battery NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 1649 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-27
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
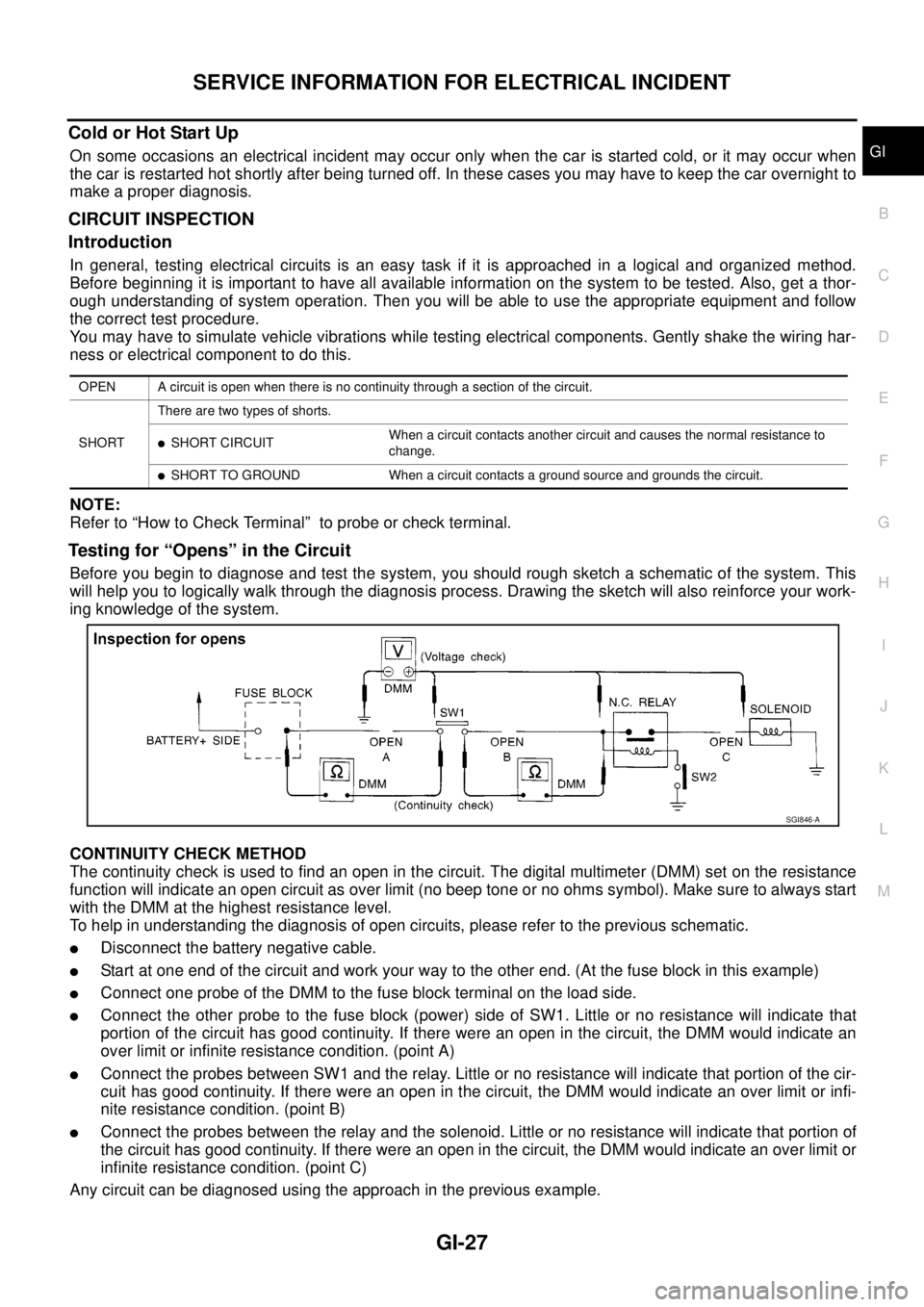
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
lDisconnect the battery negative cable.
lStart at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
lConnect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
lConnect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
lConnect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
lConnect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORTThere are two types of shorts.
lSHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
lSHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Page 1650 of 3171
GI-28
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
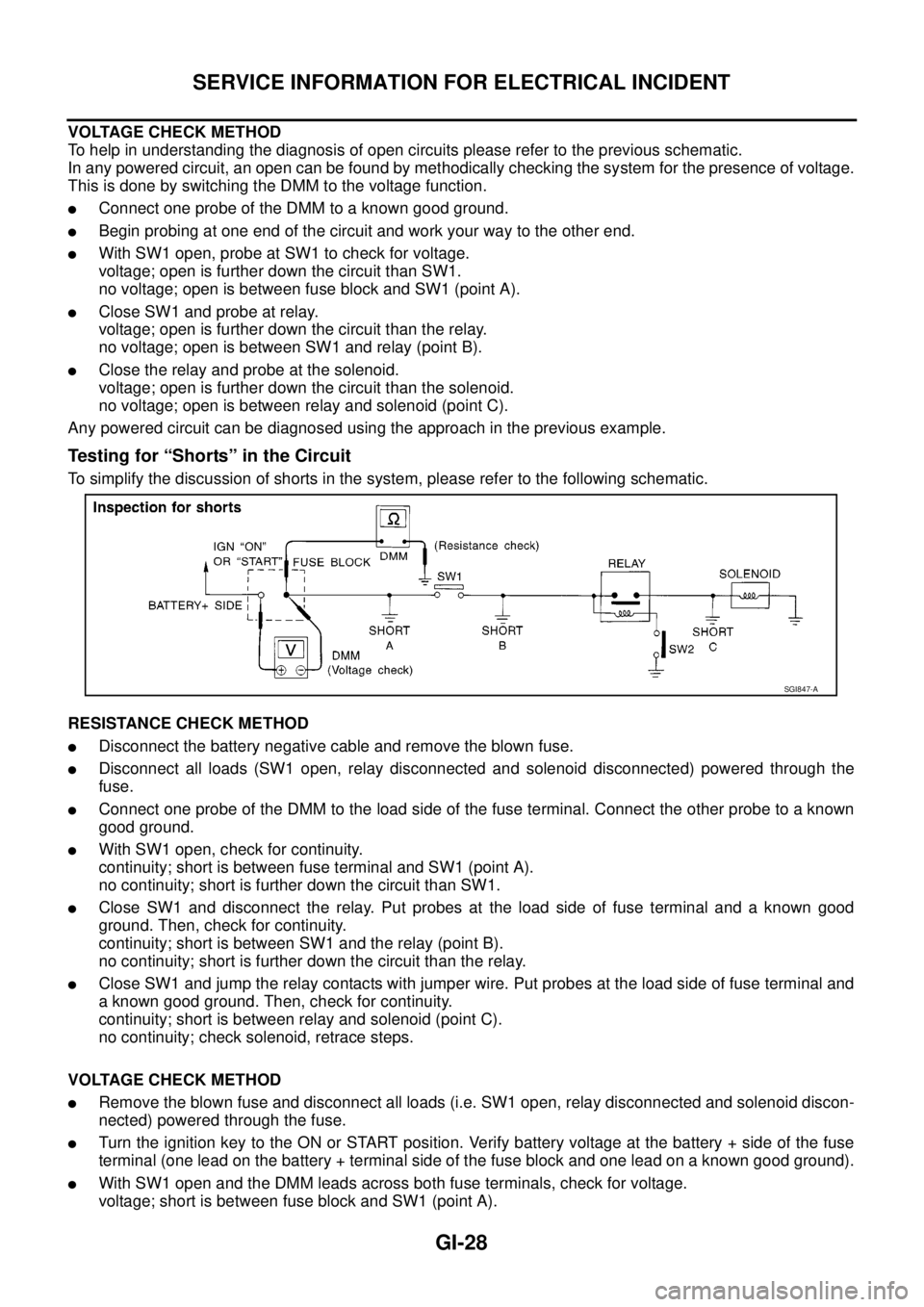
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
lBegin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
lWith SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
lClose SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
lClose the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
lDisconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
lDisconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
lWith SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
lClose SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
lClose SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
lRemove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
lTurn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse
terminal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
lWith SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
SGI847-A
Page 1652 of 3171
GI-30
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
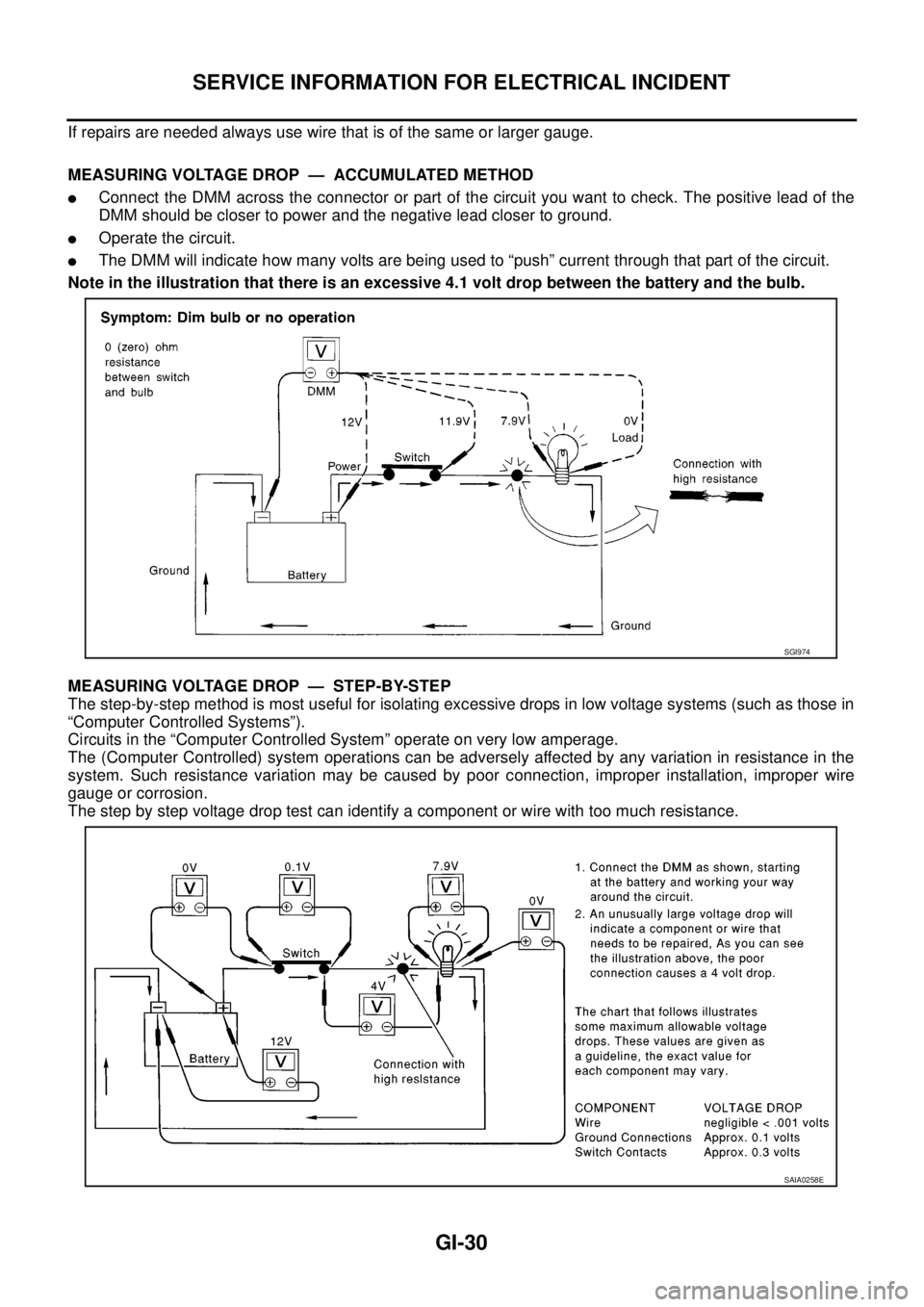
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — ACCUMULATED METHOD
lConnect the DMM across the connector or part of the circuit you want to check. The positive lead of the
DMM should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
lOperate the circuit.
lThe DMM will indicate how many volts are being used to “push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — STEP-BY-STEP
The step-by-step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those in
“Computer Controlled Systems”).
Circuits in the “Computer Controlled System” operate on very low amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in the
system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper wire
gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
SGI974
SAIA0258E
Page 1653 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-31
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Control Unit Circuit Test
System Description:When the switch is ON, the control unit lights up the lamp.
INPUT-OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHART
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
*:If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 1 does not detect battery voltage. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not supply power to light up the
lamp.
INPUT-OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHART
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
*:If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 2 does not detect approx. 0V. Control unit does
not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not control ground to light up the lamp.
MGI034A
Pin
No.Item ConditionVoltage
value [V]In case of high resistance such as single strand [V] *
1 SwitchSwitch ON Battery voltage Lower than battery voltage Approx. 8 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
2LampSwitch ON Battery voltage Approx. 0 (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
MGI035A
Pin
No.Item ConditionVoltage
value [V]In case of high resistance such as single strand [V] *
1 LampSwitch ON Approx. 0 Battery voltage (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Battery voltage Battery voltage
2SwitchSwitch ON Approx. 0 Higher than 0 Approx. 4 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 5 Approx. 5
Page 1654 of 3171
GI-32
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
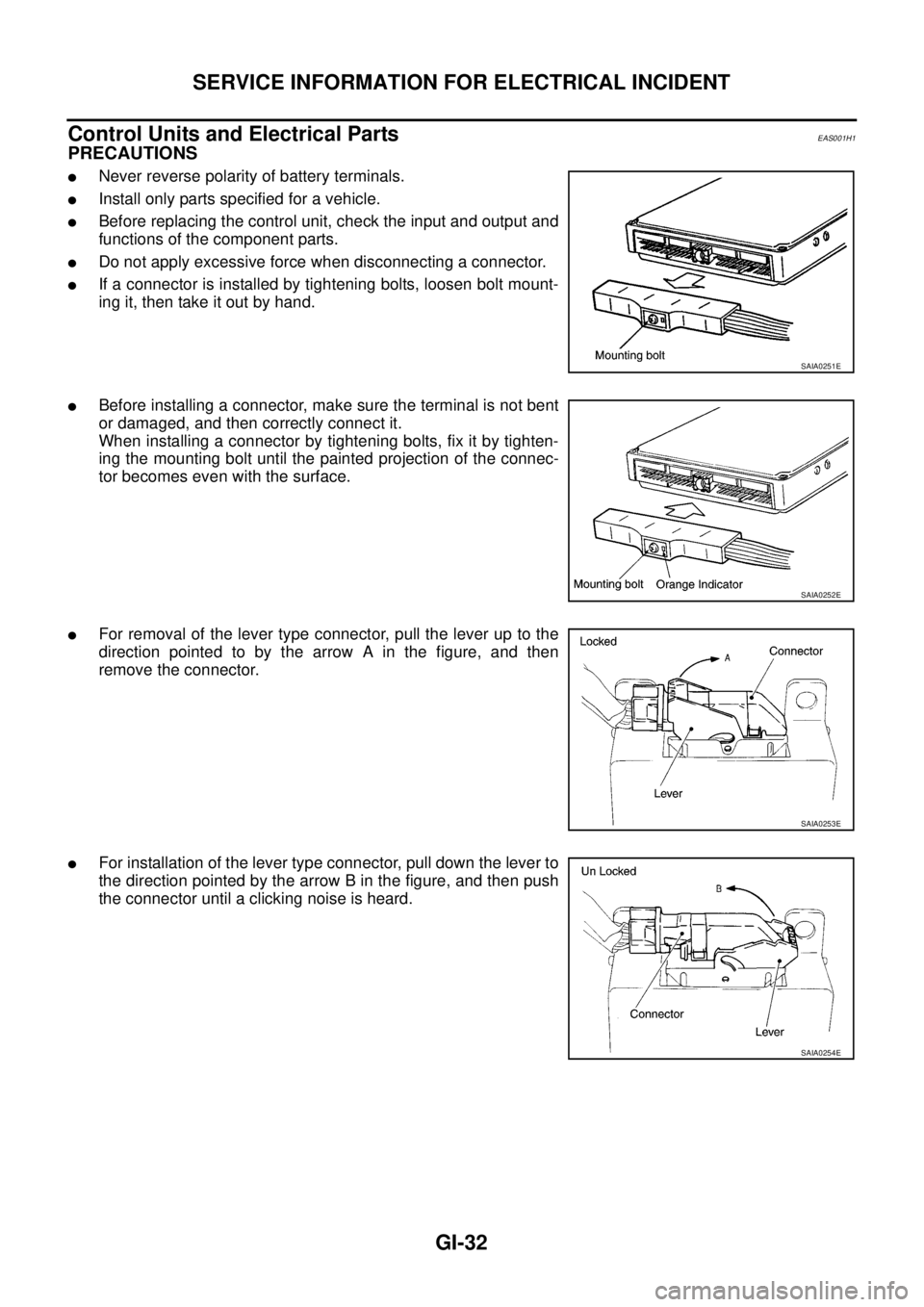
Control Units and Electrical Parts
EAS001H1
PRECAUTIONS
lNever reverse polarity of battery terminals.
lInstall only parts specified for a vehicle.
lBefore replacing the control unit, check the input and output and
functions of the component parts.
lDo not apply excessive force when disconnecting a connector.
lIf a connector is installed by tightening bolts, loosen bolt mount-
ing it, then take it out by hand.
lBefore installing a connector, make sure the terminal is not bent
or damaged, and then correctly connect it.
When installing a connector by tightening bolts, fix it by tighten-
ing the mounting bolt until the painted projection of the connec-
tor becomes even with the surface.
lFor removal of the lever type connector, pull the lever up to the
direction pointed to by the arrow A in the figure, and then
remove the connector.
lFor installation of the lever type connector, pull down the lever to
the direction pointed by the arrow B in the figure, and then push
the connector until a clicking noise is heard.
SAIA0251E
SAIA0252E
SAIA0253E
SAIA0254E
Page 1655 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-33
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
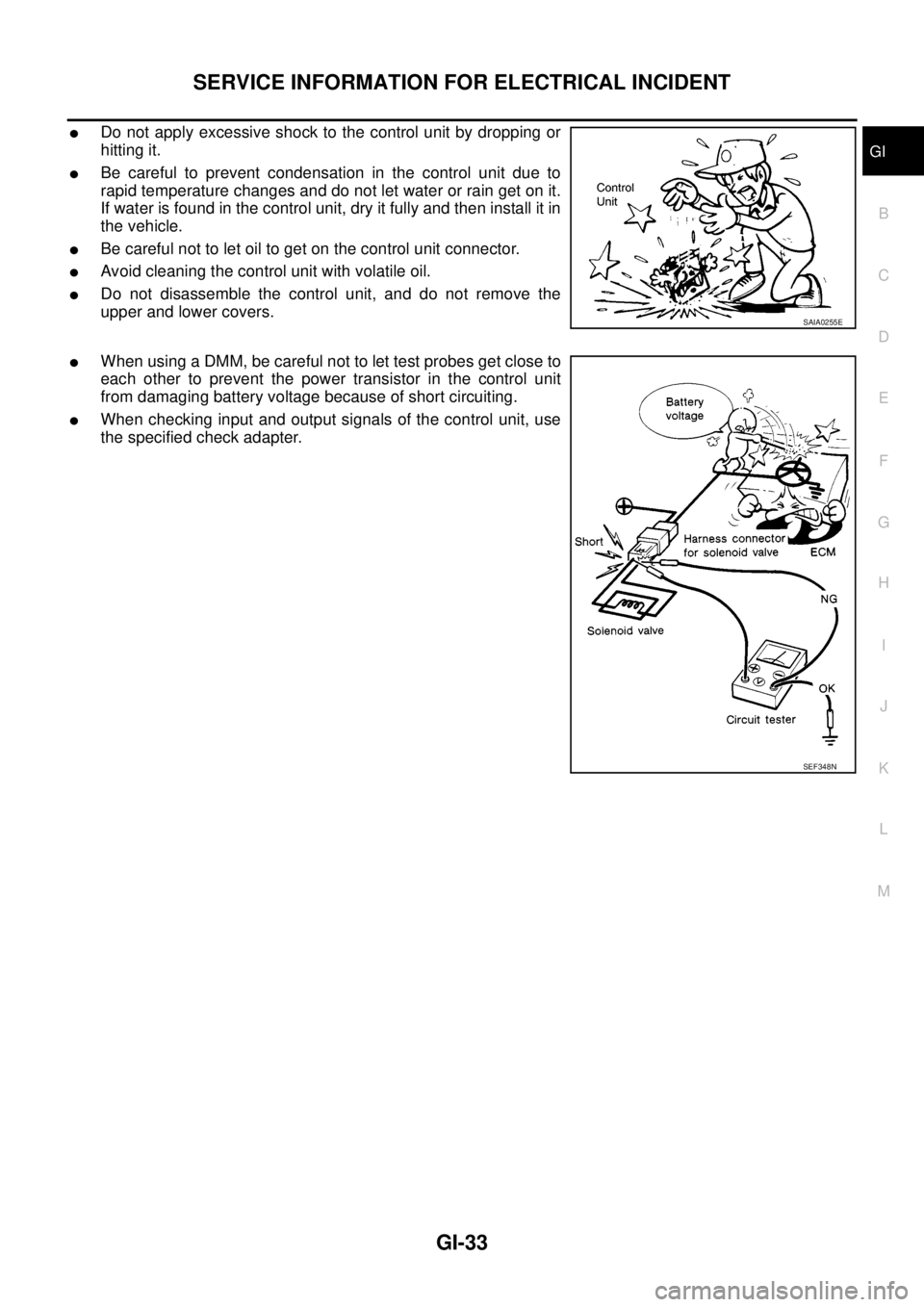
lDo not apply excessive shock to the control unit by dropping or
hitting it.
lBe careful to prevent condensation in the control unit due to
rapid temperature changes and do not let water or rain get on it.
If water is found in the control unit, dry it fully and then install it in
the vehicle.
lBe careful not to let oil to get on the control unit connector.
lAvoid cleaning the control unit with volatile oil.
lDo not disassemble the control unit, and do not remove the
upper and lower covers.
lWhen using a DMM, be careful not to let test probes get close to
each other to prevent the power transistor in the control unit
from damaging battery voltage because of short circuiting.
lWhen checking input and output signals of the control unit, use
the specified check adapter.
SAIA0255E
SEF348N
Page 1670 of 3171

GI-48
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement
EAS001H4
CONSULT-II contains a nickel metal hydride battery. When replacing the battery obey the following:
WARNING:
Replace the nickel metal hydride battery with Genuine CONSULT-II battery only. Use of another bat-
tery may present a risk of fire or explosion. The battery may present a fire or chemical burn hazard if
mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble or dispose of in fire.
Keep the battery out of reach of children and discard used battery conforming to the local regulations.
Page 1710 of 3171
GW-24
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
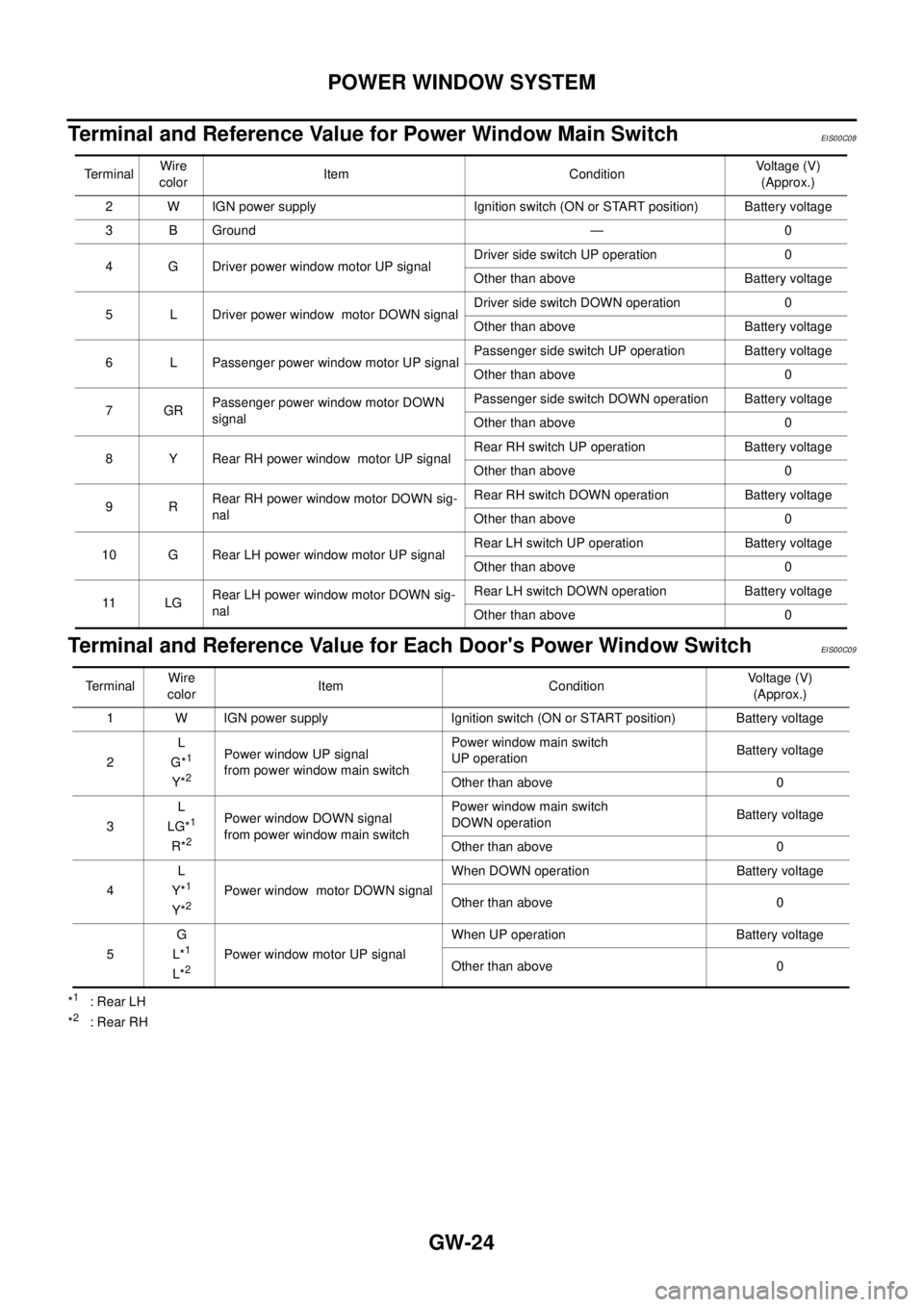
Terminal and Reference Value for Power Window Main Switch
EIS00C08
Terminal and Reference Value for Each Door's Power Window SwitchEIS00C09
*1:RearLH
*2:RearRH TerminalWire
colorItem ConditionVoltage (V)
(Approx.)
2 W IGN power supply Ignition switch (ON or START position) Battery voltage
3 B Ground — 0
4 G Driver power window motor UP signalDriver side switch UP operation 0
Other than above Battery voltage
5 L Driver power window motor DOWN signalDriver side switch DOWN operation 0
Other than above Battery voltage
6 L Passenger power window motor UP signalPassenger side switch UP operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
7GRPassenger power window motor DOWN
signalPassenger side switch DOWN operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
8 Y Rear RH power window motor UP signalRear RH switch UP operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
9RRear RH power window motor DOWN sig-
nalRear RH switch DOWN operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
10 G Rear LH power window motor UP signalRear LH switch UP operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
11 L GRear LH power window motor DOWN sig-
nalRear LH switch DOWN operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
TerminalWire
colorItem ConditionVo l ta g e (V )
(Approx.)
1 W IGN power supply Ignition switch (ON or START position) Battery voltage
2L
G*
1
Y*2
Power window UP signal
from power window main switchPower window main switch
UP operationBattery voltage
Other than above 0
3L
LG*
1
R*2
Power window DOWN signal
from power window main switchPower window main switch
DOWN operationBattery voltage
Other than above 0
4L
Y*
1
Y*2Power window motor DOWN signalWhen DOWN operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
5G
L*
1
L*2Power window motor UP signalWhen UP operation Battery voltage
Other than above 0
Page 1711 of 3171

POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
GW-25
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Terminal and Reference Value for BCMEIS00B7P
Work FlowEIS00B7Q
1. Check the symptom and customer's requests.
2. Understand the outline of system. Refer toGW-15, "
System Description".
3. According to the trouble diagnosis chart, repair or replace the cause of the malfunction.
Refer toGW-25, "
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart".
4. Does power window system operate normally? Yes, GO TO 5, If No, GO TO 3.
5. Inspection end.
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom ChartEIS00C0A
Terminal Wire color Item ConditionVoltage (V)
(Approx.)
3 Y Ignition switch (ON or START)Ignition switch
(ON or START position)Battery voltage
41 Y Battery power supply (Fuse) — Battery voltage
53 W Power window pow er supply (IGN)When ignition switch ON Battery voltage
When ignition switch OFF 0
55 B Ground — 0
57 W Battery power supply (Fusible link) — Battery voltage
58 P Power window power supply (BAT) — Battery voltage
Symptom Diagnosis / service procedure Refer to page
None of the power window can be operated using any
switch1. BCM power supply and ground circuit check.GW-26
2. Power window main switch power supply and
ground circuit check.GW-27
Driver side power window cannot be operated 1. Driver side power window motor check.GW-28
Passenger side power window cannot be operated1. Passenger side power window motor circuit checkGW-292. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. passenger side power window circuit checkGW-31
Rear LH side power window cannot be operated1. Rear LH power window motor circuit checkGW-302. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. Rear LH power window circuit checkGW-32
Rear RH side power window cannot be operated1. Rear RH power window motor circuit checkGW-312. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. Rear RH power window circuit checkGW-33
Power window does not operate using power window
switch. (Power window can be operated using power win-
dow main switch)1. Power window switch check 2GW-34
Anti-pinch system does not operate normal
Replace front power window motor and control unit
(driver side)—
Power window timer does not operated
Page 1712 of 3171
![NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block ( NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block (](/img/5/57362/w960_57362-1711.png)
GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 50A fusible link (letterGlocated in the fuse and fusible link box).
NOTE:
Refer toGW-15, "
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before installing new fuse.
2.CHECK POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector.
3. Turn ignition switch ON.
4. Check voltage between BCM connector M42, 43, 44 terminal 3,
41, 57 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.
3.CHECK GROUND CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM.
3. Check continuity between BCM connector M44 terminal 55 and
ground.
OK or NG
OK >> Power supply and ground circuit is OK.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.3 - Ground : Battery voltage
41 - Ground : Battery voltage
57 - Ground : Battery voltage
MIIB0733E
55 - Ground : Continuity should exist.
MIIB0594E