steering MAZDA 626 1987 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 626, Model: MAZDA 626 1987Pages: 1865, PDF Size: 94.35 MB
Page 1294 of 1865

10 OUTLINE
SPECIFICATIONS
—-———Type
Item ^— Manual steering Power steering
Steering wheel
Outer diameter
mm (in)
380 (15.0) Steering wheel Turns lock
to
lock 4 32 2.93
Steering shaft and joints
Shaft type Collapsible
Steering shaft and joints Joint type Cross joints
(2)
Steering shaft and joints
Tilt stroke
mm (in)
40 (1.6)
Front steering gear
Type Rack and pinion
Front steering gear Gear ratio
oo
(infinite)
Power steering fluid
Capacity liter (US qt, Imp)
2WS
—
0.9 (0.95, 0.79)
Power steering fluid
Capacity liter (US qt, Imp) 4WS
—
1.0 (1.06, 0.88) Power steering fluid
Type 2WS
4WS
—
Dexron
II or M III
86U10X-006
Note
2-Wheel steering is abbreviated 2WS.
10—6
Page 1295 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1 0
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
MANUAL STEERING
Problem Probable Cause Remedy Page
Steering "heavy" Poor lubrication, foreign material, or abnormal wear of Refer to Section 13
(vehicle jacked up, steering bail-joints
both wheels off Stuck or damaged ball-joints Replace 10--18 ground) Improperly adjusted steering pinion preload Adjust 10--56
Damaged steering gear Replace 10--28 Worn or damaged steering bushing Replace 10--53 Stuck lower-arm ball-joint Refer to Section 13
Malfunction of steering-shaft joint Replace 10--21
Steering wheel Incorrect tire pressure Refer to Section 12
pulls to one side Unevenly worn tires Refer to Section 12
Weakened front spring Refer to Section 13 Worn or damaged stabilizer and/or lower arm bushing Refer to Section 13
Dragging brake Refer to Section 11
Loose lower arm Refer to Section 13
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Refer to Section 13
General instability Incorrect tire pressure Refer to Section 12
while driving Damaged or unbalanced wheel Refer to Section 13
Worn or damaged steering joints Replace 10--21 Improperly adjusted steering pinion preload Adjust 10--56
Weakened front spring Refer to Section 13
Worn or damaged stabilizer and/or lower arm bushing Refer to Section 13
Malfunctioning shock absorber Refer to Section 13 Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Refer to Secton 13
Steering wheel Incorrect tire pressure Refer to Section 12
vibrates Unevenly worn tires Refer to Section 12
Worn wheel bearing, or incorrect adjustment Refer to Section 13
Worn or damaged steering joints Replace 10--21
Improperly adjusted steering pinion preload Adjust 10--56
Loose gear housing mounting bolts Tighten 10--30
Worn steering gear bearing Replace
Worn or damaged stabilizer and/or lower arm bushing Refer to Section 13
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Refer to Section 13
Worn lower-arm ball-joint Refer to Section 13
Damaged unbalanced wheel Refer to Section 13
Malfunctionina or loose shock absorber Refer to Section 13
Excessive steering Improperly adjusted steering gear backlash Adjust 10--56
wheel play Worn rack and pinion gear Replace 10--51
Worn or damaged steering joints Replace 10--21
Worn or damaaed lower-arm bushinq Refer to Section 13
Poor steering Incorrect tire pressure Refer to Section 12
wheel return Stuck or damaged steering joints Replace 10 -21
Improperly adjusted front wheel alignment Refer to Section 13
Improperly adjusted steering pinion preload Adjust 10--56
Abnormal noise Loose steering linkage Tighten 10--28
from steering Worn steering joints Replace 10--21
system ImDroDerlv adiusted steerina aear backlash Adiust 10--56
86U10X-007
10—7
Page 1296 of 1865

1 0 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
POWER STEERING
Problem Possible cause Remedy Page
Hard steering
Loose
or
damaged belt Low fluid level,
or air in
fluid Leakage
of
fluid
Malfunctioning electrical system* Insufficient oil pump pressure Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Malfunctioning steering gear Linkage ball joint not operating smoothly
Adjust
or
replace Add fluid
or
bleed
air
Repair
or
replace Repair
or
replace Repair
or
replace Refer
to
Section
13
Repair
or
replace Replace
10—12 10-11 10-13 10-87 10-16
10—28,
37
10-18
Poor return
Insufficient tire pressure
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment
Ball-joint not operating smoothly
Steering shaft contacting something
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
13
Replace
Repair
10-20 10-21
Excessive play
Loose gear box housing mounting bolts Worn linkage
or
tie-rod ball joint Worn lower ball joint Worn
or
damaged steering joint Worn rack and pinion gear
Tighten Replace
Refer
to
Section
13
Replace
Replace
10—30
10—18
10—21
10-58,
75
Steering wheel
vibrates
Insufficient tire pressure Damaged
or
unbalanced wheel Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Loose gear box housing mounting bolts Incorrect pinion preload adjustment Worn ball joints
Loose shock absorber mounting Malfunctioning shock absorber
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
13
Refer
to
Section
13
Tighten Adjust
Replace Refer
to
Section
13
Refer
to
Section
13
10-30 10-72,
81
10—18
Steering wheel
pulls
Unevenly worn tires
Incorrect tire pressure
Dragging brake
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
11
Refer
to
Section
13 —
Excessively light
steering at high
speed*
Malfunctioning electrical system Repair
or
replace 10-87
*... Only
for
electronically
-
controlled type
76G10X-002
10—8
Page 1297 of 1865
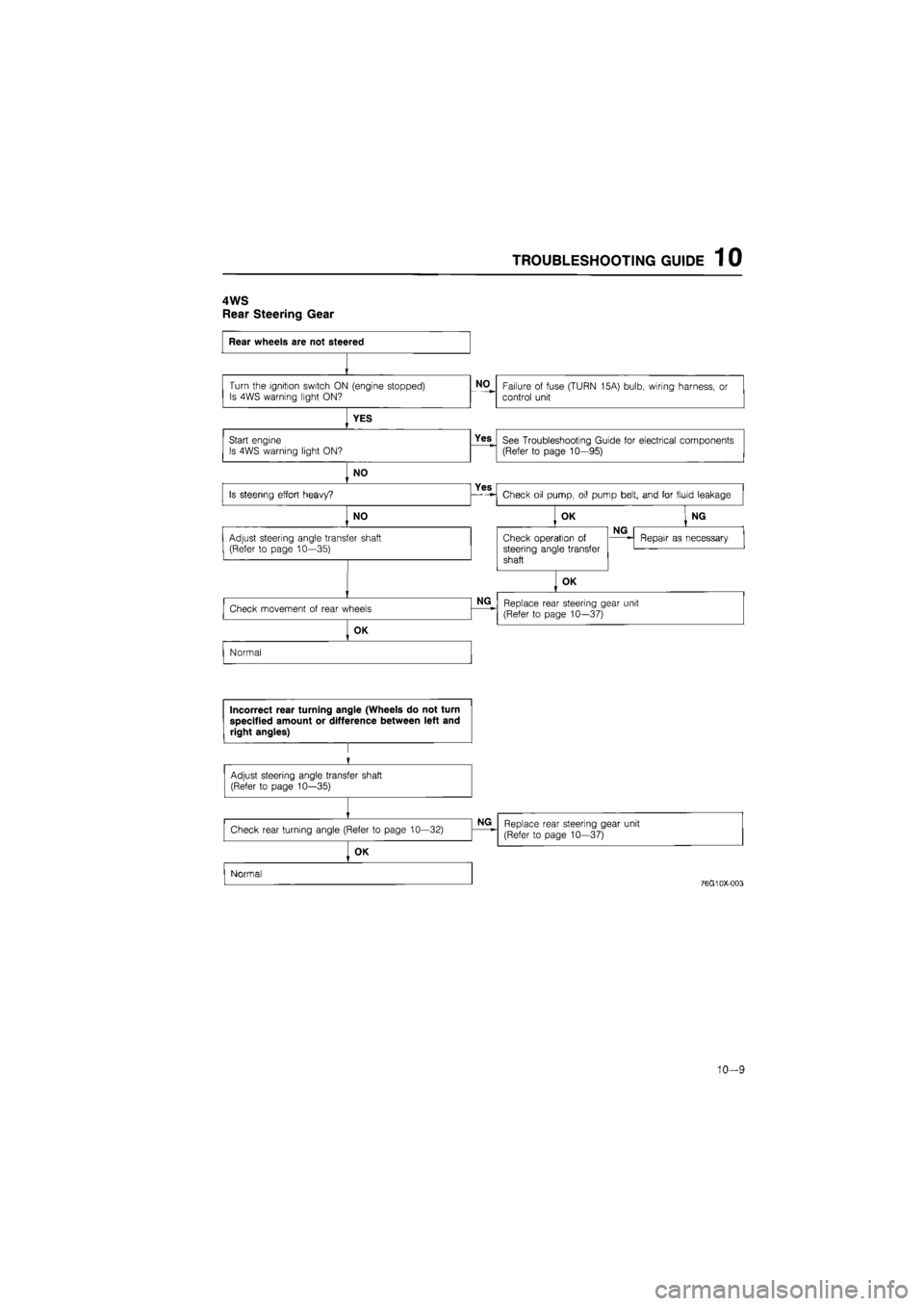
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1 0
4WS
Rear Steering Gear
10—9
Page 1298 of 1865
1 0 ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
86U10X-010
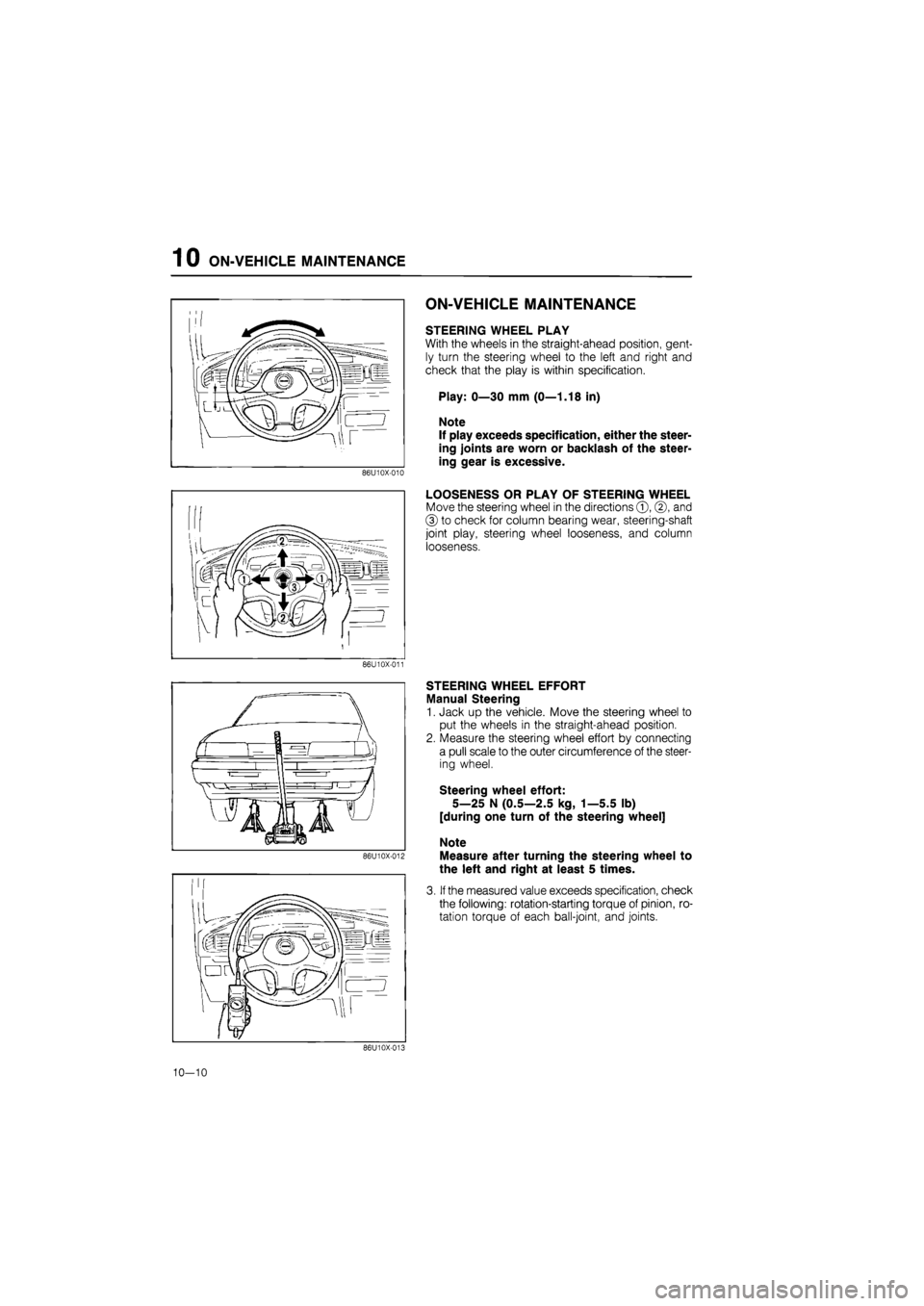
ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
STEERING WHEEL PLAY
With the wheels in the straight-ahead position, gent-
ly turn the steering wheel to the left and right and
check that the play is within specification.
Play: 0—30 mm (0—1.18 in)
Note
If play exceeds specification, either the steer-
ing joints are worn or backlash of the steer-
ing gear is excessive.
LOOSENESS OR PLAY OF STEERING WHEEL
Move the steering wheel in the directions ©, ©, and
© to check for column bearing wear, steering-shaft
joint play, steering wheel looseness, and column
looseness.
86U10X-011
86U10X-012
STEERING WHEEL EFFORT
Manual Steering
1. Jack up the vehicle. Move the steering wheel to
put the wheels in the straight-ahead position.
2. Measure the steering wheel effort by connecting
a pull scale to the outer circumference of the steer-
ing wheel.
Steering wheel effort:
5—25 N (0.5—2.5 kg, 1—5.5 lb)
[during one turn of the steering wheel]
Note
Measure after turning the steering wheel to
the left and right at least 5 times.
3. If the measured value exceeds specification, check
the following: rotation-starting torque of pinion, ro-
tation torque of each ball-joint, and joints.
86U10X-013
10—10
Page 1299 of 1865

ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE 1 0
"{krf
'"""^JlW^M 1
V
^A-X
Power Steering
1.
86U10X-014
86U10X-015
With the vehicle on a hard level surface, move the
steering wheel to put the wheels in the straight
ahead position.
Start the engine and warm the power steering flu-
id to 50—60°C (122—140°F), pull scale.
Attach a pull scale to the outer circumference of
the steering wheel. Then, starting with the wheels
in the straight-ahead position, check the steering
effort required to turn the steering wheel to the left
and to the right.
If the measured value exceeds specification, check
the following: fluid level, air in system, fluid leak-
age at hose or connections, function of oil pump
and gear box, and tire pressure.
Steering wheel effort:
ESPS Type
25—31N (2.6—3.2 kg, 6—7 lb)
ECPS Type
15—23 N (1.7—2.3 kg, 3—5 lb)
4WS Type
25—35N (2.5—3.5 kg, 6—8 lb)
[during one turn of the steering wheel]
Note (4WS)
1)lf not within specification, separate the
transfer shaft from the front steering gear
and check again.
2) If still not within specification, there is a
malfunction of the front steering gear.
3) If the measured value is now within specifi-
cation, check the transfer shaft and rear
steering gear. (Refer to Page 10—45.)
86U10X-016
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
Check the power steering fluid level, and add fluid
to the specified level if necessary.
Caution
Use only the specified power steering fluid.
86U10X-017
10—11
Page 1300 of 1865

1 0 ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
Gasoline engine Adjust bolt
Idler pulley fM ,.. Lock nut
1 / I
Drive pulley Power steering oil
pump pulley
76G10X-004
Diesel engine
Vacuum pump
Rear
camshaft
pulley
Power steering oil
pump pulley
76G10X-005
86U10X-019
LOOSE OR DAMAGED OIL PUMP BELT
Inspection
Inspect the oil pump belt for looseness or damage.
Power steering
oil
pump drive belt
Deflection Power steering
oil
pump drive belt New Used
Gasoline engine 8—10
mm
(0.31-0.39
in)
9—11
mm
(0.35—0.43
in)
Diesel engine 6.5—7.5
mm
(0.26—0.30
in)
7—8
mm
(0.28—0.31
in)
[When depressed with a force of 98 N (10 kg,
22 lb)]
Adjustment
Gasoline engine
1. Loosen the lock nut on the idler pulley.
2. Turn the adjust bolt on the idler pulley until the cor-
rect tension is obtained.
3. Tighten the lock nut and recheck the tension.
Tightening torque:
49—59 Nm (5—6 m-kg, 36—43 ft-lb)
Diesel engine
1. Loosen the vacuum pump bolt ©and (B).
2. Lever the vacuum pump outward and apply ten-
sion to the belt.
3. Tighten the adjust bolt (|).
Tightening torque:
49—59
N
m (5—6 m-kg, 36—43 ft-lb)
4. Tighten the mounting bolt
Tightening torque:
37—52 N-m (3.8—5.3 m-kg, 27—38 ft-lb)
REAR STEERING GEAR OIL
Fluid Level (4WS)
Remove the bleeder valve, and check the fluid level
with a wire.
Caution
Be careful not to let dirt in.
Fluid level
44 ± 3 mm (1.7 ± 0.1 in)
0.9 ± 0.1 liters (1.0 ± 0.1 US qt,
0.8 ± 0.1 Imp qt)
86U10X-250
10-12
Page 1301 of 1865

ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE 1 0
LEAKAGE OF POWER STEERING FLUID
Check the following points for fluid leakage:
1. Gear
2. Oil pump
3. All fluid pipes and connections
4. Solenoid valve (ECPS Type, 4WS Type)
Note
a) Start the engine, and check for fluid leakage after turning the steering wheel completely
to the left and right to apply fluid pressure. Do not, however, keep the steering wheel
in the fully turned position for more than 15 seconds.
b)The points where fluid leakage may occur are indicated by the arrows in the figure.
Power Steering (2WS)
86U10X-020
10-13
Page 1303 of 1865

INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT 1 0
INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
BLEEDING OF POWER STEERING SYSTEM
1. Check the fluid level, and add fluid if necessary.
2. Turn the steering wheel fully in both directions 5
times (engine not running).
3. Recheck the fluid level. If the level has lowered,
add fluid, and repeat from step 1.
86U10X-021
4. Start the engine, and run it at idle.
5. Turn the steering wheel fully in both directions 5
times to bleed air from the system.
6. Check that the fluid is not foamy and the fluid lev-
el has not lowered.
If a problem is found, add fluid as necessary and
repeat from step 5.
Note
If bleeding is not done completely, the follow-
ing problems may appear:
• Foamy fluid on level gauge.
• Noise from power steering oil pump.
86U10X-022
10—15
Page 1304 of 1865
![MAZDA 626 1987 Owners Guide
1 0 INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
86U10X023
2WS
To oil pump
Si£r To gear housing
86U10X-024
86U10X-025
Thermometer [50—60°C (122—140°C)]
ii ^
Gauge
Close valve
completely
POWER STEERIN MAZDA 626 1987 Owners Guide
1 0 INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
86U10X023
2WS
To oil pump
Si£r To gear housing
86U10X-024
86U10X-025
Thermometer [50—60°C (122—140°C)]
ii ^
Gauge
Close valve
completely
POWER STEERIN](/img/28/57059/w960_57059-1303.png)
1 0 INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
86U10X023
2WS
To oil pump
Si£r To gear housing
86U10X-024
86U10X-025
Thermometer [50—60°C (122—140°C)]
ii ^
Gauge
Close valve
completely
POWER STEERING PRESSURE
1. Disconnect the high-pressure hose of the gear
housing side, and attach the SST.
Tightening torque:
39—49 N-m (4.0—5.0 m-kg, 29—36 ft-lb)
2. Bleed air from the system.
3. Open the gauge valve fully, then start the engine
and turn the steering wheel fully left and right to
raise the fluid temperature to 50—60°C
(122—140°F)
4. To measure the fluid pressure generated by the
oil pump, close the gauge valve completely and
increase the engine speed to 1,000—1,500 rpm.
If the fluid pressure is low, replace the oil pump
assembly.
Warning
If the valve is left closed for more than 15 sec-
onds, the fluid temperature will increase ex-
cessively and adversely affect the oil pump.
Oil pump fluid pressure
2WS
7,355—7,846 kPa
(75—80 kg/cm2, 1,066—1,138 psi)
4WS
Front 8,093—8,829 kPa
(82.5—90.0 kg/cm2, 1,173—1,280 psi)
Rear 7,112—7,848 kPa
(72.5—80.0 kg/cm2, 1,031—1,138 psi)
To measure the fluid pressure generated at the
gear housing, first open the gauge valve complete-
ly, increase the engine speed to 1,000—1,500
rpm, and then turn the steering wheel fully to the
left and right.
Warning
If the steering wheel is kept in the fully turned
position for more than 15 seconds, the fluid
temperature will rise excessively.
80U10X-026
10—16