ESP NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 1222 of 3171

EC-242
DTC P1268 - P1271 FUEL INJECTOR
3.CHECK ECM OUTPUT SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR OPEN AND SHORT
1. Check harness continuity between the following terminals corresponding to the malfunctioning cylinder.
Refer to Wiring Diagram.
2. Also check harness for short to ground and short to power.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 4.
NG >> Repair open circuit or short to ground or short to power in harness or connectors.
4.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR-I
Refer toEC-243, "
Component Inspection".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 5.
NG >> Replace fuel injector.
DTCTerminal
Cylinder
ECM Fuel injector
P1268 42, 43 2 No.1
P1269 21, 22 2 No.2
P1270 23, 24 2 No.3
P1271 40, 41 2 No.4
Continuity should exist.
Page 1275 of 3171

GLOW CONTROL SYSTEM
EC-295
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
GLOW CONTROL SYSTEMPFP:25230
DescriptionEBS01KLM
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
*: The output signal is sent from the ECM through CAN communication line.
When engine coolant temperature is more than approximately 80°C(176°F), the glow relay turns off.
When engine coolant temperature is lower than approximately 80°C(176°F):
lIgnition switch ON
After ignition switch has turned to ON, the glow relay turns ON for a certain period of time in relation to
engine coolant temperature, allowing current to flow through glow plug.
lCranking
The glow relay turns ON, allowing current to flow through glow plug.
lSta rti ng
After engine has started, current continues to flow through glow plug (after-glow mode) for a certain period
in relation to engine coolant temperature.
The glow indicator lamp turns ON for a certain period of time in relation to engine coolant temperature at the
time glow relay is turned ON.
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
Glow Plug
The glow plug is provided with a ceramic heating element to obtain a
high-temperature resistance. It glows in response to a signal sent
from the ECM, allowing current to flow through the glow plug via the
glow relay.
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor Engine speed
Glow controlGlow lamp*
Glow relay
Glow plugs Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
SEF376Y
Page 1282 of 3171
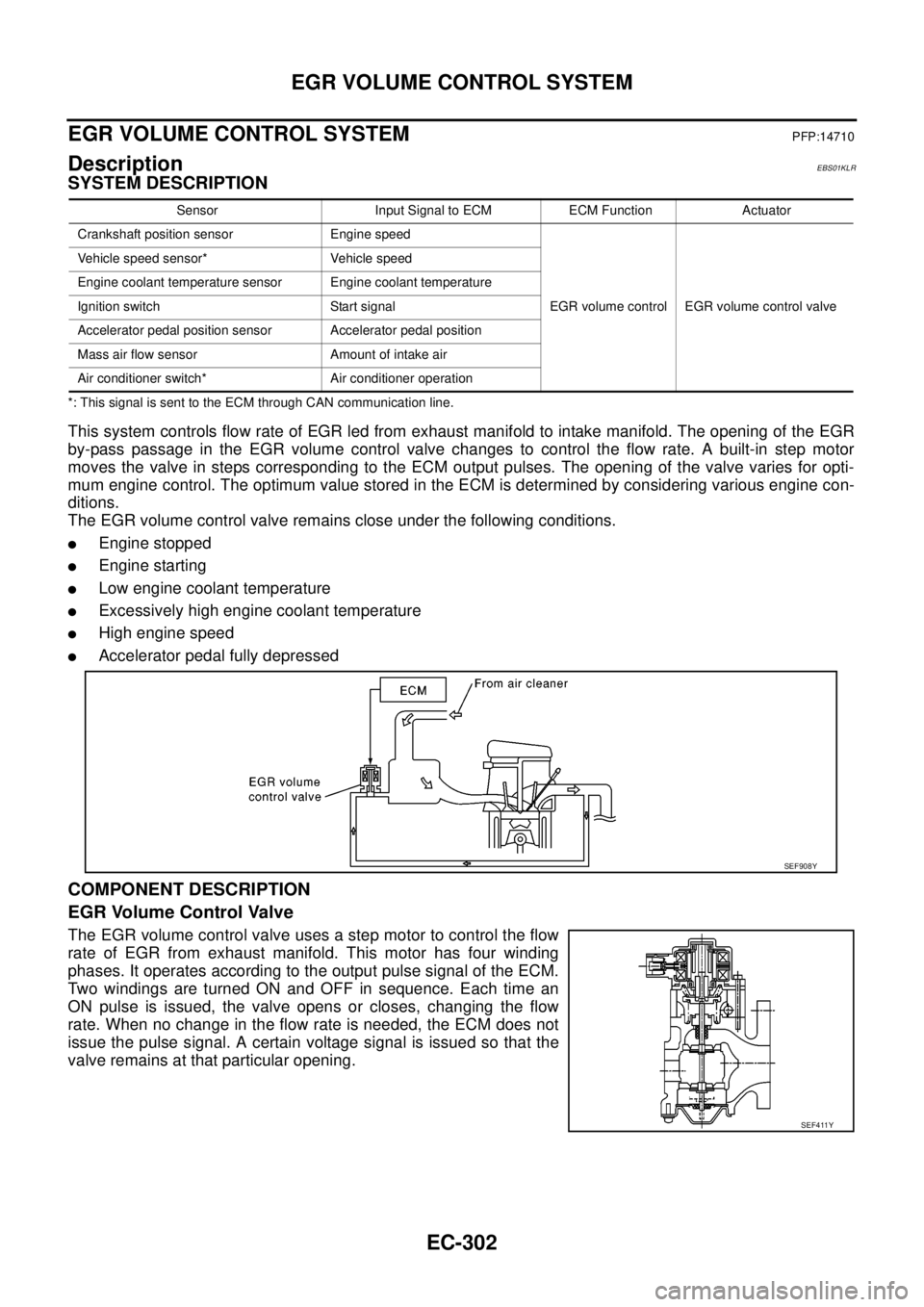
EC-302
EGR VOLUME CONTROL SYSTEM
EGR VOLUME CONTROL SYSTEM
PFP:14710
DescriptionEBS01KLR
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
*: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communication line.
This system controls flow rate of EGR led from exhaust manifold to intake manifold. The opening of the EGR
by-pass passage in the EGR volume control valve changes to control the flow rate. A built-in step motor
moves the valve in steps corresponding to the ECM output pulses. The opening of the valve varies for opti-
mum engine control. The optimum value stored in the ECM is determined by considering various engine con-
ditions.
The EGR volume control valve remains close under the following conditions.
lEngine stopped
lEngine starting
lLow engine coolant temperature
lExcessively high engine coolant temperature
lHigh engine speed
lAccelerator pedal fully depressed
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
EGR Volume Control Valve
The EGR volume control valve uses a step motor to control the flow
rate of EGR from exhaust manifold. This motor has four winding
phases. It operates according to the output pulse signal of the ECM.
Two windings are turned ON and OFF in sequence. Each time an
ON pulse is issued, the valve opens or closes, changing the flow
rate. When no change in the flow rate is needed, the ECM does not
issue the pulse signal. A certain voltage signal is issued so that the
valve remains at that particular opening.
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor Engine speed
EGR volume control EGR volume control valve Vehicle speed sensor* Vehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Accelerator pedal position sensor Accelerator pedal position
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Air conditioner switch* Air conditioner operation
SEF908Y
SEF411Y
Page 1344 of 3171
EI-6
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
PFP:00000
Work FlowEIS00DY5
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer toEI-10, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
lThe customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
lIf there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
lAfter identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
lSqueak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces = higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
lCreak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
lRattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
lKnock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
lTick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
lThump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
lBuzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
lOften the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
lWeather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 1367 of 3171

SIDE GUARD MOLDING
EI-29
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
REMOVAL
CAUTION:
Never apply tack-paper adhesive remover to body panel surface finished with lacquer-based paints.
lOriginal side guard molding is affixed to body panel with double-faced adhesive tape.
1. Heat molding to between 30°and 40°C(86°to 104°F) with a heat gun.
2. Raise end of molding and cut away tape to remove molding. Remove all traces of tape.
INSTALLATION
lOn vehicles coated with Hard Clear Coat, use double-faced 3M adhesive tape Product No. 4210 or equiv-
alent, after priming with 3M primer Product No. N200, C-100 or equivalent.
lThe repair parts are also affixed with double-faced adhesive tape.
lTo re-use existing molding, clean all traces of double sided tape from the molding and apply new double-
facedtapetothemolding.
1. Clean the panel surface with isopropyl alcohol or equivalent to degrease the surface.
2. Heat the panel and molding tape surface to 30°to 40°C(86°to 104°F).
3. Remove the backing sheet from the tape surface.
lAlign the locating pin into the hole in the outer door.
lContinue aligning the pins into their corresponding holes in the outer door during installation.
4. Press ends by hand and use a roller to apply 5 kg-f (11 lbs-f) to press molding to door surface.
lApply even pressure along molding to insure proper wet out.
CAUTION:
To secure contact, do not wash vehicle for 24 hours after installation.
Page 1426 of 3171
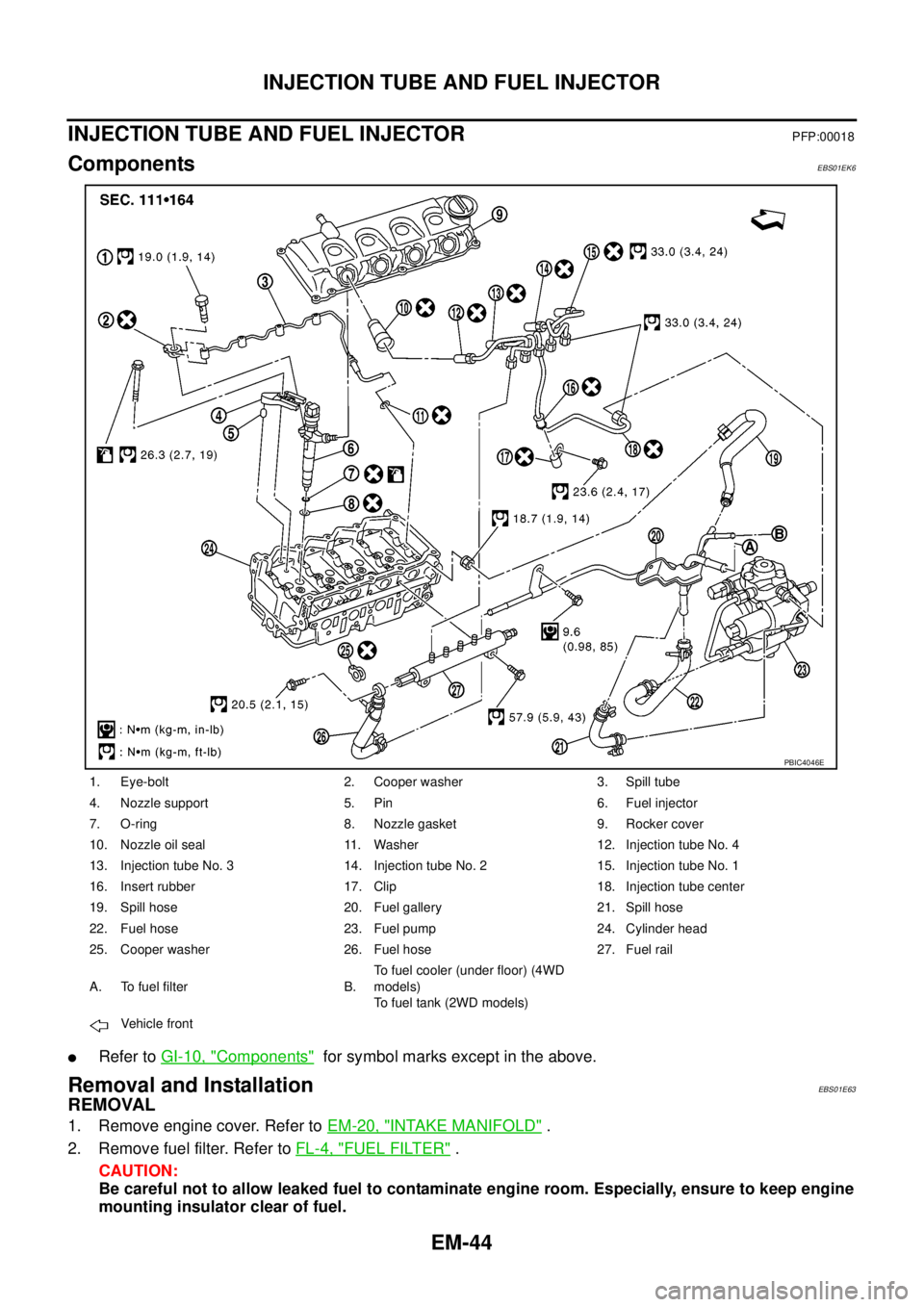
EM-44
INJECTION TUBE AND FUEL INJECTOR
INJECTION TUBE AND FUEL INJECTOR
PFP:00018
ComponentsEBS01EK6
lRefer toGI-10, "Components"for symbol marks except in the above.
Removal and InstallationEBS01E63
REMOVAL
1. Remove engine cover. Refer toEM-20, "INTAKE MANIFOLD".
2. Remove fuel filter. Refer toFL-4, "
FUEL FILTER".
CAUTION:
Be careful not to allow leaked fuel to contaminate engine room. Especially, ensure to keep engine
mounting insulator clear of fuel.
1. Eye-bolt 2. Cooper washer 3. Spill tube
4. Nozzle support 5. Pin 6. Fuel injector
7. O-ring 8. Nozzle gasket 9. Rocker cover
10. Nozzle oil seal 11. Washer 12. Injection tube No. 4
13. Injection tube No. 3 14. Injection tube No. 2 15. Injection tube No. 1
16. Insert rubber 17. Clip 18. Injection tube center
19. Spill hose 20. Fuel gallery 21. Spill hose
22. Fuel hose 23. Fuel pump 24. Cylinder head
25. Cooper washer 26. Fuel hose 27. Fuel rail
A. To fuel filter B.To fuel cooler (under floor) (4WD
models)
To fuel tank (2WD models)
Vehicle front
PBIC4046E
Page 1427 of 3171
INJECTION TUBE AND FUEL INJECTOR
EM-45
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
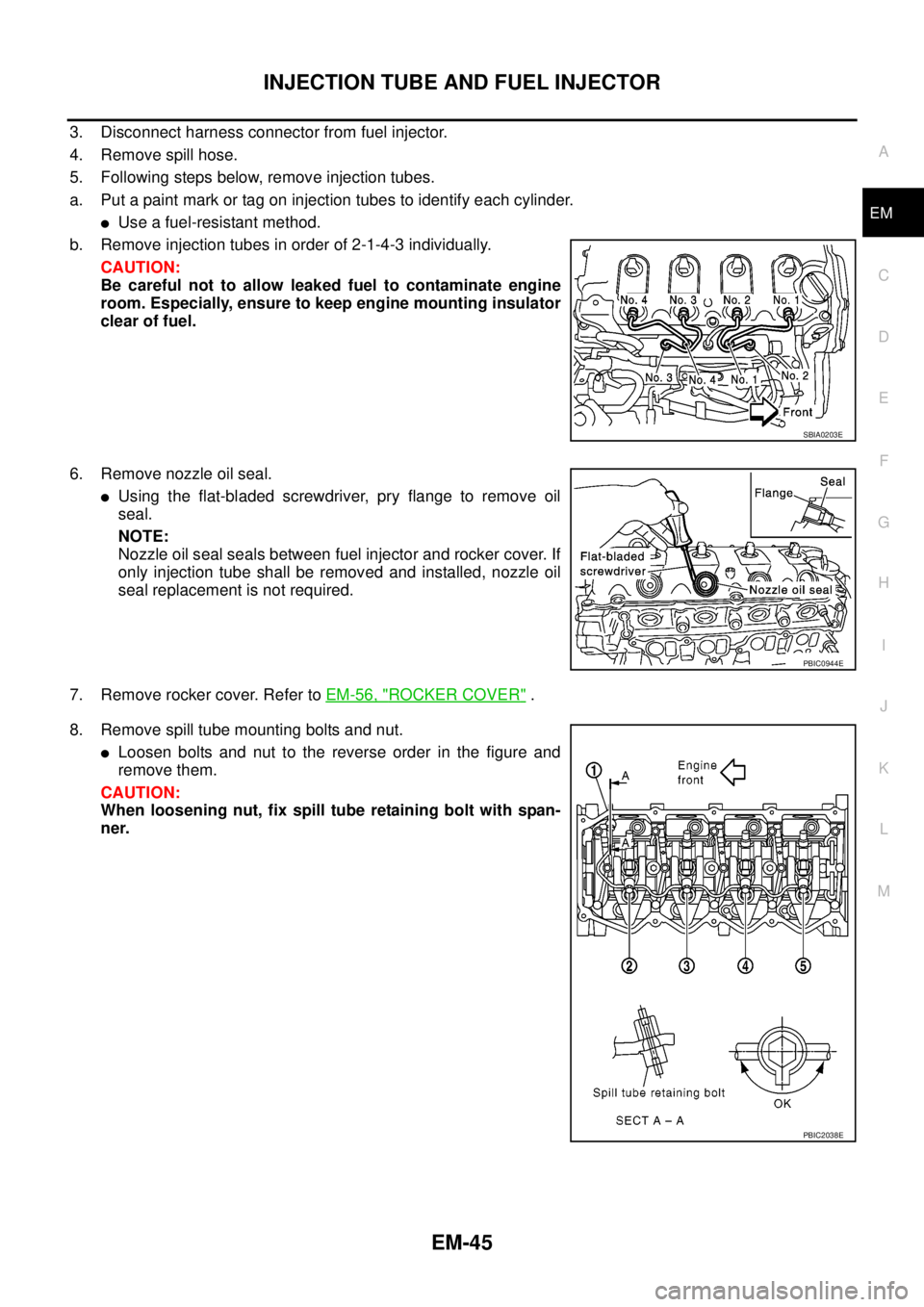
3. Disconnect harness connector from fuel injector.
4. Remove spill hose.
5. Following steps below, remove injection tubes.
a. Put a paint mark or tag on injection tubes to identify each cylinder.
lUse a fuel-resistant method.
b. Remove injection tubes in order of 2-1-4-3 individually.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to allow leaked fuel to contaminate engine
room. Especially, ensure to keep engine mounting insulator
clear of fuel.
6. Remove nozzle oil seal.
lUsing the flat-bladed screwdriver, pry flange to remove oil
seal.
NOTE:
Nozzle oil seal seals between fuel injector and rocker cover. If
only injection tube shall be removed and installed, nozzle oil
seal replacement is not required.
7. Remove rocker cover. Refer toEM-56, "
ROCKER COVER".
8. Remove spill tube mounting bolts and nut.
lLoosen bolts and nut to the reverse order in the figure and
remove them.
CAUTION:
When loosening nut, fix spill tube retaining bolt with span-
ner.
SBIA0203E
PBIC0944E
PBIC2038E
Page 1438 of 3171
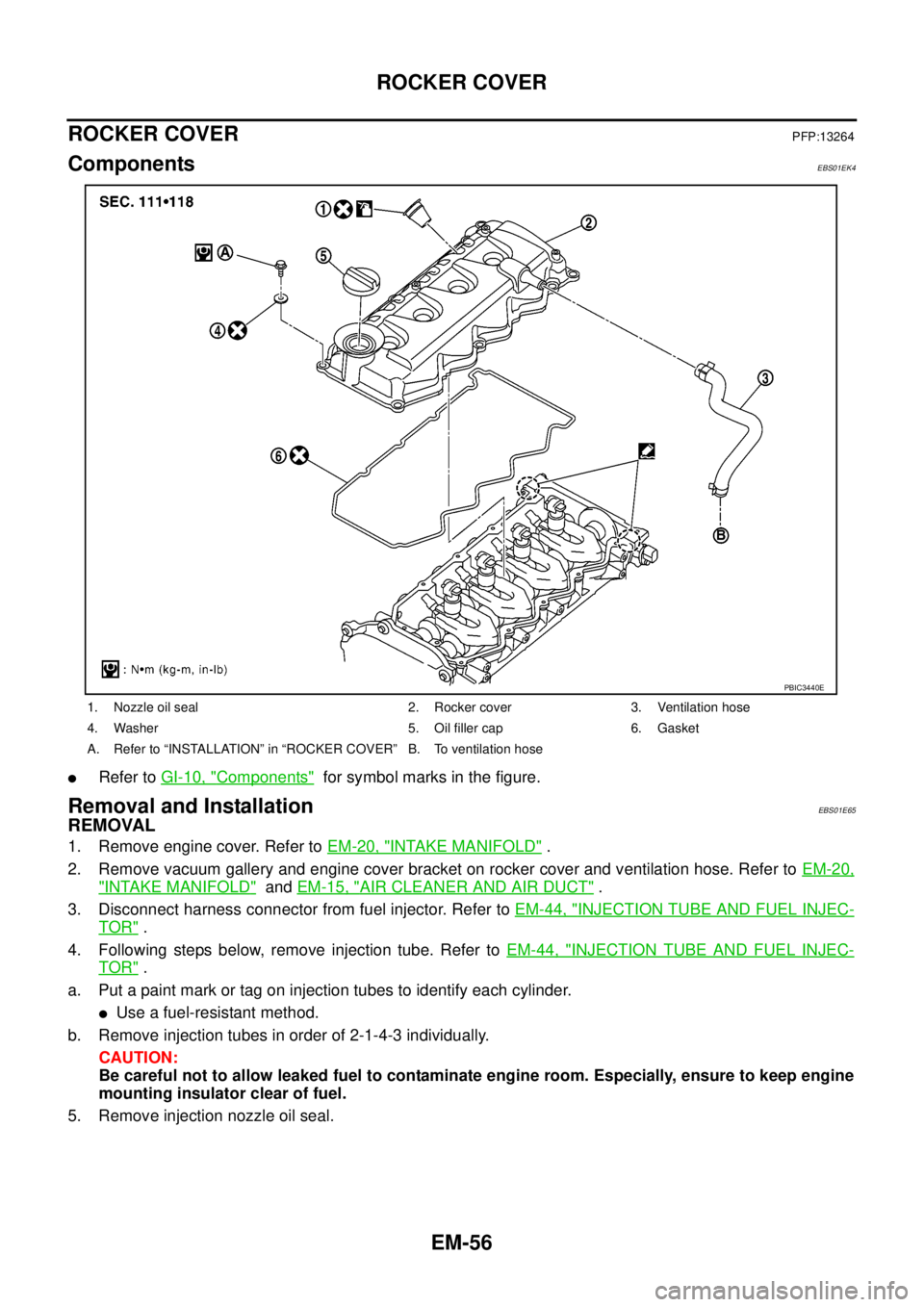
EM-56
ROCKER COVER
ROCKER COVER
PFP:13264
ComponentsEBS01EK4
lRefer toGI-10, "Components"for symbol marks in the figure.
Removal and InstallationEBS01E65
REMOVAL
1. Remove engine cover. Refer toEM-20, "INTAKE MANIFOLD".
2. Remove vacuum gallery and engine cover bracket on rocker cover and ventilation hose. Refer toEM-20,
"INTAKE MANIFOLD"andEM-15, "AIR CLEANER AND AIR DUCT".
3. Disconnect harness connector from fuel injector. Refer toEM-44, "
INJECTION TUBE AND FUEL INJEC-
TOR".
4. Following steps below, remove injection tube. Refer toEM-44, "
INJECTION TUBE AND FUEL INJEC-
TOR".
a. Put a paint mark or tag on injection tubes to identify each cylinder.
lUse a fuel-resistant method.
b. Remove injection tubes in order of 2-1-4-3 individually.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to allow leaked fuel to contaminate engine room. Especially, ensure to keep engine
mounting insulator clear of fuel.
5. Remove injection nozzle oil seal.
1. Nozzle oil seal 2. Rocker cover 3. Ventilation hose
4. Washer 5. Oil filler cap 6. Gasket
A. Refer to “INSTALLATION” in “ROCKER COVER” B. To ventilation hose
PBIC3440E
Page 1450 of 3171
![NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Repair Manual EM-68
CAMSHAFT
4. Withvalvespringinacompressedstate,removethecamshaft
pliers [SST] by securely setting the outer circumference of the
valve lifter with the end of the lifter stopper [SST].
lHold the l NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Repair Manual EM-68
CAMSHAFT
4. Withvalvespringinacompressedstate,removethecamshaft
pliers [SST] by securely setting the outer circumference of the
valve lifter with the end of the lifter stopper [SST].
lHold the l](/img/5/57362/w960_57362-1449.png)
EM-68
CAMSHAFT
4. Withvalvespringinacompressedstate,removethecamshaft
pliers [SST] by securely setting the outer circumference of the
valve lifter with the end of the lifter stopper [SST].
lHold the lifter stopper by hand until the shim is removed.
CAUTION:
Do not retrieve the camshaft pliers forcefully, as cam-
shaft will be damaged.
5. Move the round hole of adjusting shim to the front with the very
thin screwdriver or like that.
lWhen adjusting shim on valve lifter will not rotate smoothly,
restart from step 3 to release the end of the lifter stopper
[SST] from touching adjusting shim.
6. Remove adjusting shim from valve lifter by blowing air through
the round hole of the adjusting shim with the air gun.
CAUTION:
To prevent any remaining engine oil from being blown
around, thoroughly wipe the area clean and wear protective
goggles.
7. Remove adjusting shim by using the magnet hand.
8. Measure the thickness of adjusting shim using the micrometer.
lMeasure near the center of the shim (the part that touches
camshaft).
9. Select the new adjusting shim from the following methods.
PBIC2322E
PBIC2323E
PBIC2324E
FEM032
Calculation method of the adjusting shim thickness:
R = Thickness of removed shim
N = Thickness of new shim
M = Measured valve clearance
Intake
N=R+[M-0.28mm(0.0010in)]
Exhaust
N=R+[M-0.30mm(0.0118in)]
Page 1467 of 3171
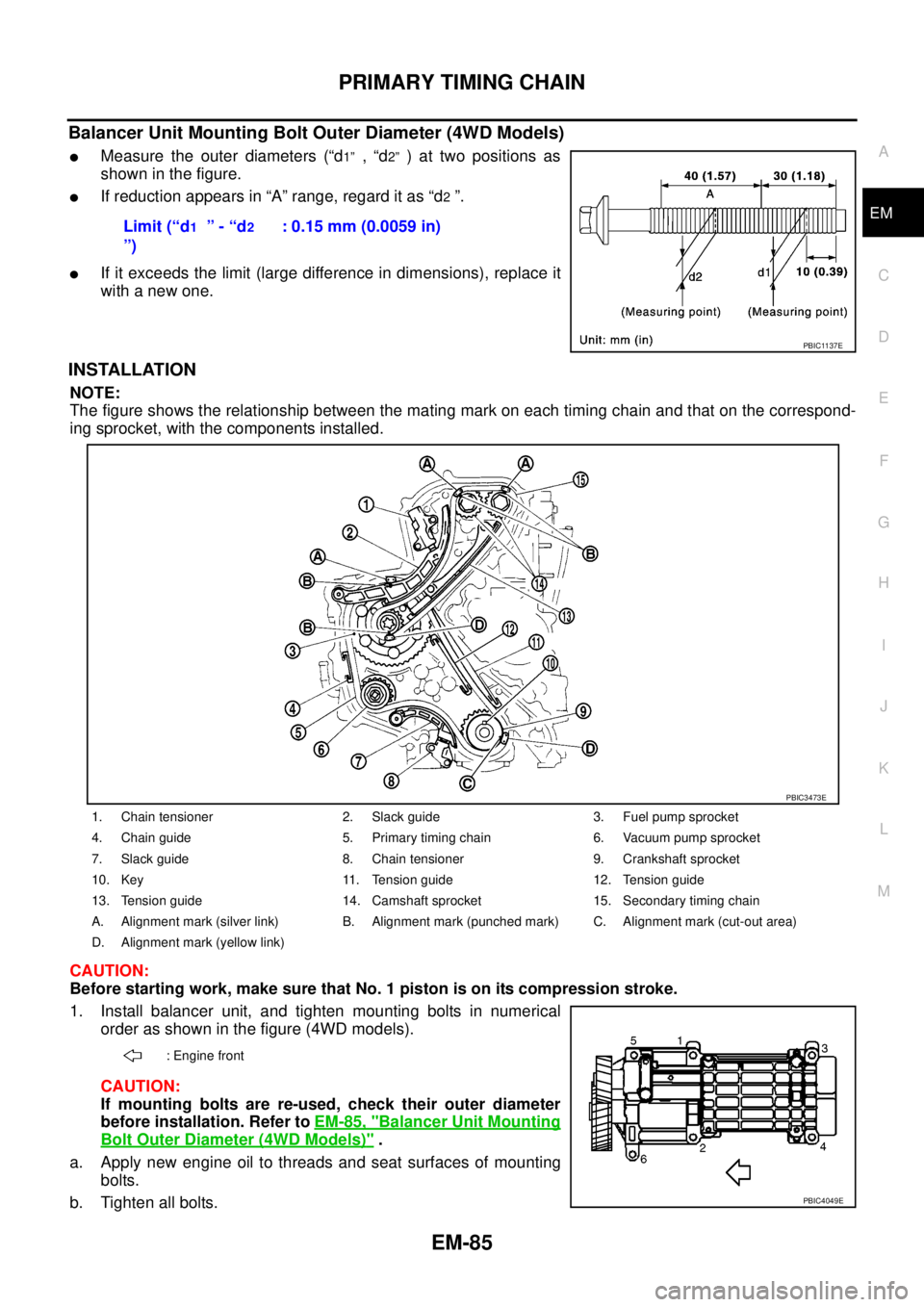
PRIMARY TIMING CHAIN
EM-85
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
Balancer Unit Mounting Bolt Outer Diameter (4WD Models)
lMeasure the outer diameters (“d1”,“d2”)attwopositionsas
showninthefigure.
lIf reduction appears in “A” range, regard it as “d2”.
lIf it exceeds the limit (large difference in dimensions), replace it
with a new one.
INSTALLATION
NOTE:
The figure shows the relationship between the mating mark on each timing chain and that on the correspond-
ing sprocket, with the components installed.
CAUTION:
Before starting work, make sure that No. 1 piston is on its compression stroke.
1. Install balancer unit, and tighten mounting bolts in numerical
order as shown in the figure (4WD models).
CAUTION:
If mounting bolts are re-used, check their outer diameter
before installation. Refer toEM-85, "
Balancer Unit Mounting
Bolt Outer Diameter (4WD Models)".
a. Apply new engine oil to threads and seat surfaces of mounting
bolts.
b. Tighten all bolts.Limit (“d
1”-“d2
”): 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
PBIC1137E
1. Chain tensioner 2. Slack guide 3. Fuel pump sprocket
4. Chain guide 5. Primary timing chain 6. Vacuum pump sprocket
7. Slack guide 8. Chain tensioner 9. Crankshaft sprocket
10. Key 11. Tension guide 12. Tension guide
13. Tension guide 14. Camshaft sprocket 15. Secondary timing chain
A. Alignment mark (silver link) B. Alignment mark (punched mark) C. Alignment mark (cut-out area)
D. Alignment mark (yellow link)
: Engine front
PBIC3473E
PBIC4049E