sensor LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1995, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995Pages: 873, PDF Size: 12.89 MB
Page 198 of 873
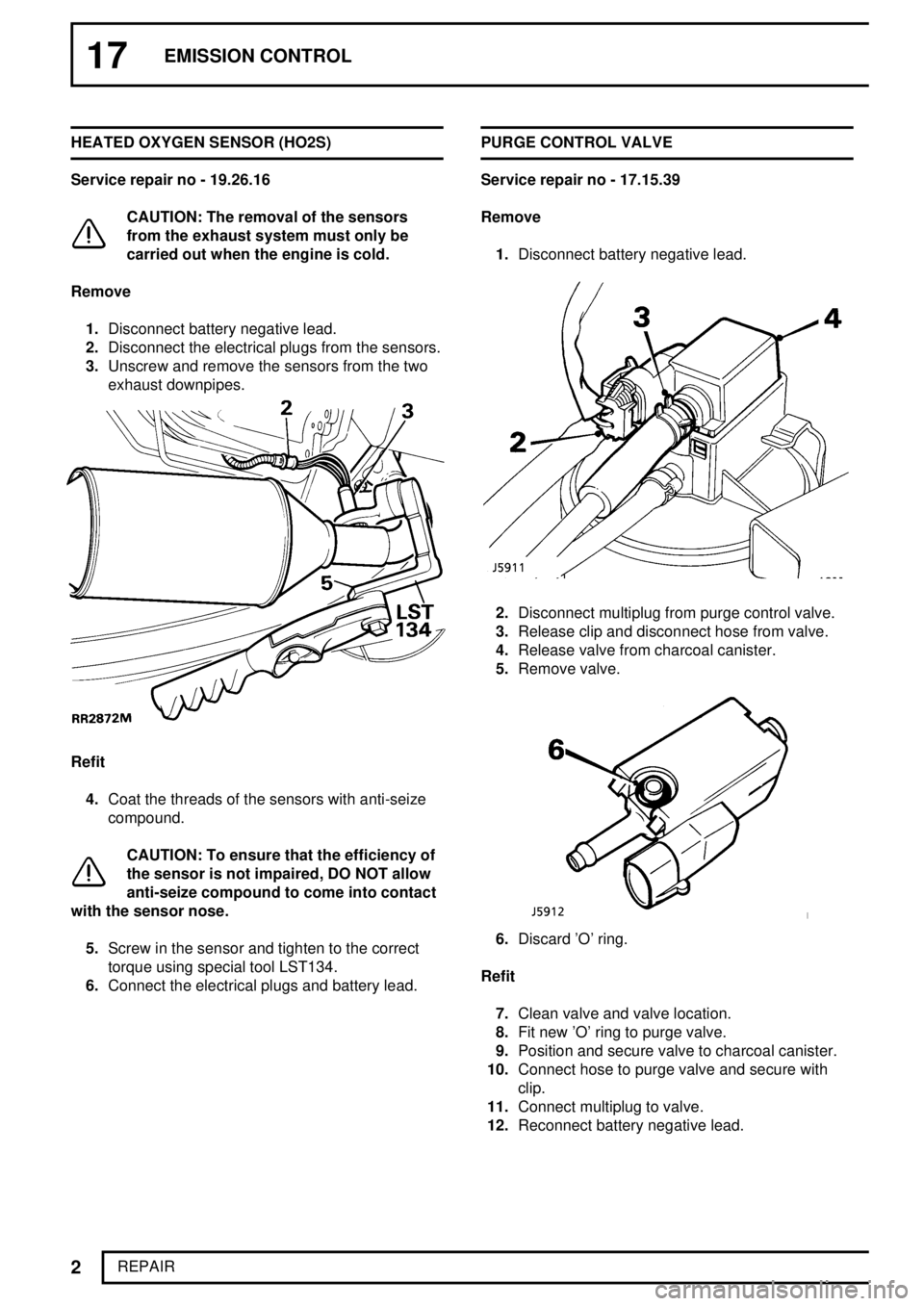
17EMISSION CONTROL
2
REPAIR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S)
Service repair no - 19.26.16
CAUTION: The removal of the sensors
from the exhaust system must only be
carried out when the engine is cold.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect the electrical plugs from the sensors.
3.Unscrew and remove the sensors from the two
exhaust downpipes.
Refit
4.Coat the threads of the sensors with anti-seize
compound.
CAUTION: To ensure that the efficiency of
the sensor is not impaired, DO NOT allow
anti-seize compound to come into contact
with the sensor nose.
5.Screw in the sensor and tighten to the correct
torque using special tool LST134.
6.Connect the electrical plugs and battery lead.PURGE CONTROL VALVE
Service repair no - 17.15.39
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect multiplug from purge control valve.
3.Release clip and disconnect hose from valve.
4.Release valve from charcoal canister.
5.Remove valve.
6.Discard 'O' ring.
Refit
7.Clean valve and valve location.
8.Fit new 'O' ring to purge valve.
9.Position and secure valve to charcoal canister.
10.Connect hose to purge valve and secure with
clip.
11.Connect multiplug to valve.
12.Reconnect battery negative lead.
Page 200 of 873
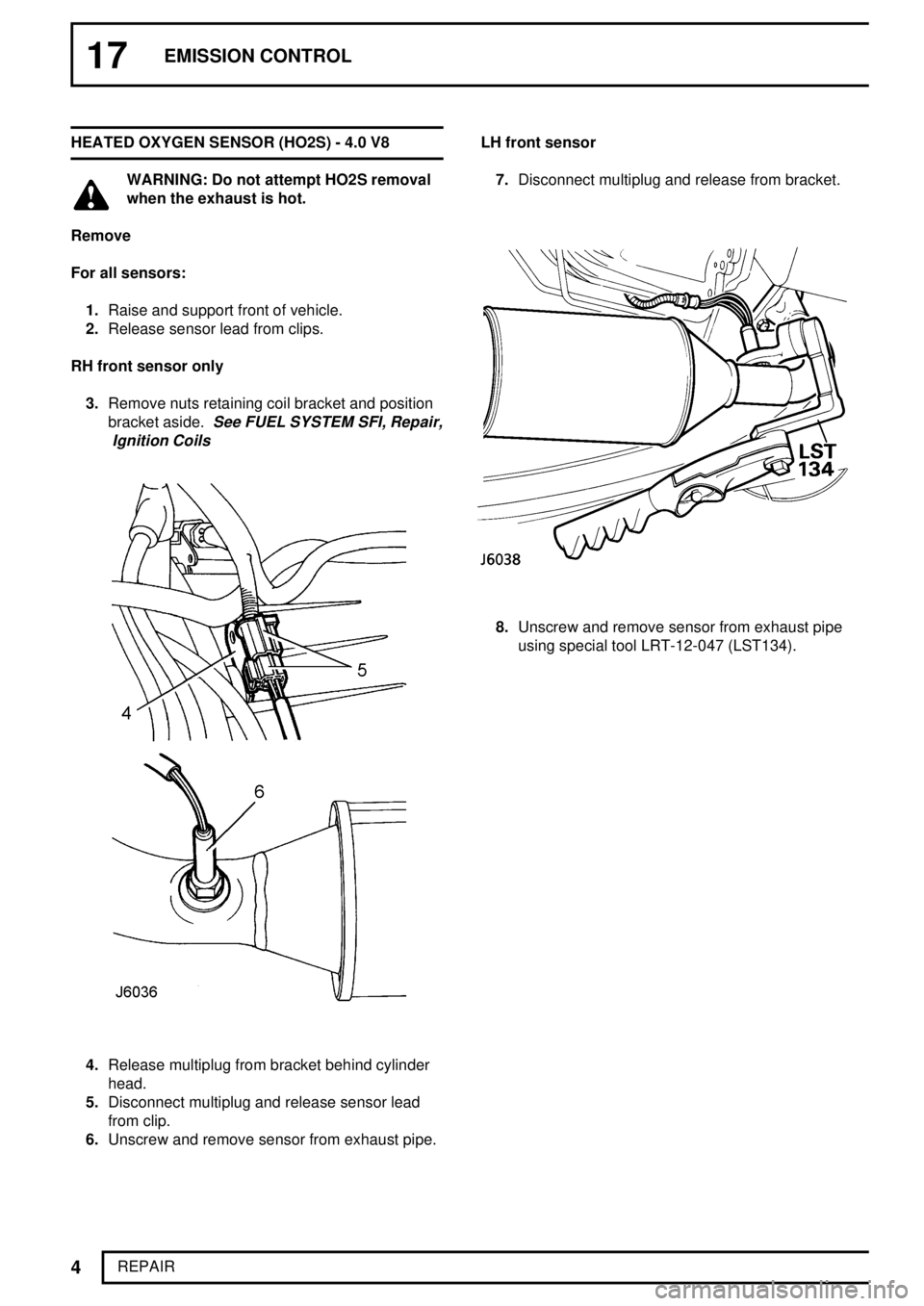
17EMISSION CONTROL
4
REPAIR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S) - 4.0 V8
WARNING: Do not attempt HO2S removal
when the exhaust is hot.
Remove
For all sensors:
1.Raise and support front of vehicle.
2.Release sensor lead from clips.
RH front sensor only
3.Remove nuts retaining coil bracket and position
bracket aside.
See FUEL SYSTEM SFI, Repair,
Ignition Coils
4.Release multiplug from bracket behind cylinder
head.
5.Disconnect multiplug and release sensor lead
from clip.
6.Unscrew and remove sensor from exhaust pipe.LH front sensor
7.Disconnect multiplug and release from bracket.
8.Unscrew and remove sensor from exhaust pipe
using special tool LRT-12-047 (LST134).
Page 201 of 873
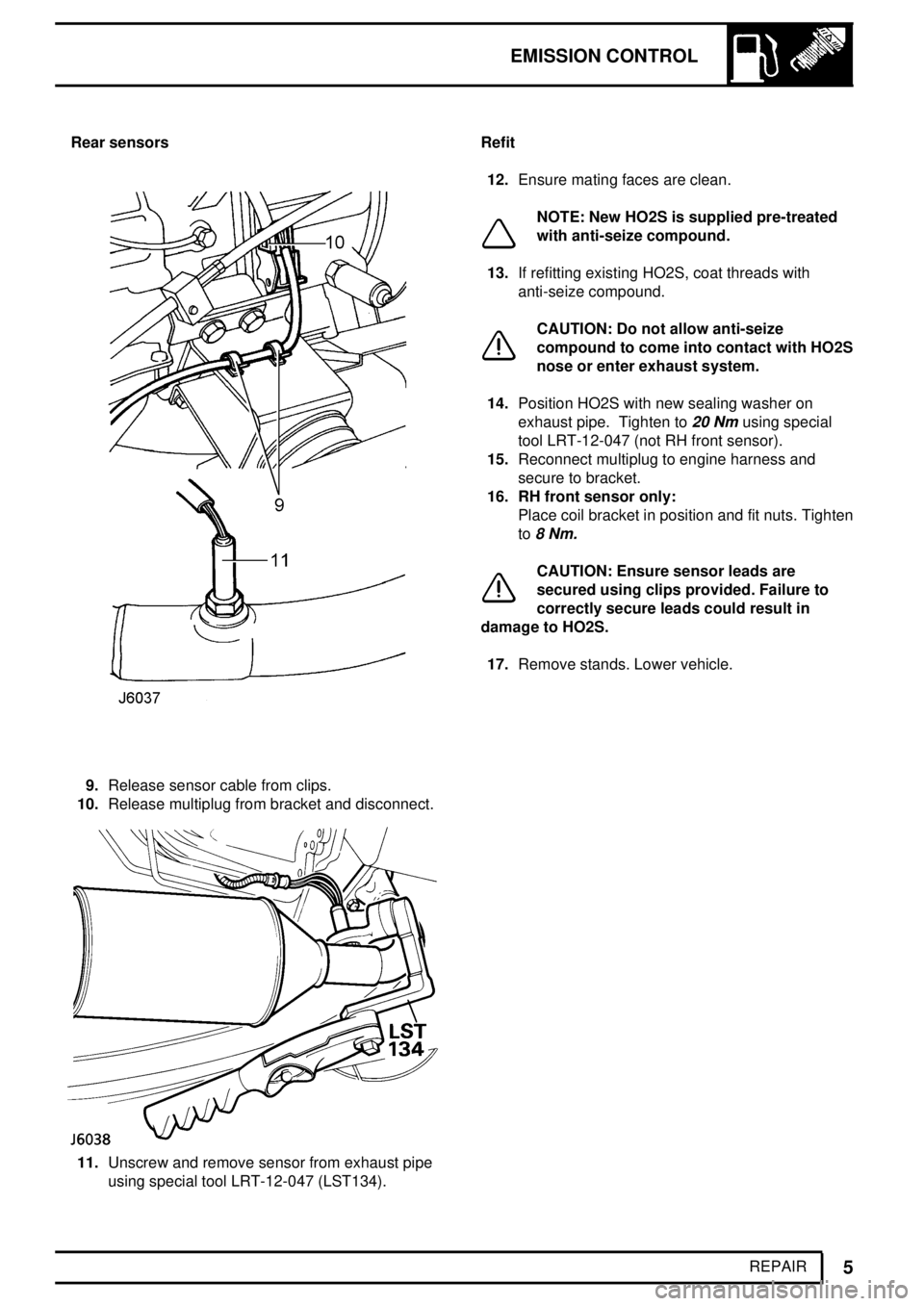
EMISSION CONTROL
5
REPAIR Rear sensors
9.Release sensor cable from clips.
10.Release multiplug from bracket and disconnect.
11.Unscrew and remove sensor from exhaust pipe
using special tool LRT-12-047 (LST134).Refit
12.Ensure mating faces are clean.
NOTE: New HO2S is supplied pre-treated
with anti-seize compound.
13.If refitting existing HO2S, coat threads with
anti-seize compound.
CAUTION: Do not allow anti-seize
compound to come into contact with HO2S
nose or enter exhaust system.
14.Position HO2S with new sealing washer on
exhaust pipe. Tighten to
20 Nmusing special
tool LRT-12-047 (not RH front sensor).
15.Reconnect multiplug to engine harness and
secure to bracket.
16. RH front sensor only:
Place coil bracket in position and fit nuts. Tighten
to
8 Nm.
CAUTION: Ensure sensor leads are
secured using clips provided. Failure to
correctly secure leads could result in
damage to HO2S.
17.Remove stands. Lower vehicle.
Page 202 of 873
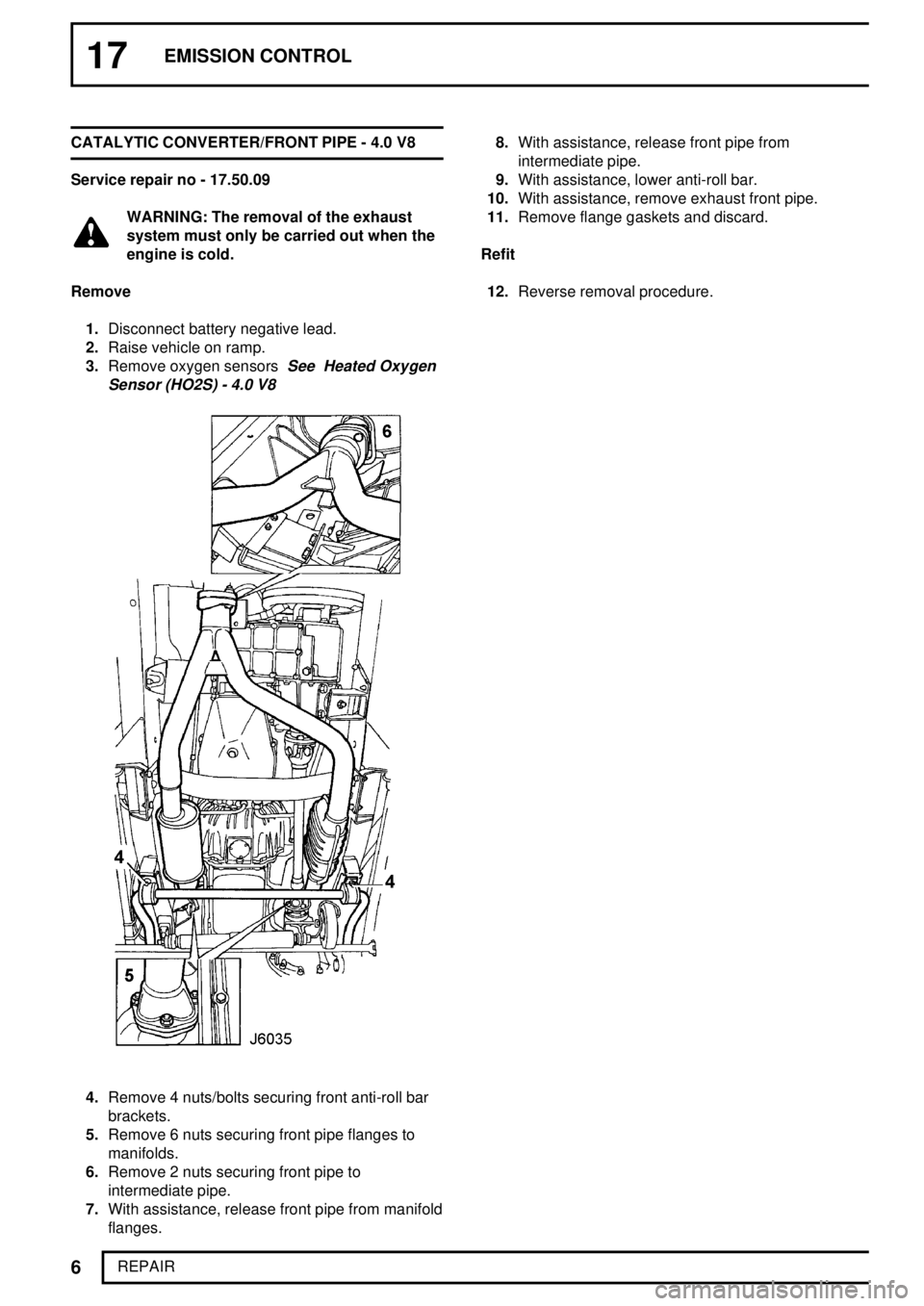
17EMISSION CONTROL
6
REPAIR CATALYTIC CONVERTER/FRONT PIPE - 4.0 V8
Service repair no - 17.50.09
WARNING: The removal of the exhaust
system must only be carried out when the
engine is cold.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Raise vehicle on ramp.
3.Remove oxygen sensors
See Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) - 4.0 V8
4.Remove 4 nuts/bolts securing front anti-roll bar
brackets.
5.Remove 6 nuts securing front pipe flanges to
manifolds.
6.Remove 2 nuts securing front pipe to
intermediate pipe.
7.With assistance, release front pipe from manifold
flanges.8.With assistance, release front pipe from
intermediate pipe.
9.With assistance, lower anti-roll bar.
10.With assistance, remove exhaust front pipe.
11.Remove flange gaskets and discard.
Refit
12.Reverse removal procedure.
Page 206 of 873

Tdi
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Air intake
The air cleaner is positioned to the right of the engine
and connected by hoses to a cold air intake duct and
the turbocharger inlet. A crankcase breather hose is
fitted between the air cleaner and the separator.
A single stage turbocharger, fitted between the
exhaust manifold and exhaust pipe, is connected by
hoses to the air cleaner and to an intercooler mounted
on the right of the radiator. The intercooler is
connected by a hose to the inlet manifold.
Fuel system
A 89 litre fuel tank is mounted at the rear of the
vehicle beneath the load space floor. The tank is
vented by a 2 way valve in the filler cap.
A mechanical lift pump, driven by the camshaft, is
mounted on the side of the engine.
A fuel filter, fitted with a replaceable element and
incorporating a water separator, is positioned on the
LH side of the bulkhead.
A Bosch Type injection pump, incorporating a cold
start advance unit and a high idle setting is mounted
on the LH side of the engine and is directly driven by
gears from the crankshaft. The pump meters and
distributes fuel to 4 pintle type injectors located in
pre-combustion chambers in the cylinder heads.
A return line passes excess fuel from the injection
pump and injectors back to the fuel tank.
Glow plugs
Four glow plugs are located in the cylinder head,
directly below each injector.Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
Exhaust gas recirculation is controlled by the EGR
control unit mounted in the passenger compartment
on the RH 'A' post behind the fascia and receives the
following inputs:
a. Engine temperature from coolant temperature
transmitter in No. 4 cylinder head.
b. Throttle position from the sensor on the injection
pump.
c. Engine speed from the tachometer.
d. EGR valve lift position.
When all correct signals are received, the EGR
solenoid allows vacuum to open the EGR valve and
recirculate a portion of the exhaust gas.
Page 207 of 873
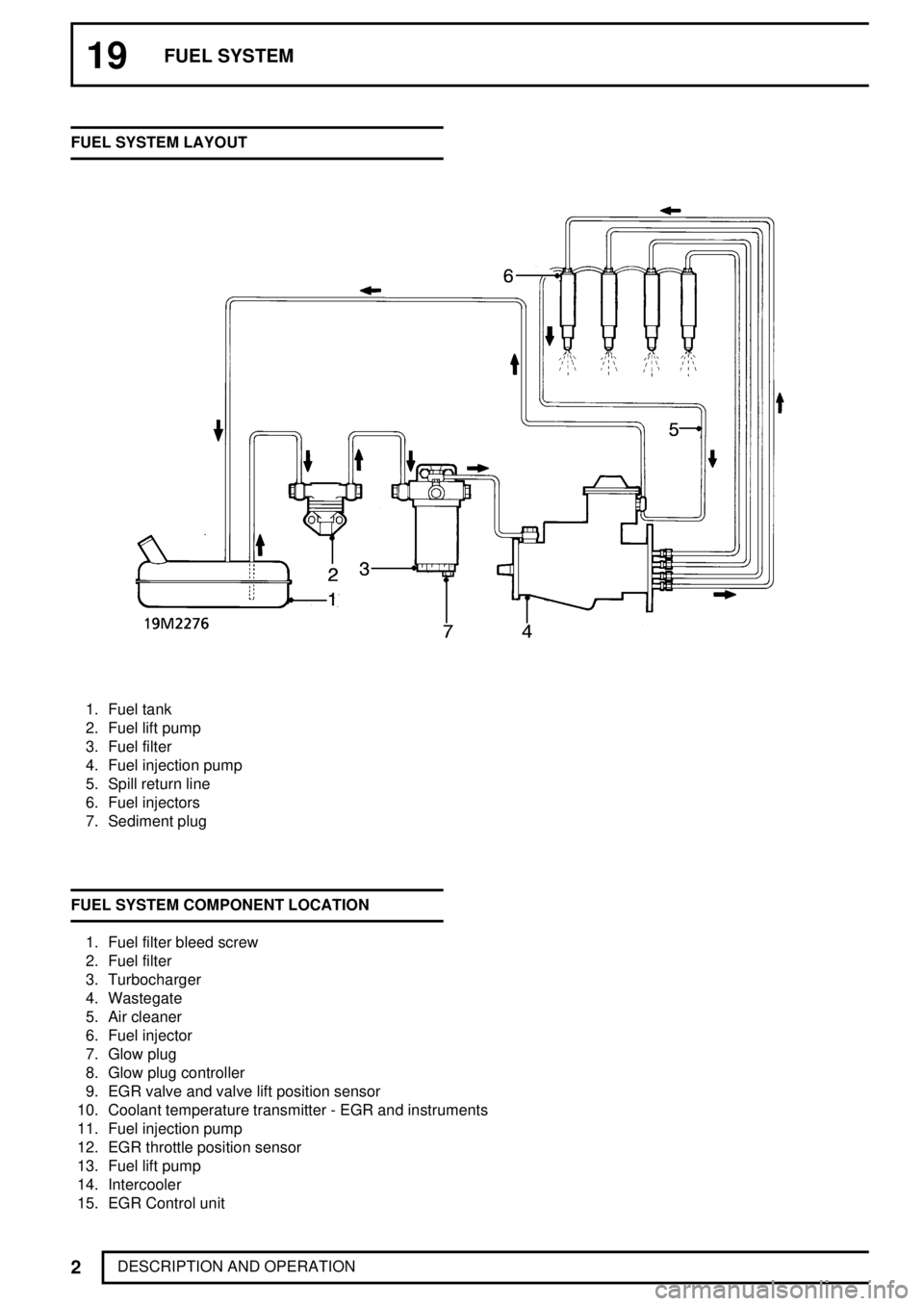
19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL SYSTEM LAYOUT
1. Fuel tank
2. Fuel lift pump
3. Fuel filter
4. Fuel injection pump
5. Spill return line
6. Fuel injectors
7. Sediment plug
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT LOCATION
1. Fuel filter bleed screw
2. Fuel filter
3. Turbocharger
4. Wastegate
5. Air cleaner
6. Fuel injector
7. Glow plug
8. Glow plug controller
9. EGR valve and valve lift position sensor
10. Coolant temperature transmitter - EGR and instruments
11. Fuel injection pump
12. EGR throttle position sensor
13. Fuel lift pump
14. Intercooler
15. EGR Control unit
Page 209 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Diesel engines operate by compression ignition. The
rapid compression of air in the cylinder during the
compression cycle heats the injected fuel, causing it
to self ignite. During cold starting, automatically
controlled glow plugs assist in raising the temperature
of the compressed air to ignition point.
A cold start advance unit advances the injection timing
to further assist starting. Idle quality is improved by
the high idle setting.
The engine is supplied with pre-compressed air by a
single stage turbocharger.
Exhaust gases passing over a turbine cause it to
rotate, driving a compressor mounted on the turbine
shaft. Air drawn from the cold air intake passes, via
the air cleaner, to the turbocharger where it is
compressed. The compressed air passes to the
cylinders via an intercooler, which reduces the
temperature of the compressed air, increasing its
density.
Fuel is drawn from the tank by a mechanical lift pump
and passes to the injection pump via a filter. In
addition to removing particle contamination from the
fuel, the filter incorporates a water separator, which
removes and stores both bound and unbound water.
The injection pump meters a precisely timed, exact
quantity of fuel to the injectors in response to throttle
variations, injection timing varying with engine speed.
Any excess fuel delivered to the injection pump is not
injected, passing back to the tank via the fuel return
line.
Fuel is injected in a finely atomised form into a
pre-combustion chamber in the cylinder head where it
ignites. The burning fuel expands rapidly into the main
combustion chamber, creating extreme turbulence
which mixes the burning fuel thoroughly with the
compressed air, providing complete combustion.
Cold Starting is assisted by glow plugs, a cold start
advance unit and a high idle setting.Glow plugs
Glow plug operation is controlled by a timer unit, start
relay and resistor. When the ignition is turned on the
timer unit is energised, the glow plugs start to operate
and a warning light on the dashboard illuminates,
remaining illuminated until the glow plugs are
automatically switched off.
The length of time the glow plugs will operate is
dependent on under bonnet temperature, which is
monitored by a sensor located in the timer unit.
Starting the engine results in the power supply to the
glow plugs passing through the resistor, which
reduces their operating temperature. The glow plugs
are cut out either by the temperature sensor in the
timer, or by a microswitch on the injection pump which
operates when the throttle is depressed.
Cold start advance
The cold start advance unit is connected to the engine
cooling system via hoses. It contains a temperature
sensitive element which is retracted when cold and
pulls the advance lever, via cable, towards the rear of
the pump against spring pressure. As coolant
temperature rises, the cold start element expands
releasing tension on the cable and allowing spring
pressure to move the advance lever forwards.
Page 210 of 873

Tdi
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Operation of the EGR system is dependent on the
following:
a. Engine temperature - must be between 20°C
and 100°C approx.
b. Engine speed - must be between 630 and 2850
rev/min.
c. Engine load - calculated by throttle position
sensor.
d. EGR valve lift position.
e. Duration of engine idling.
Under varying engine speed and load conditions the
control unit sends a signal to open the vacuum
modulator which allows a vacuum to be applied above
the EGR valve diaphragm, the vacuum supply being
taken from a 'T' connector in the brake servo hose.
This process is controlled by an engine speed/load
map stored in the EGR control unit memory.
Engine speed is measured by monitoring the
waveform present on one phase of the generator.
Throttle position is measured via a sensor mounted on
the fuel injection pump throttle lever. Closed loop
control is achieved by allowing the control unit to
continually monitor EGR valve lift via a position sensor
mounted on the valve; this valve lift is compared with
the actual valve lift required on the control unit map
and adjusted if necessary.
With coolant temperature between 20°C and 100°C;
the engine having just returned to idle, EGR will shut
off after 25-30 seconds idling.
Page 211 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION ELECTRONIC DIESEL CONTROL
The Electronic Diesel Control (EDC) 'drive by wire'
system derives its from the replacement of
conventional mechanical controls by electronic
components.
The EDC system supplies the exact amount of fuel to
the engine according to the prevailing engine
operating conditions. To monitor these conditions,
sensors are fitted to the engine to measure engine
parameters. Data from the sensors is received by the
Engine Control Module (ECM) which determines the
exact amount of fuel, injection timing and Exhaust
Gas Recirculation (EGR) required for any running
condition.
Safety and emergency features are built into the
system which protect the engine against overspeed
and overheating damage. In the event of component
failure the system is designed to compensate and
allow emergency start and limp home facilities to
operate. The ECM does this by substituting a default
value for the failed component which may result in a
noticeable loss in power but keeps the engine
running.FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT LOCATION EDC
1. Vehicle speed sensor
2. No. 4 injector sensor
3. Coolant temperature sensor
4. Boost pressure sensor
5. Electro-pneumatic modulator
6. Airflow sensor
7. Engine speed sensor
8. Brake/clutch switches
9. Injector pump
10. Throttle position sensor
11. Engine control module
Page 213 of 873
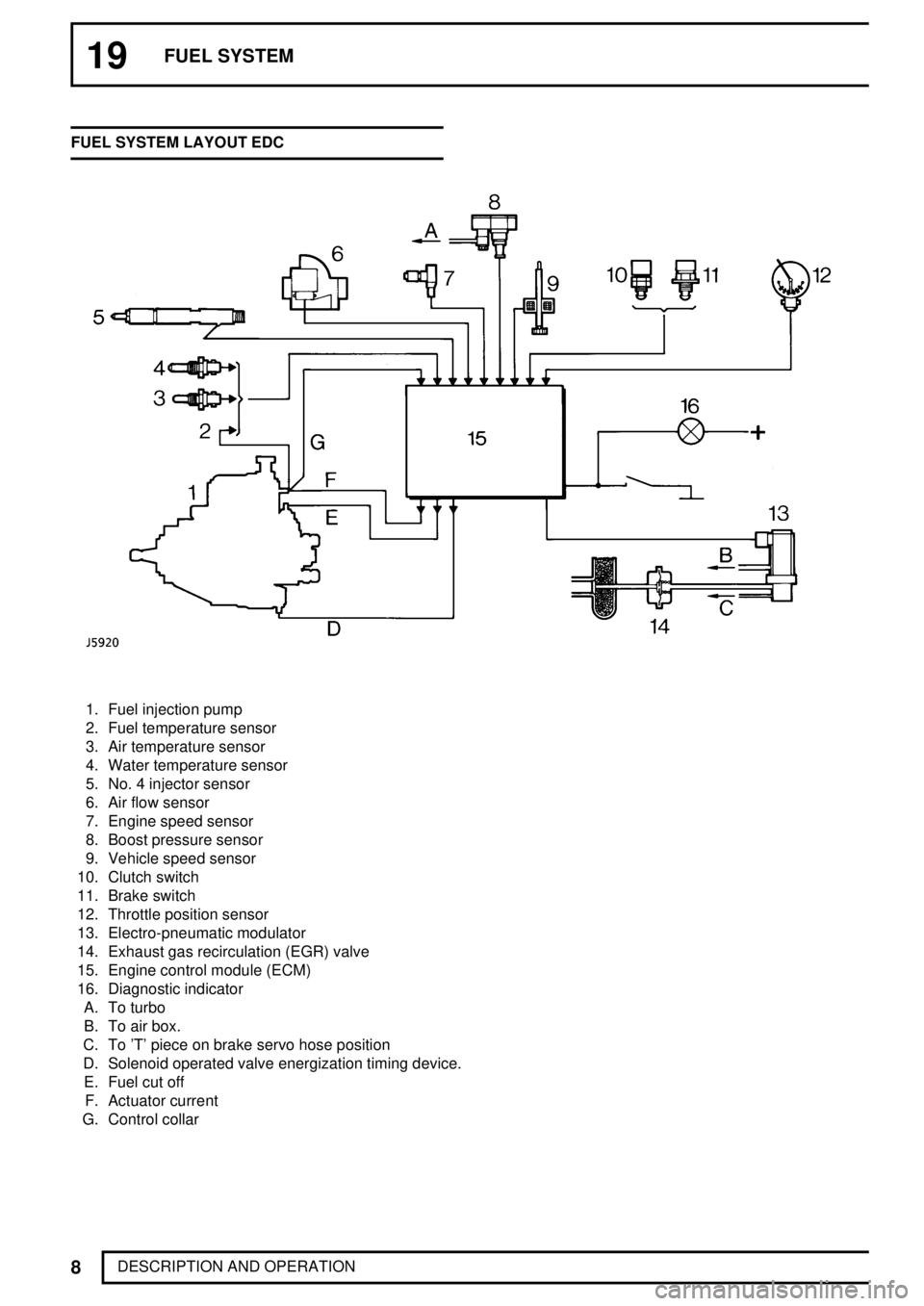
19FUEL SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL SYSTEM LAYOUT EDC
1. Fuel injection pump
2. Fuel temperature sensor
3. Air temperature sensor
4. Water temperature sensor
5. No. 4 injector sensor
6. Air flow sensor
7. Engine speed sensor
8. Boost pressure sensor
9. Vehicle speed sensor
10. Clutch switch
11. Brake switch
12. Throttle position sensor
13. Electro-pneumatic modulator
14. Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
15. Engine control module (ECM)
16. Diagnostic indicator
A. To turbo
B. To air box.
C. To 'T' piece on brake servo hose position
D. Solenoid operated valve energization timing device.
E. Fuel cut off
F. Actuator current
G. Control collar