JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 311 of 1784
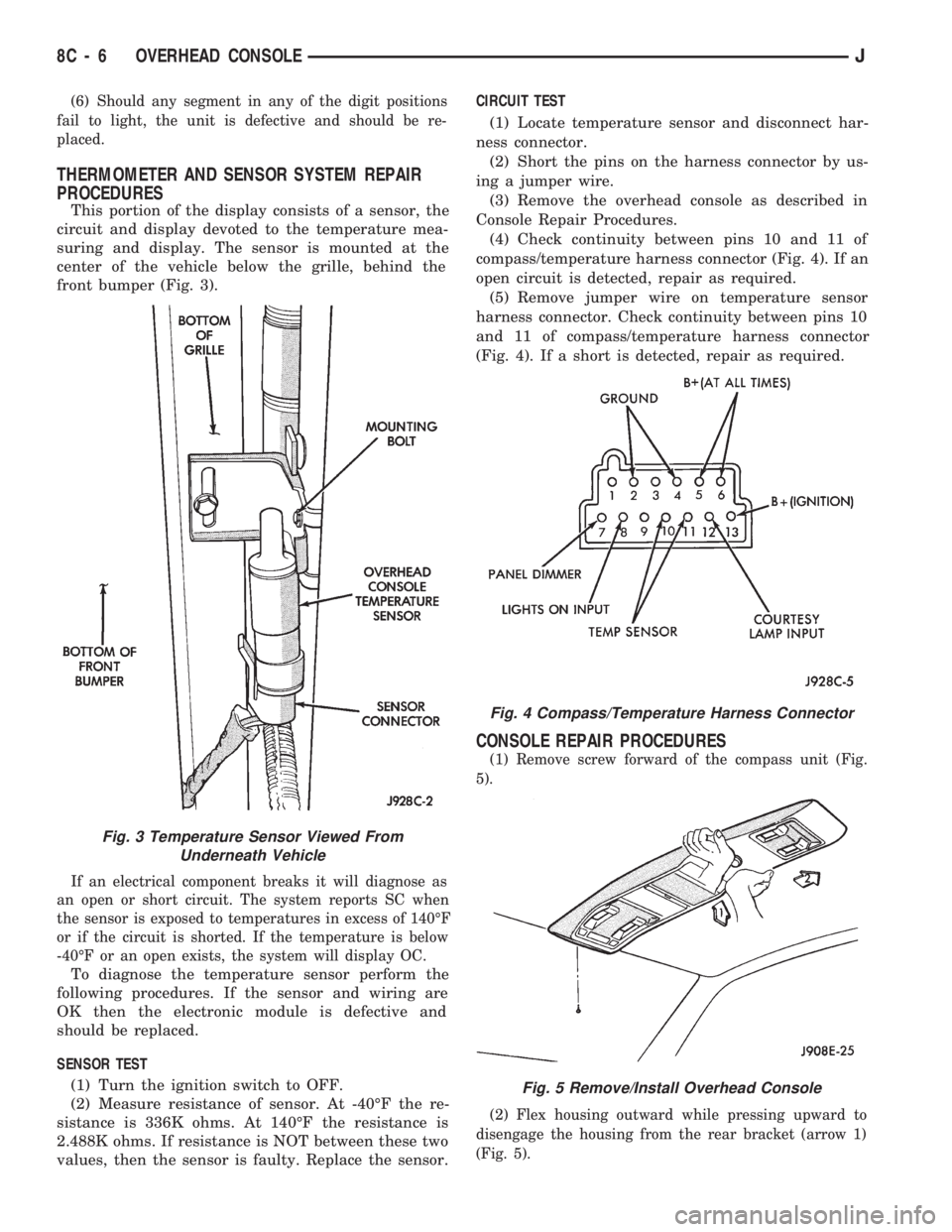
(6) Should any segment in any of the digit positions
fail to light, the unit is defective and should be re-
placed.
THERMOMETER AND SENSOR SYSTEM REPAIR
PROCEDURES
This portion of the display consists of a sensor, the
circuit and display devoted to the temperature mea-
suring and display. The sensor is mounted at the
center of the vehicle below the grille, behind the
front bumper (Fig. 3).
If an electrical component breaks it will diagnose as
an open or short circuit. The system reports SC when
the sensor is exposed to temperatures in excess of 140ÉF
or if the circuit is shorted. If the temperature is below
-40ÉF or an open exists, the system will display OC.
To diagnose the temperature sensor perform the
following procedures. If the sensor and wiring are
OK then the electronic module is defective and
should be replaced.
SENSOR TEST
(1) Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
(2) Measure resistance of sensor. At -40ÉF the re-
sistance is 336K ohms. At 140ÉF the resistance is
2.488K ohms. If resistance is NOT between these two
values, then the sensor is faulty. Replace the sensor.CIRCUIT TEST
(1) Locate temperature sensor and disconnect har-
ness connector.
(2) Short the pins on the harness connector by us-
ing a jumper wire.
(3) Remove the overhead console as described in
Console Repair Procedures.
(4) Check continuity between pins 10 and 11 of
compass/temperature harness connector (Fig. 4). If an
open circuit is detected, repair as required.
(5) Remove jumper wire on temperature sensor
harness connector. Check continuity between pins 10
and 11 of compass/temperature harness connector
(Fig. 4). If a short is detected, repair as required.
CONSOLE REPAIR PROCEDURES
(1) Remove screw forward of the compass unit (Fig.
5).
(2) Flex housing outward while pressing upward to
disengage the housing from the rear bracket (arrow 1)
(Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Compass/Temperature Harness Connector
Fig. 5 Remove/Install Overhead Console
Fig. 3 Temperature Sensor Viewed From
Underneath Vehicle
8C - 6 OVERHEAD CONSOLEJ
Page 312 of 1784
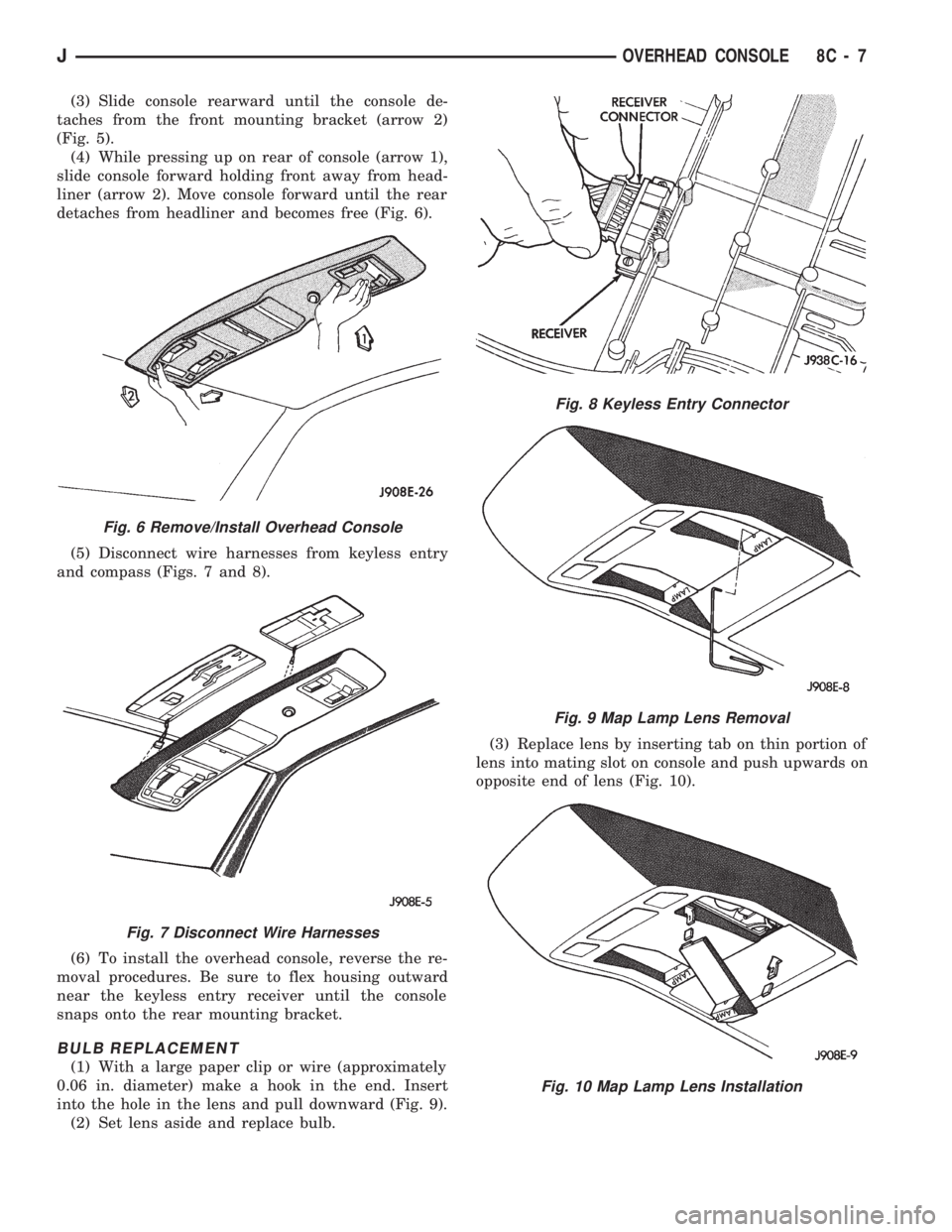
(3) Slide console rearward until the console de-
taches from the front mounting bracket (arrow 2)
(Fig. 5).
(4) While pressing up on rear of console (arrow 1),
slide console forward holding front away from head-
liner (arrow 2). Move console forward until the rear
detaches from headliner and becomes free (Fig. 6).
(5) Disconnect wire harnesses from keyless entry
and compass (Figs. 7 and 8).
(6) To install the overhead console, reverse the re-
moval procedures. Be sure to flex housing outward
near the keyless entry receiver until the console
snaps onto the rear mounting bracket.
BULB REPLACEMENT
(1) With a large paper clip or wire (approximately
0.06 in. diameter) make a hook in the end. Insert
into the hole in the lens and pull downward (Fig. 9).
(2) Set lens aside and replace bulb.(3) Replace lens by inserting tab on thin portion of
lens into mating slot on console and push upwards on
opposite end of lens (Fig. 10).
Fig. 6 Remove/Install Overhead Console
Fig. 7 Disconnect Wire Harnesses
Fig. 8 Keyless Entry Connector
Fig. 9 Map Lamp Lens Removal
Fig. 10 Map Lamp Lens Installation
JOVERHEAD CONSOLE 8C - 7
Page 313 of 1784
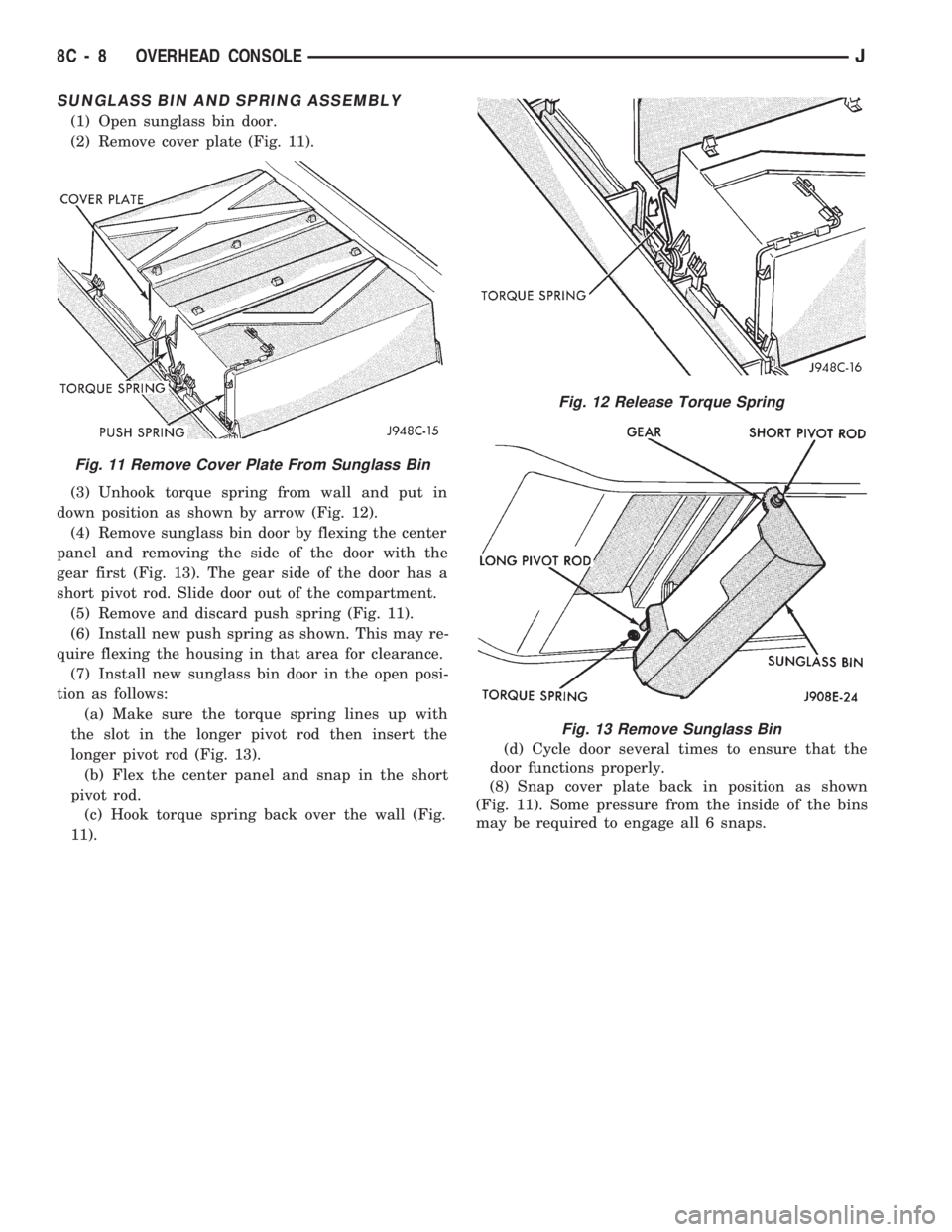
SUNGLASS BIN AND SPRING ASSEMBLY
(1) Open sunglass bin door.
(2) Remove cover plate (Fig. 11).
(3) Unhook torque spring from wall and put in
down position as shown by arrow (Fig. 12).
(4) Remove sunglass bin door by flexing the center
panel and removing the side of the door with the
gear first (Fig. 13). The gear side of the door has a
short pivot rod. Slide door out of the compartment.
(5) Remove and discard push spring (Fig. 11).
(6) Install new push spring as shown. This may re-
quire flexing the housing in that area for clearance.
(7) Install new sunglass bin door in the open posi-
tion as follows:
(a) Make sure the torque spring lines up with
the slot in the longer pivot rod then insert the
longer pivot rod (Fig. 13).
(b) Flex the center panel and snap in the short
pivot rod.
(c) Hook torque spring back over the wall (Fig.
11).(d) Cycle door several times to ensure that the
door functions properly.
(8) Snap cover plate back in position as shown
(Fig. 11). Some pressure from the inside of the bins
may be required to engage all 6 snaps.
Fig. 11 Remove Cover Plate From Sunglass Bin
Fig. 12 Release Torque Spring
Fig. 13 Remove Sunglass Bin
8C - 8 OVERHEAD CONSOLEJ
Page 314 of 1784

IGNITION SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM
OPERATION.......................... 1
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION..... 20DIAGNOSTICS/SERVICE PROCEDURES....... 8
IGNITION SWITCH...................... 30
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 33
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay............ 1
Camshaft Position Sensor................... 1
Crankshaft Position Sensor.................. 2
Distributors.............................. 3
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor........... 4
General Information........................ 1Ignition Coil.............................. 4
Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor........ 5
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor...... 5
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............. 6
Throttle Position Sensor.................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of alphabetical designa-
tions is included in the Introduction group at the be-
ginning of this manual.
This section of the group, Component Identifica-
tion/System Operation, will discuss ignition system
operation and will identify ignition system compo-
nents.
For diagnostic procedures and adjustments, refer to
the Diagnostics/Service Procedures section of this
group.
For removal and installation of ignition system
components, refer to the Component Removal/Instal-
lation section of this group.
For other useful information, refer to On-Board Di-
agnostics in the General Diagnosis sections of Group
14, Fuel System in this manual.
For operation of the DRB Scan Tool, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
An Ignition specifications section is included at the
end of this group. A general Maintenance Schedule
(mileage intervals) for ignition related items can be
found in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. This
schedule can also be found in the Owners Manual.
IGNITION SYSTEMS
A multi-port, fuel injected engine is used on all
models. The ignition system is controlled by the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) on all engines. The
PCM was formerly referred to as the SBEC or engine
controller.
The ignition system consists of:
²Spark Plugs
²Ignition Coil
²Secondary Ignition Cables
²Ignition distributor (contains rotor and camshaft
position sensor)
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY
The automatic shut down (ASD) relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC) near the bat-
tery (Fig. 1 or 2). As one of its functions, it will sup-
ply battery voltage to the ignition coil. The ground
circuit for the ASD relay is controlled by the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). The PCM regulates
ASD relay operation by switching the ground circuit
on-and-off.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor is located in the igni-
tion distributor (Figs. 3 or 4) on all engines.
The camshaft position sensor contains a hall effect
device called a sync signal generator to generate a
fuel sync signal. This sync signal generator detects a
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 1
Page 315 of 1784
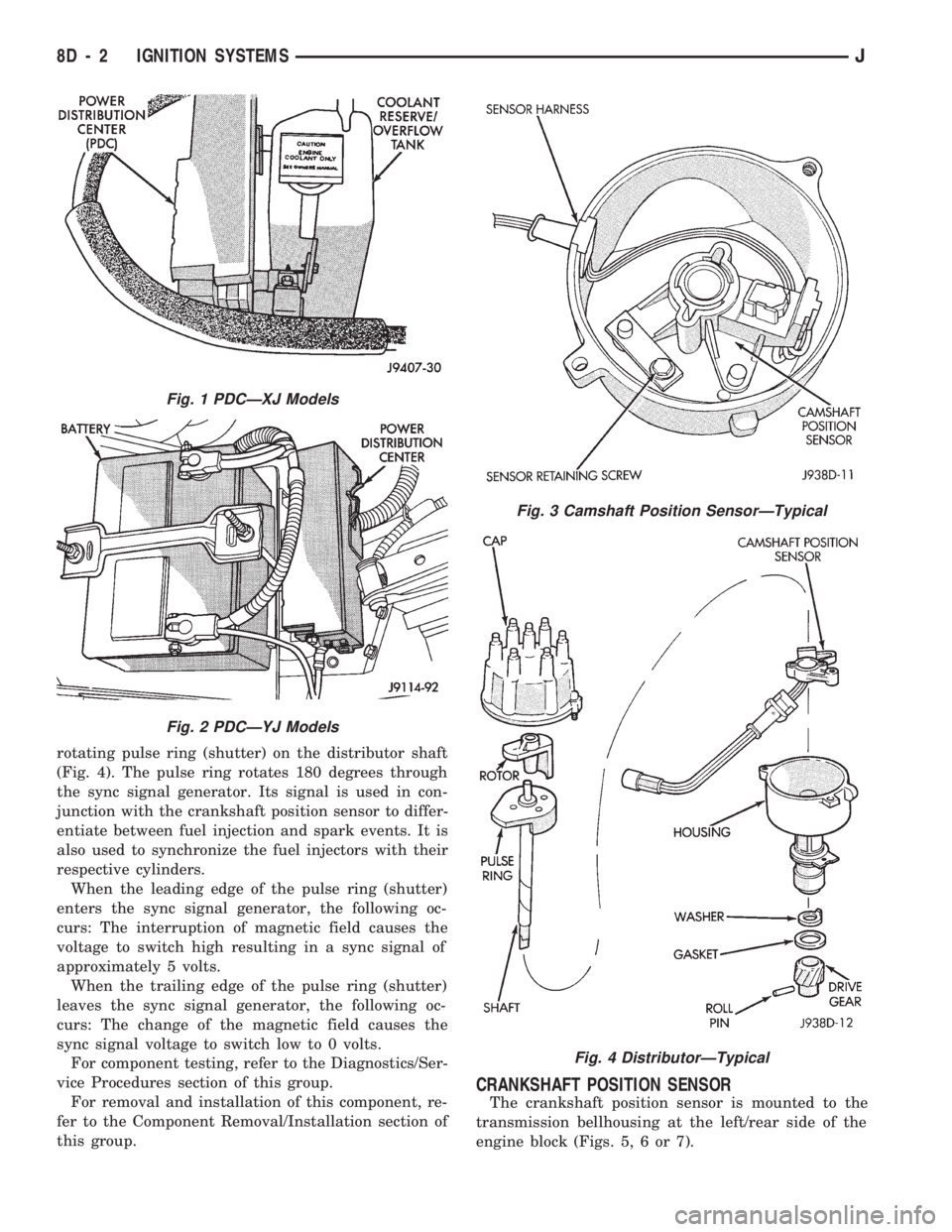
rotating pulse ring (shutter) on the distributor shaft
(Fig. 4). The pulse ring rotates 180 degrees through
the sync signal generator. Its signal is used in con-
junction with the crankshaft position sensor to differ-
entiate between fuel injection and spark events. It is
also used to synchronize the fuel injectors with their
respective cylinders.
When the leading edge of the pulse ring (shutter)
enters the sync signal generator, the following oc-
curs: The interruption of magnetic field causes the
voltage to switch high resulting in a sync signal of
approximately 5 volts.
When the trailing edge of the pulse ring (shutter)
leaves the sync signal generator, the following oc-
curs: The change of the magnetic field causes the
sync signal voltage to switch low to 0 volts.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The crankshaft position sensor is mounted to the
transmission bellhousing at the left/rear side of the
engine block (Figs. 5, 6 or 7).
Fig. 1 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 2 PDCÐYJ Models
Fig. 3 Camshaft Position SensorÐTypical
Fig. 4 DistributorÐTypical
8D - 2 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 316 of 1784

Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the crankshaft position sensor. The sensor
generates pulses that are the input sent to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM interprets
the sensor input to determine the crankshaft posi-
tion. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and ig-
nition timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.
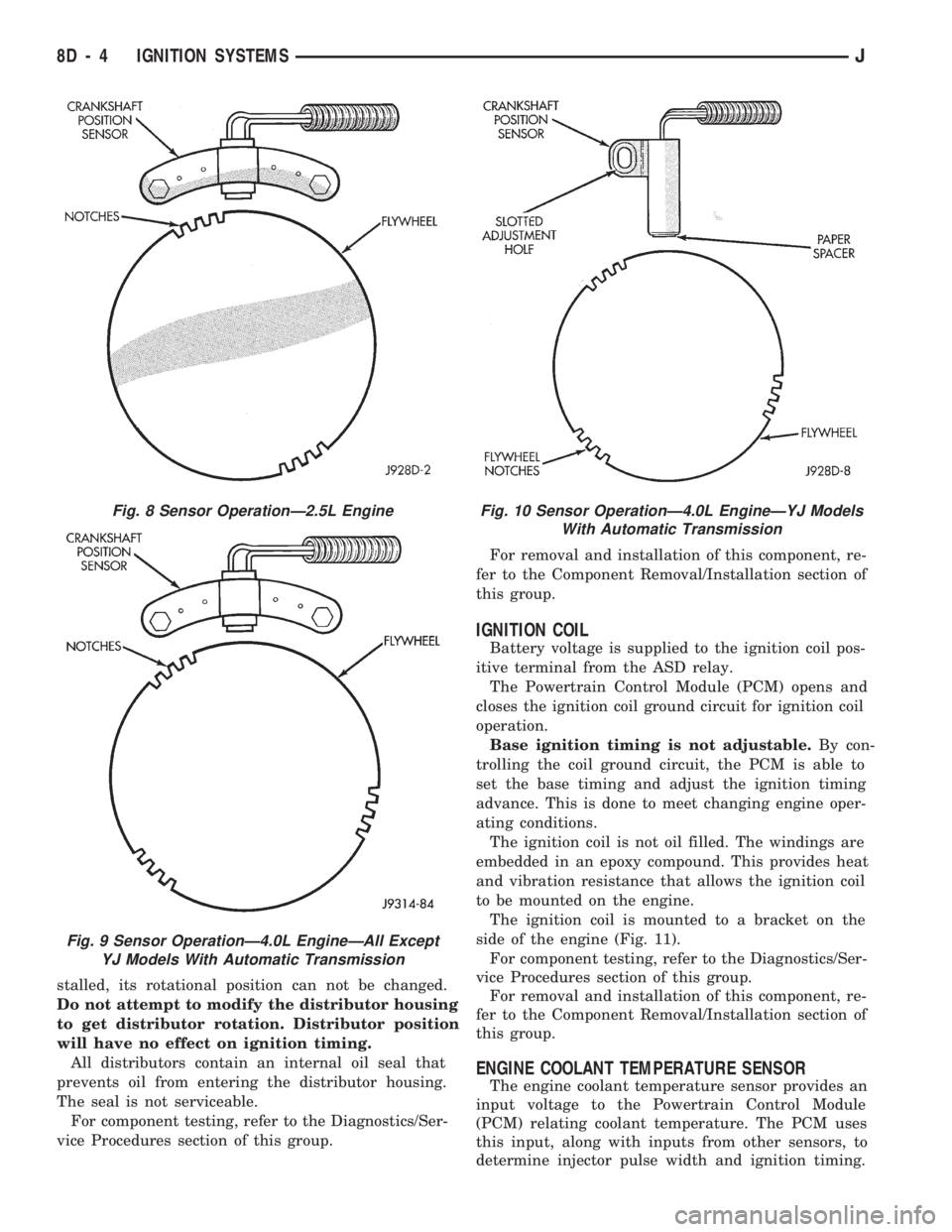
SENSOR OPERATION
The flywheel/drive plate has groups of four notches
at its outer edge. On 4.0L 6 cylinder engines there
are three sets of notches (Figs. 9 or 10). On 2.5L 4
cylinder engines there are two sets of notches (Fig.
8).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the inputto the PCM. For each engine revolution there are
two groups of four pulses generated on 2.5L 4 cylin-
der engines. There are 3 groups of four pulses gener-
ated on 4.0L 6 cylinder engines.
The trailing edge of the fourth notch, which causes
the pulse, is four degrees before top dead center
(TDC) of the corresponding piston.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not re-
ceive a crankshaft position sensor input.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this sensor, refer to
the Component Removal/Installation section of this
group.
DISTRIBUTORS
All engines are equipped with a camshaft driven
mechanical distributor containing a shaft driven dis-
tributor rotor. All distributors are equipped with an
internal camshaft position (fuel sync) sensor. This
sensor provides fuel injection synchronization and
cylinder identification.
The distributors on the 2.5L and 4.0L engines do
not have built in centrifugal or vacuum assisted ad-
vance. Base ignition timing and all timing advance
is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). Because ignition timing is controlled by the
PCM,base ignition timing is not adjustable on
any of these engines.
The distributor is locked in place by a notch on the
distributor housing. The distributor holddown clamp
bolt passes through this notch when installed. Be-
cause the distributor position is locked when in-
Fig. 5 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ2.5L
EngineÐTypical
Fig. 6 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L EngineÐAll
Except YJ models With Automatic Transmission
Fig. 7 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L EngineÐYJ
models With Automatic Transmission
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 3
Page 317 of 1784
stalled, its rotational position can not be changed.
Do not attempt to modify the distributor housing
to get distributor rotation. Distributor position
will have no effect on ignition timing.
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
IGNITION COIL
Battery voltage is supplied to the ignition coil pos-
itive terminal from the ASD relay.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) opens and
closes the ignition coil ground circuit for ignition coil
operation.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable.By con-
trolling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to
set the base timing and adjust the ignition timing
advance. This is done to meet changing engine oper-
ating conditions.
The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are
embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat
and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil
to be mounted on the engine.
The ignition coil is mounted to a bracket on the
side of the engine (Fig. 11).
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The engine coolant temperature sensor provides an
input voltage to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) relating coolant temperature. The PCM uses
this input, along with inputs from other sensors, to
determine injector pulse width and ignition timing.
Fig. 8 Sensor OperationÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 9 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L EngineÐAll Except
YJ Models With Automatic Transmission
Fig. 10 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L EngineÐYJ Models
With Automatic Transmission
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 318 of 1784

As coolant temperature varies, the sensor resistance
will change, resulting in a different input voltage to
the PCM.
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
the Open Loop Cycle. It will demand slightly richer
air-fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds, until nor-
mal operating temperatures are reached. Refer to
Modes Of Operation in Group 14, Fuel System for a
description of Open and Closed Loop operation.
This sensor is installed in the thermostat housing
(Fig. 12).
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The sensor element extends into the intake mani-
fold air stream. It provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) indicating intakemanifold air temperature. The input from this sensor
is used along with inputs from other sensors to de-
termine injector pulse width. As the temperature of
the air-fuel stream in the manifold varies, the sensor
resistance will change. This will result in a different
input voltage to the PCM. For more information, re-
fer to Group 14, Fuel System.
This sensor is installed in the intake manifold (Fig.
13, 4.0L engine or Fig. 14, 2.5L engine).
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
The MAP sensor reacts to absolute pressure in the
intake manifold and provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). As engine load
changes, manifold pressure varies, causing the MAP
Fig. 11 Ignition CoilÐTypical
Fig. 12 Coolant Temperature SensorÐTypical
Fig. 13 Air Temperature Sensor LocationÐ4.0L
Engine
Fig. 14 Air Temperature Sensor LocationÐ2.5L
Engine
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 5
Page 319 of 1784

sensor voltage to change. This change results in a
different input voltage to the PCM. The input volt-
age level supplies the PCM with information. This
relates to ambient barometric pressure during engine
start-up (cranking) and to engine load while the en-
gine is running. The PCM uses this input, along with
inputs from other sensors, to adjust air-fuel mixture.
For more information, refer to Group 14, Fuel Sys-
tem.
The MAP sensor is located in the engine compart-
ment near the rear of engine cylinder head (valve)
cover (Fig. 15). It is connected to the throttle body
with a vacuum hose and to the PCM electrically.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The PCM was formerly referred to as the SBEC or
engine controller. On XJ models, the PCM is located
in the engine compartment next to the air cleaner
(Fig. 16). On YJ models, the PCM is located in the
engine compartment behind the windshield washer
fluid reservoir (Fig. 17).
The ignition system is controlled by the PCM.
Base ignition timing by rotation of distributor
is not adjustable.The PCM opens and closes the ig-
nition coil ground circuit to operate the ignition coil.
This is done to adjust ignition timing, both initial
(base) and advance, for changing engine operating
conditions.
The amount of electronic spark advance provided
by the PCM is determined by five input factors: En-
gine coolant temperature, engine rpm, intake mani-
fold air temperature, intake manifold absolute
pressure and throttle position.For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB scan tool.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
The sensor is mounted on the throttle body (Figs.
18 or 19). It is connected to the throttle blade shaft.
The sensor is a variable resistor. It provides the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) with an input signal
(voltage) that represents throttle blade position. As
the position of the throttle blade changes, the resis-
tance of the sensor changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
sensor. The sensor output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the sen-
sor. This will vary in an approximate range of from 1
volt at minimum throttle opening (idle), to 4 volts at
wide open throttle. Along with inputs from other sen-
sors, the PCM uses the sensor input to determine
Fig. 15 MAP SensorÐTypical
Fig. 16 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 17 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
8D - 6 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 320 of 1784

current engine operating conditions. It will also ad-
just fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing.For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re-
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
Fig. 18 Throttle Position SensorÐ2.5L EngineFig. 19 Throttle Position SensorÐ4.0L Engine
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 7