tire type MAZDA 626 1987 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 626, Model: MAZDA 626 1987Pages: 1865, PDF Size: 94.35 MB
Page 679 of 1865

INTAKE AIR SYSTEM 4D
AIR DUCT AND AIR CLEANER
Removal and Installation
1. Remove in the sequence shown in the figure.
2. Install in the reverse order of removal.
3. Check for air leakage.
1. Tire house cover
2. Air duct
3. Air hose
4. Air cleaner case
5. Air cleaner cover
6. Air cleaner
element
Inspection
Air cleaner
1. Inspect the silencer in the air cleaner cover for
damage.
2. Inspect the air cleaner element for excessive dirt,
damage, or oil. Replace if necessary.
Caution
(Wet type)
Do not clean the air cleaner element with com-
ressed air, replace it if necessary.
(Dry type)
When cleaning the air cleaner element, blow
dust off from the inside first, then blow off the
outside.
Air duct
Inspect the silencer in the air duct for damage. Re-
place if necessary.
76G04D-017
4D—8
Page 1122 of 1865
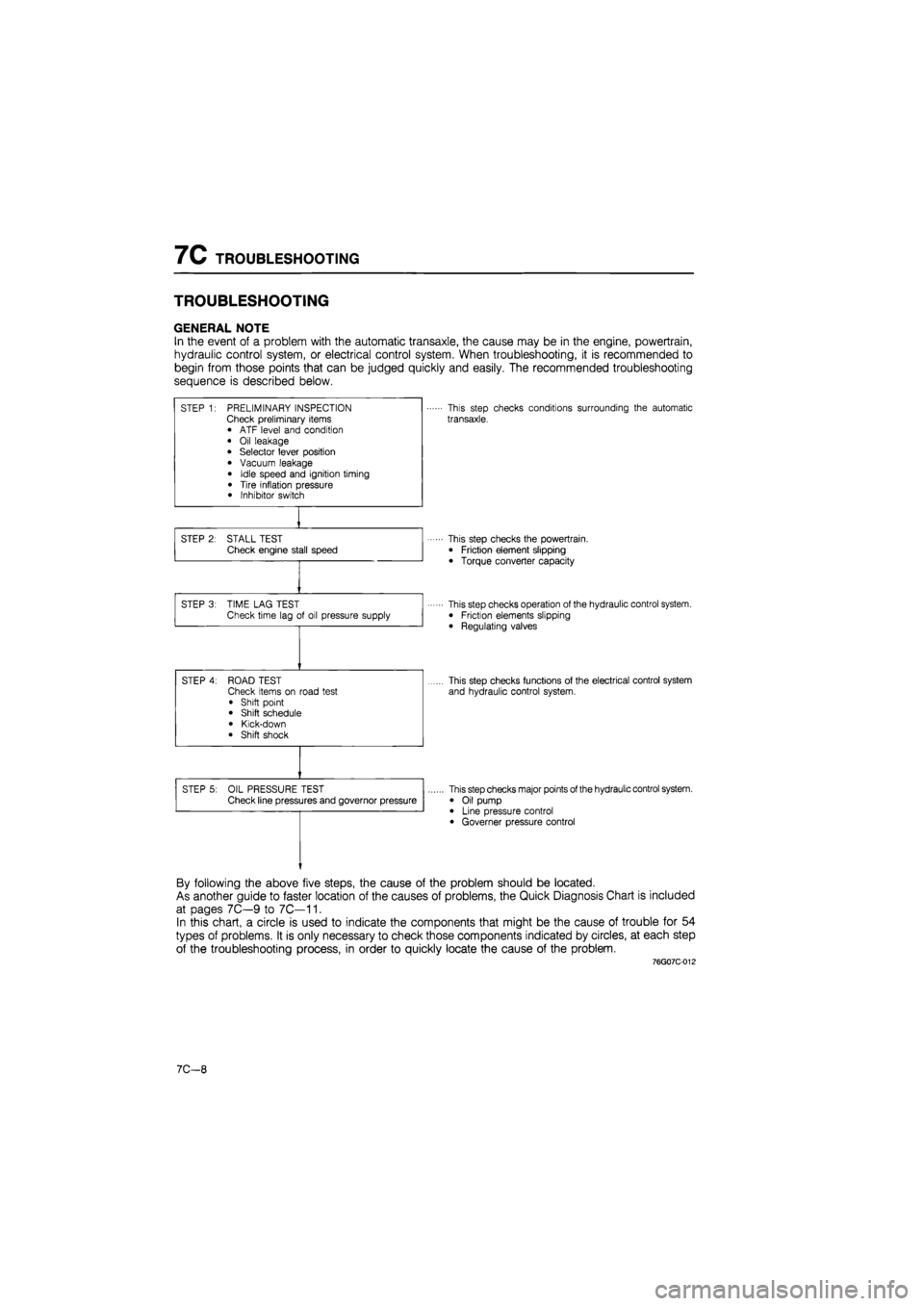
7C TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
GENERAL NOTE
In the event of a problem with the automatic transaxle, the cause may be in the engine, powertrain,
hydraulic control system, or electrical control system. When troubleshooting, it is recommended to
begin from those points that can be judged quickly and easily. The recommended troubleshooting
sequence is described below.
STEP 1: PRELIMINARY INSPECTION Check preliminary items • ATF level and condition
• Oil leakage • Selector lever position
• Vacuum leakage
• Idle speed and ignition timing
• Tire inflation pressure • Inhibitor switch
This step checks conditions surrounding the automatic
transaxle.
STEP 2: STALL TEST Check engine stall speed This step checks the powertrain.
• Friction element slipping
• Torque converter capacity
STEP 3: TIME LAG TEST Check time lag of oil pressure supply This step checks operation of the hydraulic control system. • Friction elements slipping
• Regulating valves
STEP 4: ROAD TEST Check items on road test
• Shift point • Shift schedule
• Kick-down • Shift shock
This step checks functions of the electrical control system
and hydraulic control system.
STEP 5: OIL PRESSURE TEST Check line pressures and governor pressure This step checks major points of the hydraulic control system.
• Oil pump • Line pressure control • Governer pressure control
By following the above five steps, the cause of the problem should be located.
As another guide to faster location of the causes of problems, the Quick Diagnosis Chart is included
at pages 7C—9 to 7C—11.
In this chart, a circle is used to indicate the components that might be the cause of trouble for 54
types of problems. It is only necessary to check those components indicated by circles, at each step
of the troubleshooting process, in order to quickly locate the cause of the problem.
76G07C-012
7C—8
Page 1296 of 1865

1 0 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
POWER STEERING
Problem Possible cause Remedy Page
Hard steering
Loose
or
damaged belt Low fluid level,
or air in
fluid Leakage
of
fluid
Malfunctioning electrical system* Insufficient oil pump pressure Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Malfunctioning steering gear Linkage ball joint not operating smoothly
Adjust
or
replace Add fluid
or
bleed
air
Repair
or
replace Repair
or
replace Repair
or
replace Refer
to
Section
13
Repair
or
replace Replace
10—12 10-11 10-13 10-87 10-16
10—28,
37
10-18
Poor return
Insufficient tire pressure
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment
Ball-joint not operating smoothly
Steering shaft contacting something
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
13
Replace
Repair
10-20 10-21
Excessive play
Loose gear box housing mounting bolts Worn linkage
or
tie-rod ball joint Worn lower ball joint Worn
or
damaged steering joint Worn rack and pinion gear
Tighten Replace
Refer
to
Section
13
Replace
Replace
10—30
10—18
10—21
10-58,
75
Steering wheel
vibrates
Insufficient tire pressure Damaged
or
unbalanced wheel Improperly adjusted wheel alignment Loose gear box housing mounting bolts Incorrect pinion preload adjustment Worn ball joints
Loose shock absorber mounting Malfunctioning shock absorber
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
13
Refer
to
Section
13
Tighten Adjust
Replace Refer
to
Section
13
Refer
to
Section
13
10-30 10-72,
81
10—18
Steering wheel
pulls
Unevenly worn tires
Incorrect tire pressure
Dragging brake
Improperly adjusted wheel alignment
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
12
Refer
to
Section
11
Refer
to
Section
13 —
Excessively light
steering at high
speed*
Malfunctioning electrical system Repair
or
replace 10-87
*... Only
for
electronically
-
controlled type
76G10X-002
10—8
Page 1299 of 1865

ON-VEHICLE MAINTENANCE 1 0
"{krf
'"""^JlW^M 1
V
^A-X
Power Steering
1.
86U10X-014
86U10X-015
With the vehicle on a hard level surface, move the
steering wheel to put the wheels in the straight
ahead position.
Start the engine and warm the power steering flu-
id to 50—60°C (122—140°F), pull scale.
Attach a pull scale to the outer circumference of
the steering wheel. Then, starting with the wheels
in the straight-ahead position, check the steering
effort required to turn the steering wheel to the left
and to the right.
If the measured value exceeds specification, check
the following: fluid level, air in system, fluid leak-
age at hose or connections, function of oil pump
and gear box, and tire pressure.
Steering wheel effort:
ESPS Type
25—31N (2.6—3.2 kg, 6—7 lb)
ECPS Type
15—23 N (1.7—2.3 kg, 3—5 lb)
4WS Type
25—35N (2.5—3.5 kg, 6—8 lb)
[during one turn of the steering wheel]
Note (4WS)
1)lf not within specification, separate the
transfer shaft from the front steering gear
and check again.
2) If still not within specification, there is a
malfunction of the front steering gear.
3) If the measured value is now within specifi-
cation, check the transfer shaft and rear
steering gear. (Refer to Page 10—45.)
86U10X-016
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
Check the power steering fluid level, and add fluid
to the specified level if necessary.
Caution
Use only the specified power steering fluid.
86U10X-017
10—11
Page 1493 of 1865

1 2 OUTLINE, TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
OUTLINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Type
Item Standard Temporary spare (if equipped)
Wheel
Size
5-J
x 13
4-T
x 15
Wheel
Size 5 1/2-JJ
x 14
4-T
x 15
Wheel
Size
6-JJ
x 15
4-T
x 15
Wheel
Off set mm (in) 42 (1.65) 53 (2.09)
Wheel Diameter
of
pitch circle
mm
(in) 114.3 (4.5) Wheel
Material Steel
or
aluminum alloy Steel
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts
13 inch-wheel 4
4
or 5
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts 14 inch-wheel 5 4
or 5
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts 15 inch-wheel 5 4
or 5
Tire
Size
13 inch-wheel
6.45—13—6PR
165 SR13 165/80R13 82S 185/70HR13 185/70R13 85H
T125/70D15
Tire
Size 14 inch-wheel
185/70HR14 185/70R14 87H 185/70R14 88H 185/70VR14
T125/70D15
Tire
Size
15 inch-wheel 195/60R15 86H
195/60VR15
T125/70D15
Tire
Air pressure
kPa (kg/cm2,
psi)
Front 216 (2.2, 31) or 196 (2.0, 28) "See tire labels for application 412(4.2, 60)
Tire
Air pressure
kPa (kg/cm2,
psi) Rear 177 (1.8, 26)
412(4.2, 60)
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 76G12X-001
Problem Possible Cause Remedy Page
Premature tire wear
Incorrect tire pressure Adjust 12-
2
Tire squeal
Incorrect tire pressure Tire deterioration
Adjust ReDlace
12-
2
Road noise or body vibration
Insufficient tire pressure Unbalanced wheel(s) Deformed wheel(s)
or
tire(s) Irregular tire wear
Adjust Adjust Repair
or
replace Reolace
-1
12-
2
12-
5
Steering wheel vibration
Irregular tire wear Right and left tread depths different Deformed
or
unbalanced wheel(s) Deformed tire(s) Unequal tire pressures Loose lug nuts
Replace Replace
Replace
or
adjust Replace Adjust Tiahten
12-
5
12—
2
12-
5
Uneven (one-sided) braking
Unequal tire pressures Adjust 12-
2
Steering wheel doesn't return properly, or pulls to either left or right while vehicle moving on level road surface
Incorrect tire pressure Irregular tire wear (left and right are different) Unequal tire pressures Different types
or
brands
of
tires mixed (right/left) Improperly tightened lug nuts
Adjust Replace Adjust Replace Tighten
12-
2
12—
2
12-
5
General driving in-stability
Unequal tire pressures Deformed
or
unbalanced wheel(s) Loose lug nuts
Adjust Replace
or
adjust Tiahten
12-
2
12-
5
12-
5
Excessive steering wheel play
Loose lug nuts Tighten 12-
5
76G12X-002
12-2
Page 1496 of 1865

WHEELS AND TIRES 1 2
WHEEL BALANCE
If a wheel becomes unbalanced or if a tire is replaced
or repaired, the wheel must once again be balanced
to within specification.
Maximum unbalance (at rim edge): g (oz)
13 inch-wheel 11 (0.39)
14 inch-wheel 10 (0.35)
15 inch-wheel 9 (0.32)
76G12X-005
Balance
weight
Outside
Balance
weight
86U12X-011
Caution
a) Do not use more than two balance weights
on the inner or outer side of the wheel, if
the total weight exceeds 100 g (3.5 oz), re-
balance after moving the tire around on the
rim.
b) Attach the balance weights tightly so that
they do not protrude more than 3 mm (0.12
in) beyond the wheel edge.
c) Select suitable balance weights for steel or
aluminum alloy wheels.
d)Do not use an on-car balancer on ATX
models. Use of this type of balancer may
cause clutch damage.
WHEEL MOUNTING
Tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque in a criss-
cross fashion.
Tightening torque:
88—118 N-m (9—12 m-kg, 65—87 ft-lb)
Caution
a) The wheel-to-hub contact surfaces must be
clean.
b) Never apply oil to the nuts, bolts, or wheels;
doing so might cause looseness or seizure
of the lug nuts.
86U12X-012
SPECIAL NOTE
Regarding wheels and tires:
1. Do not use wheels or tires other than the specified types.
2. Aluminum wheels are easily scratched. When washing them, use a soft cloth, never a wire brush.
If the vehicle is steam cleaned, do not allow boiling water to contact the wheels.
3. If alkaline compounds (such as salt water or road salts), get on aluminum wheels, wash them as
soon as possible to prevent damage. Use only a neutral detergent.
86U12X-013
12-5
Page 1852 of 1865

30 TECHNICAL DATA
12. WHEEL AND TIRE
* ~— - Type
Item ~ ———_____ Standard Temporary spare
(if equipped)
Wheel
Size
5-Jx13
4-T
x 15
Wheel
Size 5 1/2-JJx14 4-T
x 15
Wheel
Size
6JJx15
4-T
x 15
Wheel
Offset
mm (in)
42 (1.65) 53 (2.09)
Wheel Diameter
of
pitch circle
mm
(in) 114.3 (4.5) Wheel
Material Steel
or
aluminum alloy Steel
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts
13 inch-wheel 4
4
or 5
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts 14 inch-wheel 5 4
or 5
Wheel
Number
of
fixing nuts 15 inch-wheel 5 4
or 5
Tire
Size
13 inch-wheel
6.45-13-6PR 165SR13 165/80R13 82S
185/70HR13 185/70R13 85H
T125/70D15
Tire
Size
14 inch-wheel
185/70HR14 185/70R14 87H 185/70R14 88H 185/70VR14
T125/70D15
Tire
Size
15 inch-wheel 195/60R15 86H 195/60VR15
T125/70D15
Tire
Air pressure kPa (kg/cm2, psi)
Front 216 (2.2, 31)
or
196 (2.0, 28)
Refer to tire labels for applications 412 (4.2, 60)
Tire
Air pressure kPa (kg/cm2, psi) Rear 177 (1.8,
26)
412 (4.2, 60)
Wheel and tire
Runout
mm (in)
Horizontal Steel wheel: 2.5 (0.098), Alminum allov wheel: 2.0 (0.079) max.
Wheel and tire
Runout
mm (in) Vertical 2.0 (0.079) max.
Wheel and tire Unbalance
g
(oz)
13 inch-wheel 11 (0.39) max. Wheel and tire Unbalance
g
(oz) 14 inch-wheel 10 (0.35) max.
Wheel and tire Unbalance
g
(oz) 15 inch-wheel 9 (0.32) max.
13. SUSPENSION
Item Specification
Front suspension
Type Strut
Toe-in
mm
(in) 0 ±
3 (0
±
0
12)
Front wheel alignment Camber angle 0°17' ±
45'
Front wheel alignment Caster angle 1 °13' ±
45'
King pin angle 12C 47'
Maximum front Inner 36°26'33"
steering angle Outer 30°59'15"
Stabilizer Type Torsion
bar
Stabilizer Diameter
mm (in)
20.0 (0.79)
Shock absorbers Standard suspension Oil type Shock absorbers Auto adjust suspension Low-pressure gas sealed type
Identification color Orange Green Light green Pink Brown Purple Gray Blue
Wire diameter
mm (in)
12.5
(0.49)
12.6
(0.49) 12.8 (0.50) 12.9 (0.51) 13.1 (0.52) 13.3 (0.53) 13.6 (0.54) 13.7 (0.54)
Coil springs* Coil inner diameter mm (in) 147.5 (5.8)
Free length
mm
(in) 344 (13.5)
CO <35
362
(14.3)
370
(14.6)
372 (14.6) 365 (14.4) 350 (13.8) 358 (14.1)
Coil number 4.99 5.09 5.31 5.42 5.53 5.46 5.34 5.45
* Refer
to
pages 13—5,6,7
for
coil spring applications
30-38