NISSAN PULSAR 1987 User Guide
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 11 of 238

General Information 11
Lifting Equipment
When using lifting equipment to lift heavy com-
ponents such as the engine and/or transmission, use
metal slings or chain in preference to rope. If rope
must be used, ensure that it is not placed against sharp
edges on the component.
Automotive Lubricants and Solvents
Avoid prolonged skin contact with oils, greases
and solvents as some can cause skin irritations and
dermatitis.
Exercise caution when us ing cleaning solvents as
many are inflammable. Do not smoke. Keep naked
flames and sparks clear of the work area.
Compressed Air
Never point an air hose at another person or allow
compressed air to blow onto your skin. High pressure
air forced against the skin can enter the bloodstream
and prove fatal.
Suspension and Steering Components
Damaged suspension and steering components
should not be welded. Many of these components are
fabricated from toughened metals. If welded they may
lose their strength or become brittle. Damaged com-
ponents should be renewed.
Air Conditioning
Avoid disconnecting air conditioning hoses as
escaping refrigerant can cause frostbite. The refriger-
ant is highly flammable and when burnt, a poisonous
gas is produced.
VEHICLE SAFETY
To prevent damage to the vehicle during servicing
or repair work, note the following precautions.
Brake Fluid
If spilt on the vehicle paintwork, brake fluid
should be immediately washed away with clean water
and allowed to dry naturally, not wiped with a cloth.
Catalytic Converter
The following should be observed to prevent
damage to the catalytic converter:
Do not operate the vehicle on leaded fuel.
Do not push or tow start the vehicle.
Do not allow the engine to idle for prolonged
periods.
Do not switch the ignition off while the vehicle is
in motion and the transmission is in gear.
Do not 'prime' the engine by pouring fuel into the
inlet manifold.
Do not operate the vehicle if the engine is
misfiring.
Avoid running the vehicle out of fuel.
Ensure that the engine oil is formulated to contain
low phosphorus levels.
Electronic Components
The electronic components of the ignition and
fuel injection systems can be damaged by the use of
incorrect testing equipment.
It is essential in all tests where voltage or resis-
tance is to be measured that a digital display multi-
meter with a minimum 10 megohm input impedance
be used.
Some types of tachometers, timing lights and
ignition system analyzers are not compatible with
certain engine electronic systems. It is therefore
recommended that the manufacturer of the test equip-
ment be consulted before using the equipment.
Jump starting, or being jump started by another
vehicle can cause damage to the electronic compon-
ents of the vehicle. Refer to the Roadside Trouble
shooting section for the correct jump starting proce-
dure.
3. GENERAL REPAIR PROCEDURES
SEIZED FASTENERS
Seized bolts, nuts or screws should first have a
liberal amount of penetrating oil applied. The fastener
should be left for a period of time to allow the oil to
penetrate and soften the corrosion which is causing
the binding.
Often, a sharp hammer blow to the head of the
fastener can dislodge the corrosion and permit it to be
loosened.
An impact driver, which can be fitted with a
socket or screwdriver bit, can be used to loosen a
seized fastener.
Another method is to heat the component in
which the fastener is seized. However, extreme cau-
tion should be exercised when heating aluminum
alloy components as the melting point is much lower
than that of steel.
If the above methods fail to free a seized nut,
carefully hacksaw through one side of the nut until it
can be split. Care should be taken that the threads of
the bolt or stud are not damaged.
Should a bolt or stud break below the surface of
the component, it will be necessary to use a screw
extractor to remove the remaining part. Follow the
screw extractor manuf acturers instructions.
Tap and die set and assorted screw extractors.
Page 12 of 238
12 General Information
Damaged threads can be repaired using a die nut
on studs and bolts, and a tap on nuts and threaded
holes in castings. If the threads of a threaded hole are
damaged beyond repair, it will be necessary to drill
and tap the hole to a larger size. Alternatively, a
Helicoil insert can be used to Testore the hole to the
original thread size.
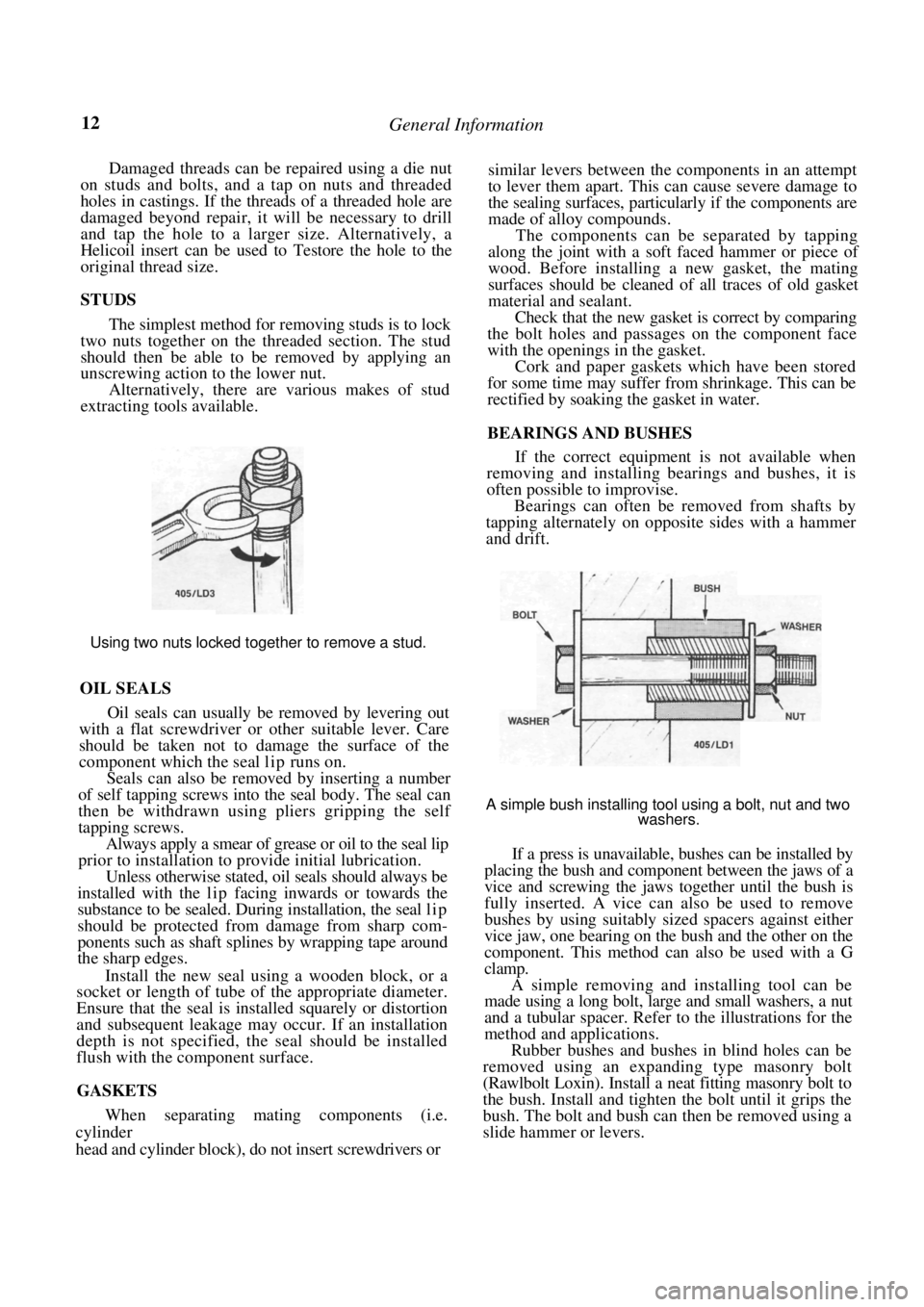
STUDS
The simplest method for removing studs is to lock
two nuts together on the threaded section. The stud
should then be able to be removed by applying an
unscrewing action to the lower nut.
Alternatively, there are various makes of stud
extracting tools available.
Using two nuts locked together to remove a stud.
OIL SEALS
Oil seals can usually be removed by levering out
with a flat screwdriver or other suitable lever. Care
should be taken not to damage the surface of the
component which the seal lip runs on.
Seals can also be removed by inserting a number
of self tapping screws into the seal body. The seal can
then be withdrawn using pliers gripping the self
tapping screws.
Always apply a smear of grease or oil to the seal lip
prior to installation to provide initial lubrication.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals should always be
installed with the lip facing inwards or towards the
substance to be sealed. Duri ng installation, the seal l i p
should be protected from damage from sharp com-
ponents such as shaft splines by wrapping tape around
the sharp edges.
Install the new seal using a wooden block, or a
socket or length of tube of the appropriate diameter.
Ensure that the seal is installed squarely or distortion
and subsequent leakage may occur. If an installation
depth is not specified, th e seal should be installed
flush with the component surface.
GASKETS
When separating mating components (i.e.
cylinder
head and cylinder block), do not insert screwdrivers or
similar levers between the components in an attempt
to lever them apart. This can cause severe damage to
the sealing surfaces, particularly if the components are
made of alloy compounds.
The components can be separated by tapping
along the joint with a soft faced hammer or piece of
wood. Before installing a new gasket, the mating
surfaces should be cleaned of all traces of old gasket
material and sealant.
Check that the new gasket is correct by comparing
the bolt holes and passages on the component face
with the openings in the gasket.
Cork and paper gaskets which have been stored
for some time may suffer from shrinkage. This can be
rectified by soaking the gasket in water.
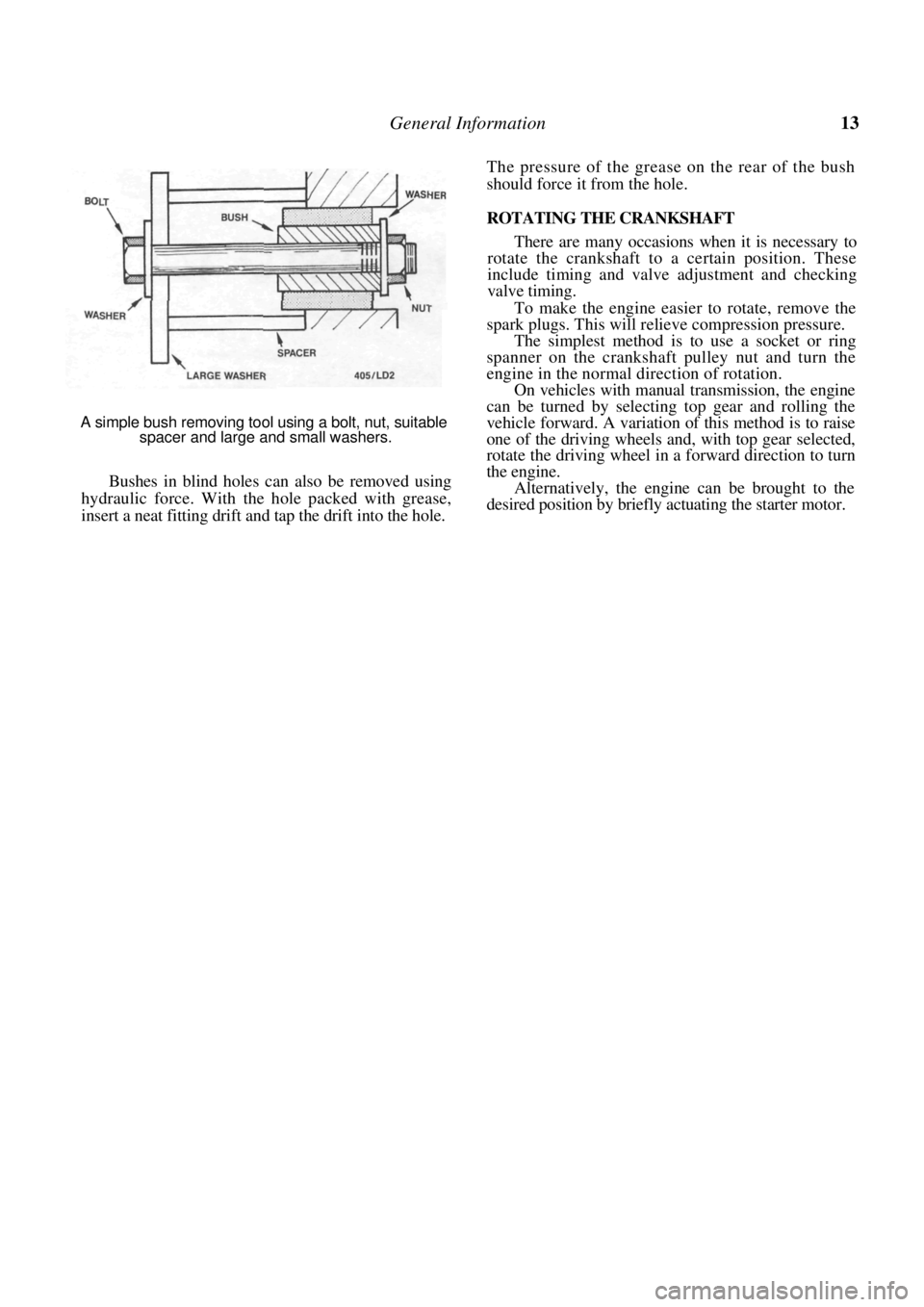
BEARINGS AND BUSHES
If the correct equipment is not available when
removing and installing bearings and bushes, it is
often possible to improvise.
Bearings can often be removed from shafts by
tapping alternately on opposite sides with a hammer
and drift.
A simple bush installing tool using a bolt, nut and two
washers.
If a press is unavailable, bushes can be installed by
placing the bush and component between the jaws of a
vice and screwing the jaws together until the bush is
fully inserted. A vice can also be used to remove
bushes by using suitably sized spacers against either
vice jaw, one bearing on the bush and the other on the
component. This method can also be used with a G
clamp.
A simple removing and installing tool can be
made using a long bolt, large and small washers, a nut
and a tubular spacer. Refer to the illustrations for the
method and applications.
Rubber bushes and bushes in blind holes can be
removed using an expanding type masonry bolt
(Rawlbolt Loxin). Install a neat fitting masonry bolt to
the bush. Install and tighten the bolt until it grips the
bush. The bolt and bush can then be removed using a
slide hammer or levers.
Page 13 of 238
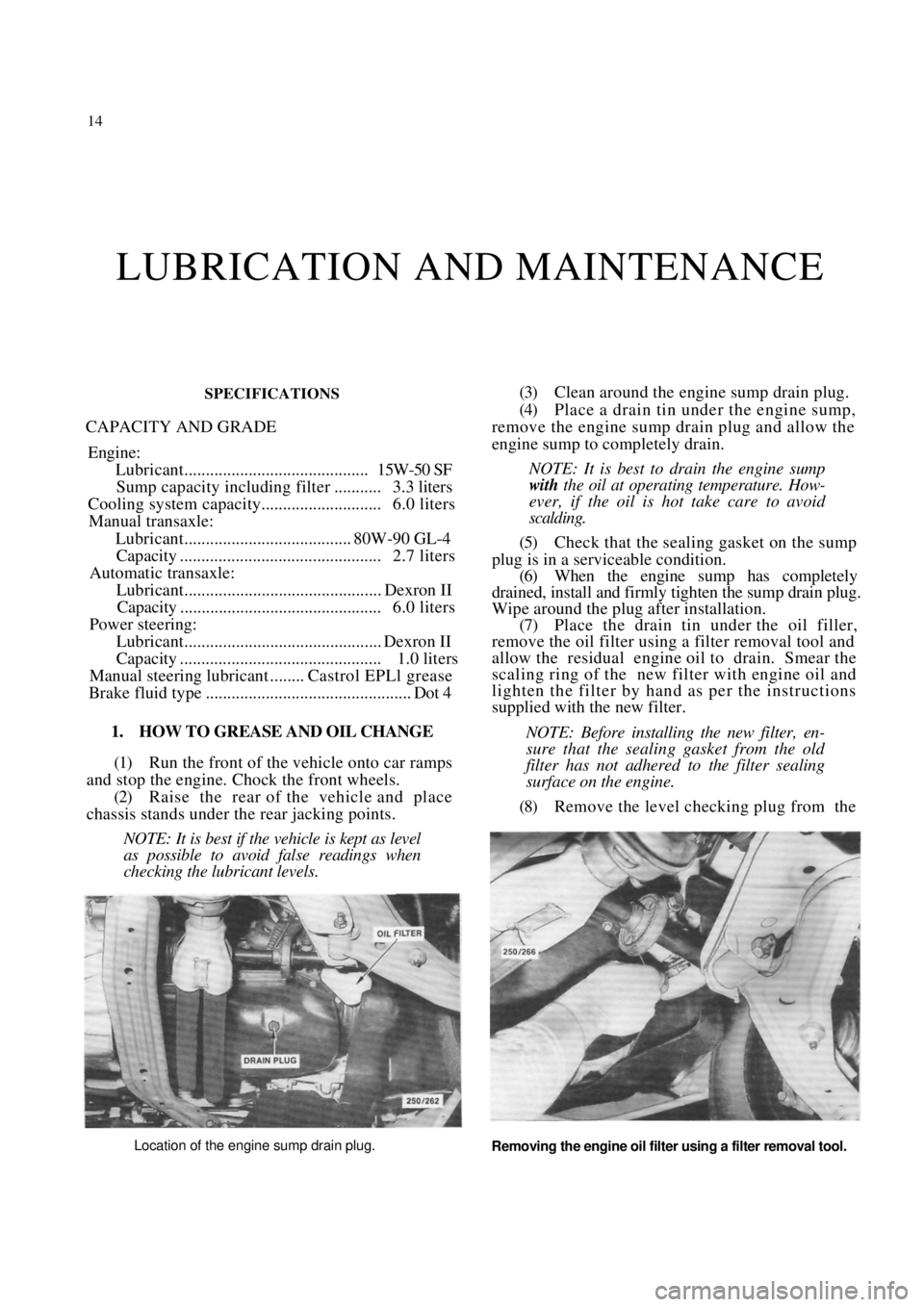
General Information 13
A simple bush removing tool using a bolt, nut, suitable spacer and large and small washers.
Bushes in blind holes can also be removed using
hydraulic force. With the hole packed with grease,
insert a neat fitting drift and tap the drift into the hole.
The pressure of the grease on the rear of the bush
should force it from the hole.
ROTATING THE CRANKSHAFT
There are many occasions when it is necessary to
rotate the crankshaft to a certain position. These
include timing and valve adjustment and checking
valve timing.
To make the engine easier to rotate, remove the
spark plugs. This will re lieve compression pressure.
The simplest method is to use a socket or ring
spanner on the crankshaft pulley nut and turn the
engine in the normal direction of rotation.
On vehicles with manual transmission, the engine
can be turned by selecting top gear and rolling the
vehicle forward. A variation of this method is to raise
one of the driving wheels and, with top gear selected,
rotate the driving wheel in a forward direction to turn
the engine.
Alternatively, the engine can be brought to the
desired position by briefly actuating the starter motor.
Page 14 of 238

14
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
SPECIFICATIONS
CAPACITY AND GRADE
Engine:
Lubricant........................................... 15W-50 SF
Sump capacity including filter ........... 3.3 liters
Cooling system capacity............................ 6.0 liters
Manual transaxle:
Lubricant....................................... 80W-90 GL-4
Capacity ............................................... 2.7 liters
Automatic transaxle:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 6.0 liters
Power steering:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 1.0 liters
Manual steering lubricant ........ Castrol EPLl grease
Brake fluid type ................................................ Dot 4
1. HOW TO GREASE AND OIL CHANGE
(1) Run the front of the vehicle onto car ramps
and stop the engine. Chock the front wheels. (2) Raise the rear of the vehicle and place
chassis stands under the rear jacking points.
NOTE: It is best if the vehicle is kept as level
as possible to avoi d false readings when
checking the lubricant levels.
(3) Clean around the engine sump drain plug.
(4) Place a drain tin under the engine sump,
remove the engine sump drain plug and allow the
engine sump to completely drain.
NOTE: It is best to drain the engine sump
with the oil at operating temperature. How-
ever, if the oil is hot take care to avoid
scalding.
(5) Check that the sealing gasket on the sump
plug is in a serviceable condition. (6) When the engine sump has completely
drained, install and firmly tighten the sump drain plug.
Wipe around the plug after installation. (7) Place the drain tin under the oil filler,
remove the oil filter using a filter removal tool and
allow the residual engine oil to drain. Smear the
scaling ring of the new filter with engine oil and
lighten the filter by hand as per the instructions
supplied with the new filter.
NOTE: Before installing the new filter, en-
sure that the sealing gasket from the old
filter has not adhered to the filter sealing
surface on the engine.
(8) Remove the level checking plug from the
Location of the engine sump drain plug.
Removing the engine oil filter using a filter removal tool.
Page 15 of 238
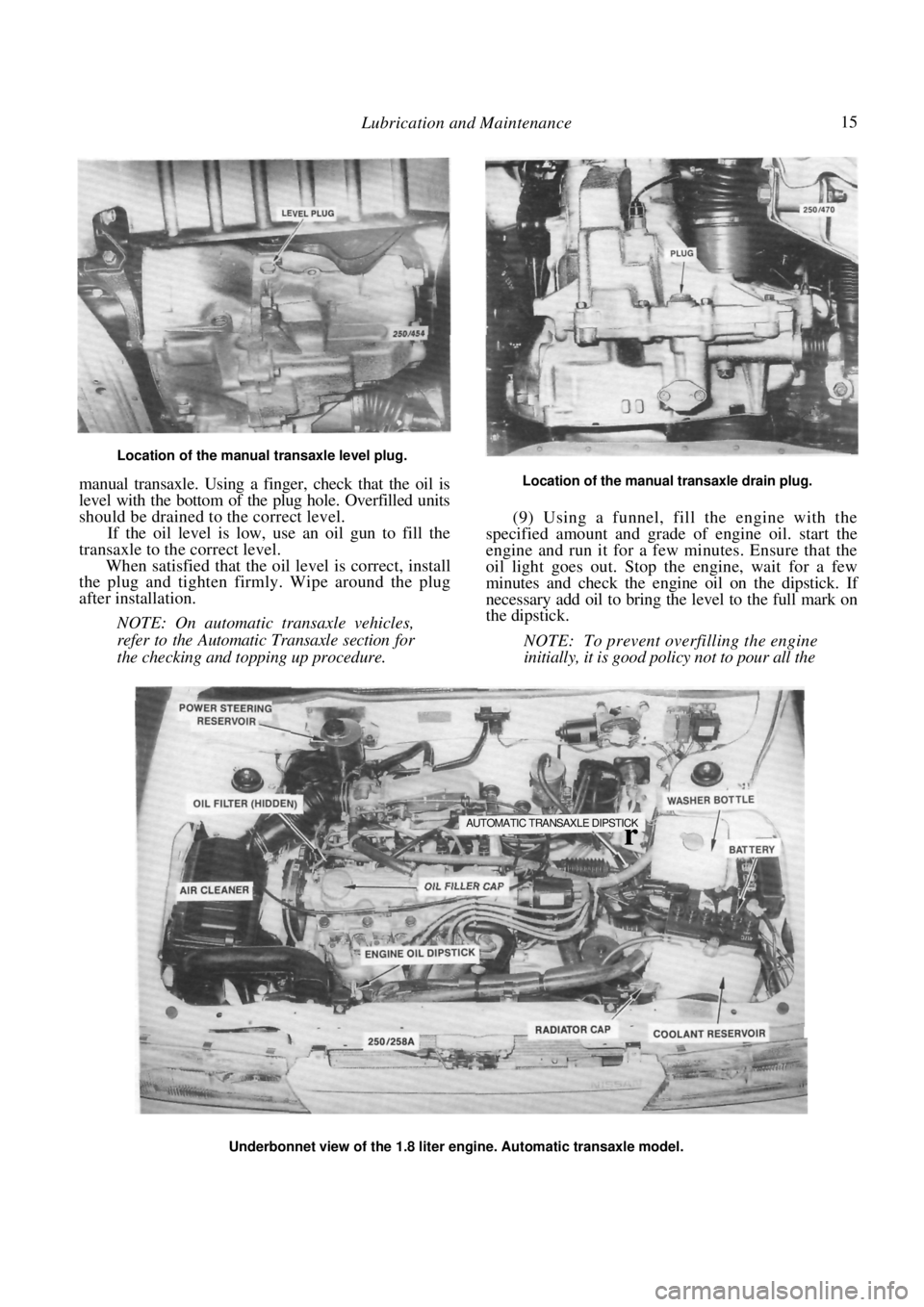
Lubrication and Maintenance 15
Location of the manual transaxle level plug.
manual transaxle. Using a finger, check that the oil is
level with the bottom of the plug hole. Overfilled units
should be drained to the correct level.
If the oil level is low, use an oil gun to fill the
transaxle to the correct level.
When satisfied that the oil level is correct, install
the plug and tighten firmly. Wipe around the plug
after installation.
NOTE: On automatic transaxle vehicles,
refer to the Automatic Transaxle section for
the checking and topping up procedure.
Location of the manual transaxle drain plug.
(9) Using a funnel, fill the engine with the
specified amount and grade of engine oil. start the
engine and run it for a few minutes. Ensure that the
oil light goes out. Stop the engine, wait for a few
minutes and check the engine oil on the dipstick. If
necessary add oil to bring the level to the full mark on
the dipstick.
NOTE: To prevent overfilling the engine
initially, it is good policy not to pour all the
Underbonnet view of the 1.8 liter engine. Automatic transaxle model.
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
r
Page 16 of 238
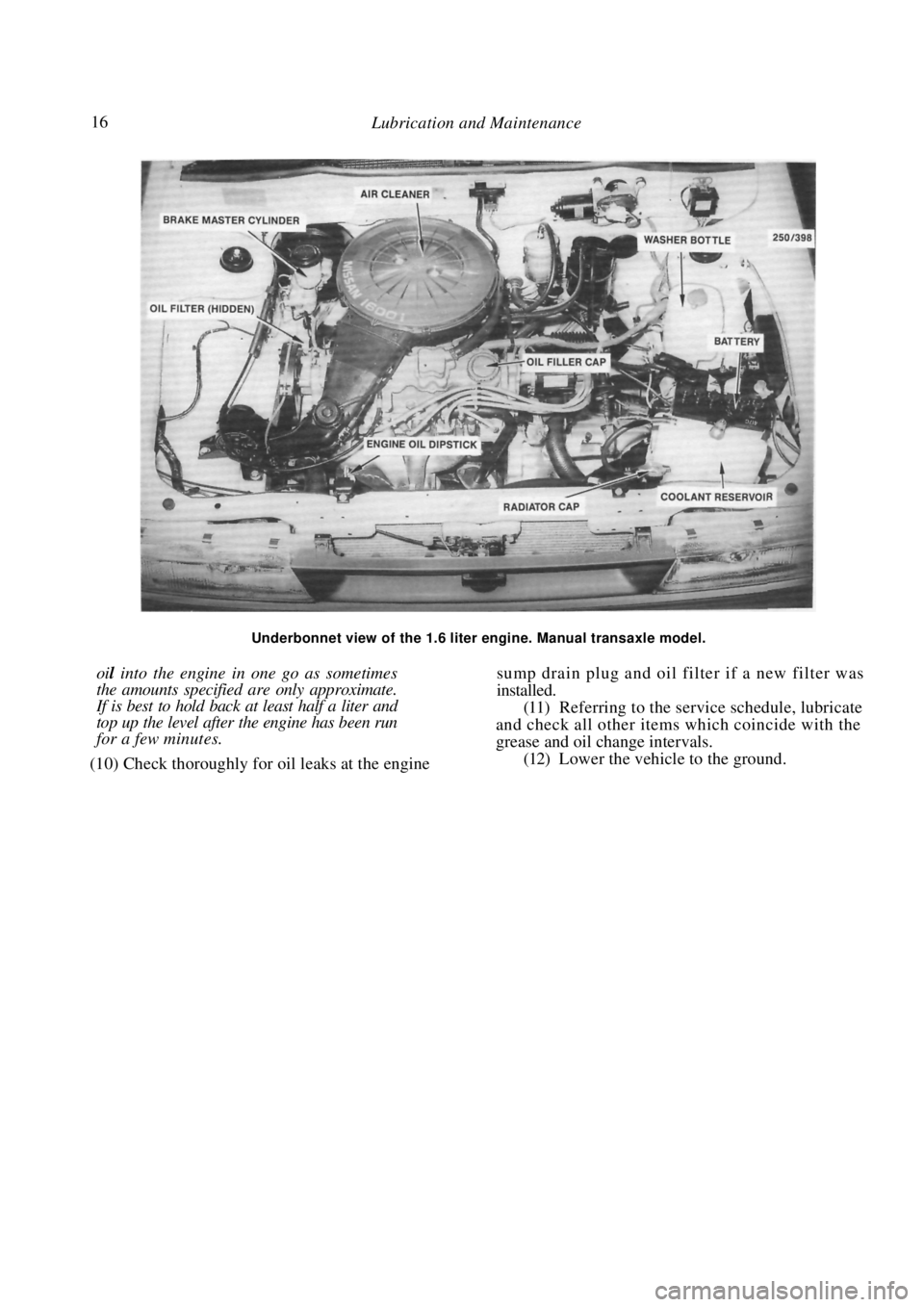
16 Lubrication and Maintenance
Underbonnet view of the 1.6 liter engine. Manual transaxle model.
oil into the engine in one go as sometimes
the amounts specified are only approximate.
If is best to hold back at least half a liter and
top up the level after the engine has been run
for a few minutes.
(10) Check thoroughly for oil leaks at the engine
sump drain plug and oil filter if a new filter was
installed.
(11) Referring to the service schedule, lubricate
and check all other items which coincide with the
grease and oil change intervals.
(12) Lower the vehicle to the ground.
Page 17 of 238

Lubrication and Maintenance 17
2. SERVICE SCHEDULE
This Section Removed
Page 18 of 238

18 Lubrication and Maintenance
This Section Removed
Page 19 of 238

Lubrication and Maintenance
This Section Removed
19
Page 20 of 238

20 Lubrication and Maintenance
This Section Removed