brakes LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 188 of 455
51REAR AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
6
REPAIRREV: 05/99 Refit
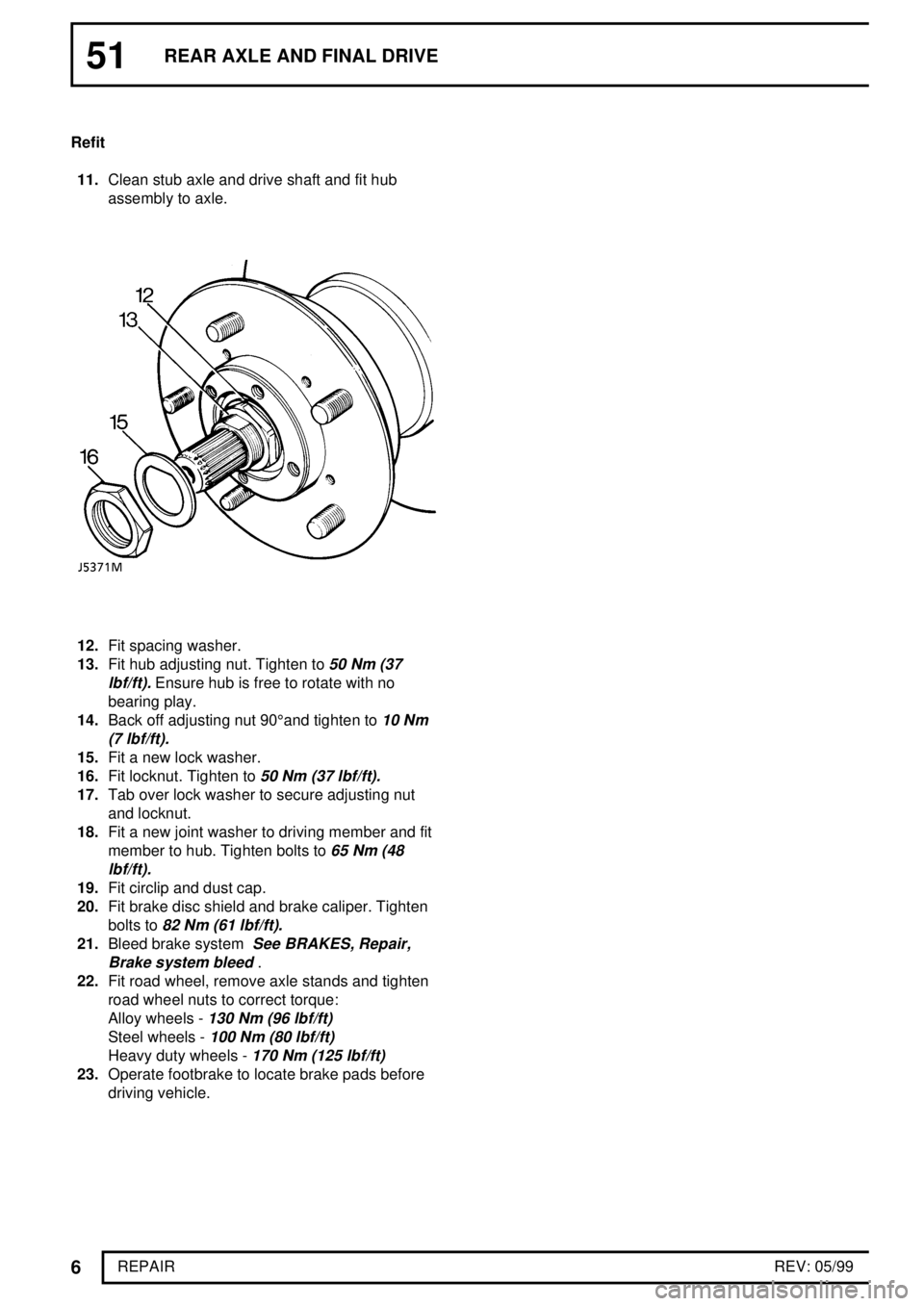
11.Clean stub axle and drive shaft and fit hub
assembly to axle.
12.Fit spacing washer.
13.Fit hub adjusting nut. Tighten to
50 Nm (37
lbf/ft).
Ensure hub is free to rotate with no
bearing play.
14.Back off adjusting nut 90°and tighten to
10 Nm
(7 lbf/ft).
15.Fit a new lock washer.
16.Fit locknut. Tighten to
50 Nm (37 lbf/ft).
17.Tab over lock washer to secure adjusting nut
and locknut.
18.Fit a new joint washer to driving member and fit
member to hub. Tighten bolts to
65 Nm (48
lbf/ft).
19.Fit circlip and dust cap.
20.Fit brake disc shield and brake caliper. Tighten
bolts to
82 Nm (61 lbf/ft).
21.Bleed brake systemSee BRAKES, Repair,
Brake system bleed
.
22.Fit road wheel, remove axle stands and tighten
road wheel nuts to correct torque:
Alloy wheels -
130 Nm (96 lbf/ft)
Steel wheels -100 Nm (80 lbf/ft)
Heavy duty wheels -170 Nm (125 lbf/ft)
23.Operate footbrake to locate brake pads before
driving vehicle.
Page 211 of 455
FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
3
REPAIR REV: 05/99 Refit
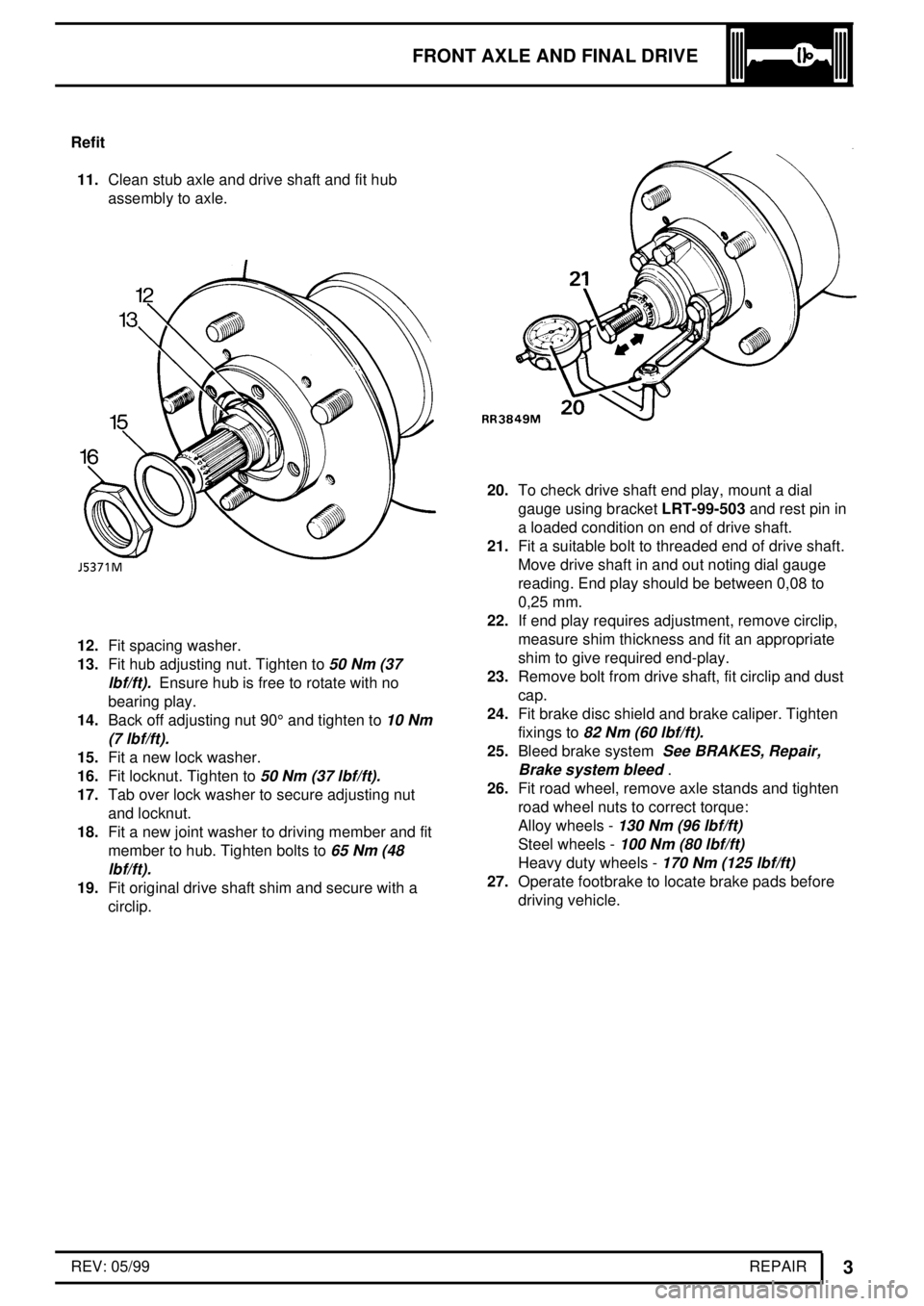
11.Clean stub axle and drive shaft and fit hub
assembly to axle.
12.Fit spacing washer.
13.Fit hub adjusting nut. Tighten to
50 Nm (37
lbf/ft).
Ensure hub is free to rotate with no
bearing play.
14.Back off adjusting nut 90°and tighten to
10 Nm
(7 lbf/ft).
15.Fit a new lock washer.
16.Fit locknut. Tighten to
50 Nm (37 lbf/ft).
17.Tab over lock washer to secure adjusting nut
and locknut.
18.Fit a new joint washer to driving member and fit
member to hub. Tighten bolts to
65 Nm (48
lbf/ft).
19.Fit original drive shaft shim and secure with a
circlip.
20.To check drive shaft end play, mount a dial
gauge using bracketLRT-99-503and rest pin in
a loaded condition on end of drive shaft.
21.Fit a suitable bolt to threaded end of drive shaft.
Move drive shaft in and out noting dial gauge
reading. End play should be between 0,08 to
0,25 mm.
22.If end play requires adjustment, remove circlip,
measure shim thickness and fit an appropriate
shim to give required end-play.
23.Remove bolt from drive shaft, fit circlip and dust
cap.
24.Fit brake disc shield and brake caliper. Tighten
fixings to
82 Nm (60 lbf/ft).
25.Bleed brake systemSee BRAKES, Repair,
Brake system bleed
.
26.Fit road wheel, remove axle stands and tighten
road wheel nuts to correct torque:
Alloy wheels -
130 Nm (96 lbf/ft)
Steel wheels -100 Nm (80 lbf/ft)
Heavy duty wheels -170 Nm (125 lbf/ft)
27.Operate footbrake to locate brake pads before
driving vehicle.
Page 239 of 455
57STEERING
2
REPAIR
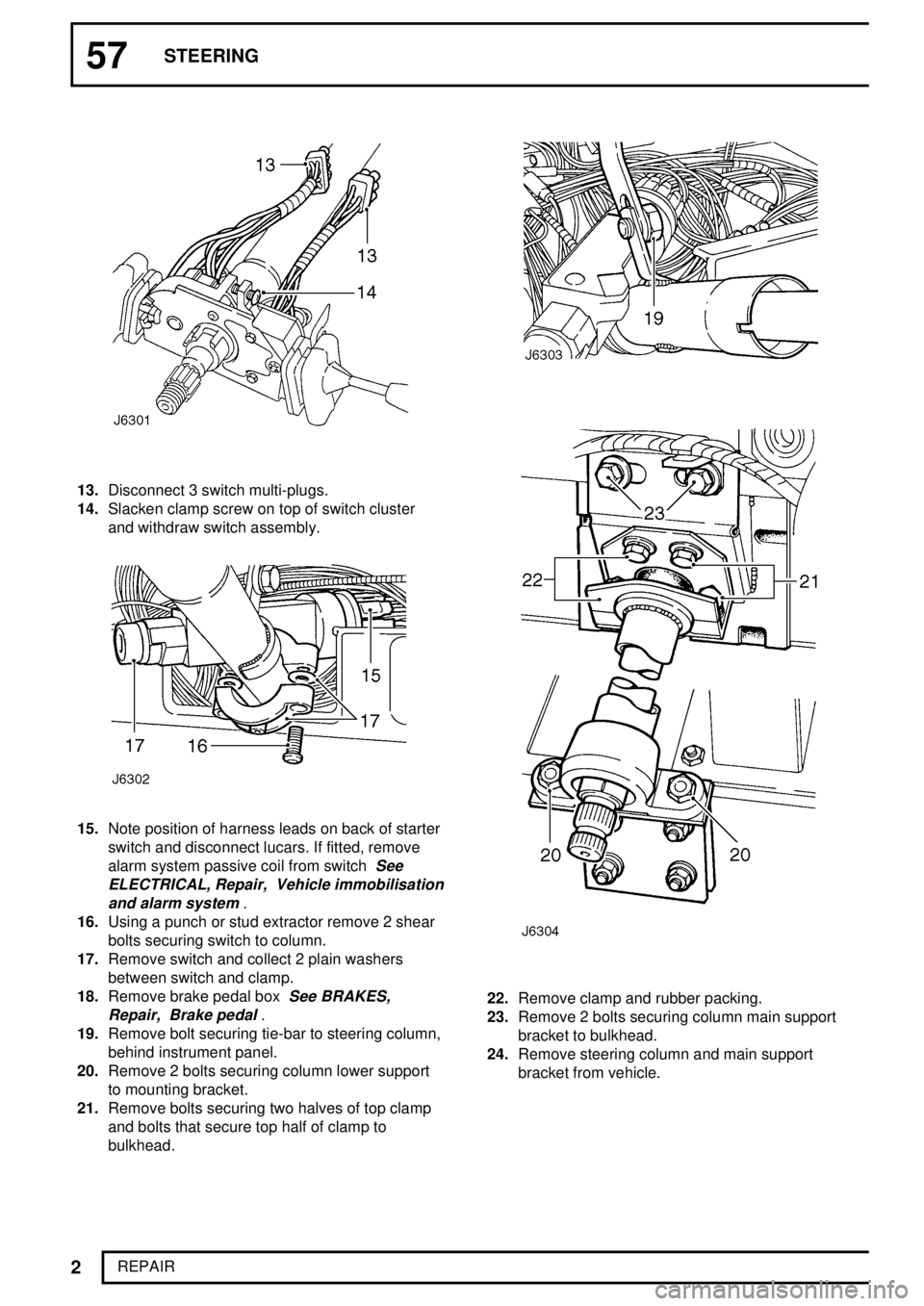
13.Disconnect 3 switch multi-plugs.
14.Slacken clamp screw on top of switch cluster
and withdraw switch assembly.
15.Note position of harness leads on back of starter
switch and disconnect lucars. If fitted, remove
alarm system passive coil from switch
See
ELECTRICAL, Repair, Vehicle immobilisation
and alarm system
.
16.Using a punch or stud extractor remove 2 shear
bolts securing switch to column.
17.Remove switch and collect 2 plain washers
between switch and clamp.
18.Remove brake pedal box
See BRAKES,
Repair, Brake pedal
.
19.Remove bolt securing tie-bar to steering column,
behind instrument panel.
20.Remove 2 bolts securing column lower support
to mounting bracket.
21.Remove bolts securing two halves of top clamp
and bolts that secure top half of clamp to
bulkhead.
22.Remove clamp and rubber packing.
23.Remove 2 bolts securing column main support
bracket to bulkhead.
24.Remove steering column and main support
bracket from vehicle.
Page 240 of 455

STEERING
3
REPAIR REV: 05/99
NOTE: The steering column is a non
serviceable component and can only be
serviced as a complete assembly.
25.Fit main support bracket and padding to steering
column and manoeuvre column into position in
vehicle.
26.Loosely secure main support bracket and
harness bracket to bulkhead.
27.Loosely fit clamp and rubber packing strip to
column.
28.Loosely secure lower end of column to lower
support bracket.
29.Loosely secure clamp bracket to main support
bracket.
30.Working inside vehicle cab, fit tie-bar to column
bracket and secure with single bolt to
22 Nm (16
lbf/ft).
31.Finally, tighten main support bracket, clamp
bracket, upper clamp, and lower support bracket
nuts and bolts. (M6 bolts
9 Nm (6 lbf/ft),M8
bolts
22 Nm (16 lbf/ft).
32.Fit brake pedal boxSee BRAKES, Repair,
Brake pedal
.
33.Fit steering lock/switch in position and rotate
steering column inner shaft to line up slot with
switch plunger.
34.Secure lock to column with clamp and shear
bolts. Evenly tighten bolts but do not shear them.
35.Temporarily fit steering wheel and operate
switch and lock mechanism several times to
ensure it functions correctly.
36.Fully tighten switch retaining bolts until heads
shear.
37.Connect electrical leads to rear of switch. Fit
alarm system passive coil, if applicable.
See
ELECTRICAL, Repair, Vehicle immobilisation
and alarm system
.
38.Fit switch assembly on steering column and
tighten clamping screw.
39.Connect switch assembly multi-plugs and
electrical leads to main harness.
40.Offer up instrument panel, connect speedometer
cable, multi-plugs and electrical leads to main
harness. If applicable, fit vehicle alarm system
connections.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair,
Vehicle immobilisation and alarm system
.
41.Secure panel with 4 screws.
42.Locate top half of nacelle in position and fit to
switch gaiters/grommets.43.Fit lower half of nacelle and loosely tighten fixing
screws.
44.Ensure switch gaiters/grommets are correctly
located and fully tighten fixings.
45.Turn indicator cancelling ring so that slots are
vertical and lug with arrow points to the left, in
direction of indicator switch.
46.Fit steering wheel with finisher attachment lug at
bottom, ensuring that indicator cancelling forks
locate in cancelling ring slots.
47.Secure wheel with nut and new shake-proof
washer. Tighten to
43 Nm (32 lbf/ft).
48.Fit steering wheel decal.
49.If necessary, fit new universal joints to support.
Note that long joint is fitted to short length of
shaft and short joint to long end. Joints can only
be fitted one way to shaft.
50.With steering lock engaged and road wheels in
straight ahead position, align reassembly marks,
and fit collapsible shaft assembly with long leg of
shaft to steering box. Fit pinch bolts and tighten
to
25 Nm (18 lbf/ft).
Page 279 of 455

BRAKES
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
The mechanical components of the hydraulic braking
system consists of four piston caliper disc brakes at
the front and two piston caliper disc brakes at the rear.
Vented front brake discs are fitted as standard on
110/130 models, while 90 models have solid discs.
However, on 90 models with a heavy duty chassis,
vented front discs may also be fitted.A cable controlled parking brake operates a single
drum brake mounted on the output shaft of the
transfer gearbox and is completely independent of the
main braking system.
The basic hydraulic system involves 2 separate and
independent primary and secondary circuits which
permits a degree of braking should a fault occur in
one of the circuits. The primary circuit operates the
rear brake calipers and the secondary circuit the front
brake calipers.
Master cylinder components
1.Secondary plunger
2.Secondary spring
3.Recuperation seal4.Primary spring
5.Recuperation seal
6.Primary plunger
Page 280 of 455

70BRAKES
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 05/99 OPERATION
Master cylinder
A tandem master cylinder, which is assisted by a light
weight, short, compact servo, is fed by a divided fluid
reservoir. The rear section supplies fluid for the
primary circuit and the front section the secondary
circuit.
When the brakes are off, the fluid can move
unrestricted between the dual line system and the
separate reservoirs in the fluid supply tank.
When the footbrake is applied, the primary plunger
assembly moves up the cylinder bore and the
pressure created acts in conjunction with the primary
spring to overcome the secondary springs, thus
moving the secondary plunger assembly up the bore.
At the same time initial movement of both plungers
takes the recuperating seals past the cut-off holes in
the cylinder chambers 'A' and 'C',see J6321, and
applies pressure to the fliud in those chambers, which
is directed to the respective circuits.
The fluid in chambers 'B' and 'D'is unaffected by
movement of the plungers and can move unrestricted
between the separate chambers and respective
reservoirs in the fluid supply tank, both before and
during brake application. When the brakes are
released, the plunger assemblies, aided by the return
springs are retracted faster than the fluid; this creates
a depression between the fluid in chambers 'A' and
'C'and the recuperation seals.
The recuperation seals momentarily collapse allowing
fluid in chambers 'B' and 'D'to flow through the holes
in the plungers, over the collapsed seals and into
chambers 'A' and 'C'respectively. The movement of
fluid from one set of chambers to the other, is
compensated for by fluid from the separate reservoirs
in the supply tank moving through the feed holes in
the cylinder. Conversely, the final return movement of
the plunger assemblies causes the extra fluid in
chambers 'A' and 'C'to move through the cut off holes
into the fluid reservoir.The servo unit provides controlled power assistance
to to the brake pedal when pressure is applied. Power
is obtained from a vacuum pump located on the RH
side of the engine cylinder block. The vacuum is
applied to both sides of a flexing diaphragm, and by
admitting atmosheric pressure to the rear diaphragm,
assistance is obtained. The servo unit is mounted
between the brake pedal and master cylinder and is
linked to these by push rods. Should a vacuum failure
occur, the two push rods will act as a single rod
allowing the brakes to function in the normal way,
although more effort will be required to operate the
brake pedal.
Hydraulic system
A brake fluid loss switch is fitted to the master cylinder
reservoir filler cap. The switch is wired to a warning
light on the vehicle fascia and will illuminate as a bulb
check when the ignition is switched on and
extinguishes when the engine is running and the
handbrake is released. A hydraulic failure in the
system will result in fluid loss, causing the warning
light to illuminate.
On 90 models a pressure reducing valve (PRV), fitted
to the RH bulkhead in the engine compartment,
maintains the braking balance, see J6322. Pressure
to the rear calipers is regulated by the PRV, this valve
is of the failure by-pass type, allowing full system
pressure to the rear brake calipers in the event of a
front (secondary) circuit failure.
NOTE: In some countries, a pressure
reducing valve may be fitted to 110 models
to conform to legal requirements.
Page 281 of 455

BRAKES
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
90 Models
110/130 Models
Hydraulic system
A- Primary circuit
B- Secondary circuit
C- Pressure reducing valve (PRV)1.LH rear brake caliper
2.T connector
3.RH rear brake caliper
4.Brake servo
5.Master cylinder and reservoir
6.LH front brake caliper
7.RH front brake caliper
Page 282 of 455

BRAKES
1
REPAIR GENERAL BRAKE SERVICE PRACTICE
Brake fluid precautions
WARNING: Do not allow brake fluid to
come into contact with eyes or skin.
CAUTION: Brake fluid can damage
paintwork, if spilled wash off immediately
with plenty of clean water.
CAUTION: Use only correct grade of brake
fluid. If an assembly fluid is required use
ONLY brake fluid. Do NOT use mineral oil,
i.e. engine oil etc.
CAUTION: Thoroughly clean all brake
calipers, pipes and fittings before
commencing work on any part of the brake
system. Failure to do so could cause foreign
matter to enter the system and cause damage to
seals and pistons which will seriously impair the
efficiency of the brake system. To ensure the
brake system efficiency is not impaired the
following warnings must be adhered to :-
·DO NOT use any petroleum based cleaning
fluids or any proprietary fluids containing
petrol.
·DO NOT use brake fluid previously bled from
the system.
·DO NOT flush the brake system with any fluid
other than the recommended brake fluid.
The brake system should be drained and flushed
at the recommended service intervals.
Cover all electrical terminals carefully to make
absolutely certain that no fluid enters the
terminals and plugs.FLUID LEVEL CHECK/TOP UP
WARNING: Clean reservoir body and filler
cap before removing cap. Use only fluid
from a sealed container.
1.Park vehicle on level ground.
2.Check level is between 'MIN' and 'MAX' marks.
3.If level is below 'MIN' mark top up fluid level to
'MAX' mark on reservoir, using correct fluid.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES,
Information, Recommended lubricants and
fluids
CAUTION: Do not fill reservoir above
maximum line.
Page 283 of 455

70BRAKES
2
REPAIR BRAKE SYSTEM BLEED
Service repair no - 70.25.02
Preparation
WARNING: Before bleeding the brake
system refer to general brake service
practice.
See General Brake Service
Practice
.
·During bleed procedure, brake fluid level must
not be allowed to fall below the MIN level.
·To bleed the hydraulic circuits, four bleed
nipples are provided, one at each caliper.
·There are two methods by which air can be
removed from the braking system:-
1. MANUAL BLEED PROCEDURE.
2. PRESSURE BLEED PROCEDURE.
Pressure bleed procedure
Purpose designed equipment for pressure filling and
bleeding of hydraulic systems may be used on Land
Rover vehicles. The equipment manufacturer's
instructions must be followed and the pressure must
not exceed 4.5 bar, 65 lb/in
2.
Manual bleed procedure
Equipment required
·Clean glass receptacle
·Bleed hose
·Wrench
·Approx 2 litres (3 pints) brake fluid.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES,
Information, Recommended lubricants and
fluids
Master cylinder bleed
1.Disconnect battery.
2.Depress brake pedal fully and slowly 5 times.
3.Release the pedal and wait for ten seconds.
4.Air bubbles will rise into the reservoir during
these instructions.
5.Repeat instructions until a firm resistance is felt
at the pedal.
Complete circuit bleed
1.Disconnect battery.
2.Bleed front calipers, driver's side first. Fit bleed
hose to bleed screw.
3.Dip free end of bleed hose into brake fluid in
bleed bottle.
4.Open bleed screw of caliper.
5.Depress brake pedal fully several times until fluid
is clear of air bubbles.
6.Keeping pedal fully depressed, tighten bleed
screw, then release pedal.
7.Repeat procedure on other front caliper followed
by rear calipers.
8.Fit all bleed screw protection caps.
9.Check/top-up fluid level when bleeding is
complete
See Fluid Level Check/Top-Up.
Page 284 of 455

BRAKES
3
REPAIR MASTER CYLINDER
Service repair no - 70.30.08
Before starting repair refer to general brake service
practice
See General Brake Service Practice.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery.
2.Place a container under the master cylinder to
catch escaping brake fluid.
3.Clean area round master cylinder ports.
4.Disconnect pipes from master cylinder ports.
Cover, not plug, the pipe ends to prevent entry of
dirt.
5.Disconnect electrical leads from reservoir cap.
6.Remove two nuts securing master cylinder to
servo and withdraw cylinder.
7.Remove reservoir cap and drain fluid into
suitable container for disposal.
8.The reservoir is a push fit in the master cylinder
and secured by seals. Carefully ease the
reservoir from the master cylinder by rolling it
from the seals. Note that the two seals are
different sizes.
Refit
9.Insert new reservoir seals in the master cylinder
ports and fit reservoir to master cylinder.
10.Ensuring that water ingress seal is in position, fit
master cylinder to servo. Tighten fixings to
26
Nm (19 lbf/ft).
11.Connect brake pipes to master cylinder ports
and tighten to
15 Nm (11 lbf/ft).
12.Fit electrical leads to reservoir cap
13.Fill reservoir with recommended brake fluid.
See
LUBRICANTS, FLUIDS AND CAPACITIES,
Information, Recommended lubricants and
fluids
14.Bleed the brake systemSee Brake system
bleed
.
15.Reconnect battery and road test vehicle.