fuel type MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: ECLIPSE, Model: MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990Pages: 391, PDF Size: 15.27 MB
Page 18 of 391

o-14GENERAL - General Data and Specifications
tiems
Chassis
TireFront suspension
Type
Rear suspensionType
Brake
TypeFront
RearSteering
Gear type
Gear ratio
Fuel tankCapacity liters (gals.)
P205/55HR16 or
205l55VR 16Independent strut
3-Link
Torsion axleDisc
Disc
Rack and pinion
m
60 (16)
P205/55VR 16 or205155VR16Independent strut
3-Link
Torsion axleDisc
Disc
Rack and pinion
00
60 (16)
P205155VR16 or205155VR16Independent strut
Double wishbone
Disc
Disc
Rack and pinion
co
60 (16)ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Items
TypeNumber of cylinders
Boremm (in.)Stroke
mm (in.)Piston displacement
Compression ratio
Firing order
cm3 (cu.in.)
4G63 (2.OL) Non-Turbo1 4663 (2.OL) Turbo
In-line DOHC~ In-line DOHC
4‘4
85.0 (3.35)
85.0 (3.35)
88.0 (3.46)88.0 (3.46)
1,997 (122)
1,997 (122)
9.0
7.8l-3-4-2l-3-4-2
TRANSAXLE SPECIFICATIONS
Items
Type
Gear ratioTransfer ratio
gearFinal drive ratio
gear
1st
2nd
3rd4th5th
ReverseF5M22F5M33
W5M33F4A22
5-speed M/T5-speed M/T&speed ArF4-speed AiT
3.3633.038
3.0832.846
1.9471.8331.6841.581
1.2851.2171.1151 .ooo0.9390.8880.8330.686
0.756
0.7410.666
3.0833.166
’3.1662.176
-1.090
3.9413.4373.8663.562
Page 32 of 391
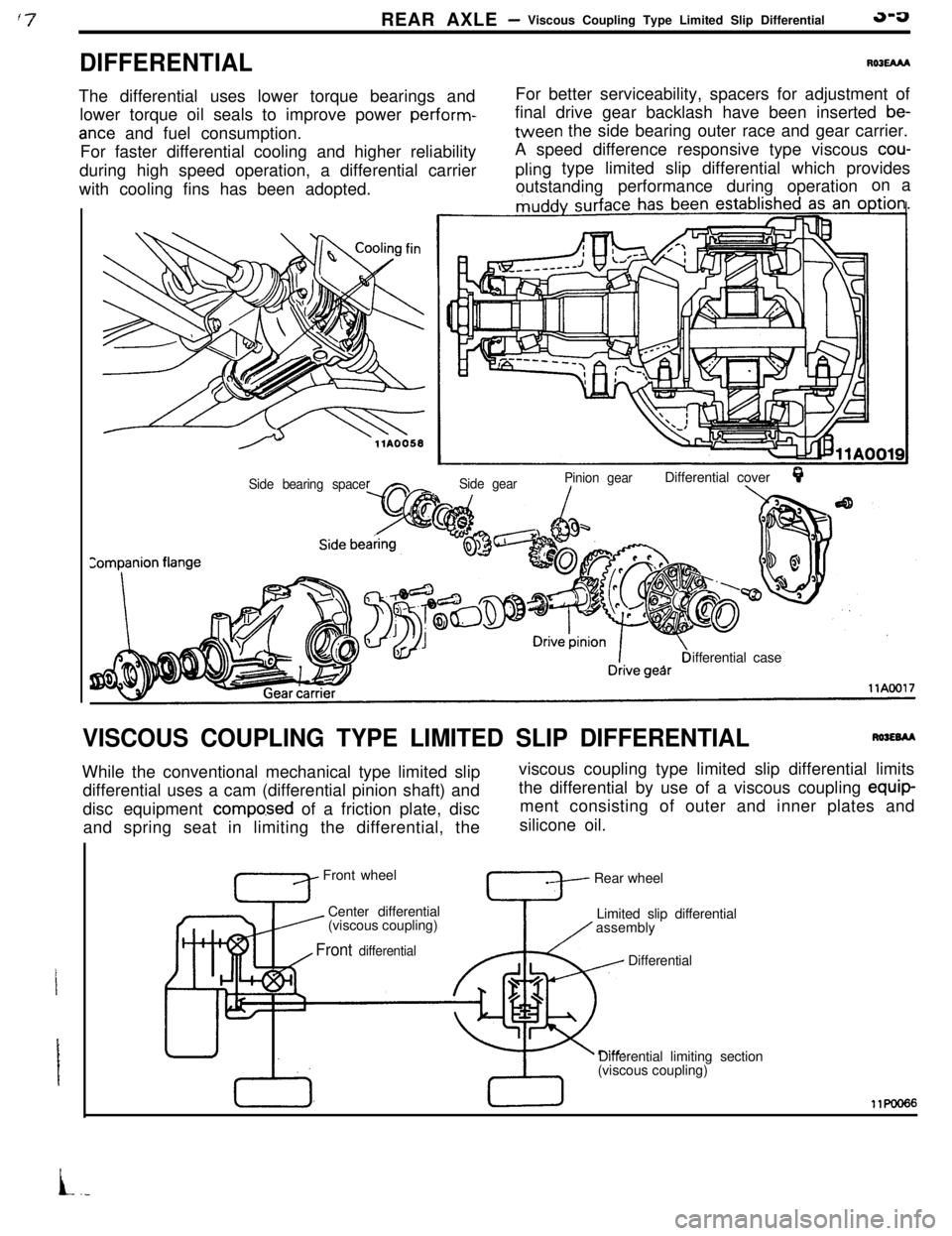
REAR AXLE- Viscous Coupling Type Limited Slip Differential3-a
DIFFERENTIALROlEAM
The differential uses lower torque bearings and
lower torque oil seals to improve power perform-
ante and fuel consumption.
For faster differential cooling and higher reliability
during high speed operation, a differential carrier
with cooling fins has been adopted.For better serviceability, spacers for adjustment of
final drive gear backlash have been inserted
be-tween the side bearing outer race and gear carrier.
A speed difference responsive type viscous
cou-
pling type limited slip differential which provides
outstandingperformance during operationon a
Side gearPinion gearDifferential coverQ./\Side bearing spaceifferential case
VISCOUS COUPLING TYPE LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIALRWEBAAWhile the conventional mechanical type limited slip
differential uses a cam (differential pinion shaft) and
disc equipment
compo.sed of a friction plate, disc
and spring seat in limiting the differential, theviscous coupling type limited slip differential limits
the differential by use of a viscous coupling equip-
ment consisting of outer and inner plates and
silicone oil.
Front wheel
Center differential
’ (viscous coupling)Rear wheel
Limited slip differential
assembly
Front differential, I
TDifferential
Differential limiting section
(viscous coupling)11KmI66
L.-
Page 83 of 391
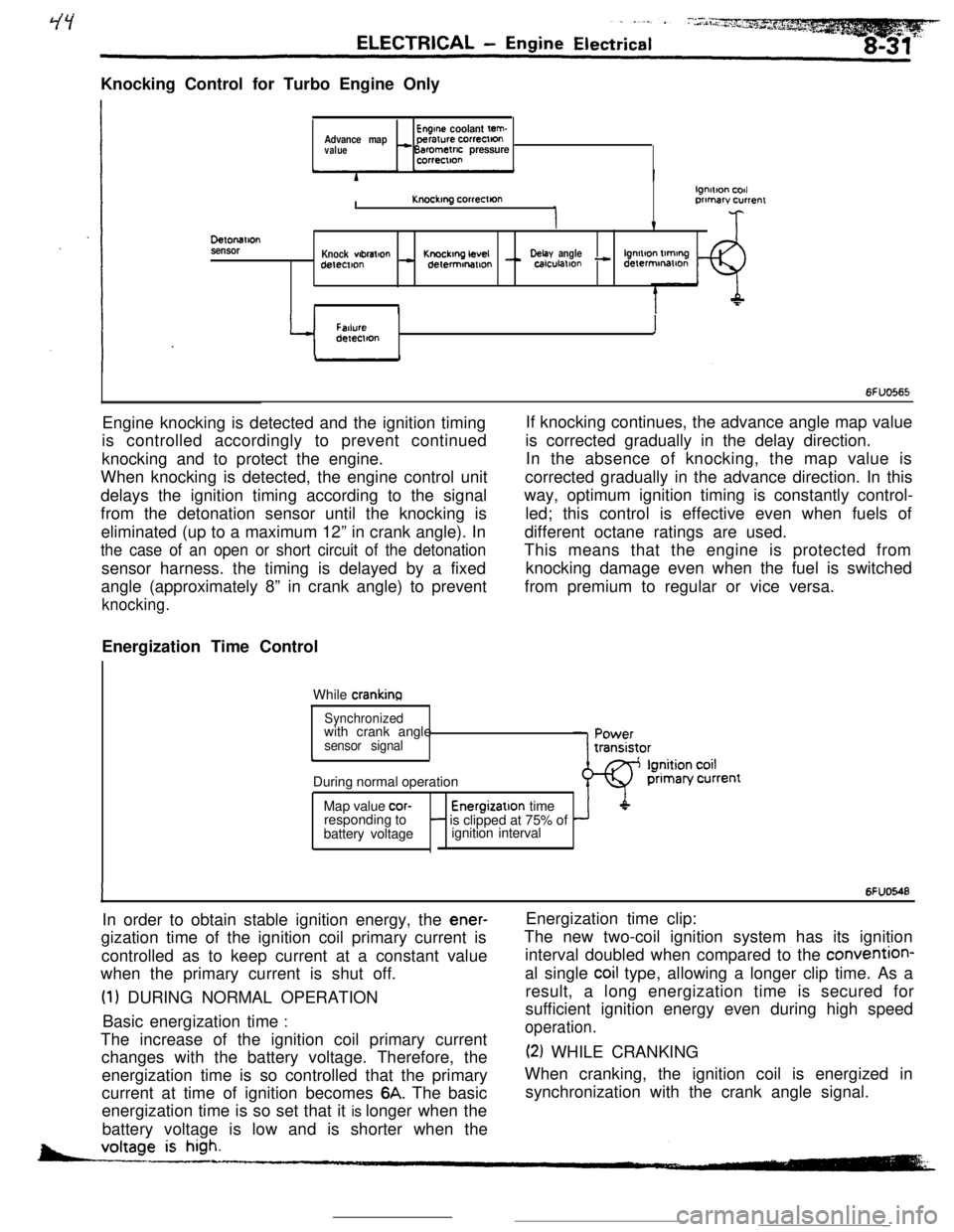
Knocking Control for Turbo Engine OnlyEngine coolant tern.Advance mapperarure correctton
value- Barometric pressurecorrectton
DelonaIlon
sensorI
lgnmon codKnockmg correcllonprimary currenr
v
Knock wbral+onKnockmg LevelDelay anglelgnmon tlmtngdetemon- delermonmon - calculallon - derermmatlon
II
Y
FatlureIdeIeclton
6FUO565Engine knocking is detected and the ignition timing
is controlled accordingly to prevent continued
knocking and to protect the engine.
When knocking is detected, the engine control unit
delays the ignition timing according to the signal
from the detonation sensor until the knocking is
eliminated (up to a maximum 12” in crank angle). In
the case of an open or short circuit of the detonationsensor harness. the timing is delayed by a fixed
angle (approximately 8” in crank angle) to prevent
knocking.Energization Time Control
While
crankinaIf knocking continues, the advance angle map value
is corrected gradually in the delay direction.
In the absence of knocking, the map value is
corrected gradually in the advance direction. In this
way, optimum ignition timing is constantly control-
led; this control is effective even when fuels of
different octane ratings are used.
This means that the engine is protected from
knocking damage even when the fuel is switched
from premium to regular or vice versa.
Synchronizedwith crank angle
sensor signalcDuring normal operation
Map value
cor-Energizatlon time
responding to- is clipped at 75% of
battery voltageignition interval
IIn order to obtain stable ignition energy, the
ener-gization time of the ignition coil primary current is
controlled as to keep current at a constant value
when the primary current is shut off.
(1) DURING NORMAL OPERATION
Basic energization time
:The increase of the ignition coil primary current
changes with the battery voltage. Therefore, the
energization time is so controlled that the primary
current at time of ignition becomes
6A. The basic
energization time is so set that it is longer when the
battery voltage is low and is shorter when the
6FUO548Energization time clip:
The new two-coil ignition system has its ignition
interval doubled when compared to the convention-
al single
coil type, allowing a longer clip time. As a
result, a long energization time is secured for
sufficient ignition energy even during high speed
operation.
(2) WHILE CRANKING
When cranking, the ignition coil is energized in
synchronization with the crank angle signal.
-
Page 87 of 391

=--Y
jl
1 /
i "
_. ---“._ _ _ ._ ..-..+_LI_y_--- -
9-2ENGINE- General Information
GENERAL INFORMATION
MAJOR
SPEClFlCATiONS
Row- -
Items
Number and arrangement of cylinderCylinder bore x stroke
mm (in.)
Total displacementcc (cu.in.1Compression ratio
Combustion chamber
Valve mechanismNumber of valve
Intake
Exhaust
Valve timing
IntakeOpen/CloseExhaust Open/Close
Lubrication
Oil pump
Fuel system
SuperchargerCooling system
Water pump
Alternator
Starter motor
Ignition system
Exhaust gas recirculation systemCatalytic converter
Crankcase ventilation system
Evaporative emission control system
Non-Turbo engineTurbo engine4 in-line, longitudinal
4 in-line, longitudinal
85 x
88 (3.346 x 3.465)85 x 88 (3.346 x 3.465)1997 (121.9)
1997 (121.7)
9.07.8
Pentroof typePentroof type
Double overhead camshaftDouble overhead camshaft
(DOHC)(DOHC)
88
88
26 “BTDU46”ABDC21”BTDC/Sl”ABDC56BBDUS”ATDC55”BBDUS”ATDC
Pressure feed-full flow filtrationPressure feed-full flow filtration
Gear typeGear type
Electronic control multipoint
fuelElectronic control multipoint fuel
injectioninjection
Turbo typeLiquid cooled-forced circulationLiquid cooled-forced circulation
-Impeller typeImpeller type
AC generator with a built-involtage regulatorAC generator with a built-in
voltage regulator
Planetary gear reduction drivePlanetary gear reduction drivetype
Two-coil type, electronic controlTwo-coil type, electronic control
ignitionignition
Conventional type: For FederalConventional type: For Federal
and Canadaand Canada
Electronical control type:Electronical control type:
For CaliforniaFor CaliforniaMonolithic type,
under-floorMonolithic type, under-floor
installationinstallation
Closed typeClosed type
Charcoal canister typeCharcoal canister type
I
Page 88 of 391

q7 --_-.-ENGINE
- General Information9-3TECHNICAL FEATURES
HIGH PERFORMANCE AND . . .._..............1. The DOHC 16-valve engine ensures excellent intake and exhaust
FUEL ECONOMYefficiency.
2. The rocker arm is of the roller-type-cam-follower design which Iminimizes friction loss.
3. The combustion chamber is of the pentroof type with a squish
area that offers outstanding combustion efficiency.
4. The multipoint fuel injection system is electronically
controlled.5. The intake manifold is the inertia supercharging type which
improves intake efficiency and the dual-type exhaust manifold
offers good exhaust efficiency.
6. The two-coil type electronic control ignition system ensures
good ignition performance.
LOW VIBRATION AND. . . . . . ..I.................1. The hydraulic lash adjuster, together with the roller rocker arm,
LOW NOISEcontributes to reduced operating noise of the valve mechanism.
2. A cogged type belt is used to drive the camshaft.
3. The auto tensioner maintains the optimum timing belt tension.
4. The torsional damper reduces twisting vibration in the crankshaft’
to a minimum.
5. The silent shaft system reduces engine vibration and rolling
’moment to a minimum
SERVICEABILITY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1. The self-diagnosis system makes troubleshooting easier.
2. The lash adjuster eliminates the need for valve clearance
adjustment.3. The auto tensioner eliminates the need for timing belt
tension adjustment.
-.--..-. --.-
Page 92 of 391
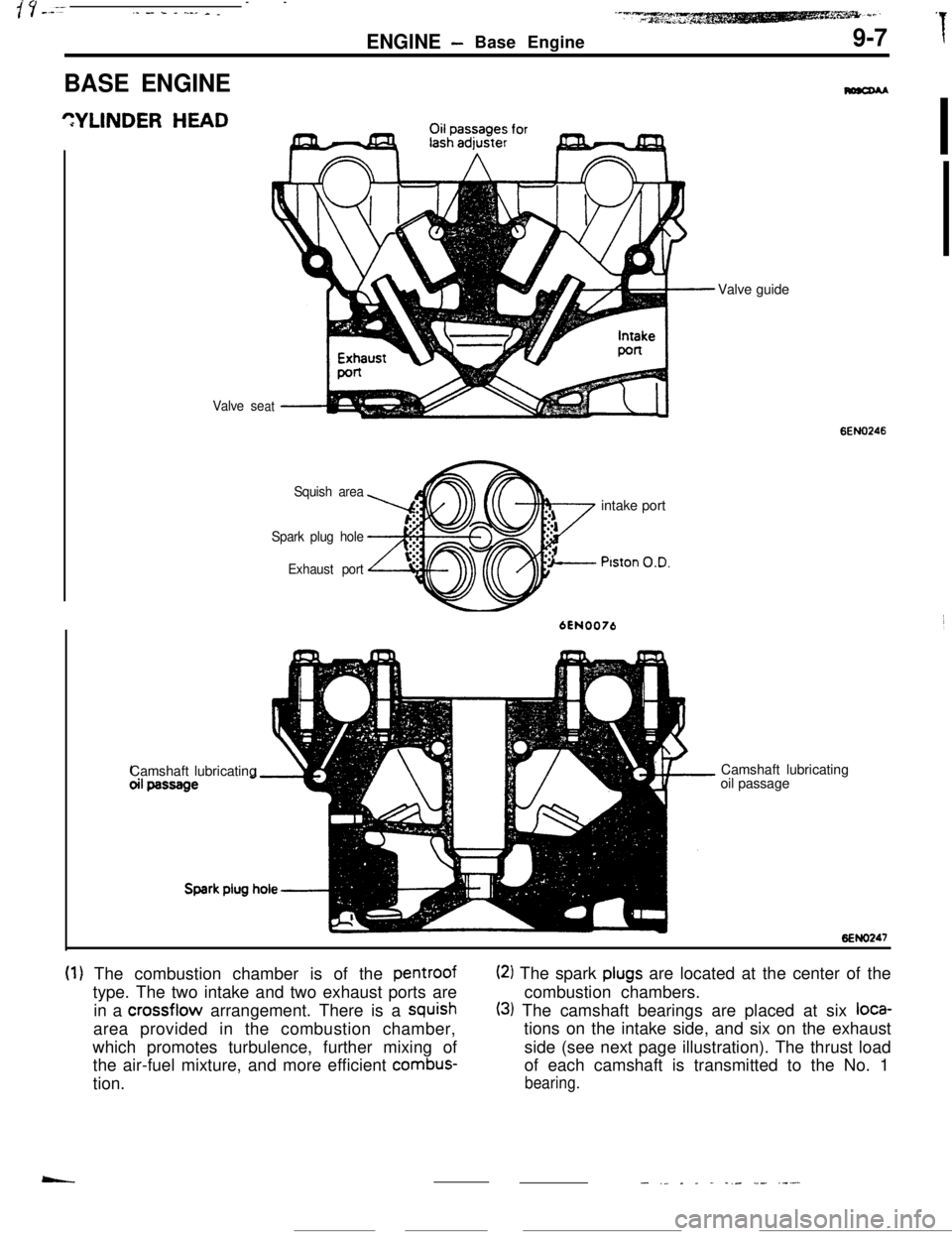
s’ y _._----,_ - k - ..-_ _ _
ENGINE- Base Engine9-7I
BASE ENGINE
Valve seat
Squish area
Spark plug hole
Exhaust portintake port
Piston O.D.
6EN0076Camshaft lubricatingValve guide
6ENO246Camshaft lubricating
oil passage
6ENO247
(1) The combustion chamber is of the pentroof(2) The spark plugs are located at the center of the
type. The two intake and two exhaust ports arecombustion chambers.
in a crossflow arrangement. There is a
squish(3) The camshaft bearings are placed at six loca-area provided in the combustion chamber,tions on the intake side, and six on the exhaust
which promotes turbulence, further mixing ofside (see next page illustration). The thrust load
the air-fuel mixture, and more efficient
combus-of each camshaft is transmitted to the No. 1
tion.
bearing.
- ._ _ _ - -,- -- .---
Page 99 of 391
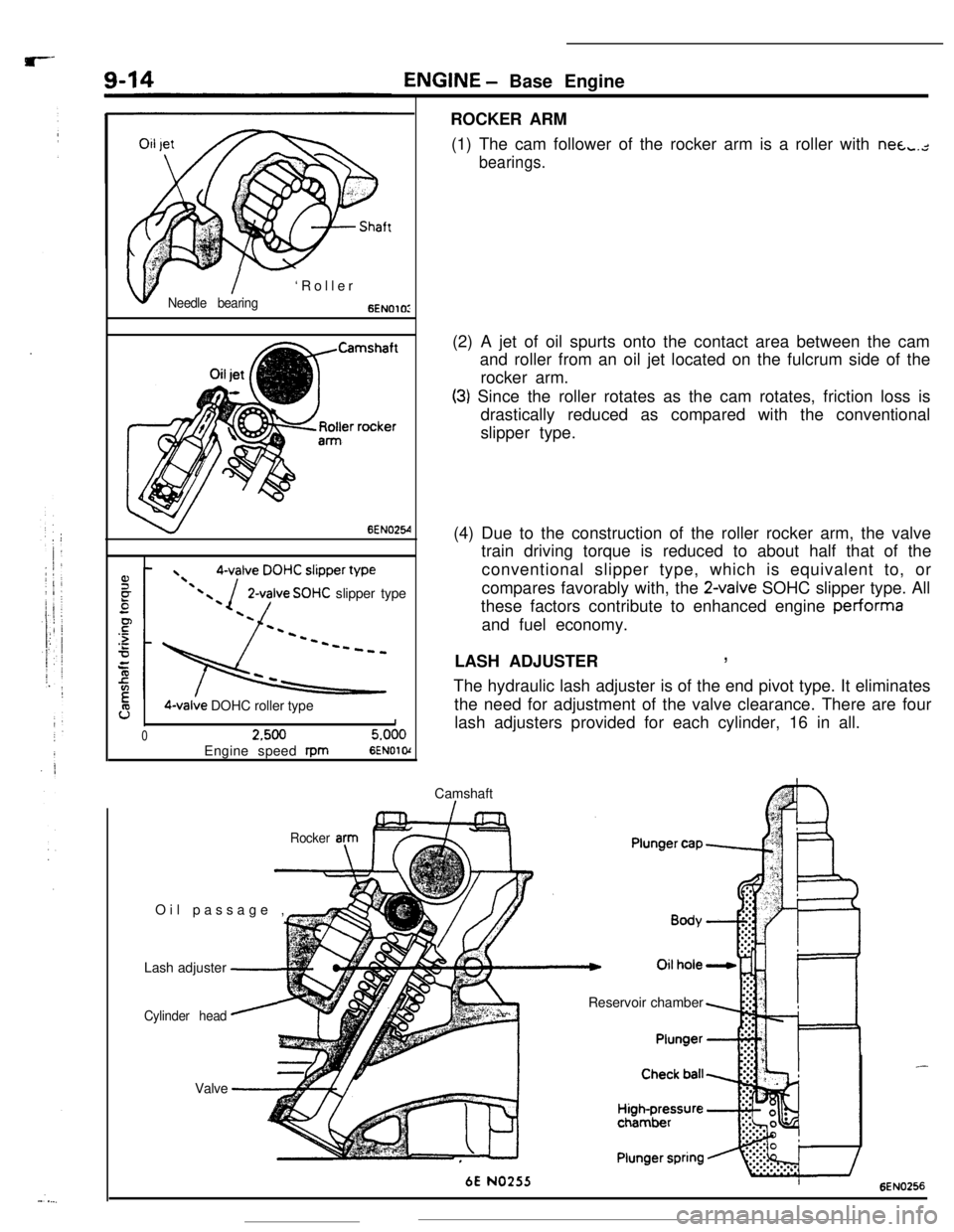
ENGINE - Base Engine
ROCKER ARM
(1) The cam follower of the rocker arm is a roller with nea,.,-
bearings.
v
,I$- I- ‘Roller
Needle bearing6ENOlOI
6EN025-4
2-valve SOHC slipper type
9O-valve DOHC roller type1
02.5005.000Engine speed
rpm6ENOl o(Camshaft
I-Oil passage ,
EIr(2) A jet of oil spurts onto the contact area between the cam
and roller from an oil jet located on the fulcrum side of the
rocker arm.
(3) Since the roller rotates as the cam rotates, friction loss is
drastically reduced as compared with the conventional
slipper type.
(4) Due to the construction of the roller rocker arm, the valve
train driving torque is reduced to about half that of the
conventional slipper type, which is equivalent to, or
compares favorably with, the
2-valve SOHC slipper type. All
these factors contribute to enhanced engine performa
and fuel economy.
LASH ADJUSTER
,The hydraulic lash adjuster is of the end pivot type. It eliminates
the need for adjustment of the valve clearance. There are four
lash adjusters provided for each cylinder, 16 in all.
Rocker anIF=Lash adjuster
-
Cylinder head
--Valve
‘-Reservoir chamber
6E NO255
-6EN0256
Page 114 of 391

sors and the engine control unit, tooether with
actuators and
related components, and k controlled
according to nine control functions as shown below.
Of these nine, No.
1 and, Nos. 3 to 9 are supplied by
II
EngineSensors - control -unit
r--------‘-1
l--cIFuel-pressureIcontrol valveII
‘4 Fuel DumoI13 I I or-’I
,--c 1. ;;EILT!I;ELSSURE1J
Fuel presJ1regulatorI
- Throttle valve
i
7
_c Speed adjusting
screw
14-2
“GENERALFUEL SYSTEM
- GeneralRl484AB
The fuel system is of the Electronic Control
Multi-point Fuel Injection type, which has an injector forthe engine control unit.
each cylinder. The system comprises various sen-Refer to Group 8 ELECTRICAL for No. 6 IGNITION
TIMING CONTROL.
-Fast idle air valve
- idle speed
control servo-
IrI
- Injectors
- 4. IOLESPEEO
CONTROL
-I5. POWER SUPPLYCONTROLControl relay
-) 6. V$&iRq3NLTIMING- Power transistor
b
-c 7. AIR CONDITIONERRELAY CONTROL- Air conditioner
relay
c-------------Tp----------1
NOTEI
The [‘-,l> is applicable to theI
.-( 8. ZJJ\~RR~LARGING k-- -4 Wastepate
Liturbo only.-----w--------IL solenoid valve--B--------d
Ir-‘---‘---“‘-7c------v--w-1
L’ 9.
-I
‘C;RB;zLETER--A Turbo meterI--------c----J+ L----------a
k’6FU1145
Page 115 of 391
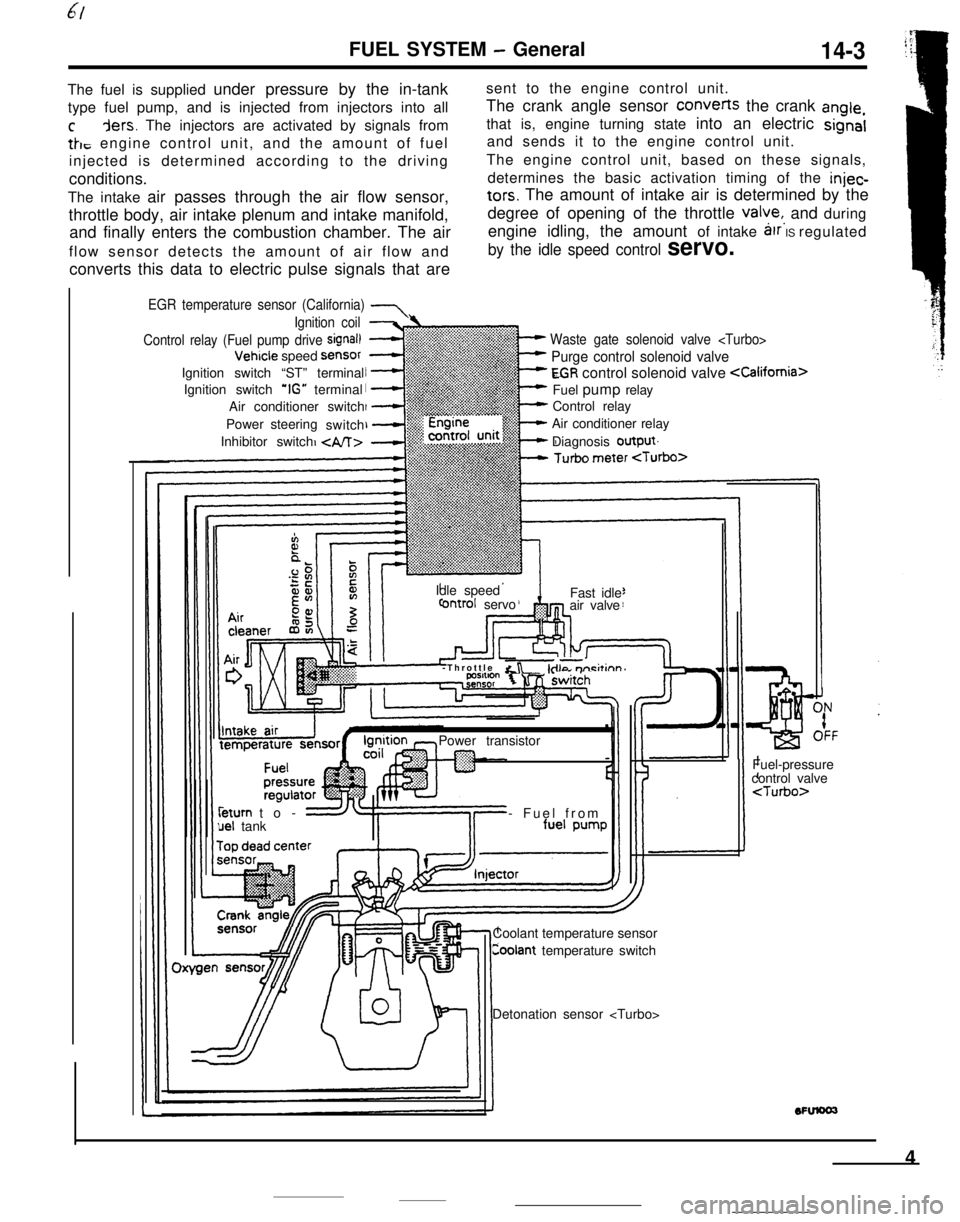
FUEL SYSTEM - General14-3The fuel is supplied under pressure by the in-tanksent to the engine control unit.
type fuel pump, and is injected from injectors into allThe crank angle sensor converts the crank
angle,
cders. The injectors are activated by signals fromthat is, engine turning state into an electric signal
tk, engine control unit, and the amount of fueland sends it to the engine control unit.
injected is determined according to the drivingThe engine control unit, based on these signals,
conditions.determines the basic activation timing of the
injec-The intake air passes through the air flow sensor,
tars. The amount of intake air is determined by the
throttle body, air intake plenum and intake manifold,degree of opening of the throttle
valye,, and during
and finally enters the combustion chamber. The airengine idling, the amount of intake
arr IS regulated
flow sensor detects the amount of air flow and
by the idle speed control servo.converts this data to electric pulse signals that are
EGR temperature sensor (California) 7
Waste gate solenoid valve
Purge control solenoid valve
EGR control solenoid valve
Control relay
Air conditioner relay
Diagnosis output
Ignition coil
Control relay (Fuel pump drive
signal)Vehicle speed
SensorIgnition switch “ST” terminal
Ignition switch
‘IG” terminal
Air conditioner switch
Power steering
switch
Inhibitor switch
Idle speed
ontrol servoFast idle
air valve
-Throttle
&r -kilo m-i&inn’Power transistorleturn to-
uel tank- Fuel from
Coolant temperature sensor
Coolant temperature switchFuel-pressure
control valve
4
Page 118 of 391
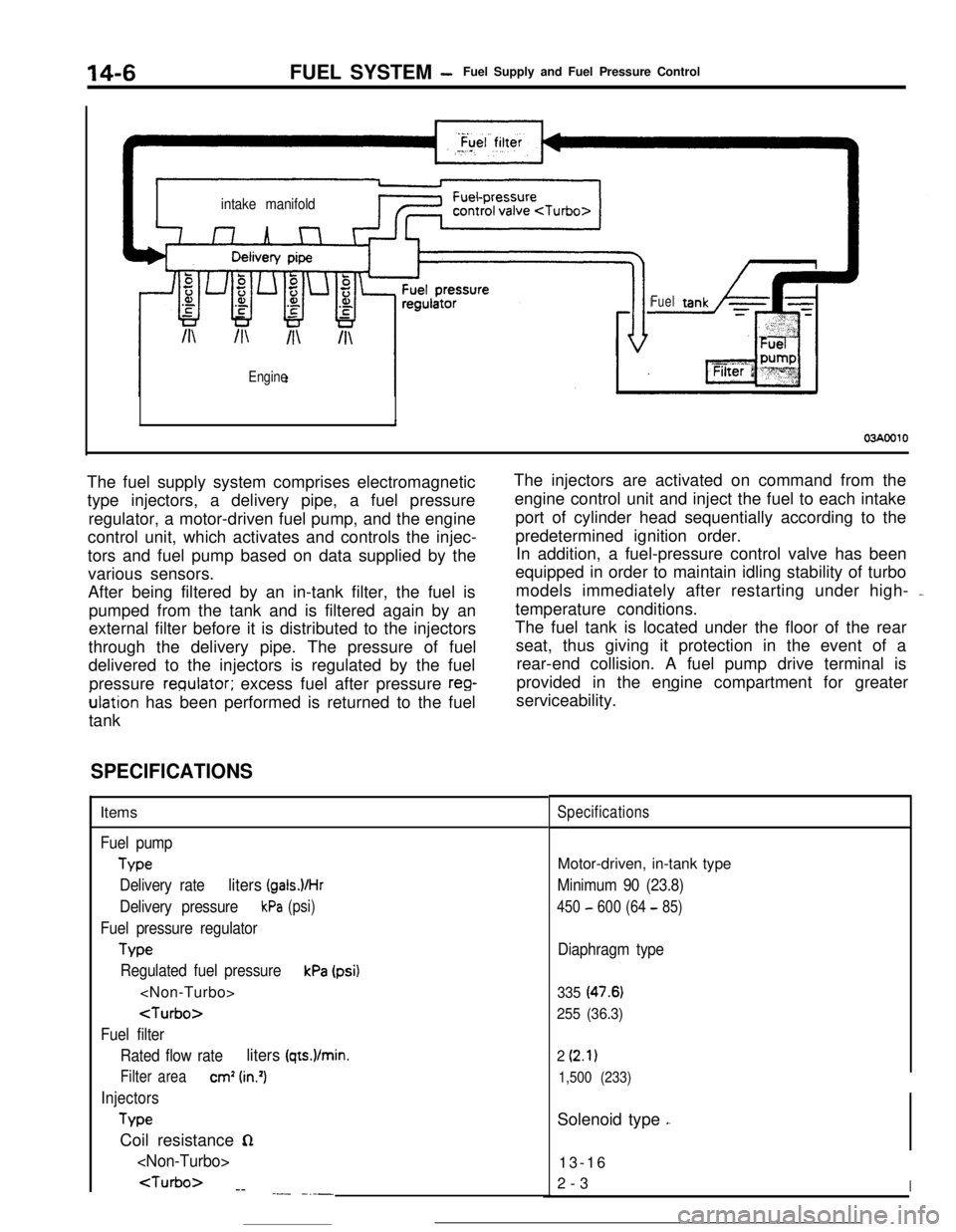
14-6FUEL SYSTEM -Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control
intake manifold/I\
Engine
Fuel
03AOOlOThe fuel supply system comprises electromagnetic
type injectors, a delivery pipe, a fuel pressure
regulator, a motor-driven fuel pump, and the engine
control unit, which activates and controls the injec-
tors and fuel pump based on data supplied by the
various sensors.
After being filtered by an in-tank filter, the fuel is
pumped from the tank and is filtered again by an
external filter before it is distributed to the injectors
through the delivery pipe. The pressure of fuel
delivered to the injectors is regulated by the fuel
pressure
reoulator; excess fuel after pressure reg-ulation has been performed is returned to the fuel
tankThe injectors are activated on command from the
engine control unit and inject the fuel to each intake
port of cylinder head sequentially according to the
predetermined ignition order.
In addition, a fuel-pressure control valve has been
equipped in order to maintain idling stability of turbo
models immediately after restarting under high- -
temperature conditions.
The fuel tank is located under the floor of the rear
seat, thus giving it protection in the event of a
rear-end collision. A fuel pump drive terminal is
provided in the engine compartment for greater
serviceability.
-
SPECIFICATIONSItems
Fuel pump
Type
Delivery rate
liters (gals.VHr
Delivery pressurekPa (psi)
Fuel pressure regulator
Tvw
Regulated fuel pressurekPa (psi)
Fuel filter
Rated flow rate
liters (qts.)/min.
Filter areacm’ (in.‘)
Injectors
TypeCoil resistance
n
--
.- -_-_
SpecificationsMotor-driven, in-tank type
Minimum 90 (23.8)
450 - 600 (64 - 85)
Diaphragm type
335 (47.6)
255 (36.3)
2
(2.1)
1,500 (233)Solenoid type
,.13-16
2-3
I