.
3The system is analogous to the central
nervous system in the human body: The
sensors (nerve endings) constantly relay
signals to the ECU (brain), which processes
the data and, if necessary, sends out a
command to change the operating
parameters of the engine (body).
4Here’s a specific example of how one
portion of this system operates: An oxygen
sensor, located in the exhaust manifold,
constantly monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. If the percentage of oxygen in
the exhaust gas is incorrect, an electrical
signal is sent to the ECU. The ECU takes this
information, processes it and then sends a
command to the fuel injection system telling it
to change the air/fuel mixture. This happens in
a fraction of a second and it goes on
continuously when the engine is running. The
end result is an air/fuel mixture ratio which is
constantly maintained at a predetermined
ratio, regardless of driving conditions.
5In the event of a sensor malfunction, a
backup circuit will take over to provide
driveability until the problem is identified and
fixed.
Precautions
6Follow these steps:
a) Always disconnect the power by either
turning off the ignition switch or
disconnecting the battery terminals before
removing electrical connectors.
Warning: Later models are
equipped with airbags. To
prevent accidental deployment ofthe airbag, which could cause personal
injury, DO NOT work in the vicinity of the
steering column or instrument panel. The
manufacturer recommends that, on airbag
equipped models, the following procedure
should be left to a dealer service
department or other repair workshop
because of the special tools and techniques
required to disable the airbag system.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
b) When refitting a battery, be particularly
careful to avoid reversing the positive and
negative battery cables. Also, make sure
the ignition key is in the Off position when
connecting or disconnecting the battery.
c) Do not subject EFI components,
emissions-related components or the
ECU to severe impact during removal or
refitting.
d) Do not be careless during fault diagnosis.
Even slight terminal contact can invalidate
a testing procedure and damage one of
the numerous transistor circuits.
e) Never attempt to work on the ECU or
open the ECU cover. The ECU is
protected by a government-mandated
extended warranty that will be nullified if
you tamper with or damage the ECU.
f) If you are inspecting electronic control
system components during rainy weather,
make sure that water does not enter any
part. When washing the engine
compartment, do not spray these parts or
their electrical connectors with water.
g) These models are susceptible to ECU
damage if water is allowed to build up in
the front cowl drain and overspill into the
dash area. Inspect and clear the front
cowl drain system as a regular
maintenance item to keep the water
draining properly. Remove the duckbill
type rubber hose and inspect it for
clogging, collapsing or deterioration.
ECU removal and refitting
7Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery (see Chapter 5).
Warning: Later models are
equipped with airbags. To
prevent the accidental deploy-
ment of the airbag, which could
cause personal injury, DO NOT work in the
vicinity of the steering column or
instrument panel. The manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department or other
repair workshop because of the special
tools and techniques required to disable
the airbag system.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.8Remove the lower instrument panel on the
passenger side under the glove compartment
(see Chapter 11).
9Remove the glove compartment from the
passenger compartment (see Chapter 11).
10Remove the screws from the ECU bracket
(see illustration).
11Lower the ECU and unplug the electrical
connectors.
12Refitting is the reverse of removal.
3 On Board Diagnosis (OBD)
system- description and fault
code access
2
Note: 1990 and 1991 models may set
Code 69 erroneously. If the battery voltage
drops sufficiently and the ignition key is
switched quickly from OFF to START, battery
voltage will be lowered and during cranking
causing a delayed park/neutral signal from the
decoder module to the ECU. Check all the
battery connections and the condition of the
battery and then check the rotary switch
adjustment in Chapter 7 to remedy this code.
General information
1The ECU contains a built-in self-diagnosis
system which detects and identifies
malfunctions occurring in the network. When
the ECU detects a problem, three things
happen: the CHECK ENGINE light comes on,
the fault is identified and a diagnostic code is
recorded and stored. The ECU stores the
failure code assigned to the specific problem
area until the diagnosis system is cancelled.
Note: 1988 and 1989 models are not
equipped with long term memory. It is
possible to access the codes but the operator
must remember to NOT turn the ignition key to
the OFF position after the CHECK ENGINE
light has been noticed. The codes will be lost
and it will be necessary to start the engine and
operate the vehicle through a complete drive
cycle to allow the fault code(s) to be set once
again. Instead of turning the ignition key to the
OFF position, simply stop at position II (key
ON but engine not running) to retain the fault
codes.
6•2 Emissions and engine control systems
3261 Jaguar XJ6
2.10 The ECU is located behind the
passenger’s side glovebox near the footrest
area. Remove the mounting screws
(arrowed) and carefully lower the ECU
Page 113 of 227

2The CHECK ENGINE warning light, which is
located on the instrument panel, comes on
when the ignition switch is turned to ON and
the engine is not running. When the engine is
started, the warning light should go out. If the
light remains on, the self-diagnosis system
has detected a malfunction. Note: The
CHECK ENGINE light on early models is
displayed on the dashboard VCM panel on the
right side. Later models are equipped with a
separate CHECK ENGINE light on the left side
of the instrument cluster.Note:Not all the
codes will cause the CHECK ENGINE light to
activate. When performing any fuel or
emissions systems diagnosis, always check
for codes that may be stored but not indicated
by the CHECK ENGINE light.
Obtaining fault code output
3To obtain an output of diagnostic codes,
verify first that the battery voltage is above 11
volts, the throttle is fully closed, the
transmission is in Park, the accessory
switches are off and the engine is at normal
operating temperature.
4Turn the ignition switch to ON but don’t
start the engine (Position II). Note:On 1988
and 1989 models, remember to turn the
ignition switch to position II without turning
the key to OFF.
5Press the VCM button on the display panel
(see illustration)and observe the LED display
on the dash for the designated codes. An
asterisk next to the code indicates that there
are multiple codes stored.
6The numerical values will be displayed on
the trip computer display on the dashboard.
7If there are any malfunctions in the system,
the corresponding fault codes are displayed in
numerical order, lowest to highest.
Cancelling a diagnostic code
8After the faulty component has been
repaired/renewed, the fault code(s) stored in
computer memory must be cancelled.
a) On 1988 to 1991 vehicles, simply drive
the vehicle faster than 19 mph and the
computer will automatically erase the
stored fault code from memory.b) On 1992 to 1994 models, disconnect the
negative battery lead for 30 seconds or
more to erase the stored fault codes.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
9A stored code can also be cancelled on
early models by removing the cable from the
battery negative terminal, but other items with
memory (such as the clock and radio presets)
will also be cancelled.
10If the diagnosis code is not cancelled, it
will be stored by the ECU and appear with any
new codes in the event of future trouble.
11Should it become necessary to work on
engine components requiring removal of the
battery terminal, always check to see if a
diagnostic code has been recorded before
disconnecting the battery.
4 Information sensors
Note: Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for additional
information on the location and the diagnostic
procedures for the output actuators (ISC
motor, air supplementary valve, distributor,
amplifier, etc.) that are not directly covered in
this section.
Coolant temperature sensor
General description
1The coolant temperature sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which varies the value of
its voltage output in accordance with
temperature changes) which is threaded into
the thermostat housing. As the sensor
temperature DECREASES, the resistance
values will INCREASE. As the sensor
Emissions and engine control systems 6•3
6
3.5 To access the self-diagnosis system
fault codes, locate the VCM button on the
dash and with the ignition key ON (engine
not running) press it to display the codes
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Fault code chart for 1988 and 1989 models
Code System affected Probable cause
1 Oxygen sensor Open oxygen sensor circuit
2 Airflow sensor Not in operating range
3 Coolant temperature sensor Not in operating range
4 Oxygen sensor System indicates full rich
5 Throttle potentiometer/airflow sensor Low throttle potentiometer signal
with high airflow sensor signal
6 Throttle potentiometer/airflow sensor High throttle potentiometer signal
with low airflow sensor signal
7 Throttle potentiometer Idle fuel adjustment failure
8 Intake air temperature sensor Open or shorted circuit in IAT sensor
harness
Fault code chart for 1990 to 1994 models
Code System affected Probable cause
11 Idle potentiometer Not in operating range
12 Airflow sensor Not in operating range
14 Coolant temperature sensor Not in operating range
16 Air temperature sensor Not in operating range
17 Throttle potentiometer Not in operating range
18 Throttle potentiometer/airflow sensor Signal resistance low
at wide open throttle
19 Throttle potentiometer/airflow sensor Signal resistance high at idle
22 Heated oxygen sensor Open or short circuit
22 Fuel pump circuit Open or short circuit
23 Fuel supply Rich exhaust Indicated
24 Ignition amplifier circuit Open or short circuit
26 Oxygen sensor circuit Lean exhaust/vacuum leak
29 ECU Self check
33 Fuel injector circuit Open or short circuit
34 Fuel injector circuit Faulty injector indicated
37 EGR solenoid circuit Short or open circuit
39 EGR circuit Faulty system operation
44 Oxygen sensor circuit Rich or lean condition
46 Idle speed control valve - (coil 1) Open or short circuit
47 Idle speed control valve - (coil 2) Open or short circuit
48 Idle speed control valve Not within specification
68 Road speed sensor Incorrect signal voltage
69 Neutral safety switch circuit Engine cranks in Drive
(adjust or renew switch)
89 Purge control valve circuit Open or short circuit