ESP NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 2331 of 3171
MT-14
SHIFT CONTROL
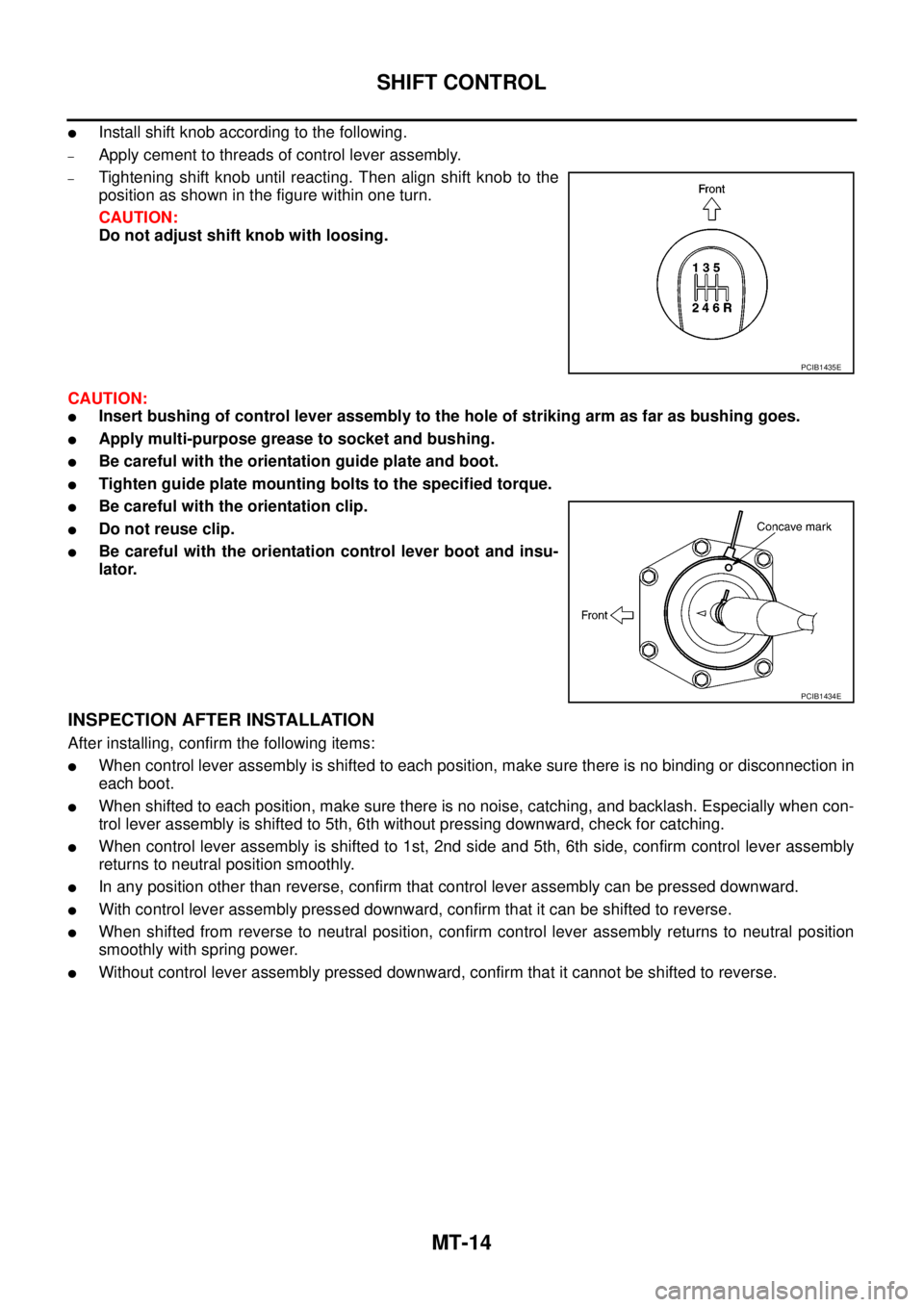
lInstall shift knob according to the following.
–Apply cement to threads of control lever assembly.
–Tightening shift knob until reacting. Then align shift knob to the
position as shown in the figure within one turn.
CAUTION:
Do not adjust shift knob with loosing.
CAUTION:
lInsert bushing of control lever assembly to the hole of striking arm as far as bushing goes.
lApply multi-purpose grease to socket and bushing.
lBe careful with the orientation guide plate and boot.
lTighten guide plate mounting bolts to the specified torque.
lBe careful with the orientation clip.
lDo not reuse clip.
lBe careful with the orientation control lever boot and insu-
lator.
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION
After installing, confirm the following items:
lWhen control lever assembly is shifted to each position, make sure there is no binding or disconnection in
each boot.
lWhen shifted to each position, make sure there is no noise, catching, and backlash. Especially when con-
trol lever assembly is shifted to 5th, 6th without pressing downward, check for catching.
lWhen control lever assembly is shifted to 1st, 2nd side and 5th, 6th side, confirm control lever assembly
returns to neutral position smoothly.
lIn any position other than reverse, confirm that control lever assembly can be pressed downward.
lWith control lever assembly pressed downward, confirm that it can be shifted to reverse.
lWhen shifted from reverse to neutral position, confirm control lever assembly returns to neutral position
smoothly with spring power.
lWithout control lever assembly pressed downward, confirm that it cannot be shifted to reverse.
PCIB1435E
PCIB1434E
Page 2404 of 3171
PREPARATION
MTC-17
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Recovery/Recycling/
Recharging equipment (ACR4)Function: Refrigerant recovery and
recycling and recharging
Electrical leak detectorPower supply:
DC 12V (Cigarette lighter)
(J-43926)
Refrigerant dye leak detection kit
Kit includes:
(J-42220)
UV lamp and UV safety goggles
(J-41459)
HFC-134a (R-134a) dye injector
Use with J-41447, 1/4 ounce
bottle
(J-41447)
HFC-134a (R-134a) fluorescent
leak detection dye
(Box of 24, 1/4 ounce bottles)
(J-43872)
Refrigerant dye cleanerPower supply:
DC 12V (Battery terminal)
(J-42220)
UV lamp and UV safety gogglesPower supply:
DC 12V (Battery terminal)
For checking refrigerant leak when
fluorescent dye is installed in A/C
system
Includes:
UV lamp and UV safety goggles
(J-41447)
HFC-134a (R-134a) fluorescent
leak detection dye
(Box of 24, 1/4 ounce bottles)Application: For HFC-134a (R-134a)
PA G o i l
Container: 1/4 ounce (7.4 cc) bottle
(Includes self-adhesive dye
identification labels for affixing to
vehicle after charging system with
dye.) Tool number
Tool nameDescription
RJIA0195E
SHA705EB
ZHA200H
SHA438F
SHA439F
Page 2439 of 3171

MTC-52
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
SELF-DIAGNOSIS CODE CHART
Code No. Reference page
02 EE changed by calibration
04 Mode switch circuit open or shortMTC-58, "
Mode Door Motor Circuit"
05 Blower motor failureMTC-71, "Blower Motor Circuit"
20 BCM not responding to A/C requestMTC-79, "Magnet Clutch Circuit"
21 BCM not responding to rear defroster requestGW-47, "REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER"
22 Air mix door motor (front) circuit failureMTC-63, "Air Mix Door Motor Circuit"
34 Front potentio temperature control (PTC) failure
36 Air mix door motor (front) PBR circuit failureMTC-63, "
Air Mix Door Motor Circuit"
38 Air mix door motor (rear) circuit failureMTC-63, "Air Mix Door Motor Circuit"
56 Intake sensor circuit short
MTC-95, "Intake Sensor Circuit"57 Intake sensor circuit open
62 Defroster door motor circuit failure
80 CAN bus fault
LAN-3, "
Precautions When Using CONSULT-II"81 BCM CAN message missing
82 Intake door motor circuit failureMTC-68, "
Intake Door Motor Circuit"
90 Stuck switch
92 Mode door motor circuit failureMTC-58, "
Mode Door Motor Circuit"
Page 2500 of 3171
DUCTS AND GRILLES
MTC-113
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
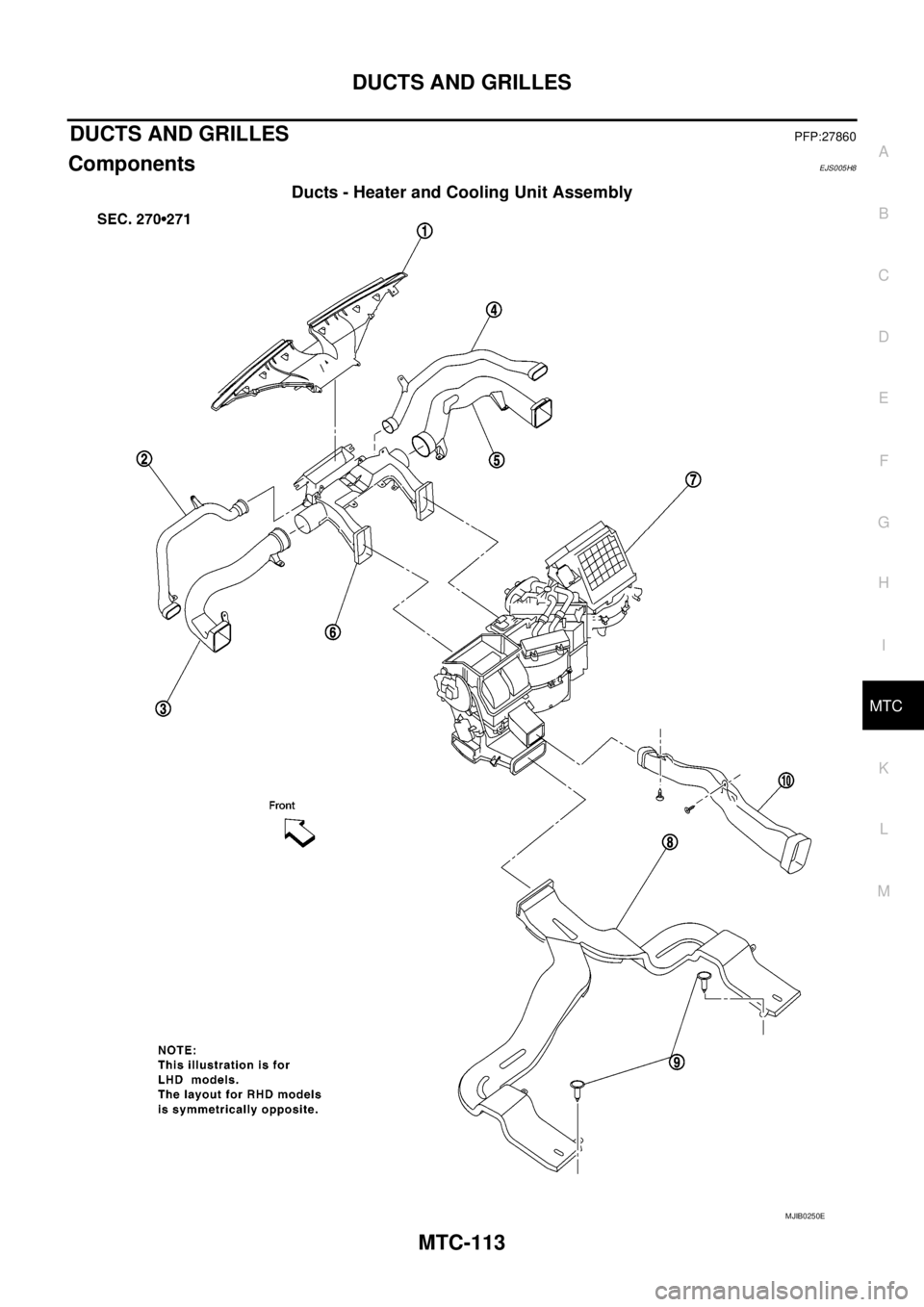
DUCTS AND GRILLESPFP:27860
ComponentsEJS005H8
Ducts - Heater and Cooling Unit Assembly
MJIB0250E
Page 2605 of 3171
PG-76
HARNESS CONNECTOR
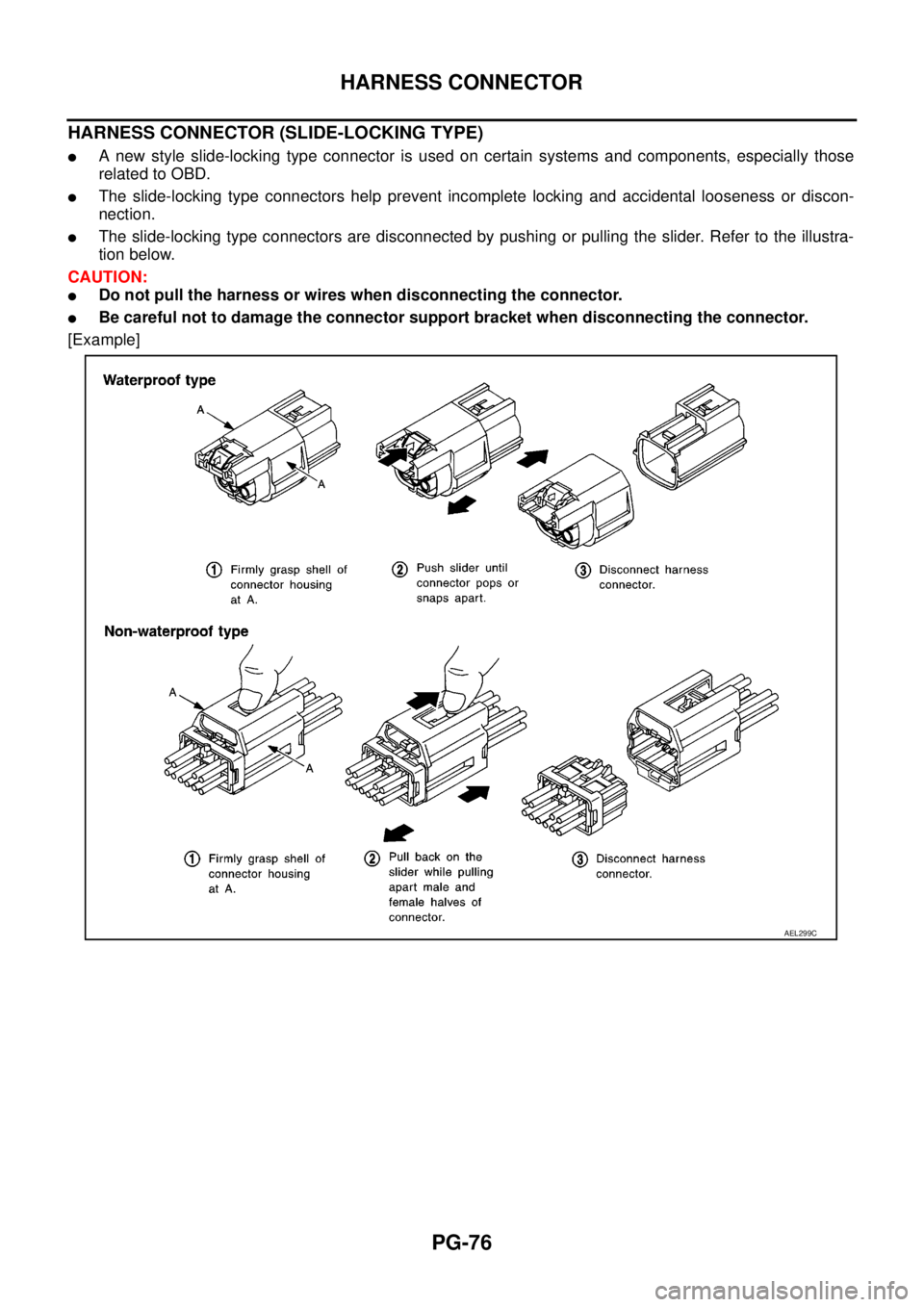
HARNESS CONNECTOR (SLIDE-LOCKING TYPE)
lA new style slide-locking type connector is used on certain systems and components, especially those
related to OBD.
lThe slide-locking type connectors help prevent incomplete locking and accidental looseness or discon-
nection.
lThe slide-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or pulling the slider. Refer to the illustra-
tion below.
CAUTION:
lDo not pull the harness or wires when disconnecting the connector.
lBe careful not to damage the connector support bracket when disconnecting the connector.
[Example]
AEL299C
Page 2681 of 3171
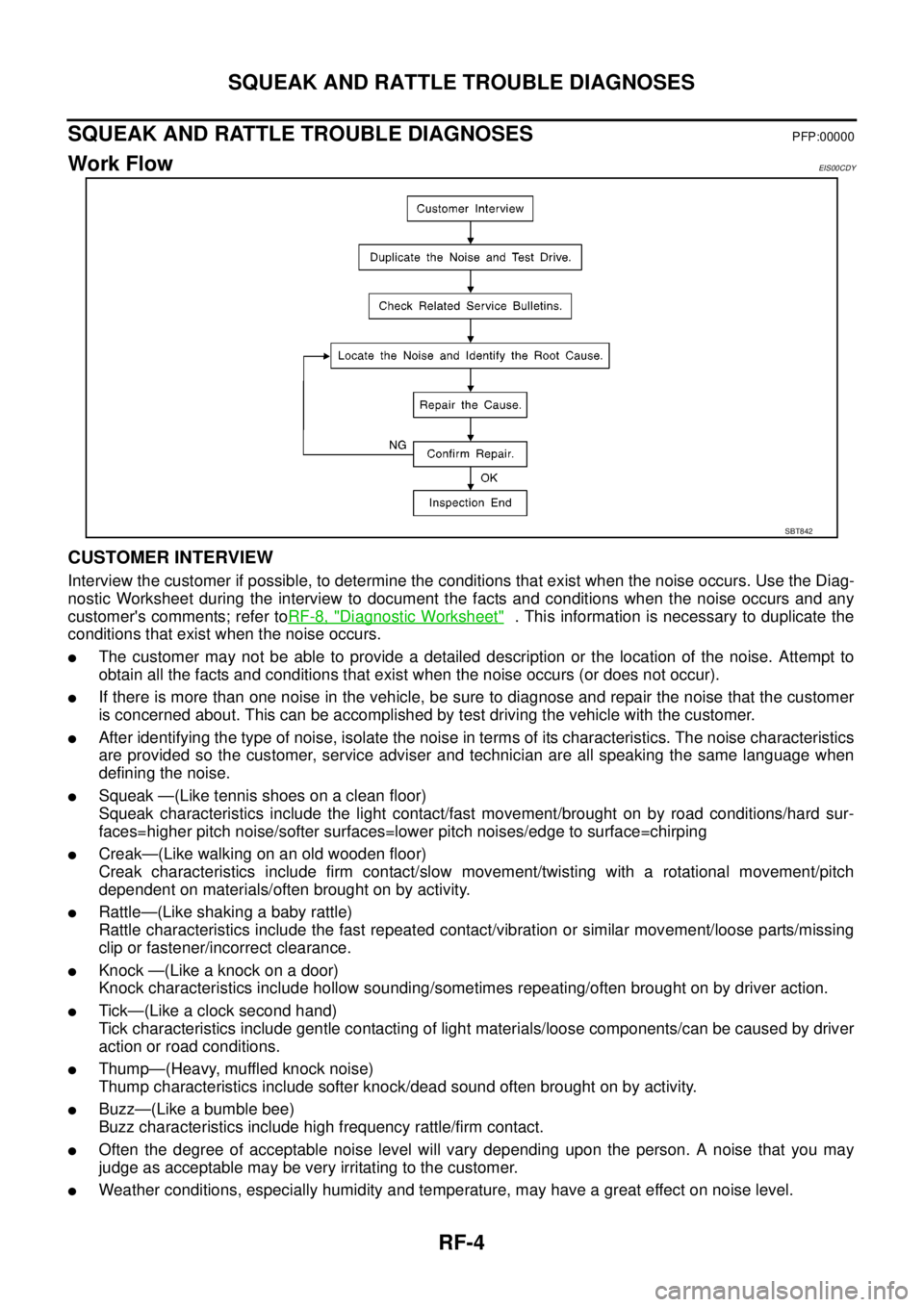
RF-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
PFP:00000
Work FlowEIS00CDY
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer toRF-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
lThe customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
lIf there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
lAfter identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
lSqueak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
lCreak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
lRattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
lKnock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
lTick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
lThump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
lBuzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
lOften the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
lWeather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 2769 of 3171
![NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Manual Online RFD-66
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
2.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK SOLENOID CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock control unit ha NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Manual Online RFD-66
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
2.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK SOLENOID CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock control unit ha](/img/5/57362/w960_57362-2768.png)
RFD-66
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
2.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK SOLENOID CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock control unit harness connector.
3. Check resistance between differential lock control unit harness
connector terminals 11 and 12.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 6.
NG >> GO TO 3.
3.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK SOLENOID RESISTANCE
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock solenoid harness connector.
3. Check resistance between differential lock solenoid harness
connector C23 terminals 1 and 2.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 4.
NG >> Replace differential lock solenoid. Refer toRFD-86, "
Dif-
ferential Assembly".
4.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK SOLENOID OPERATION
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock solenoid harness connector.
3. Check operation of differential lock solenoid by applying battery
voltage to differential lock solenoid harness connector terminals.
CAUTION:
Be sure to apply the voltage of the correct polarity to the
respective terminals. Otherwise, the part may be damaged.
Does solenoid operate?
YES >> GO TO 5.
NO >> Replace differential lock solenoid. Refer toRFD-86, "
Dif-
ferential Assembly".
Connector Terminal Resistance (Approx.)
M107 11 - 12 3.4W
SDIA2566E
1-2 :Approx.3.4W
SDIA3431E
Connector Terminal
C23 1 (Battery voltage) - 2 (Ground)
SDIA3432E
Page 2771 of 3171
![NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Manual Online RFD-68
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock solenoid harness connector.
3. Check NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Manual Online RFD-68
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock solenoid harness connector.
3. Check](/img/5/57362/w960_57362-2770.png)
RFD-68
[WITH ELECTRONIC LOCKING DIFFERENTIAL]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYSTEM
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch “OFF”.
2. Disconnect differential lock solenoid harness connector.
3. Check resistance between differential lock solenoid harness
connector C23 terminals 1 and 2.
4. If NG, replace differential lock solenoid. Refer toRFD-86, "
Differ-
ential Assembly".
5. Check operation by applying battery voltage to differential lock
solenoid harness connector terminals.
CAUTION:
Be sure to apply the voltage of the correct polarity to the
respective terminals. Otherwise, the part may be damaged.
6. If NG, replace differential lock solenoid.
ABS SystemEDS003B7
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
1.CHECK DTC WITH ABS ACTUATOR AND ELECTRIC UNIT (CONTROL UNIT)
Perform self-diagnosis with ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit). Refer toBRC-18, "
Self-Diagnosis".
Is any malfunction detected by self-diagnosis?
YES >> Check the malfunctioning system.
NO >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK DIFFERENTIAL LOCK CONTROL UNIT
Check differential lock control unit input/output signal. Refer toRFD-48, "
Differential Lock Control Unit Input/
Output Signal Reference Values".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Check differential lock control unit pin terminals for damage or loose connection with harness con-
nector. If any items are damaged, repair or replace damaged parts.
3.CHECK DTC
Perform the self-diagnosis, after driving the vehicle for a while.
OK or NG
OK >>INSPECTION END
NG >> Perform self-diagnosis with ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit) again. Refer toBRC-18,
"Self-Diagnosis". 1-2 :Approx.3.4W
SDIA3431E
Connector Terminal
C23 1 (Battery voltage) - 2 (Ground)
SDIA3432E
Page 2875 of 3171
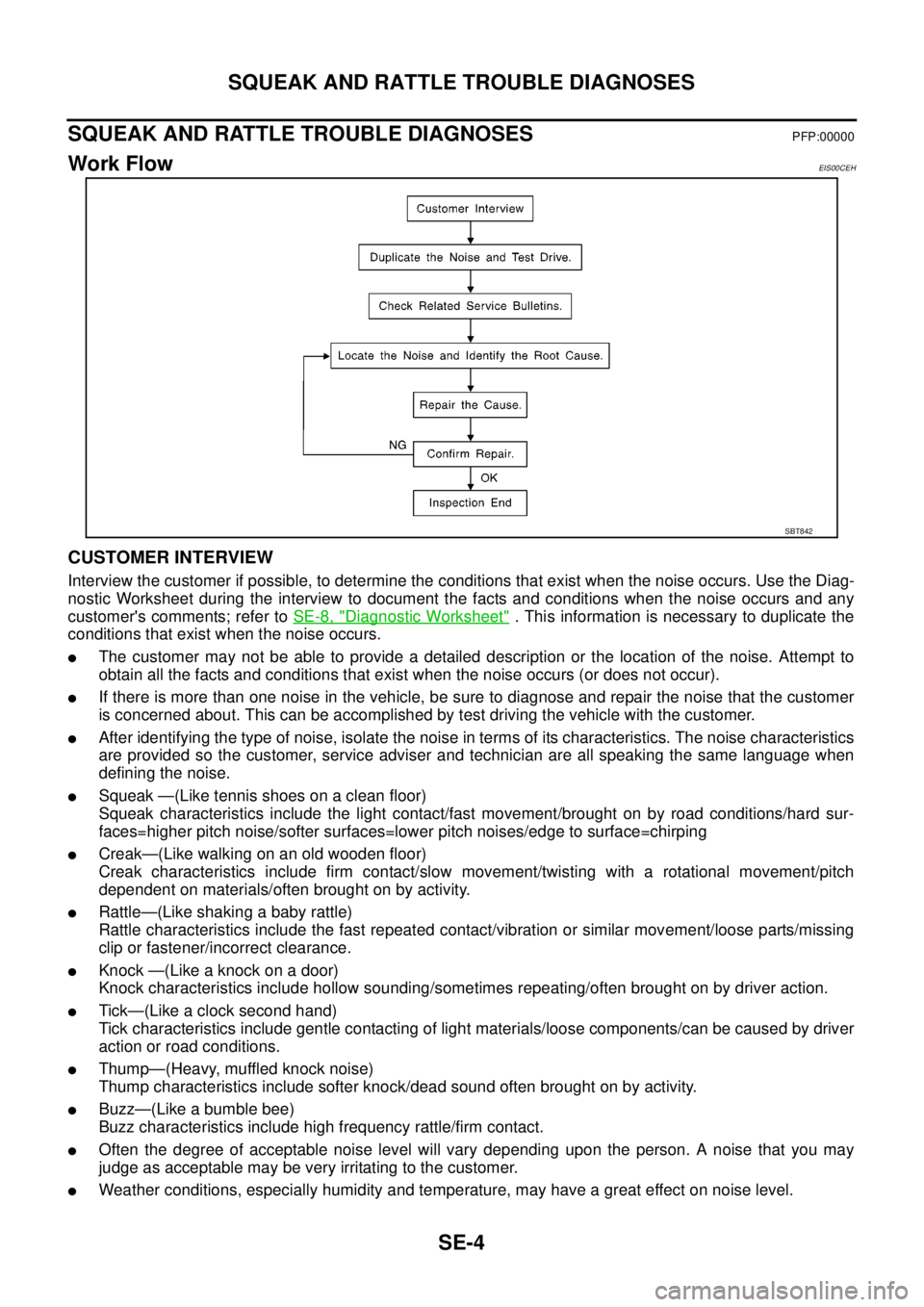
SE-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
PFP:00000
Work FlowEIS00CEH
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer toSE-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
lThe customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
lIf there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
lAfter identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
lSqueak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
lCreak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
lRattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
lKnock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
lTick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
lThump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
lBuzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
lOften the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
lWeather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 2937 of 3171

SRS-28
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
14. Repair the system as outlined by the “Repair order” in “Intermittent Malfunction Diagnostic Code Chart”,
that corresponds to the self-diagnostic result. For replacement procedure of component parts, refer to the
Removal and Installation procedure for the appropriate component.
15. Go toSRS-24, "
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE 3", for final checking.
CONSULT-II Diagnostic Code Chart ("SELF-DIAG [PAST]" or "TROUBLE DIAG RECORD")
Diagnostic item ExplanationRepair order
Recheck SRS at each replacement
NO DTC IS DETECTEDWhen malfunction is
indicated by the “AIR
BAG” warning lamp in
User mode.
lLow battery voltage (Less than
9V)lGo toSRS-24, "DIAGNOSTIC PRO-
CEDURE 3".
lSelf-diagnostic result “SELF-DIAG
[PAST]” (previously stored in the
memory) might not be erased
after repair.
lIntermittent malfunction has been
detected in the past.
lGo toSRS-26, "DIAGNOSTIC PRO-
CEDURE 4 (CONTINUED FROM
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE 2)".
lGo toSRS-26, "DIAGNOSTIC PRO-
CEDURE 5".
lNo malfunction is detected. —
DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE
[OPEN]
[B1049] or [B1054]
lDriver air bag module circuit is open (including the spiral
cable).1. Visually check the wiring harness
connection.
2. Replace the harness if it has visible
damage.
3. Replace driver air bag module.
(Before disposal, it must be
deployed.)
4. Replace the spiral cable.
5. Replace the air bag diagnosis sen-
sor unit.
6. Replace the related harness. DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE
[VB-SHORT]
[B1050] or [B1055]
lDriver air bag module circuit is shorted to some power sup-
ply circuit (including the spiral cable).
DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE
[GND-SHORT]
[B1051] or [B1056]
lDriver air bag module circuit is shorted to ground (including
the spiral cable).
DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE
[SHORT]
[B1052] or [B1057]
lDriver air bag module circuits are shorted to each other.
ASSIST A/B MODULE
[OPEN]
[B1065] or [B1070]
lFront passenger air bag module circuit is open.
1. Visually check the wiring harness
connection.
2. Replace the harness if it has visible
damage.
3. Replace front passenger air bag
module. (Before disposal, it must be
deployed.)
4. Replace the air bag diagnosis sen-
sor unit.
5. Replace the related harness. ASSIST A/B MODULE
[VB-SHORT]
[B1066] or [B1071]
lFront passenger air bag module circuit is shorted to some
power supply circuit.
ASSIST A/B MODULE
[GND-SHORT]
[B1067] or [B1072]
lFront passenger air bag module circuit is shorted to
ground.
ASSIST A/B MODULE
[SHORT]
[B1068] or [B1073]
lFront passenger air bag module circuits are shorted to
each other.
SIDE MODULE LH
[OPEN]
[B1134]
lFront LH side air bag module circuit is open. 1. Visually check the wiring harness
connection.
2. Replace the harness if it has visible
damage.
3. Replace front LH seat back assem-
bly (front LH side air bag module).
(Before disposal, it must be
deployed.)
4. Replace the air bag diagnosis sen-
sor unit.
5. Replace the related harness. SIDE MODULE LH
[VB-SHORT]
[B1135]
lFront LH side air bag module circuit is shorted to some
power supply circuit.
SIDE MODULE LH
[GND-SHORT]
[B1136]
lFront LH side air bag module circuit is shorted to ground.
SIDE MODULE LH
[SHORT]
[B1137]
lFront LH side air bag module circuits are shorted to each
other.