Brake hose MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: ECLIPSE, Model: MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991Pages: 1216, PDF Size: 67.42 MB
Page 35 of 1216
LUBRICATION AND’ I
MAINTENANCE
CONTENTSGENERAL INFORMATION
..............................2MAINTENANCE SERVICE
...............................7Air
CleanerElement.....................................7Automatic Transaxle....................................
11Ball Joint and Steering Linkage Seals
........13Brake Hoses
.................................................12
DiscBrakePads...........................................12-lbDrive Belt (For Water Pump and
Alternator).....................................................8
DriveShaftBoots.........................................13
EngineCoolant.............................................12
EngineOil.....................................................9
EngineOilFilter...........................................9Exhaust System
............................................13
FuelHose.....................................................7
FuelSystem.................................................7
ManualTransaxle..........................................10
RearAxle......................................................13
SparkPlugs...................................................8
TimingBelt......................................................8RECOMMENDED LUBRICANTS AND
LUBRICANT CAPACITIES TABLE
..................4SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE
............3
Page 37 of 1216

LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE - Scheduled MaintenanCe Table. &3
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE1
- SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE SERVICES FOR EMISSION CONTROL AND PRO;;
VEHICLE PERFORMANCEInspection and Services should be performed any time a malfunction is observed or suspected. Retain
receipts for all vehicle emission services to protect your emission warranty.
Kilometers in Thousands 24 48 72 80 96
No.Emission Control System Maintenance
Service IntervalsMileage in Thousands 15 30 45 50 60
1Check Fuel System (Tank, Line and Connections and Fuel Filler Cap) for Leaks
Every 5 YearsorX
2Check Fuel Every 2 Years for Leaks or DamageorXX
3Replace Air Cleaner Element
atXX
4Replace Spark Plugs
atXXGENERAL MAINTENANCE SERVICE FOR PROPER VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
Yo. General Maintenance
Service IntervalsKilometers in Thousands 24 48 72 80 9cMileage in Thousands 15 30 45 50
6C
5Timing Belt (Including theBalancer Belt)ReplaceatX
6Drive Belt (for Water Pump
and Alternator)Inspect for tensionatXX.’
Non-TurboChange Every YearEvery 12 000 kmOr (7,500 miles).
7Engine Oil
TurboChange Every 6 MonthsEvery 8,000 km
(5,000 miles)
Non-TurboChange Every Yearor X X XX
8Engine Oil
Filter
TurboChange Every YearEvery 16,000 km
(10,000 miles)
9Manual Transaxle OilInspect Oil LevelatX.X
Inspect Fluid Level Every Yearor X X XX
10Automatic Transaxle Fluid
Change FluidatXX11 Engine Coolant
Replace Every 2 YearsorXX
12Disc Brake PadsInspect for Wear Every Yearor X X XX13 Brake Hoses
Check for Deterioration or Leaks Every YearX X XX
l 4Beiloint and Steering Linkageinspect for Grease Leaks and Damage Every
2 YearsorXX
15Drive Shaft BootsInspect for Grease Leaks and Damage Every Yearor XXXX
Rear Axle
With LSDChange OilXX1 6
Exhaust System (Connection17Portion of Muffler, Pipings andCheck and Service as Required Every 2 Yearsorx -xConverter Heat Shields)
NOTELSD: Limited-slip differential
Page 46 of 1216
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE - Maintenance Service
L-4GoodOOA0051C9FW1014K512(9) Supply 4 liters (8.5 pints) of specified ATF into case
through dipstick hole. [Total quantity of ATF required is
6.1 liters (12.9 pints).
Actually however, approx. 4.5 liters (9.5 pints) of fluid
can be replaced because rest of fluid remains in torque
converter.]Specified fluid: MOPAR ATF PLUS (Automatic
Transmission Fluid Type 7176) or
Dia ATF SP or Equivalent
(10)Start engine and allow to idle for at least two minutes.
Then, with parking brake on, move selector lever
momentarily to each position, ending in “N” Neutral
position.
(1 l)Add sufficient ATF to bring fluid level to lower mark.
Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal operating
temperature.
Fluid level should be between upper and lower marks of“HOT” range. Insert dipstick fully to prevent dirt from
entering transaxle.
11 .ENGINE COOLANT (Change)NOOSBEAcCheck the cooling system parts, such as radiator, heater,
and oil cooler hoses, thermostat and connections for
leakage and damage.
CHANGE COOLANT
1. Remove the radiator cap.
2. Loosen the drain plug to drain the coolant.
3. Drain the coolant from the reserve tank.
4. After draining the coolant, tighten the drain plug
securely.
5.Supply the coolant into the radiator until it is filled up to
its filler neck.
6. Supply the coolant into the reserve tank.
7. After warming the engine until the thermostat opens,
remove the radiator cap and check the coolant level.
8.Supply the coolant into the radiator until it is filled up to
its filler neck, and install the
.radiator, cap securely.
9.Fill the reserve tank with coolant up to the “FULL” line.12DISC BRAKE PADS (Inspect for wear)
NOOSBFA~Check for fluid contamination and wear. Replace complete
set of pads if defective.
Caution
The pads for the right and left wheels should be
replaced at the same time. Never “split” or intermix
brake pad sets.
All four pads must be replace as a complete set.
Thickness of lining (A)
Limit
:2.0 mm (.08 in.)
Page 47 of 1216
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE - Maintenance Serviceo-13
OOAOlB6
13.BRAKE HOSES (Check for deteriorati.on or
leaks)NwBBnAs
Inspection of brake hoses and tubing should be included inall brake service operations.
The hoses should be checked for:
1. Correct length, severe surface cracking, pulling, scuf-
fing or worn spots. (If the fabric casing of the hoses is
exposed by cracks of abrasion in the rubber hose cover,
the hoses should be replaced. Eventual deterioration ofhose may occur with possible bursting failure.)
2. Faulty installation, casing twisting or interference with
wheel, tire of chassis.
14.BALL JOINT AND STEERING LINKAGE SEALS
(Inspect for grease leaks and damage)
NWSBJAb1. These components, which are permanently lubricated
at the factory, do not require periodic lubrication.
Damaged seals and boots should be replaced to
prevent leakage or contamination of the grease.
2. Inspect the dust cover and boots for proper sealing,
leakage and damage. Replace them if defective.
15.DRIVE SHAFT BOOTS (Inspect for grease leaksand damage)
NWSBJAc1. These components, which are permanently lubricated
at the factory, do not require periodic lubrication.
Damaged boots should be replaced to prevent leakage
or contamination of the grease.
2. Inspect the boots for proper sealing, leakage and
damage. Replace it if defective.
16.REAR AXLE (CONVENTIONAL DIFFERENTIAL)(Inspect oil level)-AWD
NWSBFCa
Remove the filler plug and inspect the oil level at bottom offiller hole. If the oil level is slightly below the filler hole, it is
in satisfactory condition.
16.REAR AXLE (LIMITED-SLIP DIFFERENTIAL)
(Oil change)-AWD
N66SBFCcBefore changing the rear axle oil, check to make sure that
there is no oil leakage from the rear axle housing.
Remove the drain plug and drain out of the oil.
Put the oil plug back in place, and then pour new oil in
through the filler hole.
17.EXHAUST SYSTEM (CONNECTION PORTION
OF MUFFLER, PIPING AND CONVERTER HEATSHIELDS) (Check and service as
require$dBu.
1. Check for holes and gas leaks due to damage, corro-
sion, etc.
2.Check the joints and connections for looseness and gas
leaks.3. Check the hanger rubber and brackets for damage.
Page 77 of 1216
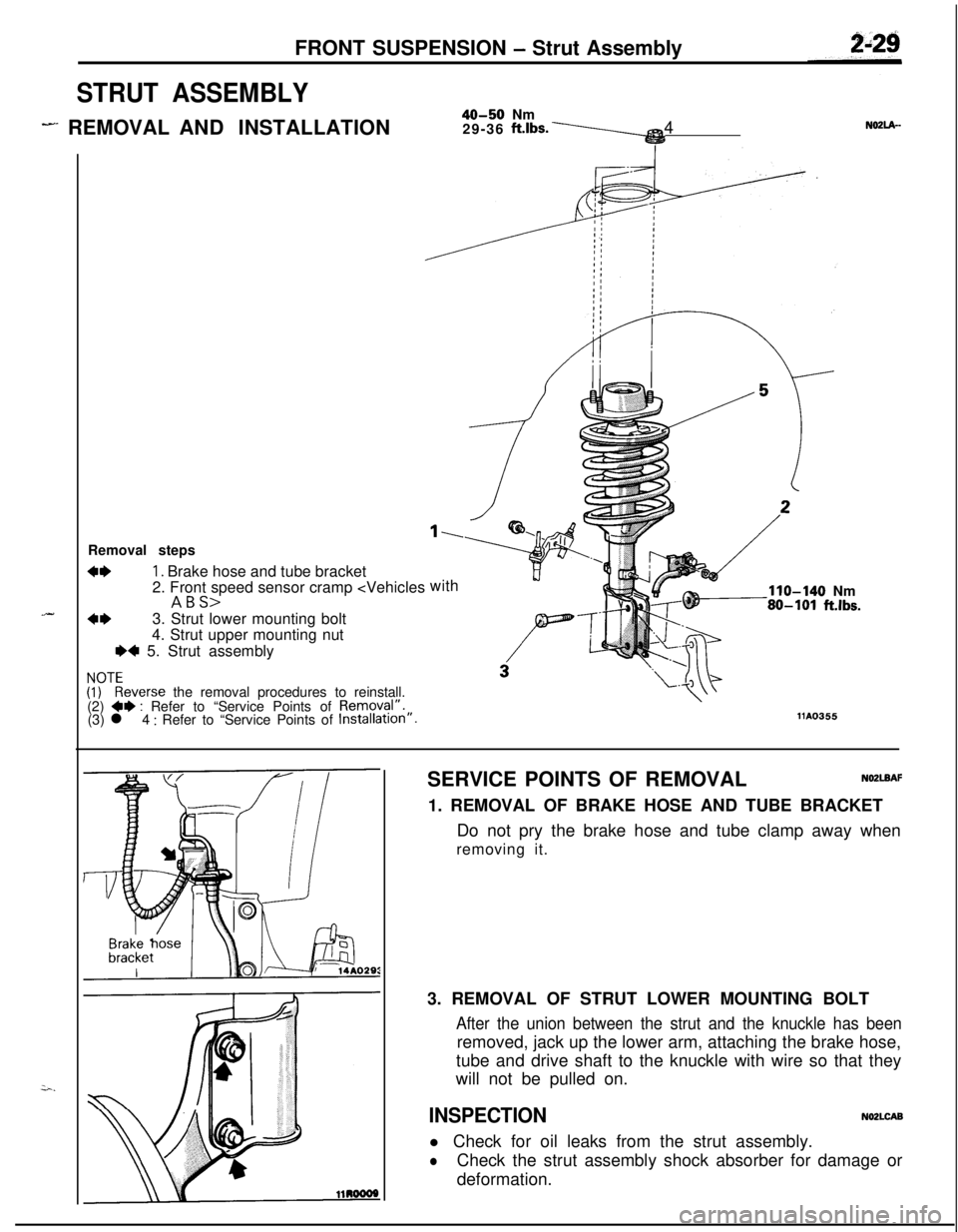
FRONT SUSPENSION - Strut Assembly
STRUT ASSEMBLY
- REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION40-50 Nm
29-36 ft.lbs.\4N02lA-
.-Removal steps
4*1. Brake hose and tube bracket
2. Front speed sensor cramp
4*3. Strut lower mounting bolt
4. Strut upper mounting nut
e+ 5. Strut assembly
!rEeverse the removal procedures to reinstall.
(2) **: Refer to “Service Points of Removal”.
(3) l 4 : Refer to “Service Points of Installation”.
1.with
110-140 Nm80-101 ft.lbs.
1110355SERVICE POINTS OF REMOVAL
NO2LBAF1. REMOVAL OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBE BRACKET
Do not pry the brake hose and tube clamp away when
removing it.
3. REMOVAL OF STRUT LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
After the union between the strut and the knuckle has beenremoved, jack up the lower arm, attaching the brake hose,
tube and drive shaft to the knuckle with wire so that they
will not be pulled on.
INSPECTIONNO2LCABl Check for oil leaks from the strut assembly.
lCheck the strut assembly shock absorber for damage or
deformation.
Page 145 of 1216

BRAKES - Specifications5-5Items
Nmftlbs.Master cylinder to brake booster
8-126-9
Piston stopper bolt
1.5-3.0l-2Nipple installation screw
1.5-3.0l-2Brake booster installation nuts
11-178-12
Fitting15-1811-13
Flared brake line nuts
13-179-12
Brake hose bracket installation bolts
17-2612-19
Front disc brake assembly installation bolts
80-10058-72
Lock pin (front)
64-8646-62
Guide pin (front)
64-8646-62
Bleeder screw
7-95-7
Wheel bearing nut
200-260144-188
Dust shield to axle beam
9-14
7-10Rear disc brake assembly installation bolts
50-6036-43
Drive shaft to companion flange
55-6539-47
companion flange to rear axle shaft160-200116-159
Brake hose to caliper body (rear)
25-35
18-25Lock
pin (rear)
22-3216-23
Guide pin (rear)
22-32
16-23Spindle lever to parking brake lever
40-5529-40
3ear speed sensor installation bolt
9-147-10Speed sensor bracket installation bolt
9-14
7-10
3otor to front hub
7-115-8
3otor to rear hub
9-147-10
LUBRICANTSNO5CP-
ItemsBrake fluidSpecified lubricant
MOPAR Brake
Fluid/Conforming to
DOT3Brake pedal bushing inner surface
Clevis pin and washer
Parking brake lever sliding parts
Bushing inner surfaceMOPAR Multi-mileage Lubricant
Part No. 2525035 or equivalent
Page 149 of 1216

BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting5-9
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM
-- TROUBLESHOOTINGNO!JEBAE
PARTICULAR CHARACTERISTICS OF
THE ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEMModels equipped with the anti-lock braking system
(A.B.S.) may exhibit one or more of the following
characteristics from time to time, but none of these
is abnormal.
(1) A pulsing feeling in the brake pedal, or vibration
of the body or the steering wheel, when the
anti-lock braking system is activated by sudden
braking or by braking on a slippery road surface.Actually, this phenomenon is an indication that
the anti-lock braking system is functioning nor-
mally.(2) When the vehicle speed reaches approximately
6 km/h (4 mph) after the engine is started and
the vehicle starts off (for the first time), a
whining motor noise may be heard from the
engine compartment if the vehicle is traveling in
a quiet place, but this noise is simply the result
of a self-check being made of the anti-lock
braking system operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING METHODSProblems related to the anti-lock braking system
(A.B.S.) can be classified into two general categor-
ies: problems in the electrical system and those in
the hydraulic system.For problems in the electrical system, the
self-diagnosis function is built into the electronic control
unit (E.C.U.) causing the A.B.S. warning light to
illuminate as a warning to the driver.
Problems in the hydraulic system (poor braking,
etc.) can be located in the same way as for ordinary
brakes. There is, however, the necessity to check todetermine whether the problem is related to ordin-
ary brake components or to the components relatedto the A.B.S.
HOW TO USE THE TROUBLESHOOTING
FLOW CHART(1) Using the flow chart, check the ABS warning
light light-up sequence and check the condition
of braking operation.
(2) Following the check chart listed in the remedy
column, perform the checks. There are [Explana-tion] and [Hint] in each check chart. Refer to
them when troubleshooting.
NOTEECU: Electronic control unit
HU: Hydraulic unit
MUT: Multi-use tester
Page 162 of 1216
![MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991 Service Manual 5-22BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
1 E-4 1 Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]
The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
drive circuit.
If no current fl MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991 Service Manual 5-22BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
1 E-4 1 Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]
The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
drive circuit.
If no current fl](/img/19/57104/w960_57104-161.png)
5-22BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
1 E-4 1 Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]
The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
drive circuit.
If no current flows in the solenoid even if the ECU
when turned OFF, the ECU determines the solenoidcoil wire is broken/short circuited or the harness
isbroken short circuited and then warning light lights
turns the solenoid ON or if it continues to flow even
up.
J/B
HU
(
x:OMBINATION ME
:TER
MA0603
Is the resistance value for
the solenoid valve, that the
displayed trouble code indi-cates, within the range of
the standard values?
Standard value: 3.0-3.2 Q
Is the solenoid valve resist-
ance value, that the output
trouble code displays, withinthe range of the standard
values when measured at
the ECU connector?
Standard value: 3.0-3.2 B
nOrmll/
Solenoid valve drive circuit is
NoReplace HU.I
NoThe harness wire for thesolenoid valvecircuit
whose resistance value is
outside the range of the
standard value is broken
or short circuited.
I
1 Repair ABS harness.
Page 178 of 1216
![MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991 Service Manual 5-38BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
E-5Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]*>The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
when turned OFF, the ECU determines MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1991 Service Manual 5-38BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
E-5Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]*>The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
when turned OFF, the ECU determines](/img/19/57104/w960_57104-177.png)
5-38BRAKES - Anti-lock Braking System Troubleshooting
E-5Abnormality of solenoid valve drive circuit
[Explanation]*>The ABS ECU normally monitors the solenoid valve
when turned OFF, the ECU determines the solenoid%’ -’drive circuit.coil wire is broken/short circuited or the harness is
If no current flows in the solenoid even if the ECUbroken/short circuited and then the warning light
turns the solenoid ON or if it continues to flow evenlights up.
IGNITIONSWITCH(IGI)
7JIB------_-_tor and check with the
side connector.
Connect HU
1OP connec-
disconnect ECU con-
>Is the solenoid valve resis-
tance value within the range
of the standard values when
measured at the ECU con-
nector?Standard value:
3.0-3.2 Q
Yes1
II
I
Solenoid valve drive circuit isnormal.I
NoReplace HU.I
NoIs the resistance value for
the solenoid valve within the
range ofthe standard
values?Standard value:
3.0-3.2 Q, IYes ,
1
JThe harness wire for the
solenoidvalvecircuit
whose resistance value is
outside the range of the
standard value is broken
or short circuited.,-‘he-
-Repair
Page 183 of 1216
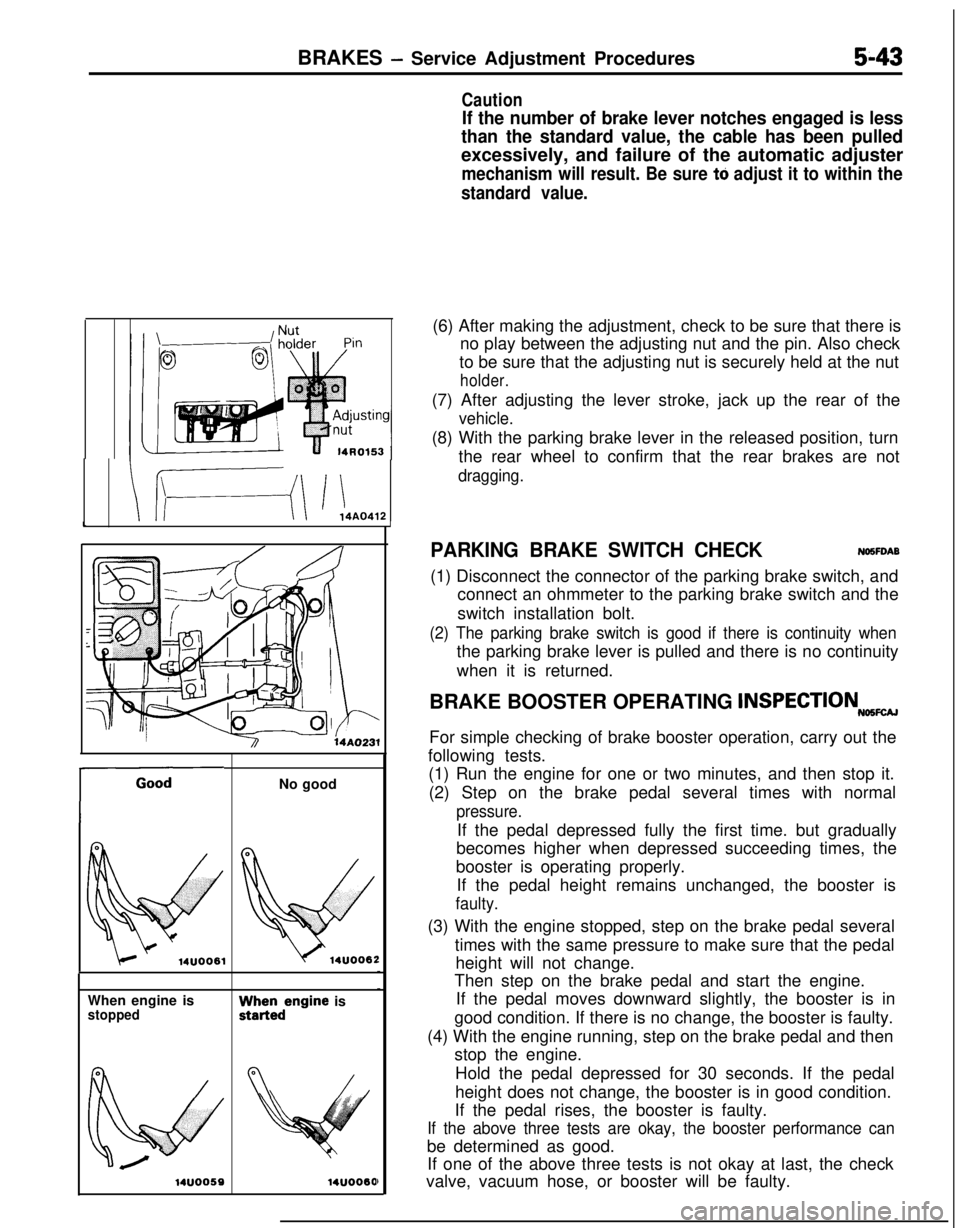
BRAKES - Service Adjustment Procedures5-43When engine is
stoppedNo good
0
wtwo061
VV;Videngine is
t4uoo60
Caution
If the number of brake lever notches engaged is less
than the standard value, the cable has been pulledexcessively, and failure of the automatic adjuster
mechanism will result. Be sure tti adjust it to within the
standard value.(6) After making the adjustment, check to be sure that there is
no play between the adjusting nut and the pin. Also check
to be sure that the adjusting nut is securely held at the nut
holder.(7) After adjusting the lever stroke, jack up the rear of the
vehicle.(8) With the parking brake lever in the released position, turn
the rear wheel to confirm that the rear brakes are not
dragging.
PARKING BRAKE SWITCH CHECKN05FDAB
(1) Disconnect the connector of the parking brake switch, and
connect an ohmmeter to the parking brake switch and the
switch installation bolt.
(2) The parking brake switch is good if there is continuity whenthe parking brake lever is pulled and there is no continuity
when it is returned.
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING
lNSPECTIONNoSFcuFor simple checking of brake booster operation, carry out the
following tests.
(1) Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it.
(2) Step on the brake pedal several times with normal
pressure.If the pedal depressed fully the first time. but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times, the
booster is operating properly.
If the pedal height remains unchanged, the booster is
faulty.(3) With the engine stopped, step on the brake pedal several
times with the same pressure to make sure that the pedal
height will not change.
Then step on the brake pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is faulty.
(4) With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and then
stop the engine.
Hold the pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If the pedal
height does not change, the booster is in good condition.
If the pedal rises, the booster is faulty.
If the above three tests are okay, the booster performance canbe determined as good.
If one of the above three tests is not okay at last, the check
valve, vacuum hose, or booster will be faulty.