check engine LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 908 of 1672
STEERING
ADJUSTMENTS 57-21
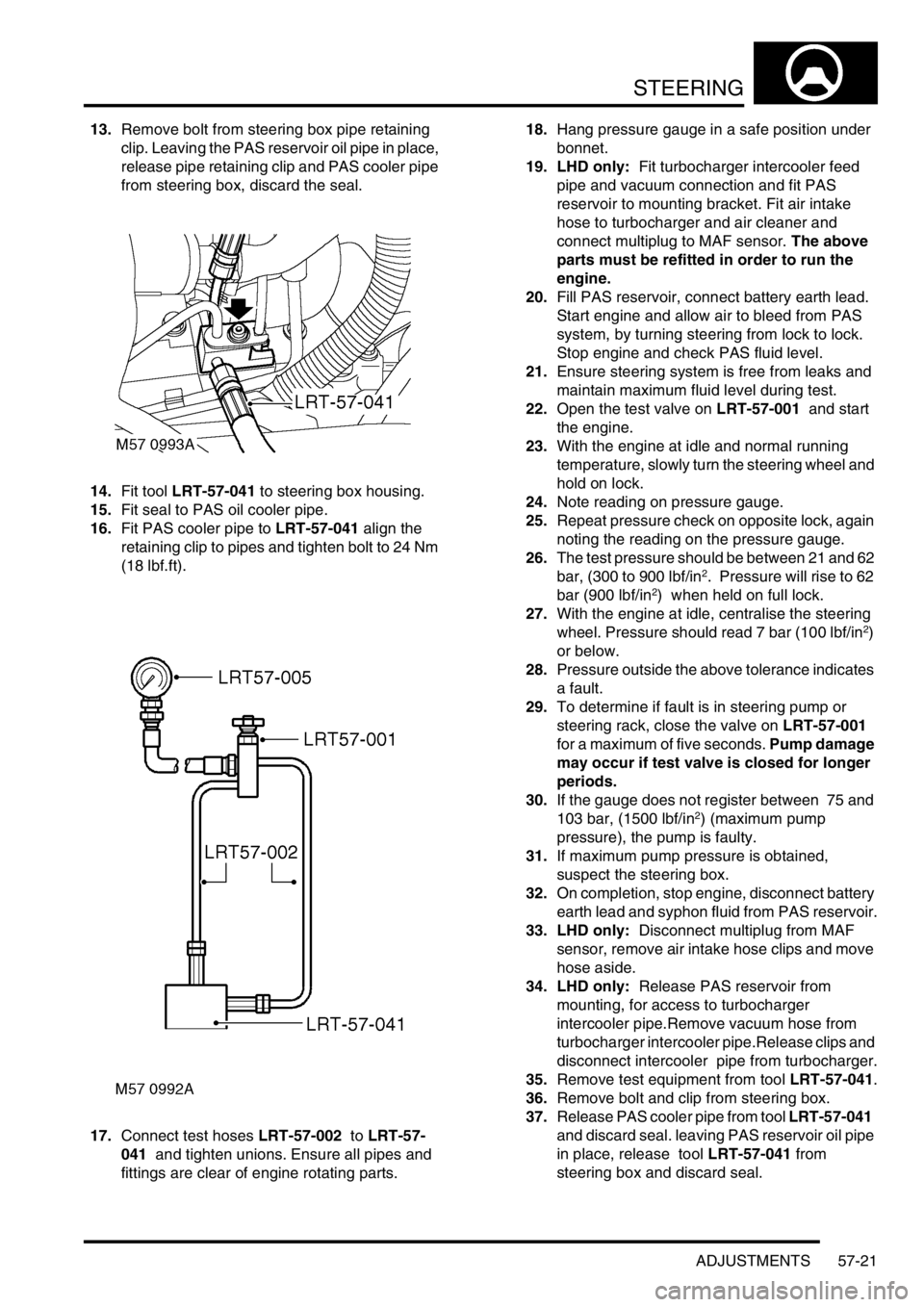
13.Remove bolt from steering box pipe retaining
clip. Leaving the PAS reservoir oil pipe in place,
release pipe retaining clip and PAS cooler pipe
from steering box, discard the seal.
14.Fit tool LRT-57-041 to steering box housing.
15.Fit seal to PAS oil cooler pipe.
16.Fit PAS cooler pipe to LRT-57-041 align the
retaining clip to pipes and tighten bolt to 24 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
17.Connect test hoses LRT-57-002 to LRT-57-
041 and tighten unions. Ensure all pipes and
fittings are clear of engine rotating parts.18.Hang pressure gauge in a safe position under
bonnet.
19. LHD only: Fit turbocharger intercooler feed
pipe and vacuum connection and fit PAS
reservoir to mounting bracket. Fit air intake
hose to turbocharger and air cleaner and
connect multiplug to MAF sensor. The above
parts must be refitted in order to run the
engine.
20.Fill PAS reservoir, connect battery earth lead.
Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system, by turning steering from lock to lock.
Stop engine and check PAS fluid level.
21.Ensure steering system is free from leaks and
maintain maximum fluid level during test.
22.Open the test valve on LRT-57-001 and start
the engine.
23.With the engine at idle and normal running
temperature, slowly turn the steering wheel and
hold on lock.
24.Note reading on pressure gauge.
25.Repeat pressure check on opposite lock, again
noting the reading on the pressure gauge.
26.The test pressure should be between 21 and 62
bar, (300 to 900 lbf/in
2. Pressure will rise to 62
bar (900 lbf/in2) when held on full lock.
27.With the engine at idle, centralise the steering
wheel. Pressure should read 7 bar (100 lbf/in
2)
or below.
28.Pressure outside the above tolerance indicates
a fault.
29.To determine if fault is in steering pump or
steering rack, close the valve on LRT-57-001
for a maximum of five seconds. Pump damage
may occur if test valve is closed for longer
periods.
30.If the gauge does not register between 75 and
103 bar, (1500 lbf/in
2) (maximum pump
pressure), the pump is faulty.
31.If maximum pump pressure is obtained,
suspect the steering box.
32.On completion, stop engine, disconnect battery
earth lead and syphon fluid from PAS reservoir.
33. LHD only: Disconnect multiplug from MAF
sensor, remove air intake hose clips and move
hose aside.
34. LHD only: Release PAS reservoir from
mounting, for access to turbocharger
intercooler pipe.Remove vacuum hose from
turbocharger intercooler pipe.Release clips and
disconnect intercooler pipe from turbocharger.
35.Remove test equipment from tool LRT-57-041.
36.Remove bolt and clip from steering box.
37.Release PAS cooler pipe from tool LRT-57-041
and discard seal. leaving PAS reservoir oil pipe
in place, release tool LRT-57-041 from
steering box and discard seal.
Page 910 of 1672
STEERING
ADJUSTMENTS 57-23
9.Release clips and remove air intake hose from
air cleaner housing.
Note: Pre 03 MY air intake hose illustrated.
10.Discard intake 'O' ring and move intake aside
for access.
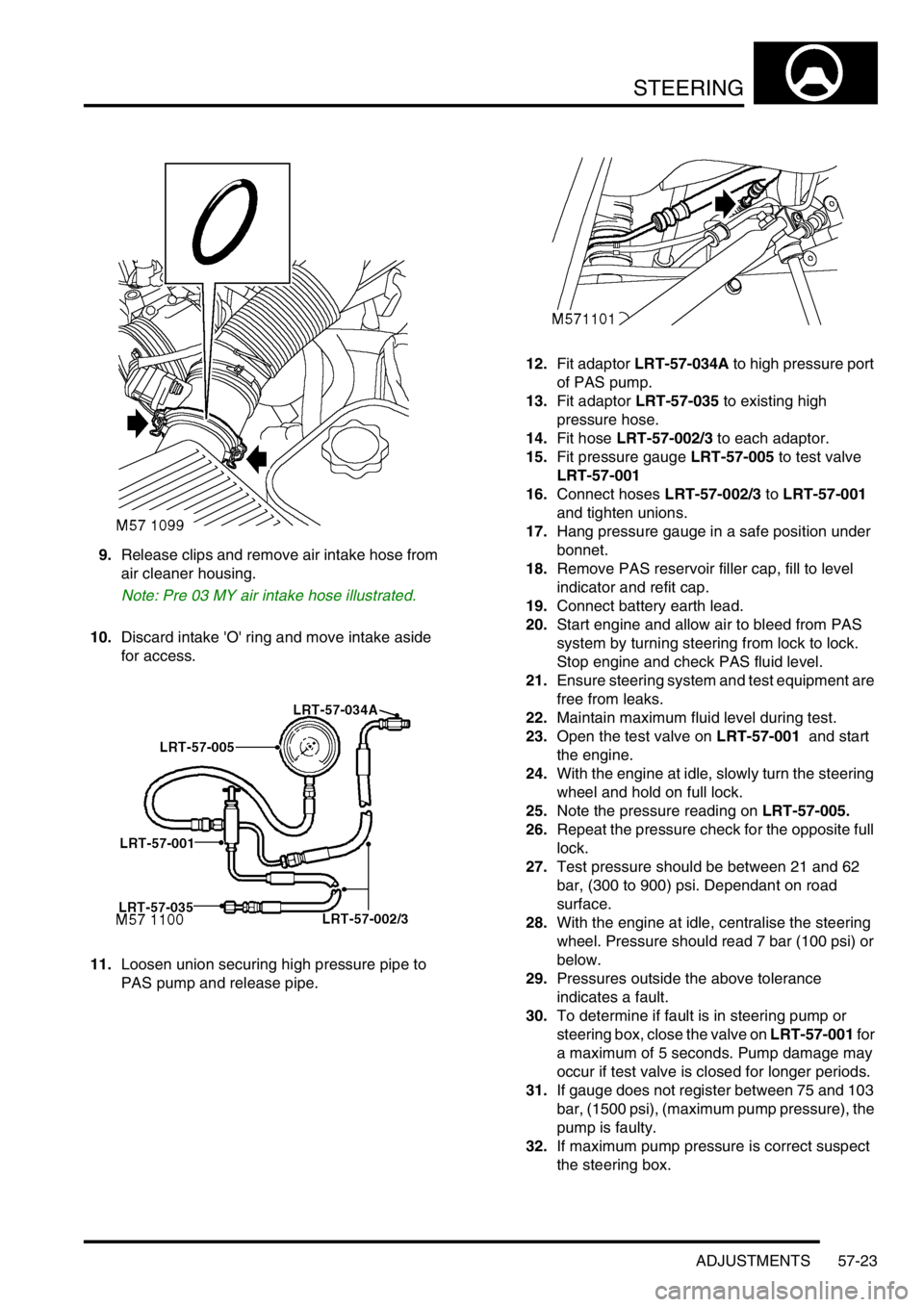
11.Loosen union securing high pressure pipe to
PAS pump and release pipe.12.Fit adaptor LRT-57-034A to high pressure port
of PAS pump.
13.Fit adaptor LRT-57-035 to existing high
pressure hose.
14.Fit hose LRT-57-002/3 to each adaptor.
15.Fit pressure gauge LRT-57-005 to test valve
LRT-57-001
16.Connect hoses LRT-57-002/3 to LRT-57-001
and tighten unions.
17.Hang pressure gauge in a safe position under
bonnet.
18.Remove PAS reservoir filler cap, fill to level
indicator and refit cap.
19.Connect battery earth lead.
20.Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system by turning steering from lock to lock.
Stop engine and check PAS fluid level.
21.Ensure steering system and test equipment are
free from leaks.
22.Maintain maximum fluid level during test.
23.Open the test valve on LRT-57-001 and start
the engine.
24.With the engine at idle, slowly turn the steering
wheel and hold on full lock.
25.Note the pressure reading on LRT-57-005.
26.Repeat the pressure check for the opposite full
lock.
27.Test pressure should be between 21 and 62
bar, (300 to 900) psi. Dependant on road
surface.
28.With the engine at idle, centralise the steering
wheel. Pressure should read 7 bar (100 psi) or
below.
29.Pressures outside the above tolerance
indicates a fault.
30.To determine if fault is in steering pump or
steering box, close the valve on LRT-57-001 for
a maximum of 5 seconds. Pump damage may
occur if test valve is closed for longer periods.
31.If gauge does not register between 75 and 103
bar, (1500 psi), (maximum pump pressure), the
pump is faulty.
32.If maximum pump pressure is correct suspect
the steering box.
Page 911 of 1672

STEERING
57-24 ADJUSTMENTS
33.On completion stop engine, disconnect battery
earth lead and syphon fluid from PAS reservoir.
34.Remove test equipment from LRT-57-002.
35.Clean PAS pump and pipe union.
36.Fit new 'O' ring to high pressure pipe, align to
PAS pump and tighten union to 25 Nm (18
lbf.ft).
37.Secure PAS pipes in clip.
38.Using new 'O' ring fit intake hose to air cleaner
and secure clips.
39.Remove PAS reservoir filler cap, fill to level
indicator and refit cap.
40.Connect battery earth lead.
41.Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system, by turning steering from lock to lock.
42.Visually check PAS system for leaks.
43.Clean chassis member.
44.Check power steering fluid, if aerated, wait until
fluid is free from bubbles then top-up reservoir
to 'UPPER' level mark.
45.Lower vehicle.
46.Dismantle test equipment.
Power steering pressure check - V8 RHD
models
$% 57.90.10.01
Check
1.Fit gauge and hose LRT-57-005 to valve
assembly LRT-57-001, tighten union.
2.Fit 2 hoses LRT-57-002 to valve assembly
LRT-57-001 and tighten unions.
3.Fit adaptor hoses LRT-57-041 to LRT-57-002
and tighten unions.
4.Disconnect battery earth lead.
5.Remove 5 screws securing front splash shield
to chassis. Remove shield.
6.Clean PAS fluid reservoir around filler cap and
fluid level indicators.
Page 912 of 1672
STEERING
ADJUSTMENTS 57-25
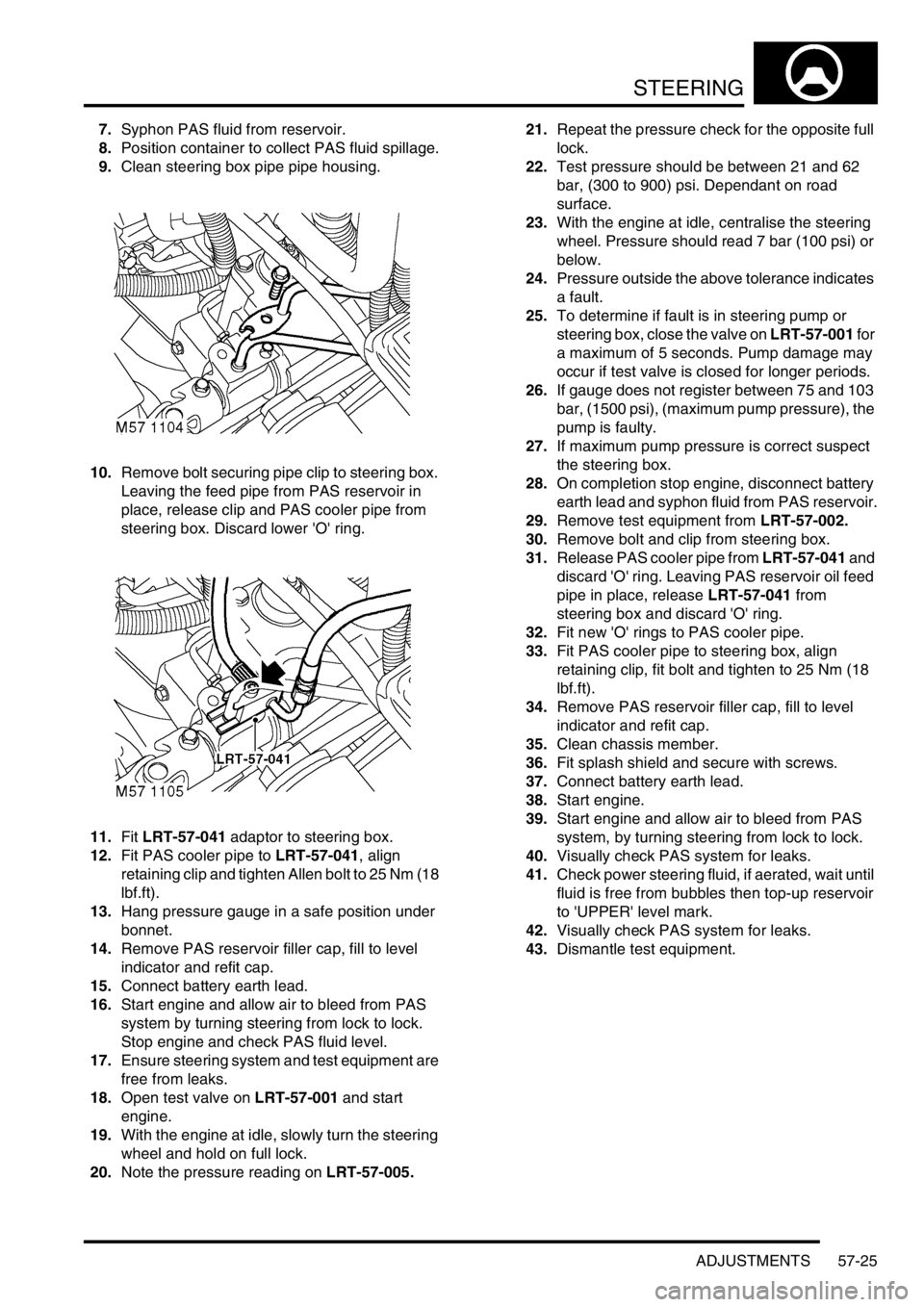
7.Syphon PAS fluid from reservoir.
8.Position container to collect PAS fluid spillage.
9.Clean steering box pipe pipe housing.
10.Remove bolt securing pipe clip to steering box.
Leaving the feed pipe from PAS reservoir in
place, release clip and PAS cooler pipe from
steering box. Discard lower 'O' ring.
11.Fit LRT-57-041 adaptor to steering box.
12.Fit PAS cooler pipe to LRT-57-041, align
retaining clip and tighten Allen bolt to 25 Nm (18
lbf.ft).
13.Hang pressure gauge in a safe position under
bonnet.
14.Remove PAS reservoir filler cap, fill to level
indicator and refit cap.
15.Connect battery earth lead.
16.Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system by turning steering from lock to lock.
Stop engine and check PAS fluid level.
17.Ensure steering system and test equipment are
free from leaks.
18.Open test valve on LRT-57-001 and start
engine.
19.With the engine at idle, slowly turn the steering
wheel and hold on full lock.
20.Note the pressure reading on LRT-57-005.21.Repeat the pressure check for the opposite full
lock.
22.Test pressure should be between 21 and 62
bar, (300 to 900) psi. Dependant on road
surface.
23.With the engine at idle, centralise the steering
wheel. Pressure should read 7 bar (100 psi) or
below.
24.Pressure outside the above tolerance indicates
a fault.
25.To determine if fault is in steering pump or
steering box, close the valve on LRT-57-001 for
a maximum of 5 seconds. Pump damage may
occur if test valve is closed for longer periods.
26.If gauge does not register between 75 and 103
bar, (1500 psi), (maximum pump pressure), the
pump is faulty.
27.If maximum pump pressure is correct suspect
the steering box.
28.On completion stop engine, disconnect battery
earth lead and syphon fluid from PAS reservoir.
29.Remove test equipment from LRT-57-002.
30.Remove bolt and clip from steering box.
31.Release PAS cooler pipe from LRT-57-041 and
discard 'O' ring. Leaving PAS reservoir oil feed
pipe in place, release LRT-57-041 from
steering box and discard 'O' ring.
32.Fit new 'O' rings to PAS cooler pipe.
33.Fit PAS cooler pipe to steering box, align
retaining clip, fit bolt and tighten to 25 Nm (18
lbf.ft).
34.Remove PAS reservoir filler cap, fill to level
indicator and refit cap.
35.Clean chassis member.
36.Fit splash shield and secure with screws.
37.Connect battery earth lead.
38.Start engine.
39.Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system, by turning steering from lock to lock.
40.Visually check PAS system for leaks.
41.Check power steering fluid, if aerated, wait until
fluid is free from bubbles then top-up reservoir
to 'UPPER' level mark.
42.Visually check PAS system for leaks.
43.Dismantle test equipment.
Page 916 of 1672

STEERING
REPAIRS 57-29
12. RH drive models with ACE: Position ACE
control arms to access steering box bolts.
13.With assistance remove 4 securing bolts and
remove steering box.
14.Remove centralising bolt from steering box. Refit
1.Fit centralising bolt to steering box.
2. With assistance, position steering box, fit bolts
and tighten to 90 Nm (66 lbf.ft).
3. RH drive models with ACE: Ensure washer is
in place on lower ball joint of anti-roll bar link,
then connect lower ball joint to axle. Tighten nut
to 100 Nm (74 lbf.ft).
4.Position drag link, fit nut and tighten to 80 Nm
(59 lbf.ft).
5.Position Panhard rod, fit bolt and nut and
tighten to 230 Nm (170 lbf.ft).
6.Clean PAS pipe ends and 'O' ring recess.
7.Lubricate new 'O' rings for PAS pipes with clean
PAS fluid.
8.Fit 'O' rings to PAS pipes and position pipes in
steering box. Fit PAS pipe bracket and tighten
bolt to 22 Nm (16 lbf.ft).
9. RHD models: Fit oil filter and housing:
lClean oil filter housing and engine mating
faces.
lLubricate new 'O' ring with clean engine oil
and fit to housing.
lPosition oil filter housing and tighten bolts to
9 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
10.Ensure steering wheel is centralised. Fit
universal joint between steering box and
intermediate shaft and tighten bolts to 25 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
11.Remove centralising bolt from steering box.
12.Fit road wheel(s) and tighten nuts to 140 Nm
(103 lbf.ft)..
13.Remove stand(s) and lower vehicle.
14.Check and top up engine oil.
15.Bleed PAS system.
+ STEERING, ADJUSTMENTS,
Hydraulic system - bleed.
16.Centralise steering linkage
+ STEERING, ADJUSTMENTS,
Steering linkage - centralise.
Page 952 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-13
Lateral acceleration of the body is sensed by two accelerometers and signals are transmitted to the ECU. The engine
driven hydraulic pump supplies a constant hydraulic flow to the valve block. Two directional control valves are
solenoid operated by the ECU and these supply fluid to the applicable side of each actuator to apply an equal and
opposite force to the torsion bar. In operation the ACE system maintains the attitude of the vehicle body when
cornering.
The ACE system uses a semi-synthetic hydraulic fluid which is the same as the fluid used for the PAS system. The
total capacity of the ACE system is 1.62 litres (0.42 US Gallons).
CAUTION: The ACE hydraulic system is extremely sensitive to the ingress of dirt or debris. The smallest
amount could render the system unserviceable. It is imperative that the following precautions are taken.
lACE components are thoroughly cleaned externally before work commences;
lall opened pipe and module ports are capped immediately;
lall fluid is stored in and administered through clean containers.
In the event of an ECU or hydraulic failure the system will fail safe to a 'locked bars' condition. The 'locked bars'
condition will allow the torsion bars to operate in a similar manner as conventional 'passive' anti-roll bars. Prolonged
cornering forces will allow a progressive increase in roll angle due to hydraulic leakage through the actuators and
valve block. Failures will be relayed to the driver by the illumination of the ACE warning lamp in the instrument pack.
Faults are recorded by the ECU and can be retrieved using TestBook.
When the ignition switch is moved to position II, the warning lamp will illuminate for two seconds to check functionality.
The warning lamp functionality can also be checked using TestBook.
TestBook must also be used to perform a bleeding procedure after maintenance operations have been performed to
ensure that complete system bleeding is performed. Trapped air in the system can seriously reduce the system
performance.
Fluid reservoir
The moulded plastic fluid reservoir is mounted on the left hand side of the engine compartment on a bracket which is
attached to the inner wing. The reservoir is dual purpose, being divided into two separate chambers; one for the ACE
system and one for the PAS system. Each chamber has its own filler neck and cap and is identified by moulded
lettering on the reservoir adjacent to each filler.
A non-serviceable filter assembly is fitted in the base of each chamber. The filter is made from fine stainless steel
mesh which is moulded into the body of the reservoir. The filter removes particulate matter from the fluid before it is
drawn into the hydraulic pump.
Upper and lower fluid level marks are moulded onto the reservoir body. The capacity of the ACE reservoir chamber
to the upper level mark is 0.5 litre (0.13 US Gallon).
Page 966 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
ADJUSTMENTS 60-27
ADJUST ME NTS
ACE hydraulic system bleeding
$% 60.60.13
Introduction
CAUTION: The ACE hydraulic system is
extremely sensitive to the ingress of dirt or
debris. The smallest amount could render the
system unserviceable. It is imperative that the
following precautions are taken.
lACE components are thoroughly cleaned
externally before work commences;
lall opened pipe and module ports are
capped immediately;
lall fluid is stored in and administered
through clean containers.
Check
1.Check the ACE system fluid level.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION,
ADJUSTMENTS, Fluid level check - ACE
system.
Bleed
1.With vehicle on ramp, connect TestBook and
follow bleed procedure as described.
Fluid level check - ACE system
$% 60.60.14
Introduction
CAUTION: The ACE hydraulic system is
extremely sensitive to the ingress of dirt or
debris. The smallest amount could render the
system unserviceable. It is imperative that the
following precautions are taken.
lACE components are thoroughly cleaned
externally before work commences;
lall opened pipe and module ports are
capped immediately;
lall fluid is stored in and administered
through clean containers.
Check
1.Clean reservoir around fluid level marks.
2.Visually check fluid level through side of
reservoir. Fluid level must be between upper
and lower fluid level marks.
Top-up
1.Clean reservoir around filler cap.
2.Remove filler cap from reservoir and fill to
upper fluid level mark with recommended fluid.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Fluids.
3.Fit filler cap to reservoir
4.Start and run engine for 2 minutes to circulate
fluid.
5.If necessary, top-up reservoir to upper fluid
level mark.
Page 988 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
REPAIRS 60-49
Refit
1.Ensure new filter has 'O' ring fitted, then fit filter
to valve block.
2.Fit new 'O' ring to filter cap. Fit cap and tighten
to 35 Nm (26 lbf.ft).
3.Lower vehicle.
4.Check fluid level in ACE/PAS reservoir.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION,
ADJUSTMENTS, Fluid level check - ACE
system.
5.Start and run engine for 2 minutes, then re-
check fluid level in ACE/PAS reservoir.
+ FRONT SUSPENSION,
ADJUSTMENTS, Fluid level check - ACE
system.
Pressure transducer - ACE
$% 60.60.22
CAUTION: The ACE hydraulic system is
extremely sensitive to the ingress of dirt or
debris. The smallest amount could render the
system unserviceable. It is imperative that the
following precautions are taken.
lACE components are thoroughly cleaned
externally before work commences;
lall opened pipe and module ports are
capped immediately;
lall fluid is stored in and administered
through clean containers.
Remove
1.Raise vehicle on a ramp.
2.Disconnect multiplug from transducer.
3.Position container to collect fluid spillage.
4.Remove pressure transducer and discard 'O'
ring.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
Page 1023 of 1672
REAR SUSPENSION
64-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The ECU supplies a 5 V current to each of the height sensors. Each height sensor uses the current to supply an
analogue input to the ECU. The ECU can calculate from the input received from each height sensor the height of the
vehicle and can then power the air supply unit as necessary to raise or lower one or both air springs to level the
vehicle.
When SLS compressor operation is required, the ECU provides a battery supply to energise the SLS relay located in
the engine compartment fusebox. When the relay contacts close, a 12 V supply passes through fusible link 9 in the
engine compartment fusebox, through the relay contacts and operates the air supply unit compressor. The ECU will
then supply power to operate one or both air control valve solenoids and/or the exhaust valve solenoid to inflate or
deflate the air springs as required. The compressor does not need to be powered to deflate the air springs.
The ECU also controls the operation of the SLS audible warning, the SLS warning lamp and the ORM warning lamp.
When the ignition is switched to position II, the ECU performs a three second bulb check and illuminates the SLS and
ORM warning lamps in the instrument pack to check for operation. When the system is operating or a fault is sensed
by the ECU, the ECU will operate the appropriate warning lamp and audible warning as required. The audible warning
is operated by the Body Control Unit (BCU) when it receives a signal from the SLABS ECU. The audible warning is
emitted from a speaker at the rear of the instrument pack.
Depressing the ORM switch for a minimum of 0.5 seconds, completes an earth which the ECU uses as a signal to
initiate the ORM if conditions allow. When the ECU starts ORM, the same earth that was completed by the ORM
switch is pulled to earth by the ECU to activate the ORM warning lamp. The ECU checks for a further operation of the
ORM switch by continuously and very quickly removing the earth for the ORM warning lamp. If the ORM switch is
operated for more than 0.5 seconds, the ECU will detect this and de-activate the ORM.
The SLS part of the SLABS ECU also uses the road speed data generated within the SLABS ECU by the ABS system.
Operation of ORM and extended mode are road speed sensitive and use the ABS signal to monitor the vehicle speed.
When the accessory remote handset is used for the SLS lower and raise functions, the handset transmits RF signals
which are received by the same RF receiver used for the alarm/remote door locking system. The RF receiver passes
this data as a 25 Hz PWM signal to the BCU. The BCU then transmits this data to the SLABS ECU as raise or lower
data. TestBook is required to program the BCU for remote handset operation.
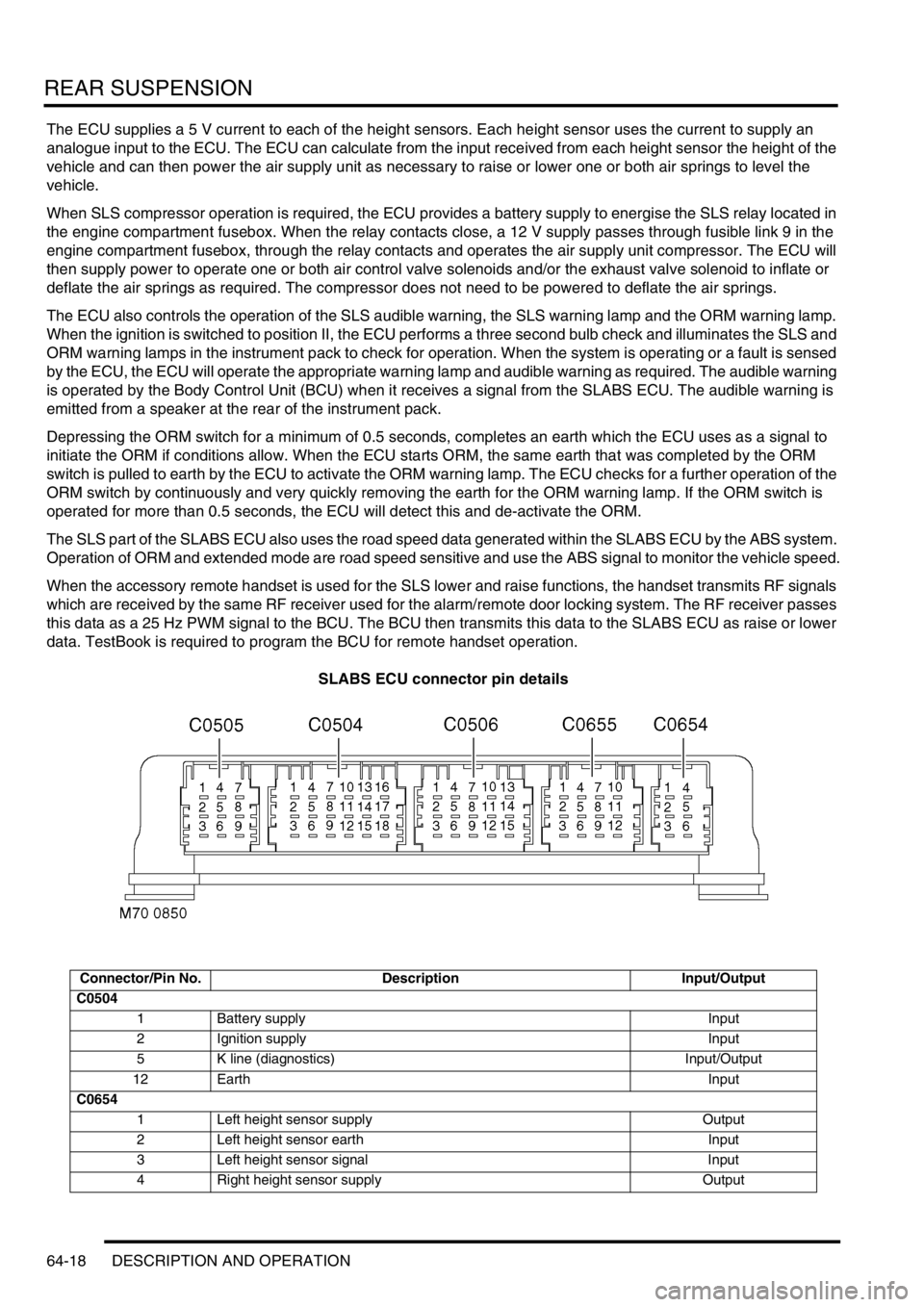
SLABS ECU connector pin details
Connector/Pin No. Description Input/Output
C0504
1 Battery supply Input
2 Ignition supply Input
5 K line (diagnostics) Input/Output
12 EarthInput
C0654
1 Left height sensor supply Output
2 Left height sensor earth Input
3 Left height sensor signal Input
4 Right height sensor supply Output
Page 1068 of 1672

BRAKES
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 70-23
Typical disabled times
Diagnostics
While the ignition is on, the diagnostics function of the SLABS ECU monitors the system for faults. In addition, the
return pump is tested by pulsing it briefly immediately after the engine starts provided vehicle speed exceeded 4.4
mph (7 km/h) during the previous ignition cycle. If a fault exists in a warning lamp circuit, the lamp will not illuminate
during the lamp check at ignition on but, provided there are no other faults, the related function will otherwise be fully
operational. If a fault is detected during the power up, the SLABS ECU stores a related fault code in memory and
illuminates the appropriate fault warning lamps. If a fault is detected later in the drive cycle, the SLABS ECU also
sounds the audible warning three times.
Fault codes and diagnostic routines can be accessed by connecting Testbook to the vehicle's diagnostic connector
in the driver's footwell.
Warning lamp fault operation
After detecting a fault, the SLABS ECU selects an appropriate default strategy which, where possible, retains some
operational capability. A shuttle valve switch fault and throttle position signal fault are classified as permanent faults.
If a permanent fault is detected, the related warning lamp illumination and default strategies are automatically
employed in subsequent ignition cycles, even if the fault is intermittent, until the fault has been rectified and cleared
from memory. If a non permanent fault is detected, the related warning lamp illumination and default strategies will
only be employed in subsequent ignition cycles if the fault is still present.
After rectification of an ABS sensor fault, the ABS and ETC functions are disabled, and the ABS warning lamp remains
illuminated after the lamp check, until vehicle speed exceeds 9.4 mph (15 km/h) (to allow additional checks to be
performed).
Vehicle speed, mph (km/h) Time, minutes
1.3 (2) 40
12.5 (20) 33
15.6 (25) 17
25.0 (40) 9
31.3 (50) 6
Item Check Warning lamp
ABS Brake ETC HDC
fault
ABS sensors Resistance (to check status) On On On On
Brake lamps relay Open/Short circuit Off Off Off On
Engine data Sticking throttle, signal failure, data corruption Off Off On On
Inlet solenoid valves Open/Short circuit On On On On
Outlet solenoid valves Open/Short circuit On On On On
Reference earth Connection to earth On On On On
Return pump monitor Correct pump operation On On On On
Return pump relay Open/Short circuit On On On On
Shuttle valve switches Open/Short circuit On On On On
SLABS ECU Internal failure On On On On
Supply voltages Range (10 to 16 V) On On On On