oil LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 236 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
OVERHAUL 12-1-97
8. Remove and discard big-end bearing shell
from connecting rod.
NOTE: Engine Serial No. Prefixes 10P to 14P:–
The 'sputter type' connecting rod bearing shells
fitted to these engines, identified by them
having a slightly darker colour than the bearing
cap shells should be replaced with the 'plain
type' bearing shells fitted to Engine Serial No.
Prefixes 15P to 19P.
9.Repeat above procedures for remaining big-
end bearings. Keep bearing caps in their
fitted order.
Inspection
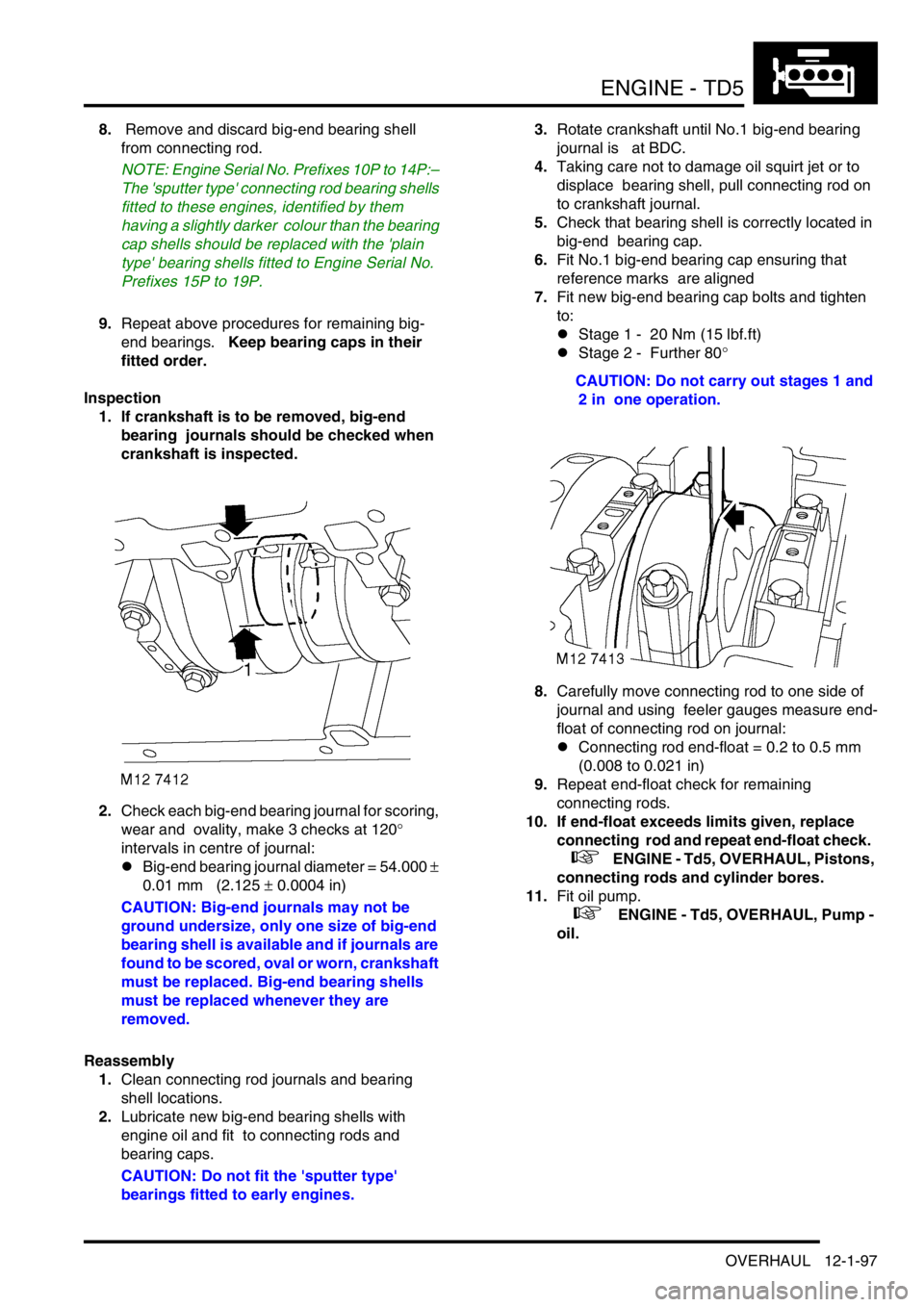
1. If crankshaft is to be removed, big-end
bearing journals should be checked when
crankshaft is inspected.
2.Check each big-end bearing journal for scoring,
wear and ovality, make 3 checks at 120
°
intervals in centre of journal:
lBig-end bearing journal diameter = 54.000
±
0.01 mm (2.125
± 0.0004 in)
CAUTION: Big-end journals may not be
ground undersize, only one size of big-end
bearing shell is available and if journals are
found to be scored, oval or worn, crankshaft
must be replaced. Big-end bearing shells
must be replaced whenever they are
removed.
Reassembly
1.Clean connecting rod journals and bearing
shell locations.
2.Lubricate new big-end bearing shells with
engine oil and fit to connecting rods and
bearing caps.
CAUTION: Do not fit the 'sputter type'
bearings fitted to early engines.3.Rotate crankshaft until No.1 big-end bearing
journal is at BDC.
4.Taking care not to damage oil squirt jet or to
displace bearing shell, pull connecting rod on
to crankshaft journal.
5.Check that bearing shell is correctly located in
big-end bearing cap.
6.Fit No.1 big-end bearing cap ensuring that
reference marks are aligned
7.Fit new big-end bearing cap bolts and tighten
to:
lStage 1 - 20 Nm (15 lbf.ft)
lStage 2 - Further 80
°
CAUTION: Do not carry out stages 1 and
2 in one operation.
8.Carefully move connecting rod to one side of
journal and using feeler gauges measure end-
float of connecting rod on journal:
lConnecting rod end-float = 0.2 to 0.5 mm
(0.008 to 0.021 in)
9.Repeat end-float check for remaining
connecting rods.
10. If end-float exceeds limits given, replace
connecting rod and repeat end-float check.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Pistons,
connecting rods and cylinder bores.
11.Fit oil pump.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Pump -
oil.
Page 237 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-98 OVERHAUL
Pistons, connecting rods and cylinder
bores
$% 12.17.02.03
Disassembly
1.Remove cylinder head gasket.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Gasket
- cylinder head.
2.Remove connecting rod bearings.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL,
Bearings - connecting rods.
3.Remove ridge of carbon from top of cylinder
bore.
4.Suitably identify each piston and connecting
rod assembly to its respective cylinder bore.
5.Carefully push connecting rod to top of cylinder
bore taking care that connecting rod does not
contact oil squirt jet or cylinder wall; remove
each piston and connecting rod in turn.
6.Using a suitable expander, remove and discard
piston rings from pistons.
7.Clean carbon from piston crown and skirt. Do
not use abrasives on graphited area of
piston skirt, do not use a wire brush or
scraper on any part of pistons.
8.Secure connecting rod in a soft jawed vice.
9.Suitably identify each piston to its connecting
rod and fitted position of piston on rod.
10.Using suitable circlip pliers, remove and
discard 2 circlips securing gudgeon pin.
11.Push gudgeon pin out of piston and connecting
rod; remove piston.
12.Suitably identify each gudgeon pin to its
respective piston.
13.Repeat above procedures for remaining
pistons. Inspect
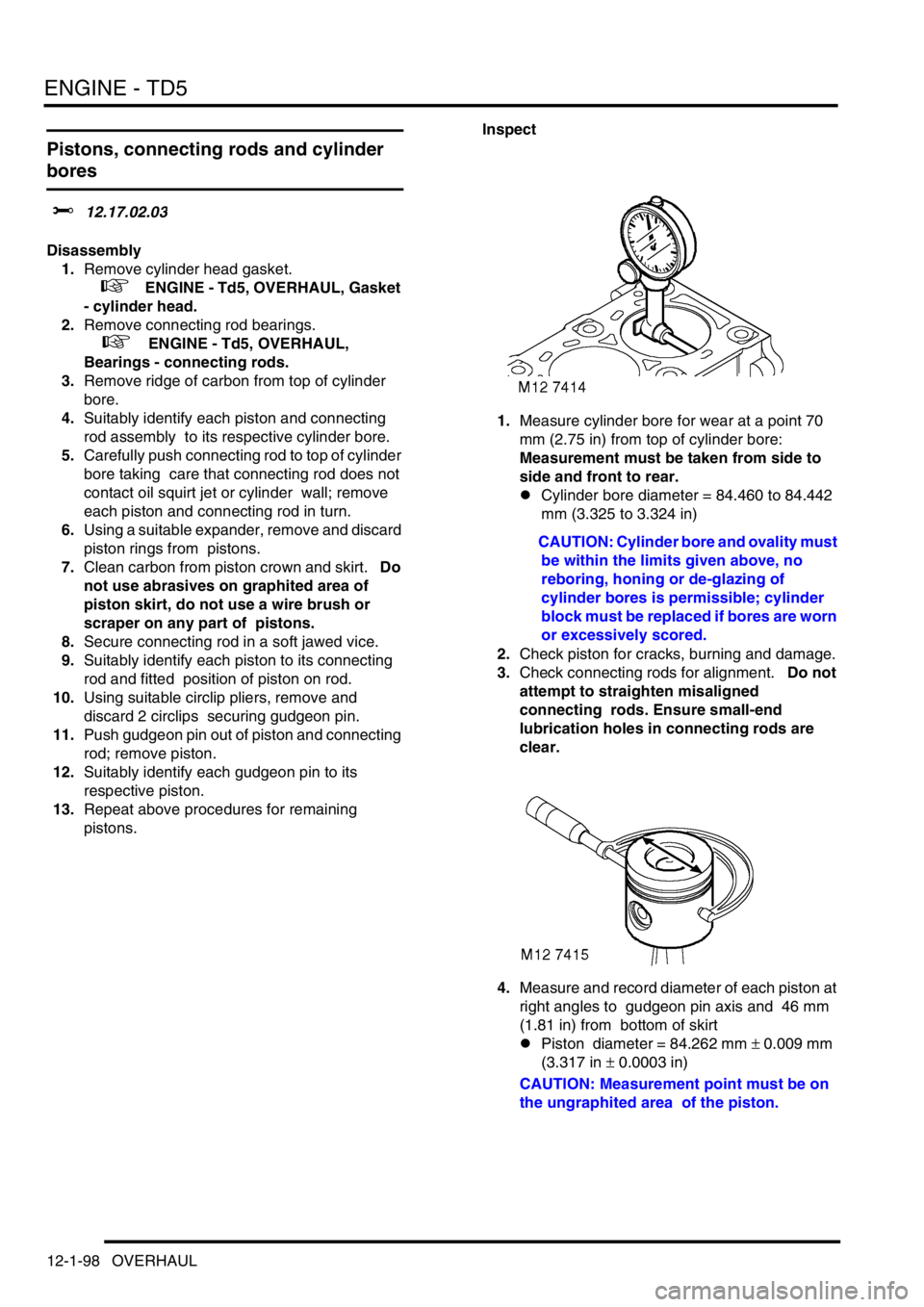
1.Measure cylinder bore for wear at a point 70
mm (2.75 in) from top of cylinder bore:
Measurement must be taken from side to
side and front to rear.
lCylinder bore diameter = 84.460 to 84.442
mm (3.325 to 3.324 in)
CAUTION: Cylinder bore and ovality must
be within the limits given above, no
reboring, honing or de-glazing of
cylinder bores is permissible; cylinder
block must be replaced if bores are worn
or excessively scored.
2.Check piston for cracks, burning and damage.
3.Check connecting rods for alignment. Do not
attempt to straighten misaligned
connecting rods. Ensure small-end
lubrication holes in connecting rods are
clear.
4.Measure and record diameter of each piston at
right angles to gudgeon pin axis and 46 mm
(1.81 in) from bottom of skirt
lPiston diameter = 84.262 mm
± 0.009 mm
(3.317 in
± 0.0003 in)
CAUTION: Measurement point must be on
the ungraphited area of the piston.
Page 239 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-100 OVERHAUL
12.Insert new compression and oil control rings in
turn into No.1 cylinder bore 30 mm (1.25 in)
from top of bore and check ring fitted gaps;
ensure rings are kept square to bore when
checking gaps:
l1st compression ring fitted gap = 0.30 to
0.40 mm (0.012 to 0.016 in).
l2nd compression ring fitted gap = 0.40 to
0.60 mm (0.016 to 0.024 in).
lOil control ring fitted gap = 0.25 to 0.50 mm
0.01 to 0.02 in).
CAUTION: 1st compression rings fitted to
Engine Serial No. Prefixes 10P to 14P are
not interchangeable with those fitted to
Engine Serial No. Prefixes 15P to 19P. The
later rings may, however, be fitted to early
engines together with the later type pistons
in engine sets only.
13.Repeat for each cylinder bore in turn.
CAUTION: Ensure rings are suitably
identified with the cylinder bore in which
they were checked and are fitted to the
piston for that bore.
14.Fit oil control expander and ring to piston.
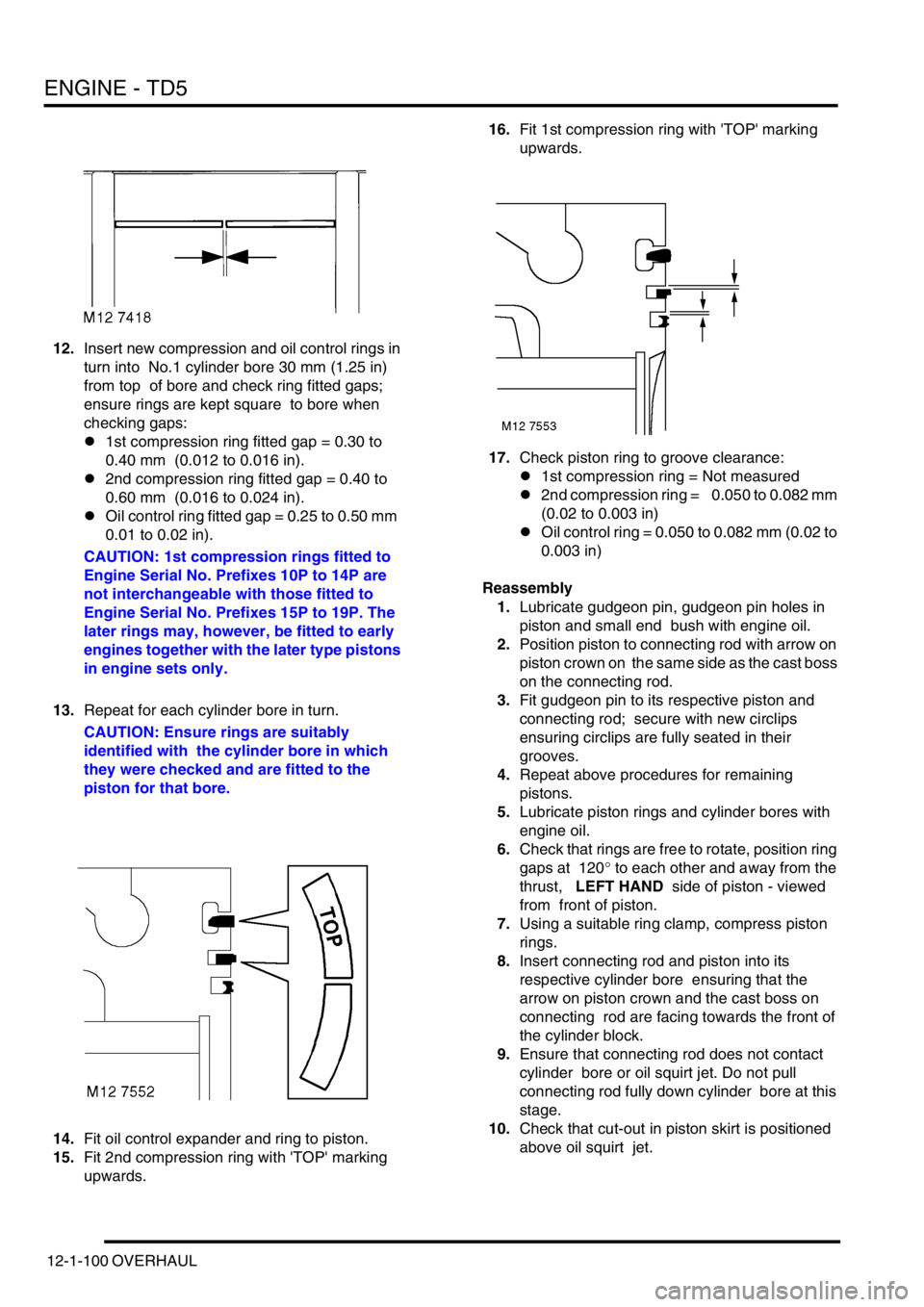
15.Fit 2nd compression ring with 'TOP' marking
upwards. 16.Fit 1st compression ring with 'TOP' marking
upwards.
17.Check piston ring to groove clearance:
l1st compression ring = Not measured
l2nd compression ring = 0.050 to 0.082 mm
(0.02 to 0.003 in)
lOil control ring = 0.050 to 0.082 mm (0.02 to
0.003 in)
Reassembly
1.Lubricate gudgeon pin, gudgeon pin holes in
piston and small end bush with engine oil.
2.Position piston to connecting rod with arrow on
piston crown on the same side as the cast boss
on the connecting rod.
3.Fit gudgeon pin to its respective piston and
connecting rod; secure with new circlips
ensuring circlips are fully seated in their
grooves.
4.Repeat above procedures for remaining
pistons.
5.Lubricate piston rings and cylinder bores with
engine oil.
6.Check that rings are free to rotate, position ring
gaps at 120
° to each other and away from the
thrust, LEFT HAND side of piston - viewed
from front of piston.
7.Using a suitable ring clamp, compress piston
rings.
8.Insert connecting rod and piston into its
respective cylinder bore ensuring that the
arrow on piston crown and the cast boss on
connecting rod are facing towards the front of
the cylinder block.
9.Ensure that connecting rod does not contact
cylinder bore or oil squirt jet. Do not pull
connecting rod fully down cylinder bore at this
stage.
10.Check that cut-out in piston skirt is positioned
above oil squirt jet.
Page 241 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-102 OVERHAUL
Crankshaft
$% 12.21.33.01
Disassembly
1.Remove timing chain and sprockets.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Timing
chain and sprockets.
2.Remove crankshaft rear oil seal.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Seal -
crankshaft - rear - manual models.
3.Remove connecting rod bearings.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL,
Bearings - connecting rods.
4.Check that cylinder reference number is on
each main bearing cap and make alignment
marks between each main bearing cap and
cylinder block.
5.Starting at No.3 main bearing cap and working
outwards, progressively loosen, then remove 2
bolts securing each cap. Discard main bearing
cap bolts. 6.Fit 2 slave bolts into main bearing cap in turn
and ease bearing caps from cylinder block.
7.Remove and discard plain bearing shells from
each main bearing cap.
8.Using assistance, remove crankshaft.
9.Remove and discard grooved main bearing
shells and 2 thrust washers from cylinder
block.
10.Remove Torx screw securing each oil squirt jet
to cylinder block, remove squirt jets.
11.Clean main bearing shell and thrust washer
locations in cylinder block, ensure bolt holes
are clean and dry.
12.Clean main bearing caps.
13.Clean crankshaft bearing journals, check
oilways are clear.
14.Ensure drillings in oil squirt jets are clear.
Page 242 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
OVERHAUL 12-1-103
15.Check core plugs in cylinder block for corrosion
or signs of leakage, seal replacement plugs
with Loctite 243.
Crankshaft - Inspection
1.Check crankshaft main and big-end bearings
for scoring, wear and ovality, make 3 checks at
120
° intervals in centre of journals.
lMain bearings = 62.0 mm
± 0.013 mm
(2.441 in
± 0.001 in).
lBig-end bearings = 54.000 mm
± 0.01 mm
(2.125 in
± 0.0004 in).
2. Crankshafts may not be reground, only one
size of main and big-end bearing shell is
available and if journals are found to be
scored, oval or worn, crankshaft must be
replaced. Main and big-end bearing shells
and thrust washers must be replaced
whenever they are removed.
3.Check crankshaft spigot bush for wear, replace
if necessary using the following procedures:
4.Secure crankshaft in a suitably padded vice.
5.Tap a thread in spigot bush to accommodate a
suitable impulse extractor.
6.Fit impulse extractor to spigot bush.
7.Remove spigot bush.
8.Clean spigot bush recess in crankshaft.
9.Fit new spigot bush to crankshaft using a
suitable mandrel. Reassembly
1.Fit oil squirt jets, fit Torx screws and tighten to
8 Nm (6 lbf.ft).
2.Lubricate new, grooved, main bearing shells
with engine oil and fit to cylinder block.
3.Lubricate new thrust washers with engine oil
and fit, grooved side facing outward, to recess
in each side of No.3 main bearing in cylinder
block.
4.Lubricate crankshaft journals with engine oil
and using assistance, position crankshaft in
cylinder block.
5.Lubricate new, plain, main bearing shells with
engine oil and fit to main bearing caps.
6.Fit main bearing caps in their original fitted
positions ensuring reference marks are
aligned.
7.Fit and lightly tighten new main bearing cap
bolts. Do not lubricate bolt threads.
8.Starting with No.3 main bearing cap and
working outwards, tighten main bearing cap
bolts to:
lStage 1 - 33 Nm (24 lbf.ft)
lStage 2 - Further 90
°
CAUTION: Do not carry out stages 1 and
2 in one operation.
9.Check that crankshaft rotates smoothly.
10. Attach a magnetic base DTI to front of cylinder
block with stylus of gauge on end of crankshaft.
Page 243 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-104 OVERHAUL
11.Using suitably padded levers, move crankshaft
rearwards and zero DTI.
12.Move crankshaft forwards and note end-float
reading on gauge:
lCrankshaft end-float = 0.02 to 0.025 mm
(0.001 to 0.11 in)
CAUTION: Oversize thrust washers are
not available, if end-float exceeds figure
given, crankshaft must be replaced.
13.Remove DTI.
14.Fit connecting rod bearings.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL,
Bearings - connecting rods.
15.Fit timing chain and sprockets.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Timing
chain and sprockets.
16.Fit crankshaft rear oil seal.
+ ENGINE - Td5, OVERHAUL, Seal -
crankshaft - rear - manual models.
Page 246 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-2-3
1Split pin
2Washers
3Spring
4Rocker arm
5Pedestal bolt
6Pedestal
7Push rod
8Hydraulic tappet
9Rocker shaft
10Cylinder head - left hand
11Gasket - rocker cover
12Rocker cover - left hand
13Bolt - rocker cover
14Valve spring cap
15Valve stem oil seals
16Collets
17Valve spring18Bolt - engine lifting bracket
19Engine lifting bracket
20Valve seat insert
21Exhaust valve
22Clamp - inlet manifold gasket
23Seal - inlet manifold gasket
24Bolt - inlet manifold gasket clamp
25Gasket - inlet manifold
26Inlet valve
27Gasket - cylinder head
28Gasket - exhaust manifold
29Cylinder head - right hand
30Spark plug
31Bolt - cylinder head
32Valve guide
33Rocker cover - right hand
34Engine oil filler cap
Page 248 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-2-5
1Core plugs
2Cylinder block
3Camshaft
4Dipstick tube, clamp and bolt
5Woodruff key
6Timing chain
7Camshaft timing gear
8Washer
9Bolt - camshaft timing gear
10Thrust plate - camshaft end-float
11Bolt - camshaft thrust plate
12Gasket - timing cover
13Timing cover
14Oil pressure switch
15Bolt
16Crankshaft front oil seal
17Oil filter element
18Crankshaft front pulley
19Washer
20Bolt - crankshaft front pulley
21Upper main bearing shell
22Upper centre main bearing shell and thrust
washer
23Crankshaft
24Woodruff key
25Crankshaft timing gear
26Lower main bearing shells
27Numbers 1, 2 and 3 main bearing caps
28Bolt - main bearing caps
29Oil pick-up pipe and strainer
30'O' ring31Bolt - oil pick-up pipe
32Gasket - sump
33Sump
34Bolt - sump
35Sump oil drain plug
36Sealing washer
37Spacer, washers and nut - oil pick-up pipe
38Number 4 main bearing cap
39Bolt - connecting rod big-end bearing cap
40Connecting rod big-end bearing shell - lower
41Connecting rod big-end bearing cap
42Number 5 - rear main bearing cap
43Cruciform seal - rear main bearing cap
44Number 5 - rear main bearing shell
45Crankshaft rear oil seal
46Crankshaft knock sensor
47Side bolt - main bearing cap
48Side Allen bolt - main bearing cap
49Dowty washers
50Connecting rod big-end bearing shell - upper
51Connecting rod
52Piston
53Gudgeon pin
54Oil control ring
55Top compression ring
562nd compression ring
57Flywheel/drive plate and starter ring gear
58Bolt - flywheel/drive plate
Page 249 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The V8 petrol engine is an eight cylinder, water cooled unit having two banks of four cylinders positioned at 90 degrees
to each other. The engine comprises five main castings - two cylinder heads, cylinder block, timing cover and the oil
sump, all of which are manufactured from aluminium alloy.
NAS market vehicles from 03 model year receive a 4.6 litre version of the V8 engine to replace the previous 4.0 litre
version.
Cylinder heads
The cylinder heads are fitted with replaceable valve guides and valve seat inserts with the combustion chambers
formed in the head. Each cylinder head is sealed to the cylinder block with a gasket. The exhaust manifolds are bolted
to the outside of each cylinder head whilst the inlet manifolds are located in the centre of the 'Vee' and are bolted to
the inside face of each head. Inlet and exhaust manifolds are sealed to the cylinder heads by means of gaskets.
Each cylinder has a single inlet and exhaust valve. The exhaust valves are of the 'carbon break' type, a recess on the
valve stem prevents a build-up of carbon in the valve guide by dislodging particles of carbon as the valve stem moves
up and down the guide. Inlet and exhaust valve stem oil seals are fitted at the top of each valve guide. Valve operation
is by means of rocker arms, push rods and hydraulic tappets. Each of the rocker arms is located on a rocker shaft
which is supported by means of pedestals bolted to the cylinder heads. A spring, positioned on either side of each
rocker arm, maintains the correct relative position of the arm to its valve stem. The rocker arms are operated directly
by the push rods which pass through drillings in the cylinder heads and cylinder block. The bottom end of each push
rod locates in a hydraulic tappet operated by the single, chain driven camshaft.
The rocker covers are bolted to the cylinder heads and are sealed to the heads by a rubber gasket. Stub pipes for
crankcase ventilation hose connections are fitted to each rocker cover, the pipe in the right hand cover incorporates
an oil separator. The engine oil filler cap is situated in the right hand cover.
Cylinder block and camshaft
The cylinder block is fitted with cast iron cylinder liners which are shrink fitted and locate on stops in the block. The
camshaft is positioned in the centre of the cylinder block and runs in one piece bearing shells which are line bored
after fitting. Camshaft end-float is controlled by a thrust plate bolted to the front of the cylinder block. A timing gear,
chain driven by the crankshaft timing gear is bolted to the front of the camshaft.
Crankshaft and main bearings
The crankshaft is carried in five main bearings. The upper main bearing shell locations are an integral part of the
cylinder block casting. The lower main bearing caps are bolted to the cylinder block on either side of the upper bearing
shell locations with an additional bolt being inserted into each cap from either side of the cylinder block. The rear
main bearing cap carries the crankshaft rear oil seal and is sealed to the cylinder block by means of cruciform shaped
seals in each side of the cap. Number four main bearing cap carries the stud fixing for the oil pick-up pipe. Lower
main bearing shells are plain whilst the upper shells have an oil feed hole and are grooved. Crankshaft end-float is
controlled by the thrust faces of the upper centre shell. The crankshaft timing gear is located on the front of the
crankshaft by means of a Woodruff key which is also used to drive the gear type oil pump. The flywheel/drive plate
carries the crankshaft position sensor reluctor ring and is dowel located and bolted to the flywheel.
Timing cover
The timing cover is bolted to the front of the cylinder block and is sealed to the block with a gasket. The disposable,
full flow oil filter canister is screwed on to the timing cover which also carries the oil pressure switch, oil pressure relief
valve and crankshaft front oil seal. The gear type oil pump is integral with the cover which also has an internal oilway
to direct oil from the oil cooler to the filter.
NOTE: Oil coolers are only fitted to vehicles up to VIN 756821.
Page 250 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 12-2-7
Oil sump
The oil sump is bolted to the bottom of the cylinder block and the timing cover and is sealed to both components with
a one piece gasket. A removable baffle to prevent oil surge is fitted in the sump. The oil pick-up pipe and strainer
assembly is positioned within the sump and is attached at the pick-up end to a stud screwed into number four main
bearing cap and at the delivery end to the oil pump. The oil drain plug is located in the bottom of the sump and is
sealed with a washer.
Pistons and connecting rods
Each of the aluminium alloy pistons has two compression rings and an oil control ring. The pistons are secured to the
connecting rods by semi-floating gudgeon pins. Each gudgeon pin is offset by 0.5 mm (0.02 in). The top of each piston
is recessed, the depth of recess determining the compression ratio of the engine. Plain, big-end bearing shells are
fitted to each connecting rod and cap.