NISSAN PULSAR 1987 Owner's Guide
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 31 of 238

Engine Tune-up
View of the engine timing marks showing the 10 deg
BTDC crankshaft notch aligned with the pointer on the
front of the engine.
(5) If adjustment is necessary, loosen the distrib-
utor body retaining nuts and turn the distributor body
until the correct setting is obtained.
(6) Tighten the distributor body retaining nuts
and ensure that the timing is still correct.
(7) Remove the jumper lead from the diagnostic
link connector.
(8) Disconnect the timing light from the engine.
TO ADJUST IDLE SPEED AND MIXTURE
The idle speed and mixt ure are not adjusted as
normal service procedure. However, should the per-
formace of the vehicle indicate that the mixture is
incorrect, refer to the Fuel and Engine Management
section for the procedures to test for faulty compo-
nents in the engine management system.
Page 32 of 238

32
ROADSIDE TROUBLE SHOOTING
CAUTION: To prevent severe electrical shock extreme care must be taken w\
hen
working on or near the electronic ignition system as dangerous high tension voltages
are produced in both the primary and secondary circuits. See the text fo\
r
precautionary notes.
This section deals with the common causes of
engine failure to start, as inevitably there will come a
time when every driver will experience this problem
and will therefore need to call upon his own resources
to rectify the trouble. Roadside breakdowns other
than engine failure can be identified by reference to
the Trouble Shooting section on the particular com-
ponent affected.
1. TROUBLE SHOOTING
Trouble shooting is only a process of elimination
and provided the procedure is carried out correctly
and systematically an accur ate diagnosis of the trouble
can be made in the minimum amount of time.
For an internal combustion engine to run there
are three basic requirements, these are ignition, fuel
and compression. There are other factors of course
but as a rule an engine's failure to start can be
attributed to a fault in one of these three systems.
Reports from field engineers of motoring organi-
sations prove that the bigg est percentage of engine
breakdowns are in the order of ignition or electrical
failure first, followed by fuel, with mechanical or
compression failure the least common.
Should the engine fail to start, first check that
there is adequate fuel in the tank and if so. carry out
the following checking procedures in the order de-
scribed.
TO JUMP START A VEHICLE
NOTE: Jump starting a vehicle can be
dangerous if the procedure described below
is not performed correctly. If any doubt
exists, it is recommended that the services of
a competent mechanic be obtained.
The vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with complex electronic circuitry
which can be damaged by voltage surges.
These voltage surges can be generated when
jump starting, or being jump started by
another vehicle. If av ailable use jumper
leads equipped with a surge protection de-
vice and follow the lead manufacturers in-
structions carefully, particularly regarding
the connection and disconnection of the
leads.
(1) Ensure that the booster battery is 12 volts
and the negative terminal is earthed.
(2) Ensure that the vehicles are not touching and
that the ignition and all accessories on both vehicles
are switched Off. (3) Ensure that the transmissions on both vehi-
cles are in Park or Neutral and the handbrakes are
firmly applied. (4) Remove the vent caps from the battery and
check the electrolyte level. Replenish with distilled
water as necessary.
View showing the correct jumper lead connections for
jump starting a vehicle. The leads shown are equipped
with a surge protection device.
Page 33 of 238
Roadside Trouble Shooting
(5) Place the vent caps loosely over the cell
apertures.
(6) Connect one end of the red jumper lead to
the positive ( + ) battery terminal of the booster
battery and the other end of the red lead to the
positive (+) battery terminal of the discharged bat-
tery.
NOTE: The battery emits hydrogen gas
which is explosive. Do not expose the battery
to naked /lames or sparks.
Do not lean over the battery when con-
necting the jumper leads.
Do not allow the ends of the jumper leads
to touch one another or any part of the
engine.
(7) Connect one end of the black juniper lead to
the negative (-) battery terminal of the booster
battery and the other end of the black lead to a good
earthing point on the engine of the vehicle with the
discharged battery.
NOTE: Do not connect the jumper lead
directly to the negative (-) battery terminal
of the discharged battery.
(8) Start the engine on the vehicle with the
booster battery and run the engine at a moderate
speed. (9) Start the engine on the vehicle with the
discharged battery.
(10) If possible, leave the engines of both vehi-
cles running for 10 minutes.
(11) Disconnect the jumper leads in the reverse
order of the sequence in which they were connected.
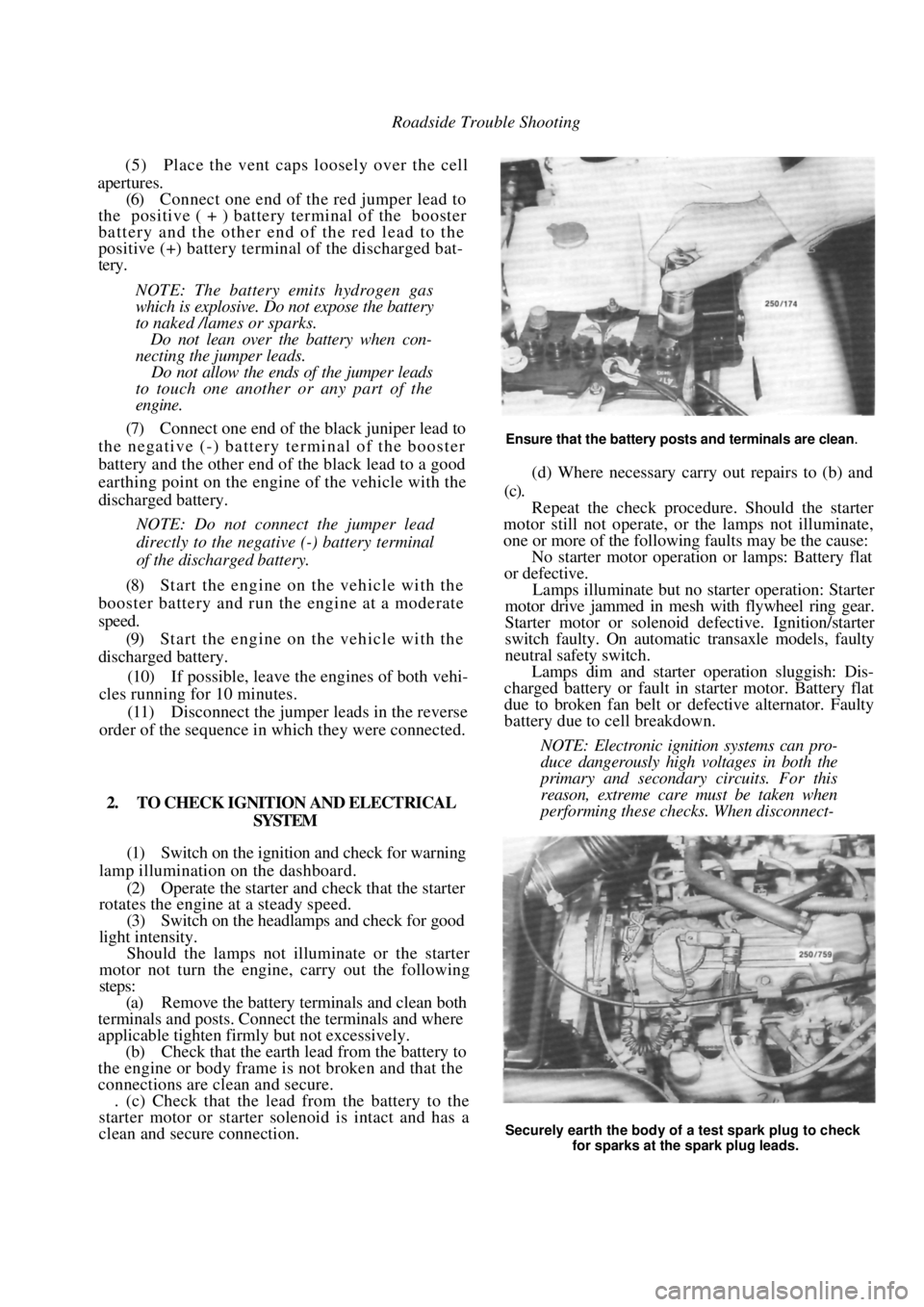
2. TO CHECK IGNITION AND ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
(1) Switch on the ignition and check for warning
lamp illumination on the dashboard. (2) Operate the starter and check that the starter
rotates the engine at a steady speed.
(3) Switch on the headlamps and check for good
light intensity. Should the lamps not illum inate or the starter
motor not turn the engine, carry out the following
steps:
(a) Remove the battery terminals and clean both
terminals and posts. Connect the terminals and where
applicable tighten firmly but not excessively.
(b) Check that the earth lead from the battery to
the engine or body frame is not broken and that the
connections are clean and secure. . (c) Check that the lead from the battery to the
starter motor or starter solenoid is intact and has a
clean and secure connection.
Ensure that the battery posts and terminals are clean.
(d) Where necessary carry out repairs to (b) and
(c).
Repeat the check procedur e. Should the starter
motor still not operate, or the lamps not illuminate,
one or more of the following faults may be the cause:
No starter motor operation or lamps: Battery flat
or defective.
Lamps illuminate but no starter operation: Starter
motor drive jammed in mesh with flywheel ring gear.
Starter motor or solenoid defective. Ignition/starter
switch faulty. On automatic transaxle models, faulty
neutral safety switch.
Lamps dim and starter operation sluggish: Dis-
charged battery or fault in starter motor. Battery flat
due to broken fan belt or de fective alternator. Faulty
battery due to cell breakdown.
NOTE: Electronic ignition systems can pro-
duce dangerously high voltages in both the
primary and secondary circuits. For this
reason, extreme care must be taken when
performing these checks. When disconnect-
Securely earth the body of a test spark plug to check
for sparks at the spark plug leads.
Page 34 of 238

Roadside Trouble Shooting
ing the wiring from any component, ensure
that the ignition switch is off and the
negative battery terminal is disconnected to
prevent damage to the solid state circuitry.
(4) Open the electrode gap of a serviceable spark
plug to 6 mm. Securely earth the plug using a jumper
lead or by tying the plug to an earthed engine
component.
(5) Disconnect the high tension lead from a
spark plug and connect it to the test spark plug.
(6) Have an assistant operate the starter motor.
(7) Check that a spark, if any, jumps the gap on
the test spark plug. If the spark is satisfactory, proceed to operation
(8).
If there is no spark, proceed as follows:
(a) Check the high tension leads to ensure that
they are dry and that the insulation is not cracked or
perished. Check the ends of the leads for burning. Using an ohmmeter, measure the resistance in
each high tension lead. The resistance should be no
more than 15 000 ohms per lead.
(b) Check the distributor cap to ensure that it is
dry and clean. Examine both the inside and outside of
the cap for cracks or tracki ng, particularly between the
high tension lead segments.
Check that the carbon brush in the centre of the
distributor cap interior fa ce is clean and dry and
ensure that the brush moves freely in and out of its
locating hole.
(c) Check the rotor arm for cracks, deposits and
burning on the metal arm. (d) Ensure that the high tension leads have dry.
clean and secure connections on the distributor cap. (8) If the above checks r esult in a good spark at
the spark plug high tension leads but the engine is still
not operating satisfac torily, remove all the spark plugs
and check the condition and electrode gap as de-
scribed in the Engine Tune-up section under the
appropriate heading.
3. TO CHECK FUEL SYSTEM
Due to the complex nature of the EFI system, it is
recommended that should the following checks prove
satisfactory but the engine fail to start, reference be
made to the Fuel and Engine Management section of
this manual or a Nissan workshop be consulted.
(1) Check that the fuel tank contains a reason-
able amount of fuel. (2) Have an assistant switch the ignition on and
off while squeezing the fuel supply hose with the
fingers. If the fuel pump is operating it should be
possible to feel the fuel pr essure increase for approx-
imately two seconds.
NOTE: When conducting the above test it
should be possible to hear the fuel pump and
ignition relays clicking when the ignition is
switched on and off
If the fuel pump relay fails, power will be
supplied to the fuel pump via the oil pressure
Check the distributor cap for cracks or tracking between the terminals. Squeeze the fuel supply hose while the ignition is
switched On. An increase in pressure should be felt.
Check the spark plug high tension leads for cracks and
burnt or corroded terminals.
Page 35 of 238

Roadside Trouble Shooting 35
View showing the location of the fuel pump fuse and the EGI and fuel pump relays.
switch. When starting the engine, the fuel
pump will not operate until the oil pressure
is sufficient to extinguish the oil pressure
warning lamp. Therefore it will be necessary
to operate the starter motor for a longer
period than usual to start the engine.
(3) If the fuel pump cannot be felt operating,
check the fuel pump fuse located in the fuse panel
adjacent to the steering column.
If the fuel pump fuse is serviceable, refer to the
Fuel and Engine Management section for detailed
tests on the fuel pump.
(4) Check that all fuel hose connections are
secure.
(5) Remove the spark plugs and check for petrol
saturation of the electrodes which indicates flooding.
Thoroughly clean and dry the spark plugs before
replacement. Fully depress the throttle pedal and turn the
ignition switch to the start position. If the engine does
not start, proceed as follows.
Check that the MAP sensor hose is not blocked or split
and ensure that all electrical connections are clean and
secure.
If flooding persists, refer to the Fuel and Engine
Management section.
(6) Check that all EFI electrical wiring connec-
tors are clean and secure.
(7) Check that the MAP sensor vacuum hose is
securely connected at each end and is not split or
blocked.
4. TO CHECK MECHANICAL SYSTEM
The following check procedure assumes that the
starter motor will rotate the engine. If not, on manual
transaxle models, depress the clutch pedal to disen-
gage the engine from the tr ansaxle in case the fault lies
within the transaxle.
If the starter motor will not rotate the engine, it
will be necessary to remove the starter motor and
attempt to turn the engine over manually. This will
establish whether the fault lies with the starter motor,
which could be jammed or defective, or with the
engine, which could be seized or have broken internal
components such as connecting rods, pistons and
crankshafts etc.
If the starter motor is not at fault and the engine
will not rotate manually, refer to the Engine Mechan-
ical Trouble Shooting heading in the Engine section.
It should be noted that the only way that cylinder
compression can be accurately tested is with a com-
pression gauge. The method described in the following
procedure is only intended to give a rough indication
when checking for causes of engine breakdown,
(I) When the engine is cool, check for loss of
coolant from the cooling system.
If coolant loss is evident, check carefully for any
indication of external leakage. Remove the engine oil
dipstick and check for wate r contamination (emulsi-
fication) of the oil. When oil mixes with water it will
Ensure that all fuel connections are securely tightened.
Page 36 of 238
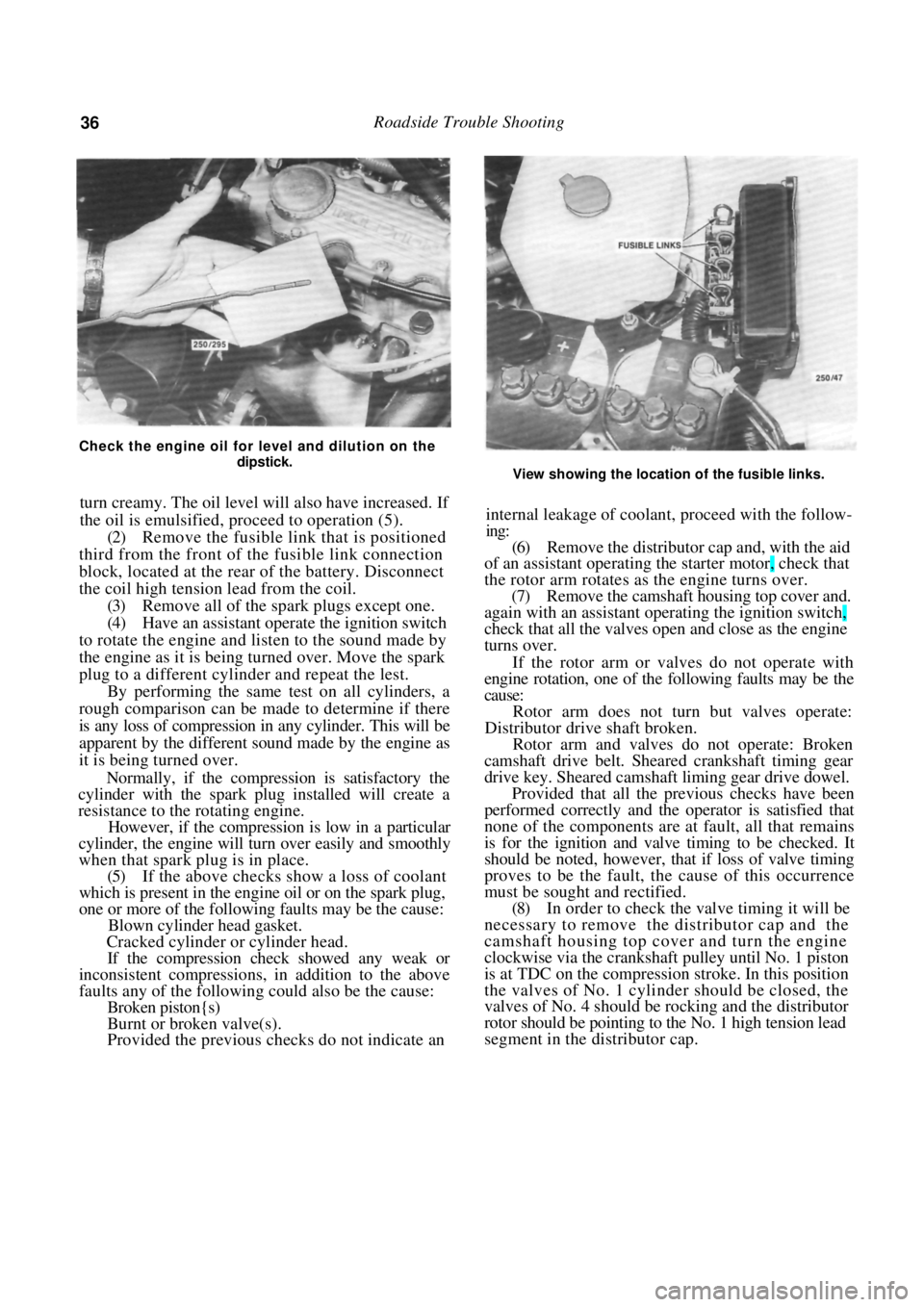
36 Roadside Trouble Shooting
Check the engine oil for level and dilution on the dipstick.
turn creamy. The oil level will also have increased. If
the oil is emulsified, proceed to operation (5).
(2) Remove the fusible link that is positioned
third from the front of th e fusible link connection
block, located at the rear of the battery. Disconnect
the coil high tension lead from the coil. (3) Remove all of the spark plugs except one.
(4) Have an assistant operate the ignition switch
to rotate the engine and listen to the sound made by
the engine as it is being turned over. Move the spark
plug to a different cylinder and repeat the lest. By performing the same test on all cylinders, a
rough comparison can be made to determine if there
is any loss of compression in any cylinder. This will be
apparent by the different sound made by the engine as
it is being turned over.
Normally, if the compression is satisfactory the
cylinder with the spark plug installed will create a
resistance to the rotating engine.
However, if the compression is low in a particular
cylinder, the engine will tu rn over easily and smoothly
when that spark plug is in place.
(5) If the above checks show a loss of coolant
which is present in the engine oil or on the spark plug,
one or more of the following faults may be the cause:
Blown cylinder head gasket.
Cracked cylinder or cylinder head.
If the compression check showed any weak or
inconsistent compressions, in addition to the above
faults any of the following could also be the cause:
Broken piston{s)
Burnt or broken valve(s).
Provided the previous checks do not indicate an
View showing the location of the fusible links.
internal leakage of coolant, proceed with the follow-
ing:
(6) Remove the distributor cap and, with the aid
of an assistant operating th e starter motor, check that
the rotor arm rotates as the engine turns over. (7) Remove the camshaft hous ing top cover and.
again with an assistant operating the ignition switch,
check that all the valves open and close as the engine
turns over.
If the rotor arm or valves do not operate with
engine rotation, one of the following faults may be the
cause:
Rotor arm does not turn but valves operate:
Distributor drive shaft broken.
Rotor arm and valves do not operate: Broken
camshaft drive belt. Sheare d crankshaft timing gear
drive key. Sheared camshaft liming gear drive dowel.
Provided that all the previous checks have been
performed correctly and the operator is satisfied that
none of the components are at fault, all that remains
is for the ignition and valve timing to be checked. It
should be noted, however, that if loss of valve timing
proves to be the fault, th e cause of this occurrence
must be sought and rectified.
(8) In order to check the valve timing it will be
necessary to remove the distributor cap and the
camshaft housing top cover and turn the engine
clockwise via the crankshaft pulley until No. 1 piston
is at TDC on the compression stroke. In this position
the valves of No. 1 cylinder should be closed, the
valves of No. 4 should be rocking and the distributor
rotor should be pointing to the No. 1 high tension lead
segment in the distributor cap.
Page 37 of 238

37
ENGINE
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Type........................................................... 4cyl OHC
Models ............................................. 1.6 liter, 1.8 liter
Capacity:
1.6 liter ................................................... 1 598 cc
1.8 liter ................................................... 1 796 cc
Firing order ...................................................... 1 -3-4-2
Bore:
1.6 liter.................................................. 80.0 mm
1.8 liter.................................................. 84.8 mm
Stroke ........................................................... 79.5 mm
Maximum compression pressure
variation between cylinders ......................... 100 kPa
NOTE: Specifications re garding engine tun-
ing arc listed in the Engine Tune-up section.
CYLINDER BLOCK
Type......................................................... 4 cyl in line
Material ........................................................ Cast iron
Bore diameter:
1.6 liter ............... 79. 995-80.065 in three groups
1.8 liter .................84. 755-84.905 in four groups
Bore taper limit ......................................... 0. 013 mm
Bore ovality limit ..................................... 0.013 mm
Block face distortion limit .......................... 0.10 mm
Maximum height of piston above block
face at top dead centre:
1.6 liter.................................................. 0.00 mm
1.8 liter.................................................. 0.50 mm
Bore oversize................................................ 0.50 mm
CYLINDER HEAD
Type........................................... One piece, cross flow
Material ............................................ Aluminum alloy
Distortion limit .......................................... 0.025 mm
Machining li mit ........................................... 0.25 mm
Minimum overall height after machining:
1.6 liter .................................................95.50 mm
1.8 liter .................................................94.80 mm
Valve seat angle ..........................................45 degrees
Valve seat contact width:
Inlet................................................... 1.0-1.5 mm
Exhaust ............................................. 1.7-2.2 mm
Valve stem protrusion ................. 18.4 mm from top
of cylinder head
Valve guide height .......... 12.2-12.5 mm from top of
cylinder head
VALVES AND SPRINGS
Valve length .............................................. 104. 2 mm
Valve head diameter:
1.6 liter —
Inlet........................................................ 36.0 mm
Exhaust .................................................. 32.0 mm
1.8 liter -
Inlet....................................................... 41.8 mm
Exhaust ................................................. 36.5 mm
Valve stem diameter:
Inlet...........................................6. 998-7.012 mm
Exhaust .....................................6.978-6.992 mm
Valve stem to guide clearance:
Inlet...........................................0.018-0.052 mm
Exhaust .....................................0.038-0.072 mm
Oversize valve system availability......... 0.075, 0.150
and 0.250 mm
Valve face angle ......................................... 44 degrees
Valve spring tension:
Valve closed .......................... 300 N at 37.5 mm
Valve open............................. 765 N at 26.5 mm
TAPPETS
Type .............................................................Hydraulic
Operating length ........................................ 63.26 mm
Diameter ....................................... 21.392-21.405mm
Leak down rate ............. 2-10 sec onds for 3.175 mm
PISTONS AND GUDGEON PINS
Piston type ....................................... Aluminum alloy
Diameter:
1.6 liter ........ 79. 955-80.035 mm in 8 categories
in increments of 0.01 mm
1.8 liter .......84.725-84.885 mm in 16 categories
in increments of 0.01 mm
Page 38 of 238

38 Engine
*Piston skirt to cylinder bore clearance:
1.6 liter .....................................0. 020-0.040 mm
1.8 liter .....................................0. 010-0.030 mm
Gudgeon pin length:
1.6 liter ...................................................... 53 mm
1.8 liter .................................................. 61.5 mm
Gudgeon pin diameter.................20.990-20.995 mm
Gudgeon pin clearance in piston:
1.6 liter .....................................0. 010-0.020 mm
1.8 liter ..................................0. 0055-0.0115 mm
Gudgeon pin offset in piston:
1.6 liter......... 0.35-0.65 mm towards thrust side
1.8 liter................... 0.8 mm towards thrust side
*Measured 9 mm from the bottom of the piston skirt
for 1.6 liter models and 6 mm from the bottom of the
piston skirt for 1.8 liter models.
PISTON RINGS
Rings per piston:
Compression .......................................................2
Oil contro l .......................................................... 1
End gap:
Compression ................................ 0.30-0.50 mm
Oil control —
1.6 liter ......................................... 0.33-1.10 mm
1.8 liter ......................................... 0.40-1.40 mm
CONNECTING RODS AND BEARINGS
Connecting rod side clearance............ 0.07-0.24 mm
Maximum connecting rod weight variation..8 grams
Crankpin bearing oil clearance ....... 0. 019-0.063 mm
CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN BEARINGS
Number of bearings .................................................. 5
End float taken at ...................... No. 3 main bearing
End float .......................................... 0.070-0.302 mm
Bend limit ...................................................0.03 mm
Main bearing oil clearance .............0. 015-0.040 mm
Main bearing journal diameter.. .57.982-57.995 mm
Crankpin diameter .......................48.971-48.987 mm
FLYWHEEL
Ring gear run out limit.................................. 0.3 mm
Clutch face regrind limit .............................. 0.3 mm
CAMSHAFT
Drive ...................................................... Toothed belt
End float .............................................. 0.04-0.14 mm
Bend limit ................................................... 0.03 mm
Bearings ...........................................Direct in housing
Journal diameter:
Standard —
No. 1 ..................................... 42. 455-42.470 mm
No. 2 ..................................... 42. 705-42.720 mm
No. 3 ..................................... 42.955-42.970 mm
No. 4 ..................................... 43.205-43.220 mm
No. 5 ..................................... 43.455-43.470 mm
Undersize —
No. 1 .....................................42.355-42.370 mm
No. 2 ......................................42.605-42.620 mm
No. 3 .....................................42.855-42.880 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.105-43.120 mm
No. 5 .....................................43. 355-43.370 mm
*An undersize camshaft can be identified by a violet
flash between the inlet and exhaust lobes of No. 2
cylinder.
Housing diameter;
Standard —
No. 1 .....................................42. 500-42.525 mm
No. 2 .....................................42.750-42.775 mm
No. 3 .....................................43.000-43.025 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.250-43.275 mm
No. 5 .....................................43.500-43.525 mm
*Undersize —
No. 1 .....................................42.400-42.425 mm
No. 2 .....................................42.650-42.675 mm
No. 3 .....................................42.900-42.925 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.150-43.175 mm
No. 5 .....................................43.400-43.425 mm
*An undersize camshaft housing can be identified by
a violet flash on the centre camshaft bearing support.
LUBRICATION
Oil pump type .......................................Involute gear
Filter type................................... Full flow disposable
Oil pressure at 4 000 rpm .....................480-620 kPa
Rotor assembly end float .................. 0.03-0. 010 mm
Rotor teeth backlash ......................... 0.010-0.20 mm
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
*Cylinder head bolts:
Initial torque ............................................. 25 Nm
1st stage ......................................... + 60 degrees
2nd stage ........................................ + 60 degrees
3rd stage......................................... + 60 degrees
4th stage, engine at operating
temperature .............................. + 30-50 degrees
Exhaust manifold nuts .................................... 22 Nm
Exhaust manifold flange nuts ......................... 22 Nm
Inlet manifold nuts.......................................... 22 Nm
Throttle body to inlet manifold nuts ..............12 Nm
Camshaft liming gear bolt ...............................45 Nm
Camshaft retainin g plate bolts ......................... 7 Nm
Camshaft cover bolts......................................... 8 Nm
Thermostat cover bolts ....................................15 Nm
*Main bearing bolts..................60 Nm + 45 degrees
Connecting rod bearing
cap nuts ................................... 35 Nm + 45 degrees
* Crankshaft timing
gear bolt.................................. 145 Nm + 35 degrees
*Flywheel bolts
(microencapsulated) ................ 60 Nm + 30 degrees
*Drive plate bolts (microencapsulated)........... 60 Nm
Water pump bolts............................................ 25 Nm
Page 39 of 238
Engine 39
Oil pump cover plate screws............................ 6 Nm
Oil pump mounting bolts.................................. 6 Nm
Oil pump pickup bolts
(coat with Loctite 242)..................................... 8 Nm
Sump bolts (coat with Loctite 242) .................. 5 Nm
Sump drain plug .............................................. 35 Nm
*Use new bolts
Head bolts maximum torque 135 Nm
1. ENGINE MECHANICAL TROUBLE
SHOOTING
ENGINE MISSES AT IDLING SPEED
NOTE: For other causes of engine misfire,
refer to the Fuel and Engine Management
section.
(1) Blown head gasket: Check the cylinder com-
pressions and renew the he ad gasket as necessary.
(2) Burnt valves or seats in the cylinder head:
Check the cylinder compressions and overhaul the
cylinder head as necessary. (3) Broken or worn piston rings: Check the
cylinder compressions and renew the piston rings as
necessary.
(4) Weak or broken valve springs: Remove the
camshaft housing top cover and check the condition
of the valve springs. (5) Air leak at the inlet manifold gasket; Check
for air leaks by applying oil around the manifold
joints. Renew the gasket if an air leak is evident.
NOTE: Use a compre ssion gauge and check
the compression pressure in each cylinder as
described in the Engine Tune-up section. If
a low pressure reading is indicated in one or
more cylinders, remove the cylinder head for
gasket and valve inspection. Should the
gasket and valves prove satisfactory, inspect
the cylinder bores, pistons and rings.
Check for air leaks at the inlet manifold
by applying engine oil around the manifold
joints. If the oil can be seen or heard sucking
into the manifold or excessive smoke begins
to issue from the exhaust system, there is an
air leak at the inlet manifold.
NOISY VALVE OPERATION
(1) Faulty hydraulic tappets: Renew the faulty
tappet assemblies. (2) Weak or broken valve springs: Remove the
camshaft housing top cover and check the condition
of the valve springs. (3) Worn valve guides: Overhaul the cylinder
head as described in this section. (4) Worn rocker gear: Remove (he rocker gear
and check the components for wear.
Camshaft lobe wear is also a cause of noisy valve
operation.
BIG END BEARING NOISE
(1) Inadequate oil supply: Check the oil level in
the sump and the condition of the oil pump and relief
valve. Renew the oil filter.
(2) Excessive bearing clearance: Renew the bear-
ing shells, check and regrind the big end journals if
oval or tapered. (3) Thin oil or oil diluted by petrol or water:
Change to the correct oil grade. Check and rectify the
cause of the oil dilution. Ch eck that the engine is not
operating in overheat conditions.
(4) Low oil pressure: Check the engine oil level.
Check the pressure relief valve and spring and the oil
filter bypass valve. (5) Misaligned big end bearings: Align the con-
necting rods and renew the big end bearing shells.
NOTE: Big end bearing noise is indicated
by a metallic knock wh ich is usually loudest
at approximately 60 km/h with the throttle
Air leaks at the inlet manifold can be located by
applying engine oil around the suspect joints.
Page 40 of 238

40 Engine
Check the engine oil for level and dilution on the dipstick.
dosed. Before dismantling the engine to
inspect the big ends check the engine oil for
correct level and dilution on the dipstick.
Also, remove the oil pressure sender unit
and connect an oil pressure gauge into the
oil gallery to check the oil pressure readings.
MAIN BEARING NOISE (APPARENT)
(1) Loose flywheel: Tighten the flywheel securing
bolls to the specified torque. (2) Low oil pressure: Check the bearing to
journal clearance. Check the condition of the oil
pump and pressure relief valve. Recondition the oil
pump as necessary. (3) Excessive crankshaft end float: Renew the
main bearings. (4) Crankshaft journals out of round and exces-
sive bearing to journal clear ance: Regrind the journals
and renew the bearings (undersize).
(5) Insufficient oil supply: Replenish the oil in
the sump to the correct level.
NOTE: Main bearing noise is indicated by a
heavy but dull knock when the engine is
under load. A loose flywheel is indicated by
a thud or dull click when the ignition is
turned off. It is us ually accompanied by
vibration.
Crankshaft end float noise is indicated by
a sharp rap at idle speed. The crankshaft
can be readily checked for excessive end
float by levering the crankshaft backwards
and forwards.
If the oil pressure is not satisfactory,
remove the main bearing caps and assess
the bearing clearance using the Plastigage
method as described in this section. Ovality
and wear on the main bearing journals can
only be checked with a micrometer after the
crankshaft has been removed.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
(1) Oil leaks: Check and renew the engine gas-
kets or seals as necessary.
(2) Damaged or worn valve stem oil seals:
Dismantle the cylinder head and renew the damaged
or worn oil seals. (3) Excessive valve stem to valve guide clear-
ance: Ream the valve guides and renew the valves as
necessary. (4) Worn or broken piston rings: Renew the
piston rings on all pistons. (5) Rings too tight or stuck in the grooves:
Renew the rings and clean the ring grooves.
(6) Excessive wear in the cylinders, pistons and
rings: Recondition the cylinders and renew the pistons
and rings. (7) Compression rings incorrectly installed. Oil
rings clogged or broken: Renew the piston rings.
NOTE: Before checking the engine for oil
leaks the engine should be completely de-
greased and cleaned. Run the engine at
operating temperature for a period and
visually check for oil leakage. By placing
white paper on the floor directly beneath the
engine any excessive leak can be readily
pinpointed.
Damaged or worn valve stem oil seals
which allow oil to be drawn down past the
valve stems into the combustion chambers
can be diagnosed by allowing the engine to
idle for a few minutes and then opening the
throttle. If oil is being drawn past the valve
stems a heavy discharge of blue smoke will
be seen at the tailpipe.
Piston, ring and cylinder bore troubles are
normally accompanied by a loss of compres-
sion. Cylinder compression can only be
accurately assessed by using a compression
gauge.
Run the engine over white paper to check for oil leaks.