stop start MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 767 of 1146
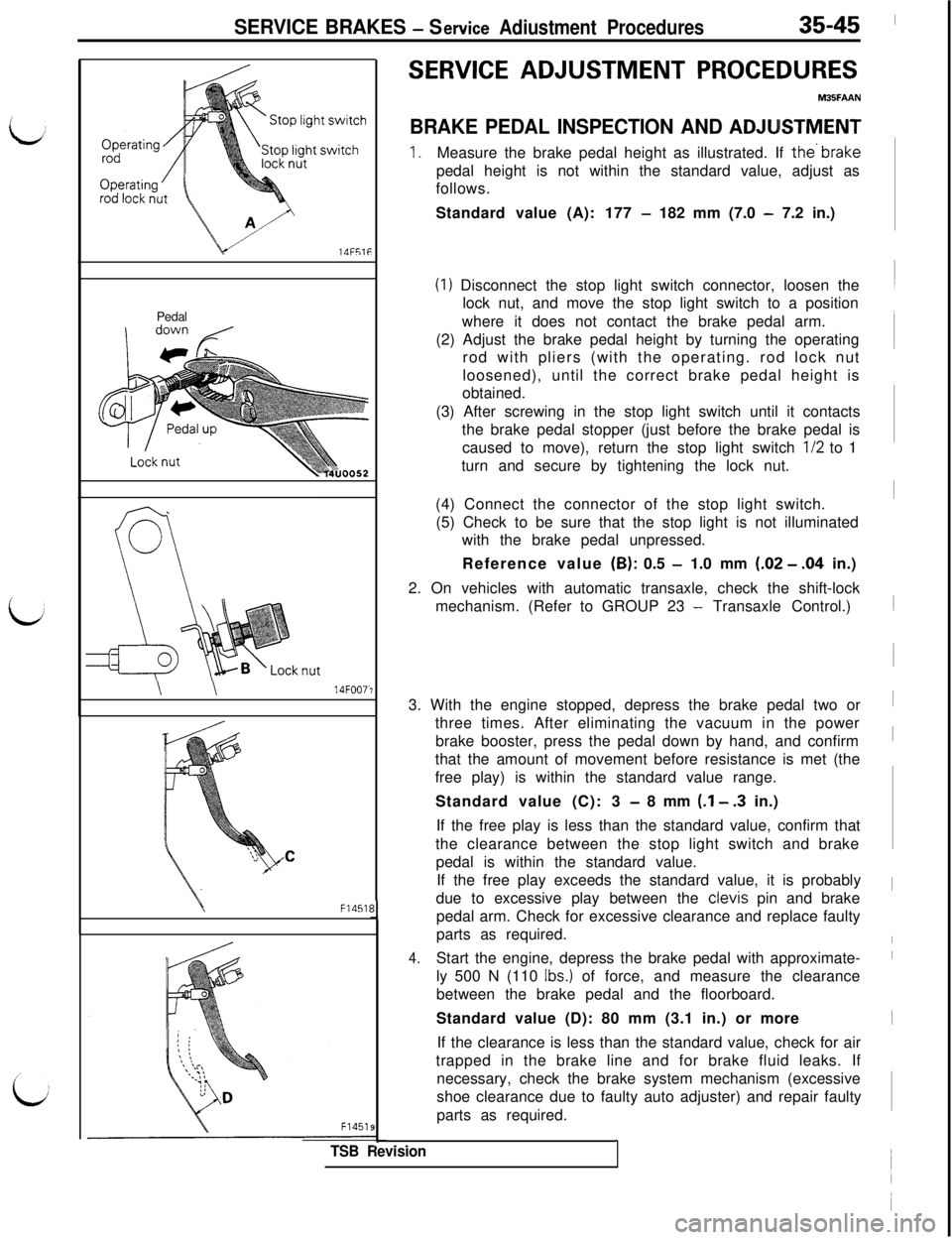
SERVICE BRAKES - Set-vice Adiustment Procedures35-45lUF51F
Pedal
7\ \!4FOO7.
F14511
F14519
TSB Revision-_.1
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
BRAKE PEDAL INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
1.Measure the brake pedal height as illustrated. If the’brakepedal height is not within the standard value, adjust as
follows.
Standard value (A): 177
- 182 mm (7.0 - 7.2 in.)
(I) Disconnect the stop light switch connector, loosen the
lock nut, and move the stop light switch to a position
where it does not contact the brake pedal arm.
(2) Adjust the brake pedal height by turning the operating
rod with pliers (with the operating. rod lock nut
loosened), until the correct brake pedal height is
obtained.
(3) After screwing in the stop light switch until it contacts
the brake pedal stopper (just before the brake pedal is
caused to move), return the stop light switch
l/2 to 1
turn and secure by tightening the lock nut.
(4) Connect the connector of the stop light switch.
(5) Check to be sure that the stop light is not illuminated
with the brake pedal unpressed.
Reference value (6): 0.5
- 1.0 mm (.02 - .04 in.)
2. On vehicles with automatic transaxle, check the shift-lock
mechanism. (Refer to GROUP 23
- Transaxle Control.)
3. With the engine stopped, depress the brake pedal two or
three times. After eliminating the vacuum in the power
brake booster, press the pedal down by hand, and confirm
that the amount of movement before resistance is met (the
free play) is within the standard value range.
Standard value (C): 3
- 8 mm (.I - .3 in.)
If the free play is less than the standard value, confirm that
the clearance between the stop light switch and brake
pedal is within the standard value.
If the free play exceeds the standard value, it is probably
due to excessive play between the clevis pin and brake
pedal arm. Check for excessive clearance and replace faulty
parts as required.
4.Start the engine, depress the brake pedal with approximate-
ly 500 N (110
Ibs.) of force, and measure the clearance
between the brake pedal and the floorboard.
Standard value (D): 80 mm (3.1 in.) or more
If the clearance is less than the standard value, check for air
trapped in the brake line and for brake fluid leaks. If
necessary, check the brake system mechanism (excessive
shoe clearance due to faulty auto adjuster) and repair faulty
parts as required.~1~1
I
I
I
I
I
Page 768 of 1146
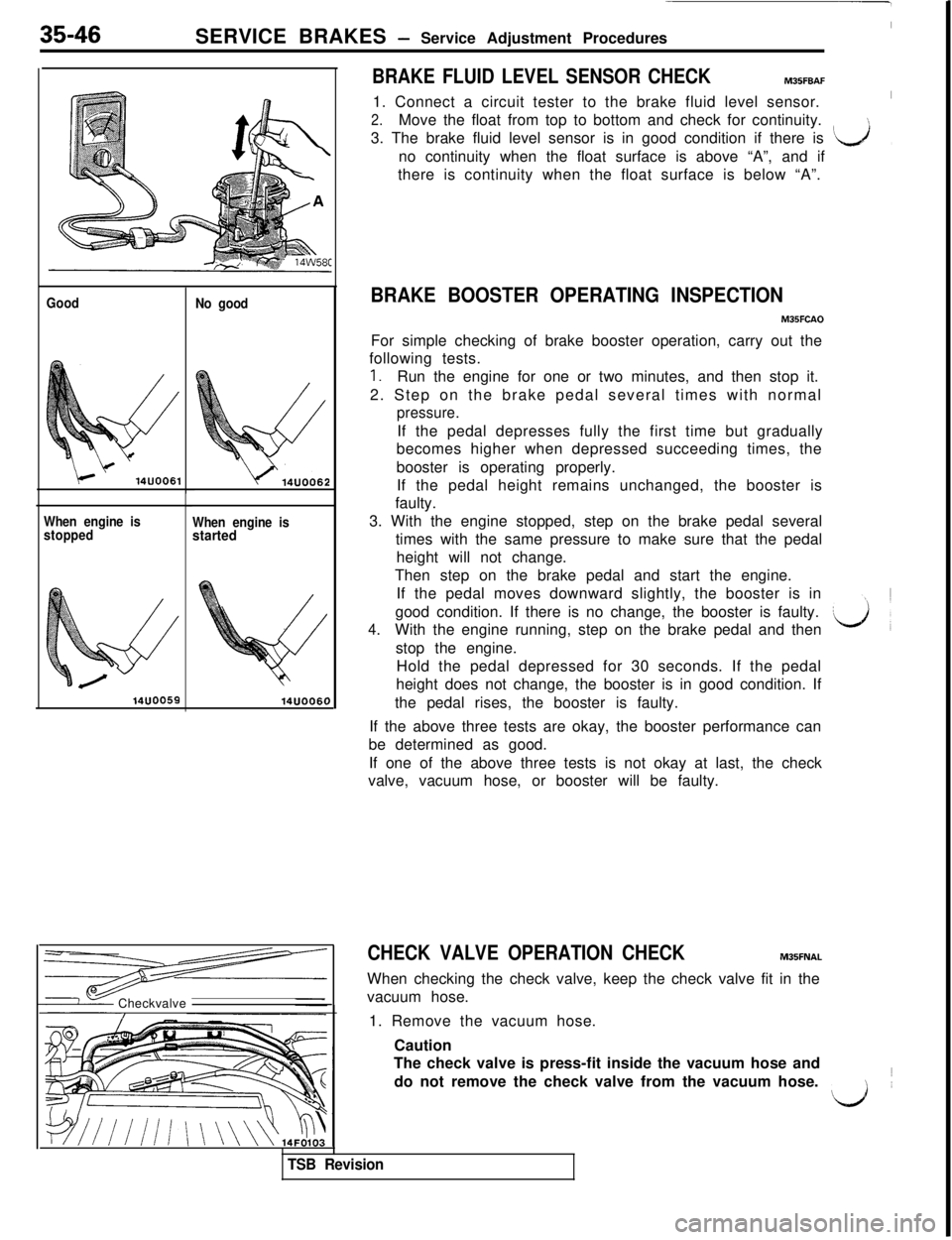
35-46SERVICE BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR CHECK
I
MBSFBAF
Good
k‘14UOO61
When engine is
stoppedNo good
When engine isstarted
14UOO6C)Checkvalve/1. Connect a circuit tester to the brake fluid level sensor.
I
2.Move the float from top to bottom and check for continuity.
3. The brake fluid level sensor is in good condition if there is
‘k&Jno continuity when the float surface is above “A”, and if,there is continuity when the float surface is below “A”.
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING INSPECTION
M35FCAOFor simple checking of brake booster operation, carry out the
following tests.
1.Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it.
2. Step on the brake pedal several times with normal
pressure.If the pedal depresses fully the first time but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times, the
booster is operating properly.
If the pedal height remains unchanged, the booster is
faulty.
3. With the engine stopped, step on the brake pedal several
times with the same pressure to make sure that the pedal
height will not change.
Then step on the brake pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is faulty.
4.With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and then
stop the engine.
Hold the pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If the pedal
height does not change, the booster is in good condition. If
the pedal rises, the booster is faulty.
If the above three tests are okay, the booster performance can
be determined as good.
If one of the above three tests is not okay at last, the check
valve, vacuum hose, or booster will be faulty.
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECKM35FNALWhen checking the check valve, keep the check valve fit in the
vacuum hose.
1. Remove the vacuum hose.
Caution
The check valve is press-fit inside the vacuum hose and
do not remove the check valve from the vacuum hose.1
d~
TSB Revision
Page 772 of 1146
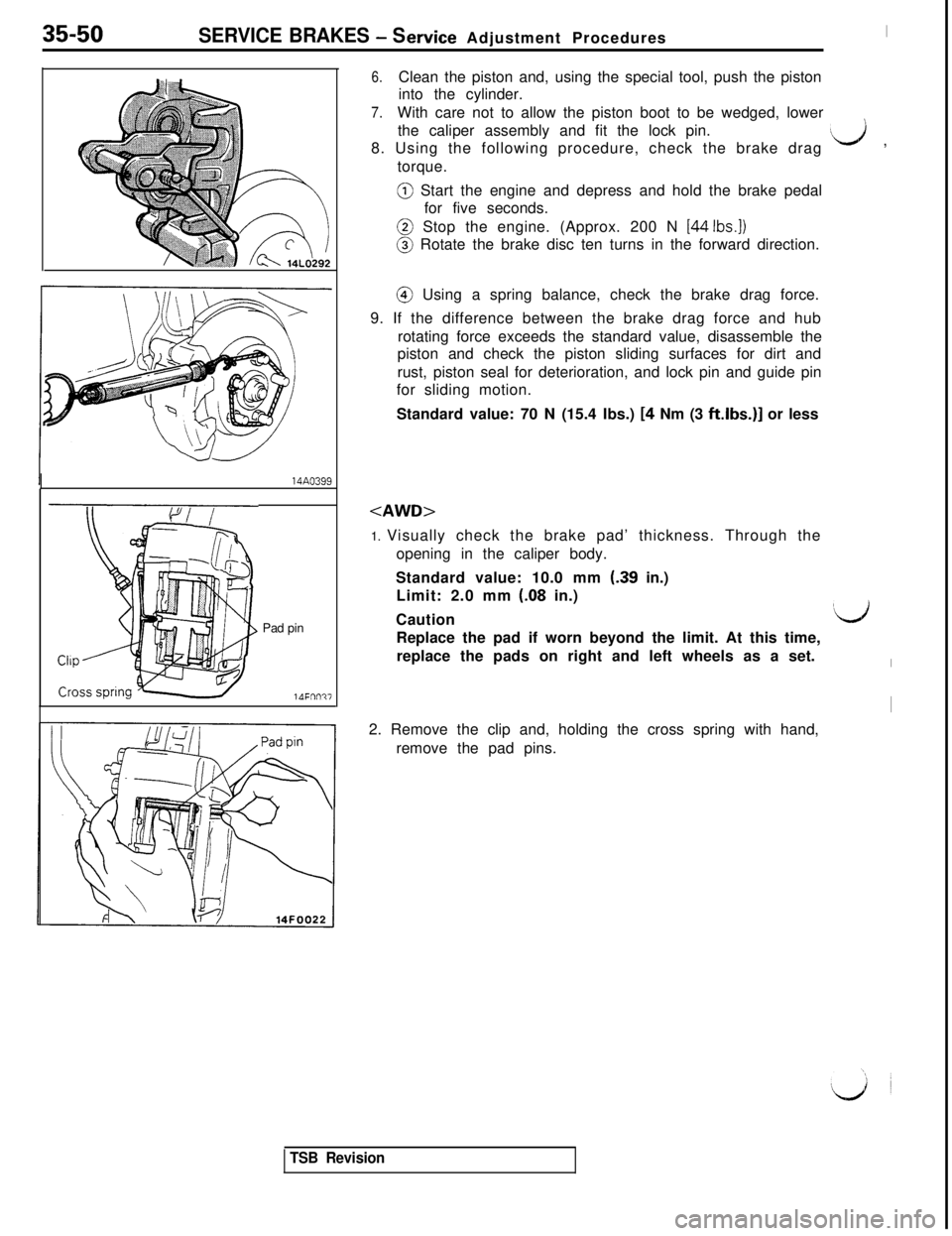
35-50SERVICE BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures
Pad pin
1 AFnn97
6.Clean the piston and, using the special tool, push the piston
into the cylinder.
7.With care not to allow the piston boot to be wedged, lower
the caliper assembly and fit the lock pin.
8. Using the following procedure, check the brake drag
‘d ,
torque.@ Start the engine and depress and hold the brake pedal
for five seconds.@ Stop the engine. (Approx. 200 N
[44 Ibs.])@ Rotate the brake disc ten turns in the forward direction.@ Using a spring balance, check the brake drag force.
9. If the difference between the brake drag force and hub
rotating force exceeds the standard value, disassemble the
piston and check the piston sliding surfaces for dirt and
rust, piston seal for deterioration, and lock pin and guide pin
for sliding motion.
Standard value: 70 N (15.4 Ibs.)
[4 Nm (3 ftlbs.)] or less
opening in the caliper body.
Standard value: 10.0 mm
(-39 in.)
Limit: 2.0 mm
(.08 in.)
Caution
‘L&iReplace the pad if worn beyond the limit. At this time,
replace the pads on right and left wheels as a set.
I2. Remove the clip and, holding the cross spring with hand,
remove the pad pins.
TSB Revision
Page 774 of 1146
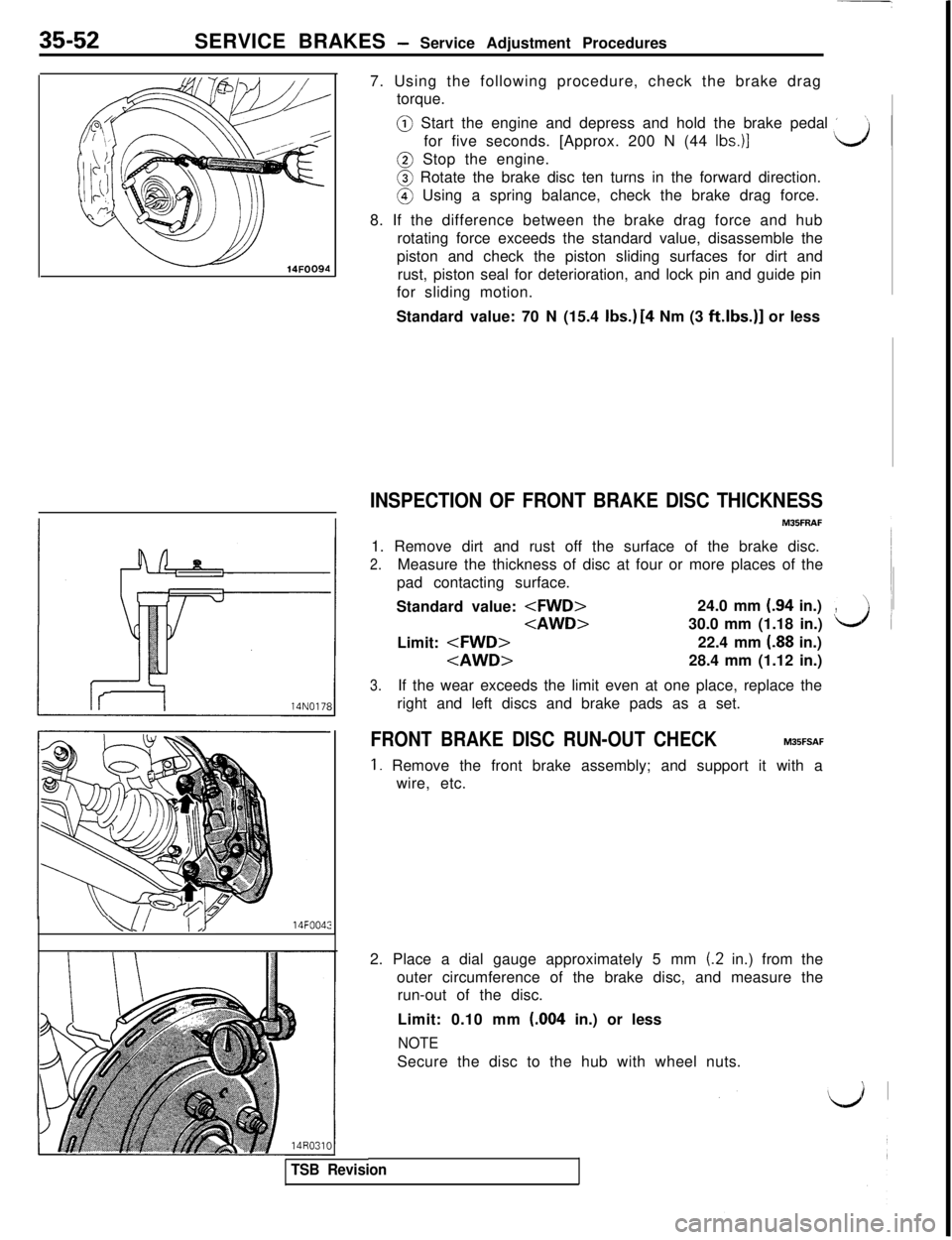
35-52SERVICE BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures
14FOO94
k.!! I14FOO427. Using the following procedure, check the brake drag
torque.@ Start the engine and depress and hold the brake pedal
’for five seconds. [Approx. 200 N (44
Ibs.)]@ Stop the engine.@ Rotate the brake disc ten turns in the forward direction.@ Using a spring balance, check the brake drag force.
8. If the difference between the brake drag force and hub
rotating force exceeds the standard value, disassemble the
piston and check the piston sliding surfaces for dirt and
rust, piston seal for deterioration, and lock pin and guide pin
for sliding motion.
Standard value: 70 N (15.4
Ibs.) [4 Nm (3 ft.lbs.)] or less
INSPECTION OF FRONT BRAKE DISC THICKNESS1. Remove dirt and rust off the surface of the brake disc.
2.Measure the thickness of disc at four or more places of the
pad contacting surface.
Standard value:
,Limit:
3.If the wear exceeds the limit even at one place, replace the
right and left discs and brake pads as a set.
FRONT BRAKE DISC RUN-OUT CHECKM35FSAF
1. Remove the front brake assembly; and support it with a
wire, etc.
TSB Revision2. Place a dial gauge approximately 5 mm
(.2 in.) from the
outer circumference of the brake disc, and measure the
run-out of the disc.
Limit: 0.10 mm (.004 in.) or less
NOTESecure the disc to the hub with wheel nuts.
Page 776 of 1146
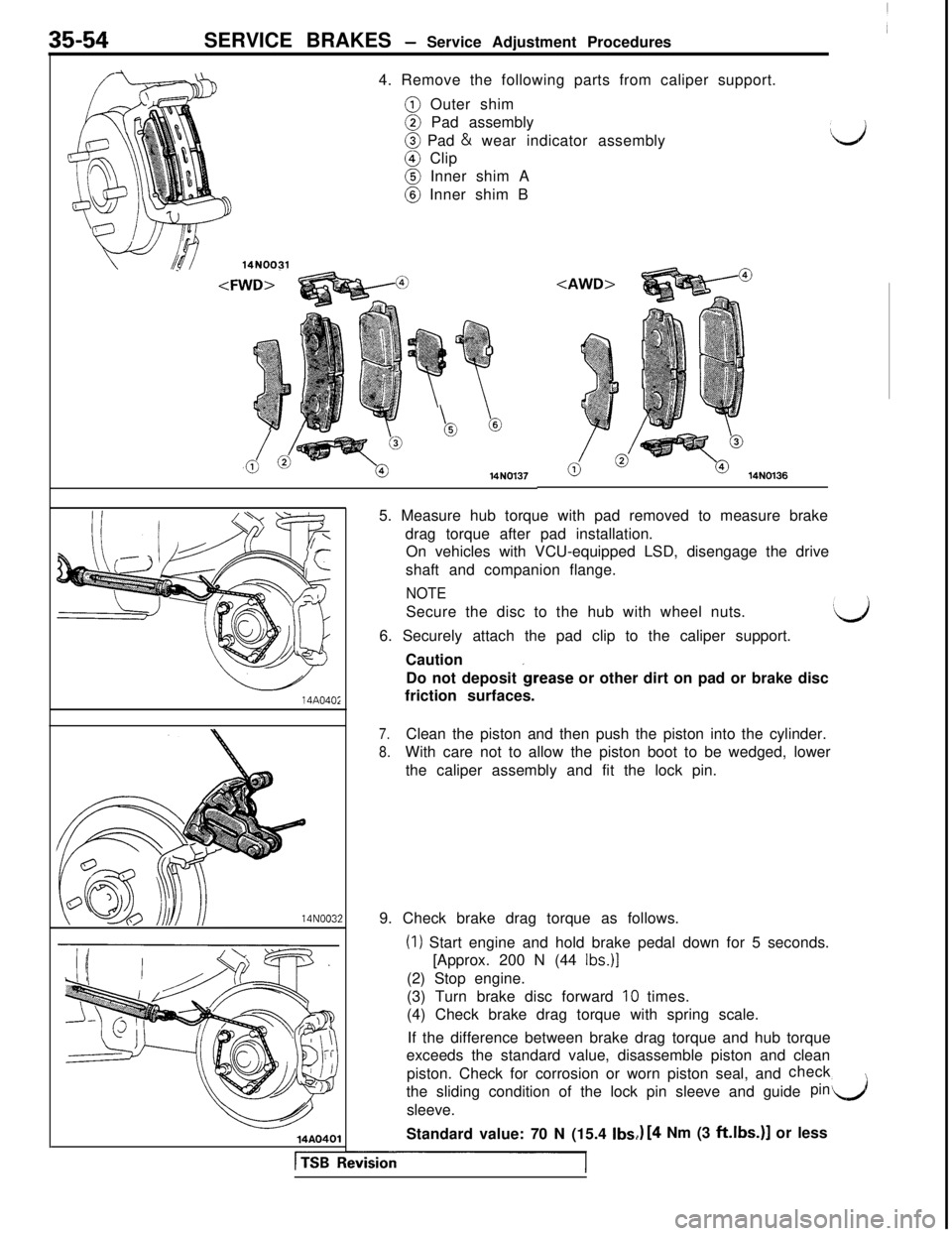
SERVICE BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures
4. Remove the following parts from caliper support.@ Outer shim@ Pad assembly@ Pad & wear indicator assembly@ Clip@ Inner shim A@ Inner shim B
d
14N0031
/0014N013714A040;14N003:
14AO401
l%FLision
14N01365. Measure hub torque with pad removed to measure brake
drag torque after pad installation.
On vehicles with VCU-equipped LSD, disengage the drive
shaft and companion flange.
NOTESecure the disc to the hub with wheel nuts.
6. Securely attach the pad clip to the caliper support.
Caution
Do not deposit
&ease or other dirt on pad or brake disc
friction surfaces.
7.Clean the piston and then push the piston into the cylinder.
8.With care not to allow the piston boot to be wedged, lower
the caliper assembly and fit the lock pin.
9. Check brake drag torque as follows.
(I) Start engine and hold brake pedal down for 5 seconds.
[Approx. 200 N (44
Ibs.)](2) Stop engine.
(3) Turn brake disc forward
10 times.
(4) Check brake drag torque with spring scale.
If the difference between brake drag torque and hub torque
exceeds the standard value, disassemble piston and clean
piston. Check for corrosion or worn piston seal, andcheck
the sliding condition of the lock pin sleeve and guide
pinl/jsleeve.
Standard value: 70 N (15.4
Ibs,,) [4 Nm (3 ft.lbs.)] or less
Page 796 of 1146
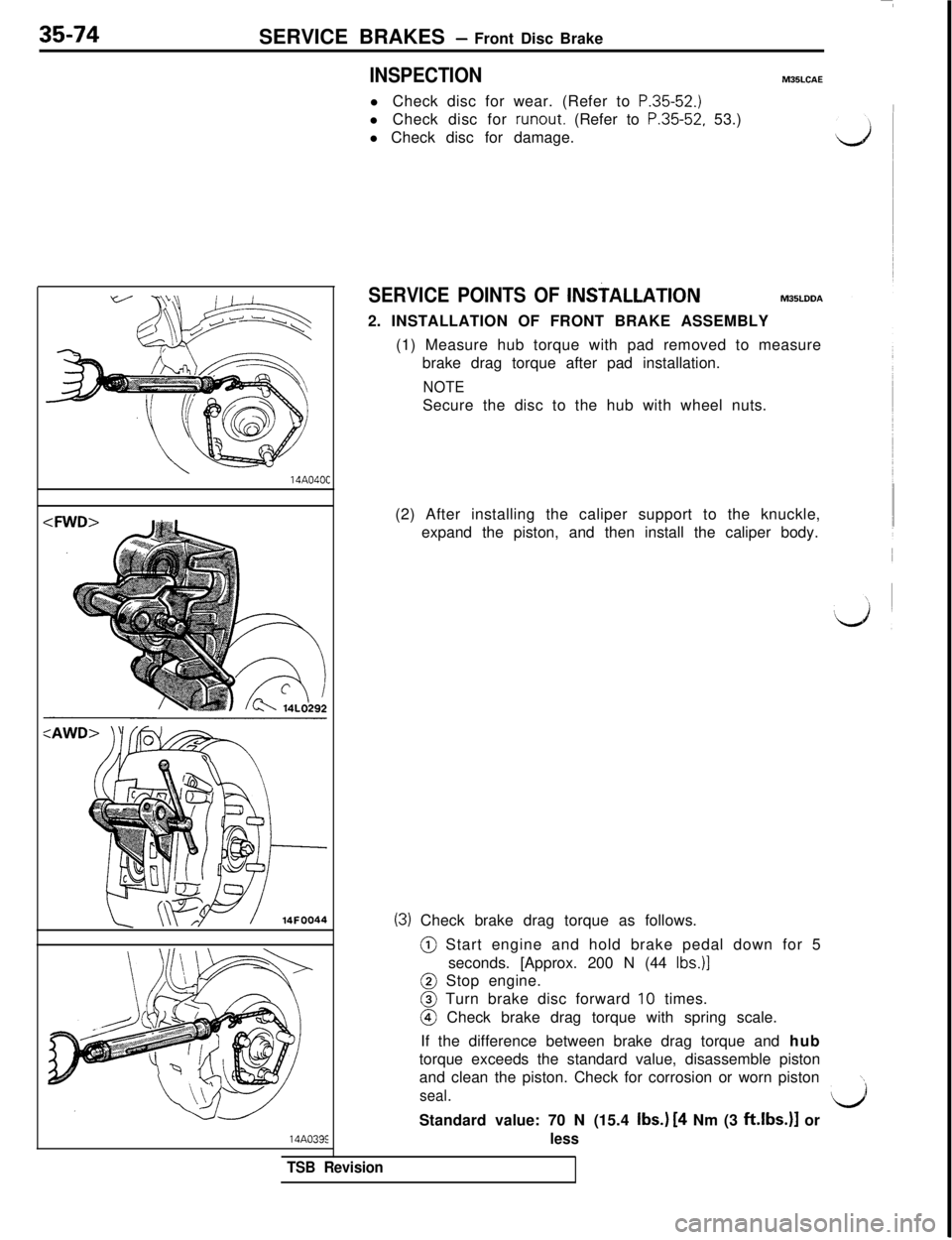
35-74
SERVICE BRAKES - Front Disc Brake
INSPECTIONM35LCAEl Check disc for wear. (Refer to
P.35-52.)l Check disc for runout. (Refer to
P.35-52, 53.)Il Check disc for damage.14A040C
(2) After installing the caliper support to the knuckle,
expand the piston, and then install the caliper body.
(3) Check brake drag torque as follows.@ Start engine and hold brake pedal down for 5
seconds. [Approx. 200 N (44
Ibs.)]@ Stop engine.@ Turn brake disc forward
10 times.@ Check brake drag torque with spring scale.
If the difference between brake drag torque and hub
torque exceeds the standard value, disassemble piston
and clean the piston. Check for corrosion or worn piston
\\
seal.l/iStandard value: 70 N (15.4 Ibs.)
[4 Nm (3 ft.lbs.)l or14A033E
less
SERVICE POINTS OF lNS?ALLATlONM35LDDA2. INSTALLATION OF FRONT BRAKE ASSEMBLY
(1) Measure hub torque with pad removed to measure
brake drag torque after pad installation.
NOTESecure the disc to the hub with wheel nuts.
TSB Revision
Page 830 of 1146

37A-2SPECIFICATIONS
STEERING - Specifications
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
M37CA-A
LA,Items
Steering wheel
Steering wheel O.D.
mm (in.)
Gear box
Steering gear type
Power steering oil pump
Oil pump type
Displacementcm3/rev. (cu.in./rev.)
Relief set pressureMPa (psi)
Specifications
390 (15.4)
Rack and pinion
Vane type
9.6 t.59)
8(1,138)
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONSM37CB-A
!msSpecifications
andard value
Steering wheel free play (with engine stopped)
mm (in.)11 (43)
Steering angle
Inner wheel33”45’ 2 2”
Outer wheel28”21’
Tie rod end ball joint starting torqueNm (in.lbs.)
FWD0.5 - 3.0 (4 - 26)
AWDl.O-3.0(9-26)
Stationary steering effortN (Ibs.)35 (8) or less
V-belt deflectionmm (in.)
When belt tension is inspected or readjusted9-11 (.35-.43)
When new belt is installed7 - 8.5 (.28 - .33)
Oil pump pressureMPa (psi)
Pressure gauge valve closed7.5-8.2 (1,067- 1,166)
Pressure gauge valve opened0.8-1.0(114-142)
Oil pressure switch operating pressureMPa (psi)
Oil pressure switch contacts closed (continuity)
1.5-2.0(213-284)
Oil pressure switch contacts opened (no continuity)0.7-1.2(100-171)
Total pinion torqueNm (in.lbs.)0.6-1.3(5-11)
Tie-rod joint swing resistanceN (Ibs.)8-18(1.8-4.0)
Tie-rod joint swing torqueNm (in.lbs.)2-5(17-43)nit
Steering wheel free play (when hydraulic operation)mm (in.) 30 (1.2)
Variation of tie rod end ball joint shaft direction
mm (in.)1.5 i.059)
Oil pump pressure
Pressure gauge valve opened
MPa (psi)1.5 (213)
Space between vane and rotormm (in.)0.06 (0024)
LJ’
I
I
L’l
1 TSB Revision
Page 833 of 1146
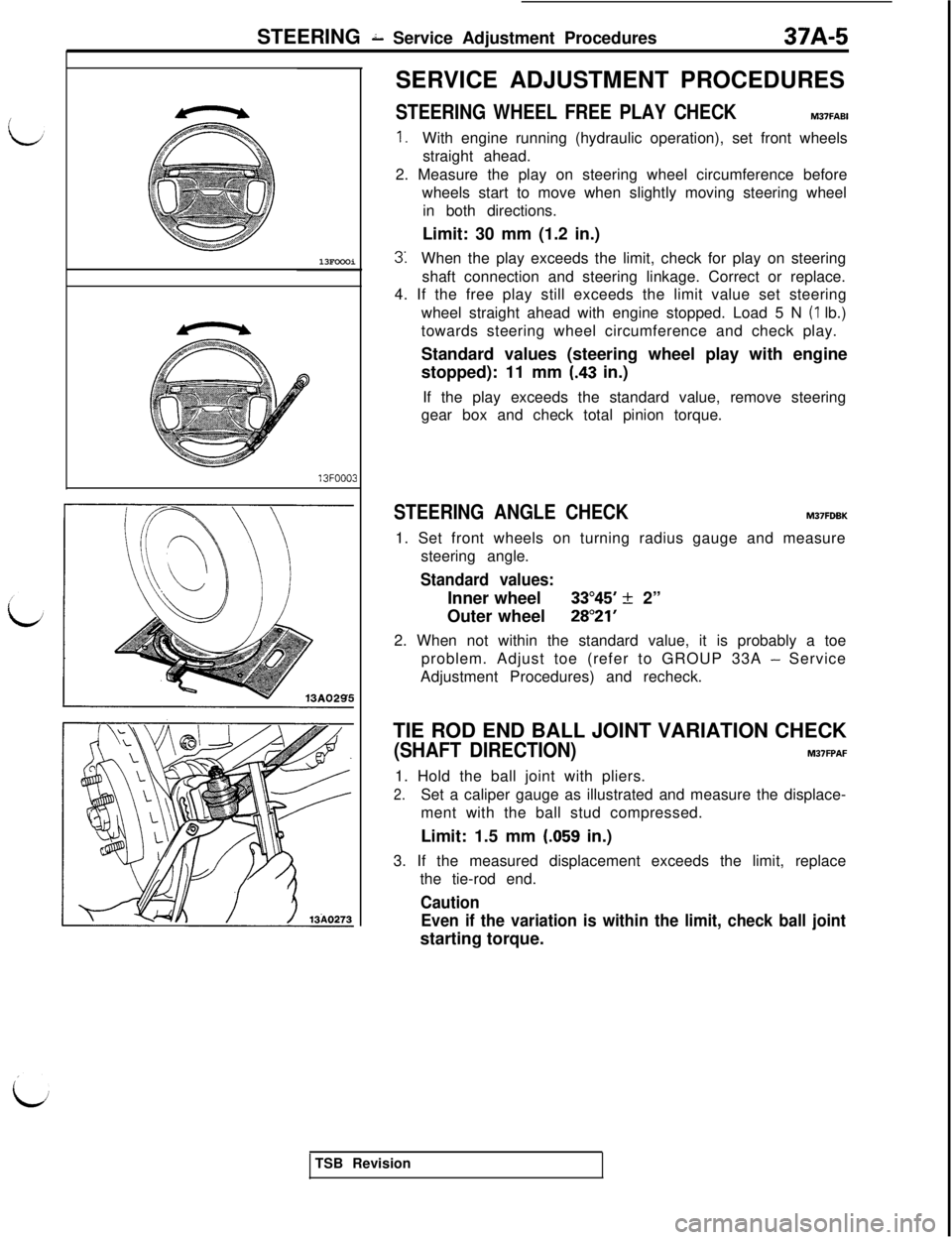
STEERING 2 Service Adjustment Procedures37A-5
13FOOOi13FOOO3SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
STEERING WHEEL FREE PLAY CHECKM37FABI
1.With engine running (hydraulic operation), set front wheels
straight ahead.
2. Measure the play on steering wheel circumference before
wheels start to move when slightly moving steering wheel
in both directions.
Limit: 30 mm (1.2 in.)
3:When the play exceeds the limit, check for play on steering
shaft connection and steering linkage. Correct or replace.
4. If the free play still exceeds the limit value set steering
wheel straight ahead with engine stopped. Load 5 N
(1 lb.)
towards steering wheel circumference and check play.
Standard values (steering wheel play with engine
stopped): 11 mm
(.43 in.)
If the play exceeds the standard value, remove steering
gear box and check total pinion torque.
STEERING ANGLE CHECKM37FDBK1. Set front wheels on turning radius gauge and measure
steering angle.
Standard values:Inner wheel
33”45’ k 2”
Outer wheel
28”21’2. When not within the standard value, it is probably a toe
problem. Adjust toe (refer to GROUP 33A
- Service
Adjustment Procedures) and recheck.
TIE ROD END BALL JOINT VARIATION CHECK
(SHAFT DIRECTION)M37FPAF1. Hold the ball joint with pliers.
2.Set a caliper gauge as illustrated and measure the displace-
ment with the ball stud compressed.
Limit: 1.5 mm
(.059 in.)
3. If the measured displacement exceeds the limit, replace
the tie-rod end.
Caution
Even if the variation is within the limit, check ball jointstarting torque.
TSB Revision
Page 834 of 1146

STEERING - Service Adjustment Procedures13G005E
Tape or markon steering
wheel hub
13FOO4:
Lines atstraight-position-ahead
Dotted linesshow wheel
at desired
positlon
Tape or mark
on
steenngwheel rim
tanceRuler 7’off-center13FOO4;
36 splines
13W589/13FOO45
TIE ROD END. BALL JOINT STARTING TORQUE
CHECK~M37FEBF
1. Disconnect tie rod and knuckle with special tool.~
LJ2. Move ball joint stud several times and install nut on stud.
Measure ball joint starting torque.
Standard value:
tie rod end.
4.When the starting torque is under the standard value, check
for play or ratcheting in ball joint.
If none of these, it is still
serviceable.
STEERING WHEEL CENTERINGM37FNAI
SIMPLIFIED STEERING WHEEL CENTERINGDetermining Steering Wheel’s Off Center
1. For the road test, take along chalk or tape and a ruler.
2. Drive straight ahead on an uncambered level surface.
3. When the vehicle’s wheels are pointing straight ahead,
mark the steering wheel hub and column cover with a chalk
or tape line.
4. Stop the vehicle and line up the marks on the hub and
column cover.
5. Place a tape strip
01 mark on the steering wheel rim.
6.Hold a ruler next to the rim as shown in the illustration, and
then steer the steering wheel until it is in the desired
centered position.
7.Record the distance the strip or mark on the rim has moved.
This is how far the steering wheel is off center. If it is more
than 16 mm
(518 in.) off center, it can be centered by
indexing it ten degrees towards the center.
Indexing Steering Wheel to Center It
The steering wheel shaft has 36 splines, allowing the steering
wheel to be indexed in ten-degree increments.
1. Remove the steering wheel.
2.Without disturbing the position of the steering wheel shaft,
re-install the wheel as near on-center as possible.
TSB Revision
Page 836 of 1146
37A-8STEERING - Service Adjustment Procedures13FOOO3
13FOOOl
STATIONARY STEERING EFFORT CHECKM37FFAM
1.With the vehicle stopped on a flat, paved surface, turn the
steering wheel to the straight ahead position.
2. Start the engine and set it to 1,000
+ 100 rpm.d
Caution
After checking the engine speed, there must be a returnto the standard idling speed.
3. Attach a spring balance to the outer circumference of the
steering wheel and measure the steering force required to
turn the steering wheel from the straight ahead position to
the left and right (within a range of 1.5 turns).
Also check to be sure that there is no significant fluctuation
of the required steering force.
Standard value:
Steering effort35 N (8 Ibs.) or less
Fluctuation allowance
6 N (1.3 Ibs.) or less
STEERING WHEEL RETURN TO CENTER CHECK
M37FGACiTo make this test, conduct a road test and check as follows.
1.Make both gradual and,sudden turns and check the steering
“feeling” to be sure that there is no difference in the
steering force required and the wheel return between left
and right turns.
2. At a speed of 35 km/h (22 mph), turn the steering wheel
90”. and release the steering wheel after 1 or 2 seconds. If
the steering wheel then returns 70” or more, the return can
be judged to the satisfactory.
NOTEThere will be a momentary feeling of “heaviness” when the
wheel is turned quickly, but this is not abnormal. (This is
because the oil pump discharge amount is especially apt to
be insufficient during idling.)
V-BELT TENSION CHECKM37FHAJCheck to be sure that the belt is not damaged and that the
V-belt is correctly attached to the groove of the pulley.
NOTEIf there is abnormal noise or belt slippage, check the belt
tension and check for unusual wear or abrasion, or damage, of
the pulley contact surface, and for scars or scratches on the
pulley.d
TSB RevisionI